Abstract
Current taxonomical keys are essential for better biodiversity knowledge. Moreover, accurate identification of groups of organisms known to act as disease vectors is vital in today’s world of change and the spread of zoonotic disease threats. This is especially relevant to bats and their parasites, given the events of recent years. The available keys of European Nycteribiidae (Diptera) are outdated and do not cover all the species currently known from Europe. Therefore, a summary key of 16 European species is provided in this paper. Based on published data from Europe, a total of 173 host–parasite interactions were observed between 16 European bat fly species and 31 host species (bats). The highest number of associations with different host species and the lowest specialization was observed in Penicillidia (P.) dufourii dufourii, followed by Nycteribia (N.) kolenatii, N. (N.) schmidlii and Phthiridium biarticulatum; most of the other species also had low specialization. Most species are oligoxenous, parasitizing on several families, and three species are stenoxenosus. Only one nycteribiid species, Basilia daganiae, was linked with only one host (Pipistrellus kuhlii). Myotis myotis has 12 associations with different bat fly species, followed by Plecotus auritus and Myotis daubentonii with 12 associations. A relatively high number of bat species were associated with only one bat fly species. In addition, we performed a bipartite analysis complemented by network indices and host specificity at the species and whole network levels, yielding new information in terms of ecology and the host–parasite relationships related to these groups of potential vectors (Nycteribiidae) and sources of zoonoses (bats). The parasite–host network composed of 16 nycteribiid species and 31 bat host species was characterized by a low network level specialization, low modularity, and low nestedness. Our findings also suggest a high probability of associated Nycteribiidae in bat taxa with a similar roosting ecology and phylogenetic relationship.
1. Introduction
Bats (Mammalia: Chiroptera) are the second most numerous mammalian group after rodents, with more than 1430 species (https://batnames.org/; accessed 19 March 2023) [1], and they provide crucial ecosystem services as seed dispersers, pollinators, controllers of insects, and nutrient recyclers [2]. On the other hand, bats are also considered to be natural reservoirs of a wide range of microorganisms, especially viruses [3]. The fact that they are reservoirs for a staggering number of viruses and other potential pathogens is due to their biology, ecology, and behavior (e.g., diversity of food, colonial sociality, mobility, and migration, etc.) [4]. Although bats on average harbor a higher diversity of parasites and pathogens than any other mammalian group, the likelihood of bat flies vectoring disease agents across host species of bats may be relatively small [5].
Many ectoparasites, such as acarines (ticks, chiggers, and mites), bat flies, and fleas, specialize in bats as hosts. Bat flies (Diptera: Nycteribiidae) form a fascinating and largely disregarded group of obligate, blood-feeding, highly specialized ectoparasites of bats [6,7]. This family is included in the superfamily Hippoboscoidea, along with the families Hippoboscidae (keds or louse flies), Glossinidae (tse-tse flies), and Streblidae [8]. Phylogenetic studies suggest monophyly among Hippoboscoidea members and that the ancestor of this superfamily was a free-living insect feeding on mammals’ blood [9,10]. One of the most interesting characteristics of bat flies is that they are obligate parasites of bats [11]. Their ecological origins are obscure, but Jobling [12] envisioned an ancestral association with caves and guano accumulations before their switch to an ectoparasitic lifestyle. Bat fly morphology reflects their role as ectoparasites. The wings of many species are strongly reduced or absent, and long limbs facilitate locomotion in the host body. Nycteribiids possess several ctenidia or combs. Various theories have been published on the function of ctenidia. One theory claims that the ctenidia help them to hold onto the fur and wing membrane [13,14]. Observations by other authors suggest that ctenidia function not as organs of attachment, but rather to protect highly mobile joints and their associated membranes, which are not otherwise protected [15]. One of the most consistent morphological features of bat flies is the rudimentary manifestation of their visual system [16]. Their eyes are completely missing or reduced to relatively few facets and ocelli are absent [17]. Worldwide, three subfamilies (Archinycteribiinae Maa, 1975, Cyclopodiinae Maa, 1965, Nycteribiinae Westwood, 1835), 11 genera, and more than 276 nycteribiid species are known [18]. In Europe, only 16 species from the subfamily Nycteribiinae have been recorded [19,20,21].
Adult bat flies of both sexes spend their lives on bats where they can be observed in the fur or on the wing membranes. Bat flies reproduce via viviparous puparity [16]. Eggs are internally fertilized and all larval stages develop within the females [22]. Larvae molt twice inside the female, and gravid females deposit a single terminal (3rd-instar) larva on the roosting substrate. Once deposited, the larva (referred to as a prepupa) immediately forms a puparium. The pupal stage lasts 3–4 weeks [23]. Bat flies deposit their larva on substrates, such as the host roost wall. After larviposition, females return to their host. When the offspring emerge, they actively search for bat hosts [24].
On the behavioral side, bat flies have been observed to react to sudden strong light flashes. Upon exposure, they consistently respond with a startle reflex resulting in flight. Bat flies are covered in setae, many of which seem to function as mechanoreceptors, aiding in the sensation of air currents or vibrations. Little is known about the olfactory faculties and preferences of bat flies, but presumably, olfactory cues are important in host finding. Some bat flies exhibit strong plumose modification of the arista, which in other Diptera is known to contain thermo- and hygroreceptors [25].
As obligate blood-feeding parasites, bat flies seem to be excellent candidates for vectors of zoonotic agents, and recent studies have shown that bat flies could carry pathogens, such as bacteria and viruses, and transmit them among bat individuals in a colony [1,2,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33]. The likelihood of disease transmission by bat flies to distantly related mammals, such as humans, is considered to be relatively small [5]. Further, interspecies transmission via bat flies is unlikely under normal conditions, because Nycteribiids are usually highly specific parasites, with each species of bat fly parasitizing a single bat species or genus [15] or rarely, families, as in the case of Penicillidia fulvida [34]. Bats occasionally form species-specific groups in colonies [35], which may lead to low ectoparasite overlap between bat species. However, they very often form mixed species colonies [36].
Although identification and knowledge of the ecology and biology of bats are at a high level, this is not the case for some of their parasites (such as Nycteribiidae) [37].
Moreover, apart from the epidemiological perspective, the study of host–parasite interactions is an opportunity to understand the ecological relationships between organisms. Parasites, together with their hosts, constitute an ideal system for investigating the patterns and mechanisms of community structure and dynamics [38]. Analyses of the relations between parasites and hosts are possible using so-called ecological network analysis, which is a representation of interactions within the studied ecosystems [39,40,41]. Ecological networks can inform us about the evolutionary and ecological processes that generate and shape biodiversity. The structure of ecological networks can also provide information on the vulnerability of ecological communities to various kinds of disturbances: from climate change to the illegal hunting of keystone species and extinctions of species-to-species invasions [42], or they can help to better understand the phoretic relationships between arthropods [43]. Ecological networks and host–parasite associations remain understudied in bats and their parasites, including nycteribiids. Despite growing knowledge on diversity and bat-Nycteribiidae associations [35,38,44,45,46,47,48,49,50] and the existence of literary records on the host species of bat flies from Europe [7,51,52], many gaps need to be filled.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Updating of Identification Key
Using the records of Szentivanyi et al. [21] as a starting point, we checked the literature on the host associations of European bat louse for new, overlooked, or misattributed records [53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132,133,134,135,136,137,138,139,140,141,142]. In addition, we conducted a literature search using the keywords ‘Nycteribiidae*’, ‘European bat flies*’, ‘host associations *’, ‘bats *’, and ‘Europe*’ in Scopus and Google Scholar [7,51,52,143,144,145,146,147,148,149,150,151,152,153,154]. Figures are redrawn and modified based on the original illustration by Theodor (1954) [155] (pp. 66 a. Nycteribiidae. Taf. I-IV, VI-VII, IX, XIII-XVI); Theodor (1967) [57] (pp. 1–506, figures compared with [50]); Hůrka (1970) [53]. (p. 243: Figure 1); Hůrka (1972) [54] (p. 711: Figure 1); Beaucournu and Noblet (1685) [68] (p. 637: Figure 1).
2.2. Host Specificity, Bipartite Networks, and Statistics
For the host associations of European bat flies, we used information published by Szentivanyi et al. [21] and the recent literature [7,51,52,143,144,145,146,147,148,149,150,151,152,153,154]. The terminology for the host specificity of particular bat fly species follows [156,157].
To illustrate the parasite–host relationship between bat flies and bats, we used a bipartite network. The boxes of the bipartite graph represent species, and their width represents the summary of interactions among these species. The number of interactions is shown by lines linking the species, and the number of lines means the number of species interactions. To do this, we used a function visualizing a bipartite interaction named matrixplotweb, through which a two-dimensional matrix is plotted as a bipartite graph [158]. Another function of the bipartite package for R—plotModuleWeb takes an object of class in moduleWeb and plots the modules found by function computeModules(...) function into the graph [159].
To carry out the analyses of patterns in the host–parasite network, we used the bipartite package (version 2.18) for R software [160]. For quantitative indices, the number of bat fly species infesting each bat species was used. We prepared matrices with bat species (host) in the columns and bat flies in the rows. In the next step, we calculated these bipartite indexes: connectance (C), network specialization (H2‘), nestedness (N), modularity (Q), and species’ specialization metrics (d‘).
Connectance (C) is one of the most popular and earliest metrics proposed to characterize species interaction networks: it is defined as the proportion of realized interactions from the pool of all possible interactions between the species of a network [161]. The Networklevel function of the bipartite package analyzes bipartite webs at the level of the entire network and calculates a variety of indices and values for a bipartite network, including connectance [162].
The index of network specialization (H2‘) reflects the deviation of a species’ realized number of interactions and the expected number from each species’ total quantity of interactions [163]. The value of this index varies from 0 to 1, where 0 suggests high specialization and 1 implies low specialization. To calculate this index, we used the H2fun function of the bipartite package with two arguments: web, which is a matrix representing the interactions observed between higher trophic level species in columns and lower trophic level species in rows, and H2_intriger, which is a logical argument indicating whether web entries are integer numbers [164].
Nestedness (N) is a measure of the structure of an ecological system and expresses how many interactions realized by specialists are a subset of those performed by generalists. The unit of nestedness is the nestedness temperature T, ranging from 0 to 100°. However, in this study, we used a binary system, where metrics define N = (100 − T)/100. It measures the departure from a perfectly nested interaction matrix [165]. In the range of 0–1, value 1 implies maximum nestedness [166,167,168]. To compute this index, we used a function of the bipartite package named nestedness, which calculates matrix temperature using the BinMatNest approach of Miguel Rodriguez-Girones [169].
