Abstract
Coccolithophores are an important component of phytoplankton abundance and biomass in the brackish environments of the Black Sea. Here, the abundance, composition, and distribution of coccolithophores were investigated in water samples taken from the first 50 m at 18 stations in the western Black Sea during a coccolithophore bloom, in June 2016. The total cell abundances ranged from 2 to 763 × 104 coccospheres L−1; Emiliania huxleyi was the most dominant species, but also Syracosphaera spp. (S. dilatata and S. molischii), Acanthoica (A. acanthifera and A. quattrospina), and Algirosphaera robusta displayed remarkably high concentrations. The formation of the seasonal thermocline significantly affects the vertical distribution of coccolithophores. Emiliania huxleyi, Syracosphaera spp., and Acanthoica spp. were restricted to the upper part of the water column, whereas high abundances of Algirosphaera robusta occurred below the thermocline. Overall, our results show significant differences in the vertical (ANOSIM R = 0.50, p = 0.0001) and spatial (ANOSIM R = 0.18, p = 0.0006) distribution of coccolithophores. Higher abundances of E. huxleyi and Syracosphaera spp. were recorded in the northwestern inner shelf region when compared to the open-sea samples. The observed coccolithophore spatial distribution is suggested to be mostly associated with the influx of less saline river water with high nutrient concentrations.
1. Introduction
Coccolithophores are small, single-celled phytoplankton less than 30 µm in diameter with an external skeleton (coccosphere) formed by multiple calcium carbonate plates called coccoliths. Two structurally different types of coccoliths are produced during the alteration of the haplodiplontic life cycle of coccolithophores: heterococcoliths formed by a radial array of complex crystal units, during the diploid stage (heterococcolithophore phase, HET), and holococcoliths formed of numerous minute euhedral crystallites during the haploid stage (holococcolithophore phase, HOL) [1].
Coccolithophores are widely distributed in the oceanic photic zone from polar to tropical waters. There are approximately 300 extant coccolithophore species [2] and some of these, such as Emiliania huxleyi, have the potential to produce large seasonal blooms in both oceanic and marginal environments [3,4,5]. These blooms cause an increase in complex biogeochemical activity [5,6]. In particular, coccolithophores contribute to the marine biological carbon pump by fixing large amounts of inorganic carbon through photosynthesis and consequently exporting and sequestering particulate organic carbon [7]. Furthermore, they contribute to the carbonate counter pump through the biocalcification of their coccoliths [8,9]. During this process, seawater alkalinity decreases, CO2 is released, and inorganic carbon is exported to the seafloor. Coccolithophores also affect the global sulfur cycle; they act as a source of dimethyl sulfide (DMS), a bioactive gas that enhances cloud formation in the atmosphere [10]. Because of their role in global biogeochemical cycles and their sensitivity to forthcoming climate change, coccolithophores have attracted much attention in recent decades [11,12,13].
As a marginal ecosystem, the Black Sea is very sensitive to environmental changes, in particular to changes caused by climatic factors and anthropogenic pressures [14,15], which can have significant impacts on the phytoplankton biomass and taxonomic structure [16,17]. Today, coccolithophores, mainly represented by Emiliania huxleyi, constitute a significant component of phytoplankton communities in the Black Sea (e.g., [18,19,20]). Over the past four decades, this species has shown an increasing trend in phytoplankton abundance and biomass [16,17] and is also responsible for intense summer and winter blooms, with cell concentrations of up to 10 × 106 cells L−1 common in coastal and deep waters [16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27]. The most extensive and regular E. huxleyi blooms occur from May to July, covering 45–75% of the Black Sea surface [23]. Particularly strong E. huxleyi blooms are related to colder winters with deep vertical mixing that increases nutrient availability in the surface layer [16,17,26,28]. In late winter, phytoplankton blooms occur as the seasonal thermocline starts to develop. Emiliania huxleyi blooms begin when inorganic nutrients are recycled in waters following diatom blooms and are linked with high summer irradiance conditions, high phosphate availability, and low nitrate-to-phosphate ratios [16,26,29].
Despite the significant role of living coccolithophores in Black Sea phytoplankton communities, detailed investigations of their species composition and cell abundances are limited. Available studies on the water column plankton assemblages (e.g., [22,30]) and the sinking material (e.g., [31,32]) have shown that E. huxleyi can be strongly dominant in terms of cell abundance, but some species of Syracosphaera, Acanthoica, Calciosolenia, and holococcolithophores are also present in the communities. Further studies on the distribution of these taxa will contribute to a better understanding of the ecology and diversity of living coccolithophores in the Black Sea. This study focused on the coccolithophore assemblages from the western Black Sea during the E. huxleyi bloom in June 2016. The main objectives are (1) to investigate the vertical ecology and distribution of coccolithophore communities and (2) to document differences in the coccolithophore communities between the continental shelf and open-sea environments.
2. Study Area
The Black Sea is a semi-enclosed basin with an area of 4.2 × 105 km2 and a volume of 5.3 × 105 km3 [33], connected to the eastern Mediterranean Sea through the narrow (0.76–3.60 km) and shallow (<93 m) Bosporus Strait, the Sea of Marmara, and the Dardanelles Strait (Figure 1A). According to the bathymetrical and morphological features, the central deep basin occupies more than 60% of the total area, with a maximum depth of around 2250 m and an average depth of 1240 m. At the periphery of the basin, the continental slope is steep, and the continental shelf is broad, up to 200 km wide in the northwest, narrow, and rarely more than 20 km wide along the rest of the basin. Numerous rivers flow into the Black Sea, particularly into the northwestern part of the basin, including some of the longest and largest European rivers (Danube, Dnieper, and Dniester).
Wind stress and thermohaline forcing drive the general cyclonic circulation of the Black Sea [34,35,36]. The surface circulation primarily consists of the quasi-permanent cyclonic jet “Rim current” surrounding the basin along the continental slope, multi-cell cyclonic circulation gyres in the interior of the eastern and western sub-basins, and several anticyclonic mesoscale eddies located between the Rim Current and the coastline (Figure 1B) [33,35,36].
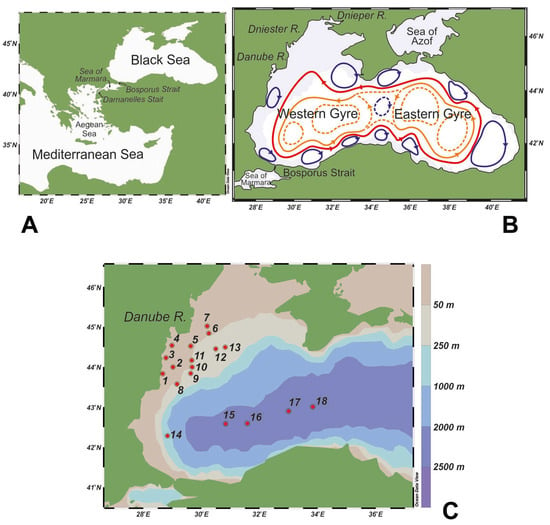
Figure 1.
