Population Survey Combined with Genomic-Wide Genetic Variation Unravels the Endangered Status of Quercus gilva
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Population Survey
2.2. Plant Material Samples, Resequencing, Control, and Mapping
2.3. SNP and Insertion/Deletion (InDels) Calling
2.4. Phylogenetic Inference and Population Genomic Analysis
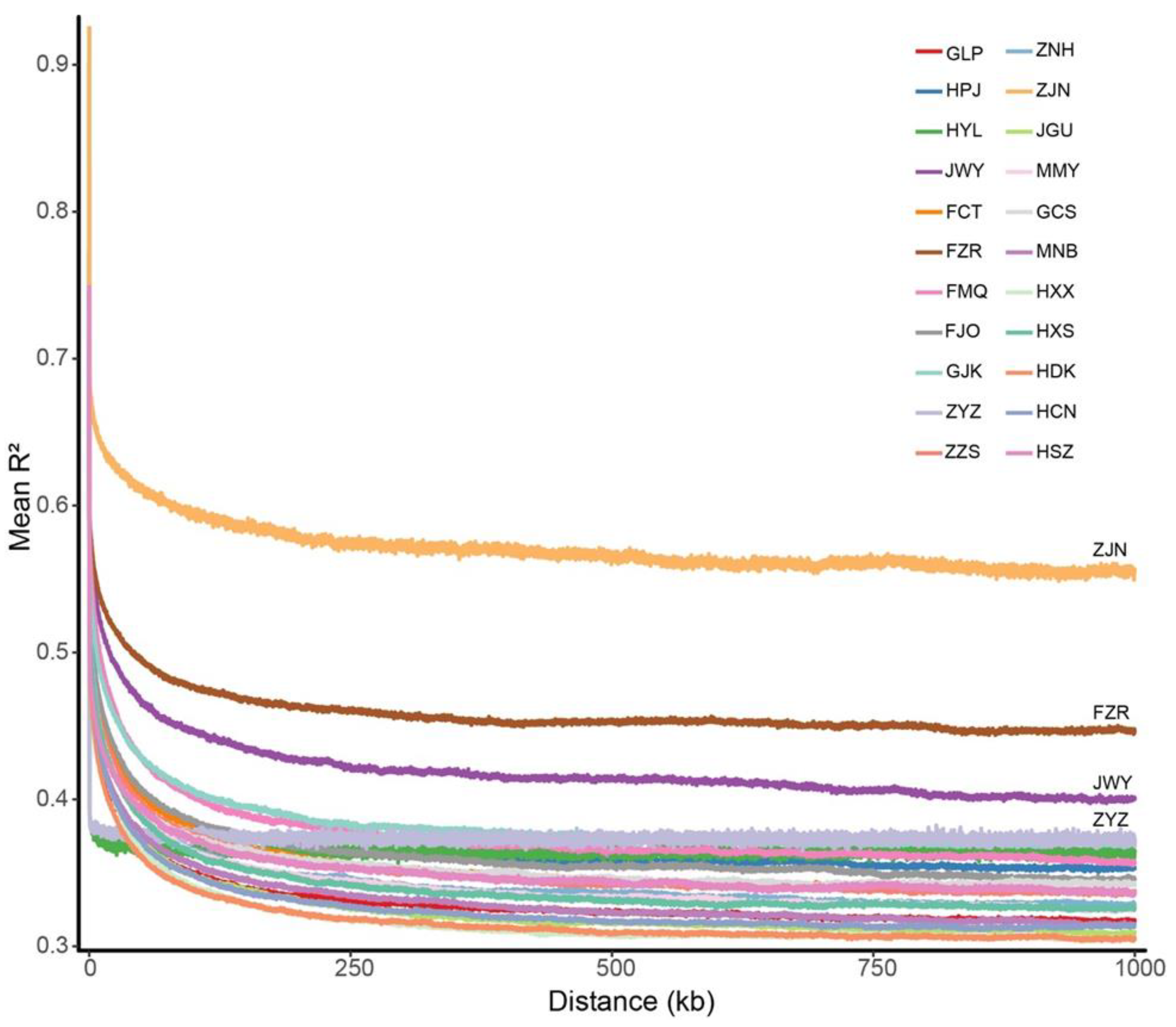
2.5. Population Genetic Diversity and Linkage Disequilibrium (LD) Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Reassessment of Q. gilva
3.2. Detection of Genome-Wide Variant
3.3. Phylogenetic and Population Structure Analyses of Q. gilva
3.4. Genome-Wide Patterns of Nucleotide Diversity and LD Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Botanic Gardens Conservation International (BGCI). State of the World’s Trees; BGCI: Richmond, UK, 2021; pp. 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Crowther, T.W.; Glick, H.B.; Covey, K.R.; Bettigole, C.; Maynard, D.S.; Thomas, S.M.; Smith, J.R.; Hintler, G.; Duguid, M.C.; Amatulli, G.; et al. Mapping tree density at global scale. Nature 2015, 525, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazan, L.; Song, Y.G.; Kozlowski, G. The woody planet: From past triumph to manmade decline. Plants 2020, 9, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrero, C.; Jerome, D.; Beckman, E.; Byrne, A.; Coombes, A.J.; Deng, M.; González-Rodríguez, A.; Hoang, V.S.; Khoo, E.; Nguyen, N.; et al. The Red List of Oaks 2020; The Morton Arboretum: Lisle, IL, USA, 2020; pp. 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Cavender-Bares, J. Diversification, adaptation, and community assembly of the American oaks (Quercus), a model clade for integrating ecology and evolution. New Phytol. 2019, 221, 669–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.G.; Petitpierre, B.; Deng, M.; Wu, J.P.; Kozlowski, G. Predicting climate change impacts on the threatened Quercus arbutifolia in montane cloud forests in southern China and Vietnam: Conservation implications. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 444, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sork, V.L.; Cokus, S.J.; Fitz-Gibbon, S.T.; Zimin, A.V.; Puiu, D.; Garcia, J.A.; Gugger, P.F.; Henriquez, C.L.; Zhen, Y.; Lohmueller, K.E.; et al. High-quality genome and methylomes illustrate features underlying evolutionary success of oaks. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, H.H.; Gao, X.Y.; Song, Y.G.; Cao, G.L.; Li, J. Biodiversity arks in the Anthropocene. Reg. Sustain. 2021, 2, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Convention on Biological Diversity. In Strategic Plan for Biodiversity 2011–2020, Including Aichi Biodiversity Targets; UNEP: Nagoya, Japan, 2010.
