Genetic Structure and Selection Signature in Flora Scent of Roses by Whole Genome Re-Sequencing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. DNA Extraction and Quantification
2.3. Library Construction and Whole Genome Re-Sequencing
2.4. Read Mapping, SNP Calling and Annotation
2.5. Genetic Diversity Estimation
2.6. Population Structure
2.7. Screening for Selection Signatures Related to Flora Scent
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sequencing Statistics and Variation in the Rose Genome
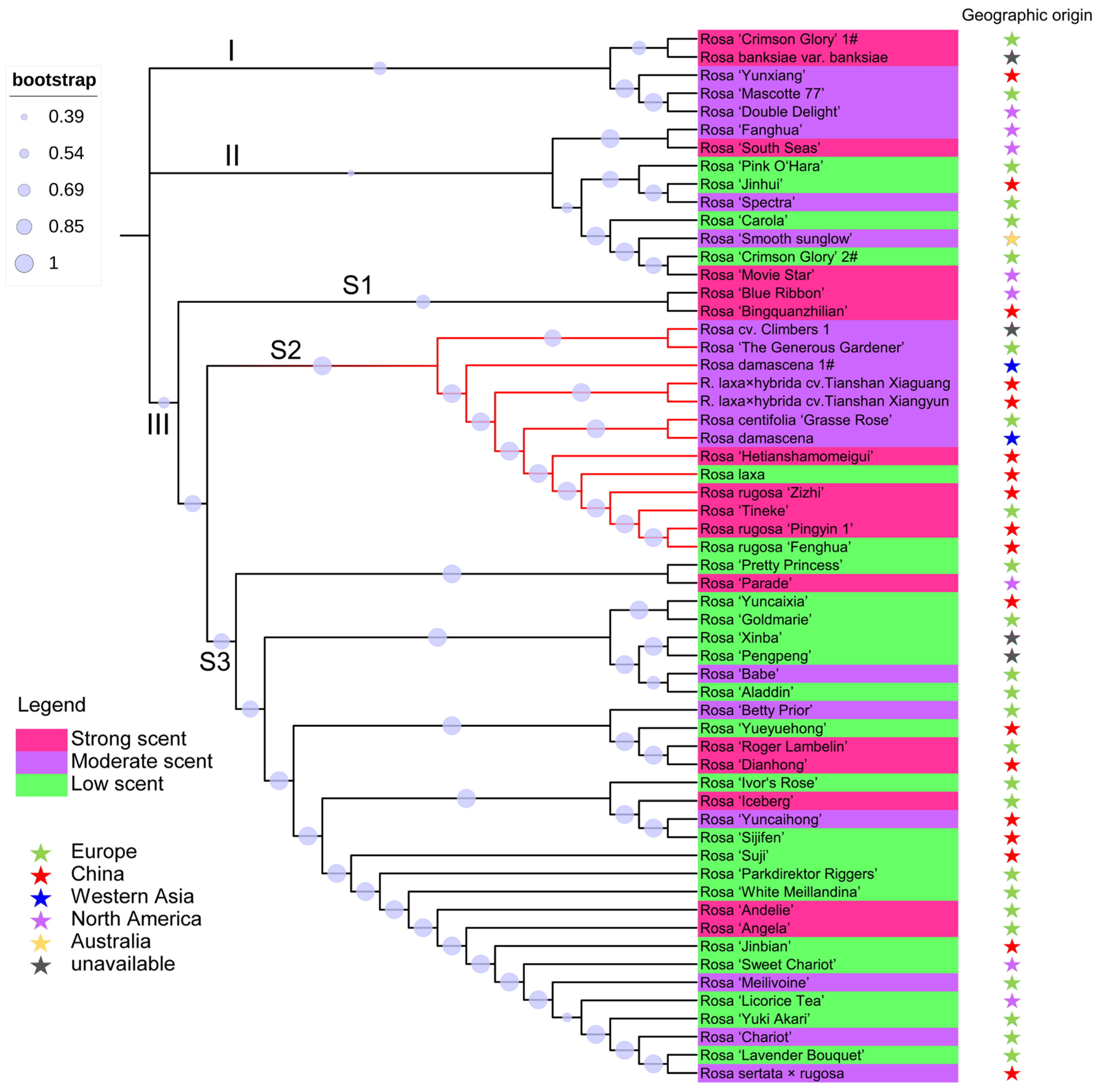
3.2. Genetic Relationships Based on SNP Data
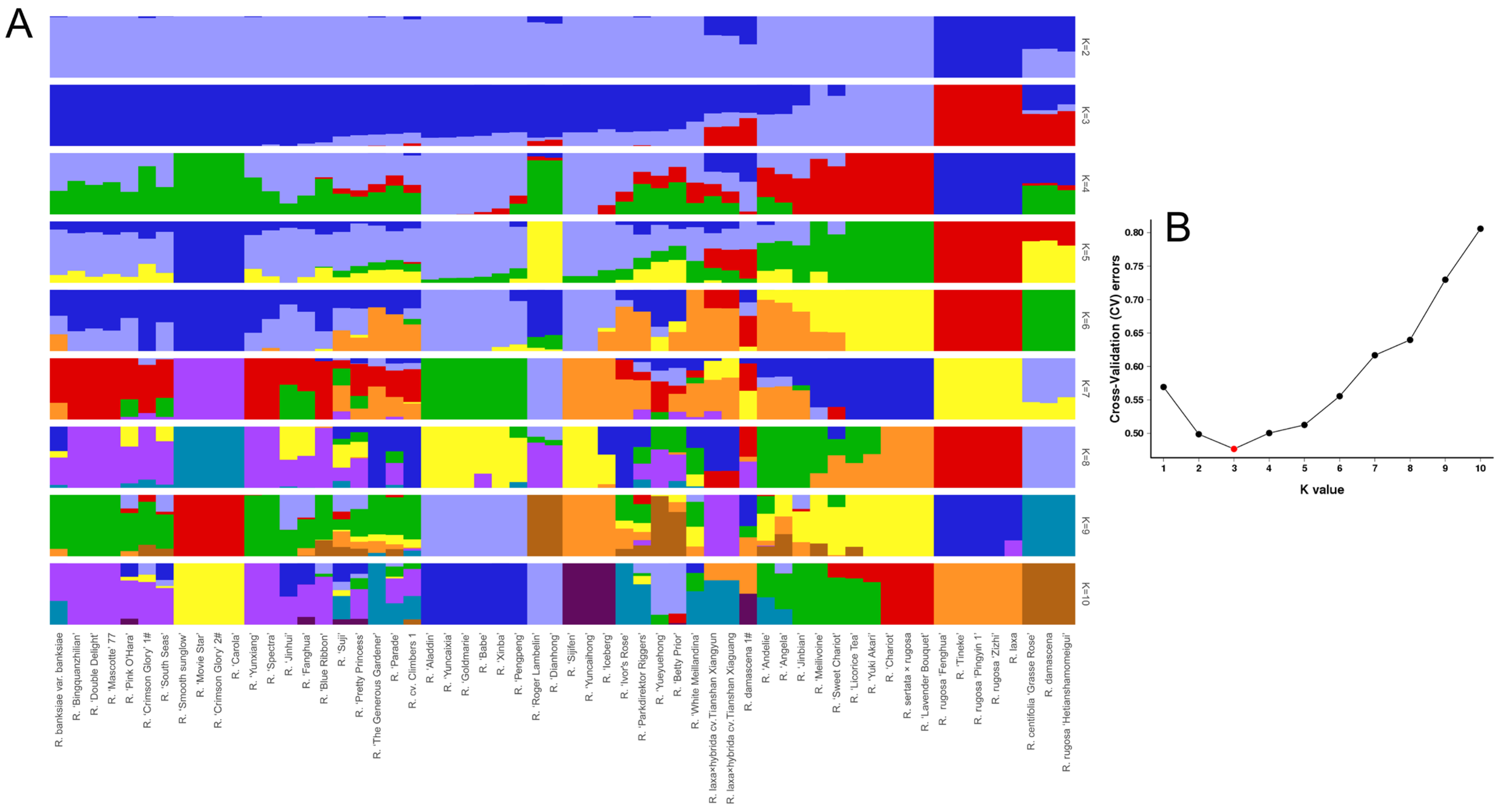
3.3. Population Structure of Roses
3.4. Genetic Diversity
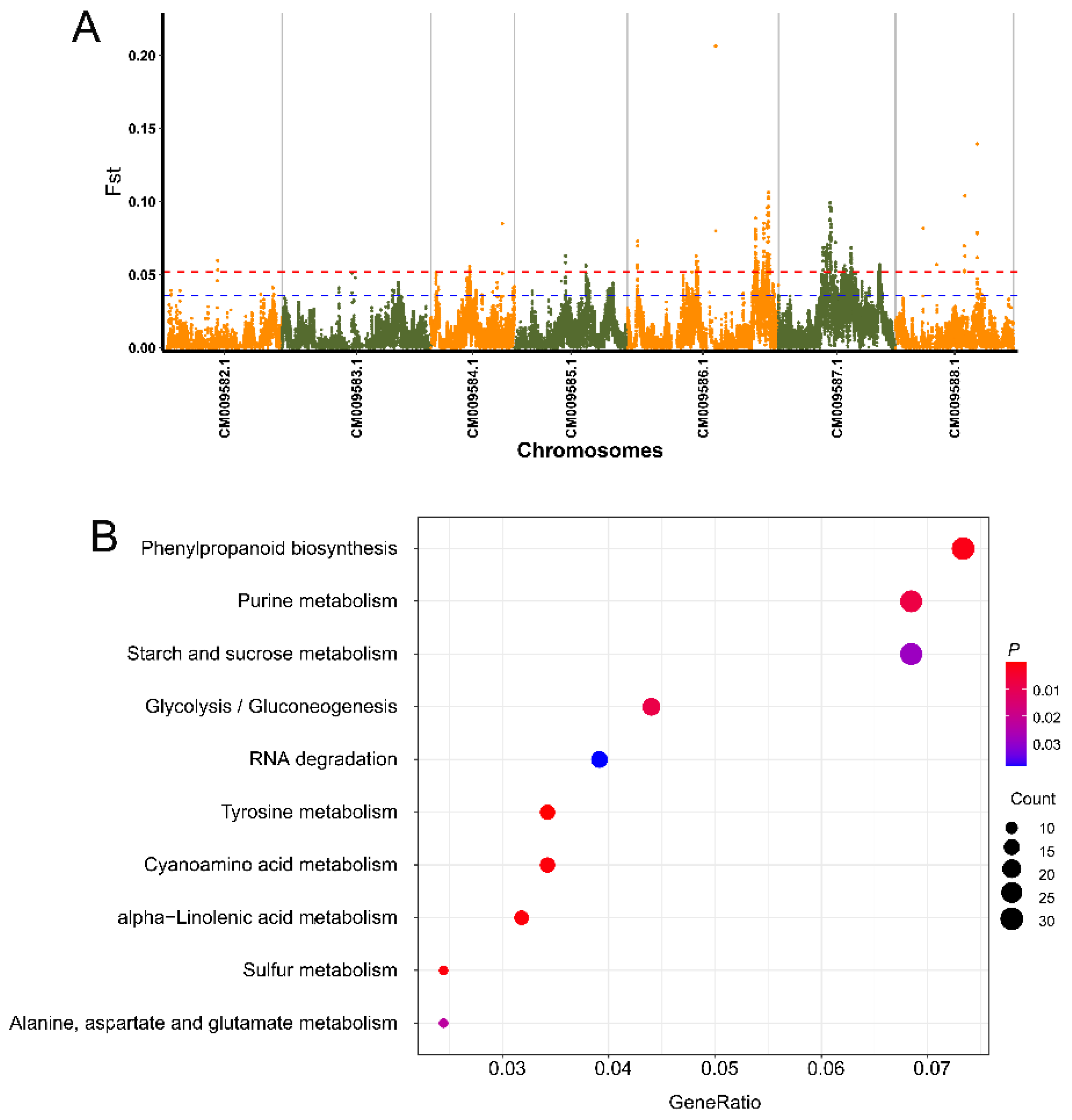
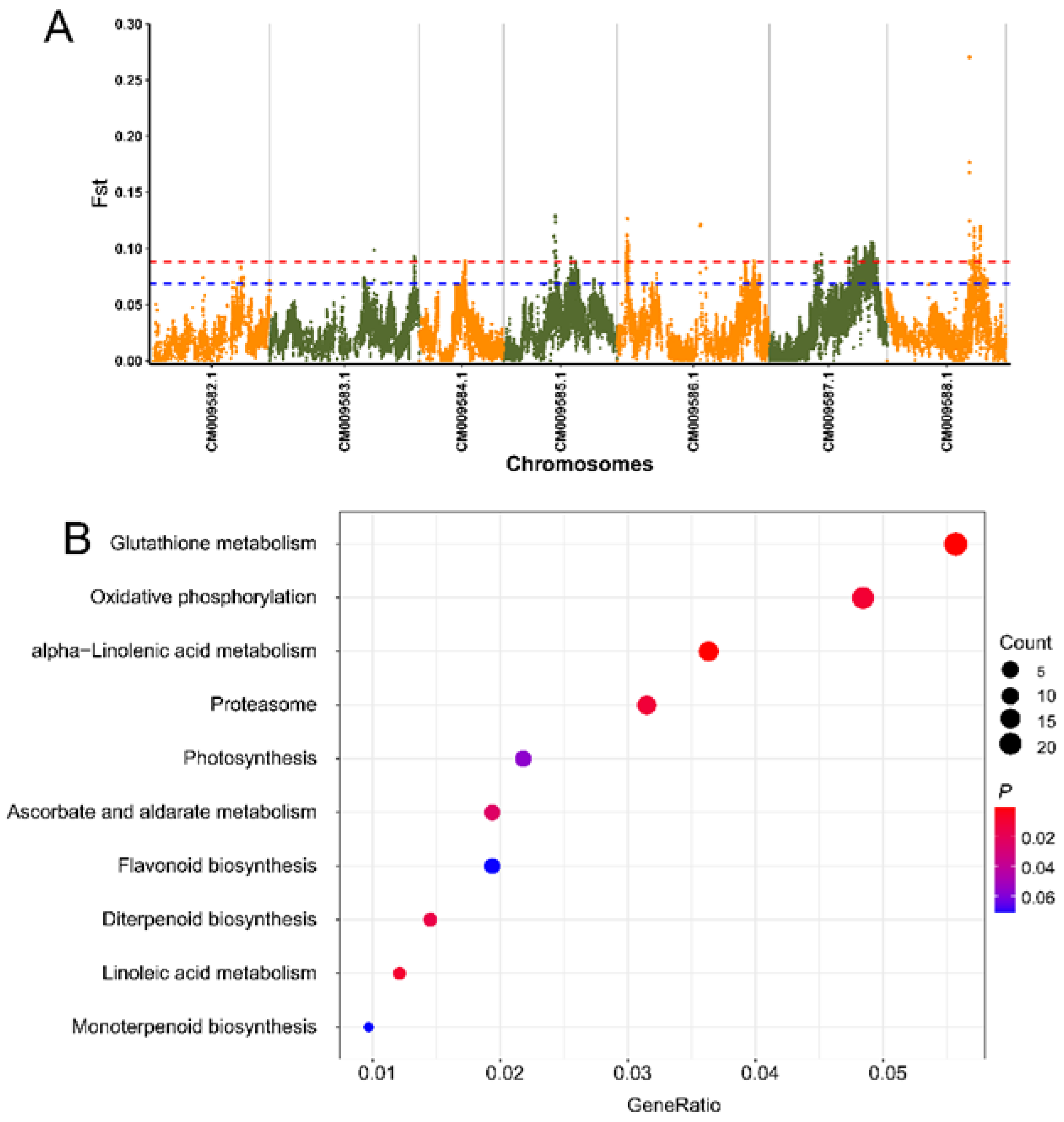
3.5. Genome-Wide Detection of Selective Candidate Loci and Genes Associated with Flower Scent
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raymond, O.; Gouzy, J.; Just, J.; Badouin, H.; Verdenaud, M.; Lemainque, A.; Vergne, P.; Moja, S.; Choisne, N.; Pont, C.; et al. The Rosa genome provides new insights into the domestication of modern roses. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liorzou, M.; Pernet, A.; Li, S.B.; Chastellier, A.; Thouroude, T.; Michel, G.; Malecot, V.; Gaillard, S.; Briee, C.; Foucher, F.; et al. Nineteenth century French rose (Rosa sp.) germplasm shows a shift over time from a European to an Asian genetic background. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 4711–4725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touw, M. Roses in the middle ages. Econ. Bot. 1982, 36, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G. A study on the history of Chinese roses from ancient works and images. Acta Hortic. 2005, 751, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esselink, G.D.; Nybom, H.; Vosman, B. Assignment of allelic configuration in polyploids using the MAC-PR (microsatellite DNA allele counting-peak ratios) method. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 109, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saint-Oyant, L.H.; Ruttink, T.; Hamama, L.; Kirov, I.; Lakhwani, D.; Zhou, N.N.; Bourke, P.M.; Daccord, N.; Leus, L.; Schulz, D.; et al. A high-quality genome sequence of Rosa chinensis to elucidate ornamental traits. Nat. Plants 2018, 4, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, A.; Debener, T.; Gudin, S. Encyclopedia of Rose Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, M.; Piola, F.; Chessel, D.; Jay, M.; Heizmann, P. The domestication process of the Modern Rose: Genetic structure and allelic composition of the rose complex. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2001, 102, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smulders, M.J.M.; Arens, P.; Koning-Boucoiran, C.F.S.; Gitonga, V.W.; Krens, F.A.; Atanassov, A.; Atanassov, I.; Rusanov, K.E.; Bendahmane, M.; Dubois, A.; et al. Rosa. In Wild Crop Relatives: Genomic and Breeding Resources; Kole, C., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 243–275. