Two Species of the Family Cyatholaimidae (Nematoda: Chromadorida) from Korea †
Abstract
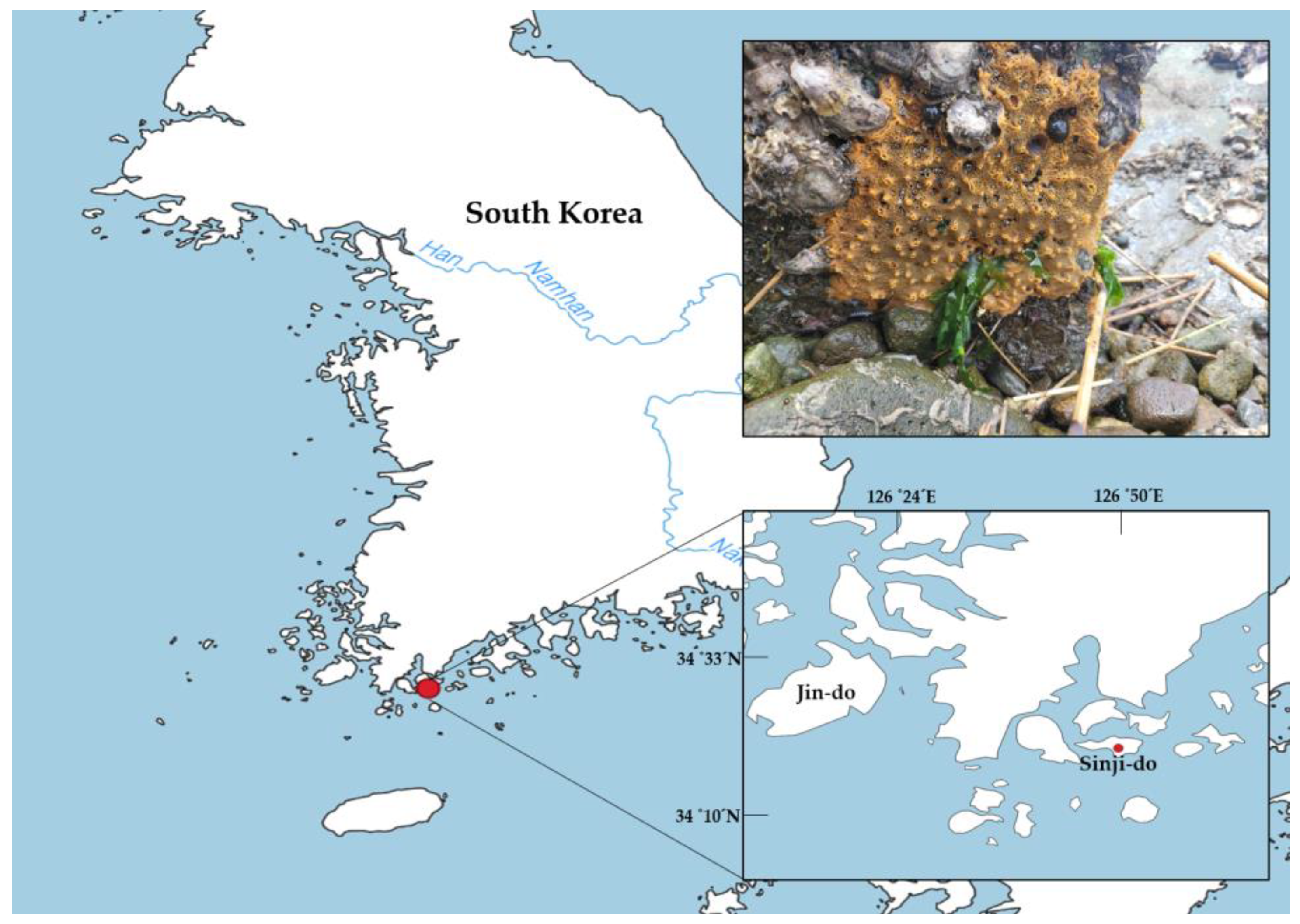
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Morphological Analysis
2.2. gDNA Extraction and Amplification
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
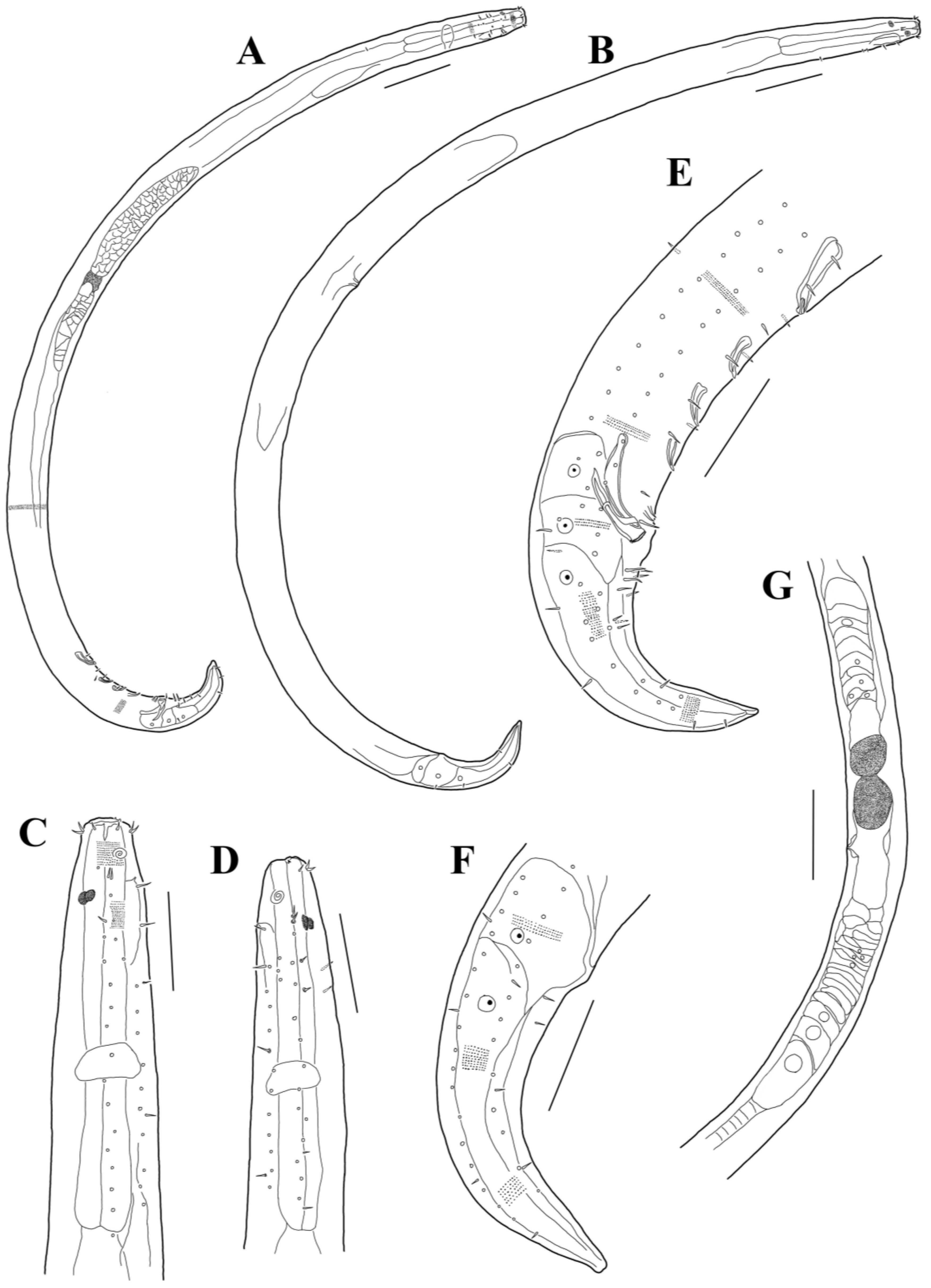
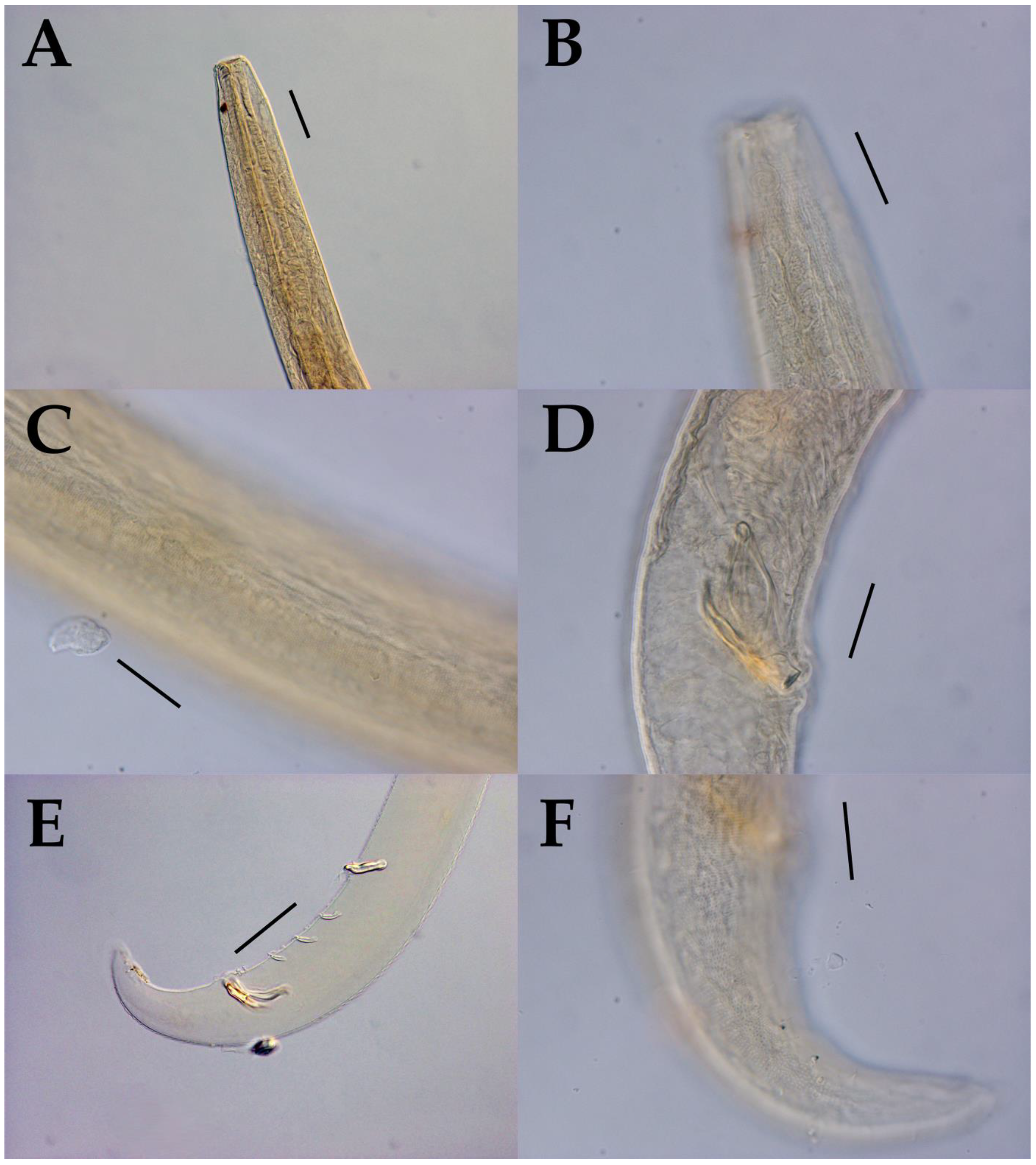
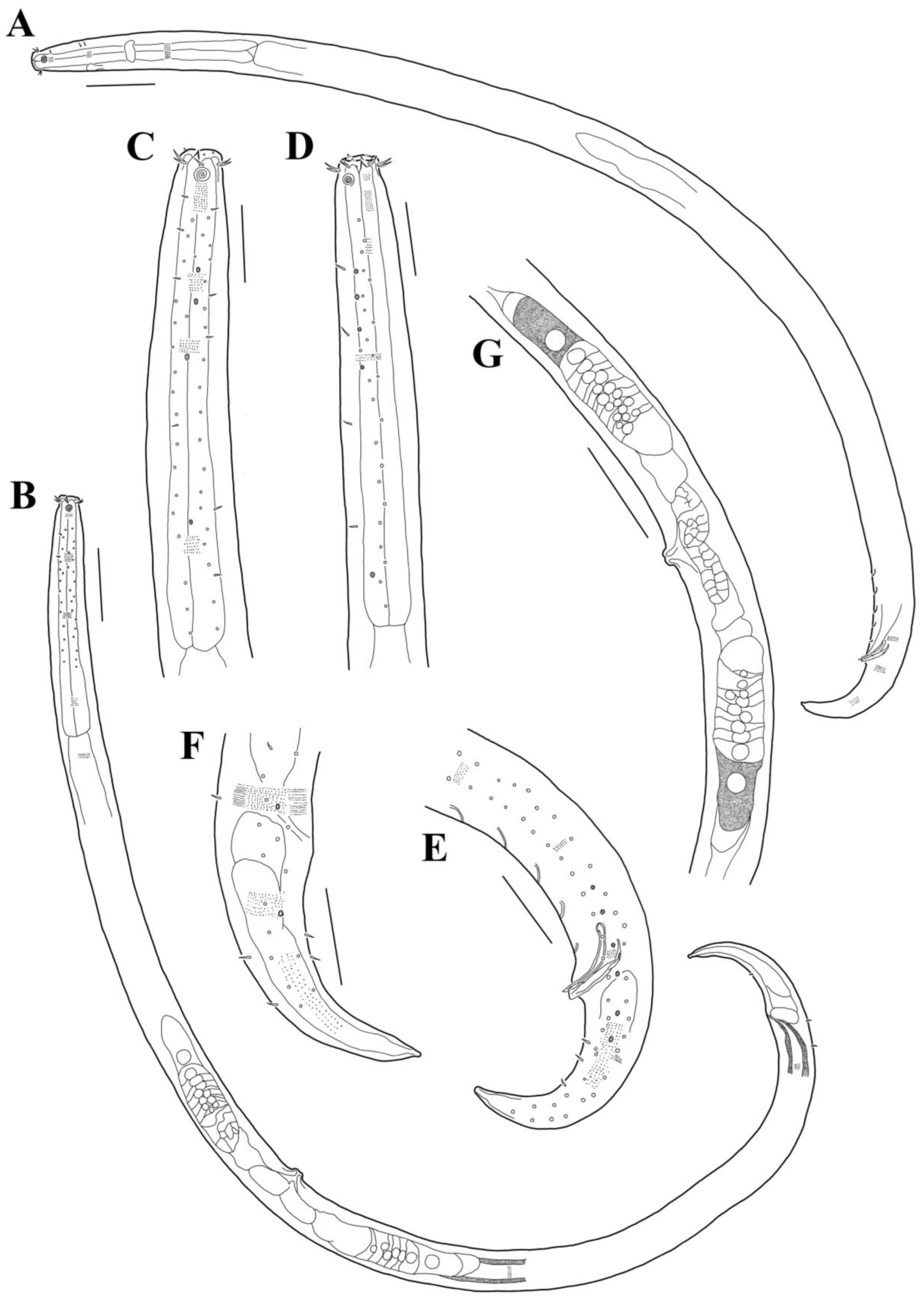
