Assessment of Genetic Diversity and Discovery of Molecular Markers in Durian (Durio zibethinus L.) in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials, Leaf Characterization, and DNA Isolation
2.2. RAD-Seq and SNP Calling
2.3. Population Structure and Genetic Diversity Analyses
2.4. SSR Identification and Primer Design
3. Results
3.1. Summary of Sequencing and SNP Characteristics
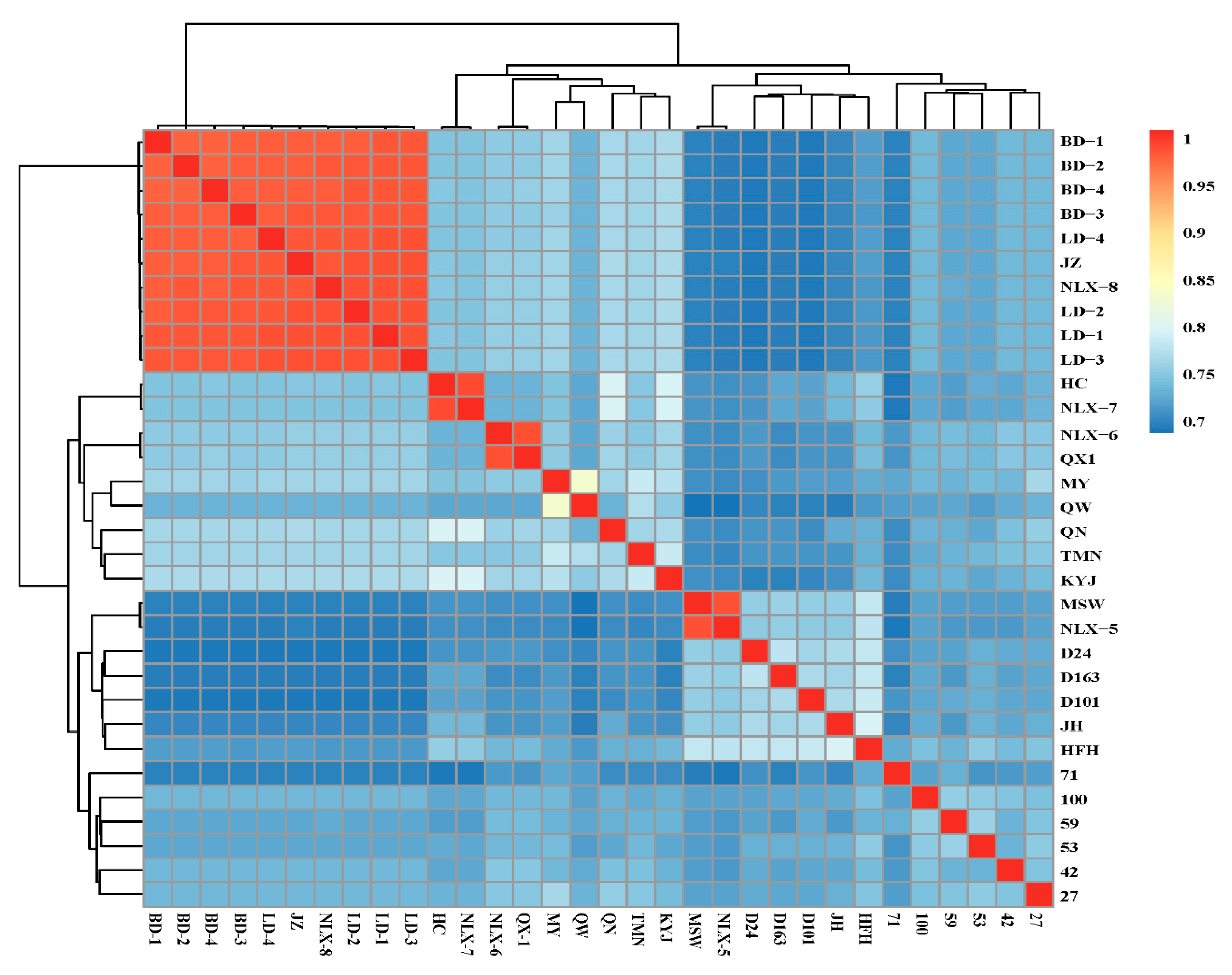
3.2. Genetic Distance of the Conserved Population of the 32 Durian Accessions
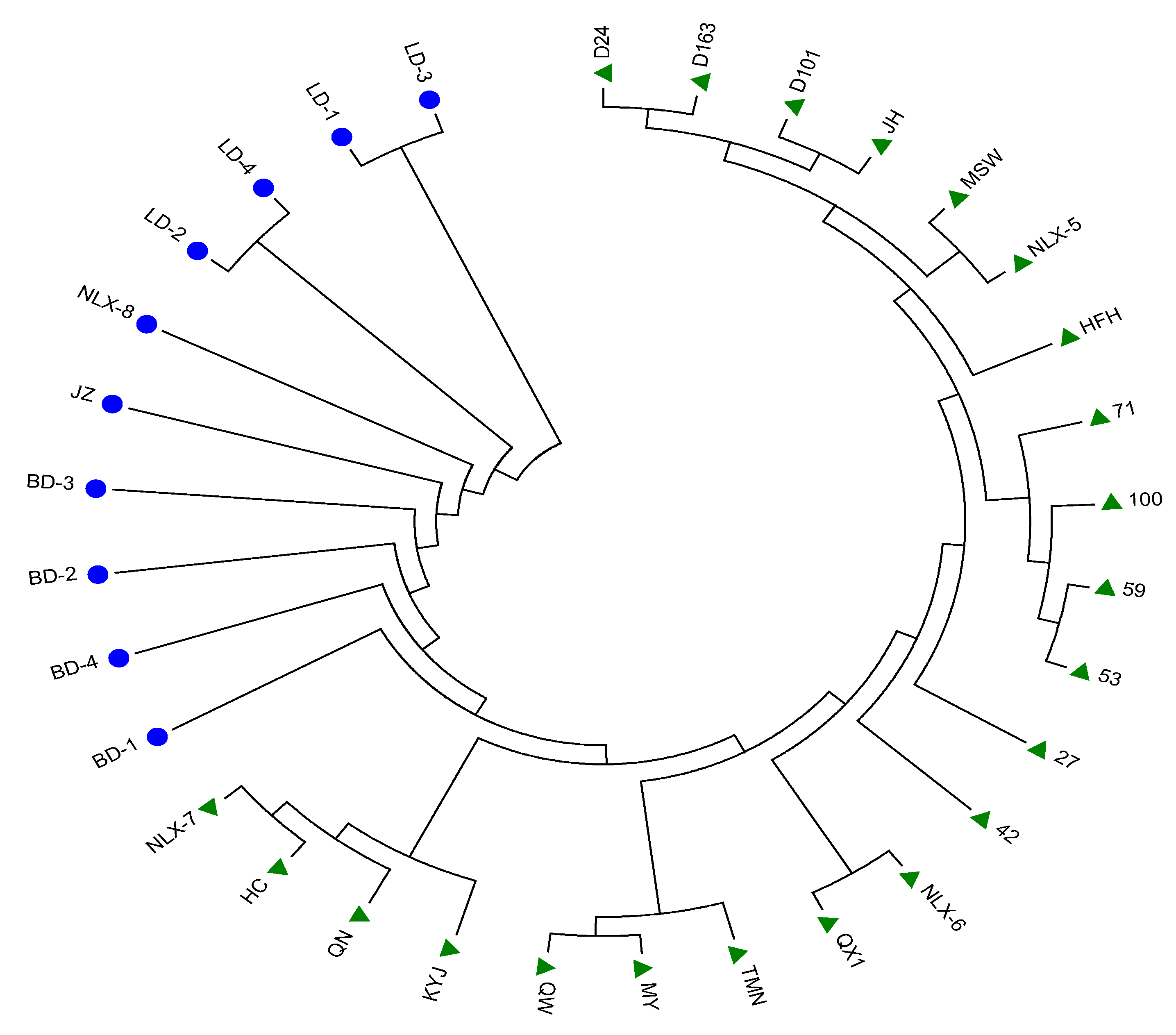
3.3. Phylogenetic Tree
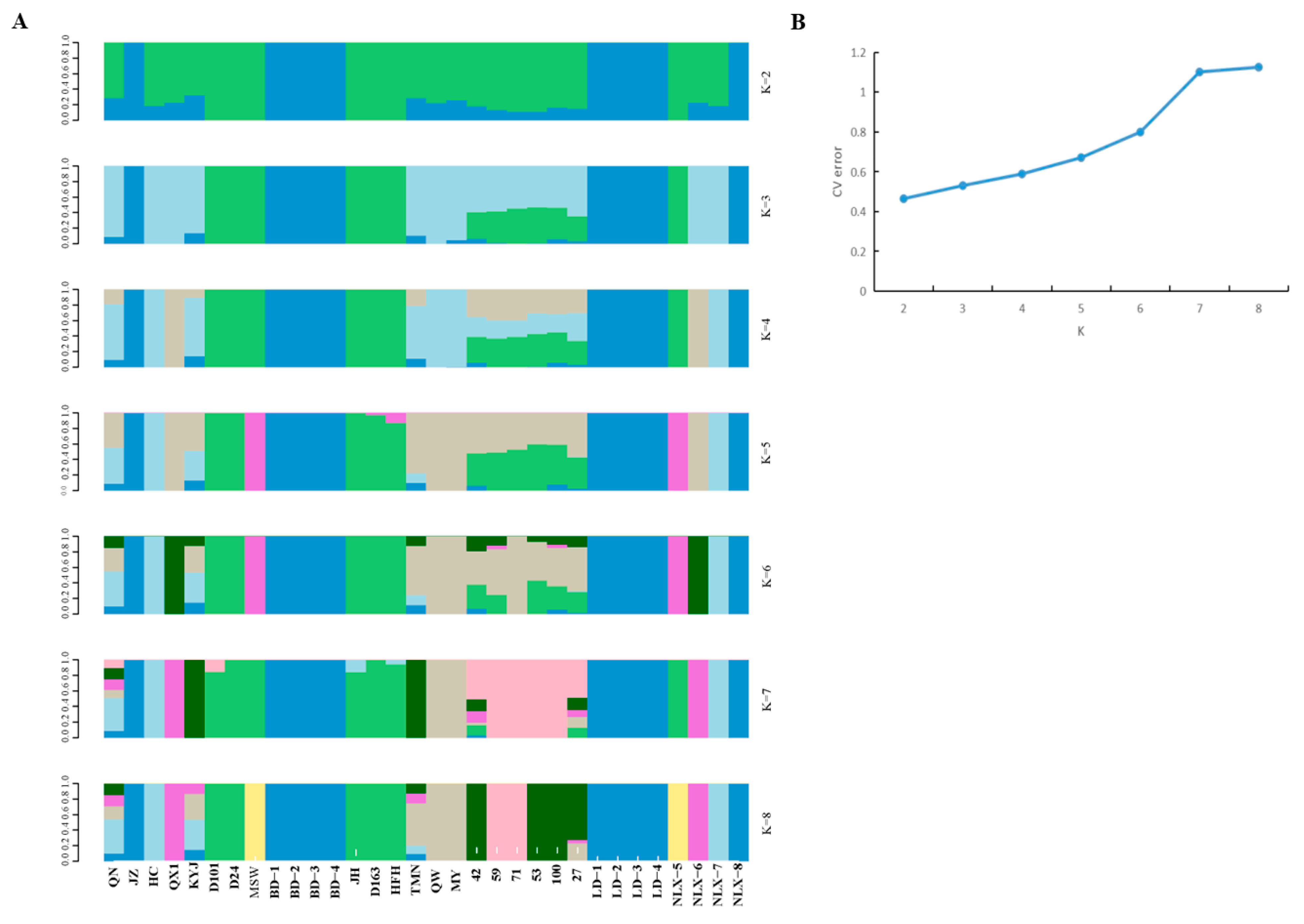
3.4. Model-Based Population Structure
3.5. Principal Component Analysis
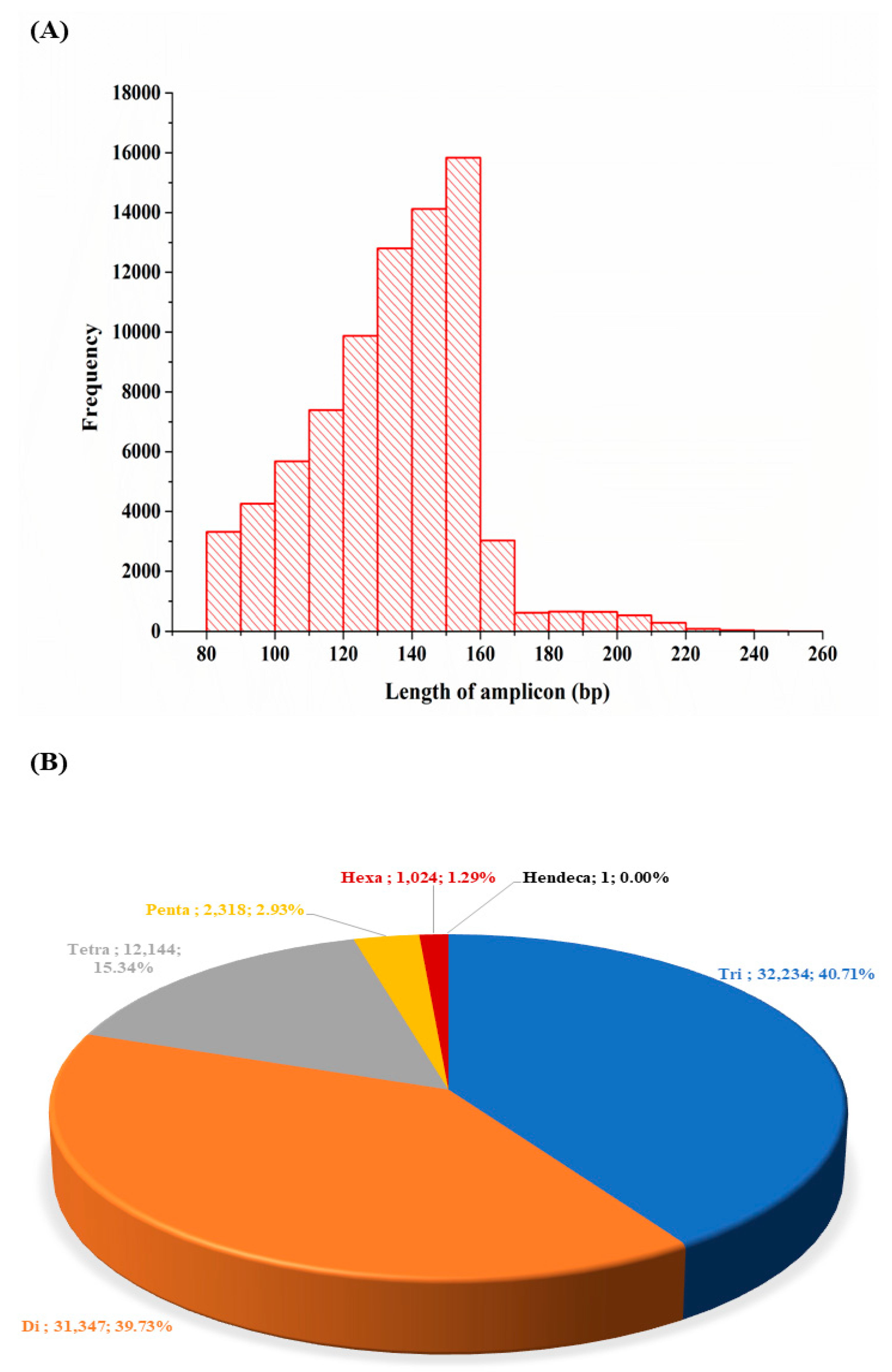
3.6. Simple Sequence Repeats Discovered and Their Characteristics
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, Y.-B. Understanding crop genetic diversity under modern plant breeding. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2015, 128, 2131–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowling, W.A.; Li, L.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Henryon, M.; Berg, P.; Banks, R.G.; Kinghorn, B.P. Evolving gene banks: Improving diverse populations of crop and exotic germplasm with optimal contribution selection. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 68, 1927–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wambugu, P.W.; Ndjiondjop, M.-N.; Henry, R.J. Role of genomics in promoting the utilization of plant genetic resources in genebanks. Briefings Funct. Genom. 2018, 17, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketsa, S.; Wisutiamonkul, A.; Palapol, Y.; Paull, R.E. The Durian: Botany, Horticulture, and Utilization. Hortic. Rev. 2020, 47, 125–211. [Google Scholar]
