Abstract
Extreme weather events such as hurricanes and tornadoes have been found to change the spatial and temporal abundance of raptors by decreasing survival and forcing the emigration of individuals, or by increasing habitat heterogeneity and facilitating recolonization of disturbed areas. Nonetheless, little is known about how extreme weather events could affect raptors’ movements and their space use in areas disturbed by large-scale weather events. We studied how extreme weather affected the movements of black and turkey vultures (Coragyps atratus and Cathartes aura, respectively) in Mississippi, USA, facing Hurricane Zeta in November 2020, winter storm Viola in February 2021, and tornados MS-43 and MS-44 in May 2021. We GPS-tracked 28 vultures in the paths of these events. We compared movement rates, net-squared displacements, and use of forest cover, before, during, and after the events. Since storm avoidance behavior has been observed in other birds, we expected that vultures would shift their movements out of the path of these events before storms hit. Further, we forecasted that vultures would make greater use of forested areas as protection against harsh conditions such as strong winds and heavy rain. Vultures responded differently to each weather event; they shifted their movements out of the predicted path of the hurricane and tornadoes but not the snowstorm. These findings reveal that both species use avoidance behavior and adjust their navigation and hazard detection accordingly. Avoidance behavior was more pronounced in turkey vultures than in black vultures. In general, vultures did not make greater use of forest areas as we expected, but turkey vultures did select forest areas during the snowstorm. We propose that olfaction and audition may be key in vultures’ response to extreme weather events.
1. Introduction
Climate has long-term impacts on the geographic distribution and population growth of various animals [1]. As climate changes, extreme weather events may become more frequent in some regions, leading to the redistribution of species and novel ecological communities [2]. Studying the extremes of weather and the response of animals to these extremes allows for greater understanding and management of populations, as extremes can pose greater threats or benefits to various taxa, as opposed to more typical conditions [3].
Whereas climate change reflects long-term changes in conditions, weather reflects more localized-short term events. Herein, we ascribe to the definition of extreme weather events, as posited in Stephenson et al. [4], that an extreme weather event is one that imbues meteorological values that exceed typical pre-existing conditions. Climate change influences the assemblage of a biological community and health of that community over time, whereas extreme weather can have immediate effects and cause behavioral changes. Both climate change and extreme weather conditions can facilitate the redistribution of plant and animals, as well as diseases that affect these organisms and situations that promote human–wildlife interactions [5,6,7].
Although the influence of climate is most noticeable within large temporal scales, though context-dependent and related to the demographics and vagility of the species of focus [8], weather clearly affects the occurrence and abundance of organisms at fine temporal and spatial scales. Examples evidencing these effects are changes in the size of geographic ranges; for instance, Kuhl’s pipistrelle (Pipistrellus kuhlii) extended its geographic range fourfold northward concomitant with increases in winter temperatures between 1980 and 2012 [9]. Climate can also affect intrinsic features limiting populations, such as the case of the Eastern Massasauga (Sistrurus catenatus), where survivorship was reduced and this species exhibited local extirpation with increased intensity of winter drought in a 60-year period (1950–2008 [10]).
Little is known regarding how extreme weather events can influence animal movements and their patterns of space use. Extreme weather events, such as cyclones (referenced as hurricanes hereafter), tornadoes, and winter storms, change the spatial and temporal abundance of animal populations by increasing heterogeneity in resource availability and through direct and indirect mortality [11,12]. Changes in resources can also influence the immigration and the emigration of residents that survived harmful weather and are reflected in redistributions of species across landscapes [13,14]. Extreme weather events can pose serious demographic threats to avian populations that fail to sense them. For instance, substantial population decline due to these events at the beginning of the migratory season can exert long-term negative population growth [15,16]. Similarly, resident birds that fail to sense extreme weather events and trigger an avoidance response may be unable to replenish resources during the occurrence of the event; therefore, their poor body condition would compromise their breeding investment months after the weather event occurred [17].
Our understanding of the perception of extreme weather by wildlife prior to, during, and after these events has been clarified through evidence collected using various telemetry methods. In some species, such as the white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus), females increase their movement rate during storm days, whereas males reduce their movement rates, and both sexes shift their space use to areas with higher elevation and forest cover [18]. It is known that some migratory bird species have the ability to sense storms hours or days in advance and change their movement patterns to avoid bad weather [19]. Raptors also change their movement in response to bad weather; for instance, migratory Eleonora’s falcons (Falco eleonorae) can adjust or change their migratory flight path and move from areas with low atmospheric pressure to those with more stable conditions [20].
These examples provide insight into the behavior of animals that depend on trophic resources that might be influenced by weather. How extreme weather events affect the movements of obligate scavengers is yet to be studied, however, and can help to address fundamental questions (why, when, and where to move) in movement ecology [21]. Here, we analyzed the movements of black and turkey vultures (Coragyps atratus and Cathartes aura, respectively) in response to the passage of Hurricane Zeta in October 2020, winter storm Viola in February 2021, and the tornadoes Duffee and Toomsuba in May 2021 through our study area in Mississippi, southeastern United States of America.
