Effects of Stand Structure of Artificial Shelter Forest on Understory Herb Diversity in Desert-Oasis Ecotone
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
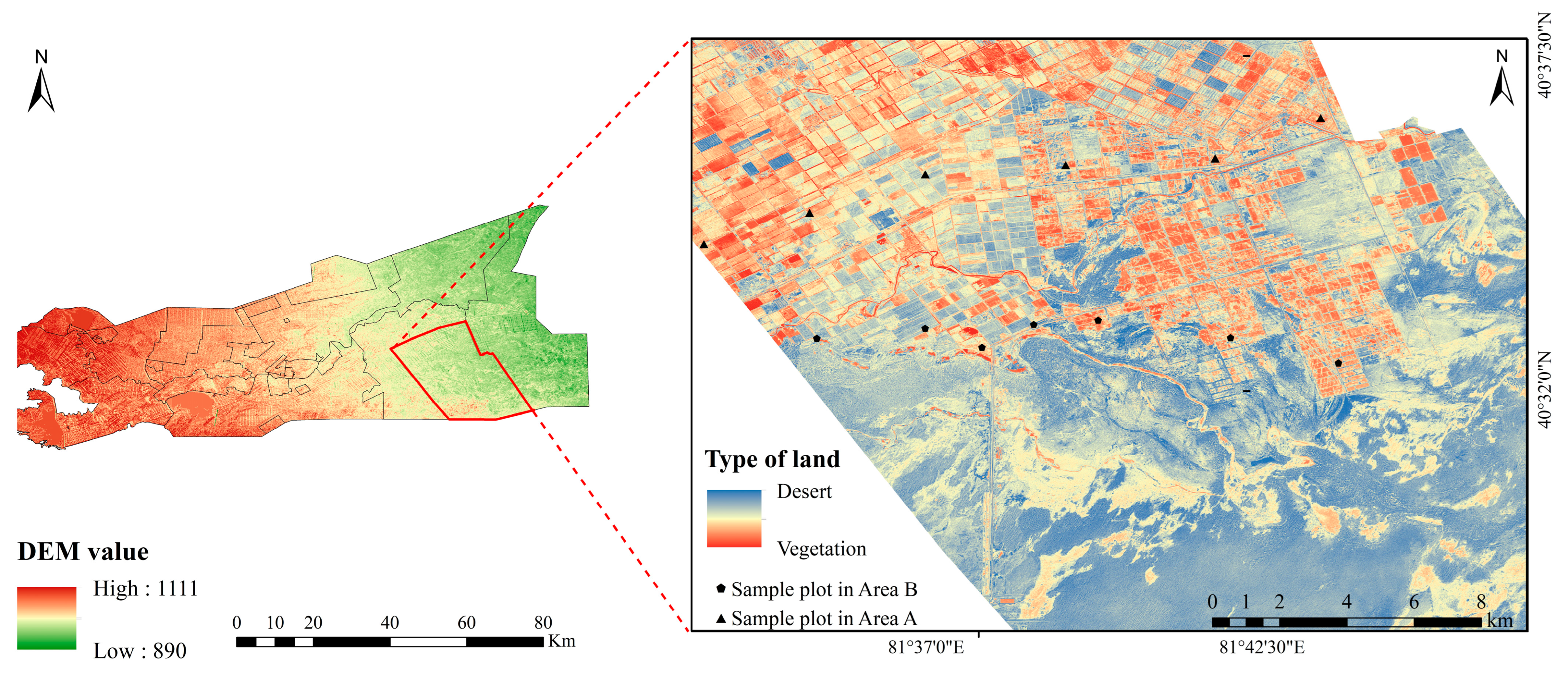
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Sample Plot Setting
2.3. Research Methods
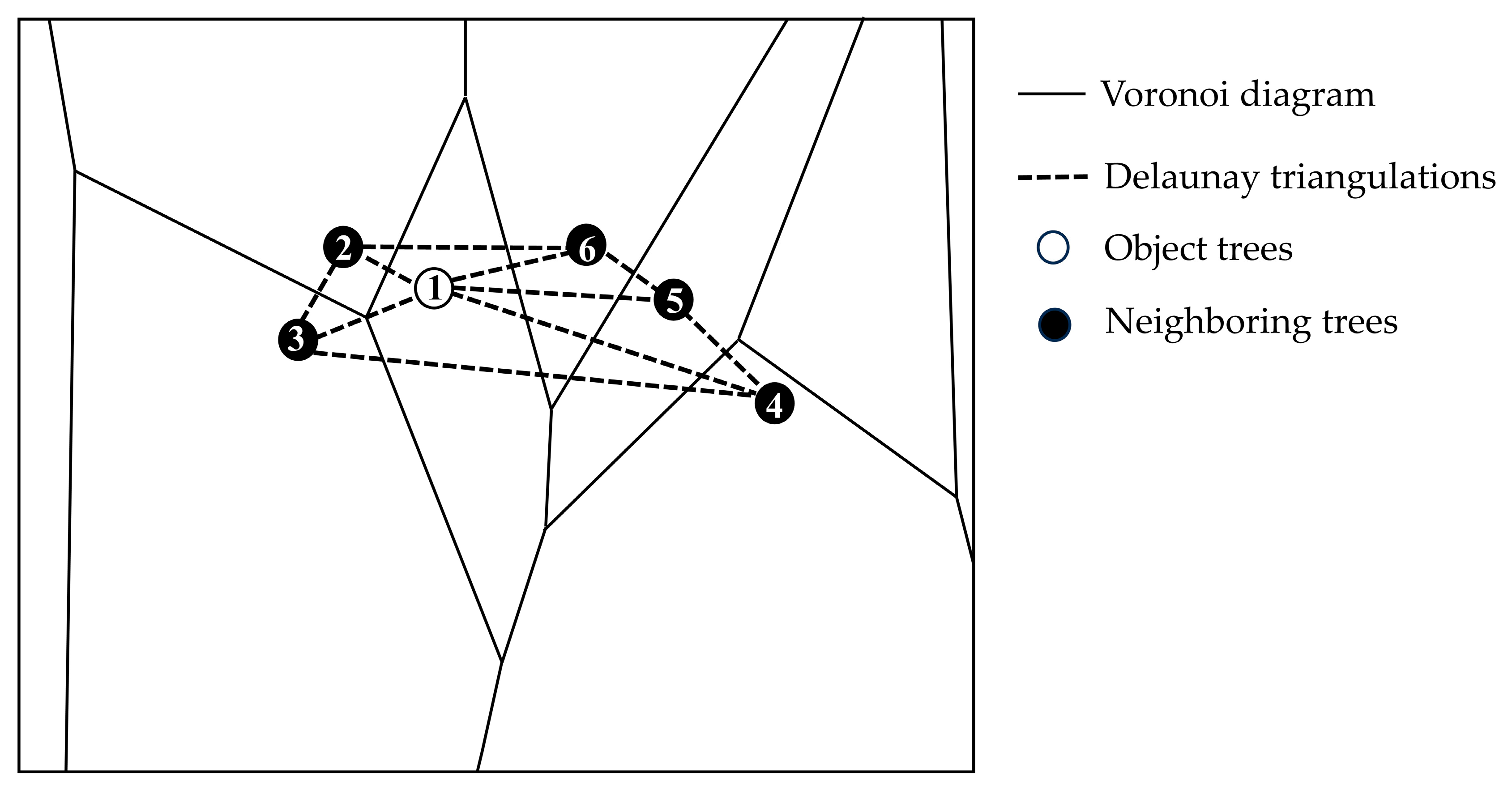
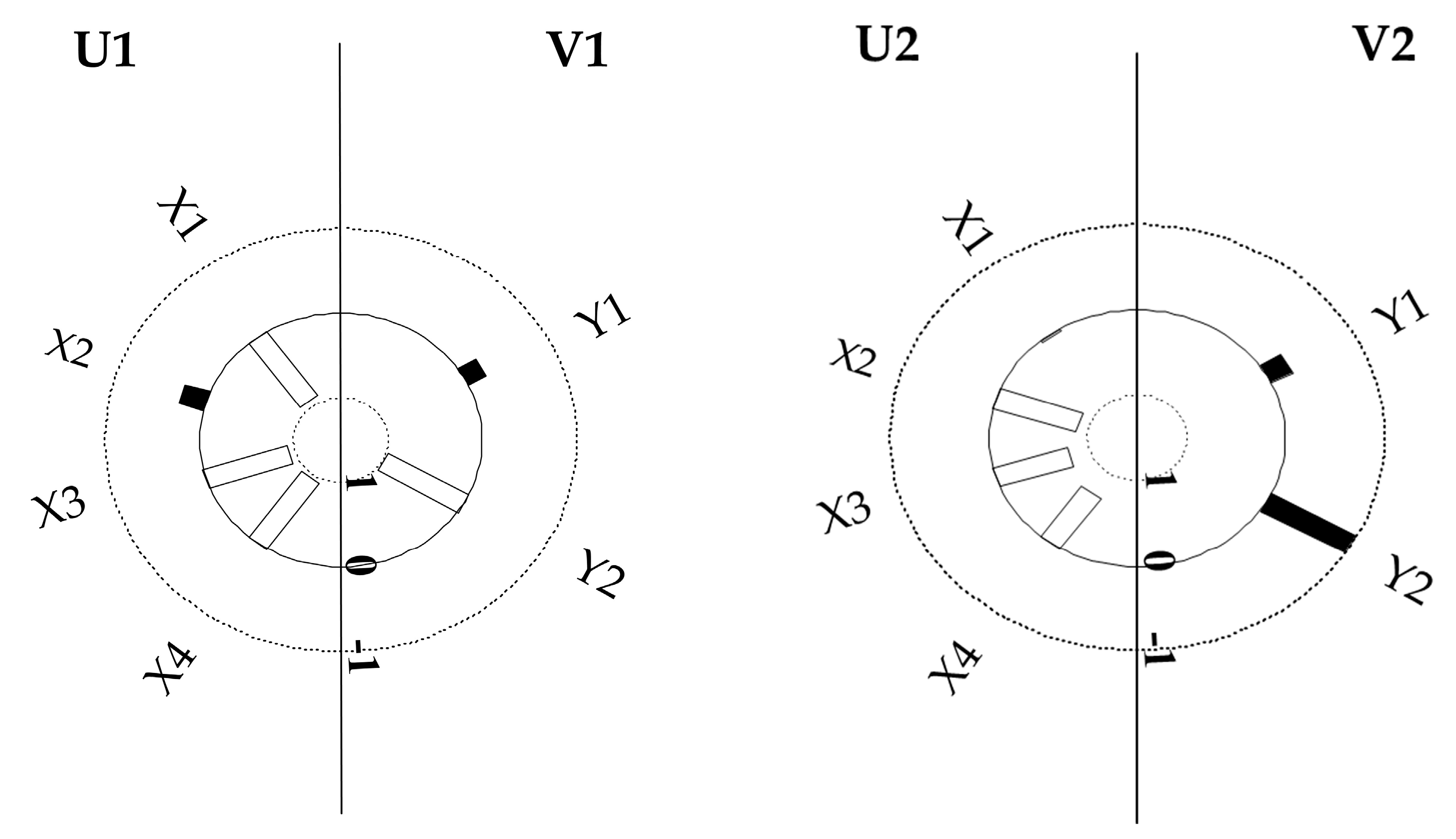
2.3.1. Stand Structure Calculation
2.3.2. Calculation of Understory Herbaceous Plant Diversity Index
2.3.3. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Understory Herbaceous Species Diversity Characteristics
3.2. Basic Characteristics of Stand Structure
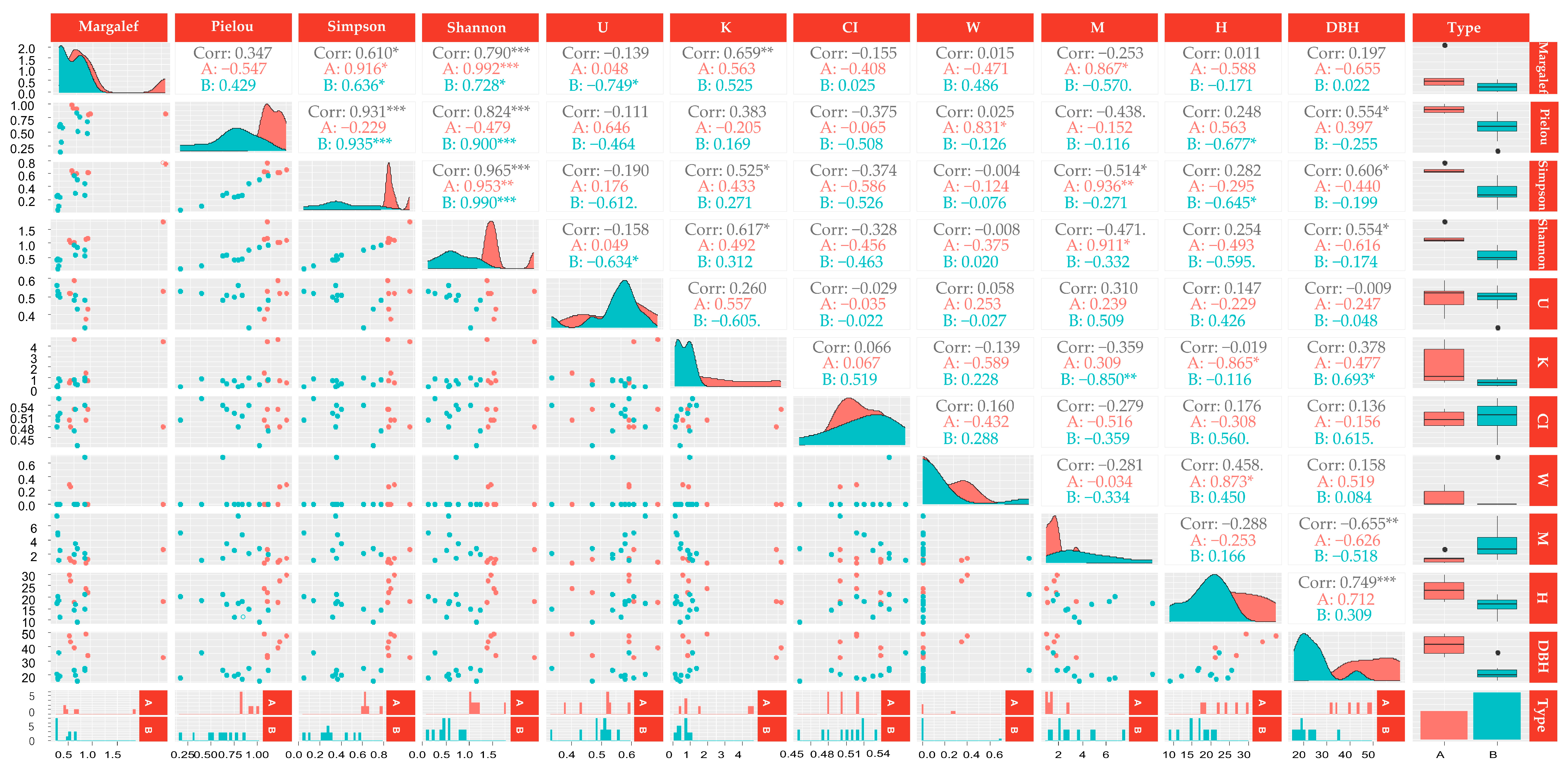
3.3. Correlation Analysis between Stand Structure Factors and Herb Diversity Index
3.4. Canonical Correlation Analysis between Stand Structure and Understory Herb Diversity
