Abstract
Harmful algae blooms (HABs) can have significant adverse effects on coastal ecosystems and aquaculture resiliency. We collected samples from March to August at eight different stations in Haizhou Bay (China), a region with a high frequency of HABs, and used Illumina Novaseq high-throughput sequencing and multivariate statistical analysis to characterize the bacterial communities and their relationships with different environmental factors. We identified 27 phyla, 49 classes, 158 orders, 294 families, and 522 genera. Gammaproteobacteria, Alphaproteobacteria, Bacteroidia, Acidimicrobiia, Bacilli, Actinobacteria, Cyanobacteria, Clostridia, and Acidobacteria were the most abundant classes, and Acidobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes, Actinobacteria, Chloroflexi, Proteobacteria, and Cyanobacteria were the keystone phyla. Based on the Mantel test and redundancy analysis, temperature was the main environmental factor affecting the structure of the bacterial communities, followed by silicate, dissolved organic phosphorus (DOP), and dissolved oxygen (DO). Among the genera with high OTU abundance, Nautella was co-related positively with DO and negatively with salinity; Planktomarina was co-related positively with salinity and negatively with nitrate and nitrite. Certain families (Flavobacteriaceae, Rhodobacteraceae, and Clade_I (SAR11 clade)) and genera (Methylophaga, Alteromonas, Oleiphilus, Marinobacter, Bacillus, Nautella, and Vibrio) had associations with phytoplankton species that were responsible for HABs. This research provides new insights into the characteristics of the bacterial communities that occur in coastal areas that have HABs and provides detailed descriptions of the spatial and temporal changes in the structure of these communities.
1. Introduction
Harmful algal blooms (HABs) are increasing globally in the frequency and spatial extent worldwide in coastal waters and can be highly detrimental to marine ecosystems and commercial aquaculture [1]. HABs mostly consist of massive accumulations of phytoplankton (diatoms, dinoflagellates, and cyanobacteria) on the ocean surface, leading to decreased water transparency and adverse effects in many marine organisms [2,3]. One significant concern is the production of toxins by certain algae or phytoplankton, which can impede the growth of both animals and microorganisms, resulting in a decline in fishery productivity [4,5]. In addition, the decomposition of dying algal blooms by bacteria can result in a decrease in oxygen levels in the water, leading to hypoxia and anoxia, which can be harmful to fish and may cause mortality [6]. Non-photosynthetic prokaryotes have dual roles in HABs in that they facilitate phytoplankton growth through the remineralization of organic matter, and they also compete with phytoplankton for vital nutrients [7,8]. Hence, there exists an intricate and dynamic interplay between non-photosynthetic prokaryotes and phytoplankton in coastal HAB marine environments [6].
Many recent studies have used 16S ribosomal RNA gene-based surveys to characterize the bacterial communities that are associated with HABs. For example, within the Roseobacter genus, the SAR86 and SAR11 clades were abundant in HABs of the North Atlantic region [9]. Another study that used denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) of DNA reported that the Roseobacter and Cytophaga genera were dominant in the attached and free-living communities at the Bay of Fundy (northeastern Canada), where dinoflagellates and diatoms were the predominant phytoplankton [6]. A study showed that diatoms can regulate interactions with different groups of bacteria through intracellular lipids and extracellular metabolites [10]. Research has shown that an association exists between Proteobacteria and Cyanobacteria during the bloom [11]. Gammaproteobacteria Vibrio spp. and Firmicutes Planococcus spp. were the predominant taxa during the diatom bloom of Pseudonitzschia [12]. Four Flavobacteria and eight bacterial sequence variants were potentially associated with a HAB of the toxic dinoflagellate Karenia brevis on the western coast of Florida (United States) [8]. The decay of an HAB by the dinoflagellate Gymnodinium impudicum was characterized by a dominance of the archaeal MGII group (Thalassarchaeaceae), Pelagibacterales (SAR11), Rhodobacterales, and Flavobacteriales in the community of the coastal region of Tunisia [13].
Haizhou Bay is on the western margin of the southern Yellow Sea, is located near the border of Shandong and Jiangsu provinces, and is a typical semi-open bay. Seventeen large rivers flow into the Yellow Sea at this bay. HABs have become common in Haizhou Bay, and it had 23 reported harmful algal species from 2004 to 2017 (Table S1). The excessive use of aquaculture feed and fertilizers by the seaweed and shellfish industries in the southern region of Haizhou Bay has increased water eutrophication, and this has been a major reason for the increasing frequency of HABs in this region [3].
The general purpose of the current study was to investigate the spatial and temporal dynamics of the bacterial communities that are associated with HABs in Haizhou Bay. The two specific aims were to investigate the seasonal variations in the diversity of bacterioplankton and to analyze the relationships of environmental factors, algal blooms, and the composition of the marine bacterial community. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to characterize these taxa in the nearshore coastal environment of Haizhou Bay. Our identification of the abundance of different bacterial groups and their relationships with HABs in Haizhou Bay will provide new and valuable information regarding the spatial and temporal changes in community structure during the spring and summer seasons in this region.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Areas and Sample Collection
Samples of seawater were collected in March, April, May, June, and August of 2021 at eight locations in Haizhou Bay in the southern Yellow Sea of China (Figure 1). Stations A1 (34.85° N, 119.38° E), A2 (34.79° N, 119.47° E), and A3 (34.73° N, 119.55° E) were closest to the shore, and A1 and A2 were located in areas where laver and shellfish aquaculture was conducted. Stations B1 (34.91° N, 119.47° E), B3 (34.79° N, 119.63° E), C1 (34.97° N, 119.72° E), C2 (34.91° N, 119.63° E), and C3 (34.85° N, 119.72° E) were further offshore, and C1 and C2 were in close proximity to areas with shellfish farming. These sites are situated along the coastal area of the South Yellow Sea, neighboring the Lianyungang coast to the west. The region receives inflows from rivers including the New Shoo River and Qiangwei River. Furthermore, the suspended matter and nutrient substances in the area are noticeably impacted by prominent rivers such as the Yangtze River and Yellow River. The climate and hydrology of the region are strongly influenced by terrestrial inputs [14].
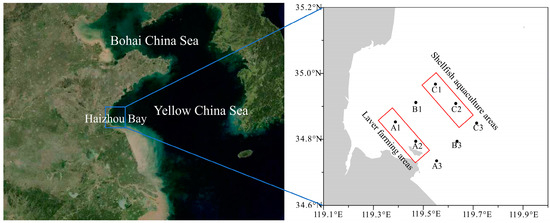
Figure 1.
Location of Haizhou Bay (left) and the eight sample sites (right).