Black and turkey vultures are the most widely distributed vultures in the Western Hemisphere; both species are partial migrants with a soaring–gliding flying strategy that allows for long-distance displacement in short periods of time at low energetic cost [22]. Since these species can displace at an average of 99 km/day, and storm avoidance behavior has been observed in other birds [19,20,23], we expect that tracked vultures would shift their movements out of the predicted path of the storms before storm days. We predict that if vultures shift their movements in relation to extreme weather events, they should exhibit a large movement rate (m/h) and displacement before and after the storms, with significantly lower movement rate and displacement during the extreme weather events. Although vultures do not greatly use forested areas, but may use wooded areas that provide thermal refuge during cold weather [24,25,26], we anticipated that vultures will make greater use of forested areas during storm days, as such areas would provide cover and protection against harsh conditions such as strong winds and heavy rain [27].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The state of Mississippi is in the southeastern United States, specifically within the Southeastern Plains and the Mississippi Alluvial ecoregions [28]. Mississippi is characterized by a temperate, no dry season, hot summer climate [29], and annual mean range of temperatures of 11–24 °C, with annual mean precipitation of 1500 mm [30]. Mississippi has a relatively flat topography characterized by an elevation gradient from sea level up to 246 m above mean sea level, and terrain slopes 0–190%. Land cover is characterized by 15 classes (see [31]), of which evergreen forest, woody wetlands, and cultivated crops cover 50% of the state.
2.2. Vulture Data
We trapped black and turkey vultures using baited walk-in traps (Wildlife Dominion Management LLC) placed in two locations, 130 km apart, within solid waste management facilities in Mississippi. Trapping efforts were performed from July 2020–March 2021. Seventeen black vultures and 11 turkey vultures were fitted with 30 g GPS-GSM telemetry units (CTT ES-400, Cellular Tracking Technologies LLC) attached in a backpack configuration [32]. Telemetry units were programmed to record one fix every five minutes, 24 h per day. All trapping and vulture handling activities were performed under federal (USGS No. 23835) and state permits, as well as Mississippi State University IACUC protocol (18–551).
2.3. Extreme Weather Events
Hurricane Zeta (AL282020; hereafter “Zeta”) was a late season category 3 hurricane that caused five human fatalities and USD 4.4 billion in damage between 24–29 October 2020. Zeta made landfall in Cocodrie, LA, USA, on 28 October 2020 with a wind intensity of 185 km/h and central pressure of 970 mb [33]. After landfall, Zeta continued moving northeastward though Mississippi, where >76 mm of rainfall accumulated at locations along the storm’s path (Figure 1), until this storm degraded into a tropical storm in Tuscaloosa, Alabama, on 29 October 2020.
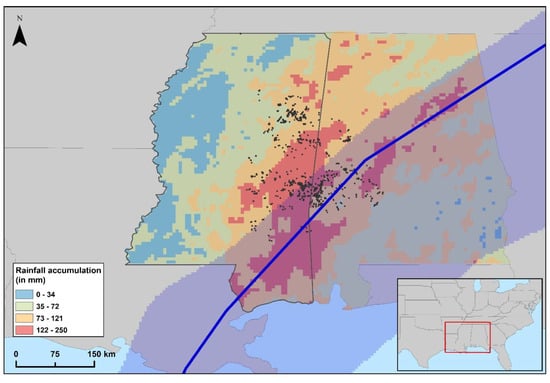
Figure 1.
Rainfall accumulation from Hurricane Zeta between 24–29 October 2020. Black dots = vultures’ GPS fixes. Blue line and shadow correspond to Hurricane Zeta observed track and wind swaths, respectively.
Winter storm Viola was a winter storm with snow and ice precipitation that affected the southeastern United States of America from 15–20 February 2021. Through this storm, Mississippi experienced temperatures down to 3.3 °C below normal, and > 100 mm of total precipitation accumulated on the ground (Figure 2 [34]). At the end of two days, when this storm passed through our study area (16–17 February), there was 50–150 mm of snowfall accumulation and 2.5–16 mm of freezing rain and ice accumulated on the ground [35].
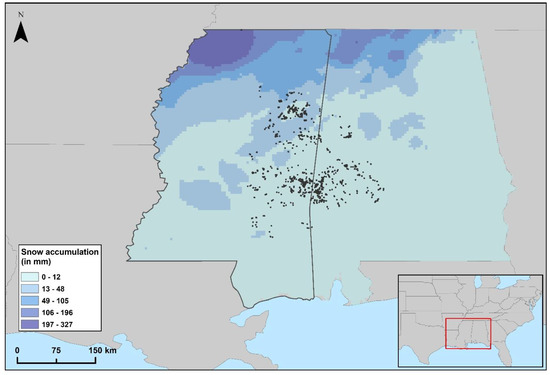
Figure 2.
Snowfall accumulation from winter storm Viola between 15–20 February 2021.
Tornadoes Duffee (MS-46) and Toomsuba (MS-47) occurred 40 km apart in Lauderdale County, Mississippi, on 4 May 2021. Both extreme weather events were classified as weak tornados (EF Scale 1) causing moderate damage without human fatalities [36]. MS-46 started at 20:43 UTC, exhibiting maximum winds, path length, and width of 144 km/h, 9 km, and 0.3 km, respectively. MS-47 started at 21:08 UTC, holding maximum wind speed of 169 km/h in a path of 5.6 km length and 0.4 km width.