3.1. Morphological Analysis
- Class Chromadorea Inglis, 1983
- Order Chromadorida Chitwood, 1933
- Family Cyatholaimidae Filipjev, 1918 (De-Coninck & Schuurmans-Stekhoven, 1933)
- Subfamily Paracanthonchiinae De-Coninck, 1965
- Genus Acanthonchus Cobb, 1920
- Subgenus Acanthonchus (Seuratiella) (Ditlevsen, 1921) Wieser, 1955
- Acanthonchus (Acanthonchus) arcuatus (Kreis, 1928) Wieser, 1955 (Kreis, 1928: 18−20, Taf. IV, Figure 9a–f; Italy, Tarmina, intertidal, algae) [32].
- Acanthonchus (Acanthonchus) cobbi Chitwood, 1951 (Chitwood, 1951: 639, Figure 7D,E; USA, Texas, Rockport Harbor, Piling, 1 m depth) [33].
- Acanthonchus (Acanthonchus) duplicatus Wieser, 1959 (Wieser 1959: 42–43, Figure 42a,b; USA, Seatle, Vashon Island, fine to medium fine sand) [34].
- Acanthonchus (Acanthonchus) setoi Wieser, 1955 (Wieser 1955: 8–9, Figure 3a,b; Japan, Shirahama, from Sargassum on the rocks below water mark) [8].
- Acanthonchus (Acanthonchus) viviparus Cobb, 1920 (Cobb 1920: 321–323, fig 101; California, San Pedro, mud. Allgén 1947: 142, Figure 45; California, San Pedro, harbor) [35].
- Acanthonchus (Seuratiella) gracilis (Ditlevsen, 1918) Wieser, 1955 (Ditlevsen 1918: 197–198, Pl. V, Figures 1 and 9: Pl. VII, Figure 7; Denmark, among algae and hydrozoa on stones) [36].