(A) Location map of the study area; (B) main pattern of the upper layer circulation (based on data from Oguz et al. [35] and Korotaev et al. [36]); (C) locations of the sampled stations.
The Black Sea is one of the largest meromictic basins in the world. The large freshwater inputs from the rivers, the high rate of precipitation, and the limited water exchange with the Mediterranean Sea create a low salinity surface layer with values around 18 [37,38]. Therefore, the water column of the Black Sea exhibits strong density stratification, with fresher and lower-density surface waters overlying saltier and higher-density waters of Mediterranean origin [33,39]. The formation of a steep halocline/pycnocline separates the surface from deep waters between 50 and 100 m [38,40]. The permanent stratification prevents vertical mixing, causing continuing anoxia and high hydrogen sulfide concentrations below 100 m depth. In general, the upper well-oxygenated layer (O2 = 8.89 ± 1.19 mg/L) is followed by a suboxic zone (O2 < 2 mg/L) of about 50 m thick [41]. Below this suboxic zone, a sulfide layer extends to the seafloor. The sea surface temperature shows typical seasonal variation, ranging from 8 °C to 30 °C, while the deep-sea temperature is about 8.5 °C [37]. One of the most distinctive features of the thermohaline structure of the Black Sea is the cold intermediate layer (CIL). The water in this layer is characterized by temperatures below 8 °C and is formed by winter convection processes on the northwest shelf and in the center of the western gyre [33,35,42]. The CIL is usually found at depths between 30 and 100 m [43].
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Sample Collection and Analysis
Forty-eight samples were collected from eighteen stations, seven on the inner (<50 m depth), six on the outer (50–200 m depth) northwestern continental shelf, and five in the open sea (>200 m depth) of the western Black Sea (between 42°17′ to 45°02′ latitude N and 28°40′ to 33°50′ longitude E) by the R/V Akademik during the BIO-OPT-2016 EUROFLEETS expedition on 2–24 June 2016 (Figure 1C, Table S1). Seawater samples were taken at different depths (1 to 50 m) in the well-oxygenated upper water column using 5 L Niskin bottles attached to a rosette with a CTD (conductivity–temperature–depth) system. Water column temperature, salinity, density, and chlorophyll (chl-α) fluorescence were measured using the SBE 9/11plus CTD (Sea-Bird Electronics Inc., Bellevue, WA, USA).
For coccolithophore analysis, seawater subsamples (0.2–2 L in volume; Table S1) were filtered under low pressure (<200 mm Hg) onboard onto cellulose nitrate membrane filters (47 mm diameter, 0.45 μm pore size), dried, and stored in plastic Petri dishes. In the laboratory, a quarter of each filter was cut and mounted between the microscope slide and cover slip and made optically translucent with immersion oil. The filter was examined under a Leica DMLSP polarized light microscope (PLM) at 1250× magnification. Coccolithophore concentrations were estimated by counting a field area of 4–7 mm2 along the radial transects. The coccosphere abundance was calculated using the following equation of Bollmann et al. [44]:
where CD = coccosphere abundance (number of coccospheres L−1); N = total number of coccospheres counted; S = filtered area (mm2); A = analyzed area (mm2); and V = filtered seawater volume (l).
CD = N × S/(A × V),
Further species identification and documentation of small-size species in the coccolithophore assemblages was performed on selected samples via scanning electron microscopy (SEM). For the analysis, a small portion of the dried filter, approximately 8 × 8 mm2, was cut and attached to a copper electron microscope stub with double-sided adhesive tape, and then coated with Au. The samples were examined with a Jeol JSM 6360 SEM (National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Department of Geology and Geoenvironment) at a magnification of 2000× or 5000× as needed. All the individual coccospheres in the studied filter area were identified at the species level according to the taxonomic references of Young et al. [1], Cros and Fortuño [45], and the electronic guide to the biodiversity and taxonomy of coccolithophores Nannotax 3 [46].
The small and rare holococcolithophores were difficult to identify and enumerate using light microscopy. Their presence was documented via SEM, but their concentrations were not counted. Counting from SEM allows for a more accurate analysis of the total coccolithophore biodiversity and cell counts [44], but this technique could not be useful for studying the high abundances of the Black Sea, where the high concentrations of shed coccoliths and biogenic particles make individual coccospheres difficult to distinguish.
CTD measurements and coccolithophore abundances were plotted with Ocean Data View (ODV 5.6.7, https://odv.awi.de, accessed on 15 November 2023) software [47].
3.2. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using the PAST (PAleontological STatistics Version 4.14) software (Natural History Museum, University of Oslo, Norway) [48]. Before analysis, the coccolithophore abundances and environmental data were logarithmically transformed to reduce the magnitude difference between the variables. Non-metric multidimensional scaling (nMDS) based on Bray–Curtis dissimilarity was used to visualize the spatial and vertical distribution patterns in the coccolithophore community structure. A stress value of less than 0.2 indicates a reasonable ordination [49]. Significant differences among the coccolithophore assemblages in different sub-regions (inner, outer continental shelf, and open sea) and sampling depths were tested using the one-way analysis of similarity (ANOSIM, 9999 permutations). In addition, the simple nonparametric Spearman’s ρ correlation was carried out to determine possible relationships between the coccolithophore taxa and environmental variables (temperature, salinity, and chlorophyll fluorescence).
4. Results
4.1. Environmental Conditions (CTD Measurements)
In the surface layer (≤5 m depth), the temperature varied from 15.6 °C (St 1) to 23.8 °C (St 13) with an average value of 21.5 °C (Figure 2). The vertical profiles show a well-stratified water column with a shallow thermocline at ca. 10–25 m, increasing from the inner shelf towards the outer shelf and open sea. On the shelf, the sea surface salinity ranged from 12.76 (St 7) to 17.23 (St 1) with an average of 14.94, and 15.01 (St 10) to 18.86 (St 15) with an average of 17.79 in the deeper waters (>25 m depth) (Figure 2). In the open-sea area, the salinity was nearly constant (18.53–18.89) throughout the water column. In the shelf area, high concentrations of chl-α (>10 μg L−1) were found in the subsurface layer (<20 m depth), with peak values (>60 μg L−1) at 5–10 m depth in stations 6, 7, and 8 (Figure 2). Lower concentrations (1–7 μg L−1) were observed in the open sea, with maximum values at 40–50 m depth.