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, F.Q.; Ma, Y.; Tu, X.L.; Huang, P.; Wu, Q.C.; Li, Z.M.; Liu, T.; Lin, F.R.; Pei, S.R.; Zang, D.K.; et al. A high-quality chromosome-level genome of wild Rosa rugosa. DNA Res. 2021, 28, dsab017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercure, M.; Bruneau, A. Hybridization between the escaped Rosa rugosa (Rosaceae) and native R-blanda in eastern North America. Am. J. Bot. 2008, 95, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruun, H.H. Rosa rugosa Thunb. ex Murray. J. Ecol. 2005, 93, 441–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamitsu, T. Genetic structure in chloroplast and nuclear microsatellites in Rosa rugosa around sea straits in northern Japan. Plant Spec. Biol. 2017, 32, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.Y.; Zang, D.K. Analysis of genetic relationships in Rosa rugosa using conserved DNA-derived polymorphism markers. Biotechnol. Biotec. Equip. 2018, 32, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baydar, N.G.; Baydar, H.; Debener, T. Analysis of genetic relationships among Rosa damascena plants grown in Turkey by using AFLP and microsatellite markers. J. Biotechnol. 2004, 111, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, H.; Raju, D.V.S.; Kumar, M.B.A.; Janakiram, T.; Namita; Krishnan, S.G.; Rana, J.C. Characterization and analysis of genetic diversity among different species of rose (Rosa species) using morphological and molecular markers. Indian J. Agr. Sci. 2015, 85, 240–245. [Google Scholar]
- Jurgens, A.H.; Seitz, B.; Kowarik, I. Genetic differentiation of Rosa canina (L.) at regional and continental scales. Plant Syst. Evol. 2007, 269, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusanov, K.; Kovacheva, N.; Vosman, B.; Zhang, L.; Rajapakse, S.; Atanassov, A.; Atanassov, I. Microsatellite analysis of Rosa damascena Mill. accessions reveals genetic similarity between genotypes used for rose oil production and old Damask rose varieties. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2005, 111, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaurav, A.K.; Namita; Raju, D.V.S.; Ramkumar, M.K.; Singh, M.K.; Singh, B.; Krishnan, S.G.; Panwar, S.; Sevanthi, A.M. Genetic diversity analysis of wild and cultivated Rosa species of India using microsatellite markers and their comparison with morphology based diversity. J. Plant Biochem. Biot. 2022, 31, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.G.; Sheng, L.X.; Shao, D.W.; Tao, J.; Zhao, L.Y. Fluorescent amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) analysis of genetic diversity and relationship of Chinese Rosa rugosa germplasm resources. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 4524–4531. [Google Scholar]