Modules are aggregated sets of species that interact. Their defining feature is that interactions within a module are more common than interactions between modules [170,171,172]. Modularity (Q) is calculated as likelihood, which is implemented in the bipartite computeModules function. This function takes a bipartite weighted graph and computes modules by applying Newman’s modularity measure in a bipartite weighted version to it [173].
The last index we calculated was species’ specialization metrics (d’). This index measures interactions at the species level and refers to each bat fly species related to bats in the network [174]. To determine this index, the function dfun was used, which returns the specialization index d’ for the lower level, which expresses how specialized the species is in relation to what higher-level partners are on offer. The mentioned function has two arguments: web, which is a matrix representing the interactions observed between higher level species (columns) and lower-level species (rows), and abuns, which is a vector of abundance for the higher level, usually from independent information [175]. For a more detailed description of these methods, see [157].
3. Results
Identification Key for European genera of Nycteribiidae
1 eyes absent (Figure 1(1,4))… 2
– eyes present (Figure 1(2,3))… 4
2 tibiae longer and narrower, 4.5 to 5 times longer than wide (Figure 1(6))… Phthiridium biarticulatum Hermann, 1804
– tibiae short, curved ventrally… 3
3 tibiae nearly semicircular, 2 to 2.5 times longer than wide (Figure 1(5))… Nycteribia (Nycteribia)
– tibiae more slender, 3.5 times as long as wide… Nycteribia (Acrocholidia) vexata Westwood, 1835
4 eyes pigmented, with at least 2 lenses, specimens to 3 mm… Basilia
– unpigmented eyes with one lens (Figure 1(2,3)), specimens from 3.5 to 4 mm… Penicillidia
Key for sex determination
1 ventral abdomen with claspers (Figure 1(8))… males
Keys to species of European genera of Nycteribiidae
Genus Basilia Miranda Ribeiro, 1903
Males
1 sternite 5 with one row of spines… 2
– sternite 5 with two or more rows of spines… 4
2 sternite 5 with 6–8 spines with convex posterior margin (Figure 1(9))… Basilia nattereri Kolenati, 1857
– sternite 5 with more than 8 spines… 3
3 sternite 5 with 8–10 short spines (Figure 1(10))… Basilia nana Theodor & Moscona, 1954
– sternite 5 with 11–13 spines with convex posterior margin (Figure 1(11))… Basilia mediterranea Hurka, 1970
4 sternite 5 convex, 4 times wider than long, with a group of about 20–25 soft spines in 2 rows in the middle of posterior margin…5
– sternite 5 rectangular, 3 times wider than long, with a group of about 15 spines in a double row (Figure 1(12))… Basilia daganiae Theodor & Moscona, 1954
5 sternite 5 significantly convex, with a group of about 20 soft spines in 2 rows in the middle of the posterior margin (Figure 1(13))… Basilia italica Theodor, 1954
– sternite 5 slightly convex, with a group of about 25 soft spines in 2 rows in the middle of the posterior margin (Figure 1(14))… Basilia mongolensis nudior Hurka, 1972
Females
1 tergal plate 2 trapezoidal… 3
– tergal plate 2 parallel… 2
2 tergal plate 2 transversely rectangular, lower edge 2 times narrower than upper (Figure 2(15))… Basilia nattereri Kolenati, 1857
– tergal plate 2 square (Figure 2(16))… Basilia nana Theodor & Moscona, 1954
3 posterior margin 2 times narrower than upper, with a row of 18–22 setae at the posterior margin which has a small indentation in the middle (Figure 2(17))… Basilia italica Theodor, 1954
– the posterior margin 3 times narrower than upper…4
4 tergal plate 2 with 6 long setae and a second row of small setae at the posterior margin which has a big indentation in the middle (Figure 2(18))… Basilia daganiae Theodor & Moscona, 1954
– tergal plate 2 with one row of 6 or fewer long setae in the middle of the posterior margin, which has an indentation in the middle…
5 tergal plate 2 with 6 long setae in the middle of the posterior margin, which has a strong indentation in the middle (Figure 2(19))… Basilia mediterranea Hurka, 1970
– tergal plate 2 with 4 long setae in the middle of the posterior margin, which has a strong indentation in the middle (Figure 2(20))… Basilia mongolensis nudior Hurka, 1972
Genus Nycteribia Latreille, 1796
Subgenus Acrocholidia Kolenati, 1857—one species only
Nycteribia (Acrocholidia) vexata Westwood, 1835
Male—sternite 5 with a row of 8–10 strong spines of concave posterior margin (Figure 3 (21)). Aedeagus with a rounded end, which is as wide as the base, narrower in the middle. Parameres slender, triangular, three-quarters the length of the aedeagus.
Female—genital plate consisting of a strongly sclerotised arc with about 4 (to 7) short spines. Tergite 1 with a row of long setae posteriorly (Figure 3(22)).
Subgenus Nycteribia Latreille, 1796
Males
1 sternite 5 three to 4 times wider than long… 2
– sternite 5 two times wider than long, strongly convex posteriorly, with a double row of 14–16 short, thick spines (Figure 3(23)). Anal segment very long, nearly parallel-sided. Aedeagus with a long bifid tip which is curved backwards and has scales at the base of the dorsal membrane… Nycteribia (Nycteribia) schmidlii Schiner, 1853
2 sternite 5 with a row of 14–18 spines in the middle of the concave posterior margin (Figure 3(24)). Phallobase conical, aedeagus conical with a ventral tooth near the tip… Nycteribia (Nycteribia) latreillii (Leach, 1817)
– sternite 5 with a row of 9–12 short spines in the middle of the convex posterior margin (Figure 3(25)). Phallobase with a marked dorsal bulge. Aedeagus wide and short, with a rounded end and a ventral tooth at about the distal third… Nycteribia (Nycteribia) pedicularia Latreille, 1805
3 sternite 5 with a row of 7–8 spines in the middle of the row, posterior margin (Figure 3(26)). Phallobase conical, without the dorsal bulge. Aedeagus slender, with a ventral tooth at the distal fifth… Nycteribia (Nycteribia) kolenatii Theodor & Moscona, 1954
Females
1 dorsal sternite 5 with 2 small lateral plates, with 2 long setae posteriorly. Sternite 6 with 2 lateral plates narrowed toward the centre. Sternite 7 with plate as long as the width of the plates on sternite 6. Ventral genital plate wide. Tergite 2 of abdomen about as long or longer than the width of tergite 1, strongly convex posteriorly. Dorsal genital plate triangular with truncated sides and 11–15 strong spines (Figure 4(27))… Nycteribia (Nycteribia) latreillii (Leach, 1817)
– dorsal sternite 5 with 2 lateral plates, with 5 and more long setae…2
2 dorsal sternite 5 with 2 lateral plates with 7 to 9 long setae. Sternite 6 with 2 lateral plates touching each other. Sternite 7 with plate as long as two-thirds of the plates on sternite 6. Ventral genital plate narrow. Tergite 2 similar to that of N. latreillii or pointed posteriorly. Dorsal genital plate triangular, with 8–10 long setae (Figure 4(28))… Nycteribia (Nycteribia) kolenatii Theodor & Moscona, 1954
– dorsal sternite 5 with 2 lateral plates, with 5–7 long setae centrally. Sternite 6 with 2 lateral plates not touching each other. Sternite 7 with plate longer than two-thirds of the plates on sternite 6, concave at front. Ventral genital plate narrow, length 2.5 mm. Tergite 2 shorter in the middle than the width of tergite 1. Dorsal genital plate triangular with a row of about 12 short spines (Figure 4(29))… Nycteribia (Nycteribia) pedicularia Latreille, 1805
3 dorsal sternite 5 with 2 lateral plates, with 15–17 long setae in two lines. Sternite 6 with 2 lateral plates not touching each other. Sternite 7 with plate longer than two-thirds of the plates on sternite 6, concave at front. Genital plate elliptical with a row of very short spines posteriorly. Tergite 3 about three-quarters as wide as tergite 2, surface covered with short spines (Figure 4(30))… Nycteribia (Nycteribia) schmidlii Schiner, 1853
Genus Penicillidia Kolenati, 1863
Subgenus Penicillidia Kolenati, 1863
Males
1 posterior angle of sternite 5 pronounced. About 15 spines in 1–2 rows at each side of the posterior margin (Figure 4(31)). Apex of the triangle bare. Surface of the sternite bare except for groups of setae at the lateral corners. Aedeagus with an apical dorsal tooth… Penicillidia (Penicillidia) conspicua Speiser, 1901
– posterior angle of sternite 5 not pronounced… 2
2 sternite 5 with two lateral broad, rounded processes covered with numerous short, thick spines and with only a median group of spines between the lateral processes (Figure 4(32)). Frons not prolonged (Figure 1(2))… Penicillidia (Penicillidia) dufourii dufourii (Westwood, 1835)
– sternite 5 with two shorter lateral broad, rounded processes covered with numerous short, thick spines and with a group of spines between the lateral processes (Figure 4(33)). Frons prolonged into a long horn (Figure 1(3))… Penicillidia (Penicillidia) monoceros Speiser, 1900
Females
1 tergite 1 triangular, with a few short spines at the apex. Tergal plate 2 large, rounded, with a marginal row of about 20 long setae and covered with short hairs on the surface (Figure 5(34)). Sclerotised processes lacking. Genital plate with an angular row of 10–14 setae… Penicillidia (Penicillidia) conspicua Speiser, 1901
– tergite 1 rounded posteriorly… 2
2 tergite 1 with a row of short, thick setae with a gap in the middle. Tergal plate 2 rectangular, bare on the surface, with 2 groups of long spines at the posterior margin. Two sclerotised processes with a sharp posterior edge on the connexivum behind tergal plate 2 (Figure 5(35)). Genital plate small, rounded, with 6–8 setae. Frons not prolonged (Figure 1(2))… Penicillidia (Penicillidia) dufourii dufourii (Westwood, 1835)
– tergite 1 with a row of short, thick setae with a gap in the middle. Tergal plate 2 rectangular, bare on the surface, with 2 groups of long spines at the posterior margin. Two sclerotised processes with a sharp posterior edge on the connexivum behind tergal plate 2. Genital plate small, rounded, with 6–8 setae. Frons prolonged into a long horn (Figure 1 (3))… Penicillidia (Penicillidia) monoceros Speiser, 1900
Genus Phthiridium Hermann, 1804
Males
1 sternite 5 four times wider than long, with a row of 15–18 strong spines in the middle and an upper row with soft spines of strong convex posterior margin (Figure 5(36))… Phthiridium biarticulatum Hermann, 1804
– sternite 5 three times wider than long, with a row of about 25 small spines in 1–2 rows of slightly convex posterior margin (Figure 5(37))... Phthiridium integrum (Theodor and Moscona, 1954)
Females
1 tergite 2 very long, covering about half the abdomen. Tergite 6 very large, triangular, with some short setae on the surface (Figure 5(38))… Phthiridium biarticulatum Hermann, 1804
– tergite 2 shorter, covering about one-third of the abdomen, broadly rounded. Tergite 6 smaller, rectangular, with a bare surface, with 6 long and 4 short setae posterior (Figure 5(39))... Phthiridium integrum (Theodor and Moscona, 1954)
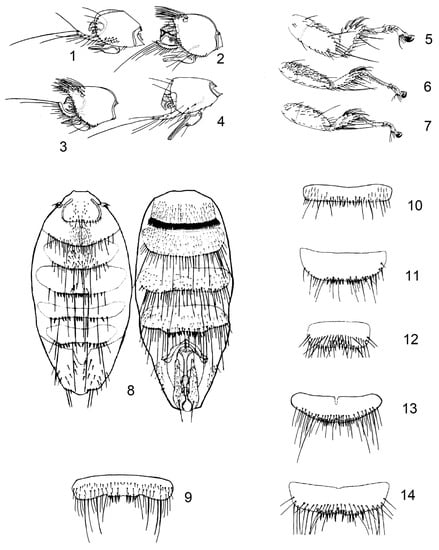
Figure 1.