3.5. Multiple Stepwise Regression Analysis of Stand Structure and Understory Herb Diversity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, C. Study in Desert-oasis Ecological Fragile Zone. Arid Land Geogr. 2001, 24, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J. Review on ecological benefit evaluation of shelter forest. Prot. For. Sci. Technol. 2012, 1, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wang, G.; Peng, S. Role of desert annuals in nutrient flow in arid area of Northwestern China: A nutrient reservoir and provider. Plant Ecol. 2009, 201, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Liu, Y. Measurement methods for biodiversity in ecological communities: Part I—Measurement methods for α diversity (continued). Biodivers. Sci. 1994, 2, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Qin, F.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Niu, X.; Liu, L. Environmental interpretation of herb species diversity under different site types of Hippophae rhamnoides forest in feldspathic sandstone region. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 5132–5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, F.W.; Lamb, E.G.; Sharma, M.; Hunt, S.; Anand, M.; Dacosta, J.; Newmaster, S.G. Relative influence of climate, soils, and disturbance on plant species richness in northern temperate and boreal forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 381, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márialigeti, S.; Tinya, F.; Bidló, A.; Ódor, P. Environmental drivers of the composition and diversity of the herb layer in mixed temperate forests in Hungary. Plant Ecol. 2016, 217, 549–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, A.L.; Puettmann, K.J. Overstory composition and stand structure influence herbaceous plant diversity in the mixed aspen forest of northern Minnesota. Am. Midl. Nat. 2000, 143, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cao, Y. Response of tree regeneration and understory plant species diversity to stand density in mature Pinus tabulaeformis plantations in the hilly area of the Loess Plateau, China. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 73, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Yan, E.; Chen, H.; Chang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X.; Xu, M. Stand structural diversity rather than species diversity enhances aboveground carbon storage in secondary subtropical forests in Eastern China. Biogeosciences 2016, 13, 4627–4635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J.E. Structural effects on understory attributes in second-growth forests of northern Wisconsin, USA. For. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 347, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Pan, P.; Ning, J.; Lai, G.; Ouyang, X.; Xu, H.; Guo, L.; Wu, Z.; Yi, Z. Effects of Stand Spatial Structure on Understory Vegetation Diversity of Aerial Seeding Pinus massoniana Plantations. J. Northeast For. Univ. 2016, 44, 31–35+40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, P.; Qi, S.; Zhang, D.; Wu, B.; Cui, R. Difference Influence of Spatial Structure of Platycladus orientalis Plantations on Diversity of Understory Herbaceous and Its Correlation Degree. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2022, 31, 1794–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; He, L.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, X.; Sha, H.; He, B.; Jin, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; et al. Effects of spatial structure on understory vegetation and soil properties in Pinus tabuliformis plantation of different succession types in Beijing. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 1959–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climate Conditions. Series. Available online: http://www.ale.gov.cn/ssgk/qhtj (accessed on 15 June 2023).
- Basic Meteorological Observation Data of China’s Surface. Series. Available online: http://data.cma.cn/ (accessed on 15 July 2023).