- Panwar, S.; Singh, K.P.; Sonah, H.; Deshmukh, R.K.; Namita; Prasad, K.V.; Sharma, T.R. Molecular fingerprinting and assessment of genetic diversity in rose (Rosa x hybrida). Indian J. Biotechnol. 2015, 14, 518–524. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.R.; Wang, J.; Luo, L.; Yu, C.; Xu, T.L.; Wu, Y.Y.; Cheng, T.R.; Wang, J.; Pan, H.T.; Zhang, Q.X. Genetic relationships and evolution of old Chinese garden roses based on SSRs and chromosome diversity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparna, V.; Bhat, K.V.; Janakiram, T.; Prasad, K.V.; Raju, D.V.S.; Sapna, P.; Namitha; Singh, K.P. Assessment of genetic diversity and population structure of fragrant rose (Rosa x hybrida) cultivars using microsatellite markers. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 89, 212–218. [Google Scholar]
- Scariot, V.; Akkak, A.; Botta, R. Characterization and genetic relationships of wild species and old garden roses based on microsatellite analysis. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2006, 131, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, A.N.; Yang, A.A.; Meng, X.S.; Dong, G.Z.; Tang, X.J.; Lei, S.M.; Liu, Y.G. Development and application of rose (Rosa chinensis Jacq.) SNP markers based on SLAF-seq technology. Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 2022, 69, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Ruperao, P.; Batley, J.; Edwards, D.; Martin, W.; Hobson, K.; Sutton, T. Genomic prediction of preliminary yield trials in chickpea: Effect of functional annotation of SNPs and environment. Plant Genome 2022, 15, e20166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.D.; Zhang, Z.L.; Gong, Z.L.; Liang, Y.J.; Ai, X.T.; Sang, Z.W.; Guo, J.P.; Li, X.Y.; Zheng, J.Y. Analysis of the genetic structure and diversity of upland cotton groups in different planting areas based on SNP markers. Gene 2022, 809, 146042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xanthopoulou, A.; Manioudaki, M.; Bazakos, C.; Kissoudis, C.; Farsakoglou, A.M.; Karagiannis, E.; Michailidis, M.; Polychroniadou, C.; Zambounis, A.; Kazantzis, K.; et al. Whole genome re-sequencing of sweet cherry (Prunus. avium L.) yields insights into genomic diversity of a fruit species. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cingolani, P.; Platts, A.; Wang, L.L.; Coon, M.; Nguyen, T.; Wang, L.; Land, S.J.; Lu, X.Y.; Ruden, D.M. A program for annotating and predicting the effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms, SnpEff: SNPs in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster strain w(1118); iso-2; iso-3. Fly 2012, 6, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meirmans, P.G.; Van Tienderen, P.H. GENOTYPE and GENODIVE: Two programs for the analysis of genetic diversity of asexual organisms. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2004, 4, 792–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graebner, R.C.; Hayes, P.M.; Hagerty, C.H.; Cuesta-Marcos, A. A comparison of polymorphism information content and mean of transformed kinships as criteria for selecting informative subsets of barley (Hordeum vulgare L. s. l.) from the USDA Barley Core Collection. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2016, 63, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D.H.; Novembre, J.; Lange, K. Fast model-based estimation of ancestry in unrelated individuals. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danecek, P.; Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.; Albers, C.A.; Banks, E.; DePristo, M.A.; Handsaker, R.E.; Lunter, G.; Marth, G.T.; Sherry, S.T.; et al. The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2156–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aflitos, S.; Schijlen, E.; de Jong, H.; de Ridder, D.; Smit, S.; Finkers, R.; Wang, J.; Zhang, G.Y.; Li, N.; Mao, L.K.; et al. Exploring genetic variation in the tomato (Solanum section Lycopersicon) clade by whole-genome sequencing. Plant J. 2014, 80, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cao, K.; Zhu, G.R.; Fang, W.C.; Chen, C.W.; Wang, X.W.; Zhao, P.; Guo, J.; Ding, T.Y.; Guan, L.P.; et al. Genomic analyses of an extensive collection of wild and cultivated accessions provide new insights into peach breeding history. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.C.; Duan, S.C.; Sheng, J.; Zhu, S.S.; Ni, X.M.; Shao, J.H.; Liu, C.H.; Nick, P.; Du, F.; Fan, P.G.; et al. Whole-genome resequencing of 472 Vitis accessions for grapevine diversity and demographic history analyses. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, R.K.; Saxena, R.K.; Upadhyaya, H.D.; Khan, A.W.; Yu, Y.; Kim, C.; Rathore, A.; Kim, D.; Kim, J.; An, S.; et al. Whole-genome resequencing of 292 pigeonpea accessions identifies genomic regions associated with domestication and agronomic traits. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1082–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.X.; Zhang, H.; Sun, L.D.; Fan, G.Y.; Ye, M.X.; Jiang, L.B.; Liu, X.; Ma, K.F.; Shi, C.C.; Bao, F.; et al. The genetic architecture of floral traits in the woody plant Prunus mume. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.L.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Lin, G.C. Preliminary study on the phylogenetic relationship of Rosa. rugosa ‘Hetian shamomeigui’. Acta Bot. Boreal. Occident. Sin. 2021, 41, 222–233. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, R.H.; Sui, Y.J.; Yang, F.Y.; Liu, H. A new cold-resistant rose cultivar‘Tianshan Xiangyun’. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2011, 38, 1417–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.J.; Guo, R.H.; Yang, F.Y.; He, L. Comparative experiment on biological characteristics of cold-resistant rose ‘Tianshan Xiangyun’. Pract. For. Technol. 2012, 9, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, H.; Ohnishi, T.; Tomida, K.; Ishida, H.; Kanda, M.; Sakai, M.; Yoshimura, J.; Suzuki, H.; Ishikawa, T.; Dohra, H.; et al. Seasonal induction of alternative principal pathway for rose flower scent. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joichi, A.; Yomogida, K.; Awano, K.; Ueda, Y. Volatile components of tea-scented modern roses and ancient Chinese roses. Flavour Frag. J. 2005, 20, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guterman, I.; Shalit, M.; Menda, N.; Piestun, D.; Dafny-Yelin, M.; Shalev, G.; Bar, E.; Davydov, O.; Ovadis, M.; Emanuel, M.; et al. Rose scent: Genomics approach to discovering novel floral fragrance-related genes. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 2325–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalliet, G.; Journot, N.; Jullien, F.; Baudino, S.; Magnard, J.L.; Channelière, S.; Vergne, P.; Dumas, C.; Bendahmane, M.; Cock, J.M.; et al. Biosynthesis of the major scent components 3,5-dimethoxytoluene and 1,3,5-trimethoxybenzene by novel rose O-methyltransferases. FEBS Lett. 2002, 523, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Zang, S.; Wang, J.; Wei, T.; Xu, Y.; Feng, L. Overexpression of a Rosa rugosa Thunb. NUDX gene enhances biosynthesis of scent volatiles in petunia. PeerJ 2021, 2, e11098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharoni, A.; Giri, A.P.; Verstappen, F.W.; Bertea, C.M.; Sevenier, R.; Sun, Z.; Jongsma, M.A.; Schwab, W.; Bouwmeester, H.J. Gain and loss of fruit flavor compounds produced by wild and cultivated strawberry species. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 3110–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.J.; Yu, C.; Cheng, B.X.; Han, Y.; Luo, L.; Pan, H.T.; Zhang, Q.X. Studies on the volatile compounds in flower extracts of Rosa odorata and R. chinensis. Ind. Crop Prod. 2020, 146, 112143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnard, J.L.; Roccia, A.; Caissard, J.C.; Vergne, P.; Sun, P.L.; Hecquet, R.; Dubois, A.; Hibrand-Saint Oyant, L.; Jullien, F.; Nicole, F.; et al. Biosynthesis of monoterpene scent compounds in roses. Science 2015, 349, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiller, M.; Berger, R.G.; Debener, T. Genetic dissection of scent metabolic profiles in diploid rose populations. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2010, 120, 1461–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croteau, R.; Karp, F. Origin of Natural Odorants. In Perfume: Art, Science and Technology; Muller, P., Lamparsky, D., Eds.; Elsevier Applied Sciences: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 101–126. [Google Scholar]
| No. | Cultivar Name | SNPs | Indels | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Intron | Intergenic | CDS | Total | Intron | Intergenic | CDS | |||||||
| Total | Syn | nSyn | Total | Fram shf | Inser | Del | ||||||||
| 1 | Rosa ‘Ivor’s Rose’ | 1,307,661 | 180,871 | 357,630 | 182,001 | 99,076 | 80,251 | 432,255 | 78,418 | 97,408 | 16,497 | 10,600 | 1700 | 1871 |
| 2 | Rosa ‘Aladdin’ | 1,258,866 | 180,125 | 338,831 | 181,433 | 98,846 | 80,034 | 426,430 | 79,445 | 94,316 | 16,092 | 10,281 | 1663 | 1846 |
| 3 | Rosa ‘Andelie’ | 1,238,244 | 176,240 | 332,253 | 176,035 | 95,560 | 77,895 | 406,270 | 75,078 | 89,911 | 15,188 | 9746 | 1543 | 1743 |
| 4 | Rosa ‘Angela’ | 1,257,173 | 175,758 | 335,130 | 174,741 | 95,036 | 77,153 | 421,227 | 76,141 | 93,052 | 15,838 | 10,203 | 1599 | 1783 |
| 5 | Rosa ‘Babe’ | 1,254,028 | 179,014 | 335,073 | 179,772 | 97,829 | 79,282 | 423,004 | 78,533 | 93,541 | 15,850 | 10,159 | 1589 | 1863 |
| 6 | Rosa banksiae var. banksiae | 1,220,569 | 174,592 | 329,302 | 174,754 | 95,366 | 76,933 | 414,672 | 77,310 | 90,923 | 15,299 | 9816 | 1587 | 1742 |
