Genetic Diversity and Structure of Quercus petraea (Matt.) Liebl. Populations in Central and Northern Romania Revealed by SRAP Markers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
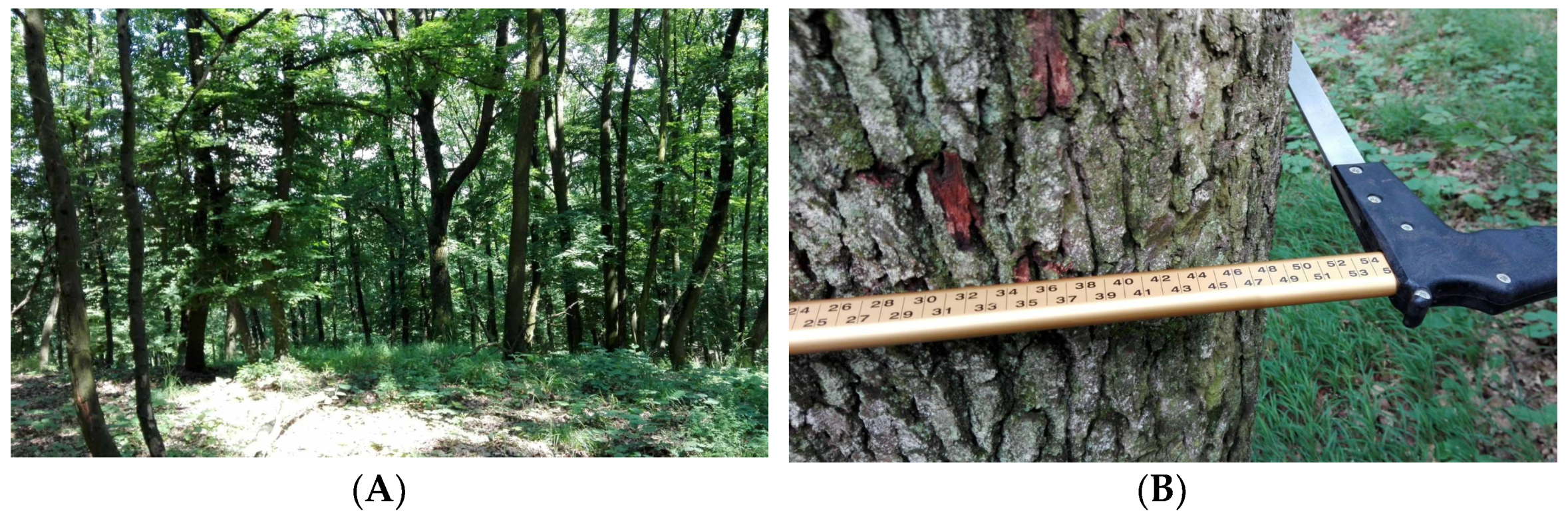
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Molecular Analyses
2.3. Data Interpretation and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kremer, A.; Casasoli, M.; Barreneche, T.; Bodénès, C.; Sisco, P.; Kubisiak, T.; Scalfi, M.; Leonardi, S.; Bakker, E.; Buiteveld, J.; et al. Fagaceae Trees. In Genome Mapping and Molecular Breeding in Plants; Kole, C., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 7, pp. 161–187. [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod, D.I. Biogeography of oaks in the Arcto-Tertiary province. Ann. Missouri Bot. Gard. 1983, 70, 629–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, K.C. Infrageneric classification of Quercus (Fagaceae) and typification of sectional names. Ann. For. Sci. 1993, 50, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crăciunesc, I.I. Evaluation of Natural Hybridization in Native Species of Oaks: A Case Study in Bejan-Deva Natural Reserve. Ph.D. Thesis, Transilvania University of Braşov, Brașov, Romania, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Georgescu, C.C.; Moraru, I. Monograph of Romanian Oaks; Univers Publisher: Bucharest, Romania, 1948; p. 36. [Google Scholar]
- Săvulescu, T. Flora of the Romanian People’s Republic; Publisher House of the Academy of the Romanian People’s Bucharestc: Bucharest, Romania, 1952; Volume I, pp. 224–256. [Google Scholar]
- Stănescu, V.; Şofletea, N.; Popescu, O. Romania’s Woody Forest Flora; Publisher Ceres: Bucharest, Romania, 1997; Volume 1, p. 451. [Google Scholar]
- Şofletea, N.; Curtu, L. Dendrologia; Publisher of Transylvania University: Brașov, Romania, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmit, J. Intraspecific variation of growth and adaptive traits in European oak species. Ann. Sci. Forest. 1993, 50, 166–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, R.J.; Bodénès, C.; Ducousso, A.; Roussel, G.; Kremer, A. Hybridization as amechanism of invasion in oaks. New Phytol. 2004, 161, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neophytou, C.; Aravanopoulos, F.A.; Fink, S.; Dounavi, A. Detecting interspecific and geographic differentiation patterns in two interfer- tile oak species (Quercus petraea (Matt.) Liebl. and Q. robur L.) using small sets of microsatellite markers. For. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 259, 2026–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, F.M.; Blank, R.; Hartmann, G. Abiotic and biotic factors and their interactions as causes of oak decline in Central Europe. For. Pathol. 2002, 32, 277–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrichs, D.A.; Buntgen, U.; Frank, D.C.; Esper, J.; Neuwirth, B.; Loffler, J. Complex climate controls on 20th century oak growth in Central-West Germany. Tree Phys. 2009, 29, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Härdtlea, W.; Niemeyera, T.; Fichtnerb, A.; Ying, L.; Riesc, C.; Schuldta, A.; Walmsleya, D.; von Oheimb, G. Climate imprints on tree-ring δ15N signatures of sessile oak (Quercus petraea Liebl.) on soils with contrasting water availability. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 45, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petritan, A.M.; Biris, I.A.; Merce, O.; Turcu, D.O.; Petritan, I.C. Structure and diversity of a natural temperate sessile oak (Quercus petraea L.)—European Beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2012, 280, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohner, B.; Bigler, C.; Wunder, J.; Brang, P.; Bugmann, H. Fifty years of natural succession in Swiss forest reserves: Changes in stand structure and mortality rates of oak and beech. J. Veg. Sci. 2012, 23, 892–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petritan, I.C.; Marzanoc, R.; Petritan, A.M.; Lingua, E. Overstory succession in a mixed Quercus petraea–Fagus sylvatica old growth forest revealed through the spatial pattern of competition and mortality. For. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 326, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badea, O.; Silaghi, D.; Taut, I.; Neagu, Ș.; Leca, S. Forest monitoring—Assessment, analysis and warning system for forest ecosystem status. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. 2013, 41, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Șimonca, V.; Tăut, I. Oaks decline in the north and west of Transylvania. ProEnvironment 2010, 3, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Şimonca, V.; Blaga, T.; Colişar, A.; Moldovan, C.; Petrişor, R.; Tăut, I. Comparative determination between healthy and decline oak stands regarding growth losses. Curr. Trends Nat. Sci. 2018, 8, 211–217. [Google Scholar]