- Czembor, E.; Czembor, J.H.; Suchecki, R.; Watson-Haigh, N.S. DArT-based evaluation of soybean germplasm from Polish Gene Bank. BMC Res. Notes 2021, 14, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melomey, L.D.; Danquah, A.; Offei, S.K.; Ofori, K.; Danquah, E.; Osei, M. Review on tomato (Solanum lycopersicum, L.) improvement programmes in Ghana. In Recent Advances in Tomato Breeding and Production; Seloame Tatu Nyaku, A.D., Ed.; Chapter 4; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017; Volume 49, pp. 49–69. [Google Scholar]
- Teh, B.T.; Lim, K.; Yong, C.H.; Ng, C.C.Y.; Rao, S.R.; Rajasegaran, V.; Lim, W.K.; Ong, C.K.; Chan, K.; Cheng, V.K.Y.; et al. The draft genome of tropical fruit durian (Durio zibethinus). Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1633–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devran, Z.; Kahveci, E.; Hong, Y.; Studholme, D.J.; Tör, M. Identifying molecular markers suitable for Frl selection in tomato breeding. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2018, 131, 2099–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karikari, B.; Bhat, J.A.; Denwar, N.N.; Zhao, T. Exploring the genetic base of the soybean germplasm from Africa, America and Asia as well as mining of beneficial allele for flowering and seed weight. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascher, M.; Schreiber, M.; Scholz, U.; Graner, A.; Reif, J.C.; Stein, N. Genebank genomics bridges the gap between the conservation of crop diversity and plant breeding. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 1076–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, R.K.; Sinha, P.; Singh, V.K.; Kumar, A.; Zhang, Q.; Bennetzen, J.L. 5Gs for crop genetic improvement. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2020, 56, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasuriya, A.M.; Dunwell, J.M. Cacao biotechnology: Current status and future prospects. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhadrabandhu, S.; Ketsa, S. Durian: King of Tropical Fruit; Daphne Brasell Associates: Wellington, New Zealand, 2001; p. 194.