Samples of surface water (approximately 500 mL) were collected from each station in Haizhou Bay and filtered through a 200 μm mesh to remove large planktonic organisms. These samples were then passed sequentially through polycarbonate filters (Millipore) that had pore sizes of 2 μm and 0.22 μm for the collection of prokaryotic biomass. The filters were wrapped in aluminum foil and immediately stored at −80 °C until the extraction and processing of DNA.
The phytoplankton samples were preserved using Lugol iodine solution and stored in the dark. The morphology was determined using an upright microscope (DM2500, Leica, Wetzlar, Germany) at a magnification of 400×. A certain volume of the sample was taken out and counted under the microscope to calculate algal density.
Using a sterile capillary tube under the microscope, a single cell of the bloom-forming species was taken from the fresh samples and cultured by enrichment. Finally, it was cultured in 100 mL Erlenmeyer flasks containing Li-Si medium (32 salinity, autoclaved seawater) [15] and exposed to a light intensity of 100 μE/(m2·s) under a 14 h light:10 h dark cycle.
Physical and chemical indices were recorded directly at the sampling site using a multi-parameter water quality meter (RBRconcertro3, Mettler Toledo, Columbus, America) that measured temperature, salinity, pressure (depth), and chlorophyll a. For the measurement of nutrients, 100 mL of surface seawater was collected, passed through a 200 µm sieve, and then passed through a 0.68 μm glass fiber filter (GF/F) membrane. Each sample was then placed in a nutrient sampling bottle and frozen prior to subsequent analysis. Nitrate, nitrite, ammonium, dissolved total nitrogen (DTN), dissolved organic nitrogen (DON), phosphate, dissolved organic phosphate (DOP), dissolved total phosphorus (DTP), and silicate were measured using an automated nutrient analyzer (QuAAtro39, Seal).
2.2. DNA Extraction and Illumina DNA Sequencing
Total nucleic acids were extracted from the filtered biomass. Before pyrosequencing, the V3–V4 regions of the 16S rDNA were amplified using primers 338F (5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCA-3′) and 806R (5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′). Then, PCR was utilized to amplify target sequences, and the resulting products were purified, quantified, and homogenized to obtain a sequencing library. A library quality control (QC) procedure was implemented to enable library construction, and the Illumina Novaseq 6000 platform was used for the sequencing of qualified libraries. Raw reads were filtered using Trimmomatic version 0.33 [16], and primer sequences were eliminated using Cutadapt version 1.9.1 [17]. FLASH version 1.2.7 [18] was used to assemble high-quality reads, and these reads were clustered into operational taxonomic units (OTUs) using Usearch [19], with a similarity threshold of 97.0%. Taxonomic annotation was conducted using SILVA as a reference database [20]. QIIME2 [21] was used to calculate the abundance of different taxa, and RStudio was used to generate distribution histograms.
The genomic DNA was extracted from a 10 mL culture using the modified cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) method [22]. The DNA was dissolved in 30 μL Tris-EDTA buffer as a template for PCR. The 28S rDNA D1-D2 region was amplified using the primers F (5′-ACCCGCTGAATTTTAAGCATA-3′) and R (5′-CCTTGGTCCGTGTTTCAAGA-3′). The amplification process consisted of an initial denaturation at 94 °C for 5 min, followed by 35 cycles of denaturation at 94 °C for 20 s, annealing at 52 °C for 20 s, and extension at 72 °C for 20 s. The final extension step was performed at 72 °C for 7 min. The PCR products were sequenced by Sangon Biotech (Shanghai, China), and the results were aligned in NCBI [23].
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Alpha-diversity indices of all samples were determined using QIIME2, and these data were subsequently analyzed using Origin 2018. Prokaryote diversity was characterized using Shannon index rarefaction curves generated using Mothur [24] and RStudio. The R package ‘ggplot2′ [25] was used to present scatter diagrams of environmental variables at different times and sites, and Origin was used to calculate the percentages of different taxa at different times and sites. MEGAN [26] was used to integrate the species abundance data from the sequencing with the taxonomy database. Predictions and annotations of functional genes were performed using the functional annotation of prokaryotic taxa (FAPROTAX) method [27]. The Mantel test was then used to determine correlations using the ‘ggcor’ package in R [28]. Redundancy analysis (RDA) was conducted using multivariate statistical analysis with Canoco5 [29] to assess the correlations between bacterial communities or samples with environmental factors. The relationships among taxa groups were computed using Galaxy (http://mem.rcees.ac.cn:8081/, accessed on 2 April 2023), and node tables and edge tables were generated as outputs [30]. These node tables and edge tables were then integrated with Gephi [31] to construct and edit the network, which allowed the visualization of positive and negative interactions among prokaryotic groups and a comparison of network prokaryotic complexity during different sampling times. LEfSe (linear discriminant analysis effect size) was utilized to evaluate the effect size and identify biomarkers based on the abundance of different OTUs [32].
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Conditions and Occurrence of Algal Blooms
We collected samples at eight stations during five months in 2021 (Figure S1). The salinity level ranged from 20 to 32 practical salinity units (PSUs). The levels of DTN (range: 7.93 to 200 μmol/L) and DON (range: 6.11 to 60 μmol/L) generally declined from March to June, and the levels of nitrate, DON, silicate, and DTN increased significantly during August. The concentration of phosphate ranged from 0.07 to 1 μmol/L, and the concentration of DOP ranged from 0.01 to 0.5 μmol/L.
Beginning in March, the DOP level had an upward trend, with some fluctuations. The chlorophyll a concentration was very low during March at all sampling stations, but it increased during subsequent months. In March, the ammonium nitrogen concentration was highest at stations A1 and A2. By late April, there was a significant decrease in ammonium nitrogen concentration at stations A1 and A2, with the ammonium nitrogen concentration at station A2 being similar to that of the other stations.
During the 5-month sampling period, we observed dominant algal species every month, and the major phytoplankton taxa were Noctiluca, Prorocentrum, Haptophyta, Heterosigma akashiwo, Karlodinium veneficum, Skeletonema costatum, Gymnodinium aeruginosum Stein, Enteromorpha prolifera, and diatoms (Table S2). In May, there was a bloom occurrence dominated by Skeletonema costatum, Heterosigma akashiwo, and Karlodinium veneficum. In August, there was a diatom bloom mainly dominated by Skeletonema costatum, with an approximate algal cell density of 2 × 106 cells/L.