- Şimonca, V.; Oroian, I.; Chira, D.; Tăut, I. Methods for quantification of the decline phenomenon and determination of the vulnerability degree for the oak stands in northwestern Transylvania, Romania. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobo. 2017, 45, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomescu, R.; Tăut, I.; Şimonca, V.; Covrig, I. Forecasting defoliators found in Transylvanian oak forests. ABAH Bioflux 2014, 6, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Tăut, I. Detection and prognosis of defoliators in northwestern transylvania hardwoods in 2016. ProEnvironment 2015, 8, 566–569. [Google Scholar]
- Tăut, I.; Şimonca, V.; Moldovan, C.; Blaga, T. Quantifying the drying phenomenon of oaks by highlighting the defoliation of stands. ProEnvironment 2015, 8, 577–582. [Google Scholar]
- Tomescu, R.; Taut, I.; Covrig, I.; Șimonca, V. Study concerning Tortrix viridana attack on oak forests from Transylvanian private forest districts. ProEnvironment 2014, 7, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Holonec, L.; Dîrja, M.; Păcurar, I.; Oroian, I.; Ilea, M.; Vlasin, H. Efficacy of some fungicides in combating mildew produced by the phyto pathogen microsphaera abbreviata in natural regenerations of oaks. Bul. USAMV-CN 2007, 64, 184–189. [Google Scholar]
- Tăut, I.; Şimonca, V.; Badea, O.; Moldovan, M. The favorable climatic regime in triggering the decline of oak stands. ProEnvironment 2015, 8, 583–589. [Google Scholar]
- Petritan, A.M.; Petritan, I.C.; Hevia, A.; Walentowski, H.; Bouriaud, O.; Sánchez-Salguero, R. Climate warming predispose sessile oak forests to drought-induced tree mortality regardless of management legacies. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 491, 119097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobiec, A.; Reif, A.; Öllerer, K. Seeing the oakscape beyond the forest: A landscape approach to the oak regeneration in Europe. Landsc. Ecol. 2018, 33, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petritan, A.M.; Nuske, R.S.; Petritan, I.C.; Tudose, N.C. Gap disturbance patterns in an old-growth sessile oak (Quercus petraea L.)–European beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) forest remnant in the Carpathian Mountains, Romania. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 308, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordács, S.; Popescu, F.; Slade, D.; Csaikl, U.M.; Lesur, I.; Borovics, A.; Kézdy, P.; König, A.O.; Gömöry, D.; Brewer, S.; et al. Chloroplast DNA variation of white oaks in northern Balkans and in the Carpathian Basin. For. Ecol. Manag. 2002, 156, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godt, M.J.W.; Hamrick, J.L. Allozyme diversity in the endangered pitcher plant Sarracenia rubra ssp. Alabamensis (Sarraceniaceae) and its close relative S. rubra ssp. Rubra. Am. J. Bot. 1998, 85, 802–810. [Google Scholar]