- Li, J.X.; Schieberle, P.; Steinhaus, M. Characterization of the major odor-active compounds in Thai durian ( Durio zibethinus L. ‘Monthong’) by aroma extract dilution analysis and headspace gas chromatography-olfactometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 11253–11262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinsorn, P.; Oikawa, A.; Watanabe, M.; Sasaki, R.; Ngamchuachit, P.; Hoefgen, R.; Saito, K.; Sirikantaramas, S. Metabolic variation in the pulps of two durian cultivars: Unraveling the metabolites that contribute to the flavor. Food Chem. 2018, 268, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uji, T. Keanekaragaman jenis dan sumber plasma nutfah Durio (Durio spp.) di Indonesia. Bul. Plasma Nutfah 2005, 11, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannum, S.; Wahyuningsih, H.; Sinaga, R.; Pasaribu, N.; Hartanto, A. Genetic diversity among durian (Durio zibethinus Murr.) Populations From Nias Island, Indonesia using RAPD markers. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2020, 18, 7337–7351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariyati, T.; Kusnadi, J.; Arumingtyas, E.L. Genetic diversity of hybrid durian resulted from cross breeding between Durio kutejensis and Durio zibethinus based on random amplified polymorphic DNAs (RAPDs). Am. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 3, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mursyidin, D.H.; Daryono, B.S. Genetic diversity of local durian (Durio zibethinus Murr.) cultivars of South Kalimantan’s province based on RAPD markers. AIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1755, 040008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prihatini, R.; Ihsan, F.; Indriyani, N.L.P. Genomic profiling of F1 hybrids of durian (Durio zibethinus) revealed by RAPD-PCR. J. Hortic. Res. 2016, 24, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mursyidin, D.H.; Makruf, M.I.; Badruzsaufari; Noor, A. Molecular diversity of exotic durian (Durio spp.) germplasm: A case study of Kalimantan, Indonesia. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2022, 20, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bylesjö, M.; Segura, V.; Soolanayakanahally, R.Y.; Rae, A.M.; Trygg, J.; Gustafsson, P.; Jansson, S.; Street, N.R. LAMINA: A tool for rapid quantification of leaf size and shape parameters. BMC Plant Biol. 2008, 8, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohse, M.; Bolger, A.M.; Nagel, A.; Fernie, A.R.; Lunn, J.E.; Stitt, M.; Usadel, B. RobiNA: A user-friendly, integrated software solution for RNA-Seq-based transcriptomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W622–W627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R.; Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, K. Genomic variant annotation and prioritization with ANNOVAR and wANNOVAR. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 1556–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D.H.; Lange, K. Enhancements to the ADMIXTURE algorithm for individual ancestry estimation. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolde, R. Pheatmap: Pretty heatmaps. R Package Version 2012, 1, 726. [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury, P.; Zhang, Z.; Kroon, D.; Casstevens, T.; Ramdoss, Y.; Buckler, E. TASSEL: Software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2633–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Levine, D.; Shen, J.; Gogarten, S.M.; Laurie, C.; Weir, B.S. A high-performance computing toolset for relatedness and principal component analysis of SNP data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3326–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, S.; Thiel, T.; Münch, T.; Scholz, U.; Mascher, M. MISA-web: A web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2583–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untergasser, A.; Nijveen, H.; Rao, X.; Bisseling, T.; Geurts, R.; Leunissen, J.A.M. Primer3Plus, an enhanced web interface to Primer3. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W71–W74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Raskin, L.; Samuels, D.C.; Shyr, Y.; Guo, Y. Genome measures used for quality control are dependent on gene function and ancestry. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; McDowell, I.C.; Nodzenski, M.; Scholtens, D.M.; Allen, A.S.; Lowe, W.L.; Reddy, T.E. Transversions have larger regulatory effects than transitions. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado dos Santos, J.V.; Valliyodan, B.; Joshi, T.; Khan, S.M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Vuong, T.D.; Oliveira, M.F.d.; Marcelino-Guimarães, F.C.; Xu, D.; et al. Evaluation of genetic variation among Brazilian soybean cultivars through genome resequencing. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Yan, J.; Jiang, S.; Li, X.; Min, H.; Wang, X.; Hao, D. Resequencing 250 Soybean Accessions: New Insights into Genes Associated with Agronomic Traits and Genetic Networks. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privé, F.; Luu, K.; Blum, M.G.B.; McGrath, J.J.; Vilhjálmsson, B.J. Efficient toolkit implementing best practices for principal component analysis of population genetic data. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 4449–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shendure, J.; Ji, H. Next-generation DNA sequencing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, N.M.; Gilles, L.M.; Gérentes, M.-F.; Richard, C.; Just, J.; Fierlej, Y.; Borrelli, V.M.G.; Gendrot, G.; Ingram, G.C.; Rogowsky, P.M.; et al. Single and multiple gene knockouts by CRISPR–Cas9 in maize. Plant Cell Rep. 2019, 38, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moin, M.; Bakshi, A.; Saha, A.; Dutta, M.; Kirti, P.B. Gain-of-function mutagenesis approaches in rice for functional genomics and improvement of crop productivity. Brief Funct Genom. 