3.2. Sequencing Quality and Diversity Patterns of Communities
After discarding ribosomal RNA and low-quality reads, we sequenced 40 samples, resulting in a total of 3,200,074 paired-end reads. After quality control and splicing, there were 3,193,243 clean reads. Each sample produced an average of 79,831 clean reads (range: 79,417 to 80,393), and there were 713 OTUs (Table S3). As the read count reached about 40,000, there was saturation of the rarefaction curve (Figure S2A,B) and the Shannon index curve (Figure S2C,D), indicating that most bacterial diversity was captured. The Shannon curve had the highest OTU diversity during August, followed by June, May, and April, and March. Except in June, the Shannon index of nearshore sampling locations was higher than offshore. We also calculated alpha indices to examine changes in the biodiversity of the bacterial community (Table S4). The Chao1 richness index was highest during August at station B1 and lowest during May at station B1. Analysis of the Chao1 indices and Ace indices during each month showed no obvious pattern among stations (Figure 2A). The Simpson and Shannon indices were highest during May at station A1 and lowest during June at station A3 (Figure 2B). In general, the Chao1 richness was higher at near-shore stations than offshore stations. The heterogeneity among the indices was highest at stations A1 and B1 during May, and the low Chao1 indices and high Shannon indices indicated high species evenness.
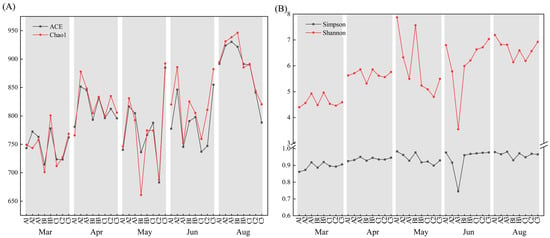
Figure 2.
Alpha diversity at the eight sample sites on the five sample dates. (A) Chao1 and ACE; (B) Shannon and Simpson.
3.3. Taxonomic Analysis and Community Structure
After removal of chimeras, chloroplasts, and other erroneous sequence data, we identified 563 species, 522 genera, 294 families, 158 orders, 49 classes, and 27 phyla using species annotation from the Ribosomal Database Project (RDP) database [33]. For visualization, we showed the relative abundances of the 10 most common phyla, classes, families, and genera, presented additional taxa as ‘others’, and presented species that lacked taxonomic annotation as ‘unclassified’ (Figure 3).
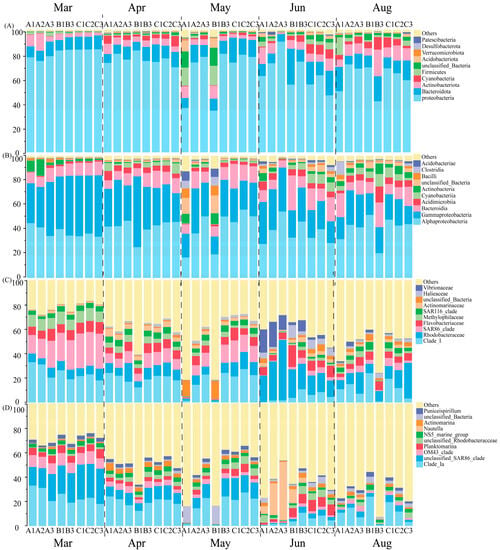
Figure 3.
Relative abundances of prokaryote pyrosequences at the level of phylum (A), class (B), family (C), and genus (D) at the eight sample sites on the five sample dates.
The ten most abundant phyla were Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Actinobacteria, Cyanobacteria, Firmicutes, Acidobacteria, Verrucomicrobia, Desulfobacterota, and Patescibacteria (Figure 3A). Proteobacteria was the predominant phylum during all five months; its abundance exceeded 80% during March and decreased to about 65% during August. Cyanobacteria had a high abundance (about 5%) during April, June, and August. During the whole sampling period, the abundance of Actinobacteriota and Bacteroidota remained relatively stable. The highest abundance of Patescibacteria (about 2%) was at station A2 during June; the highest abundance of Acidobacteria (about 10%) was at stations A1 and B1 during March; and the highest abundance of Firmicutes (about 18%) was at stations A1 and B1 during March and at station A1 during August.
The nine most abundant classes were Gammaproteobacteria, Alphaproteobacteria, Bacteroidia, Acidimicrobiia, Bacilli, Actinobacteria, Cyanobacteria, Clostridia, and Acidobacteria (Figure 3B). The abundance of Gammaproteobacteria declined over time, the abundances of Alphaproteobacteria and Bacteroidia did not change much over time, and the abundances of Acidobacteria, Bacilli, and Clostridia increased during May, June, and August. Clostridia had the highest abundance (about 15%) at station A1 during August. The abundance of Acidimicrobiia and Cyanobacteria increased over time, and the abundance of Actinobacteria was lowest during April and May.
An analysis of families indicated that the most abundant groups were Clade_Ia, Rhodobacteraceae, SAR86, Flavobacteriaceae, Methylophilaceae, SAR116, Actinomarinaceae, Vibrionaceae, and ‘others’ (Figure 3C). We identified a decrease in the abundance of SAR86 during June. Methylophilaceae, a family in the Betaproteobacteria class, had a relatively high abundance during March. During June, Vibrionaceae and SAR116 had increased abundances (in contrast to the decreases in SAR86). The abundance of Vibrionaceae was highest during June.
Analysis of genera indicated that the most abundant groups were Nautella, Clade_Ia, unclassified_SAR86_clade, OM43_clade, Planktomarina, NS5_marine_group, unclassified_Rhodobacteraceae, Candidatus_ Actinomarina, and ‘others’ (Figure 3D). Planktomarina (3–14%) and the NS5 marine group (2–6%) are known as the most common genera during coastal dinoflagellate blooms [34]. OM43 is a pivotal member of the methylotrophic bacterial community; its abundance was relatively high during March and was highest (10.7%) at station C2. Nautella was mainly present during June and had relatively high abundances at stations A1, A2, A3, B1, and B3.
3.4. Responses to Environmental Parameters
Based on the Mantel test, the community composition had significant correlations with most environmental factors, including nitrite, nitrate, silicate, temperature, salinity, DOP, and DO (Figure 4). Our examination of correlations in the ten most abundant taxa demonstrated significant correlations with temperature. The functional gene composition had a highly significant correlation with temperature and DOP and a significant correlation with silicate and DO.
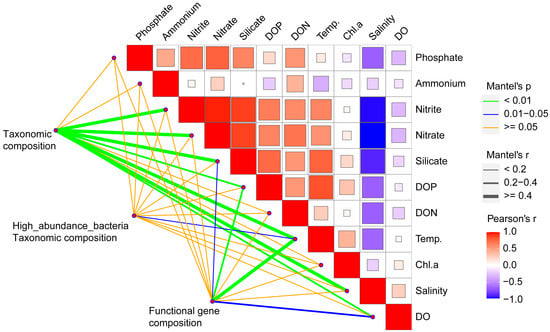
Figure 4.
Relationship of environmental factors with communities and functional genes. The relationships of different environmental factors were determined from Pearson’s correlation coefficient, and the relationships of taxonomic community composition (OTUs) and functional community composition (faprotax modules) with different environmental factors were determined using the Mantel test.