(1) Nycteribia (Nycteribia) latreillii (Leach, 1817), head; (2) Penicillidia (Penicillidia) dufourii dufourii (Westwood, 1835), head; (3) Penicillidia (Penicillidia) monoceros Speiser, 1900, head; (4) Nycteribia (Acrocholidia) vexata Westwood, 1835, head; (5) Nycteribia (Nycteribia) kolenatii Theodor and Moscona, 1954, leg; (6) Phthiridium biarticulatum Hermann, 1804, leg; (7) Basilia nana Theodor and Moscona, 1954, leg; (8) Nycteribia (Nycteribia) pedicularia Latreille, 180, male, ventral abdomen with claspers; (9) Basilia nattereri Kolenati, 1857, male, sternite 5; (10) Basilia nana Theodor and Moscona, 1954, male, sternite 5; (11) Basilia mediterranea Hurka, 1970, male, sternite 5; (12) Basilia daganiae Theodor and Moscona, 1954, male, sternite 5; (13) Basilia italica Theodor, 1954, male, sternite 5; (14) Basilia mongolensis nudior Hurka, 1972, male, sternite 5.
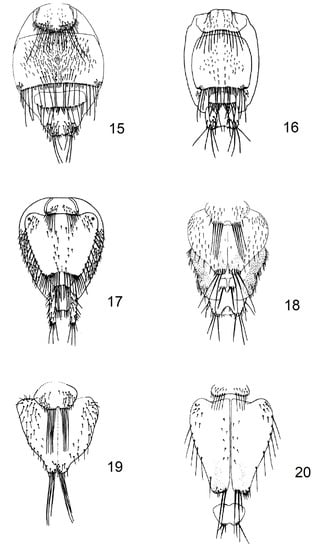
Figure 2.
(15) Basilia nattereri Kolenati, 1857, female, abdomen; (16) Basilia nana Theodor and Moscona, 1954, female, abdomen; (17) Basilia italica Theodor, 1954, female, abdomen; (18) Basilia daganiae Theodor and Moscona, 1954, female, abdomen; (19) Basilia mediterranea Hurka, 1970, female, abdomen; (20) Basilia mongolensis nudior Hurka, 1972, female, abdomen.

Figure 3.
(21) Nycteribia (Acrocholidia) vexata Westwood, 1835, male, sternite 5; (22) Nycteribia (Acrocholidia) vexata Westwood, 1835, female, abdomen, genital plate; (23) Nycteribia (Nycteribia) schmidlii Schiner, 1853, male, sternite 5; (24) Nycteribia (Nycteribia) latreillii (Leach, 1817), male, sternite 5; (25) Nycteribia (Nycteribia) pedicularia Latreille, 1805, male, sternite 5; (26) Nycteribia (Nycteribia) kolenatii Theodor and Moscona, 1954, male, sternite 5.

Figure 4.
(27) Nycteribia (Nycteribia) latreillii (Leach, 1817), female, abdomen, genital plate; (28) Nycteribia (Nycteribia) kolenatii Theodor and Moscona, 1954, female, abdomen, genital plate; (29) Nycteribia (Nycteribia) pedicularia Latreille, 1805, female, abdomen, genital plate; (30) Nycteribia (Nycteribia) schmidlii Schiner, 1853, female, abdomen, genital plate; (31) Penicillidia (Penicillidia) conspicua Speiser, 1901, male, sternite 5; (32) Penicillidia (Penicillidia) dufourii dufourii (Westwood, 1835), male, sternite 5; (33) Penicillidia (Penicillidia) monoceros Speiser, 1900, male, sternite 5.
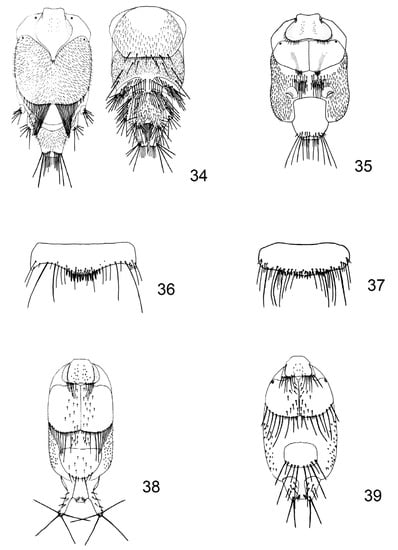
Figure 5.
(34) Penicillidia (Penicillidia) conspicua Speiser, 1901, female, abdomen; (35) Penicillidia (Penicillidia) dufourii dufourii (Westwood, 1835), female, abdomen; (36) Phthiridium biarticulatum Hermann, 1804, male, sternite 5; (37) Phthiridium integrum (Theodor and Moscona, 1954), male, sternite 5; (38) Phthiridium biarticulatum Hermann, 1804, female, abdomen; (39) Phthiridium integrum (Theodor and Moscona, 1954), female, abdomen.
Bat Fly-Bat Species Associations and the Bipartite Network
Altogether, 173 host–parasite interactions were observed between 16 European bat fly species and 31 host species (bats) (See also Supplementary). The highest number of associations (17) with different host species and the lowest value of the index of specialization (d’) was observed in Penicillidia (Penicillidia) dufourii dufourii, followed by Nycteribia (Nycteribia) kolenatii (17 host spp.), N. (N.) schmidlii (16; host spp.), and Phthiridium biarticulatum (16; host spp.). Most of the other species have low or relatively low specialization (< 0.5), and most species are oligoxenous, parasitizing on several families of one order [156]. Three species (B. maditerranea, Basilia mongolensis nudior, Phthiridium integrum) are stenoxenous, parasitizing more than one genus of hosts, but are restricted to one family [5,156], and four species (B. italica, B. mediterranea, B. mongolensis nudior, Phthiridium integrum) have high specialization. Only one nycteribiid species (Basilia daganiae) was monoxenous with only one host (Pipistrellus kuhlii) and d’ = 1 (Figure 6 and Table 1).
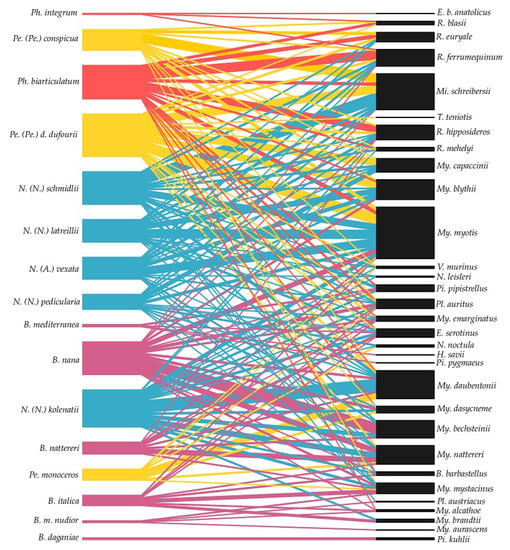
Figure 6.
Bipartite network graph of interactions between bat flies (left) and bats (right). Each color of bat fly species means one genus (Basilia—purple, Nycteribia—blue, Penicillidia—yellow, and Phthiridium—red. The overlap of lines is minimized and parasite species are ordered so that the closest are those that have the most common hosts, and on the other hand, the parasites are ordered by similarity in terms of common hosts.

Table 1.
The number of hosts published and the index of bat flies’ specialization at the species level (d’), and the specificity of European bat fly species. Grey rows mean high specialization and dark grey rows mean the highly specialized monoxenous species.
Three bat species, namely Myotis myotis (12 associations with different bat fly species) and Plecotus auritus with Myotis daubentonii with 12 associated species, were found. On the other hand, a relatively high number of bat species were associated with only one bat fly species (Eptesicus bottae anatolicus, Hypsugo savii, Myotis davidii, P. kuhlii, P. pygmaeus, and Tadarida teniotis) from Europe, according to the publications (Figure 6, Table 1, and Supplementary).
According to the results of bipartite analysis, the network of bats and bat flies has low connectance (C = 0.31), low specialization (H2′ = 0.30), and a low degree of nestedness (N = 0.31 with nestedness temperature = 29.19). The specialization on the species level (d′) ranged between 0.14 and 1.00 (Table 1). The strength of the interactions between the parasites (bat fly) and hosts (bats) is illustrated in the bipartite graph (Figure 6), as the thickness of the line connecting parasites with host species reflects the number of records published. The thickness of the box of individual bat and bat fly species represents the relative number of records of particular parasites and host species. As the network is very complex, different colors represent different bat fly genera.