| 7 | Rosa ‘White Meillandina’ | 1,455,802 | 203,664 | 398,167 | 196,823 | 106,727 | 87,123 | 492,826 | 89,670 | 110,284 | 17,921 | 11,570 | 1842 | 1987 |
| 8 | Rosa damascena 1# | 1,205,798 | 195,841 | 277,211 | 207,499 | 115,377 | 89,717 | 464,886 | 94,570 | 91,042 | 18,232 | 10,769 | 2322 | 2232 |
| 9 | Rosa ‘Bingquanzhilian’ | 1,441,849 | 202,641 | 396,580 | 206,134 | 111,911 | 91,262 | 498,437 | 91,813 | 111,189 | 18,789 | 11,987 | 1945 | 2161 |
| 10 | Rosa ‘Iceberg’ | 1,150,678 | 164,959 | 308,738 | 161,747 | 87,691 | 71,697 | 384,451 | 71,389 | 85,039 | 14,195 | 9255 | 1403 | 1595 |
| 11 | Rosa ‘Chariot’ | 1,175,700 | 161,796 | 321,378 | 148,441 | 80,045 | 66,107 | 383,316 | 67,533 | 88,729 | 13,355 | 8793 | 1240 | 1433 |
| 12 | Rosa damascena | 1,378,891 | 227,181 | 319,849 | 223,694 | 122,895 | 97,995 | 491,676 | 101,853 | 96,408 | 18,680 | 11,520 | 2177 | 2178 |
| 13 | Rosa ‘Parade’ | 1,344,859 | 188,306 | 365,677 | 188,834 | 102,472 | 83,572 | 451,013 | 82,178 | 101,481 | 16,946 | 10,762 | 1743 | 1981 |
| 14 | Rosa ‘Dianhong’ | 1,166,345 | 189,101 | 265,223 | 197,509 | 108,265 | 86,622 | 422,900 | 85,354 | 83,559 | 16,972 | 10,572 | 1902 | 2001 |
| 15 | Rosa ‘Fanghua’ | 1,385,662 | 200,772 | 368,013 | 208,754 | 114,794 | 91,101 | 474,764 | 90,202 | 104,295 | 18,452 | 11,544 | 1952 | 2225 |
| 16 | Rosa rugosa ‘Fenghua’ | 1,036,722 | 193,705 | 185,729 | 210,005 | 117,634 | 90,101 | 445,558 | 97,471 | 75,110 | 19,263 | 11,253 | 2566 | 2404 |
| 17 | Rosa ‘Licorice Tea’ | 1,136,549 | 157,251 | 304,052 | 155,326 | 84,152 | 68,800 | 382,582 | 67,155 | 86,877 | 14,304 | 9338 | 1375 | 1579 |
| 18 | Rosa ‘Pretty Princess’ | 1,328,390 | 186,719 | 360,616 | 187,256 | 101,600 | 82,930 | 449,565 | 82,503 | 100,220 | 16,832 | 10,697 | 1770 | 1958 |
| 19 | Rosa ‘Spectra’ | 1,261,911 | 183,116 | 337,586 | 182,115 | 99,394 | 80,141 | 431,660 | 81,625 | 94,174 | 16,135 | 10,180 | 1708 | 1909 |
| 20 | Rosa ‘Hetianshamomeigui’ | 1,454,887 | 243,654 | 316,090 | 259,965 | 142,942 | 113,845 | 527,405 | 110,790 | 99,509 | 21,811 | 13,210 | 2655 | 2635 |
| 21 | Rosa ‘Double Delight’ | 1,239,876 | 180,066 | 330,655 | 183,079 | 100,121 | 80,494 | 428,276 | 81,224 | 93,457 | 16,176 | 10,189 | 1697 | 1917 |
| 22 | Rosa ‘Jinbian’ | 1,389,521 | 195,333 | 374,772 | 188,660 | 102,115 | 83,692 | 462,745 | 84,153 | 103,774 | 16,969 | 11,023 | 1634 | 1875 |
| 23 | Rosa ‘Jinhui’ | 1,324,109 | 190,429 | 358,251 | 189,323 | 102,942 | 83,662 | 459,353 | 85,871 | 102,782 | 17,380 | 11,042 | 1831 | 2011 |
| 24 | Rosa ‘Goldmarie’ | 1,326,837 | 195,795 | 345,111 | 197,351 | 108,275 | 86,314 | 452,378 | 87,105 | 96,942 | 17,176 | 10,902 | 1825 | 2028 |
| 25 | Rosa ‘Mascotte’77’ | 1,348,336 | 194,927 | 360,430 | 192,203 | 104,895 | 84,567 | 469,425 | 88,000 | 103,508 | 17,083 | 10,924 | 1752 | 1948 |
| 26 | Rosa ‘Carola’ | 1,398,326 | 199,214 | 377,170 | 199,483 | 108,226 | 88,377 | 493,427 | 90,848 | 109,282 | 18,349 | 11,546 | 1975 | 2153 |
| 27 | Rosa ‘The Generous Gardener’ | 1,344,478 | 189,502 | 364,040 | 195,627 | 106,455 | 86,312 | 450,824 | 83,304 | 100,009 | 17,523 | 11,182 | 1830 | 1995 |