We performed an RDA analysis to further analyze the relationship of environmental factors with the structure of specific prokaryote communities (Figure 5). There were significant differences in community composition among different samples, as indicated by the clustering of sample points on the coordinate plot. At the genus level, the structure of the community was significantly influenced by temperature, silicate, DOP, and DO (Figure 5A). Nautella had a significant positive correlation with DO and a negative correlation with salinity. The abundance of Nautella during June was also substantially higher than during August (Figure 5B), possibly because the lower salinity during August was unsuitable for Nautella, which typically requires a salinity greater than 30 PSU [35,36]. The OM43_clade and the SAR86_clade had significant positive correlations with salinity and negative correlations with temperature, DOP, and silicate. Planktomarina had a significant positive correlation with salinity and a negative correlation with nitrate and nitrite (Figure 5A).
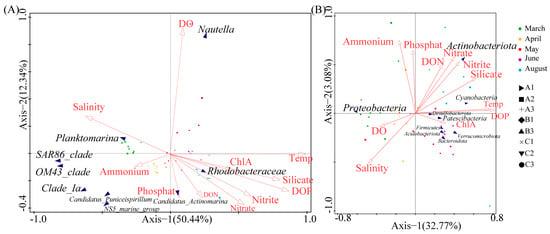
Figure 5.
Redundancy analysis of the relationship of genera (A) and phyla (B) with environmental factors. The response variables are characteristics of the community, and the explanatory variables are environmental factors and sampling characteristics.
At the phylum level, DOP, salinity, temperature, and ammonium had the greatest effects on community structure (Figure 5B). Actinobacteriota had a negative correlation with salinity; Proteobacteria had a positive correlation with DO and salinity; Desulfobacterota, Actinobacteriota, Patescibacteria, Firmicutes, Acidobacteriota, and Verrucomicrobiota had positive correlations with DON, nitrate, nitrite, silicate, temperature, and DOP; and Bacteroidota had a negative correlation with DON (Figure 5B).
3.5. Significant Biomarkers
A comparison of the spatial and temporal groups demonstrated that 96 biomarkers had LDA scores greater than 4 (27 in April, 23 in March, 18 in August, 15 in June, and 13 in May). This total included 19 biomarkers at the family level: Actinomarinaceae, Alteromonadaceae, Clade_I, Cyanobiaceae, Halieaceae, Ilumatobacteraceae, Methylophagaceae, Methylophilaceae, Microbacteriaceae, Mitochondria, Porticoccaceae, Pseudoalteromonadaceae, Rhodobacteraceae, SAR116_clade, SAR86_clade, Sphingomonadaceae, Thioglobaceae, unclassified Cyanobacteria, and Vibrionaceae (LDA score > 4, p < 0.05; Figures S3 and S4).
3.6. Network Interactions of Different Taxa with Keystone Species
We then used high-throughput sequencing data with Spearman rank correlation analysis to examine the abundance and variation of different species, with a cutoff value of 0.97 for each of the five months (Figure 6). In this analysis, we defined the keystone species as hubs and connectors, meaning that if they were eliminated, the modules and networks would not form. The five networks of communities revealed distinct patterns of co-occurrence, with the lowest network complexity during June and the highest network complexity during May (Figure 6). All five networks exhibited scale-free features, with R2 of the power law above 0.98, implying that the network structures were non-random and unlikely to be attributable to chance.
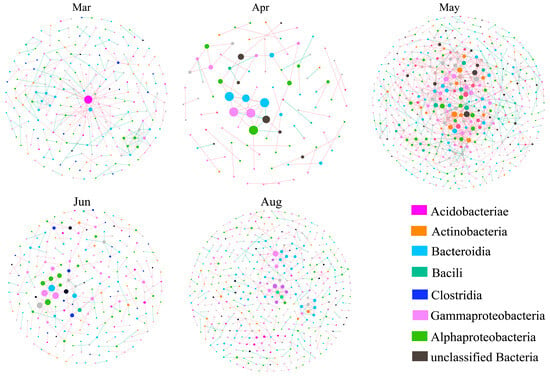
Figure 6.
Networks of bacteria during different months. Colors of nodes represent different major phyla; the top 8 modules in all OTU abundance are represented by different colors. Each circle represents an OTU, and circle size represents abundance. Each line that connects two circles represents a significant positive correlation (red) or a significant negative correlation (green).
For all months, there were no nodes on the network hubs. During April and June, all nodes were on the peripheral modules, and more than 97% of the nodes were on peripheral modules during the other months. During May, 0.8% of the nodes were on connectors, indicating that the network modules were more isolated in April and June but more tightly connected during other months (Figure S5). The co-occurrence patterns exhibited significant seasonal variations, as indicated by the topological properties of the five networks. The number of nodes ranged from 99 to 506, and the number of total links ranged from 79 to 1126. In addition, the average clustering coefficient and average degree were higher in the May network than in the other networks. Therefore, the community structure was most complex during May, followed by March and August (Table 1). In March, Acidobacteriia, Bacteroidia, Clostridia, and Flavobacteriia were identified as module hubs. In August, Gammaproteobacteria served as the module hub. The high complexity of the network in May also indicated a higher number of bacterial classes located within important modules, including Actinomycetia, Ktedonobacteria, Flavobacteriia, Alphaproteobacteria, Clostridia, and Chroobacteria, all of which were module hubs (Table S5). In the network, connectors made a greater contribution to the community structure than module hubs. Only in May, Rubrobacteria, Gammaproteobacteria, and Alphaproteobacteria were identified as connectors among all the months (Table S5).

Table 1.
Topological properties of prokaryotes and molecular ecological networks on the five different sample dates. Average degree (avgK), Average clustering coefficient (avgCC), Average path distance (GD), Centralization of degree (CD), Centralization of closeness centrality (CCL), Proportion of positive interaction (PPI), Proportion of negative interaction (PNI).
Analysis of the connections in the network demonstrated that there were mainly positive correlations, indicating more cooperation than competition (Figure 6). All keystone taxa were in the predominant phyla that were identified in large modules (Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Cyanobacteria, Actinobacteria, and Firmicutes) except for Chloroflexi, meaning that Chloroflexi had a relatively low abundance but had a significant influence (Table S5). Among all of the network nodes, the Gammaproteobacteria groups were the most abundant and had the most connections with other taxa.
4. Discussion
4.1. Correlations of Environmental Factors with Communities
During March, stations A1 and A2 had the highest recorded concentrations of ammonium. This may be related to the large-scale cultivation of nori seaweed at these two stations. In particular, during the March harvest period, workers added urea, ammonium chloride, and other fertilizers to increase growth. By the end of April, the harvest was completed, and no more fertilizers were added. These nutrient additions during March stimulated the growth of phytoplankton, which consumed the ammonium. Therefore, the concentration of ammonium at stations A1 and A2 decreased significantly during late April.