4. Discussion
There is a growing interest in bat flies due to their importance in the study of parasitic and hyperparasitic relations [38,176,177], as well as their vectorial role in pathogen transfer [32,33,178,179]. Identification and knowledge of the ecology and host–parasite network of Nycteribiidae are critical. In order to contribute to the knowledge of this interesting and important group of parasites and to fill knowledge gaps, we developed a key for the identification of European nycteribiid species. Based on published data, we analyzed their hosts, their degree of specialization, and the communities (modules) that they form within parasite–host relationships.
The outdated keys of European Nycteribiidae (Diptera) were one of the complications making it difficult to study their ecology and possible importance for pathogen transmission [180]. Therefore, we have herein provided a summary key of 16 nycteribiid species currently known from Europe.
With this method, we aimed to find broader contexts, and more generally, valid patterns, and we succeeded in doing so. For example, disturbance may in turn cause an increase in accidental or transient associations of bats and their parasites with non-primary hosts. Such dynamics may increase the likelihood of host switching, and thus the movement of pathogens to new host species and the expansion of their range, increasing the risk of transmission to other mammals, including humans [5]. Moreover, according to published papers, the fact that specialization within parasite–host networks varied over time and space in the different communities analyzed (the influence of season and associated changes on the abundance and species’ richness of bats, the influence of latitude, etc. according to [35,47,50], and differences in host–parasite associations between published studies [21] and the recent literature [7] (e.g., [51,52] and many references there), this indirectly demonstrates the greater potential for bat flies to parasitize more bat species than can be detected in a sub-study devoted to individual communities. This is consistent with the findings of our more comprehensive analysis.
Thus, our study demonstrated that the bat flies included generally showed variable degrees of host specialization, and Nycteribiidae seem to be less specialized than was supposed by Marshall [15] and Verrett et al. [34]. The information published in these two papers, that Nycteribiids are usually highly specific, with each species of bat fly parasitizing a single bat species or genus or rarely, families, contradicts the other published records from Europe used in this study. Only one bat fly species (B. daganiae) was recorded from only one host species (P. kuhlii), possibly because there are only five reports and research in the area where this species occurs. It could potentially parasitize other host species; however, we do not know as we do not have data in the area. In contrast, most of the European species are oligoxenous (parasitizing more genera from one family) according to the published records [21]. Which intrinsic and extrinsic (biotic and abiotic) factors are crucial in terms of the ecological specialization of nycteribiids to particular bat host species are debatable. Sharing resources, including roosts, by bats can involve costs as well as benefits [181].
Dolabela Falcão et al. [50] claimed that more abundant bat species had a greater richness of associated ectoparasites. On the other hand, in addition to the population density of the bat host species, other factors may influence the diversity of associated ectoparasites. The age structure of the observed bat host population, the fitness of the animals in the subpopulation and population, and the season relative to the phenology of both the host and parasite may also be important [182,183,184].
The results of the bipartite network analysis shed more light onto the complexity of the relationships between bat flies (parasites) and bats (their hosts). Similarly to other bat fly–bat network analyses [35,47,50], our results of bipartite network analysis, based on the published records from Europe, show low specialization, low modularity, and low nestedness. This seems to be a general pattern in bat fly–bat networks, although the nestedness, connectance, and the number of compartments (modules, communities) are related to bat richness [50]. When comparing our results with Durán et al. [39], the connectance and network specialization are very similar, but the modularity was much lower in our study. This difference may also be caused by different species’ richness in these studies. Despite the low specialization (H2′ and d’), according to the results of our study, some of our results indicate the importance of the phylogenetic and ecological relatedness of hosts when phylogenetically related bat species support similar associated ectoparasite communities. Such findings indicating the importance of phylogenetic relationships are consistent not only in bat flies and bats [50], but also among different types of interactions and taxonomic groups [185,186,187,188], even though comparing results from different regions and between different taxa is problematic. In our study, Nycteribiidae showed an affinity towards particular bat species that are phylogenetically related, e.g., B. m. nudior and B. italica towards three cryptic whiskered bats (Myotis alcathoe, M. mystacinus, M. brandtii). It has been observed that bat species that share roosts are prone to becoming infested by ectoparasites of other species [189], and roosting site preference and roosting behaviors of bats may be factors that significantly affect the dynamic of bat–bat flies interactions [190]. This can also be assumed based on the data in the present study. For example, N. (A.). vexata, N. (N.) latreilliid, and P. d. dufourii presented predominant associations with M. myotis, M. blythii, and Rhinolophus species, which prefer underground or attic spaces for roosting and often together exploit the same roosting site [191]. Additionally, taxons N. (N) schmidlii, P. conspicua, and Ph. biarticulatum are associated with three species of the genus Rhinolophus and with M. schreibersii, showing a similar shelter preference [192,193].
These findings suggest a high probability of specific Nycteribiidae in bat taxa with similar roosting ecology. As the complexity of the problematics of pathogen transmission by nycteribiids have not been exhaustively elucidated to date, it is extremely important to further investigate the relationships between specific species of nycteribiids and bats [11,194,195].
5. Conclusions
Current knowledge, complemented by our results, points to the importance of further research focusing on ecological networks and parasite–host relationships, particularly, but not exclusively, in groups at high risk of epidemiologically serious diseases transmissible to other mammals, including humans. This may facilitate targeted research on bat fly–bat networks, bat fly specialization, and nycteribiid-transmitted bat pathogens. At the same time, however, the legislative conditions that regulate sampling of their hosts (Chiroptera) must be respected in order to ensure minimal impact of the research on populations of protected taxa. In addition, collection methods are challenging [180].
Supplementary Materials
The Overview of the Recorded Interactions. The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/d15040573/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and administration of the project—L.M., J.O., P.M. and Ľ.K.; methodology—L.M., J.O. and P.M.; data curation—J.O. and P.M.; analysis of the literature—L.M., Ľ.K., J.O., P.M., R.S., A.O. and M.P.; statistical analysis—L.M., J.O. and P.M.; writing, original draft—L.M., Ľ.K., J.O., P.M., R.S., A.O. and M.P.; writing, review and editing—L.M., Ľ.K., J.O., P.M., R.S., A.O. and M.P.; funding acquisition—L.M., J.O., P.M., R.S. and A.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the projects KEGA No. 005UVLF-4/2022, KEGA No. 008UVLF-4/2022, and project VEGA No. VEGA-1/0876/21, all granted by the Ministry of Education, Science, Research, and Sport of the Slovak Republic and by the Grant Agency of University Prešov in Prešov under contract No. GaPU 16/2023.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data used by the authors for the analysis are available in the Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
We thank the editor and the anonymous reviewers for their valuable and constructive comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Moreno Santillán, D.D.; Lama, T.M.; Gutierrez Guerrero, Y.T.; Brown, A.M.; Donat, P.; Zhao, H.; Rossiter, S.J.; Yohe, L.R.; Potter, J.H.; Teeling, E.C.; et al. Large-scale genome sampling reveals unique immunity and metabolic adaptations in bats. Mol. Ecol. 2021, 30, 6449–6467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, T.H.; Braun de Torrez, E.; Bauer, D.; Lobova, T.; Fleming, T.H. Ecosystem services provided by bats. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1223, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Fráncel, L.A.; García-Herrera, L.V.; Losada-Prado, S. Bats and their vital ecosystem services: A global review. Integr. Zool. 2022, 17, 2–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calisher, C.H.; Childs, J.E.; Field, H.E.; Holmes, K.V.; Schountz, T. Bats: Important reservoir hosts of emerging viruses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dick, C.W.; Dittmar, K. Parasitic bat flies (Diptera: Streblidae and Nycteribiidae): Host specificity and potential as vectors. In Bats (Chiroptera) as Vectors of Diseases and Parasites; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 131–155. [Google Scholar]
- Orlova, M.V.; Klimov, P.B.; Moskvitina, N.S.; Orlov, O.L.; Zhigalin, A.V.; Smirnov, D.G.; Dzhamirzoyev, H.S.; Vekhnik, V.P.; Pavlov, A.V.; Emelyanova, A.A.; et al. New records of bat flies (Diptera: Nycteribiidae), with an updated checklist of the nycteribiids of Russia. Zootaxa 2021, 4927, 410–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Péter, A.; Mihalca, A.D.; Sándor, A.D. Annotated checklist of the bat flies (Diptera: Nycteribiidae) of Romania. Zootaxa 2022, 5120, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, W.K.; Lloyd, J.E. Louse flies, keds, and bat flies (Hippoboscoidea). In Medical and Veterinary Entomology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 421–438. [Google Scholar]
- Nirmala, X.; Hypša, V.; Žurovec, M. Molecular phylogeny of Calyptratae (Diptera: Brachycera): The evolution of 18S and 16S ribosomal rDNAs in higher dipterans and their use in phylogenetic inference. Insect Mol. Biol. 2001, 10, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmar, K.; Porter, M.L.; Murray, S.; Whiting, M.F. Molecular phylogenetic analysis of nycteribiid and streblid bat flies (Diptera: Brachycera, Calyptratae): Implications for host associations and phylogeographic origins. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2006, 38, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Seo, M.G.; Lee, S.H.; Oem, J.K.; Kim, S.H.; Jeong, H.; Kim, Y.; Jheong, W.H.; Kwon, O.D.; Kwak, D. Relationship among bats, parasitic bat flies, and associated pathogens in Korea. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobling, F. Streblidae from the Belgian Congo, with description of a new genus and three new species. Rev. Zool. Bot. Afr. 1954, 50, 89–115. [Google Scholar]
- Traub, R. The relationship between spines, combs and other skeletal features of fleas (Siphonaptera) and the vestiture, affinities and habits of their hosts. J. Med. Entomol. 1972, 9, 601. [Google Scholar]
- Dick, C.W.; Patterson, B.D. Bat flies: Obligate ectoparasites of bats. In Micromammals and Macroparasites; Morand, S., Krasnov, B.R., Poulin, R., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2006; pp. 179–194. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, A.G. The function of combs in ectoparsitic insects. In Fleas; Traub, R., Starcke, H., Eds.; AA Balkema: Rotterdan, The Netherlands, 1980; pp. 79–87. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, A.G. The Ecology of Ectoparasitic Insects; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1981; 459p. [Google Scholar]
- McAlpine, J.F. (Ed.) Manual of Nearctic Diptera; Research Branch Agriculture: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1989; Volume 2, 668p.