2.4. Data Analysis
We consider vultures to be directly impacted by Zeta if they were within the wind swath of this storm. Vultures within the perimeter of Lauderdale County, where tornados Duffee and Toomsuba occurred, were deemed to be directly affected. In the case of winter storm Viola, because of the breadth of the area affected, all telemetered vultures present within the study area were considered to be directly influenced.
For each vulture, we resampled tracks from 1-fix/5 min to 1-fix/60 min, and selected GPS fixes from 07:00 to 17:00 daily. Then, we calculated movement rates (m/h) and daily net-squared displacement (NSD) using the amt package [37] in R statistical software [38]. We aggregated these data by species to calculate and compare the average and 95% nonparametric bootstrap confidence intervals of the movement rate and NSD of each vulture before, during, and after each weather event. We used the boot package [39] of the R statistical software to calculate nonparametric bootstrap confidence intervals.
In evaluating species’ response, we applied categorical time-lags of each event (hurricane, winter storm, and tornadoes), as a set number of days before and after each weather event were considered. Here, we applied the numbers of days before and after each event as corresponding to the number of days that each event lasted. For Zeta, we assessed telemetry data derived from six days before (18–23 October 2020), six days during (24–29 October 2020), and six days after (30 October–4 November 2020) this event. A similar approach was taken for winter storm Viola, where we analyzed data from five days before (10–14 February 2021), during (15–20 February 2021), and after (21–25 February 2020) this storm. Since tornadoes are short-term events occurring in a single day, we used movement data from vultures for the periods two days before (2–3 May 2020) and two days after (5–6 May 2020) the day of these events.
In assessing support of our hypothesis regarding whether vultures selected areas with a greater proportion of tree cover as shelter during storm days versus no storm days (before and after weather events), we defined known vulture use and available locations specific to MOD44B MODIS/Terra Vegetation Continuous Fields Yearly collected at 250 m spatial resolution [40]. We then applied a third-order resource selection, in a use-availability resource selection design approach [41,42]. We fit a step-selection function [43] using the amt package in R statistical software. Available points were sampled from the suite of locations available using steps length and turning angle from observed telemetry positions following gamma and von Mises distributions, respectively [37]. We used mean step length and turning angles to create 10 available locations for each vulture GPS location.
3. Results
We analyzed 827 tracking days including 7638 GPS fixes from 17 black vultures (4688 GPS fixes) and 11 turkey vultures (2950 GPS fixes). Twelve of the 28 tagged vultures were within an area of ≤55 km of the center of Zeta, as determined by their GPS fixes within the observed wind swath of Zeta. Twenty individuals were directly impacted by the winter storm Viola. During the occurrence of tornadoes MS-46 and MS-47, six out of 19 vultures were within the boundaries of Lauderdale County before, during, and after the events. There were no vulture mortalities recorded during this work. Telemetry data showed that vultures exhibited nocturnal displacement, but this was <1 km before (0.81 ± 0.1 SE), during (0.69 ± 0.07 SE), or after (0.9 ± 0.1 SE) the weather event. We do not consider this as indication that vultures moved location nocturnally in response to extreme weather.
Vultures exhibited a high level of variability among individuals in response to weather events (Table 1, Figures S1–S3). In general, vultures, including those not directly affected, moved on average 597 m/h (95% CI: 420–959), 361 m/h (95% CI: 242–545), and 516 m/h (95% CI: 365–840) before, during, and after Zeta, respectively (Figure 3A). Black vultures stayed in the path of this storm but moved out after the rainbands of Zeta as this storm reached them. Turkey vultures displaced out of the path of wind swath before the beginning of Zeta. Net-squared displacement showed that vultures moved out the wind swath of Zeta (Figure 4A), their mean net-squared displacement increased from 740 km2 (95% CI: 355–1784) before to 1494 km2 (95% CI: 724–2935) during, and 1907 km2 (95% CI: 861–3639) after Zeta; nonetheless, black vultures that were not within the area of the wind path of Zeta did not increase their net-squared displacement (Figure 4A).

Table 1.
Average movement rate (meters/hours) and net-squared displacement (NSD, km2) of black and turkey vultures (Coragyps atratus and Cathartes aura, respectively) before, during, and after extreme weather events in Mississippi, USA. Numbers in brackets correspond to 95% confidence intervals. n = sample size (# of birds tracked). Impacted = whether birds were directly affected by the event.
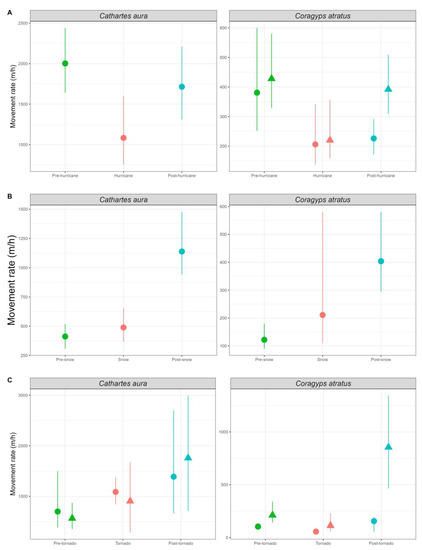
Figure 3.