- Acanthonchus (Seuratiella) pugionatus Vitiello, 1970 (Vitiello 1970: 474–475, Pl. VIII, Figure 17a–d; France, gulf of Marseille, 320 m depth, mud) [37].
- Acanthonchus (Seuratiella) rostratus Wieser, 1959 (Wieser 1959: 41–42, Figure 41a,b; USA, Seatle, Golden Gardens, medium fine to coarse sand, 0.5 m–1.5 m depth) [34].
- Acanthonchus (Seuratiella) singaporensis Chen Cheng-Ann, Nguyen Dinh Tu & Smol, 2015 (Chen et al., 2015: 71–73, Figures 3 and 4; Singapore, Paulo Ubin, Tanjung Tajam rocky area) [9].
- Acanthonchus (Seuratiella) tridentatus Kito, 1976 (Kito 1976: 570–573, Figure 2; Japan, Oshoro, on Sargassum in the subtidal zone. This study:) [38].
3.2. Molecular Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| a | body length divided by maximum body diameter |
| abd | anal body diameter (µm) |
| amp | transversal diameter of amphid (µm) |
| amp’ | diameter of amphid divided by corresponding body diameter |
| amp cbd | corresponding body diameter at the level of amphid (µm) |
| b | body length divided by esophagus length |
| bcl | distance from anterior edge to base of buccal cavity |
| c | body length divided by tail length |
| c’ | tail length divided by anal body diameter |
| cyln | length of cylindrical tail portion (µm) |
| CSL | cephalic sensilla length (µm) |
| das | distance from anus to most anterior supplement |
| dps | distance from anus to most posterior supplement |
| EL | distance from anterior edge to excretory pore (µm) |
| hd | head diameter (µm) |
| L | total body length (µm) |
| LSL | outer labial sensilla length (µm) |
| mbd | maximum body diameter (µm) |
| NL | distance from anterior edge to nerve ring (µm) |
| na | number of turns in amphid |
| ns | number of supplements |
| ncbd | corresponding body diameter at the level of nerve ring (µm) |
| PL | pharynx length (µm) |
| pcbd | corresponding body diameter at base of pharynx (µm) |
| s’ | spicule length as arc length divided by anal body diameter |
| spic | spicule length as arc (µm) |
| gub | gubernaculum length as arc (µm) |
| TL | tail length (µm) |
| V | vulva distance from anterior end divided by total body length |
| VL | distance from anterior end to vulva (µm) |
References
- Cunha, B.P.; Fonseca, G.; Amaral, A.C.Z. Diversity and Distribution of Cyatholaimidae (Chromadorida: Nematoda): A Taxonomic and Systematic Review of the World Records. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 836670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, W.C.; Jeong, R. Molecular Phylogeny of the Genus Paracanthonchus (Nematoda: Chromadorida) with Description of P. yeongjongensis sp. nov. from Korea. Diversity 2023, 15, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leduc, D.; Zhao, Z.Q. Phylogenetic relationships within the Cyatholaimidae (Nematoda: Chromadorida), the taxonomic significance of cuticle pore and pore-like structures, and a description of two new species. Mar. Biodivers. 2018, 48, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, B.P.; Fonseca, G.; Amaral, A.C.Z. Two new species of Cyatholaimidae (Nematoda: Chromadorida) from the Southeastern Brazilian coast with emphasis on the pore complex and lateral pore-like structures. PeerJ 2023, 11, e14712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchesunov, A.; García, P.R.; Simakova, U.; Mokievsky, V. Acanthopharynx Marine Nematodes (Nematoda, Chromadoria, Desmodoridae) Dwelling in Tropical Demosponges: Integrative Taxonomy with Description of a New Species. Diversity 2023, 15, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongers, T. Bionomics and reproductive cycle of the nematode leptosomatum bacillatum living in the sponge halichondria panicea. Neth. J. Sea Res. 1983, 17, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Hernández, J.E.; Hammerman, N.M.; Cruz-Motta, J.J.; Schizas, N.V. Associated organisms inhabiting the calcareous sponge Clathrina lutea in La Parguera, Puerto Rico. Caribb. J. Sci. 2019, 49, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieser, W. A Collection of marine nematodes from Japan. Publ. Seto Mar. Biol. Lab. 1955, 4, 159–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, C.A.; Nguyen, D.T.; Smol, N. Two new free-living marine nematode species from an intertidal sandy-rocky shore on Pulau Ubin, Singapore with a key to the valid species of the genera Prooncholaimus and Acanthonchus. Raffles Bull. Zool. 2015, (Suppl. S31), 68–74. [Google Scholar]