- Graciolli, G.; Dick, C.W. Checklist of World Nycteribiidae (Diptera: Hippoboscoidea). 2008. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/322579074_CHECKLIST_OF_WORLD_NYCTERIBIIDAE_DIPTERA_HIPPOBOSCOIDEA (accessed on 27 February 2023).
- Hůrka, K. Fauna Europaea: Nycteribiidae. In Fauna Europaea: Diptera, Brachycera. Pape, T., Ed.; 2011. version 2017.06. Available online: https://fauna-eu.org (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Sevcik, M.; Benda, P.; Lucan, R.K. Diptera Pupipara from bats of two large eastern Mediterranean islands, Crete and Cyprus. Turk. J. Zool. 2013, 37, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Szentiványi, T.A.; Estók, P.; Földvári, M. Checklist of host associations of European bat flies (Diptera: Nycteribiidae, Streblidae). Zootaxa 2016, 4205, 101–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, H.R. Embryology of the Viviparous Insects; Ronald Press: New York, NY, USA, 1951; 472p. [Google Scholar]
- Ching, L.M.; Marshall, A.G. The breeding biology of the bat-fly Eucampispoda sundaicum Theodor, 1955 (Diptera: Nycteribiidae). Malayan Nat. J. 1968, 21, 171–180. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, A.G. The life cycle of Basilia hipsida Theodor 1967 (Diptera: Nycteribiidae) in Malaysia. Parasitology 1970, 61, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foelix, R.F.; Stocker, R.F.; Steinbrecht, R.A. Fine structure of a sensory organ in the arista of Drosophila melanogaster and some other dipterans. Cell. Tissue Res. 1989, 258, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.J.; Wen, H.L.; Zhou, C.M.; Chen, F.F.; Luo, L.M.; Liu, J.W.; Yu, X.J. Bats as reservoirs of severe emerging infectious diseases. Virus Res. 2015, 205, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, E.; Van Doremalen, N.; Falzarano, D.; Munster, V.J. SARS and MERS: Recent insights into emerging coronaviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letko, M.; Seifert, S.N.; Olival, K.J.; Plowright, R.K.; Munster, V.J. Bat-borne virus diversity, spillover and emergence. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, C.D. Infectious disease emergence and global change: Thinking systemically in a shrinking world. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2012, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korytár, Ľ.; Ondrejková, A.; Drážovská, M.; Zemanová, S.; Prokeš, M. Serological survey of lyssaviruses in synanthropic bats and human exposure to bats in Slovakia. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. AAEM 2022, 29, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brook, C.E.; Bai, Y.; Dobson, A.P.; Osikowicz, L.M.; Ranaivoson, H.C.; Zhu, Q. Bartonella spp. in fruit bats and blood-feeding ectoparasites in Madagascar. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szentiványi, T.; Christe, P.; Glaizot, O. Bat flies and their microparasites: Current knowledge and distribution. Front. VEt Sci. 2019, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawęska, J.T.; Jansen van Vuren, P.; Storm, N.; Markotter, W.; Kemp, A. Vector Competence of Eucampsipoda africana (Diptera: Nycteribiidae) for Marburg Virus Transmission in Rousettus aegyptiacus (Chiroptera: Pteropodidae). Viruses 2021, 13, 2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrett, T.B.; Webala, P.W.; Patterson, B.D.; Dick, C.W. Remarkably low host specificity in the bat fly Penicillidia fulvida (Diptera: Nycteribiidae) as assessed by mitochondrial COI and nuclear 28S sequence data. Parasites Vectors 2022, 15, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Garcia, K.D.; Sandoval-Ruiz, C.A.; Saldana-Vazquez, R.A.; Schondube, J.E. The effects of seasonality on host-bat fly ecological networks in a temperate mountain cave. Parasitology 2017, 144, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelm, D.H.; Toelch, U.; Jones, M.M. Mixed-species groups in bats: Non-random roost associations and roost selection in neotropical understory bats. Front. Zool. 2021, 18, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallas, T.A.; Han, B.A.; Nunn, C.L.; Park, A.W.; Stephens, P.R.; Drake, J.M. Host traits associated with species roles in parasite sharing networks. Oikos 2019, 128, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastián Tello, J.; Stevens, R.D.; Dick, C.W. Patterns of species co-occurrence and density compensation: A test for interspecific competition in bat ectoparasite infracommunities. Oikos 2008, 117, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, A.A.; Saldaña-Vázquez, R.A.; Graciolli, G.; Peinado, L.C. Specialization and Modularity of a Bat Fly Antagonistic Ecological Network in a Dry Tropical Forest in Northern Colombia. Acta Chiropterologica 2018, 20, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmas, E.; Besson, M.; Brice, M.H.; Burkle, L.A.; Dalla Riva, G.V.; Fortin, M.J.; Gravel, D.; Guimarães, P.R., Jr.; Hembry, D.H.; Newman, E.A.; et al. Analysing ecological networks of species interactions: Analyzing ecological networks. Biol. Rev. 2019, 94, 16–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poisot, T.; Bergeron, G.; Cazelles, K.; Dallas, T.; Gravel, D.; MacDonald, A.; Mercier, B.; Violet, C.; Vissault, S.; Chapman, D. Global knowledge gaps in species interaction networks data. J. Biogeogr. 2021, 48, 1552–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, P.R., Jr. The Structure of Ecological Networks Across Levels of Organization. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2022, 51, 433–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.; Tan, D.J.X.; Oboňa, J.; Gustafsson, D.R.; Ang, Y.; Meier, R. Hitchhiking into the future on a fly: Toward a better understanding of phoresy and avian louse evolution (Phthiraptera) by screening bird carcasses for phoretic lice on hippoboscid flies (Diptera). Syst. Entomol. 2022, 47, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, C.W.; Esbérard, C.E.L.; Graciolli, G.; Bergallo, H.G.; Gettinger, D. Assessing host specificity of obligate ectoparasites in the absence of dispersal barriers. Parasitol. Res. 2009, 105, 1345–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, E.; Bernard, E. From the Atlantic Forest to the borders of Amazonia: Species richness, distribution, and host association of ectoparasitic flies (Diptera: Nycteribiidae and Streblidae) in northeastern Brazil. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 3043–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, E.; Graciolli, G.; Bernard, E. Structure and composition of Nycteribiidae and Streblidae flies on bats along an environmental gradient in northeastern Brazil. Can. J. Zool. 2019, 97, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Júnior, L.D.F.; De Araújo, W.S.; Falcão, L.A. Structure of the interaction networks between bats (Mammalia: Chiroptera) and ectoparasite flies (Diptera: Streblidae, Nycteribiidae) on a latitudinal gradient. Acta Chiropterologica 2020, 22, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Z.X.; Hitch, A.T.; Lee, B.P.H.; Low, D.H.; Neves, E.S.; Borthwick, S.A.; Smith, G.J.; Mendenhall, I.H. Ecology of bat flies in Singapore: A study on the diversity, infestation bias and host specificity (Diptera: Nycteribiidae). Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2020, 12, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palheta, L.R.; Urbieta, G.L.; Brasil, L.S.; Dias-Silva, K.; Da Silva, J.B.; Graciolli, G.; Aguiar, L.; Vieira, T.B. The effect of urbanization on bats and communities of bat flies (Diptera: Nycteribiidae and Streblidae) in the Amazon, northern Brazil. Acta Chiropterologica 2020, 22, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolabela Falcão, L.A.; Araújo, W.S.; Leite, L.O.; Fagundes, M.; Espírito-Santo, M.M.; Zazá-Borges, M.A.; Vasconcelos, P.; Fernandes, G.W.; Paglia, A. Network Structure of Bat-Ectoparasitic Interactions in Tropical Dry Forests at Two Different Regions in Brazil. Acta Chiropterologica 2022, 24, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makovetskaya, Y.V.; Larchenka, A.I. To the knowledge of bat-flies fauna (Diptera: Nycteribiidae) of Belarus. Aktual. Probl. Ekol. 2020, 8, 51–52. [Google Scholar]
- Péter, Á.; Mihalca, A.D.; Sándor, A.D. First report of the bat fly species Basilia italica in Romania. Biodivers. Data J. 2021, 9, e57680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hůrka, K. Revision der Nycteribiidae und Streblidae-Nycteriboscinae aus der Dipterensammlung des Zoologischen Museums in Berlin, II. Mit Beschreibung von Basilia (Basilia) mediterranea n.sp. Mitt. Aus Dem Zool. Mus. Berl. 1970, 46, 239–246. [Google Scholar]
- Hůrka, K. Basilia mongolensis nudior subsp. n. nebst Bemerkungen zur Nycteribien-und Streblidenfauna Thrakiens (Diptera: Pupipara). Ann. Des Nat. Mus. Wien. 1972, 4, 709–713. [Google Scholar]