Movement rates (meters/hours) of black and turkey vultures (Coragyps atratus and Cathartes aura, respectively) before, during, and after extreme weather events in Mississippi, MS, USA. (Panel A) = Hurricane Zeta. (Panel B) = Winter storm Viola. (Panel C) = Tornadoes Duffee and Toomsuba. Green = before the event. Pink = during the event. Blue = after the event. Circles = vultures directly affected. Triangles = vultures not directly affected. Panels without triangles = all birds were directly affected by storms evaluated.
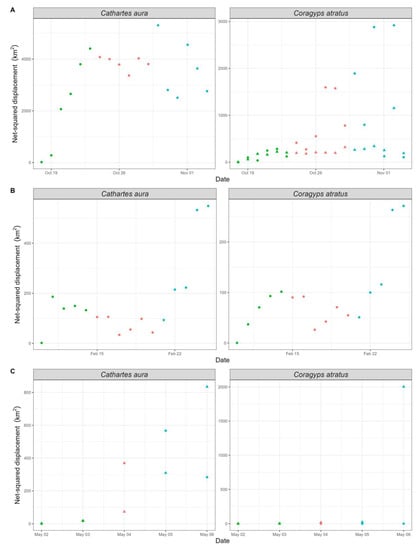
Figure 4.
Net-squared displacement (km2) of black and turkey vultures (Coragyps atratus and Cathartes aura, respectively) before, during, and after extreme weather events in Mississippi, MS, USA. (Panel A) = Hurricane Zeta. (Panel B) = Winter storm Viola. (Panel C) = Tornadoes Duffee and Toomsuba. Green = before the event. Pink = during the event. Blue = after the event. Circles = vultures directly affected. Triangles = vultures not directly affected. Panels without triangles = all birds were directly affected by storms evaluated.
Black and turkey vultures responded similarly to winter storm Viola (Figure 3B and Figure 4B). Their mean movement rate was low before the storm (157 m/h, 95% CI: 114–223) but higher during (253 m/h (95% CI: 171–374)) and after (422 m/h (95% CI: 318–566)) this storm. Although vultures increased their movement rates, their displacement reduced from 61 km2 (95% CI: 23–151) before winter storm Viola to 54 km2 (95% CI: 29–100) during the winter storm, then significantly increased to 203 km2 (95% CI: 100–360) after the event.
Overall, response to tornados was characterized by the increase of the average movement rates from 219 m/h (95% CI: 142–365) before the event to 589 m/h (95% CI: 223–932) and 672 m/h (95% CI: 332–1358) during and after the event, respectively. Similarly, average displacement increased from 6 km2 (95% CI: 1–23) before the event to 246 km2 (95% CI: 10–594) during the tornados to 284 km2 (95% CI: 16–729) after the event. Despite this response, black vultures reduced their movement rates and displacements during the occurrence of the tornados and did not leave the path of this storm (Figure 3C and Figure 4C), whilst turkey vultures increased their movement rates and displacements to move out of the areas close to the tornadoes’ paths (Figure 3C and Figure 4C).
Step-selection analysis revealed that vultures shifted their selection of forest cover before, during, and after storms. Black vulture always avoided forested areas regardless of the weather event (Figure 5). During the pass of Zeta, they negatively selected forest areas and such avoidance increased from β = −0.012 (95% CI: −0.020–0.005) before to β = −0.016 (95% CI: −0.023–−0.009) during and β = −0.024 (95% CI: −0.032–−0.017) after the hurricane. This species exhibited significant differences in their avoidance of areas with tree cover before (β = −0.015, 95% CI: −0.021–−0.008), during (β = −0.041, 95% CI: −0.047–−0.035), and after (β = −0.029, 95% CI: −0.034–−0.024) winter storm Viola. Even though black vultures negatively selected forest areas during tornados, the avoidance was lower during the occurrence of the tornado (β = −0.041, 95% CI: −0.070–−0.011) when compared to days before and after (β = −0.065, 95% CI: −0.086–0.043 and β = −0.051, 95% CI: −0.071–0.032, respectively).
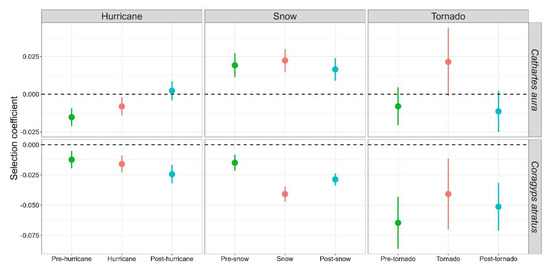
Figure 5.
Selection strength of forest cover for black and turkey vultures (Coragyps atratus and Cathartes aura, respectively) before (green), during (pink), and after (blue) extreme weather events in Mississippi.