- Miljutina, M.A.; Miljutin, D.M. A revision of the genus Paracanthonchus (Cyatholaimidae, Nematoda) with a tabular key to species and a description of P. mamubiae sp. n. from the deep North-Western Pacific. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2015, 111, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchesunov, A. Order Chromadorida Chitwood, 1933. In Handbook of Zoology; Schmidt-Rhaesa, A., Ed.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 373–398. [Google Scholar]
- Tchesunov, A.V. Free-living nematode species (Nematoda) dwelling in hydrothermal sites of the North Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2015, 69, 343–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Jung, J.; Rho, H.S. Two unrecorded marine nematode species of Paracanthonchus (Nematoda: Cyatholaimidae) from the East Sea of Korea. J. Species Res. 2016, 5, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopper, D. Drawing and measuring nematodes. In Laboratory Methods for Work with Plant and Soil Nematodes; Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food; Her Majesty’s Stationery Office: London, UK, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodda, M. Phylum Nematoda: A classification, catalogue and index of valid genera, with a census of valid species. Zootaxa 2022, 5114, 1–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, H.; Warwick, R. Free-Living Marine Nematodes; Part 2: British Chromadorids; Linnean Society of London: London, UK, 1988; p. 502. [Google Scholar]
- Derycke, S.; Vanaverbeke, J.; Rigaux, A.; Backeljau, T.; Moens, T. Exploring the Use of Cytochrome Oxidase c Subunit 1 (COI) for DNA Barcoding of Free-Living Marine Nematodes. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carta, L.K.; Li, S. Improved 18S small subunit rDNA primers for problematic nematode amplification. J. Nematol. 2018, 50, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carta, L.K.; Li, S. PCR amplification of a long rDNA segment with one primer pair in agriculturally important nematodes. J. Nematol. 2019, 51, e2019-26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ley, P.; De Ley, I.T.; Morris, K.; Abebe, E.; Mundo-Ocampo, M.; Yoder, M.; Heras, J.; Waumann, D.; Rocha-Olivares, A.; Burr, A.J.; et al. An integrated approach to fast and informative morphological vouchering of nematodes for applications in molecular barcoding. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1945–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J.; Clustal, W. Improving the Sensitivity of Progressive Multiple Sequence Alignment through Sequence Weighting, Position-Specific Gap Penalties and Weight Matrix Choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534, Erratum in Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh, B.Q.; Nguyen, M.A.T.; Von Haeseler, A. Ultrafast Approximation for Phylogenetic Bootstrap. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; Von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and high-performance computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambaut, A. FigTree, Version 1.4.4.; Institute of Evolutionary Biology, University of Edinburgh: Edinburgh, UK, 2018.
- Kreis, H.A. Weiterer Beitrag zur Kenntnis der Freilebenden Marinen Nematoden. Arch. Naturgeschichte 1928, 92, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Chitwood, B.G. North American marine nematodes. Tex. J. Sci. 1951, 3, 617–672. [Google Scholar]
- Wieser, W. Free-living nematodes and other small invertebrates of Puget Sound beaches. Univ. Wash. Publ. Biol. 1959, 19, 1–179. [Google Scholar]
- Cobb, N.A. One hundred new nemas (type species of 100 new genera). Contrib. Sci. Nematol. 1920, 9, 217–343. [Google Scholar]
- Ditlevsen, H. Marine Freeliving Nematodes from Danish Waters. Vidensk. Meddr. Dan. Naturh. Foren. 1918, 70, 147–214. [Google Scholar]
- Vitiello, P. Nématodes libres marins des vases profondes du Golfe du Lion. II. Chromadorida. Téthys 1970, 2, 449–500. [Google Scholar]
- Kito, K. Studies on the free-living marine nematodes from Hokkaido, I.J. Fac. Sci. Hokkaido University. Ser. VI Zool. 1976, 20, 568–578. [Google Scholar]
- NemysEds. Nemys: World Database of Nematodes. 2023. Available online: https://nemys.ugent.be (accessed on 1 April 2023).