Our results demonstrated that the structure of the bacteria community that co-exists with phytoplankton in Haizhou Bay was significantly co-related to temperature, salinity, silicate, nitrate, and nitrite. The results of our short-term study showed that high temperature had a significant positive effect in promoting the growth of most prokaryotes, especially high-abundance bacteria (Figure 4). Temperature can influence the cycling of nutrients within the water column and affect the diversity of planktonic bacteria [37]. During our study period, the surface water temperature increased from 7 °C in March to about 27 °C in August, creating an increasingly favorable environment for planktonic eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Our analysis using the Mantel test also indicated that temperature had the greatest impact on the bacterial community and distribution of functional genes in Haizhou Bay. A recent long-term study indicated that as the climate warms, certain prokaryotic groups that can form spores, such as Firmicutes and Actinobacteria, are more likely to survive than microbial groups such as Acidobacteria, Verrucomicrobia, and Planctomycetes [38]. Cyanobacteria showed a significant positive correlation with DON, nitrate, nitrite, and phosphate but had a weak correlation with dissolved organic phosphorus (DOP) (Figure 5B). The sampling sites were located in the coastal area of Haizhou Bay, where runoff reduced salinity and brought in nutrients, leading to increased concentrations of N and P. A previous study indicated that the formation of Cyanobacteria blooms is strongly influenced by N and P concentrations [39]. Therefore, we hypothesize that environments with high total nitrogen to DOP ratios are suitable for the growth of Cyanobacteria.
4.2. Keystone Prokaryotic Taxa during HABs
Module hubs and connectors are often considered keystone species, and they have varying degrees of importance in maintaining network structure [40,41]. In the present study, most of the keystone taxa were different during March, May, and August, although some taxa (Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, and Bacteroidetes) were generally more likely to be keystones, indicating that different keystone taxa can play critical roles in aquatic communities [40]. The allocation of keystone species to different OTUs suggests that HABs can alter the topological roles of individual OTUs and keystone species. The copiotrophic taxa (especially Proteobacteria), including OTU2199, OTU89, OTU90, OTU596, and OTU667, functioned as module hubs or connectors in the network and established a network structure during different months, particularly May and August (Table S5, Figure 6). These results are consistent with the results of previous studies in the Florida Reef Tract (United States) [42] and of a bloom in Jangmok Bay (Korea) [43].
Some Cyanobacteria can form dense blooms and provide oxygen, organic carbon, and fixed nitrogen to heterotrophic bacteria [44]. In our co-occurrence network of May, Cyanobacteria was highly connected to other nodes. Species in this genus tend to form dense blooms when there is abundant phosphorus [44]. In agreement, our RDA and Spearman correlation analyses showed that Cyanobacteria had a strong correlation with DOP and temperature. We also found that the abundance of Cyanobacteria increased over time and that the highest abundance was during August. Most species of Cyanobacteria that form blooms achieve maximal growth rates at temperatures exceeding 25 °C [45]. Since 2004, algae blooms have occurred almost every year in Haizhou Bay, but Cyanobacteria bloom has never been observed (Table S1). This may be because the other environmental conditions in Haizhou Bay were unsuitable for these blooms or because feeding by zooplankton suppressed these blooms [46].
Most keystone species influence ecosystems because of their high abundance. However, we identified that some highly connected keystone taxa had relatively low abundance, such as Ktedonobacteria (phylum Chloroflexi), Chroobacteria, and Rubrobacteria. This suggests that taxa with low abundance can also play important roles in maintaining the network structure of a prokaryotic community. For example, species in the genus Ktedonobacteria generally thrive in oligotrophic and extreme environments, and their ability to form spores may help them survive in resource-depleted and resource-rich environments [38,47]. Furthermore, Ktedonobacteria can degrade cellulose, similar to Actinomycetes [48]. Thus, even though these taxa are rare, they may provide supplemental or unique metabolic pathways that support the whole community.
4.3. Correlations of Different Prokaryotes with Species Responsible for HABs
The interactions of the photosynthetic microbes in phytoplankton with chemosynthetic prokaryotes are complex and related to many physical and ecological variables. HABs commonly occur in estuarine and coastal marine ecosystems and can have notable effects on the diversity and composition of the bacterial community [49]. Noctiluca scintillans has a high global prevalence and is responsible for HABs in numerous coastal waters, including Haizhou Bay [50]. In the present study, Noctiluca scintillans was the predominant phytoplankton species at all sample sites during March. Previous studies estimated that a single Noctiluca cell can accommodate as many as 106 bacteria, mostly species in the Gammaproteobacteria [51,52]. Zhang et al. investigated the population dynamics of free-living and attached bacteria during multiple blooms of Noctiluca scintillans and Mesodinium rubrum. They showed that the dominant taxa (Flavobacteriaceae, Rhodobacteraceae, and SAR11 subclade I) had varying degrees of correlation with bloom-causing species and environmental factors [49]. Consistent with these studies, we found that Gammaproteobacteria was the dominant class, and Flavobacteriaceae, Rhodobacteraceae, and Clade_I (SAR11 clade) were the major families in our March samples (Figure S6). Furthermore, the genus Glaciecola had low abundance throughout the entire sampling period, except during March. This could be attributed to the lower temperature (<10 °C) during March, a condition favorable for the growth of psychrophilic bacteria.
During April, the waters of Haizhou Bay had an abundance of Prorocentrum, Haptophyta, and Karlodinium veneficum. Recently, Tarazona-Janampa et al. investigated bacteria that were associated with the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima using amplification of the 16S rRNA gene marker [53]. They identified 21 associated genera in the Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, and Bacteroidetes phyla. Relative to samples collected during March, our April data demonstrated that the abundances of SAR86_clade, OM43_clade, and Planktomarina were decreased, but the abundances of Rhodobacteraceae, Candidatus, and Actinomarina were increased. SAR86, which is in the Gammaproteobacteria class, is widely distributed in the surface waters of the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans and is a dominant family in these regions [54,55]. Karlodinium veneficum is a cosmopolitan, naked, and toxic species of dinoflagellate that forms HABs. A recent study identified a core bacterial microbiome in 19 strains of Karlodinium veneficum that were isolated from six different geographic locations and were maintained in laboratory culture for several months to more than 14 years [53]. These researchers identified three members of the “core” bacterial microbiome—Alteromonas, Marinobacter, and Methylophaga—that accounted for 83.25% of the total bacterial community [56]. Notably, we found that three genera—Methylophaga, Alteromonas, and Oleiphilus—had remarkably high abundance in samples from station B1 during April. We therefore speculate that the bacterial community structure at station B1 was affected by the presence of Karlodinium veneficum.