Turkey vultures negatively selected areas with forest cover before (β = −0.015, 95% CI: −0.021–−0.09) and during (β = −0.008, 95% CI: −0.014–−0.002) the passage of Hurricane Zeta, but they positively selected (β = 0.002, 95% CI: −0.004–0.009) these areas after the pass of Zeta (Figure 5). In contrast, turkey vultures positively selected for forest areas before (β = −0.019, 95% CI: 0.011–0.027), during (β = 0.022, 95% CI: 0.015–0.03), and after (β = 0.016, 95% CI: 0.009–0.024) winter storm Viola (Figure 5). Although turkey vultures avoided forest areas before and after the occurrence of tornados (β = −0.008, 95% CI: −0.021–0.005 and β = −0.011, 95% CI: −0.025–0.002, respectively), they selected (β = 0.021, 95% CI: −0.001–0.044) areas with tree cover during the day of the event (Figure 5).
4. Discussion
Little is known about the response of avian scavengers to extreme weather events. This research is pioneering in that it addresses the movements of vultures in the context of scavenger response to extreme weather events. Vultures responded differently to each weather event, and the observed variability in movement traits among individuals are consistent with the behavioral plasticity already reported in black and turkey vultures [44].
Although vultures shifted their movements out of the predicted path of Zeta, black vultures did not move significantly until the hurricane reached them. Conversely, turkey vultures moved out the path of Hurricane Zeta before this storm reached them. These findings reveal that both species use avoidance behavior in response to hurricanes, as observed in other avian species [19,20,23]. The avoidance behavior could have been triggered by the infrasound associated with storm systems [45] that birds can sense and then adjust their navigation and hazard detection [46,47].
One potential explanation for avoidance behavior being more pronounced in turkey vultures than in black vultures is a better developed sensory system in turkey than in black vultures [48,49]. We argue that vultures, particularly turkey vultures, may be able to smell the storms within hours or days before these arrive. We sustain our speculation on the indigenous knowledge used by native people of Bangladesh and Malaysia, who can sense a muddy smell in the air at least one day before the arrival of a cyclone [50,51]. During the occurrence of hurricanes and tornadoes, odors such as burning sulfur, ozone, and petrichor can be sensed and drifted through the wind for considerable distances [52,53]. Because turkey vultures have a highly sensitive olfactory system [50], these birds may be able to sense any of these odors that can trigger a spatial avoidance behavioral response to extreme weather events.
Contrary to our expectations, vultures did not shift their movements out of the path of the winter storm. Snowstorms do not produce infrasound as hurricanes do [54], which may explain why vultures did not show avoidance behavior and move to a storm-free area. Although the decline in atmospheric pressure and temperatures before and during a snowstorm have been suggested as environmental cues to predict snowstorms by birds and alter their physiology and behavior in response [54,55], we think that the unobserved response to the decline of atmospheric pressure and temperature during winter storm Viola could be related to the fact that (i) the individuals included in the study are residents, (ii) flying during winter conditions demands the largest energy investment due to weak thermals [56], and (iii) they are winter-acclimated (phenotypic or physiological modifications to reduce the stress caused by climatic factors and increases cold resistance, sensu [54]) so they can cope with harsh conditions.
Vultures responded to tornadoes similarly to how they moved with respect to Hurricane Zeta; black vultures did not leave the area directly impacted by this storm, but turkey vultures did. Since hurricanes and tornadoes involve the occurrence of thunderstorms, we posit that the mechanisms triggering vultures’ responses to tornadoes may be similar to hurricanes: vultures’ sensory systems [48,49], and the infrasound associated with storm systems [45]. The lack of response of black vultures and the delayed response of turkey vultures to tornadoes is likely due to short duration of tornado events (<1 day) when compared to a hurricane (>3 days).
While the area of wind swath associated with hurricanes and tornadoes evaluated was narrower than the average daily range reported for black and turkey vultures (median 13–14 km2/day and 24–39 km2/day [57], respectively), the differences in displacement and movement between these species may allow them to use resources differently after the immediate effects of storms have abated. These differences in behavior exist as interesting avenues for research in understanding management for these birds as their populations continue to grow and as the frequency of extreme weather events increases.
Our results partially support our predictions of black and turkey vultures’ movement rates and net-squared displacements before, during, and after the storms. These vulture species exhibited large movement rates before and after Zeta with lower movement rates during the event. This is consistent with previous observations of vultures ceasing flying activities due to inclement weather and localized conditions (e.g., precipitation) that do not favor thermal development [58]. Contrary to our prediction, vultures did not reduce their net-squared displacement during the occurrence of a hurricane. However, once birds have moved from the path of the storm, the absence of difference in net square displacement may be due to continuation of general movement behavior as before exodus from the storm’s path albeit in a different area. Both species increased their movement rates before, during, and after the occurrence of winter storm Viola and the tornadoes. Both species reduced their net-squared displacement during the winter storm and increased it by fourfold after it. Black vultures did not change their net-squared displacement during the tornadoes examined, but turkey vultures’ increased during and after these storms.