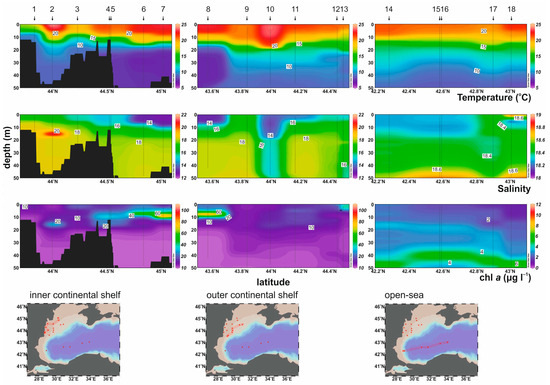
Figure 2.
Vertical profiles of physical parameters (temperature, salinity) and chl-a in the inner, the outer continental shelf, and the open sea of the study area.
4.2. Coccolithophore Abundance and Distribution
The total coccolithophore abundance varied from 2 × 104 coccospheres L−1 (St 6, 35 m depth) to 763 × 104 coccospheres L−1 (St 5, 15 m depth), with an average of 186 × 104 coccospheres L−1 (Table 1; Figure 3).

Table 1.
Coccolithophore species abundances at the investigated stations.
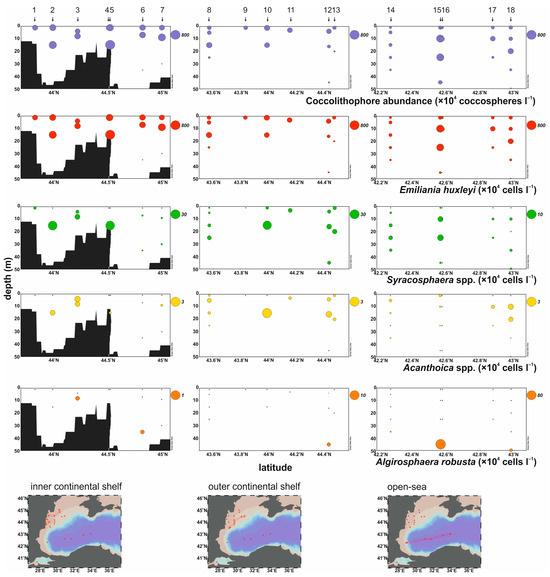
Figure 3.
Vertical profiles of total coccolithophores, Emiliania huxleyi, Syracosphaera, Acanthoica, and Algirosphaera robusta in the inner, the outer continental shelf, and the open sea of the study area.
The dominant species, E. huxleyi, constituted 31% to 100% (average = 92%) of the total assemblage, reaching a maximum abundance of 737 × 104 cells L−1 (St 5, 15 m depth). Higher values were observed across the inner shelf transect, with the maxima (>400 × 104 cells L−1) recorded in the upper 15 m of the water column (Table 1; Figure 3). In the outer shelf transect, E. huxleyi abundances were less than 200 × 104 cells L−1, except for stations 8 and 10 that peaked at 243 × 104 cells L−1 (15 m depth) and 272 × 104 cells L−1 (1 m depth), respectively. Also, a notable increase in the abundance of E. huxleyi (>200 × 104 cells L−1) was observed in the upper 25 m of the water column of the open-sea transect. Syracosphaera spp. contributed from 0% to 34% (average = 4%) of the total assemblage and reached a maximum abundance of 26 × 104 cells L−1 (St 2, 15 m depth). This taxon was more abundant in the upper 15 m of the water column of the inner shelf transect (Table 1; Figure 3). A peak value (23 × 104 cells L−1) was observed at 15 m depth at station 10 in the outer shelf transect, while in the open sea, the values did not exceed 104 cells L−1 except for stations 14 and 15 (max = 3 × 104 cells L−1, St 15, 10 m depth).
Acanthoica spp. were presented mostly in the surface layer (up to 30 m depth) in all three transects (Table 1; Figure 3), with maximum frequencies below 3% and abundances up to 3 × 104 cells L−1 (St 10, 15 m depth). Algirosphaera robusta represented 0% to 69% (average = 4%) of the total assemblage and reached a maximum abundance of 79 × 104 cells L−1 (St 15, 45 m depth). This species was rare in shallow waters and was mainly restricted to deeper layers below 30 m depth (Table 1; Figure 3).
4.3. Coccolithophore Taxonomy
According to the SEM observations, E. huxleyi type A (Figure 4A,B) was the only form of E. huxleyi found in all the examined samples. Syracosphaera spp. were identified as Syracosphaera dilatata (Figure 4C) and Syracosphaera molischii, while Acanthoica spp. as Acanthoica acanthifera and Acanthoica quattrospina (Figure 4D). The only documented representative of Algirosphaera was Algirosphaera robusta (Figure 4E). Although the holococcolithophore abundance was not counted in this study, two forms, Syracosphaera arethusae HOL and Helladosphaera cornifera (Figure 4F), were observed in the open-sea assemblages during the SEM analysis. It is interesting to notice that there were no differences in species composition between coccospheres and loose coccoliths. The loose coccoliths observed in the studied samples comprised mainly of E. huxleyi placoliths and, to a much lesser degree, S. dilatata caneoliths.
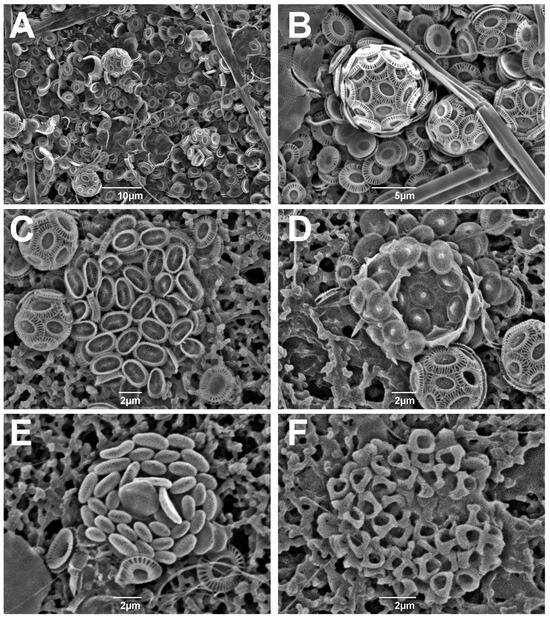
Figure 4.