During May, we identified Heterosigma akashiwo, Karlodinium veneficum, and Skeletonema costatum in Haizhou Bay. Stations A1 and B1 had notable differences in bacterial abundance compared to the other sites during May as well as other months. Specifically, Firmicutes and Acidobacteriota had the highest abundances and Proteobacteria had the lowest abundance at these two stations. The surface chlorophyll a concentration at station B1 was 2.58 μg/L, and this concentration reached a maximum of 10.7 μg/L at a depth of 7 m (middle of the water column). This high biomass of planktonic species in the water column could have affected the structure of the bacterial community at station B1. At station A1, the chlorophyll a concentration at the surface layer was about 4 μg/L, although the high nitrate nitrogen concentration at this station (21.40 μmol/L) was likely conducive to the growth of certain bacteria. We found high abundances of Marinobacter, Ligilactobacillus, Lactobacillus, Bacteroides, Akkermansia, Bacillus, Aeromonas, Acidibacter, Acidothermus, Sphingomonas, Bradyrhizobium, and Pseudomonas in water samples from stations A1 and B1. Notably, a previous study showed that Marinobacter and Bacillus were cultivable epiphytic bacteria associated with Skeletonema dohrnii [57]. In addition, Pseudoalteromonas, Pseudomonas, Alteromonas, Hydrogenophaga, Actibacter, and Oleibacter were the dominant genera in a bloom that was mainly caused by Skeletonema costatum and Akashiwo sanguine in the area of the Xiamen Sea (China) [58].
During June, we observed an OTU abundance of Enteromorpha prolifera floating on the water surface in the northern part of station C1. This species may have originated from the Nantong coast [59,60]. There was also a diatom bloom at station A1 during June, and this bloom had high abundances of Nautella and Vibrio. Compared with dinoflagellate blooms, diatom blooms are more affected by nutrient concentrations than by temperature and the N:P ratio [61]. Runoff from rivers into the ocean increases the levels of nutrients in nearshore areas, and this can lead to HABs. Vibrio can degrade chitin and plays a significant role in the marine carbon cycle [62]. The large excess of chitin that appears after diatom mortality plays a crucial role in the growth of Vibrio [63]. We found that the abundance of Vibrio decreased as the diatom blooms formed due to the high concentration of silicates.
During August, a diatom bloom that was dominated by Skeletonema costatum occurred at station C3. In addition to this species, Gymnodinium aeruginosum Stein was also present in these samples. A unique characteristic of the community structure during August was the absence of the genus Planktomarina. Species in this genus are dominant members of the Roseobacter clade and may play a vital role in the decomposition of organic matter that is produced by phytoplankton [64]. Vitamin B is a vital biotin for host algae. Most eukaryotic phytoplankton are VB-deficient types, as they require exogenous B vitamins for growth maintenance [65]. A previous study showed that Rhodobacteraceae dominate in diatom bloom caused by Skeletonema [66]. Based on functional gene inference in the study, Rhodobacteraceae may be involved in the synthesis of vitamin B1 and B2 for the host. In this study, Rhodobacteraceae showed higher abundance in June and August, leading us to speculate that Rhodobacteraceae may be associated with Skeletonema bloom.
5. Conclusions
The results of our high-throughput sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene demonstrated seasonal variability in the bacterial diversity during multiple HABs in Haizhou Bay.
This study demonstrates that changes in environmental factors can affect the seasonal stability of microbial communities in the Haizhou Bay ecosystem that is regulated by key taxa.
To our best understanding, this study is the first to assess the diversity of the bacterial communities and their dynamics during HABs in Haizhou Bay. Our analysis of temporal dynamics demonstrated that the diversity of these communities was lowest during March and reached a peak during August. Analysis of the spatial dynamics demonstrated that diversity was higher at inshore stations than offshore except in June. The network during May was the most complex; at that time, Actinobacteria, Chloroflexi, Bacteroidetes, Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, Cyanobacteria, and Proteobacteria were module hubs, and Proteobacteria and Actinobacteria were connectors. Among all network nodes, the Gammaproteobacteria groups were most abundant and had the most connections with other taxa, which indicates that it is the most critical keystone taxa in maintaining community stability. Functional gene communities had strong correlations with temperature, moderate correlations with DOP, and weak correlations with silicate and DO. We also found that some specific taxa (e.g., Methylophaga, Alteromonas, Oleiphilus, Marinobacter, Bacillus, Nautella, and Vibrio) may be associated with the phytoplankton species that are responsible for HABs. Gammaproteobacteria is a dominant bacterial taxon, and the families Flavobacteriaceae, Rhodobacteraceae, and Clade_I (SAR11 clade) may be associated with Noctiluca. Methylophaga, Alteromonas, and Oleiphilus may be associated with Karlodinium veneficum. During May and August, algal blooms occurred in Haizhou Bay, resulting in significant differences in bacterial community structure compared to other months. Vibrionaceae may be associated with the occurrence of and decline in diatoms, and Rhodobacteraceae may be related to algal bloom caused by Skeletonema. To establish the precise roles of bacteria in regulating the onset and decline of HABs and to better understand the interactions of these prokaryotes with the species responsible for HABs, frequent and ongoing monitoring in this region is essential.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/d15101051/s1, Figure S1: Physicochemical characteristics of water samples (DOP, DTN, DTP, DON, phosphate, ammonium, nitrate, DO, nitrite, silicate, PSU, temperature, Chl a, and ratio of DTN: DTP) at the eight sample sites on the five sample dates. Figure S2: Multi-sample rarefaction curves based on sample time (A) and sample site and multi-sample Shannon curves based on sample time (C) and sample site (D). Figure S3: Cladogram based on LEfSe analysis. Figure S4: LDA values of different taxa on the five sample dates. Figure S5: Topological roles of different taxa on the five sample dates. Figure S6: Richness of different taxa during the five sample dates. Table S1: Occurrences of harmful algal species in Haizhou Bay from 2004 to 2017. Table S2: Occurrences of harmful algal species in Haizhou Bay during the study period. Table S3: Number of OTUs in each sample. Table S4: Alpha diversity metrics. Table S5: Keystone network taxa.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.Z. and T.Y.; methodology, Z.Z. and H.Z.; resources, H.Z. and T.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.Z. and H.Z.; writing—review and editing, D.Z. and T.Y.; validation, Z.Z. and H.Z.; project administration, T.Y.; funding acquisition, T.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Science & Technology Basic Resources Investigation Program of China (grant no. 2018FY100200) and the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (grant no. XDA23050302).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw sequence data were deposited in the NCBI database under the BioProject accession number PRJNA967682.