Black and turkey vultures are obligate soaring birds that rely on thermal updraft to fuel their flights [59,60]. It is likely that vultures reduced their movement rates because thermal updrafts do not occur, or weaken, during rainy days [58]. On the other hand, both species increased their movement rate during the snowstorm and tornadoes; this may be the response to the lack of food resources covered by the snow [61,62] or a behavioral response to the disturbance created during the occurrence of the tornadoes.
Vultures did not make greater use of forest areas as we expected. Our results on vultures resource selection are consistent with previous studies that found that black vultures avoid forest areas, whereas turkey vultures use forest areas more often [24,25]. Black vultures have higher wing loading than turkey vultures [63], which makes it difficult to exploit updrafts close to the ground and forest canopy [64]. This may explain why black vultures avoided forest areas before, during, and after extreme weather events; they would need larger energy investment to take-off. Conversely, turkey vultures selected for forest areas during the winter storm and the occurrence of tornadoes. Their ability to fly close to the forest canopy facilitates the use of forest areas providing protection against wind gusts and low temperatures [26,64].
The results of our study add to evidence that wildlife exhibit the capacity to alter behavior with respect to some types of weather events. However, we also show existing differences between black and turkey vultures in how these birds perceive and alter behavior before, during, and after the passage of hurricanes, winter storms, and tornadoes. These differences present an interesting forum in which to explore differences in the anatomy and physiology of these animals and to explore how what we know and do not yet understand about their senses allow them to respond to changing environmental conditions, those temporally acute as well as those more protracted. The assumption of turkey vultures having better developed olfaction than black vultures needs to be more formally tested [65]. We also need to evaluate the perception of storm events among wildlife based on olfactory and other senses which may not be as developed in people.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/d15030441/s1, Figure S1: Net-squared displacement of Black and Turkey Vultures before, during and after Hurricane Zeta; Figure S2: Net-squared displacement of Black and Turkey Vultures before, during and after snowstorm Viola; Figure S3: Net-squared displacement of Black and Turkey Vultures before, during and after tornadoes Duffee and Toomsuba.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.N.-R. and S.A.R.; methodology, A.N.-R. and S.A.R.; formal analysis, A.N.-R. and S.A.R.; investigation, A.N.-R. and S.A.R.; resources, A.N.-R. and S.A.R.; data curation, A.N.-R. and S.A.R.; writing—original draft preparation, A.N.-R. and S.A.R.; writing—review and editing, A.N.-R. and S.A.R.; project administration, S.A.R.; funding acquisition, S.A.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was provided for by the National Institute of Food and Agriculture, U.S. Department of Agriculture, McIntire-Stennis project under accession number MISZ-082100. This study was prepared under contract with Mississippi State University, PI Scott Rush, with financial support from the Office of Local Defense Community Adjustment, Department of Defense. The content reflects the views of the Mississippi State University, PI Scott Rush, and does not necessarily reflect the views of the Office of Local Defense Community Adjustment.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Mississippi State University (protocol code 18-551 and 30-04-2020).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Brown, J.H.; Lomolino, M.V. Biogeography, 2nd ed.; Sinauer Associates, Inc.: Sunderland, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Monahan, W.B.; Fisichelli, N.A. Climate exposure of U.S. national parks in a new era of change. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinuzzi, S.; Allstadt, A.J.; Bateman, B.L.; Heglund, P.J.; Pidgeon, A.M.; Thogmartin, W.E.; Vavrus, S.J.; Radeloff, V.C. Future frequencies of extreme weather events in the National Wildlife Refuges of the conterminous US. Biol. Conserv. 2016, 201, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, D.B.; Diaz, H.F.; Murnane, R.J. Definition, diagnosis, and origin of extreme weather and climate events. Clim. Extrem. Soc. 2008, 340, 11–23. [Google Scholar]
- Reyer, C.P.; Leuzinger, S.; Rammig, A.; Wolf, A.; Bartholomeus, R.P.; Bonfante, A.; de Loenzi, F.; Dury, M.; Glonig, P.; Jaoudé, R.A.; et al. A plant’s perspective of extremes: Terrestrial plant responses to changing climatic variability. Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 19, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hufkens, K.; Friedl, M.A.; Kennan, T.F.; Sonnentag, O.; Bailey, A.; O’Keefe, J.; Richardson, A.D. Ecological impacts of a widespread frost event following early spring leaf-out. Glob. Change Biol. 2012, 18, 2365–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slenning, B.D. Global climate change and implications for disease emergence. Vet. Pathol. 2010, 47, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, C.J.; Kominoski, J.S.; McDowell, W.H.; Branoff, B.; Lagomasino, D.; Leon, M.; Hensel, E.; Hensel, M.J.S.; Strickland, B.A.; Aide, T.M.; et al. A general pattern of trade-offs between ecosystem resistance and resilience to tropical cyclones. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabl9155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ancillotto, L.; Santini, L.; Ranc, N.; Maiorano, L.; Russo, D. Extraordinary range expansion in a common bat: The potential roles of climate change and urbanisation. Sci. Nat. 2016, 103, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomara, L.Y.; LeDee, O.E.; Martin, K.J.; Zuckerberg, B. Demographic consequences of climate change and land cover help explain a history of extirpations and range contraction in a declining snake species. Glob. Change Biol. 2014, 20, 2087–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waide, R.B. Summary of the response of animal populations to hurricanes in the Caribbean. Biotropica 1991, 23, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, I. Population Limitation in Birds; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Morcillo, D.O.; Steiner, U.K.; Grayson, K.L.; Ruiz-Lambides, A.V.; Hernández-Pacheco, R. Hurricane-induced demographic changes in a non-human primate population. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 200173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ruiz, M.; Rueda-Hernández, R.; Renton, K. Vulture abundance and habitat association following major hurricane disturbance in the tropical dry forest of western Mexico. J. Raptor Res. 2021, 55, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbet, I.C.T.; Spendelow, J.A. Contribution of research to management and recovery of the Roseate Tern: Review of a twelve-year project. Waterbirds Int. J. Waterbird Biol. 1999, 22, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiley, J.W.; Wunderle, J.M. The effects of hurricanes on birds, with special reference to Caribbean islands. Bird Conserv. Int. 1993, 3, 319–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdomo-Velázquez, H.E.; Andresen Vega, E.; Schondube, J.E.; Cuarón, A.D. Effects of hurricanes on the understory forest birds of Cozumel Island. Trop. Conserv. Sci. 2017, 10, 1940082917737759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abernathy, H.N.; Crawford, D.A.; Garrison, E.P.; Chandler, R.B.; Conner, M.L.; Miller, K.V.; Cherry, M.J. Deer movement and resource selection during Hurricane Irma: Implications for extreme climatic events and wildlife. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 286, 20192230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streby, H.M.; Kramer, G.R.; Peterson, S.M.; Lehman, J.A.; Buehler, D.A.; Andersen, D.E. Tornadic storm avoidance behavior in breeding songbirds. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellone, U.; López-López, P.; Limiñana, R.; Urios, V. Weather conditions promote route flexibility during open ocean crossing in a long-distance migratory raptor. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2011, 55, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, R.; Getz, W.M.; Revilla, E.; Holyoak, M.; Kadmon, R.; Saltz, D.; Smouse, P.E. A movement ecology paradigm for uni-fying organismal movement research. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19052–19059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bildstein, K.L. Raptors: The Curious Nature of Diurnal Birds of Prey; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Weimerskirch, H.; Prudor, A. Cyclone avoidance behaviour by foraging seabirds. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, J.S.; Fraser, J.D. Habitat use and home ranges of black and turkey vultures. J. Wildl. Manag. 1989, 53, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, A.E.; Byrne, M.E.; Hepinstall-Cymerman, J.; Bryan, A.L.; DeVault, T.L.; Rhodes, O.E.; Beasley, J.C. Evidence of niche differentiation for two sympatric vulture species in the Southeastern United States. Mov. Ecol. 2019, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, W.L.; Yahner, R.H.; Storm, G.L. Winter use and habitat characteristics of vulture communal roosts. J. Wildl. Manag. 1990, 54, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchholz, R.; Banusiewicz, J.D.; Burgess, S.; Crocker-Buta, S.; Eveland, L.; Fuller, L. Behavioural research priorities for the study of animal response to climate change. Anim. Behav. 2019, 150, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CEC. Ecological Regions of North America; Commission for Environmental Cooperation: Québec, QC, Canada, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, H.E.; Zimmermann, N.E.; McVicar, T.R.; Vergopolan, N.; Berg, A.; Wood, E.F. Present and future Köppen-Geiger climate classification maps at 1-km resolution. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information. Climate at a Glance: Divisional Mapping. 2022. Available online: https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/cag/ (accessed on 7 June 2022).
- Dewitz, J. National Land Cover Database (NLCD) 2019 Products. ver. 2.0, June 2021 edn; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Meyburg, B.-U.; Fuller, M.R. Spatial tracking: Satellite tracking. In Raptor Research and Management Techniques; Bird, D.M., Bildstein, K.L., Eds.; Hancock House Publishers: Blaine, WA, USA, 2007; pp. 242–248. [Google Scholar]
- Blake, E.; Berg, R.; Hagen, A. Tropical Cyclone Report: Hurricane Zeta (AL282020); National Hurricane Center: University Park, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information. State of the Climate: Monthly National Climate Report for February 2021. 2021. Available online: https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/access/monitoring/monthly-report/national/202102 (accessed on 3 June 2022).
- NOAA Weather Prediction Center. Storm Summary Number 4 for Southern Plains to Mid-Atlantic and Northeast Winter Storm. 2021. Available online: https://www.wpc.ncep.noaa.gov/storm_summaries/2021/storm5/stormsum_4.html (accessed on 3 June 2022).
- NOAA National Weather Service. 2021 NWS Jackson/Mississippi Tornado Information. 2021. Available online: https://www.weather.gov/jan/2021tornadoinfo (accessed on 3 June 2022).