SEM micrographs of selected coccolithophore specimens identified in the studied samples. (A) General sample view, station 8, 5 m; (B) Emiliania huxleyi, station 8, 5 m; (C) Syracosphaera dilatata, station 17, 25 m; (D) Acanthoica acanthifera, sample 15, 1 m; (E) Algirosphaera robusta, station 16, 45 m; (F) Helladosphaera cornifera, station 17, 25 m.
4.4. Statistical Analyses
The nMDS results based on the coccolithophore composition data are represented in Figure 5. The plot shows a degree of separation between the samples collected from the inner shelf, outer shelf, and open sea, respectively. A pattern of variation between the samples from the different sampling depths was also observed. ANOSIM analysis revealed that the significant dissimilarity in the composition and abundance of coccolithophore taxa throughout the water column (ANOSIM R = 0.50, p = 0.0001) was more important than the spatial difference between the sub-regions (ANOSIM R = 0.18, p = 0.0006).
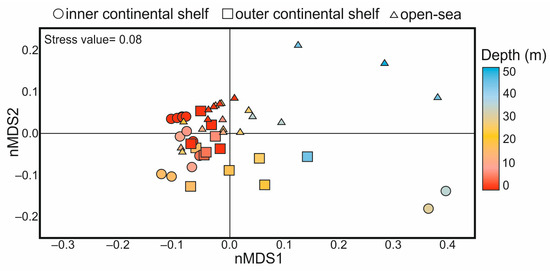
Figure 5.
Grouping of coccolithophore communities based on non-metric multidimensional scaling (nMDS), differentiated by water depth (color), and sub-regions (shape).
The Spearman correlation matrix between the coccolithophore taxa and environmental variables is presented in Table 2. Emiliania huxleyi showed strong positive correlations with the temperature and chl-α and negative correlations with the salinity. In contrast, A. robusta was positively correlated with the salinity, and negatively with the temperature. Acanthoica spp. and Syracosphaera spp. did not reveal any significant correlation with the environmental variables.

Table 2.
Matrix of Spearman’s rho correlation coefficients for coccolithophore taxa and environmental parameters.
5. Discussion
A shallow mixed layer with low salinity was observed during the sampling time, typical of summer stratification in the Black Sea. The water stratification has a significant impact on the distribution of coccolithophores, as the presence of the seasonal thermocline restricts their mixing depth, thus increasing their chance of remaining near the surface where high levels of irradiance and temperature occur. These favorable conditions for coccolithophore growth seem to prevail in the uppermost 20 m depth, within the thermocline, where they showed the highest concentrations, up to 763 × 104 coccospheres L−1. The trend in vertical distribution is consistent with previous studies of phytoplankton in the Black Sea [19,22,30], which have shown that the early summer coccolithophore bloom mainly develops in the upper mixed layer and then extends into the thermocline and sub-thermocline part. In general, the biomass of coccolithophores reaches the maximum at depths ranging from 5% to 25% of the surface Photosynthetically Available Radiation (PAR), regardless of the season [30]. It is worth noting that the bottom of the photic zone (~1% PAR) in the Black Sea increases from about 20 m in winter to 40 m in summer [30,50].
The significant amount of freshwater inflow from the Danube to the western shelf of the Black Sea is expected to have an impact on the coccolithophore assemblages. These inputs enhance pycnocline stratification due to salinity differences and increase nutrient supply, leading to an increase in phytoplankton biomass [51], as evidenced by the high chl-α levels in the studied area. The coccosphere abundance also showed a decrease from the inner shelf area (average of 375 × 104 coccospheres L−1), near the Danube river mouth, towards the outer shelf and open sea (average of 145 × 104 coccospheres L−1). These results are consistent with biogeochemical Argo data [25] and satellite observations [26] that detected a weak coccolithophore bloom (N = 1.5 × 106 cells L−1) in June 2016, in the central basin of the Black Sea, and moderate or extensive on the continental shelf mainly near the shore.
In general, the coccolithophore distribution and abundance patterns closely resembled those of E. huxleyi, which accounted for an average of 92% of the total assemblage. This species has a wide biogeographical distribution and exhibits high morphological, genetic, and physiological variability [52,53]. Environmental parameters such as temperature (e.g., [54]), light (e.g., [55]), salinity (e.g., [56,57,58]), nutrients (e.g., [59]), and carbonate chemistry (e.g., [11]) are known to influence the distribution of E. huxleyi eco-morphotypes. Emiliania huxleyi type A observed in this study is widespread, is the most common bloom-forming morphotype [53], and shows a significant variation in the degree of calcification (e.g., [32,45,60,61]). Based on the morphological observations, the E. huxleyi population in the Black Sea is characterized by lightly calcified delicate specimens that have been previously documented in sediment trap data from the study area [32,62]. Specimens of this form produce coccoliths with delicate and well-separated distal shield elements, a relatively narrow tube, and broad central area covered by lath-like elements [60]. Data from the Mediterranean Sea indicate that lightly calcified E. huxleyi type A dominates in the summer assemblages of the Aegean Sea associated with high temperature–low productivity conditions and lower bicarbonate content [60], but has also been found in the low salinity environments of the shallow environment of Thessaloniki bay [63], the upper photic zone of the northeastern Aegean Sea [62], and the Atlantic–Gibraltar Strait and southwestern Mediterranean region [61]. The E. huxleyi lightly calcified morphotype in the present study inhabited the salinity range of around 13 to 19, indicating good adaptation and growth in low salinity environments. Furthermore, the higher abundances (max. 737 × 104 cells L−1) in the inner shelf area near the Danube river mouth suggest the response of the certain morphotype to freshwater and nutrient inputs. This is also supported by the significant negative correlation with salinity (ρ = −0.43, p < 0.05). Additionally, the strong correlation observed between E. huxleyi and chl-α (ρ = 0.57, p < 0.01) indicates a direct relationship between this species and primary productivity. Despite being the most frequent and abundant coccolithophore species, E. huxleyi contributes less to the total biomass compared to other phytoplankton (e.g., diatoms and dinoflagellates) in oligotrophic regions, as its cells are relatively small (~5 µm) [5] and contain a low amount of chlorophyll a (~0.3 pg Chl cell−1; [64]). However, studies have shown that the blooms of coccolithophores in the Black Sea produce high shares of phytoplankton biomass, often exceeding that of diatoms or dinoflagellates, depending on seasons (see e.g., [27]).
