Comparative Chloroplast Genomics and Phylogenetic Analysis of Persicaria amphibia (Polygonaceae)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling, DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.2. Assembly and Annotation
2.3. Repeat and Divergence Hotspot Analysis
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristic of the P. amphibia cp Genome
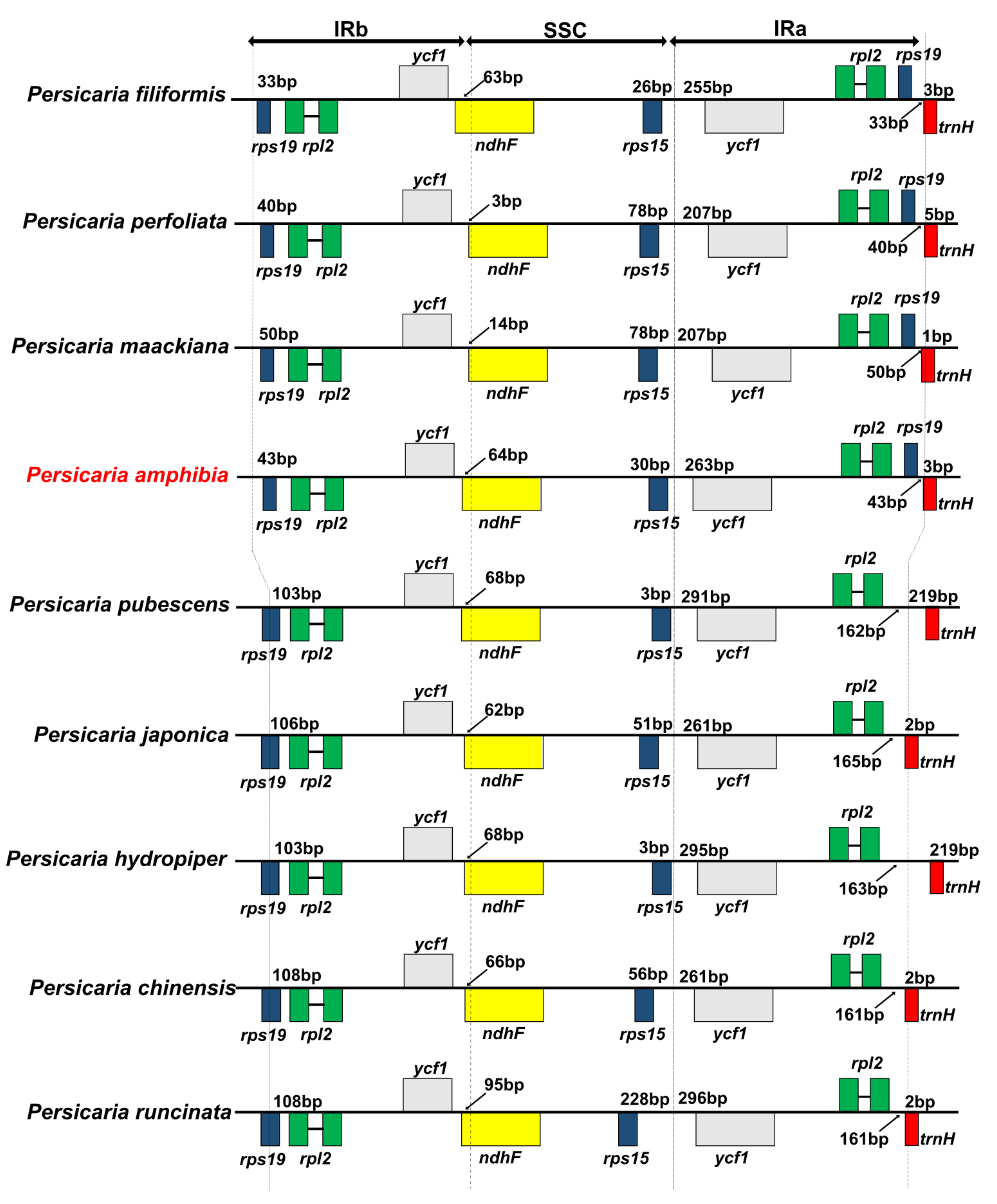
3.2. Comparison of Other Persicaria Species
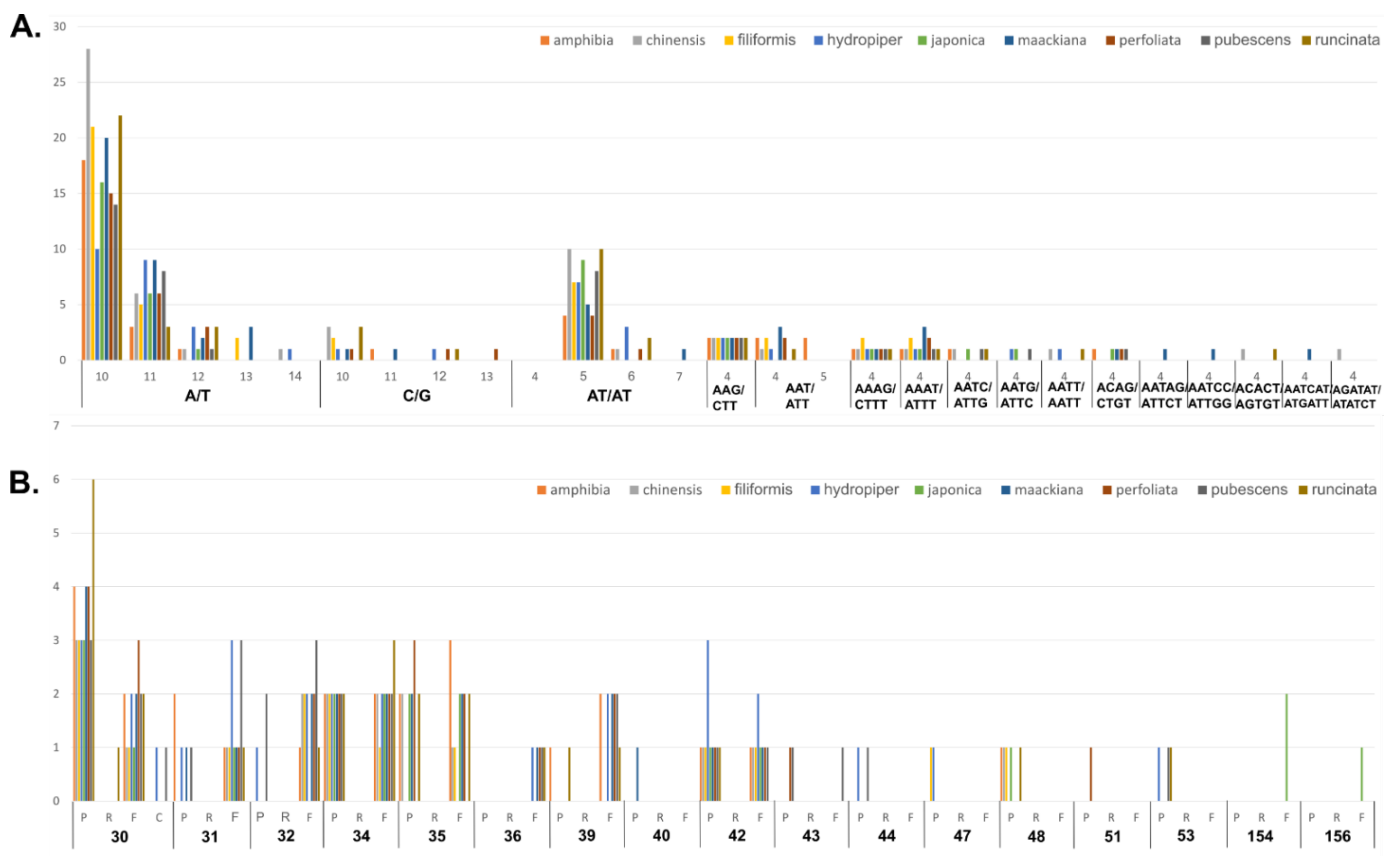
3.3. Repeat Sequence Analysis
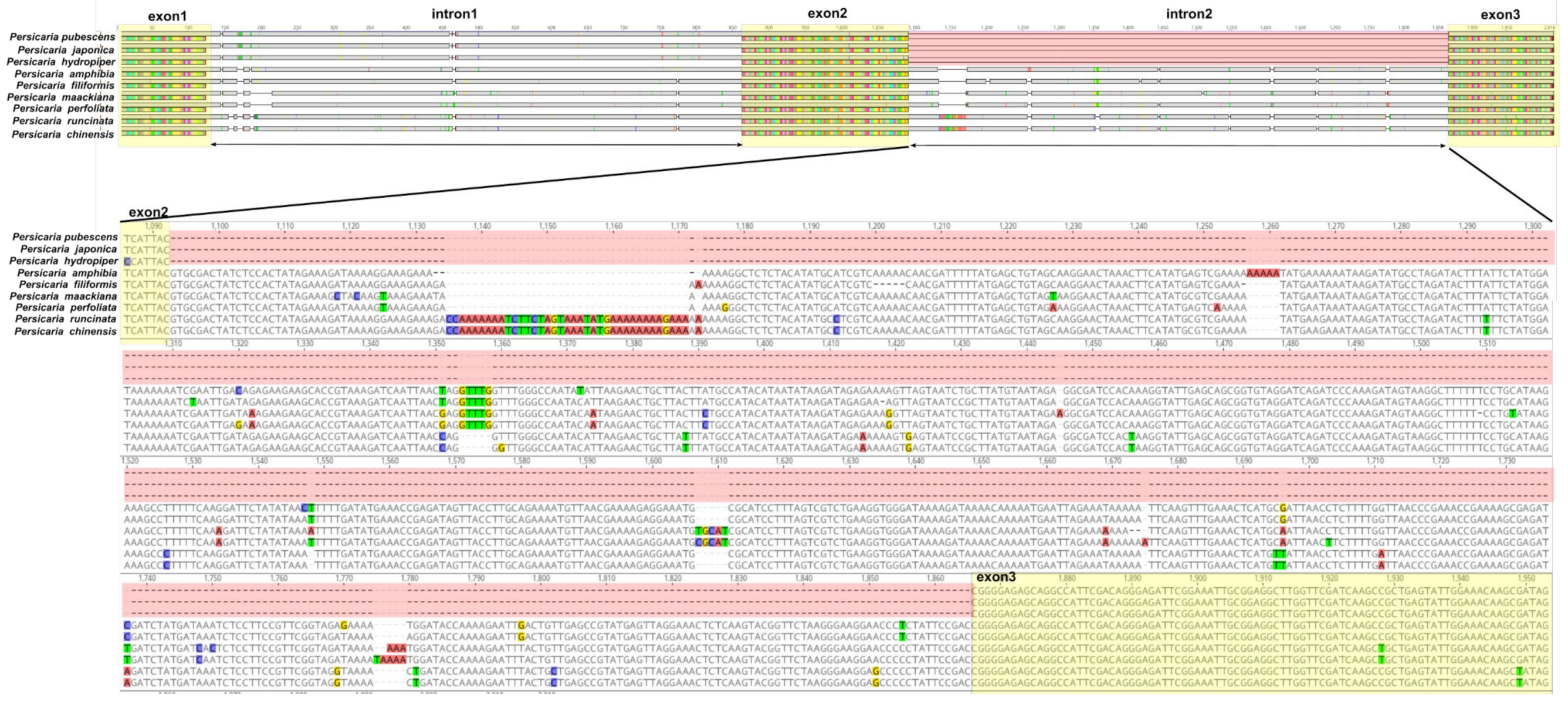
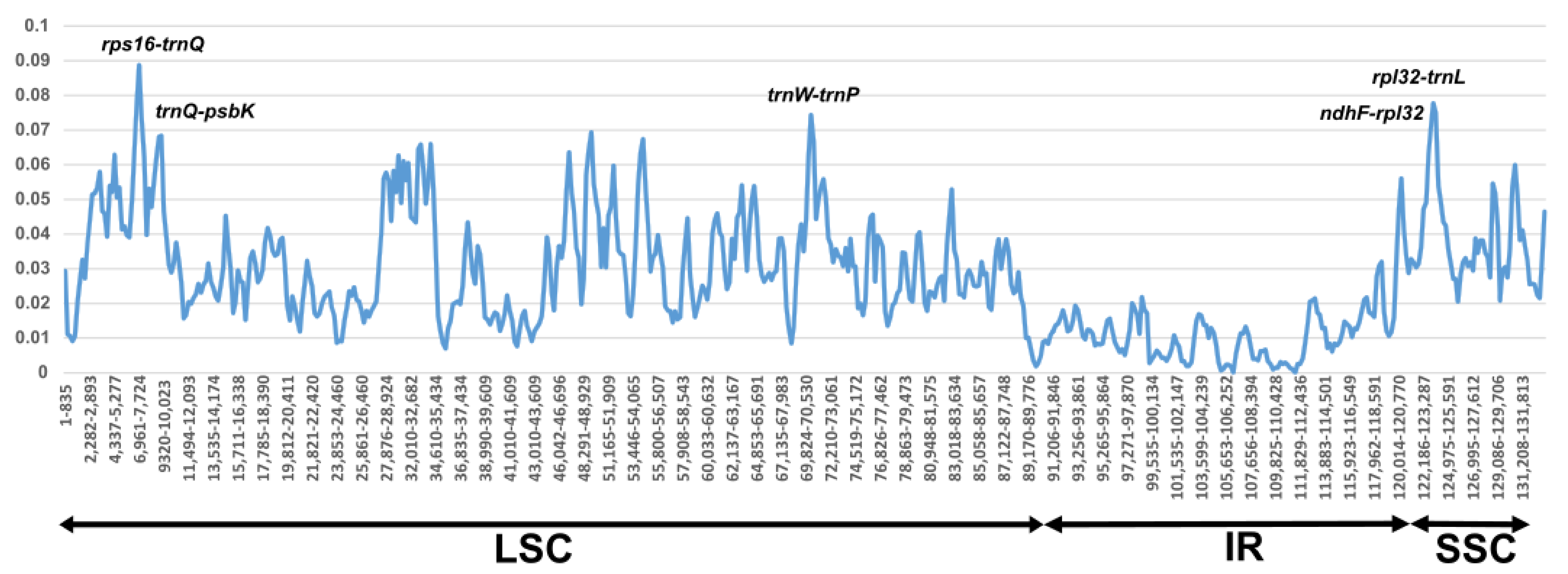
3.4. Sequences Divergence Hotspots in Persicaria
3.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, S.-T.; Sultan, S.E.; Donoghue, M.J. Allopolyploid speciation in Persicaria (Polygonaceae): Insights from a low-copy nuclear region. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 12370–12375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, A.; Schuster, T.M.; Kron, K.A. A large-Scale phylogeny of Polygonaceae based on molecular data. Int. J. Plant Sci. 2009, 170, 1044–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decraene, L.-P.R.; Akeroyd, J.R. Generic limits in Polygonum and related genera (Polygonaceae) on the basis of floral characters. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 1988, 98, 321–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galasso, G.; Ban, E.; Grassi, F.; Sgorbati, S.; Labra, M. Molecular Phylogeny of Polygonum L. s.l. (Polygonoideae, Polygonaceae), Focusing on European Taxa: Preliminary Results and Systematic Considerations Based on rbcL Plastidial Sequence Data. Atti Soc. Ital. Nat. Mus. Civ. Stor.Nat. Milano 2009, 150, 113–148. [Google Scholar]
- Gitsopoulos, T.K.; Vasilakoglou, I.; Tsoktouridis, G. Persicaria Amphibia, a serious terrestrial weed in Northern Greece: A combined molecular and morphological approach to identification and taxonomy. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2013, 27, 4236–4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-T.; Donoghue, M.J. Molecular phylogeny of Persicaria (Persicarieae, Polygonaceae). Syst. Bot. 2008, 33, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicke, S.; Schneeweiss, G.M.; dePamphilis, C.W.; Müller, K.F.; Quandt, D. The evolution of the plastid chromosome in land plants: Gene content, gene order, gene function. Plant Mol. Biol. 2011, 76, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrogojski, J.; Adamiec, M.; Luciński, R. The chloroplast genome: A review. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2020, 42, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.-S.; Fu, P.-C.; Zhou, X.-J.; Cheng, Y.-W.; Zhang, F.-Q.; Chen, S.-L.; Gao, Q.-B. The complete plastome sequences of seven species in Gentiana Sect. Kudoa (Gentianaceae): Insights into plastid gene loss and molecular evolution. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frailey, D.C.; Chaluvadi, S.R.; Vaughn, J.N.; Coatney, C.G.; Bennetzen, J.L. Gene loss and genome rearrangement in the plastids of five hemiparasites in the family Orobanchaceae. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauz-Santos, L.A.; da Costa, Z.P.; Callot, C.; Cauet, S.; Zucchi, M.I.; Bergès, H.; van den Berg, C.; Vieira, M.L.C. A repertory of rearrangements and the loss of an inverted repeat region in Passiflora chloroplast genomes. Genome Biol. Evol. 2020, 12, 1841–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.O.; Joh, H.J.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.-C.; Kim, N.-H.; Park, J.Y.; Park, H.-S.; Park, M.-S.; Kim, S.; Kwak, M.; et al. Dynamic chloroplast genome rearrangement and DNA barcoding for three Apiaceae species known as the medicinal herb “Bang-Poong”. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, T.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Lv, H.; Ren, B.; Chen, J.; Li, W. Comparison of chloroplast genomes of Gynura species: Sequence variation, genome rearrangement and divergence studies. BMC Genomics 2019, 20, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oulo, M.A.; Yang, J.-X.; Dong, X.; Wanga, V.O.; Mkala, E.M.; Munyao, J.N.; Onjolo, V.O.; Rono, P.C.; Hu, G.-W.; Wang, Q.-F. Complete chloroplast genome of Rhipsalis baccifera, the only cactus with natural distribution in the Old World: Genome rearrangement, intron gain and loss, and implications for phylogenetic studies. Plants 2020, 9, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.-Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Lü, T.-F.; Mbichi, R.W.; Wan, T.; Liu, F. The Complete chloroplast genome of Myriophyllum Spicatum reveals a 4-Kb inversion and new insights regarding plastome evolution in Haloragaceae. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 3090–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.S.; Ha, Y.