2017, 16, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, H.E.; Rosa-Valentin, G.; Hayes, C.M.; Rooney, W.L.; Hoffmann, L. Genomic characterization of a core set of the USDA-NPGS Ethiopian sorghum germplasm collection: Implications for germplasm conservation, evaluation, and utilization in crop improvement. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.-l.; Dong, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, C.-l.; Liu, F.; Xie, C.-X. A simple way to visualize detailed phylogenetic tree of huge genome-wide SNP data constructed by SNPhylo. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 1972–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aesomnuk, W.; Ruengphayak, S.; Ruanjaichon, V.; Sreewongchai, T.; Malumpong, C.; Vanavichit, A.; Toojinda, T.; Wanchana, S.; Arikit, S. Estimation of the Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Thailand’s Rice Landraces Using SNP Markers. Agronomy 2021, 11, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhang, S.; Gao, Q.; Liu, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. Genetic diversity and population structure analysis in a large collection of Vicia amoena in China with newly developed SSR markers. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kölliker, R.; Jones, E.S.; Jahufer, M.Z.Z.; Forster, J.W. Bulked AFLP analysis for the assessment of genetic diversity in white clover (Trifolium repens L.). Euphytica 2001, 121, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Han, C.; Zhou, J.; Hu, R.; Jiang, X.; Wu, F.; Tian, K.; Nie, G.; Zhang, X. Fingerprint identification of white clover cultivars based on SSR molecular markers. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 8513–8521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.K.; Luders, L. Boosting Durian Productivity; Publication No. 97/001W; Northern Territory Department of Primary Industry and Fisheries: Darwin, Australia, 1997.