- Le, T. Comparative study on natural mangrove forest stand spatial structure by Tyson polygon and traditional four trees method. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2021, 41, 35–42, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Ying, H. Analysis and application of polygon side distribution of Voronoi diagram in tree patterns. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2015, 37, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Li, J.; Li, J. Quantitative Analysis of Forest Stand Spatial Structure Based on Voronoi Diagram & Delaunay Triangulated Network. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2010, 46, 78–84. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, M.; Chen, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, G.; Zhao, M. Intraapecific and Interspecific competition analysis of community dominant plant populations based on Voronoi diagram. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2007, 27, 4707–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, C.; Cai, T.; Ju, C. Quantitative analysis of spatial structural characteristics of broadleaved Korean pine forest based on Voronoi diagram. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2021, 43, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F. The study of the stand spatial structure based on ArcGIS—A case study in Wuyi mountain Nature Reserve. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Aguirre, O.; Hui, G.; von Gadow, K.; Jiménez, J. An analysis of spatial forest structure using neighbourhood-based variables. For. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 183, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, G.; Albert, M.; Gadow, K. DasUmgebungsmaß als Parameter zur Nachbildung von Bestandesstrukturen. Forstwiss. Cent. Ver. Mit Tharandter Forstl. Jahrb. 1998, 1, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, G.; Gado, K. The neighbourhood patiern—A new structure parameter for describing distribution of forest tree position. Sci. Silvae Sin. 1999, 35, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, G.; Gadow, K.v.; Albert, M. A New Parameter for Stand Spatial Structure Neighbourhood Comparison. For. Res. 1999, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Alemdag, I. Evaluation of Some Competition Indexes for the Prediction of Diameter Increment in Planted White Spruce; Canadian Forestry Service: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1978; p. 39. [Google Scholar]
- Hegyi, F. A Simulation Model for Managing Jack-Pine Stands in Growth Models for Tree and Stand Simulation; Fries, J., Ed.; Royal College of Forestry: Stockholm, Sweden, 1974; pp. 74–90. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y. The spatial pattern of coniferous forest in Xinlong Mountain and its strategies in using sun light energy. Acta Ecol. Sin. 1984, 4, 10–20. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, C.; Zha, T.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Gao, L.; Bai, L.; Ma, Z.; Yu, Y. Spatial structure characteristics of plain ecological plantation in Tongzhou District, Beijing, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 33, 2088–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Zhang, S. A Classification and Comparison of Competition Indices. A Classif. Comp. Compet. Indices 1992, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Pei, S.; Zhang, L.; Guo, J.; Xin, X. Applicability evaluation of competition indexes for Pinus tabuliformis plantations in Beijing. J. Zhejiang A F Univ. 2019, 36, 1115–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, C.; Lai, G. Analysis and Evaluation of Stand Spatial Structure of Platycladus orientalis Ecological Forest in Jiulongshan of Beijing. For. Res. 2018, 31, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Wang, W.; Men, X.; Sun, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, D. Spatial structure optimal of Larix gmelinii plantation. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2021, 43, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Yu, R.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, M. Application of excel in calculation of biodiversity indices. Mar. Sci. 2012, 36, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Qi, Y.; George, S.K. Randomization tests and computational software on statistic significance of community biodiversity and evenness. Biodivers. Sci. 2002, 10, 431–437. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z. On the Division of Flora in China. ACTA Bot. Yunnanica 1979, 1, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J. Basics of Medical Statistics and Application of SPSS Software, 1st ed.; Gansu Culture Publishing House: Gansu, China, 2017; p. 294. [Google Scholar]