-H.; Gil, H.-Y.; Choi, K.; Kim, D.-K.; Oh, S.-H. Two Korean endemic Clematis chloroplast genomes: Inversion, reposition, expansion of the inverted repeat region, phylogenetic analysis, and nucleotide substitution rates. Plants 2021, 10, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, M.T.; Gaut, B.S.; Learn, G.H.; Morton, B.R. Rates and patterns of chloroplast DNA evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 6795–6801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.-J.; Cheng, C.-L.; Chang, C.-C.; Wu, C.-L.; Su, T.-M.; Chaw, S.-M. Dynamics and evolution of the inverted repeat-large single copy iunctions in the chloroplast genomes of Monocots. BMC Evol. Biol. 2008, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Zhao, W.; Xu, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y. Chloroplast genome evolution and species identification of Styrax (Styracaceae). BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, e5364094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.S.; Chung, M.G.; Park, S. The complete chloroplast genome sequences of three Veroniceae species (Plantaginaceae): Comparative analysis and highly divergent regions. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raman, G.; Park, K.T.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, S. Characteristics of the completed chloroplast genome sequence of Xanthium spinosum: Comparative analyses, identification of mutational hotspots and phylogenetic implications. BMC Genomics 2020, 21, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, R.K.; Kaittanis, C.; Saski, C.; Lee, S.-B.; Tomkins, J.; Alverson, A.J.; Daniell, H. Phylogenetic analyses of Vitis (Vitaceae) based on complete chloroplast genome sequences: Effects of taxon sampling and phylogenetic methods on resolving relationships among Rosids. BMC Evol. Biol. 2006, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.-B.; Tang, M.; Li, H.-T.; Zhang, Z.-R.; Li, D.-Z. Complete Chloroplast genome of the genus Cymbidium: Lights into the species identification, phylogenetic implications and population genetic analyses. BMC Evol. Biol. 2013, 13, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, W.; Duan, X.; Zhang, R.; Guo, C.; Li, L.; Xu, G.; Shan, H.; Kong, H.; Ren, Y. Chloroplast genomic data provide new and robust insights into the phylogeny and evolution of the Ranunculaceae. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2019, 135, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Lan, X.; Qu, X. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Polygonum chinense L. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2020, 5, 2139–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.-J.; Yu, W.-B.; Yang, J.-B.; Song, Y.; dePamphilis, C.W.; Yi, T.-S.; Li, D.-Z. GetOrganelle: A fast and versatile toolkit for accurate de novo assembly of organelle genomes. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillich, M.; Lehwark, P.; Pellizzer, T.; Ulbricht-Jones, E.S.; Fischer, A.; Bock, R.; Greiner, S. GeSeq—Versatile and accurate annotation of organelle genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W6–W11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.P.; Lin, B.Y.; Mak, A.J.; Lowe, T.M. TRNAscan-SE 2.0: Improved detection and functional classification of transfer RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 9077–9096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, S.; Lehwark, P.; Bock, R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW) version 1.3.1: Expanded toolkit for the graphical visualization of organellar genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W59–W64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.; Choudhuri, J.V.; Ohlebusch, E.; Schleiermacher, C.; Stoye, J.; Giegerich, R. REPuter: The manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4633–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beier, S.; Thiel, T.; Münch, T.; Scholz, U.; Mascher, M. MISA-Web: A web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2583–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazer, K.A.; Pachter, L.; Poliakov, A.; Rubin, E.M.; Dubchak, I. VISTA: Computational tools for comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W273–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K. MAFFT: A novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast fourier Transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chris Blazier, J.; Guisinger, M.M.; Jansen, R.K. Recent loss of plastid-encoded ndh genes within Erodium (Geraniaceae). Plant Mol. Biol. 2011, 76, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, M.-L.; Blazier, J.C.; Govindu, M.; Jansen, R.K. Reconstruction of the ancestral plastid genome in Geraniaceae reveals a correlation between genome rearrangements, repeats, and nucleotide substitution rates. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, T.-C.; Qiao, Q.; Ren, Z.; Zhao, J.; Yonezawa, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Crabbe, M.J.C.; Li, J.; Zhong, Y. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of holoparasite Cistanche deserticola (Orobanchaceae) reveals gene loss and horizontal gene transfer from its host Haloxylon ammodendron (Chenopodiaceae). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samigullin, T.H.; Logacheva, M.D.; Penin, A.A.; Vallego-Roman, C.M. Complete plastid genome of the recent holoparasite Lathraea squamaria reveals earliest stages of plastome reduction in Orobanchaceae. PLoS ONE. 2016, 11, e0150718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhou, T.; Ruhsam, M.; Wang, J.; Zhu, H.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Xu, F.; Wang, X. The complete chloroplast genome of Euphrasia regelii, pseudogenization of ndh genes and the phylogenetic relationships within Orobanchaceae. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.-S.; Park, S. Complete plastid and mitochondrial genomes of Aeginetia indica reveal intracellular gene transfer (IGT), horizontal gene transfer (HGT), and cytoplasmic male sterility (CMS). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downie, S.R.; Llanas, E.; Katz-Downie, D.S. Multiple independent losses of the rpoC1 intron in angiosperm chloroplast DNA’s. Syst. Bot. 1996, 21, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yang, G.; Peng, J.; Peng, X. Initial characterization of the chloroplast genome of Vicia sepium, an important wild resource plant, and related inferences about its evolution. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Ye, Y.; Bai, T.; Xu, M.; Xu, L.-A. Complete chloroplast genome of Pinus massoniana (Pinaceae): Gene rearrangements, loss of ndh genes, and short inverted repeats contraction, expansion. Molecules 2017, 22, 1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, R.K.; Wojciechowski, M.F.; Sanniyasi, E.; Lee, S.