- Steinkellner, H.; Fluch, S.; Turetschek, E.; Lexer, C.; Streiff, R.; Kremer, A.; Burg, K.; Glössl, J. Identification and characterization of (GA/CT) n—Microsatellite loci from Quercus petraea. Plant Mol.Biol. 1997, 33, 1093–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodénès, C.; Joandet, S.; Laigret, F.; Kremer, A. Detection of genomic regions differentiating two closely related oak species Quercus petraea (Matt.) Liebl., and Quercus robur L. Heredity 1997, 78, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gömöry, D.; Yakovlev, I.; Zhelev, P.; Jedináková, J.; Paule, L. Genetic differentiation of oak populations within the Quercus robur/Quercus petraea complex in Central and Eastern Europe. Heredity 2001, 86, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, J.; Bodenes, C.; Chancerel, E.; Frigerio, J.M.; Vendramin, G.; Sebastiani, F.; Buonamici, A.; Gailing, O.; Koelewijn, H.P.; Villani, F.; et al. A fast and cost-effective approach to develop and map EST-SSR markers: Oak as a case study. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 570–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gailing, O.; Lind, J.; Lilleskov, E. Leaf morphological and genetic differentiation between Quercus rubra L. and Q. ellipsoidalis E. J. Hill populations in contrasting environments. Plant Syst. Evol. 2012, 298, 1533–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, J.; Gailing, O. Genetic structure of Quercus rubra L. and Quercus ellipsoidalis E. J. Hill populations at gene-based EST-SSR and nuclear SSR markers. Tree Genet. Genomes 2013, 9, 707–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alikhani, L.; Rahmani, M.S.; Shabanian, N.; Badakhshan, H.; Khadivi-Khub, A. Genetic variability and structure of Quercus brantii assessed by ISSR, IRAP and SCoT markers. Gene 2014, 552, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmani, M.S.; Alikhani, L.; Shabanian, N.; Khadivi-Khub, A. Genetic differentiation in Quercus infectoria from northwest of Iran revealed by different nuclear markers. Tree Genet. Genomes 2015, 11, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadivi-Khub, A.; Shabanian, N.; Alikhani, L.; Rahmani, M.S. Genotypic analysis and population structure of Lebanon oak (Quercus libani G. Olivier) with molecular markers. Tree Genet. Genomes 2015, 11, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.G.; Wang, G.G.; Wu, Q.T.; Cheng, X.R.; Yu, M.K.; Wang, W.; Yu, X.B. Patterns of leaf nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry among Quercus acutissima provenances across China. Ecol. Complex 2014, 17, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, A.; Öcal, N.; Akbulut, M. Genetic diversity among the Turkish common bean cultivars (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) as assessed by SRAP, POGP and cpSSR markers. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2014, 54, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Quiros, C.F. Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP), a new marker system based on a simple PCR reaction: Its application to mapping and gene tagging in Brassica. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2001, 103, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferriol, M.; Picó, B.; Nuez, F. Genetic diversity of a germplasm collection of Cucurbita pepo using SRAP and AFLP marker. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 107, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budak, H.; Shearman, R.C.; Parmaksiz, I.; Dweikat, I. Comparative analysis of seeded and vegetative biotype buffalo grasses based on phylogentic relationship using ISSRs, SSRs, RAPDs, andSRAPs. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 109, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.X.; Zhang, X.L.; Nie, Y.C. Evaluation of application of a new molecular marker SRAP on analysis of segregation population and genetic diversity in cotton. Acta Genet. Sin. 2004, 31, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rebrean, F.A.; Fustos, A.; Tǎut, I.; Szabo, K.; Hȃrṭa, M.; Pamfil, D.; Rebrean, M.S.; Sǎlǎgean, T. Genetic diversity of Acer pseudoplatanus L. populations from Transylvania. Braz. J. Bot. 2019, 42, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, K.; Sisea, C.R.; Pop, R.; Bodea, M.; Berindean, I.V.; Bădărău, A.; Pamfil, D. Selection of DNA Isolation Method and PCR Protocol for the Study of Endemic Astragalus exscapus L. ssp. Transsilvanicus (Schur) Nyár. Bull. UASVM Hortic. 2015, 72, 231–232. [Google Scholar]
- Borsai, O.; Hârța, M.; Szabo, K.; Kelemen, C.D.; Andrecan, F.A.; Codrea, M.M.; Clapa, D. Evaluation of genetic fidelity of in vitro-propagated blackberry plants using RAPD and SRAP molecular markers. Hortic. Sci. 2020, 47, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapa, D.; Hârța, M.; Szabo, K.; Teleky, B.-E.; Pamfil, D. The Use of Wheat Starch as Gelling Agent for In Vitro Proliferation of Blackberry (Rubus fruticosus L.) Cultivars and the Evaluation of Genetic Fidelity after Repeated Subcultures. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapa, D.; Borsai, O.; Hârța, M.; Bonta, V.; Szabo, K.; Coman, V.; Bobiș, O. Micropropagation, genetic fidelity and phenolic compound production of Rheum rhabarbarum L. Plants 2020, 9, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodhi, M.A.; Guang-Ning, Z.F.N.F.; Weeden, B.I. A simple and efficient method for DNA extraction from grapevine cultivars, Vitis species and Ampelopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 1994, 12, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, R.; Ardelean, M.; Pamfil, D.; Gaboreanu, I. The efficiency of different DNA isolation and purification protocols in ten cultivars of Vitis vinifera. Bul. USAMV-CN 2003, 59, 259–262. [Google Scholar]
- Szabo, K.; Pamfil, D.; Bădărău, A.S.; Hârţa, M. Assessment of Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of the Endangered Astragalus exscapus subsp. transsilvanicus through DNA-Based Molecular Markers. Plants 2021, 10, 2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAIEx 6: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nei, M. Analysis of gene diversity in subdivided populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1973, 70, 3321–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohlf, F.J. NTSYS-pc Numerical Taxonomy and Multivariate Analysis System, Version 2.1; Exeter Software; State University of New York: New York, NY, USA, 2000.
- Yeh, F.C.; Yang, R.C.; Boyle, T. POPGENE Microsoft Windows-based Freeware for Population Genetic Analysis; Release 1.31; University of Alberta: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Excoffier, L.; Peter, E.S.; Joseph, M.Q. Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among dna haplotypes: Application to human mitochondrial dna restriction data. Genetics 1992, 131, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, S. Evolution in Mendelian populations. Genetics 1931, 16, 97–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakkad, G.; Ueno, S.; Yoshimaru, H. Genetic diversity and differen- tiation of Quercus semiserrata Roxb. in northern Thailand revealed by nuclear and chloroplast microsatellite markers. For. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 255, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Rodríguez, A.; Arias, D.M.; Oyama, K. Genetic variation and differentiation of populations within the Quercus affinis—Quercus laurina (Fagaceae) complex analyzed with RAPD markers. Can. J. Bot. 2005, 83, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, D.; Wang, C.; Qu, H.; Zou, X.; Yang, C. Genetic diversity analysis of Quercus mongolica populations with inter-simple sequence repeats (ISSR) technique. Biodivers. Sci. 2007, 15, 292–299. [Google Scholar]