- López, R.P.; Larrea-Alcázar, D.M.; Teresa, O. Positive effects of shrubs on herbaceous species richness across several spatial scales: Evidence from the semiarid Andean subtropics. J. Veg. Sci. 2009, 20, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S. Studies on the Relation between Density and Undergrowth Diversity of Pinus tablulaeformis and Populus davidana Forests in DA WO PU. Master’s Thesis, Hebei Agricultural University, Baoding, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Yang, X.; Shi, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. The influence of stand factors on species diversity of herb layer in Zhangbei poplar plantations. Chin. J. Ecol. 2018, 37, 2869–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, S.; Li, J.; Lu, J.; Wang, W. Characteristic of root biomass of three main forest types in Xinjiang. Arid Land Geogr. 2013, 36, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, N. Root Traits Spatial-Temporal Variation and Root-Water Uptake Characteristics and Mechanisms of Populus tomentosa. Master’s Thesis, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, R.; Qi, S.; Wu, B.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, P.; Ma, N.; Huang, X. The Influence of Stand Structure on Understory Herbaceous Plants Species Diversity of Platycladus orientalis Plantations in Beijing, China. Forests 2022, 13, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Wang, J.; Ma, J.; Yuan, S.; Du, Y. Evaluation of Quercus aliena var. acuteserrata forest at the western segment of Qinling Mountain, northwestern China. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2009, 31, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, X.; Yue, Y.; Gan, J.; Wang, X.; Li, J. Spatial structure of Robinia pseudoacacia plantation in Miyun Reservoir Watershed of Beijing. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2009, 31, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzaz, F. Plant species diversity in old-field successional ecosystems in southern Illinois. Ecology 1975, 56, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Xu, Q.; Lu, Y. Effects of stand spatial structure on species diversity of shrubs in Quercus spp. natural secondary forests in Hunan Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 5404–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tian, L.; Bai, c.; He, L. Investigation and ecological adaptability analysis of typical herbaceous plant resources in the southeast edge of Mu Us Desert. Shaanxi J. Agric. Sci. 2017, 63, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
| Stand Spatial Structure Parameter | Stand Spatial Structure Grade | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | IV | V | |
| Neighborhood comparison (U) | 0 | (0, 0.33) | [0.33, 0.67] | (0.67, 1) | 1 |
| Opening degree (K) | (0, 0.2] | (0.2, 0.3] | (0.3,0.4] | (0.4,0.5] | (0.5, +∞] |
| Angle scale (W) | (0, 0.475) | [0.475, 0.517] | [0.517, +∞] | - | - |
| Mingling degree (M) | 0 | (0, 0.25] | (0.25, 0.5] | (0.5, 0.75] | (0.75, 1.00] |
| Department | Genus | Plant Names | Importance Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oasis (A) | Desert (B) | |||
| Leguminosae | Glycyrrhiza | Glycyrrhiza uralensis | 0.084 | - |
| Alhagi | Alhagi sparsifolia | - | 0.052 | |
| Gramineae | Phragmites | Phragmites australis | 0.433 | 0.569 |
| Eleusine | Eleusine multiflora | 0.210 | - | |
| Compositae | Taraxacum | Taraxacum monochlamydeum | 0.141 | - |
| Cirsium | Cirsium setosum | 0.121 | - | |
| Sonchus | Sonchus wightianus | 0.145 | - | |
| Sonchus brachyotus | 0.057 | - | ||
| Karelinia | Karelinia caspia | - | 0.261 | |
| Polygonaceae | Polygonum | Polygonum patulum | 0.057 | - |
| Rumex | Rumex acetosa | 0.323 | - | |