| 28 | Rosa sertata × rugosa | 1,188,949 | 161,730 | 324,249 | 157,584 | 85,441 | 69,747 | 387,032 | 67,988 | 89,546 | 14,294 | 9370 | 1331 | 1601 |
| 29 | Rosa ‘Blue Ribbon’ | 1,186,726 | 167,403 | 323,515 | 168,171 | 91,118 | 74,532 | 401,344 | 73,976 | 89,491 | 15,054 | 9627 | 1535 | 1700 |
| 30 | Rosa ‘Pink O’Hara’ | 1,404,933 | 194,208 | 394,423 | 196,383 | 106,505 | 87,051 | 481,736 | 87,461 | 110,301 | 18,279 | 11,676 | 1871 | 2126 |
| 31 | Rosa ‘Crimson Glory’ 1# | 1,254,209 | 179,744 | 336,313 | 187,844 | 102,570 | 82,607 | 434,239 | 81,397 | 95,052 | 16,944 | 10,652 | 1889 | 1989 |
| 32 | Rosa ‘South Seas’ | 1,382,117 | 205,619 | 357,989 | 216,528 | 120,033 | 93,629 | 480,145 | 93,954 | 102,703 | 18,772 | 11,718 | 2049 | 2217 |
| 33 | Rosa ‘Pengpeng’ | 1,299,944 | 187,800 | 339,374 | 192,,915 | 105,863 | 84,373 | 445,309 | 83,736 | 96,607 | 17,124 | 10,804 | 1812 | 1963 |
| 34 | Rosa rugosa ‘Pingyin 1’ | 1,068,091 | 196,673 | 193,577 | 216,731 | 121,157 | 93,214 | 459,201 | 99,406 | 78,383 | 20,376 | 11,877 | 2717 | 2526 |
| 35 | Rosa centifolia ‘Grasse Rose’ | 1,557,369 | 248,092 | 363,014 | 264,223 | 145,427 | 115,496 | 556,043 | 113,146 | 109,083 | 22,693 | 13,764 | 2729 | 2727 |
| 36 | Rosa ‘Sijifen’ | 1,186,996 | 164,523 | 327,305 | 163,319 | 88,240 | 72,660 | 400,260 | 72,294 | 90,652 | 14,989 | 9652 | 1532 | 1691 |
| 37 | Rosa ‘Suji’ | 1,374,657 | 195,871 | 369,643 | 192,156 | 104,278 | 85,114 | 475,784 | 87,848 | 105,439 | 17,346 | 11,124 | 1736 | 1991 |
| 38 | Rosa ‘Tineke’ | 1,159,157 | 210,645 | 217,998 | 228,676 | 127,223 | 98,869 | 493,822 | 105,818 | 86,588 | 21,299 | 12,533 | 2800 | 2607 |
| 39 | Rosa ‘Meilivoine’ | 1,362,014 | 188,865 | 369,434 | 185,994 | 100,914 | 82,312 | 435,751 | 78,230 | 98,335 | 16,317 | 10,501 | 1656 | 1865 |
| 40 | Rosa cv. Climbers 1 | 1,394,736 | 201,047 | 379,712 | 188,753 | 102,074 | 83,893 | 480,969 | 89,538 | 106,393 | 16,925 | 10,894 | 1738 | 1911 |
| 41 | Rosa ‘Sweet Chariot’ | 1,265,480 | 171,094 | 349,046 | 166,832 | 90,227 | 73,989 | 420,677 | 73,409 | 97,160 | 15,370 | 10,085 | 1453 | 1680 |
| 42 | R. laxa × hybrida cv. Tianshan Xiaguang | 1,347,767 | 217,477 | 325,469 | 206,677 | 113,906 | 90,101 | 492,222 | 99,670 | 98,901 | 17,269 | 10,723 | 1960 | 2053 |
| 43 | R. laxa × hybrida cv. Tianshan Xiangyun | 1,403,917 | 217,849 | 346,639 | 224,597 | 123,844 | 97,794 | 505,945 | 101,081 | 104,130 | 19,579 | 11,928 | 2355 | 2316 |
| 44 | Rosa ‘Smooth sunglow’ | 1,254,136 | 181,357 | 330,425 | 186,622 | 101,992 | 81,998 | 437,988 | 82,501 | 95,271 | 16,695 | 10,498 | 1799 | 1966 |
| 45 | Rosa ‘Xinba’ | 1,343,121 | 195,384 | 355,231 | 194,716 | 106,549 | 85,364 | 459,931 | 86,611 | 101,426 | 17,221 | 10,929 | 1798 | 1964 |
| 46 | Rosa ‘Betty Prior’ | 1,191,623 | 171,810 | 310,885 | 172,337 | 93,700 | 76,147 | 409,689 | 75,962 | 89,231 | 15,646 | 9935 | 1611 | 1808 |
| 47 | Rosa ‘Yuki Akari’ | 1,249,571 | 171,664 | 337,954 | 166,173 | 89,677 | 73,898 | 408,318 | 71,764 | 94,283 | 14,985 | 9841 | 1430 | 1580 |