| Specimen | Species Name | Voucher Number | GenBank Accession Number | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mtCOI | 18S | D2-D3 | |||
| JB3 | 18S-CL-F | D2A | |||
| /JB5 | /530R | /D3B | |||
| (~390 bp) | (~500 bp) | (~730 bp) | |||
| 1 | Acanthonchus (Seuratiella) tridentatus | A3 | OR606577 | – | – |
| 2 | Acanthonchus (Seuratiella) tridentatus | A4 | OR606578 | – | – |
| 3 | Acanthonchus (Seuratiella) tridentatus | B2 | OR606579 | OR606555 | OR606562 |
| 4 | Acanthonchus (Seuratiella) tridentatus | C4 | OR606580 | – | OR606563 |
| 5 | Acanthonchus (Seuratiella) tridentatus | D1 | OR606581 | OR606556 | – |
| 6 | Acanthonchus (Seuratiella) tridentatus | D2 | OR606582 | OR606557 | – |
| 7 | Acanthonchus (Seuratiella) tridentatus | D3 | – | – | OR606564 |
| 8 | Acanthonchus (Seuratiella) tridentatus | D4 | OR606583 | OR606558 | – |
| 9 | Acanthonchus (Seuratiella) tridentatus | D5 | OR606584 | OR606559 | – |
| 10 | Acanthonchus (Seuratiella) tridentatus | D6 | OR606585 | OR606560 | OR606565 |
| 11 | Paracanthonchus spongius sp. nov. | A8 | OR606586 | – | – |
| 12 | Paracanthonchus spongius sp. nov. | E1 | OR606587 | – | OR606566 |
| 13 | Paracanthonchus spongius sp. nov. | E2 | OR606588 | OR606561 | OR606567 |
| 14 | Paracanthonchus spongius sp. nov. | E4 | – | – | OR606568 |
| Species | Body Length (Male) | Body Length (Female) | Lateral Differentiation of Cuticle | Development of Dorsal Tooth | Amphid Width | Turn Number of Amphid | Spicule Length as Arc | Gubernaculum Length | Number of Cusps on Distal End of Gubernaculum | Extension at the Distal End of Gubernaculum | Ocelli | Anterior Preanal Supplement Size | Difference in Size between First and Second Supplement | Number of Supplements | Tail Shape |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. (A.) arcuatus | 1184 | none | none | present | n/a | 1.5 | 31 | 29 | none | extended | none | 14 | less than 2× | 5 | conical- cylindrical or conical |
| A. (A.) cobbi | 1300 | 1500 | none | present | n/a | 3.5 | 34 | 32 | trifid claw with numerous denticles | extended | none | 24 | less than 2× | 5 | conical |
| A. (A.) duplicatus | 1940 | – | none | present | 15 | 4 | 48 | 48 | 2 denticles | extended | none | 54 | over 2× | 6 | conical |
| A. (A.) setoi | 1220 | – | only posterior | present | 12.2 | 4 | 26 | 27 | numerous denticles | extended | none | 30 | over 2× | 5 | conical |
| A. (A.) viviparus | 1300 | 1600 | anterior/posterior | present | 8 | 3.5 | n/a | n/a | none | extended | none | n/a | over 2× | 4 | n/a |
| A. (S.) gracilis | 1300 | – | none | none | 6 | n/a | 39 | 36 | none | none | present | 27 | over 2× | 4 | conical |
| A. (S.) pugionatus | 977 | – | none | present | 8.5 | 3.7–4.3 | 32 | 27 | numerous denticles | extended | present | 34 | over 2× | 6 | conical |
| A. (S.) rostratus | 1270–1540 | 1820 | anterior/posterior | weakly present | 9.5 | 2.75–3 | 46 | 42 | none | extended | present | 34 | over 2× | 6 | conical |
| A. (S.) singaporensis | 1209–1255 | – | only posterior | weakly present | 8.7–9.2 | 5.5 | 37 | 36–37 | none | extended | none | 36 | over the 2× | 6 | conical |
| A. (S.) tridentatus | 833–1350 | 810–1358 | anterior/posterior | weakly present | 5–8 | 3–3.3 | 34–40 | 26–37 | two rows small point and three large | extended | none | 26–31 | 2× | 6 | conical |
| A. (S.) tridentatus * | 1662 | 1991 | anterior/posterior | weakly present | 6.8–7.5 | 2.5–3 | 43–46 | 35–36.5 | numerous denticles | extended | present | 32.5–35 | less than 2× | 6 | conical |