- Coates, D.J.; Byrne, M.; Moritz, C. Genetic diversity and conservation units: Dealing with the species-population continuum in the age of genomics. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 6, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoban, S.; Bruford, M.; Jackson, J.D.; Lopes-Fernandes, M.; Heuertz, M.; Hohenlohe, P.A.; Paz-Vinas, I.; Sjogren-Gulve, P.; Segelbacher, G.; Vernesi, C.; et al. Genetic diversity targets and indicators in the CBD post-2020 Global Biodiversity Framework must be improved. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 248, 108654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Open-Ended Working Group. Zero Draft of the Post-2020 Global Biodiversity Framework. In Proceedings of the Convention on Biological Diversity, Kunming, China, 24-29 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Han, E.K.; Cho, W.B.; Park, J.S.; Choi, I.S.; Kwak, M.; Kim, B.Y.; Lee, J.H. A disjunctive marginal edge of evergreen broad-leaved oak (Quercus gilva) in East Asia: The high genetic distinctiveness and unusual diversity of Jeju Island populations and insight into a massive, independent postglacial colonization. Genes 2020, 11, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, N.; Tang, D.Q.; Kurokochi, H.; Saito, Y.; Ide, Y. Genetic structure of Quercus gilva Blume in Japan as revealed by chloroplast DNA sequences. Botany 2015, 93, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.Y.; Ouyang, S.; Wu, J.Y.; Zhou, Z.C.; Li, Z.H. Research progress of precious commercial tree species Cyclobalanopsis gilva. Hunan For. Sci. Technol. 2021, 48, 74–79. [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura, N.; Kurokochi, H.; Tan, E.; Asakawa, S.; Sato, N.; Saito, Y.; Ide, Y. Development of 13 polymorphic chloroplast DNA markers in Quercus gilva, a regionally endemic species in Japan. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2014, 6, 961–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.J.; Liu, Q.Y.; Luo, X.; Zeng, Q.M.; Xie, J.; Ni, B.Y.; Chen, S.P. Species diversity and niche of small populations in the natural forest Cyclobalanopsis gilva. Fujian Linye 2017, 2017, 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.R.; You, Y.H. Ecophysiological responses of Quercus gilva, endangered species and Q. glauca to long-term exposure to elevated CO2 concentration and temperature. J. Ecol. Field Biol. 2012, 35, 203–212. [Google Scholar]
- Botanic Gardens Conservation International (BGCI) & IUCN SSC Global Tree Specialist Group. Quercus gilva. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019. e.T18749666A136775665. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/18749666/136775665 (accessed on 17 October 2022).