In addition to E. huxleyi, seven species contributed in the coccolithophore assemblages of the western Black Sea: five species belonging to the genera Syracosphaera, Acanthoica, Algirosphaera, and two holococcolithophore forms. Among them, Syracosphaera is the most abundant taxon, followed by Acanthoica in the upper 20 m of the water column, while A. robusta seems to prefer the lower water layers, below 30 m depth.
Syracosphaera is the most diverse genus in the extant coccolithophore assemblages [46], including species with different ecological tolerances (e.g., [65,66,67,68]). In this study, Syracosphaera was represented by S. dilatata and S. molischii. Syracosphaera dilatata has also been documented in the coccolithophore fluxes of the western Black Sea during the warm period (May–September) [32]. Both species along with E. huxleyi exhibit a preference for the high nutrient concentrations of the cold period in Mediterranean environments [67,68,69]. Syracosphaera spp. were mostly found in shelf assemblages in Danube-influenced waters, with particularly high concentrations of up to 26 × 104 cells L−1. These values are close to the summer concentrations of Coronosphaera mediterranea (syn. Syracosphaera mediterranea) (max = 0.13 × 106 cells L−1) observed by Mikaelyan et al. [22] in the northeastern Black Sea. Despite that Syracosphaera generally represents a typical portion of the mesotrophic to oligotrophic coccolithophore assemblages (e.g., [32,66,67,68,69,70,71,72]), the extremely high concentrations exceeding 105 cells L−1, recorded in the Black Sea, have also been reported in coastal waters (Southern Benguela Upwelling System: [73]; Bay of Biscay: [74]; Krka estuary of the Eastern Adriatic Sea: [75]).
Acanthoica spp. (A. acanthifera and A. quattrospina) were uniformly distributed in both shelf and open-sea assemblages, with somewhat higher values at station 10, where the lowest salinity was observed. Acanthoica acanthifera is known to occur sporadically with low concentrations in living assemblages [76], while A. quattrospina is more commonly found in marine waters [77] as well as estuarine environments [78], indicating that it can adapt to a wide salinity range. The latter has already been described in phytoplankton assemblages of the Black Sea and is considered a cold-water dweller with the maximum biomass found in the upper mixed layer during the winter period [30].
Algirosphaera robusta, a common component of the Mediterranean coccolithophore assemblages [32,66,67,68,69,70,72,77], is reported in the Black Sea for the first time, in the present study. This species is considered a deep-water taxon [65], it prefers relatively low light and temperature conditions, and responds well to eutrophic conditions [76]. Although it has been documented to be seasonally important in oligotrophic settings, mainly restricted to the low SST and high productivity season [66], it was also found in shallower depths [67,70,79], showing an affinity for near-coastal settings. Interestingly, in the open-sea domain of the Black Sea, A. robusta showed an increase in absolute and relative abundances below the thermocline, opposite to the significant decrease in the total coccolithophore abundance. The highest concentrations of this species coincided with the deep chlorophyll maximum, which was located below 40 m depth during the sampling period, highlighting the species’ ability to thrive in low light and temperature conditions.
Holococcolithophores were not included in the counting results, but their presence in the open-sea assemblages was documented via SEM. Some holococcolithophore forms have previously been observed in living assemblages [22] and sinking particles [31] in the Black Sea. This group is a significant component of the Mediterranean coccolithophore assemblages and usually displays the highest species diversity and abundance in warm, oligotrophic, and stratified conditions [62,65,66,67,68,69,70,77,78,80,81,82]. Two forms, S. arethusae HOL and H. cornifera, were identified in this study, suggesting their ability to adapt to the low salinity conditions of the Black Sea.
Overall, the vertical and spatial distribution of the coccolithophore assemblages showed significant differences, which were also confirmed by the nMDS plot. The vertical distribution appears to be related to the formation of the seasonal thermocline. Emiliania huxleyi along with a low number of Syracosphaera and Acanthoica species were more abundant in the upper water layers within the thermocline. In contrast, A. robusta had higher abundances in the deeper water layers below the thermocline. Although the coccolithophore species composition did not reveal spatial differences between the shelf and open-sea assemblages, there were clear variations in the total coccosphere abundances. The highest concentrations, mainly consisting of E. huxleyi and Syracosphaera, were recorded in the inner shelf area near the Danube river mouth, associated with the response of these taxa to freshwater and nutrient inputs. Nevertheless, the ANOSIM results demonstrated that the vertical variation (ANOSIM R = 0.50, p = 0.0001) is more significant than the spatial variation (ANOSIM R = 0.18, p = 0.0006), suggesting that the formation of the seasonal thermocline has a greater impact on the coccolithophore distribution compared to the influence of freshwater input.
The coccolithophore assemblages in the western Black Sea consisted of only eight species that exhibited significantly high abundances. Similar low diversity assemblages have been recorded in restricted coastal environments in the Eastern Mediterranean (Thermaikos Gulf [63] and Elefsis–Saronikos Gulf [68]). The recorded differences in the species composition between these assemblages could be attributed to variations in the temperature and salinity, which have been documented to influence the taxonomic composition of phytoplankton between the Black Sea and Mediterranean coastal ecosystems [83]. Further research on the seasonal distribution of coccolithophores as well as their relationship with different physical and chemical parameters will provide a comprehensive picture of species diversity in the Black Sea.
6. Conclusions
The spatial and vertical variations of living coccolithophores were analyzed from 48 samples taken from the oxygen-rich surface waters (<50 m depth) at 18 stations in the northwestern continental shelf and from the open sea of the western Black Sea during a coccolithophore bloom in June 2016. The results of this study can be summarized as follows:
- Living coccolithophores showed high abundances, reaching a maximum of 763 × 104 coccospheres L−1 with the lightly calcified morphotype of E. huxleyi type A being the dominant species accounting for an average of 92%, confirming its typical dominance in summer coccolithophore assemblages of the Black Sea;
- Apart from E. huxleyi, and the other heterococcolithophores S. dilatata, S. molischii, A. acanthifera, and A. quattrospina, Algirosphaera robusta, and two holococcolithophore forms S. arethusae HOL and H. cornifera, contributed to the coccolithophore assemblages, indicating their ability to thrive in the low salinity conditions of the Black Sea;
- The vertical distribution of coccolithophore species appears to depend on the temperature and irradiance levels. Emiliania huxleyi, Syracosphaera spp., and Acanthoica spp. were mainly distributed in the upper water layers, within the thermocline. High abundances of A. robusta occurred below the thermocline, indicating its preference for low light and temperature conditions;
- The highest abundances of E. huxleyi (max. 737 × 104 cells L−1) and Syracosphaera (max. 26 × 104 cells L−1) were found over the northwestern inner shelf region in Danube-influenced waters, associated with increased freshwater and nutrient inputs;
- Our results indicate that the seasonal thermocline is the main factor regulating the distribution of living coccolithophores, whereas significant spatial variations in the assemblages are related to the influence of freshwater input.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/d15121194/s1, Table S1: location data, environmental parameters measured, and filtered seawater volume for coccolithophores at the investigated stations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.D.D., M.V.T., A.R., E.M., B.T.K., S.P. and A.P.K.; methodology, M.D.D., M.V.T., A.R., E.M., B.T.K., S.P. and A.P.K.; investigation, M.D.D., M.V.T., A.R., E.M., B.T.K., S.P. and A.P.K.; data curation, M.D.D., M.V.T., S.P. and A.P.K.; writing—original draft preparation M.D.D., M.V.T. and A.R.; writing—review and editing, E.M., B.T.K., S.P. and A.P.K.; visualization, M.D.D. and M.V.T.; project administration, M.V.T., S.P. and A.P.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in Table 1 and the Supplementary Material of this article.