- Falcoz, L. Pupipara (Diptères) (première série). Biospeologica XLIX. Arch. De Zool. Expérimentale Et Générale 1923, 61, 521–552. [Google Scholar]
- Hůrka, K. Čeleď Nycteribiidae–muchulovití. In Krevsajíci Mouchy a Střečci–Diptera; Chvála, M., Ed.; Fauna ČSSR, 22; Academia, Nakladatelství ČSAV Praha: Praha, Czech Republic, 1980; pp. 479–509. [Google Scholar]
- Theodor, O. An Illustrated Catalogue of the Rothschild Collection of Nycteribiidae in the British Museum (Natural History), with Keys and Short Descriptions for the Identification of Subfamilies, Genera, Species and Subspecies; British Museum (Natural History): London, UK, 1967; 506p. [Google Scholar]
- Aellen, V. Etude d’une collection de Nycteribiidae et de Streblidae (Diptera: Pupipara) de la région paléarctique occidentale, particulièrement de la Suisse. Bull. De La Société Neuchâteloise Des Sci. Nat. 1955, 78, 81–104. [Google Scholar]
- Aellen, V. Les nycteribiidés de la Suisse, diptères parasites de chauves-souris. Bull. De La Société Neuchâteloise Des Sci. Nat. 1963, 86, 143–154. [Google Scholar]
- Austen, E.E. Diptera (Flies). In The Victoria History of the County of Devon; Victoria County History: London, UK, 1906; Volume 1, 630p. [Google Scholar]
- Baagøe, H.J. Eptesicus serotinus (Schreber, 1774) Breitflügelfledermaus. In Die Fledermäuse Europas. Ein umfassendes Handbuch zur Biologie, Verbreitung und Bestimmung; Krapp, F., Niethammer, J., Eds.; Aula–Verlag: Wiebelsheim, Germany, 2011; pp. 519–559. [Google Scholar]
- Baagøe, H.J. Myotis bechsteinii (Kuhl, 1818) Bechsteinfledermaus. In Die Fledermäuse Europas. Ein umfassendes Handbuch zur Biologie, Verbreitung und Bestimmung; Krapp, F., Niethammer, J., Eds.; Aula–Verlag: Wiebelsheim, Germany, 2011; pp. 443–471. [Google Scholar]
- Balcells, R.E. Interesantes datos faunísticos y biológicos de la cueva “Sa Guitarreta” de Llucmajoro. Bol. De La Soc. De Hist. Nat. De Balear. 1968, 14, 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Balcells, R.E. Nuevas citas de murciélagos y nicteríbidos del país vasco-cantábrico. Real. Soc. Española De Hist. Nat. 1968, 66, 17–38. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, K. Zur Kenntnis der Fledermausfauna Spaniens. Bonn. Zool. Beiträge 1957, 7, 296–319. [Google Scholar]
- Beaucournu, J.C. Ectoparasites des Chiroptères de l’Ouest de la France. 1re partie: Ixodoïdés—Cimicides et Nyctéribiidés. Bull. De La Société Sci. De Bretagne 1961, 36, 315–338. [Google Scholar]
- Beaucournu, J.C. Sur quelques ectoparasites (Siphonaptères, anoploures et nyctéribies) du Portugal. An. Da Esc. Nac. De Saúde Pública E De Med. Trop. 1972, 6, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Beaucournu, J.C.; Noblet, J.F. Une nyctéribie (Diptera, Pupipara) nouvelle pour la fauna française: Présence de Basilia mediterranea Hůrka, 1970 en Corse. Ann. De Parasitol. Hum. Et Comparée 1985, 60, 635–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaucournu, J.C.; Noblet, J.F. Présence en France continentale de Basilia mediterranea Hůrka, 1970 (Diptera, Nycteribiidae). Bull. De La Société Entomol. De Fr. 1994, 99, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaucournu, J.C.; Noblet, J.F. Les Diptères pupipares parasites de chauves-souris dans les Alpes et les Préalpes françaises (Diptera, Streblidae et Nycteribiidae). Bull. De La Société Entomol. De Fr. 1996, 101, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bequaert, J.G. Exploration du Parc National Albert. Mission, G.F. de Witte (1933–1935). Hippoboscidae and Nycteribiidae. Inst. Des Parcs Natx. Belg. 1953, 79, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Czuppon, B. Denevérlegyek (Nycteribiidae) Populáció-Ökológiai Elemzése. Doctoral Thesis, Szent István University, Budapest, Hungary, 2001; 48p. [Google Scholar]
- Czuppon, B.; Molnár, V. Bat fly genus and species new to Hungary (Diptera: Nycteribiidae). Folia Entomol. Hung. 2001, 62, 313–317. [Google Scholar]
- Colyer, C.N.; Hammond, C.O. Flies of the British Isles; Frederick Warne: London, UK, 1951; 383p. [Google Scholar]
- Danko, Š.; Krištín, A.; Krištofík, J. Myotis alcathoe in eastern Slovakia: Occurrence, diet, ectoparasites and notes on its identification in the field. Vespertilio 2010, 13–14, 77–91. [Google Scholar]
- Dietz, M.; Walter, G. Zur Ektoparasitenfauna der Wasserfledermaus (Myotis daubentoni Kuhl, 1819) in Deutschland unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Flughautmilbe Spinturnix andegavinus Deunff, 1977. Nyctalus (Neue Folge) 1995, 5, 451–468. [Google Scholar]
- Dudich, E. A magyarországi denevérlegyek. Math. És Természettudományi Értesítő 1925, 41, 144–151. [Google Scholar]
- Estrada-Peña, A.; Serra-Cobo, J. The acarinia and nycteribidia zones of Miniopterus schreibersii Kuhl (Mammalia: Chiroptera) in the northeast of Spain. Folia Parasitol. 1991, 38, 345–354. [Google Scholar]
- Falcoz, L. Diptères Pupipares du Muséum National d’histoire naturelle de Paris. Muséum Natl. D’histoire Nat. 1924, 30, 223. [Google Scholar]
- Falcoz, L. Diptères Pupipares. Fauna de France, 14; Fédération Française des Sociétés de Sciences Naturelles: Paris, France, 1926; 64p. [Google Scholar]
- Gil Collado, J. Una nueva especie española de Nycteribia. Eos: Rev. Española De Entomol. 1934, 9, 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Grulich, I.; Povolný, D. Faunisticko–bionomický nástin muchulovitých (Nycteribiidae) na území ČSR. Zool. A Entomol. Listy 1955, 4, 111–134. [Google Scholar]
- Güttinger, R.; Zahn, A.; Krapp, F.; Schober, W. Myotis myotis (Borkhausen, 1797) Großes Mausohr. In Die Fledermäuse Europas; Ein umfassendes Handbuch zur Biologie, Verbreitung und Bestimmung; Krapp, F., Niethammer, J., Eds.; Aula–Verlag: Wiebelsheim, Germany, 2011; pp. 123–207. [Google Scholar]
- Haitlinger, R. Pasożyty zewnętrzne nietoperzy Dolnego Śląska. II. Nycteribiidae (Diptera). Wiadomości Parazytol. 1978, 24, 467–474. [Google Scholar]
- Haitlinger, R.; Ruprecht, A.L. Parasitic arthropods (Siphonaptera, Diptera, Acari) of bats from western part of the Bialowieża Primeval Forest. Nyctalus (Neue Folge) 1992, 4, 315–319. [Google Scholar]
- Heddergott, M. Erstnachweis der Fledermausfliege Basilia mongolensis nudior Hůrka, 1972 in Deutschland (Diptera: Nycteribiidae). Stud. Dipterol. 2009, 15, 301–304. [Google Scholar]
- Heddergott, M.; Claußen, A. Nachweise von Fledermausfliegen aus dem Nationalpark Hainich in Thüringen (Diptera: Calyptrata: Nycteribiidae). Abh. Ber. Mus. Nat. Gotha 2004, 23, 91–93. [Google Scholar]
- Humphries, D.A. Caves and bats. J. King’s Coll. Nat. Hist. Soc. 1959, 1, 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Hůrka, K. Beitrag zur Nycteribien–und Streblidenfauna Albaniens nebst Bemerkungen zur Fauna von Bulgarien, Ungarn und UdSSR. Acta Soc. Entomol. Cechoslov. 1962, 59, 156–164. [Google Scholar]
- Hůrka, K. Distribution, bionomy and ecology of the European bat flies with special regard to the Czechoslovak fauna (Diptera, Nycteribidae). Acta Univ. Carolinae. Biol. 1964, 3, 167–231. [Google Scholar]
- Hůrka, K. New taxa and new records of Palearctic Nycteribiidae and Streblidae (Diptera: Pupipara). Věstník Československé Společnosti Zool. 1984, 48, 90–101. [Google Scholar]
- Hutson, A.M. Ectoparasites of British bats. Mammal. Rev. 1972, 1, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutson, A.M. Keds, Flat–flies and Bat–flies (Diptera, Hippoboscidae and Nycteribiidae). In Handbooks for the Identification of British Insects; Royal Entomological Society of London: London, UK, 1984; 44p. [Google Scholar]
- Imaz, E.; Aihartza, J.R.; Totorika, M.J. Ectoparasites on bats (Gamasida, Ixodida, Diptera) in Biscay (N Iberian peninsula). Miscel·Lània Zoològica 1999, 22, 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Jaunbauere, G.; Salmane, I.; Spungis, V. Occurrence of bat ectoparasites in Latvia. Latv. Entomol. 2008, 45, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Jobling, B. A revision of the genus Nycteribosca. Parasitology 1934, 26, 64–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaňuch, P.; Krištín, A.; Krištofík, J. Phenology, diet, and ectoparasites of Leisler’s bat (Nyctalus leisleri) in the Western Carpathians (Slovakia). Acta Chiropterologica 2005, 7, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kock, D. Über Nycteribiiden im deutschen Faunengebiet (Ins.: Diptera). Senckenberg. Biol. 1973, 54, 343–352. [Google Scholar]
- Kock, D. Pupipare Dipteren von Säugetieren des nordöstlichen Mittelmeerraumens (Ins.: Diptera). Senckenberg. Biol. 1974, 17, 87–104. [Google Scholar]
- Kock, D. Basilia mongolensis nudior Hůrka 1972 in Österreich (Insecta: Diptera: Nycteribiidae). Senckenberg. Biol. 1984, 65, 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Kock, D. Fledermaus–Fliegen aus der E–Mediterraneis (Diptera: Nyeteribiidae). Entomol. Z. 1989, 99, 56–58. [Google Scholar]
- Kock, D. Die Fledermauslausfliegen Bayerns (Diptera: Nycteribidae). Entomol. Z. 1999, 109, 444–447. [Google Scholar]