- Pohjanmies, T.; Elshibli, S.; Pulkkinen, P.; Rusanen, M.; Vakkari, P.; Korpelainen, H.; Roslin, T. 2016: Fragmentation-related patterns of genetic differentiation in pedunculate oak (Quercus robur) at two hierarchical scales. Silva Fenn. 2016, 50, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, R.; Quesada, M.; Ashworth, L.; Herrerias-Diego, Y.; Lobo, J. Genetic consequences of habitat fragmentation in plant populations: Susceptible signals in plant traits and methodological approaches. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 5177–5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

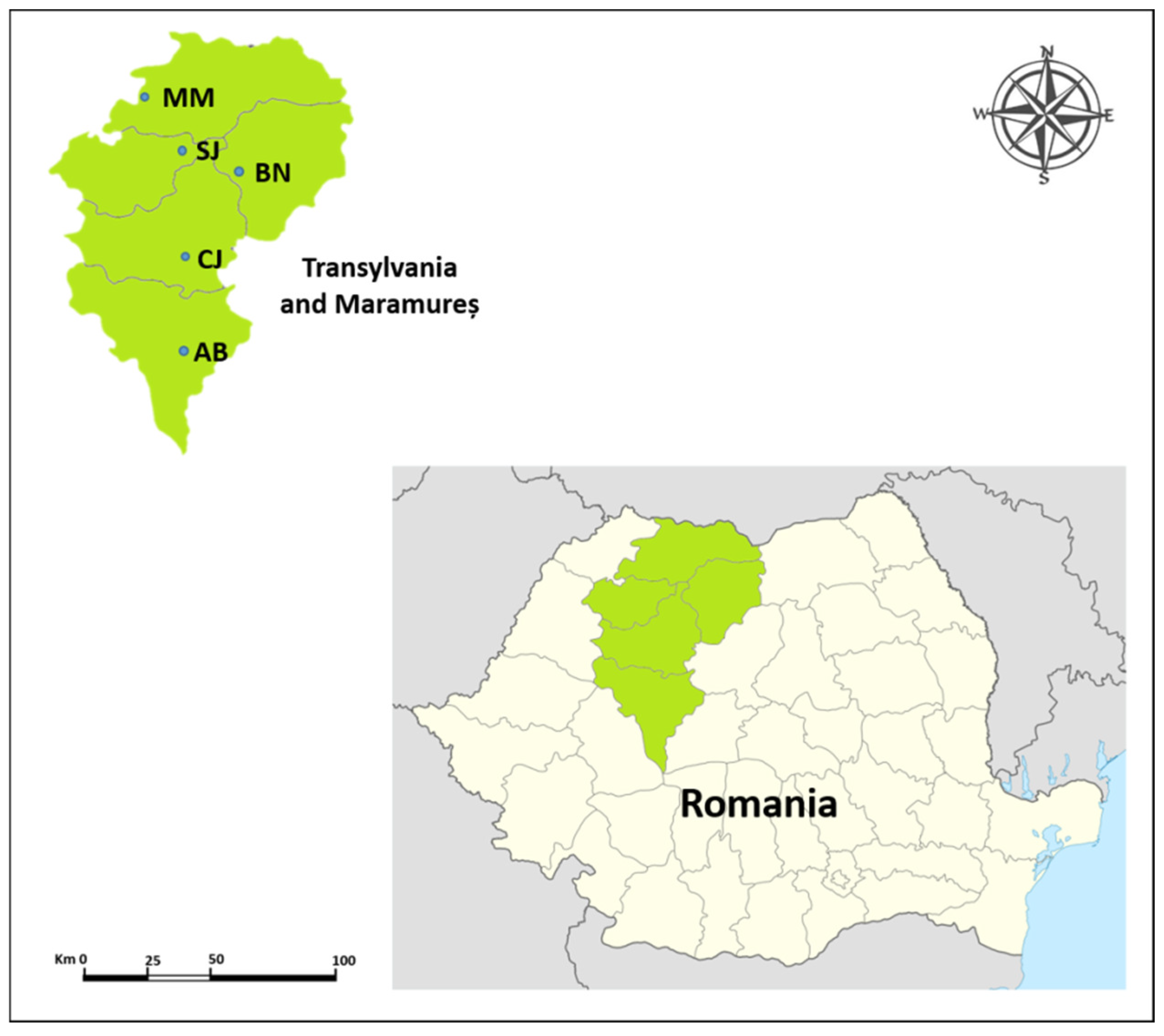
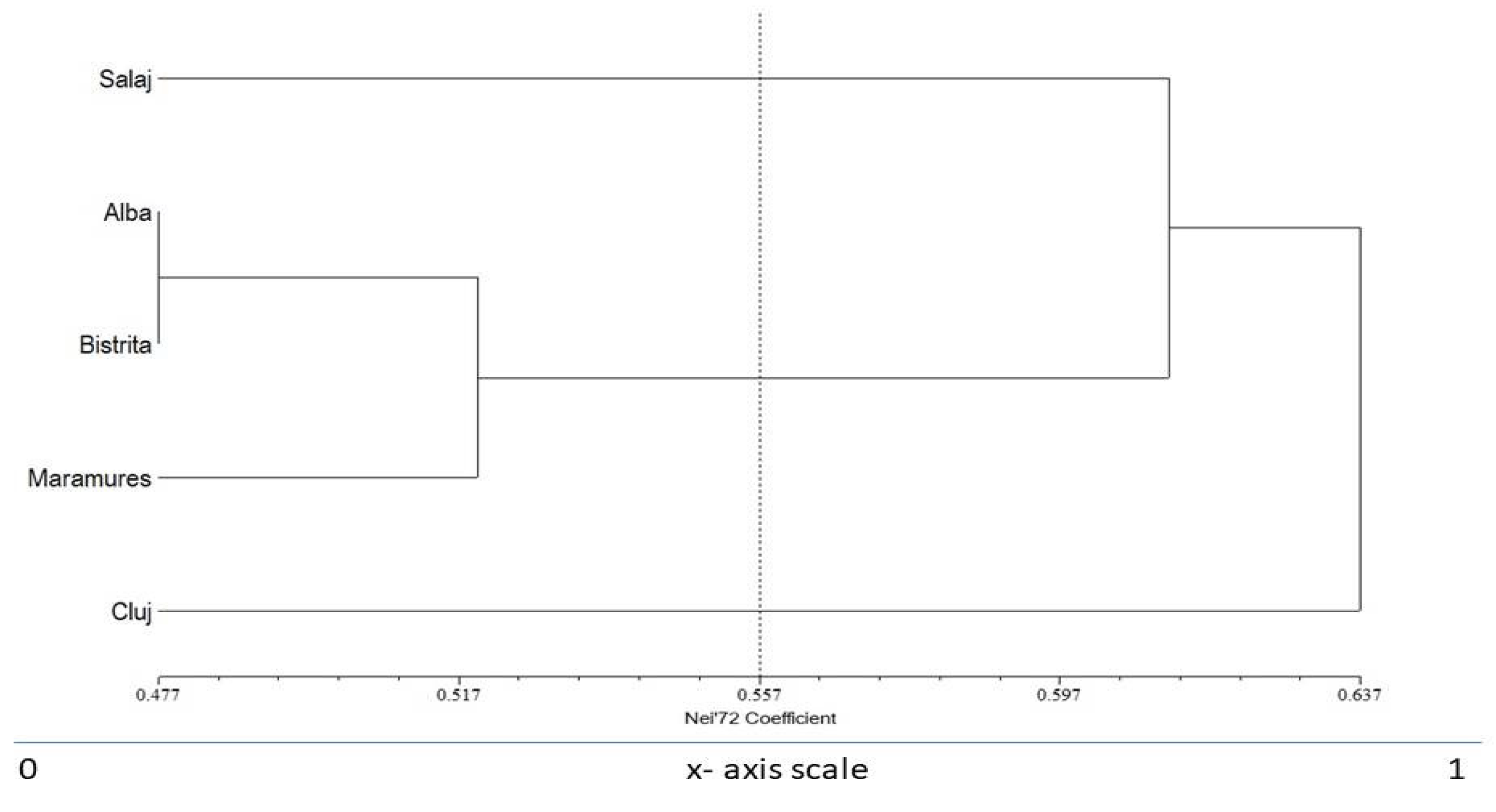
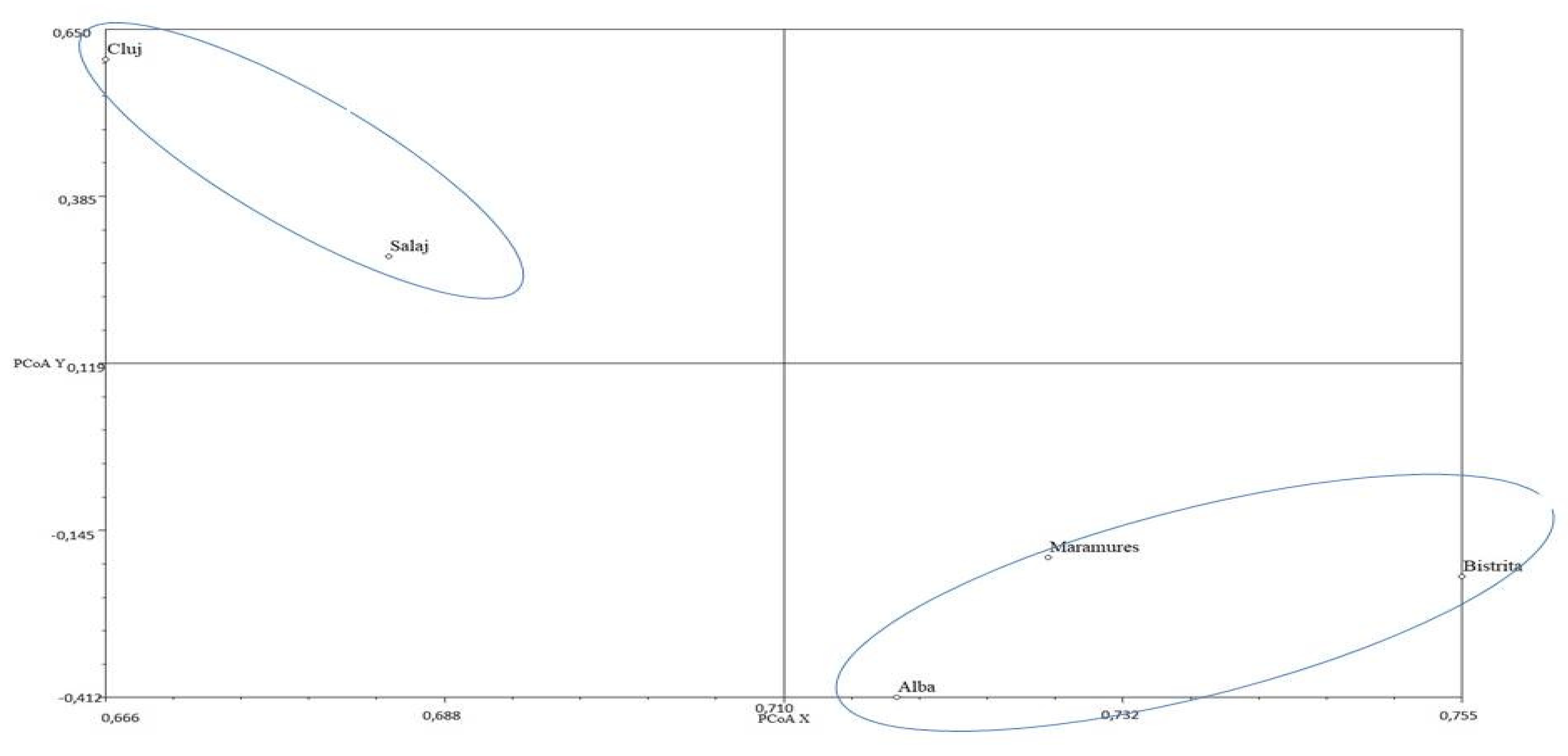

| No. | Populations | Code | No. of Samples | Altitude (m) | Longitude (E) | Latitude (N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Maramureș | MM | 15 | 200–260 | 23°20′56.25″ | 47°38′23.00″ |
| 2 | Sălaj | SJ | 15 | 250–380 | 23°41′56.84″ | 47°17′34.08″ |
| 3 | Alba | AB | 15 | 300–350 | 23°38′46.29″ | 46°06′02.34″ |
| 4 | Cluj | CJ | 15 | 710–790 | 23°36′03.28″ | 46°41′12.09″ |
| 5 | Bistrița-Năsăud | BN | 15 | 380–460 | 24°08′55.01″ | 47°11′54.44″ |
| Primer Combinations | Primer Sequences | |
|---|---|---|
| Forward Primer Sequences | Reverse Primer Sequences | |
| Me2Em1 | F: TGA GTC CAA ACC GGA GC | R: GAC TGC GTA CGA ATT AAT |
| Me2Em6 | F: TGA GTC CAA ACC GGA GC | R: GAC TGC GTA CGA ATT GCA |
| Me4Em2 | F: TGA GTC CAA ACC GGA CC | R: GAC TGC GTA CGA ATT TGC |
| Me4Em4 | F: TGA GTC CAA ACC GGA CC | R: GAC TGC GTA CGA ATT TGA |
| Me4Em5 | F: TGA GTC CAA ACC GGA CC | R: GAC TGC GTA CGA ATT AAC |
| Me5Em2 | F: TGA GTC CAA ACC GGA AG | R: GAC TGC GTA CGA ATT TGC |
| Me5Em4 | F: TGA GTC CAA ACC GGA AG | R: GAC TGC GTA CGA ATT TGA |
| Me5Em8 | F: TGA GTC CAA ACC GGA AG | R: GAC TGC GTA CGA ATT CAC |
| Me5Em5 | F: TGA GTC CAA ACC GGA AG | R: GAC TGC GTA CGA ATT AAC |
| Me4Em8 | F: TGA GTC CAA ACC GGA CC | R: GAC TGC GTA CGA ATT CAC |
| Me2Em2 | F: TGA GTC CAA ACC GGA GC | R: GAC TGC GTA CGA ATT TGC |
| Me2Em5 | F: TGA GTC CAA ACC GGA GC | R: GAC TGC GTA CGA ATT AAC |
| Me1Em2 | F: TGA GTC CAA ACC GGA TA | R: GAC TGC GTA CGA ATT TGC |
| Me1Em8 | F: TGA GTC CAA ACC GGA TA | R: GAC TGC GTA CGA ATT CAC |
| Me3Em3 | F: TGA GTC CAA ACC GGA AT | R: GAC TGC GTA CGA ATT GAC |
| Me3Em6 | F: TGA GTC CAA ACC GGA AT | R: GAC TGC GTA CGA ATT GCA |
| Me6Em6 | F: TGA GTC CAA ACC GGA CA | R: GAC TGC GTA CGA ATT GCA |
| Me6Em8 | F: TGA GTC CAA ACC GGA CA | R: GAC TGC GTA CGA ATT CAC |
| Me2Em1 | F: TGA GTC CAA ACC GGA GC | R: GAC TGC GTA CGA ATT AAT |