Acknowledgments
The material studied for coccolithophore analysis was provided during the BIO-OPT-2016 EUROFLEETS cruise, onboard the R/V Akademik.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Young, J.R.; Geisen, M.; Cros, L.; Kleijne, A.; Sprengel, C.; Probert, I.; Østergaard, J. A guide to extant coccolithophore taxonomy. J. Nannoplankton Res. 2003, 1, 1–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, R.W.; Chamberlain, A.H.L. Biodiversity among haptophyte algae. Biodivers. Conserv. 1997, 6, 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.W.; Yoder, J.A. Coccolithophorid blooms in the global ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean 1994, 99, 7467–7482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-Rodriguez, M.D.; Garcia Saez, A.; Groben, R.; Edwards, K.J.; Batley, J.; Medlin, L.K.; Hayes, P.K. Polymorphic microsatellite loci in global populations of the marine coccolithophorid Emiliania huxleyi. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2002, 2, 495–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrrell, T.; Merico, A. Emiliania huxleyi: Bloom observations and the conditions that induce them. In Coccolithophores; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 75–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holligan, P.M.; Fernandéz, E.; Aiken, J.; Balch, W.M.; Boyd, P.; Burkill, P.H.; Finc, M.; Groom, S.B.; Malin, G.; Müller, K.; et al. A biogeohemical study of the coccolithophore, Emiliania huxleyi, in the North Atlantic. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1993, 7, 879–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulton, A.J.; Adey, T.R.; Balch, W.M.; Holligan, P.M. Relating coccolithophore calcification rates to phytoplankton community dynamics: Regional differences and implications for carbon export. Deep-Sea Res. II 2007, 54, 538–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zondervan, I.; Zeebe, R.E.; Rost, B.; Riebesell, U. Decreasing marine biogenic calcification: A negative feedback on rising atmospheric pCO2. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2001, 15, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rost, B.; Riebesell, U. Coccolithophores and the biological pump: Responses to environmental changes. In Coccolithophores: From Molecular Processes to Global Impact; Thierstein, H.R., Young, J.R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 99–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.R.; Brownlee, C.; Wheeler, G. Coccolithophore cell biology: Chalking up progress. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2017, 9, 283–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riebesell, U.; Zondervan, I.; Rost, B.; Tortell, P.D.; Zeebe, R.E.; Morel, F.M.M. Reduced calcification of marine plankton in response to increased atmospheric CO2. Nature 2000, 407, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doney, S.C.; Fabry, V.J.; Feely, R.A.; Kleypas, J. Ocean acidification: The other CO2 problem. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2009, 1, 169–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, L.T.; Riebesell, U.; Gutowska, M.A.; Federwisch, L.; Schulz, K.G. A unifying concept of coccolithophore sensitivity to changing carbonate chemistry embedded in an ecological framework. Prog. Oceanogr. 2015, 135, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, T. Long-term impacts of anthropogenic forcing on the Black Sea ecosystem. Oceanography 2005, 18, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, T.; Dippner, J.W.; Kaymaz, Z. Climatic regulation of the Black Sea hydro-meteorological and ecological properties at interannual-to-decadal time scales. J. Mar. Syst. 2006, 60, 235–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikaelyan, A.S.; Silkin, V.A.; Pautova, L.A. Coccolithophorids in the Black Sea: Their interannual and long-term changes. Oceanology 2011, 51, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikaelyan, A.S.; Pautova, L.A.; Chasovnikov, V.K.; Mosharov, S.A.; Silkin, V.A. Alternation of diatoms and coccolithophores in the north-eastern Black Sea: A response to nutrient changes. Hydrobiologia 2015, 755, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eker-Develi, E.; Kideys, A.E. Distribution of phytoplankton in the southern Black Sea in summer 1996, spring and autumn 1998. J. Mar. Syst. 2003, 39, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pautova, L.A.; Mikaelyan, A.S.; Silkin, V.A. Structure of plankton phytocenoses in the shelf waters of the Northeastern Black Sea during the Emiliania huxleyi bloom in 2002–2005. Oceanology 2007, 47, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eker-Develi, E.; Konucu, M.; Psarra, S.; Slabakova, N.; Triantaphyllou, M.; Dimiza, M.; Karageorgis, A.P.; Uysal, Z.; Berthon, J.-F. Phytoplankton and pigment composition during an Emiliania huxleyi bloom in the Black Sea. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 65, 103070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cokacar, T.; Oguz, T.; Kubilay, N. Satellite-detected early summer coccolithophore blooms and their interannual variability in the Black Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part 1 Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2004, 51, 1017–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikaelyan, A.S.; Pautova, L.A.; Pogosyan, S.I.; Sukhanova, I.N. Summer bloom of coccolithophorids in the northeastern Black Sea. Oceanology 2005, 45 (Suppl. 1), S127–S138. [Google Scholar]