- Kock, D. Bestandsdichte der Wasserfledermaus, Myotis daubentonii Kuhl, 1817 (Mammalia: Chiroptera) und zunehmende Verbreitung ihres Parasiten, Penicillidia monoceros Speiser, 1900 (Diptera: Nycteribiidae) in Deutschland. Myotis 2004, 41–42, 99–107. [Google Scholar]
- Kock, D.; Quetglas, J. The bat flies of the Balearic Islands (Insecta: Diptera: Nycteribiidae). Bolletí De La Soc. D’història Nat. De Les. Balear. 2003, 46, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Krištofík, J. Nálezy múch čeľade Nycteribiidae (Diptera) na území SSR. Biol. Bratisl. 1982, 37, 191–197. [Google Scholar]
- Krištofík, J.; Danko, S. Arthropod ectoparasites (Acarina, Heteroptera, Diptera, Siphonaptera) of bats in Slovakia. Vespertilio 2012, 16, 167–189. [Google Scholar]
- Lindecke, O.; Scheffler, I. Ectoparasites of bats in Saxony–Anhalt. Hercynia Neuen Folge 2011, 44, 241–251. [Google Scholar]
- Masson, D. Sur l’infestation de Myotis nattereri (Kuhl, 1818) (Chiroptera, Vespertilionidae) par Basilia nattereri (Kolenati, 1857) (Diptera, Nycteribiidae) dans le Sud–Ouest de la France. Ann. De Parasitol. Hum. Et Comparée 1989, 64, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noblet, J.F. Els quiròpters del Parc Natural de s‘Albufera de Mallorca. Monogr. De La Soc. D’història Nat. De Les. Balear. 1995, 4, 169–173. [Google Scholar]
- Nowosad, A. Nycteribia kolenatii Theodor et Moscona i Penicillidia monoceros Speiser (Nycteribiidae, Diptera) w Polsce. Pol. Pismo Entomol. 1974, 44, 559–569. [Google Scholar]
- Nowosad, A. Materialy do znajomoéci Nycteribiidae (Diptera, Pupipara) Polski zachodniej i pohiocno-zachodniej. Pol. Pismo Entomol. 1987, 57, 263–276. [Google Scholar]
- Nowosad, A. Stan badañ nad mrokawkowatymi—Nycteribiidae (Diptera, Pupipara) w Polsce, z przeglądem gatunków i stanowisk ich występowania. Wiadomości Entomol. 1990, 9, 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Nowosad, A.; Batchvarov, G.; Petrov, P. Bat flies (Nycteribiidae, Diptera) of bats collected in Bulgaria. Pol. Pismo Entomol. 1987, 57, 673–694. [Google Scholar]
- Orlova, M.V. Ectoparasite associations of bats from the Urals (Russia). Hystrix Ital. J. Mammal. 2011, 22, 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Rageau, J.; Mouchet, J. Les arthropodes hématophages de Camargue. Cah. ORSTOM. Série Entomol. Médicale Et Parasitol. 1967, 5, 263–281. [Google Scholar]
- Reckardt, K.; Kerth, G. The reproductive success of the parasitic bat fly Basilia nana (Diptera: Nycteribiidae) is affected by the low roost fidelity of its host, the Bechstein’s bat (Myotis bechsteinii). Parasitol. Res. 2006, 93, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupp, D. Zweiflügler aus Bayern XVIQ (Diptera: Nycteribiidae). Entomofauna 1999, 25, 397–400. [Google Scholar]
- Scheffler, I. Untersuchungen zur Ektoparasitenfauna (Siphonaptera: Ischnopsyllidae; Diptera: Nycteribiidae; Heteroptera: Cimicidae) an Fledermäusen (Teil 3). Märkische Entomol. Nachr. 2008, 10, 241–248. [Google Scholar]
- Scheffler, I. Ektoparasiten der Fledermäuse in Sommerquartieren in Brandenburg: Neue Funde seltener Arten. Nyctalus (Neue Folge) 2009, 14, 126–136. [Google Scholar]
- Scheffler, I. Ektoparasiten der Fledermäuse in Winterquartieren in Brandenburg. Märkische Entomol. Nachr. 2010, 12, 119–132. [Google Scholar]
- Scheffler, I. Die Ektoparasiten der Fledermäuse Europas—Teil 1. Nyctalus (Neue Folge) 2011, 16, 246–263. [Google Scholar]
- Scheffler, I. Artenspektren und Wirtsbindung von Ektoparasiten der Fledermäuse aus Nordbulgarien. Bewertung des Zusammenhangs von Körperkondition und Ektoparasitenlast. Nyctalus (Neue Folge) 2011, 16, 119–136. [Google Scholar]
- Scheffler, I. Die Ektoparasiten der Fledermäuse Europas—Teil 2. Nyctalus (Neue Folge) 2012, 17, 104–119. [Google Scholar]
- Scheffler, I.; Bego, F.; Théou, P.; Podany, M.; Pospischil, R.; Hübner, S.; Wittenberg, L. Ektoparasiten der Fledermause in Albanien–Artenspektrum und Wirtsbindung. Nyctalus (Neue Folge) 2013, 18, 84–109. [Google Scholar]
- Scheffler, I.; Hiller, A. Zur Ektoparasitenfauna der Fledermäuse in Niedersachsen: Neue Funde am Iberg bei Bad Grund. Nyctalus (Neue Folge) 2010, 15, 309–317. [Google Scholar]
- Scheffler, I.; Ressler, R. Untersuchungen zur Ektoparasitenfauna (Siphonaptera: Ischnopsyllidae; Diptera: Nycteribiidae) an Fledermäusen in Brandenburg. Märkische Entomol. Nachr. 2005, 7, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Scheffler, I.; Ressler, R. Untersuchungen zur Ektoparasitenfauna (Siphonaptera: Ischnopsyllidae; Diptera: Nycteribiidae; Heteroptera: Cimicidae) an Fledermäusen in Brandenburg (Teil 2). Märkische Entomol. Nachr. 2007, 9, 109–119. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, H. Descriptions and records of Nycteribiidae, with a discussion of the genus Basilia. J. Linn. Soc. Lond. Zool. 1936, 39, 479–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skuratowicz, W. Przyczynek do do znajomości Nycteribiidae (Diptera, Pupipara) Polski. Fragm. Faun. 1962, 10, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ševčík, M.; Benda, P.; Uhrin, M. First records of the bat fly Phthiridium biarticulatum (Diptera: Nycteribiidae) in Crimea. Vespertilio 2011, 15, 159–160. [Google Scholar]
- Soós, Á. Bábtojó legyek—Muscidae Pupiparae; Magyarország Állatvilága—Fauna hungarie; Akadémia Kiadó: Budapest, Hungary, 1955; 20p. [Google Scholar]
- Szentiványi, T.; Genzoni, E.; Clément, L.; Radonjić, M.; Loce, E.; Théou, P.; Glaizot, O.; Christe, P. Basilia: A new genus to the Albanian bat fly fauna (Diptera: Nycteribiidae). Ecol. Montenegrina 2016, 8, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodor, O. On the genus Tripselia and the group of Basilia bathybothyra (Nycteribiidae, Diptera). Parasitology 1956, 46, 353–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodor, O.; Moscona, A. On bat parasites in Palestine. I. Nycteribiidae, Streblidae, Hemiptera, Siphonaptera. Parasitology 1954, 44, 157–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topál, G. Myotis nattereri (Kuhl, 1818) Fransenfledermaus. In Die Fledermäuse Europas. Ein umfassendes Handbuch zur Biologie, Verbreitung und Bestimmung; Krapp, F., Niethammer, J., Eds.; Aula–Verlag: Wiebelsheim, Germany, 2011; pp. 405–442. [Google Scholar]
- Uhrin, M.; Kaňuch, P.; Krištofík, J.; Paule, L. Phenotypic plasticity in the greater mouse–eared bat in extremely different roost conditions. Acta Theriol. 2010, 55, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, G. Nachweise von Nycteribia kolenatii (Diptera, Nycteribiidae) für die Bundesrepublik Deutschland und Berlin (West). Angew. Parasitol. 1987, 28, 177–178. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, G. Überblick zum Vorkommen und zur Biologie von Ektoparasiten (Siphonaptera; Cimicidae; Nycteribiidae; Calliphoridae) bei Fledermäusen in Deutschland. Nyctalus (Neue Folge) 2004, 9, 460–476. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, G.; Benk, A. Zur Ektoparasitenfauna der Fledermäuse (Chiroptera) in Niedersachsen. Angew. Parasitol. 1982, 23, 230–232. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, G.; Ebenau, C. Nachweise von Fledermausfliegen aus Syrien (Diptera: Streblidae, Nycteribiidae). Zool. Middle East. 1997, 14, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westwood, J.O. On Nycteribia, a genus of wingless insects. Zool. Soc. Lond. 1835, 1, 275–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, J.; Ohlendorf, B. Erstnachweis von Fledermausfliegen (Dipt., Nycteribiidae) aus dem Harz, DDR–Bezirk Magdeburg. Nyctalus (Neue Folge) 1984, 2, 81–84. [Google Scholar]
- Dondini, G.; Vanin, S.; Vergari, S.; Vergari, S. First record of Basilia mediterranea Hůrka, 1970 from Italy (Diptera: Nycteribiidae). Onychium 2017, 13, 139–142. [Google Scholar]
- Haelewaters, D.; Pfliegler, W.P.; Szentiványi, T.; Földvári, M.; Sándor, A.D.; Barti, L.; Pfister, D.H. Parasites of parasites of bats: Laboulbeniales (Fungi: Ascomycota) on bat flies (Diptera: Nycteribiidae) in central Europe. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemenesi, G.; Tóth, G.E.; Mayora-Neto, M.; Scott, S.; Temperton, N.; Wright, E.; Jakab, F. Isolation of infectious Lloviu virus from Schreiber’s bats in Hungary. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKee, C.D.; Krawczyk, A.I.; Sándor, A.D.; Görföl, T.; Földvári, M.; Földvári, G.; Sprong, H. Host phylogeny, geographic overlap, and roost sharing shape parasite communities in European bats. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejić, B.; Budinski, I.; Blagojević, J. Ectoparasite Bat Flies (Diptera: Nycteribiidae) of Schreiber’s Bent-Winged Bat and Their Fungus Parasite. In Programme & Abstract Book, Proceedings of the 13th European Multicolloquium of Parasitology, Belgrade, Serbia, 12–16 October 2021. Available online: https://emop2020.org/ (accessed on 27 February 2023).