- Besseau, P.; Graham, S.; Christophersen, T. Restoring forests and landscapes: The key to a sustainable future. In Global Partnership on Forest and Landscape Restoration; International Union of Forest Research Organizations: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Di Sacco, A.; Hardwick, K.A.; Blakesley, D.; Brancalion, P.H.S.; Breman, E.; Rebola, L.C.; Chomba, S.; Dixon, K.; Elliott, S.; Ruyonga, G.; et al. Ten golden rules for reforestation to optimize carbon sequestration, biodiversity recovery and livelihood benefits. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 1328–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonin, A.; Nicole, F.; Pompanon, F.; Miaud, C.; Taberlet, P. Population adaptive index: A new method to help measure intraspecific genetic diversity and prioritize populations for conservation. Conserv. Biol. 2007, 21, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, V. The Evolutionary Process, a Critical Study of Evolutionary Theory, 2nd ed.; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 121–135. [Google Scholar]
- Allendorf, F.W.; Hohenlohe, P.A.; Luikart, G. Genomics and the future of conservation genetics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardos, M.; Armstrong, E.E.; Fitzpatrick, S.W.; Hauser, S.; Hedrick, P.W.; Miller, J.M.; Tallmon, D.A.; Funk, W.C. The crucial role of genome-wide genetic variation in conservation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2104642118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Virtual Herbarium (CVH). Available online: http://www.cvh.ac.cn/ (accessed on 8 September 2022).
- Bachman, S.; Moat, J.; Hill, A.W.; De la Torre, J.; Scott, B. Supporting Red List threat assessment with GeoCAT: Geospatial conservation assessment tool. ZooKeys 2011, 150, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUCN Standards and Petitions Committee. Guidelines for Using the IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria. Version 15.1. Prepared by the Standards and Petitions Committee. 2022. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/documents/RedListGuidelines.pdf (accessed on 9 September 2022).
- Doyle, J. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem. Bull. 1987, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The sequence alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A. The genome analysis toolkit: A mapReduce framework for analyzing next generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, B.; Ulaszewski, B.; Meger, J.; Aury, J.M.; Bodénès, C.; Lesur-Kupin, I.; Pfenninger, M.; Da Silva, C.; Gupta, D.K.; Guichoux, E.; et al. A Chromosome-level genome assembly of the European Beech (Fagus sylvatica) reveals anomalies for organelle DNA integration, repeat Content and distribution of SNPs. Front. Genet. 2022, 12, 691058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, N.; Price, A.L.; Reich, D. Population structure and eigenanalysis. PLoS Genet. 2006, 2, e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D.H.; Lange, K. Enhancements to the ADMIXTURE algorithm for individual ancestry estimation. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria, 2019. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 6 May 2022).