- Oguz, T.; Merico, A. Factors controlling the summer Emiliania huxleyi bloom in the Black Sea: A modeling study. J. Mar. Syst. 2006, 59, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasakova, O.N.; Okolodkov, Y.B.; Chasovnikov, V.K. Increasing contribution of coccolithophorids to the phytoplankton in the northeastern Black Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubryakov, A.A.; Mikaelyan, A.S.; Stanichny, S.V. Summer and winter coccolithophore blooms in the Black Sea and their impact on production of dissolved organic matter from Bio-Argo data. J. Mar. Syst. 2019, 199, 103220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubryakov, A.A.; Mikaelyan, A.S.; Stanichny, S.V. Extremely strong coccolithophore blooms in the Black Sea: The decisive role of winter vertical entrainment of deep water. Deep Sea Res. Part 1 Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2021, 173, 103554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silkin, V.; Mikaelyan, A.S.; Pautova, L.; Fedorov, A. Annual Dynamics of Phytoplankton in the Black Sea in Relation to Wind Exposure. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vostokov, S.V.; Vostokova, A.S.; Vazyulya, S.V. Seasonal and Long-Term Variability of Coccolithophores in the Black Sea According to Remote Sensing Data and the Results of Field Investigations. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikaelyan, A.S.; Kubryakov, A.A.; Silkin, V.A.; Pautova, L.A.; Chasovnikov, V.K. Regional climate and patterns of phytoplankton annual succession in the open waters of the Black Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part 1 Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2018, 142, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikaelyan, A.S.; Pautova, L.A.; Fedorov, A.V. Seasonal evolution of deep phytoplankton assemblages in the Black Sea. J. Sea Res. 2021, 178, 102125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osawa, M.; Takahashi, K.; Hay, B.J. Shell-bearing plankton fluxes in the central Black sea, 1989–1991. Deep Sea Res. Part 1 Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2005, 52, 1677–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skampa, E.; Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Dimiza, M.D.; Gogou, A.; Malinverno, E.; Stavrakakis, S.; Parinos, C.; Panagiotopoulos, I.P.; Tselenti, D.; Archontikis, O.; et al. Coccolithophore export in three deep sea sites of the Aegean and Ionian Seas (Eastern Mediterranean): Biogeographical patterns and biogenic carbonate fluxes. Deep-Sea Res. II 2020, 171, 104690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özsoy, E.; Ünlüata, Ü. Oceanography of the Black Sea: A review of some recent results. Earth-Sci. Rev. 1997, 42, 231–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanev, E.V. On the mechanisms of the Black-Sea circulation. Earth-Sci. Rev. 1990, 28, 285–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, T.; Latun, V.S.; Latif, M.A.; Vladimirov, V.V.; Sur, H.I.; Markov, A.A.; Özsoy, E.; Kotovshchikov, B.B.; Eremeev, V.V.; Ünlüata, Ü. Circulation in the surface and intermediate layers of the Black-Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part 1 Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1993, 40, 1597–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotaev, G.; Oguz, T.; Nikiforov, A.; Koblinsky, C. Seasonal, interannual, and mesoscale variability of the Black Sea upper layer circulation derived from altimeter data. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean 2003, 108, 3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barale, V. The European Marginal and Enclosed Seas: An Overview. In Remote Sensing of the European Seas; Barale, V., Gade, M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talley, L.D.; Pickard, G.L.; Emery, W.L.; Swift, J.H. Gravity waves, tides, and coastal oceanography. Chapter 8. In Descriptive Physical Oceanography, 6th ed.; Swift, J.H., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, K.; Kassakian, S.; Krynytzky, M.; DiJulio, D.; Murray, J.W. Oxic, suboxic, and anoxic conditions in the Black Sea. In The Black Sea Flood Question: Changes in Coastline, Climate, and Human Settlement; Yanko-Hombach, V., Gilbert, A.S., Panin, N., Dolukhanov, P.M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.; Jannasch, H.; Honjo, S.; Anderson, R.F.; Reeburgh, W.S.; Top, Z.; Friederich, G.E.; Codispoti, L.A.; Izdar, E. Unexpected changes in the oxic/anoxic interface in the Black Sea. Nature 1989, 338, 411–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchsman, C.A.; Staley, J.T.; Oakley, B.B.; Kirkpatrick, J.B.; Murray, J.W. Free-living and aggregate-associated Planctomycetes in the Black Sea. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 80, 402–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miladinova, S.; Stips, A.; Garcia-Gorriz, E.; Macias Moy, D. Formation and changes of the Black Sea cold intermediate layer. Prog. Oceanogr. 2018, 167, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.W.; Top, Z.; Ozsoy, E. Hydrographic properties and ventilation of the Black Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part 1 Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1991, 38, S663–S689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollmann, J.; Cortés, M.Y.; Haidar, A.T.; Brabec, B.; Close, A.; Hofmann, R.; Palma, S.; Tupas, L.; Thierstein, H.R. Techniques for quantitative analyses of calcareous marine phytoplankton. Mar. Micropaleontol. 2002, 44, 163–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cros, L.; Fortuño, J.M. Atlas of Northwestern Mediterranean Coccolithophores. Sci. Mar. 2002, 66, 1–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.R.; Bown, P.R.; Lees, J.A. Nannotax3 Website. International Nannoplankton Association. 2022. Available online: http://www.mikrotax.org/Nannotax3 (accessed on 21 April 2022).