- Signer, J.; Fieberg, J.; Avgar, T. Animal movement tools (amt): R package for managing tracking data and conducting habitat selection analyses. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 880–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Canty, A.; Ripley, B. Boot: Bootstrap R (S-Plus) Functions. R Package Version 1.3-23. 2019. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/boot/index.html (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- Dimiceli, C.; Carroll, M.; Sohlberg, R.; Kim, D.H.; Kelly, M.; Townshend, J.R.G. MOD44B MODIS/Terra Vegetation Continuous Fields Yearly L3 Global 250 m SIN Grid V006; NASA EOSDIS Land Processes DAAC: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.H. The comparison of usage and availability measurements for evaluating resource preference. Ecology 1980, 61, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manly, B.F.; McDonald, L.; Thomas, D.L.; McDonald, T.L.; Erickson, W.P. Resource Selection by Animals: Statistical Design and Analysis for Field Studies; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Thurfjell, H.; Ciuti, S.; Boyce, M.S. Applications of step-selection functions in ecology and conservation. Mov. Ecol. 2014, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel, J.T.; Bildstein, K.L. Turkey Vultures use anthropogenic thermals to extend their daily activity period. Wilson J. Ornithol. 2007, 119, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, H.S.; Bedard, A.J. Observations of Infrasound and Subsonic Disturbances Related to Severe Weather. Geophys. J. Int. 1971, 26, 215–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagstrum, J.T. Infrasound and the avian navigational map. J. Exp. Biol. 2000, 203, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedard, A.J. Waterfall low-frequency vibrations and infrasound: Implications for avian migration and hazard detection. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2021, 207, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisney, T.J.; Stecyk, K.; Kolominsky, J.; Graves, G.R.; Wylie, D.R.; Iwaniuk, A.N. Comparison of eye morphology and retinal topography in two species of New World vultures (Aves: Cathartidae). Anat. Rec. 2013, 296, 1954–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigg, N.P.; Krilow, J.M.; Gutierrez-Ibanez, C.; Wylie, D.R.; Graves, G.R.; Iwaniuk, A.N. Anatomical evidence for scent guided foraging in the Turkey Vulture. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garay-Barayazarra, G.; Puri, R.K. Smelling the monsoon: Senses and traditional weather forecasting knowledge among the Kenyah Badeng farmers of Sarawak, Malaysia. Indian J. Tradit. Knowl. 2011, 10, 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, S.K.; Routray, J.K. An Analysis of the Causes of Non-Responses to Cyclone Warnings and the Use of Indigenous Knowledge for Cyclone Forecasting in Bangladesh. In Climate Change and Disaster Risk Management. Climate Change Management; Leal Filho, W., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, E.M. Tornadoes and Related Phenomena. In Compendium of Meteorology: Prepared under the Direction of the Committee on the Compendium of Meteorology; Malone, T.F., Ed.; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 1951; pp. 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bear, I.J.; Thomas, R.G. Nature of Argillaceous Odour. Nature 1964, 201, 993–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, C.; Dawson, W.R. A search for environmental cues used by birds in survival of cold winters. Curr. Ornithol. 1999, 15, 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Breuner, C.W.; Sprague, R.S.; Patterson, S.H.; Woods, H.A. Environment, behavior and physiology: Do birds use barometric pressure to predict storms? J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 216, 1982–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, H.; Shepard, E.L.C.; Holton, M.D.; Alarcón, P.A.E.; Wilson, R.P.; Lambertucci, S.A. Physical limits of flight performance in the heaviest soaring bird. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 17884–17890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, M.E.; Holland, A.E.; Turner, K.L.; Bryan, A.L.; Beasley, J.C. Using multiple data sources to investigate foraging niche partitioning in sympatric obligate avian scavengers. Ecosphere 2019, 10, e02548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallon, J.M.; Bildstein, K.L.; Fagan, W.F. Inclement weather forces stopovers and prevents migratory progress for obligate soaring migrants. Mov. Ecol. 2021, 9, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, N.J.; Kluever, B.M.; Driver, R.; Rush, S.A. Black Vulture (Coragyps atratus), version 2.0. In Birds of the World; Rodewald, P.G., Keeney, B.K., Eds.; Cornell Lab of Ornithology: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, D.A.; Mossman, M.J. Turkey Vulture (Cathartes aura), version 2.0. In Birds of the World; Rodewald, P.G., Keeney, B.K., Eds.; Cornell Lab of Ornithology: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonerud, G.A. Effect of snow cover on seasonal changes in diet, habitat, and regional distribution of raptors that prey on small mammals in boreal zones of Fennoscandia. Holarct. Ecol. 1986, 9, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyser, S.R.; Fink, D.; Gudex-Cross, D.; Radeloff, V.C.; Pauli, J.N.; Zuckerberg, B. Snow cover dynamics: An overlooked yet important feature of winter bird occurrence and abundance across the United States. Ecography 2023, 2023, e06378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, G.R. Sexual monomorphism in wing loading and wing aspect ratio in Black Vulture (Coragyps atratus) and Turkey Vulture (Cathartes aura). Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash. 2017, 130, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallon, J.M.; Bildstein, K.L.; Katzner, T.E. In-flight turbulence benefits soaring birds. Auk 2016, 133, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.H.; Santos, C.D.; Da Silva, M.L. The limits of olfactory perception in Black Vultures: A field experiment. Ethol. Ecol. Evol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).