- Pfeifer, B.; Wittelsbürger, U.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Lercher, M.J. PopGenome: An efficient Swiss army knife for population genomic analyses in R. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 1929–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danecek, P.; Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.; Albers, C.A.; Banks, E.; DePristo, M.A.; Handsaker, R.E.; Lunter, G.; Marth, G.T.; Sherry, S.T.; et al. The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2156–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of the Environment of Korea. Korean Red List of Threatened Species; National Institute of Biological Resources: Incheon, Republic of Korea, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.S.; Chen, J.; Zhao, J.; Comes, H.P.; Li, P.; Fu, C.X.; Xie, X.; Lu, R.S.; Xu, W.Q.; Feng, Y.; et al. Genomic insights on the contribution of balancing selection and local adaptation to the long-term survival of a widespread living fossil tree, Cercidiphyllum japonicum. New Phytol. 2020, 228, 1674–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Deng, M.; Jiang, X.L.; Westwood, M.; Song, Y.G.; Turkington, R. Phylogeography of Quercus glauca (Fagaceae), a dominant tree of East Asian subtropical evergreen forests, based on three chloroplast DNA interspace sequences. Tree Genet. Genomes. 2015, 11, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.N.; Wang, W.T.; Zhang, D.Y. Phylogeographic breaks within Asian butternuts indicate the existence of a phytogeographic divide in East Asia. New Phytol. 2016, 209, 1757–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.Y.; Shi, Y.; Yuan, S.; Zhou, B.F.; Chen, X.Y.; An, Q.Q.; Ingvarsson, P.K.; Plomion, C.; Wang, B.S. Link selection shapes the landscape of genomic variation in three oak species. New Phytol. 2022, 233, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.P.; Fan, G.Y.; Yin, P.P.; Sun, S.; Li, N.; Hong, X.N.; Hu, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, F.M.; Han, J.D.; et al. Resequencing 545 ginkgo genomes across the world reveals the evolutionary history of the living fossil. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.P.; Liu, D.T.; Wariss, H.M.; Zhang, R.G.; Tao, L.D.; Milne, R.I.; Sun, W.B. Demographic history and identification of threats revealed by population genomic analysis provide insights into conservation for an endangered maple. Mol. Ecol. 2021, 31, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceballos, G.; Ehrlich, P.R. Mammal population losses and the extinction crisis. Science 2002, 296, 904–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kort, H.; Prunier, J.G.; Ducatez, S.; Honnay, O.; Baguette, M.; Stevens, V.M.; Blanchet, S. Life history, climate and biogeography interactively affect worldwide genetic diversity of plant and animal populations. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.U.; Jang, K.S.; Lim, H.; Kim, E.H.; Lee, K.H. Genetic diversity of Quercus gilva in Je-ju Island. J. Korean Soc. For. Sci. 2018, 107, 151–157. [Google Scholar]

| Country | China | Japan | South Korea | Total/Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of populations | 68 | 35 | 5 | 108 |