| Me2Em6 | F: TGA GTC CAA ACC GGA GC | R: GAC TGC GTA CGA ATT GCA |
| Me4Em2 | F: TGA GTC CAA ACC GGA CC | R: GAC TGC GTA CGA ATT TGC |
| Population | PPB (%) | Na | Ne | He | I |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sălaj | 80.44 | 1.8044 | 1.3322 | 0.2103 | 0.3334 |
| Alba | 85.78 | 1.8578 | 1.4307 | 0.2582 | 0.3955 |
| Bistrița | 78.22 | 1.7822 | 1.3631 | 0.2238 | 0.3481 |
| Cluj | 69.72 | 1.6978 | 1.2948 | 0.1833 | 0.2887 |
| Maramureș | 83.11 | 1.8311 | 1.4122 | 0.2507 | 0.3857 |
| Average | 79.45 | 1.7946 | 1.3666 | 0.2253 | 0.3503 |
| Species-level | 98.22 | 1.9822 | 1.3979 | 0.2483 | 0.3918 |
| Source | df | SS | MS | Est. Var. | % | ɸPT | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Among Pops. | 4 | 297.18 | 74.29 | 2.97 | 9 | 0.088 | <0.001 |
| Within Pops. | 68 | 2101.50 | 30.90 | 30.90 | 91 | ||
| Total | 72 | 2398.68 | 33.87 | 100 |
| Populations | Sălaj | Alba | Bistrița-Năsăud | Cluj | Maramureș |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sălaj | − | ||||
| Alba | 0.0284 | − | |||
| Bistrița-Năsăud | 0.0263 | 0.0259 | − | ||
| Cluj | 0.0209 | 0.0496 | 0.0382 | − | |
| Maramureș | 0.0502 | 0.0446 | 0.0272 | 0.0518 | − |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rebrean, F.A.; Fustos, A.; Szabo, K.; Lisandru, T.-T.; Rebrean, M.S.; Varga, M.I.; Pamfil, D. Genetic Diversity and Structure of Quercus petraea (Matt.) Liebl. Populations in Central and Northern Romania Revealed by SRAP Markers. Diversity 2023, 15, 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15101093
Rebrean FA, Fustos A, Szabo K, Lisandru T-T, Rebrean MS, Varga MI, Pamfil D. Genetic Diversity and Structure of Quercus petraea (Matt.) Liebl. Populations in Central and Northern Romania Revealed by SRAP Markers. Diversity. 2023; 15(10):1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15101093
Chicago/Turabian StyleRebrean, Florin Alexandru, Adrian Fustos, Katalin Szabo, Tabita-Teodora Lisandru, Mihaela Simona Rebrean, Mircea Ioan Varga, and Doru Pamfil. 2023. "Genetic Diversity and Structure of Quercus petraea (Matt.) Liebl. Populations in Central and Northern Romania Revealed by SRAP Markers" Diversity 15, no. 10: 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15101093
APA StyleRebrean, F. A., Fustos, A., Szabo, K., Lisandru, T.-T., Rebrean, M. S., Varga, M. I., & Pamfil, D. (2023). Genetic Diversity and Structure of Quercus petraea (Matt.) Liebl. Populations in Central and Northern Romania Revealed by SRAP Markers. Diversity, 15(10), 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15101093