- Sándor, A.D.; Földvári, M.; Krawczyk, A.I.; Sprong, H.; Corduneanu, A.; Barti, L.; Földvári, G. Eco-epidemiology of novel Bartonella genotypes from parasitic flies of insectivorous bats. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 76, 1076–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sándor, A.D.; Péter, Á.; Corduneanu, A.; Barti, L.; Csősz, I.; Kalmár, Z.; Mihalca, A.D. Wide distribution and diversity of malaria-related haemosporidian parasites (Polychromophilus spp.) in bats and their ectoparasites in Eastern Europe. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szentiványi, T.; Estók, P.; Pigeault, R.; Christe, P.; Glaizot, O. Effects of fungal infection on the survival of parasitic bat flies. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szentiványi, T.; Haelewaters, D.; Pfliegler, W.P.; Clément, L.; Christe, P.; Glaizot, O. Laboulbeniales (Fungi: Ascomycota) infection of bat flies (Diptera: Nycteribiidae) from Miniopterus schreibersii across Europe. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szentiványi, T.; Haelewaters, D.; Rádai, Z.; Mizsei, E.; Pfliegler, W.P.; Báthori, F.; Glaizot, O. Climatic effects on the distribution of ant-and bat fly-associated fungal ectoparasites (Ascomycota, Laboulbeniales). Fungal Ecol. 2019, 39, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szentiványi, T.; Vincze, O.; Estók, P. Density-dependent sex ratio and sex-specific preference for host traits in parasitic bat flies. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tendu, A.; Hughes, A.C.; Berthet, N.; Wong, G. Viral hyperparasitism in bat ectoparasites: Implications for pathogen maintenance and transmission. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodor, O. Nycteribiidae. In Die Fliegen der Paläarktischen Region; Lindner, E., Ed.; Band 12 [Lieferung 174]. E.; Schweizerbart: Stuttgart, Germany, 1954; 43p. [Google Scholar]
- Caira, J.N.; Jensen, K.; Holsinger, K.I. On a new index of host specificity. In Taxonomie, Écologie et Évolution des Metazoaires Parasites; Combes, C., Jourdane, J., Eds.; Presses Universitaires de Perpignan: Perpignan, France, 2003; pp. 161–201. [Google Scholar]
- Marciniak-Musial, N.; Skoracki, M.; Kosicki, J.Z.; Unsöld, M.; Sikora, B. Host-Parasite Relationships of Quill Mites (Syringophilidae) and Parrots (Psittaciformes). Diversity 2022, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, B. Plotweb: Visualize a Bipartite Interaction Matrix (e.g., a foodweb). Available online: https://www.rdocumentation.org/packages/bipartite/versions/2.18/topics/plotweb (accessed on 18 March 2023).
- Strauss, R. plotModuleWeb: plotModuleWeb. Available online: https://www.rdocumentation.org/packages/bipartite/versions/2.18/topics/plotModuleWeb (accessed on 18 March 2023).
- Dormann, F.; Gruber, B.; Fründ, J. Introducing the bipartite package: Analysing ecological networks. R News 2008, 8, 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- May, R.M. Stability and Complexity in Model. Ecosystems, 2nd ed.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Dormann, C.F. Networklevel: Analysis of Bipartite Webs at the Level of the Entire Network. Available online: https://www.rdocumentation.org/packages/bipartite/versions/2.18/topics/networklevel (accessed on 19 March 2023).
- Blüthgen, N. Why network analysis is often disconnected from community ecology: A critique and an ecologist’s guide. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2010, 11, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dormann, C.F.; Fründ, J. H2fun: Specialisation of a Bipartite Web. Available online: https://www.rdocumentation.org/packages/bipartite/versions/2.18/topics/H2fun (accessed on 19 March 2023).
- Atmar, W.; Patterson, B.D. The measure of order and disorder in the distribution of species in fragmented habitat. Oecologia 1993, 96, 373–382. [Google Scholar]
- Bascompte, J.; Jordano, P.; Melia, C.J.; Olesen, J.M. The nested assembly of plant–animal mutualistic networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9383–9387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlopoulos, G.A.; Kontou, P.I.; Pavlopoulou, A.; Bouyioukos, C.; Markou, E.; Bagos, P.G. Bipartite graphs in systems biology and medicine: A survey of methods and applications. GigaScience 2018, 7, giy014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortuna, M.A.; Stouffer, D.B.; Olesen, J.M.; Jordano, P.; Mouillot, D.; Krasnov, B.R.; Poulin, R.; Bascompte, J. Nestedness versus modularity in ecological networks: Two sides of the same coin? J. Anim. Ecol. 2010, 79, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Girones, M.A.; Santamaria, L. A new algorithm to calculate the nestedness temperature of presence-absence matrices. J. Biogeogr. 2006, 33, 924–935. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, M.E.J. The structure and function of complex networks. SIAM Rev. 2003, 45, 167–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.E.J.; Girvan, M. Finding and evaluating community structure in networks. Phys. Rev. 2004, 69, 026113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortunato, S. Community detection in graphs. Phys. Rep. 2010, 486, 75–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, R.; Dormann, C.; Hegemann, T. Computemodules: Computemodules. Available online: https://www.rdocumentation.org/packages/bipartite/versions/2.18/topics/computeModules (accessed on 19 March 2023).
- Blüthgen, N.; Menzel, F.; Bliithgen, N. Measuring specialization in species interaction networks. BMC Ecol. 2006, 9, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Fründ, J.; Dormann, C.F. Dfun: Calculates Standardised Specialisation Index d’ (d prime) for Each Species in the Lower Trophic Level of a Bipartite Network. Available online: https://www.rdocumentation.org/packages/bipartite/versions/2.18/topics/dfun (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Dick, C.W.; Patterson, B.D. Against all odds: Explaining high host specificity in dispersal-prone parasites. Int. J. Parasitol. 2007, 37, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Groot, M.D.; Dumolein, I.; Hiller, T.; Sándor, A.D.; Szentiványi, T.; Schilthuizen, M.; Aime, M.C.; Verbeken, A.; Haelewaters, D. On the fly: Tritrophic associations of bats, bat flies, and fungi. J. Fungy 2020, 6, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szentiványi, T.; Heintz, A.C.; Markotter, W.; Wassef, J.; Christe, P.; Glaizot, O. Vector-borne protozoan and bacterial pathogen occurrence and diversity in ectoparasites of the Egyptian Rousette bat. Med. VEt Entomol. 2023, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szentiványi, T.; Markotter, W.; Dietrich, M.; Clément, L.; Ançay, L.; Brun, L.; Genzoni, E.; Kearney, T.; Seamark, E.; Estók, P.; et al. Host conservation through their parasites: Molecular surveillance of vector-borne microorganisms in bats using ectoparasitic bat flies. Conservation des hôtes grâce à leurs parasites: Surveillance moléculaire des microorganismes à transmission vectorielle chez les chauves-souris à l’aide de mouches ectoparasites. Parasite 2020, 27, 72. [Google Scholar]
- Zemanová, S.; Korytár, Ľ.; Tomčová, J.; Prokeš, M.; Drážovská, M.; Myczko, Ł.; Tryjanowski, P.; Nusová, G.; Matysiak, A.; Ondrejková, A. Opportunities and Limitations of Molecular Methods for Studying Bat-Associated Pathogens. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeus, V.M.; Puechmaille, S.J.; Kerth, G. Conspecific and heterospecific social groups affect each other’s resource use: A study on roost sharing among bat colonies. Anim. Behav. 2017, 123, 329–338. [Google Scholar]
- Zahn, A.; Rupp, D. Ectoparasite load in European vespertilionid bats. J. Zool. 2004, 262, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christe, P.; Glaizot, O.; Evanno, G.; Bruyndonckx, N.; Devevey, G.; Yannic, G.; Patthey, P.; Maeder, A.; Vogel, P.; Arlettaz, R. Host sex and ectoparasites choice: Preference for, and higher survival on female hosts. J. Anim. Ecol. 2007, 76, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sándor, A.D.; Corduneanu, A.; Péter, Á.; Mihalca, A.D.; Barti, L.; Csősz, I.; Szőke, K.; Hornok, S. Bats and ticks: Host selection and seasonality of bat-specialist ticks in eastern Europe. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mello, M.A.R.; Marquitti, F.M.D.; Guimarães, P.R., Jr.; Kalko, E.K.V.; Jordano, P.; de Aguiar, M.A.M. The missing part of seed dispersal networks: Structure and robustness of bat-fruit interactions. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnov, B.R.; Fortuna, M.A.; Mouillot, D.; Khokhlova, I.S.; Shenbrot, G.I.; Poulin, R. Phylogenetic signal in module composition and species connectivity in compartmentalized host–parasite networks. Am. Nat. 2012, 179, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellay, S.; de Oliveira, E.F.; Almeida-Neto, M.; Lima Junior, D.P.; Takemoto, R.M.; Luque, J.L. Developmental stage of parasites influences the structure of fish–parasite networks. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, S.V.; Corso, G.; Almeida, A.M.; Ferreira, F.S.; Almeida, W.O.; Anjos, L.A.; Mesquita, D.O.; Vasconcellos, A. Phylogeny and micro-habitats utilized by lizards determine the composition of their endoparasites in the semiarid Caatinga of Northeast Brazil. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 3963–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obame-Nkoghe, J.; Rahola, N.; Bourgarel, M.; Yangari, P.; Prugnolle, F.; Maganga, G.D.; Leroy, E.M.; Fontenille, D.; Ayala, D.; Paupy, C. Bat flies (Diptera: Nycteribiidae and Streblidae) infesting cave-dwelling bats in Gabon: Diversity, dynamics and potential role in Polychromophilus melanipherus transmission. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, E.S.K.; Chen, G.; Tsang, H.Y.; Shek, C.T.; Tsui, W.C.; Zhao, H.; Guénard, B.; Sin, S.Y.W. Species richness of bat flies and their associations with host bats in a subtropical East Asian region. Parasites Vectors 2023, 16, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitzenberger, F.; Weiss, E. Changes in roost occupancy and abundance in atticdwelling bats during decreasing roost availability in Burgenland, Austria. Vespertilio 2012, 16, 279–288. [Google Scholar]
- Bartonička, T.; Jedlička, P. First record of Schreiber’s bat, Miniopterus schreibersii (Kuhl, 1817), in the Czech Republic. Lynx (Praha) 2011, 42, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Pejić, B.; Budinski, I.; van Schaik, J.; Blagojević, J. Sharing roosts but not ectoparasites: High host-specificity in bat flies and wing mites of Miniopterus schreibersii and Rhinolophus ferrumequinum (Mammalia: Chiroptera). Curr. Zool. 2022, 68, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morse, S.F.; Bush, S.E.; Patterson, B.D.; Dick, C.W.; Gruwell, M.E.; Dittmar, K. Evolution, multiple acquisition, and localization of endosymbionts in bat flies (Diptera: Hippoboscoidea: Streblidae and Nycteribiidae). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 2952–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urushadze, L.; Bai, Y.; Osikowicz, L.; McKee, C.; Sidamonidze, K.; Putkaradze, D.; Imnadze, P.; Kandaurov, A.; Kuzmin, I.; Kosoy, M. Prevalence, diversity, and host associations of Bartonella strains in bats from Georgia (Caucasus). PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).