| 48 | Rosa ‘Lavender Bouquet’ | 1,185,191 | 160,931 | 324,550 | 155,339 | 84,065 | 68,890 | 385,486 | 67,797 | 89,399 | 13,992 | 9174 | 1300 | 1578 |
| 49 | Rosa ‘Movie Star’ | 1,244,338 | 180,865 | 329,689 | 179,963 | 97,636 | 79,745 | 435,785 | 81,799 | 95,067 | 16,230 | 10,287 | 1697 | 1890 |
| 50 | Rosa ‘Yueyuehong’ | 890,350 | 127,942 | 230,090 | 127,109 | 69,364 | 55,876 | 312,153 | 55,733 | 70,197 | 11,356 | 7374 | 1107 | 1305 |
| 51 | Rosa ‘Yuncaihong’ | 1,151,872 | 161,160 | 314,582 | 157,107 | 84,982 | 69,829 | 389,439 | 70,746 | 87,469 | 14,401 | 9269 | 1445 | 1635 |
| 52 | Rosa ‘Yuncaixia’ | 1,329,661 | 191,778 | 350,676 | 191,567 | 104,654 | 84,102 | 450,467 | 84,498 | 97,805 | 16,986 | 10,882 | 1755 | 1988 |
| 53 | Rosa ‘Yunxiang’ | 1,338,109 | 196,573 | 350,437 | 199,055 | 108,426 | 87,843 | 474,464 | 90,366 | 102,291 | 18,103 | 11,379 | 1956 | 2073 |
| 54 | Rosa ‘Parkdirektor Riggers’ | 1,442,596 | 209,991 | 380,201 | 200,675 | 108,729 | 88,996 | 504,133 | 94,083 | 108,625 | 18,112 | 11,620 | 1863 | 2030 |
| 55 | Rosa ‘Crimson Glory’ 2# | 1,177,506 | 170,541 | 312,935 | 174,296 | 95,016 | 76,801 | 408,205 | 76,593 | 90,015 | 15,600 | 9887 | 1682 | 1795 |
| 56 | Rosa ‘Roger Lambelin’ | 1,217,137 | 186,897 | 296,511 | 195,810 | 106,976 | 86,184 | 447,586 | 86,031 | 94,942 | 17,902 | 11,291 | 1959 | 2084 |
| 57 | Rosa rugosa ‘Zizhi’ | 1,033,306 | 193,036 | 187,447 | 210,695 | 117,920 | 90,469 | 433,119 | 95,623 | 73,890 | 18,770 | 10,960 | 2505 | 2349 |
| 58 | Rosa laxa | 1,052,914 | 190,259 | 195,950 | 211,707 | 118,848 | 90,638 | 439,522 | 94,254 | 77,090 | 19,018 | 11,129 | 2538 | 2362 |
| Group | Strong Scent | Moderate Scent | Low Scent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nei | 0.27 | 0.261 | 0.255 |
| Ho | 0.219 | 0.223 | 0.223 |
| PIC | 0.216 | 0.212 | 0.208 |
| H | 0.411 | 0.405 | 0.397 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, M.; Ren, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Hui, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lin, G.; Li, Y. Genetic Structure and Selection Signature in Flora Scent of Roses by Whole Genome Re-Sequencing. Diversity 2023, 15, 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15060701
Sun M, Ren X, Liu Y, Yang J, Hui J, Zhang Y, Cui Y, Zhang J, Lin G, Li Y. Genetic Structure and Selection Signature in Flora Scent of Roses by Whole Genome Re-Sequencing. Diversity. 2023; 15(6):701. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15060701
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Meile, Xiangrong Ren, Ya Liu, Jing Yang, Jingtao Hui, Yukun Zhang, Yanhua Cui, Jun Zhang, Guocang Lin, and Yan Li. 2023. "Genetic Structure and Selection Signature in Flora Scent of Roses by Whole Genome Re-Sequencing" Diversity 15, no. 6: 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15060701
APA StyleSun, M., Ren, X., Liu, Y., Yang, J., Hui, J., Zhang, Y., Cui, Y., Zhang, J., Lin, G., & Li, Y. (2023). Genetic Structure and Selection Signature in Flora Scent of Roses by Whole Genome Re-Sequencing. Diversity, 15(6), 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15060701