| Asclepiadaceae | Cynanchum | Cynanchum cathayense | 0.147 | 0.391 |
| Chenopodiaceae | Chenopodium | Castanopsis fissa | 0.061 | - |
| Index | Oasis (A) | Desert (B) | t Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation (%) | Mean ± Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation (%) | T | p | |
| Shannon–Wiener index | 1.206 ± 0.278 | 23.02% | 0.534 ± 0.265 | 49.65% | 4.141 | 0.001 *** |
| Simpson index | 0.658 ± 0.060 | 9.06% | 0.303 ± 0.168 | 55.49% | 3.877 | 0.001 *** |
| Margalef richness index | 0.761 ± 0.526 | 69.08% | 0.422 ± 0.170 | 40.28% | 1.665 | 0.115 |
| Pielou evenness index | 0.899 ± 0.071 | 7.86% | 0.573 ± 0.606 | 35.89% | 2.903 | 0.010 ** |
| Index | Area A | Area B | t test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation (%) | Mean ± Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation (%) | T | p | |
| Tree height (m) | 23.32 ± 0.78 | 28.53% | 17.10 ± 0.25 | 24.3% | 2.478 | 0.015 ** |
| DBH (cm) | 39.62 ± 1.73 | 37.06% | 20.53 ± 0.39 | 36.56% | 7.587 | 0.000 *** |
| Mingling degree | 0.09 ± 0.14 | 155.56% | 0.07 ± 0.22 | 316.23% | 0.210 | 0.837 |
| Neighborhood comparison | 0.50 ± 0.08 | 15.37% | 0.49 ± 0.07 | 13.30% | 0.281 | 0.783 |
| Competition index | 1.40 ± 0.67 | 47.73% | 3.29 ± 1.94 | 13.11% | −2.279 | 0.039 ** |
| Angle scale | 0.50 ± 0.023 | 4.47% | 0.51 ± 0.04 | 7.70% | −0.265 | 0.795 |
| Opening degree | 2.90 ± 1.92 | 91.51% | 0.58 ± 0.31 | 53.23% | 2.502 | 0.025 ** |
| Sample | Typical Variable Group | Canonical Correlation Coefficient | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1 | 1.000 | 0.000 ** |
| 2 | 0.915 | 0.004 * | |
| B | 1 | 0.947 | 0.000 ** |
| 2 | 0.710 | 0.013 * |
| Variable | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | Y1 | Y2 | Y3 | Y4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Standardization coefficient | U1 | −0.934 | 0.269 | −0.934 | −0.959 | - | - | - | - |
| V1 | - | - | - | - | 0.213 | −0.984 | - | - | ||
| Cross-load coefficient | U1 | −0.940 | 0.323 | −0.934 | −0.963 | - | - | - | - | |
| V1 | - | - | - | - | 0.244 | −0.978 | - | - | ||
| B | Standardization coefficient | U2 | −0.810 | −0.343 | −0.521 | −0.561 | - | - | - | - |
| V2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.971 | 0.198 | ||
| Cross-load coefficient | U2 | −0.766 | −0.325 | −0.493 | −0.531 | - | - | - | - | |
| V2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.920 | 0.188 |
| Species Diversity Index | Regression Equation | R2 | p | D-W | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Shannon–Wiener index | y = 0.911 × CI | 0.831 | 0.011 | 1.898 |
| Simpson index | y = 0.936 × CI | 0.876 | 0.006 | 1.552 | |
| Margalef richness index | y = 0.852 × C − 0.442 × W | 0.946 | 0.012 | 1.899 | |
| Pielou evenness index | y = 0.831 × CI | 0.690 | 0.041 | 2.588 | |
| B | Shannon–Wiener index | y = −0.634 × U | 0.402 | 0.049 | 1.023 |
| Simpson index | y = −0.645 × H | 0.416 | 0.044 | 0.760 | |
| Margalef richness index | y = −0.736 × U + 0.466 × M | 0.778 | 0.005 | 2.157 | |
| Pielou evenness index | y = −0.677 × H | 0.458 | 0.032 | 0.957 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Shen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, Y.; Tian, J. Effects of Stand Structure of Artificial Shelter Forest on Understory Herb Diversity in Desert-Oasis Ecotone. Diversity 2023, 15, 1083. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15101083
Yang Y, Zhou Z, Shen L, Zhao Y, Tang Y, Tian J. Effects of Stand Structure of Artificial Shelter Forest on Understory Herb Diversity in Desert-Oasis Ecotone. Diversity. 2023; 15(10):1083. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15101083
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yan, Zhengli Zhou, Liuji Shen, Yachong Zhao, Yuansheng Tang, and Jiahe Tian. 2023. "Effects of Stand Structure of Artificial Shelter Forest on Understory Herb Diversity in Desert-Oasis Ecotone" Diversity 15, no. 10: 1083. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15101083
APA StyleYang, Y., Zhou, Z., Shen, L., Zhao, Y., Tang, Y., & Tian, J. (2023). Effects of Stand Structure of Artificial Shelter Forest on Understory Herb Diversity in Desert-Oasis Ecotone. Diversity, 15(10), 1083. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15101083