| AOO (km2) | 272 | 140 | 20 | 432 |
| Future-AOO (km2) | 148 | 92 | 8 | 248 |
| EOO (km2) | 873,462 | 161,420 | 84 | 1,921,293 |
| NLP | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| NMP | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| NSP | 12 | 0 | 1 | 13 |
| NVSP | 31 | 12 | 4 | 47 |
| NISS | 23 | 23 | 0 | 46 |
| Total individuals | <5000 | <2000 | <600 | <10,000 |
| Main threats | Logging and wood harvesting; Agriculture and development | Logging; Agriculture and development | Human-mediated disturbance | Agriculture and Biological resource use |
| PTTG | Decrease noticeable | Decrease noticeable | No information | Decrease noticeable |
| Main area conserved | Fengshui forests and temples | Forests surrounding shrines and temples | Gotjawal (conserved area) | Protected Trees |
| Population Code (Location) | SNPs | Indels | Transition | Transversion | Ti/Tv | Heterozygosity | Homozygosity | Het-Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLP (Liping, Guizhou) | 3,507,918 | 1,115,687 | 1,403,828 | 547,870 | 2.56 | 1,106,329 | 845,370 | 0.5666 |
| GJK (Jiangkou, Guizhou) | 3,470,289 | 1,150,966 | 1,510,648 | 589,730 | 2.56 | 1,194,235 | 906,143 | 0.5636 |
| GCS (Changshun, Guizhou) | 3,448,941 | 1,055,047 | 1,507,376 | 579,442 | 2.597 | 1,132,727 | 954,091 | 0.5425 |
| HXX (Xiangxiang, Hunan) | 4,293,739 | 1,378,636 | 1,596,453 | 626,624 | 2.54 | 1,343,567 | 879,510 | 0.6023 |
| HXS (Xinshao, Hunan) | 3,561,533 | 1,162,826 | 1,514,130 | 589,450 | 2.56 | 1,247,186 | 856,394 | 0.5928 |
| HDK (Dongkou, Hunan) | 3,932,356 | 1,236,055 | 1,451,795 | 562,065 | 2.58 | 1,159,165 | 854,695 | 0.5755 |
| HCN (Changning, Hunan) | 3,819,985 | 1,222,766 | 1,477,122 | 574,678 | 2.57 | 1,179,174 | 872,625 | 0.5746 |
| HSZ (Sangzhi, Hunan) | 3,083,571 | 983,796 | 1,351,905 | 522,997 | 2.58 | 1,027,765 | 847,137 | 0.5453 |
| HPJ (Pingjiang, Hunan) | 3,149,545 | 1,019,904 | 1,324,570 | 516,136 | 2.56 | 931,328 | 909,378 | 0.5036 |
| HYL (Yanling, Hunan) | 2,445,579 | 850,489 | 1,370,498 | 535,637 | 2.56 | 1,046,839 | 859,296 | 0.5485 |
| JWY (Wuyuan, Jiangxi) | 3,129,945 | 1,056,778 | 1,451,178 | 566,446 | 2.56 | 1,043,045 | 974,579 | 0.5157 |
| FCT (Changting, Fujian) | 3,581,645 | 1,144,872 | 1,448,578 | 563,974 | 2.56 | 1,123,022 | 889,529 | 0.5525 |
| FZR (Zherong, Fujian) | 5,183,429 | 1,750,582 | 1,501,902 | 719,470 | 2.21 | 908,988 | 1,312,384 | 0.4290 |
| FMQ (Minqing, Fujian) | 3,486,120 | 1,157,688 | 1,578,398 | 614,521 | 2.56 | 1,296,886 | 896,033 | 0.5890 |
| FJO (Jian’ou, Fujian) | 3,361,907 | 1,112,365 | 1,471,386 | 573,316 | 2.56 | 1,128,122 | 916,580 | 0.5518 |
| ZYZ (Yinzhou, Zhejiang) | 2,428,260 | 858,412 | 1,382,278 | 544,668 | 2.54 | 986,717 | 940,225 | 0.5115 |
| ZZS (Zhoushan, Zhejiang) | 3,229,541 | 1,053,082 | 1,416,464 | 550,877 | 2.57 | 1,088,961 | 878,380 | 0.5522 |
| ZNH (Ninghai, Zhejiang) | 3,732,811 | 1,179,976 | 1,421,104 | 540,260 | 2.63 | 1,075,951 | 885,413 | 0.5442 |
| ZJN (Jingning, Zhejiang) | 2,172,504 | 699,612 | 1,112,899 | 413,417 | 2.69 | 714,120 | 812,196 | 0.4684 |
| JGU (Gueok-ri, Jeju) | 3,876,609 | 1,232,391 | 1,518,845 | 590,571 | 2.57 | 1,218,079 | 891,338 | 0.5774 |