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, J.W.; Wu, J.Y. Occurrence and potential risks of harmful algal blooms in the East China Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 4012–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marampouti, C.; Buma, A.G.J.; Boer, M.K. Mediterranean alien harmful algal blooms: Origins and impacts. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 3837–3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, G. A review of the current and emerging detection methods of marine harmful microalgae. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, I.S.; Pinnell, L.J.; Turner, J.W.; Abdulla, H.; Boyd, L.; Linton, E.W.; Zimba, P.V. Preliminary Assessment of Microbial Community Structure of Wind-Tidal Flats in the Laguna Madre, Texas, USA. Biology 2020, 9, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Via, C.W.; Glukhov, E.; Costa, S.; Zimba, P.V.; Moeller, P.D.R.; Gerwick, W.H.; Bertin, M.J. The Metabolome of a Cyanobacterial Bloom Visualized by MS/MS-Based Molecular Networking Reveals New Neurotoxic Smenamide Analogs (C, D, and E). Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 00316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney-Varga, J.N.; Giewat, M.W.; Savin, M.C.; Sood, S.; LeGresley, M.; Martin, J.L. Links between Phytoplankton and bacterial community dynamics in a coastal marine environment. Microb. Ecol. 2005, 49, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchan, A.; LeCleir, G.R.; Gulvik, C.A.; Gonzalez, J.M. Master recyclers: Features and functions of bacteria associated with phytoplankton blooms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patin, N.V.; Brown, E.; Chebli, G.; Garfield, C.; Kubanek, J.; Stewart, F.J. Microbial and chemical dynamics of a toxic dinoflagellate bloom. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, J.M.; Simó, R.; Massana, R.; Covert, J.S.; Casamayor, E.O.; Pedrós-Alió, C.; Moran, M.A. Bacterial Community Structure Associated with a Dimethylsulfoniopropionate-Producing North Atlantic Algal Bloom. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 4237–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorazyczewski, A.M.; Huang, I.S.; Abdulla, H.; Mayali, X.; Zimba, P.V. The Influence of Bacteria on the Growth, Lipid Production, and Extracellular Metabolite Accumulation by Phaeodactylum tricornutum (Bacillariophyceae). J. Phycol. 2021, 57, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefler, F.W.; Barbosa, M.; Zimba, P.V.; Smyth, A.R.; Berthold, D.E.; Laughinghouse, H.D. Spatiotemporal diversity and community structure of cyanobacteria and associated bacteria in the large shallow subtropical Lake Okeechobee (Florida, United States). Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1219261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sison-Mangus, M.P.; Jiang, S.; Kudela, R.M.; Mehic, S. Phytoplankton-Associated Bacterial Community Composition and Succession during Toxic Diatom Bloom and Non-Bloom Events. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 01433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajnef, R.; Quemeneur, M.; Abdennadher, M.; Walha, L.D.; Hamza, A.; Belhassen, M.; Zouari, A.B. Prokaryotic Diversity and Dynamics during Dinoflagellate Bloom Decays in Coastal Tunisian Waters. Diversity 2023, 15, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Yu, R.C.; Geng, H.X.; Li, Y.F. Increasing dominance of dinoflagellate red tides in the coastal waters of Yellow Sea, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 168, 112439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillard, R.R.L.; Hargraves, P.E. Stichochrysis immobilis is a diatom, not a chrysophyte. Phycologia 1993, 32, 234–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. Bioinformatics 2011, 17, 84784389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoc, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnepenninckx, B.; Backeljau, T.; De Wachter, R. Extraction of high molecular weight DNA from molluscs. Trends Genet. 1993, 9, 407. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.X.; Kong, F.Z.; Wang, Y.F.; Ji, N.J.; Song, M.J.; Hu, Z.X.; Niu, Z.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; et al. Newly recorded bloom-forming dinoflagellate Gymnodinium impudicum in Haizhou Bay, Yellow Sea, China. J. Oceanol. 2022, 40, 2430–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D. Reintroducing mothur: 10 Years Later. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e02343-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginestet, C. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A Stat. Soc. 2011, 174, 245–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huson, D.H.; Auch, A.F.; Qi, J.; Schuster, S.C. MEGAN analysis of metagenomic data. Genome Res. 2007, 17, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louca, S.; Parfrey, L.W.; Doebeli, M. Decoupling function and taxonomy in the global ocean microbiome. Science 2016, 353, 1272–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.Y.; Zhou, L.; Chen, J.; Wei, T.Y. ggcor: Extended Tools for Correlation Analysis and Visualization. R Package Version 0.9.8 2020. Available online: https://github.com/hannet91/ggcor (accessed on 22 April 2023).
- Braak, C.; Šmilauer, P. Canoco Reference Manual and User’s Guide: Software of Ordination (Version 5.0); Microcomputer Power: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2012; 496p. [Google Scholar]
- Sloggett, C.; Goonasekera, N.; Afgan, E. BioBlend: Automating pipeline analyses within Galaxy and CloudMan. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1685–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian, M.; Heymann, S.; Jacomy, M. Gephi: An Open Source Software for Exploring and Manipulating Networks. In Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, San Jose, CA, USA, 17–20 May 2009; Volume 3, pp. 361–362. [Google Scholar]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maidak, B.L.; Olsen, G.J.; Larsen, N.; Overbeek, R.; McCaughey, M.J.; Woese, C.R. The RDP (Ribosomal Database Project). Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 109–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Jiao, N.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; He, C.; Liang, X.J.; Cai, R.H.; Shi, Q.; Tang, K. Opportunistic bacteria with reduced genomes are effective competitors for organic nitrogen compounds in coastal dinoflagellate blooms. Microbiome 2021, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arahal, D.R.; Garcıa, M.T.; Vargas, C.; Canovas, D.; Nieto, J.J.; Ventosa, A. Chromohalobacter salexigens sp. nov., a moderately halophilic species that includes Halomonas elongata DSM 3043 and ATCC 33174. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Micr. 2001, 51, 1457–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandecandelaere, I.; Nercessian, O.; Segaert, E.; Achouak, W.; Mollica, A.; Faimali, M.; Vandamme, P. Nautella italica gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from a marine electroactive biofilm. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yu, S.; He, R.X.; Song, A.; Huang, Y.D.; Jin, Z.J.; Liang, Y.M.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.H.; Mueller, W.E.G.; Cao, J.H. Spatial and temporal dynamics of bacterioplankton community composition in a subtropical dammed karst river of southwestern China. Microbiologyopen 2019, 8, e00849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.W.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Ning, D.L.; Zhou, X.S.; Feng, J.J.; Yuan, M.M.; Liu, S.; Guo, J.J.; Gao, Z.P.; et al. Reduction of microbial diversity in grassland soil is driven by long-term climate warming. Nat. Microbiol. 