- Schlitzer, R. Ocean Data View. 2023. Available online: https://odv.awi.de (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological Statistics Software Package for Education and Data Analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, K.R. Non-parametric multivariate analysis of changes in community structure. Aust. J. Ecol. 1993, 18, 117–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedernikov, V.I.; Demidov, A.B. Vertical distribution of primary production and chlorophyll during different seasons in deep regions of the Black Sea. Oceanology 1997, 37, 376–384. [Google Scholar]
- Yunev, O.; Carstensen, J.; Stelmakh, L.; Belokopytov, V.; Suslin, V. Temporal changes of phytoplankton biomass in the western Black Sea shelf waters: Evaluation by satellite data (1998–2018). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 271, 107865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paasche, E. A review of the coccolithophorid Emiliania huxleyi (Prymnesiophyceae), with particular reference to growth, coccolith formation, and calcification-photosynthesis interactions. Phycologia 2002, 40, 503–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, S.S.; Whittock, L.; Wright, S.W.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Photosynthetic pigment and genetic differences between two Southern Ocean morphotypes of Emiliania huxleyi (Haptophyta). J. Phycol. 2011, 47, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas-Navarro, A.; Langer, G.; Ziveri, P. Temperature affects the morphology and calcification of Emiliania huxleyi strains. Biogeosciences 2016, 13, 2913–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balch, W.M.; Kilpatric, K.A.; Trees, C.C. The 1991 coccolithophore bloom in the central North Atlantic. 1. Optical properties and factors affecting their distribution. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1996, 41, 1669–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paasche, E.; Brubak, S.; Skatiebpl, S.; Young, J.R.; Green, J.C. Growth and calcification in the coccolithophorid Emiliania huxleyi (Haptophyceae) at low salinities. Phycologia 1996, 35, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollmann, J.; Herrle, H.O. Morphological variation of Emiliania huxleyi and sea surface salinity. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2007, 255, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebühr, C.; Sheward, R.M.; Herrle, J.O.; Bollmann, J. Strain-specific morphological response of the dominant calcifying phytoplankton species Emiliania huxleyi to salinity change. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paasche, E. Roles of nitrogen and phosphorus in coccolith formation in Emiliania huxleyi (Prymnesiophyceae). Eur. J. Phycol. 1998, 33, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantaphyllou, M.; Dimiza, M.; Krasakopoulou, E.; Malinverno, E.; Lianou, V.; Souvermezoglou, E. Seasonal variation in Emiliania huxleyi coccolith morphology and calcification in the Aegean Sea (Eastern Mediterranean). Geobios 2010, 43, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amario, B.; Ziveri, P.; Grelaud, M.; Oviedo, A. Emiliania huxleyi coccolith calcite mass modulation by morphological changes and ecology in the Mediterranean Sea. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karatsolis, B.-T.; Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Dimiza, M.D.; Malinverno, E.; Lagaria, A.; Mara, P.; Archontikis, O.; Psarra, S. Coccolithophore assemblage response to Black Sea water inflow into the north Aegean Sea (NE Mediterranean). Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 149, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimiza, M.D.; Koukousioura, O.; Michailidis, I.; Dimou, V.-G.; Navrozidou, V.; Aligizaki, K.; Seferlis, M. Seasonal living coccolithophore distribution in the enclosed coastal environments of the Thessaloniki Bay (Thermaikos Gulf, NW Aegean Sea). Rev. Micropaleontol. 2020, 69, 100449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, C.J.; Sheward, R.M.; Poulton, A.J. Biogeochemical implications of comparative growth rates of Emiliania huxleyi and Coccolithus species. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 6915–6925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andruleit, H.; Rogalla, U. Coccolithophores in surface sediment of Arabian Sea in relation to environmental gradients in surface waters. Mar. Geol. 2002, 186, 505–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Ziveri, P.; Tselepides, A. Coccolithophore export production and response to seasonal surface water variability in the oligotrophic Cretan Sea (NE Mediterranean). Micropaleontology 2004, 50 (Suppl. 1), 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimiza, M.D.; Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Dermitzakis, M.D. Seasonality and ecology of living coccolithophores in Eastern Mediterranean coastal environments (Andros Island, Middle Aegean Sea). Micropaleontology 2008, 54, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimiza, M.D.; Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Malinverno, E.; Psarra, E.; Karatsolis, B.-T.; Mara, P.; Lagaria, A.; Gogou, A. The composition and distribution of living coccolithophores in the Aegean Sea (NE Mediterranean). Micropaleontology 2015, 61, 521–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cros, L. Planktonic Coccolithophores of the NW Mediterranean. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitat de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain, 2001; 181p. [Google Scholar]
- Malinverno, E.; Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Stavrakakis, S.; Ziveri, P.; Lykousis, V. Seasonal and spatial variability of coccolithophore export production at the southwestern margin of Crete (eastern Mediterranean). Mar. Micropaleontol. 2009, 71, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviedo, A.; Ziveri, P.; Álvarez, M.; Tanhua, T. Is coccolithophore distribution in the Mediterranean Sea related to seawater carbonate chemistry? Ocean Sci. 2015, 11, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skejić, S.; Arapov, J.; Kovačević, V.; Bužancić, M.; Bensi, M.; Giani, M.; Bakrač, A.; Mihanović, H.; Ninčević Gladan, Ž.; Urbini, L.; et al. Coccolithophore diversity in open waters of the middle Adriatic Sea in pre- and post-winter periods. Mar. Micropaleontol. 2018, 143, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeks, S.J.; Pitcher, G.C.; Bernard, S. Satellite monitoring of the evolution of a coccolithophorid bloom in the Southern Benguela upwelling system. Oceanography 2003, 17, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, C.J.; Tyrrell, T.; Poulton, A.J.; Young, J.R. A mixed life-cycle stage bloom of Syracosphaera bannockii (Borsetti and Cati, 1976) Cros et al. 2000 (Bay of Biscay, April 2010). J. Nannoplankton Res. 2014, 34, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skejić, S.; Arapov, J.; Bužancić, M.; Ninčević-Gladan, Ž.; Bakrač, A.; Straka, M.; Mandić, J. First evidence of an intensive bloom of the coccolithophore Syracosphaera halldalii in a highly variable estuarine environment (Krka River, Adriatic sea). Mar. Ecol. 2021, 42, e12641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleijne, A. Morphology, Taxonomy and Distribution of Extant Coccolithophorids (Calcareous Nannoplankton). Ph.D. Thesis, Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, Enschede, The Netherlands, 1993; 321p. [Google Scholar]
- Cerino, F.; Malinverno, E.; Fornasaro, D.; Kralj, M.; Cabrini, M. Coccolithophore diversity and dynamics at a coastal site in the Gulf of Trieste (northern Adriatic Sea). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 196, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šupraha, L.; Ljubešić, Z.; Mihanović, H.; Henderiks, J. Coccolithophore life-cycle dynamics in a coastal Mediterranean ecosystem: Seasonality and species-specific patterns. J. Plankton Res. 2016, 38, 1178–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, R.W.; Winter, A. Assemblages of coccolithophorids and other living microplankton off the coast of Puerto Rico during January–May 1995. Mar. Micropaleontol. 2000, 39, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amario, B.; Ziveri, P.; Grelaud, M.; Oviedo, A.; Kralj, M. Coccolithophore haploid and diploid distribution patterns in the Mediterranean Sea: Can a haplo-diploid life cycle be advantageous under climate change? J. Plankton Res. 2017, 39, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godrijan, J.; Young, J.R.; Marić Pfannkuchen, D.; Precali, R.; Pfannkuchen, M. Coastal zones as important habitats of coccolithophores: A study of species diversity, succession, and life-cycle phases. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2018, 63, 1692–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keuter, S.; Silverman, J.; Krom, M.D.; Sisma-Ventura, G.; Yu, J.; Tsemel, A.; Ben-Ezra, T.; Sher, D.; Reich, T.; Koplovitz, G.; et al. Seasonal patterns of coccolithophores in the ultra-oligotrophic South-East Levantine Basin, Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Micropaleontol. 2022, 175, 102153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncheva, S.; Gotsis-Skretas, O.; Pagou, K.; Krastev, A. Phytoplankton Blooms in Black Sea and Mediterranean Coastal Ecosystems Subjected to Anthropogenic Eutrophication: Similarities and Differences. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2001, 53, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).