- Yaacob, O.; Subhadrabandhu, S. The Production of Economic Fruits in South-East Asia; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Zalapa, J.E.; Cuevas, H.; Zhu, H.; Steffan, S.; Senalik, D.; Zeldin, E.; McCown, B.; Harbut, R.; Simon, P. Using next-generation sequencing approaches to isolate simple sequence repeat (SSR) loci in the plant sciences. Am. J. Bot. 2012, 99, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamblin, M.T.; Warburton, M.L.; Buckler, E.S. Empirical Comparison of Simple Sequence Repeats and Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Assessment of Maize Diversity and Relatedness. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahinnia, F.; Sayed-Tabatabaei, B.E. Conversion of barley SNPs into PCR-based markers using dCAPS method. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2009, 32, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Samples | Leaf Shape | Leaf Length | Leaf Width | Petiole Length | Leaf Base | Leaf Apex | Leaf Vein Pairs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 42 | oval | 10.9 | 3.5 | 2 | round | acuminate | 10 |
| 59 | lanceolate | 11.7 | 3.5 | 1.2 | pointed | tail tip | 9 |
| 71 | oval | 9.7 | 2.6 | 1.2 | pointed | tail tip | 9 |
| 53 | lanceolate | 10.4 | 3 | 1.1 | round blunt | tail tip | 11 |
| 100 | oval | 12.5 | 4.2 | 1.5 | pointed | acuminate | 14 |
| 27 | inverted egg shape | 10.2 | 3.1 | 1.3 | pointed | tail tip | 13 |
| BD-1 | egg shape | 7.3 | 2.7 | 1 | blunt | tail tip | 11 |
| BD-2 | long oval | 12.7 | 4.9 | 1.7 | round | tail tip | 15 |
| BD-3 | long oval | 13 | 3.8 | 1.3 | pointed | tail tip | 10 |
| BD-4 | long oval | 11.6 | 4.3 | 1.2 | round | tail tip | 7 |
| LD-1 | lanceolate | 9.1 | 2.9 | 1.9 | pointed | tail tip | 10 |
| LD-2 | lanceolate | 8.9 | 3.2 | 1.5 | pointed | tail tip | 9 |
| LD-3 | long oval | 14.5 | 4.7 | 2 | pointed | tail tip | 9 |
| LD-4 | long oval | 15.2 | 4.6 | 1.7 | round | tail tip | 13 |
| JZ | oval | 10.2 | 3.1 | 1.3 | pointed | tail tip | 13 |
| QW | egg shape | 7.4 | 2.8 | 1.4 | blunt | acuminate | 7 |
| MY | egg shape | 9.5 | 3.7 | 1.1 | blunt | tail tip | 10 |
| NLX-5 | inverted egg shape | 5.8 | 2.2 | 1.1 | tooth shape | tail tip | 9 |
| NLX-6 | lanceolate | 8.7 | 2 | 1.2 | pointed | tail tip | 7 |
| NLX-7 | long oval | 13.3 | 3.7 | 1.2 | pointed | tail tip | 15 |
| NLX-8 | long oval | 13.5 | 4.7 | 1.7 | round | tail tip | 12 |
| Category | Number of SNPs | % b |
|---|---|---|
| Upstream | 7765 | 3.36 |
| Stop gain a | 122 | 0.05 |
| Stop loss a | 19 | 0.02 |
| Synonymous a | 7914 | 3.41 |
| Non-synonymous a | 10,526 | 4.53 |
| Intronic | 31,609 | 13.62 |
| Splicing | 81 | 0.04 |
| Downstream | 8817 | 3.80 |
| upstream/downstream | 1138 | 0.49 |
| Intergenic | 152,272 | 65.59 |
| Transition (ts) | 154,899 | 66.72 |
| transversion (tv) | 77,249 | 33.28 |
| ts/tv | 2.005 | - |
| Total | 232,148 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, M.; Gao, H.; Zhu, Z.; Ding, Z.; Zhou, Z. Assessment of Genetic Diversity and Discovery of Molecular Markers in Durian (Durio zibethinus L.) in China. Diversity 2022, 14, 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14090769
Lin X, Liu X, Chen M, Gao H, Zhu Z, Ding Z, Zhou Z. Assessment of Genetic Diversity and Discovery of Molecular Markers in Durian (Durio zibethinus L.) in China. Diversity. 2022; 14(9):769. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14090769
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Xinge, Xiaodi Liu, Meigu Chen, Hongmao Gao, Zhenzhong Zhu, Zheli Ding, and Zhaoxi Zhou. 2022. "Assessment of Genetic Diversity and Discovery of Molecular Markers in Durian (Durio zibethinus L.) in China" Diversity 14, no. 9: 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14090769
APA StyleLin, X., Liu, X., Chen, M., Gao, H., Zhu, Z., Ding, Z., & Zhou, Z. (2022). Assessment of Genetic Diversity and Discovery of Molecular Markers in Durian (Durio zibethinus L.) in China. Diversity, 14(9), 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14090769