2022, 7, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKindles, K.M.; Zimba, P.V.; Chiu, A.S.; Watson, S.B.; Gutierrez, D.B.; Westrick, J.; Kling, H.; Davis, T.W. A Multiplex Analysis of Potentially Toxic Cyanobacteria in Lake Winnipeg during the 2013 Bloom Season. Toxins 2019, 11, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Schlaeppi, K.; van der Heijden, M.G.A. Keystone taxa as drivers of microbiome structure and functioning. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Q.; Lu, X.; Li, Z.Q.; Cheng, Q.; Zhou, Y.M.; Lei, M. Liming alters microbial community composition and its co-occurrence patterns in Cd- and Pb-contaminated agricultural soil. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2021, 166, 104064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laas, P.; Ugarelli, K.; Absten, M.; Boyer, B.; Briceno, H.; Stingl, U. Composition of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Microbial Communities in Waters around the Florida Reef Tract. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.S.; Park, J.S.; Jung, S.W.; Kim, H.J.; Joo, H.M.; Kang, D.; Seo, H.; Kim, S.; Jang, M.C.; Lee, K.W.; et al. Zooming on dynamics of marine microbial communities in the phycosphere of Akashiwo sanguinea (Dinophyta) blooms. Mol. Ecol. 2021, 30, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, J.; Codd, G.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Ibelings, B.W.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Visser, P.M. Cyanobacterial blooms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paerl, H.W.; Otten, T.G. Harmful cyanobacterial blooms: Causes, consequences, and controls. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 995–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohrlack, T.; Dittmann, E.; Henning, M.; Börner, T.; Kohl, J.G. Role of Microcystins in Poisoning and Food Ingestion Inhibition of Daphnia galeata Caused by the Cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 737–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Saitou, A.; Wang, C.M.; Toyoda, A.; Minakuchi, Y.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Ueda, K.; Takano, H.; Sakai, Y.; Abe, K.; et al. Genome Features and Secondary Metabolites Biosynthetic Potential of the Class Ktedonobacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Maruoka, M.; Nanatani, K.; Hidaka, M.; Abe, N.; Kaneko, J.; Sakai, Y.; Abe, K.; Yokota, A.; Yabe, S. High cellulolytic potential of the Ktedonobacteria lineage revealed by genome-wide analysis of CAZymes. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2021, 131, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Xia, X. Community Dynamics of Free-Living and Particle-Attached Bacteria over Sequential Blooms of Heterotrophic Dinoflagellate Noctiluca scintillans and Mixotrophic Ciliate Mesodinium rubrum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e0132322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Lin, H.; Peng, C.H.; Sun, L.; Gao, Y.H.; Chen, B.H. Long-term changes in Noctiluca scintillans blooms along the Chinese coast from 1933 to 2020. Glob. Chang Biol. 2023, 29, 5099–5113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibold, A.; Wichels, A.; Schütt, C. Diversity of endocytic bacteria in the dinoflagellate Noctiluca scintillans. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2001, 25, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.X.; Ki Leung, S.; Cheung, S.Y.; Zhang, S.W.; Liu, H.B. Rare bacteria in seawater are dominant in the bacterial assemblage associated with the Bloom-forming dinoflagellate Noctiluca scintillans. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 135107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarazona-Janampa, U.I.; Cembella, A.D.; Pelayo-Zárate, M.C.; Pajares, S.; Márquez-Valdelamar, L.M.; Okolodkov, Y.B.; Tebben, J.; Krock, B.; Durán-Riveroll, L.M. Associated Bacteria and Their Effects on Growth and Toxigenicity of the Dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima Species Complex from Epibenthic Substrates Along Mexican Coasts. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 00569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R.M.; Vergin, K.L.; Cho, J.C.; Rappe, M.S.; Carlson, C.A.; Giovannoni, S.J. Temporal and spatial response of bacterioplankton lineages to annual convective overturn at the Bermuda Atlantic Time-series Study site. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 1687–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treusch, A.H.; Vergin, K.L.; Finlay, L.A.; Donatz, M.G.; Burton, R.M.; Carlson, C.A.; Giovannoni, S.J. Seasonality and vertical structure of microbial communities in an ocean gyre. ISME J. 2009, 3, 1148–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.Y.; Wang, K.; Hu, Z.X.; Hu, Q.; Tang, Y.Z. Identification and implications of a core bacterial microbiome in 19 clonal cultures laboratory-reared for months to years of the cosmopolitan dinoflagellate Karlodinium veneficum. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 967610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.R.; Sun, J. Bacterial Transformation and Processing of Diatom-Derived Organic Matter: A Case Study for Skeletonema dohrnii. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 840564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Li, D.; Tian, Y.; Zheng, T. Dynamics of bacterial community during the bloom caused by Skeletonema costatum and Akashiwo sanguinea in Xiamen sea area. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2012, 52, 1268–1281. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.L.; Xiao, J.; Fan, S.L.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.Q.; Liu, D.Y. Who made the world’s largest green tide in China?—An integrated study on the initiation and early development of the green tide in Yellow Sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2015, 60, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.-J.; Liu, D.-Y.; Anderson, D.M.; Valiela, I. Introduction to the Special Issue on green tides in the Yellow Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 163, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, R.; Cao, Z.; Ismar-Rebitz, S.M.H.; Sommer, U.; Zhang, H.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, M. Responses of Marine Diatom-Dinoflagellate Competition to Multiple Environmental Drivers: Abundance, Elemental, and Biochemical Aspects. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 731786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, M.T.; Wood, D.N.; Yu, L.; Kirchman, D.L. Selected Chitinase Genes in Cultured and Uncultured Marine Bacteria in the α- and γ-Subclasses of the Proteobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzulli, L.; Grande, C.; Reid, P.C.; Hélaouët, P.; Edwards, M.; Höfle, M.G.; Brettar, I.; Colwell, R.R.; Pruzzo, C. Climate influence on Vibrio and associated human diseases during the past half-century in the coastal North Atlantic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, e5062-71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, M.; Borges, N.; Silva, S.G.; da Rocha, U.N.; Lago-Lestón, A.; Keller-Costa, T.; Costa, R.; Stewart, F.J. Metagenome-Assembled Genome Sequences of Three Uncultured Planktomarina sp. Strains from the Northeast Atlantic Ocean. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2020, 9, e00127-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Droop, M.R. Vitamins, phytoplankton and bacteria: Symbiosis or scavenging? J. Plankton Res. 2007, 29, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.M.; Tang, S.; Cheng, K.K.; Cai, Z.H.; Chen, G.F.; Zhou, J. Microbial community composition and metabolic potential during a succession of algal blooms from Skeletonema sp. to Phaeocystis sp. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1147187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).