| Acanthonchus (Seuratiella) tridentatus Kito, 1976 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characters | Male 1 | Male 2 | Male 3 | Female 1 | Female 2 |
| L | 1622 | 1590 | 1597 | 1991 | 1750 |
| hd | 25 | 21 | 24 | 25 | 24 |
| LSL | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 5 | 5 |
| CSL | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 5 | 5 |
| bcl | – | – | – | 10 | – |
| anterior to amp | 17 | 16 | n/a | 15.5 | n/a |
| amp | 7.5 | 6.8 | n/a | 7 | n/a |
| na | 2.5 | 2.5 | n/a | 2.5 | n/a |
| amp cbd | 30 | 28 | n/a | 29 | n/a |
| NL | 113 | 108 | 104 | 123 | 101 |
| ncbd | 45 | 45.5 | 41.5 | 52.5 | 43.5 |
| PL | 177 | 185 | 177.5 | 206.5 | 190 |
| pcbd | 48.5 | 49 | 46.5 | 57.5 | 49 |
| ep | 32 | 32 | n/a | 31 | n/a |
| Ocelli | present | present | present | present | present |
| mbd | 57 | 57 | 57 | 67.5 | 66 |
| VL | – | – | – | 944 | 843 |
| ov | – | – | – | 617 | 621 |
| abd | 51.5 | 52 | 53 | 53 | 50 |
| spia | 43 | 46 | 46 | – | – |
| gub | 35 | 38 | 36.5 | – | – |
| ns | 6 | 6 | 6 | – | – |
| dps | 8.5 | 9.5 | 10 | – | – |
| das | 115 | 120 | 120.5 | – | – |
| first supplement size | 32.5 | 35.5 | 35 | – | – |
| second supplement size | 20 | 23.5 | 19 | – | – |
| TL | 130 | 132 | 130 | 160 | 151 |
| a | 28.5 | 27.9 | 28.0 | 29.5 | 26.5 |
| b | 9.2 | 8.6 | 9.0 | 9.6 | 9.2 |
| c | 12.5 | 12.0 | 12.3 | 12.4 | 11.6 |
| c’ | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 3.0 | 3.0 |
| V | – | – | – | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| amp’ | 0.3 | 0.2 | n/a | 0.2 | n/a |
| s’ | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.9 | – | – |
| Paracanthonchus spongius sp. nov. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Characters | Holotype | Paratype (m) | Paratype (f) |
| L | 1793 | 1911 | 2145 |
| hd | 27.5 | 27 | 22.5. |
| LSL | 11.5 | 8.5 | 9 |
| CSL | 11.5 | 8.5 | 9 |
| bcl | 8 | 6 | 6 |
| anterior to amp | 9.3 | 12 | 8.7 |
| amp | 7.5 | 10 | 8 |
| na | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 |
| amp cbd | 30 | 30 | 24.5 |
| NL | 150 | 144 | n/a |
| ncbd | 48 | 52 | n/a |
| PL | 315 | 325 | 255.5 |
| pcbd | 52 | 57 | 46 |
| mbd | 60 | 67 | 68 |
| VL | – | – | 1021 |
| ov | – | – | 570 |
| abd | 49.5 | 51.5 | 50 |
| spia | 51.5 | 49 | – |
| gub | 48.5 | 47 | – |
| ns | 5 | 5 | – |
| dps | 23 | 24.5 | – |
| das | 130 | 122 | – |
| TL | 136 | 153 | 157 |
| a | 29.9 | 28.5 | 31.5 |
| b | 5.7 | 5.9 | 8.4 |
| c | 13.2 | 12.5 | 13.7 |
| c’ | 2.7 | 3.0 | 3.1 |
| V | – | – | 0.5 |
| amp’ | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| s’ | 1.0 | 1.0 | – |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.; Jeong, R. Two Species of the Family Cyatholaimidae (Nematoda: Chromadorida) from Korea. Diversity 2023, 15, 1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15101047
Kim H, Jeong R. Two Species of the Family Cyatholaimidae (Nematoda: Chromadorida) from Korea. Diversity. 2023; 15(10):1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15101047
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hyeonggeun, and Raehyuk Jeong. 2023. "Two Species of the Family Cyatholaimidae (Nematoda: Chromadorida) from Korea" Diversity 15, no. 10: 1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15101047
APA StyleKim, H., & Jeong, R. (2023). Two Species of the Family Cyatholaimidae (Nematoda: Chromadorida) from Korea. Diversity, 15(10), 1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15101047