| MMY (Miyakonojo-shi, Miyazaki) | 3,852,953 | 1,223,121 | 1,477,301 | 572,304 | 2.58 | 1,146,487 | 903,117 | 0.5564 |
| MNB (Nobeoka-shi, Miyazaki) | 3,551,342 | 1,109,444 | 1,400,624 | 533,912 | 2.62 | 1,069,663 | 864,873 | 0.5527 |
| Total/Average | 15,377,234 | 4,405,966 | 1,440,422 | 533,912 | 2.56 | 1,097,305 | 906,786 | 0.5462 |
| Population | HO | HE | PIC | H | I | π × 10−3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLP | 0.2083 | 0.1876 | 0.15 | 0.2269 | 0.2787 | 0.863 |
| GJK | 0.2197 | 0.1807 | 0.1437 | 0.2182 | 0.2666 | 0.834 |
| GCS | 0.1867 | 0.165 | 0.131 | 0.1999 | 0.2431 | 0.735 |
| HXX | 0.2401 | 0.2199 | 0.1765 | 0.265 | 0.328 | 0.887 |
| HXS | 0.2322 | 0.1904 | 0.1516 | 0.2297 | 0.2815 | 0.964 |
| HDK | 0.216 | 0.2096 | 0.168 | 0.2534 | 0.3122 | 0.965 |
| HCN | 0.2192 | 0.2048 | 0.1639 | 0.2472 | 0.3045 | 0.727 |
| HSZ | 0.1965 | 0.1641 | 0.1301 | 0.1994 | 0.2413 | 0.727 |
| HPJ | 0.1793 | 0.1681 | 0.1337 | 0.2038 | 0.248 | 0.757 |
| HYL | 0.2077 | 0.1256 | 0.0968 | 0.1521 | 0.179 | 0.568 |
| JWY | 0.1975 | 0.1651 | 0.1307 | 0.1992 | 0.2425 | 0.762 |
| FCT | 0.2132 | 0.1945 | 0.1553 | 0.2354 | 0.2884 | 0.892 |
| FZR | 0.1913 | 0.1761 | 0.1389 | 0.2248 | 0.257 | 0.546 |
| FMQ | 0.2441 | 0.1897 | 0.1506 | 0.2285 | 0.2795 | 0.884 |
| FJO | 0.2126 | 0.1764 | 0.1409 | 0.2128 | 0.2618 | 0.815 |
| ZYZ | 0.1936 | 0.1156 | 0.089 | 0.1399 | 0.1646 | 0.522 |
| ZZS | 0.2113 | 0.1773 | 0.1408 | 0.2144 | 0.2612 | 0.812 |
| ZNH | 0.205 | 0.2021 | 0.1616 | 0.2449 | 0.3003 | 0.905 |
| ZJN | 0.1506 | 0.1207 | 0.0948 | 0.1609 | 0.175 | 0.549 |
| JGU | 0.2294 | 0.21 | 0.168 | 0.2532 | 0.3122 | 0.973 |
| MMY | 0.2161 | 0.2068 | 0.1655 | 0.25 | 0.3075 | 0.956 |
| MNB | 0.2079 | 0.1973 | 0.1576 | 0.2386 | 0.2928 | 0.891 |
| Total | 0.994 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Y.-G.; Wang, T.-R.; Lu, Z.-J.; Ge, B.-J.; Zhong, X.; Li, X.-C.; Jin, D.-M.; Yuan, Q.; Li, Y.; Kang, Y.-X.; et al. Population Survey Combined with Genomic-Wide Genetic Variation Unravels the Endangered Status of Quercus gilva. Diversity 2023, 15, 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020230
Song Y-G, Wang T-R, Lu Z-J, Ge B-J, Zhong X, Li X-C, Jin D-M, Yuan Q, Li Y, Kang Y-X, et al. Population Survey Combined with Genomic-Wide Genetic Variation Unravels the Endangered Status of Quercus gilva. Diversity. 2023; 15(2):230. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020230
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Yi-Gang, Tian-Rui Wang, Zi-Jia Lu, Bin-Jie Ge, Xin Zhong, Xiao-Chen Li, Dong-Mei Jin, Quan Yuan, Yu Li, Yi-Xin Kang, and et al. 2023. "Population Survey Combined with Genomic-Wide Genetic Variation Unravels the Endangered Status of Quercus gilva" Diversity 15, no. 2: 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020230
APA StyleSong, Y.-G., Wang, T.-R., Lu, Z.-J., Ge, B.-J., Zhong, X., Li, X.-C., Jin, D.-M., Yuan, Q., Li, Y., Kang, Y.-X., Ning, X., Zheng, S.-S., Yi, L.-T., Dai, X.-L., Cao, J.-G., Lee, J.-H., & Kozlowski, G. (2023). Population Survey Combined with Genomic-Wide Genetic Variation Unravels the Endangered Status of Quercus gilva. Diversity, 15(2), 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020230