-B.; Daniell, H. Complete plastid genome sequence of the Chickpea (Cicer arietinum) and the phylogenetic distribution of rps12 and clpP intron losses among Legumes (Leguminosae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 48, 1204–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Longevialle, A.F.; Hendrickson, L.; Taylor, N.L.; Delannoy, E.; Lurin, C.; Badger, M.; Millar, A.H.; Small, I. The Pentatricopeptide repeat gene OTP51 with two LAGLIDADG motifs is required for the cis-splicing of plastid ycf3 intron 2 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2008, 56, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albus, C.A.; Ruf, S.; Schöttler, M.A.; Lein, W.; Kehr, J.; Bock, R. Y3IP1, a nucleus-encoded thylakoid protein, cooperates with the plastid-encoded ycf3 protein in photosystem I assembly of Tobacco and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 2838–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, A.; Lu, C. Pentatricopeptide repeat protein PHOTOSYSTEM I BIOGENESIS FACTOR2 is required for splicing of ycf3. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2020, 62, 1741–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeal, J.R.; Kuehl, J.V.; Boore, J.L.; Leebens-Mack, J.; dePamphilis, C.W. Parallel loss of plastid introns and their maturase in the genus Cuscuta. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saski, C.; Lee, S.-B.; Fjellheim, S.; Guda, C.; Jansen, R.K.; Luo, H.; Tomkins, J.; Rognli, O.A.; Daniell, H.; Clarke, J.L. Complete chloroplast genome sequences of Hordeum vulgare, Sorghum bicolor and Agrostis stolonifera, and comparative analyses with other grass genomes. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2007, 115, 571–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.S.; Park, S. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Aster spathulifolius (Asteraceae); genomic features and relationship with Asteraceae. Gene 2015, 572, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, I.-S.; Choi, B.-H. The distinct plastid genome structure of Maackia fauriei (Fabaceae: Papilionoideae) and its systematic implications for genistoids and tribe Sophoreae. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Sha, L.-N.; Wang, Y.-L.; Yin, L.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, D.-D.; Kang, H.-Y.; Zhang, H.-Q.; Zhou, Y.-H.; et al. Variation in plastome sizes accompanied by evolutionary history in monogenomic Triticeae (Poaceae: Triticeae). Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 741063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.-S.; Li, P.; Qiu, Y.-X. The complete chloroplast genomes of three Cardiocrinum (Liliaceae) species: Comparative genomic and phylogenetic analyses. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 7, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-X.; Zhai, C.-C.; Fan, S.-J. Characterization of the complete chloroplast genome of Rumex nepalensis (Polygonaceae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2020, 5, 2458–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Fu, G.-F.; Wu, Z.-Q.; Li, L.; Zhao, J.-L.; Li, Q.-J. Chloroplast genome evolution in four Montane Zingiberaceae taxa in China. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 774482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timson, J. A study of hybridization in Polygonum Section Persicaria. J. Linn. Soc. Lond. Bot. 1965, 59, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patridge, J.W. Persicaria amphibia (L.) Gray (Polygonum amphibium L.). J. Ecol. 2001, 89, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, W.; Ye, J.; Saqib, S.; Liu, Y.; Shan, Z.; Hao, D.; Chen, Z.; Xiao, P. Predicting potential medicinal plants with phylogenetic topology: Inspiration from the research of traditional Chinese medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 281, 114515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, W.; Ye, J.; Ahmad, M.; Saqib, S.; Shinwari, Z.K.; Chen, Z. Phylogenetic exploration of traditional Chinese medicinal plants: A cse study on Lamiaceae. Pak. J. Bot. 2022, 54, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, M.N.; Yamashita, J.; Fuse, S.; Haraguchi, M. Molecular phylogeny of monocotyledons inferred from combined analysis of plastid matK and rbcL gene sequences. J. Plant Res. 2004, 117, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topik, H.; Yukawa, T.; Ito, M. Molecular phylogenetics of subtribe Aeridinae (Orchidaceae): Insights from plastid matK and nuclear ribosomal ITS sequences. J. Plant Res. 2005, 118, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokuoka, T. Molecular phylogenetic analysis of Euphorbiaceae sensu stricto based on plastid and nuclear DNA sequences and ovule and seed character evolution. J. Plant Res. 2007, 120, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Hong, J.-K.; Chase, M.W.; Fay, M.F.; Kim, J.-H. Familial relationships of the monocot order Liliales based on a molecular phylogenetic analysis using four plastid loci: matK, rbcL, atpB and atpF-H. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2013, 172, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
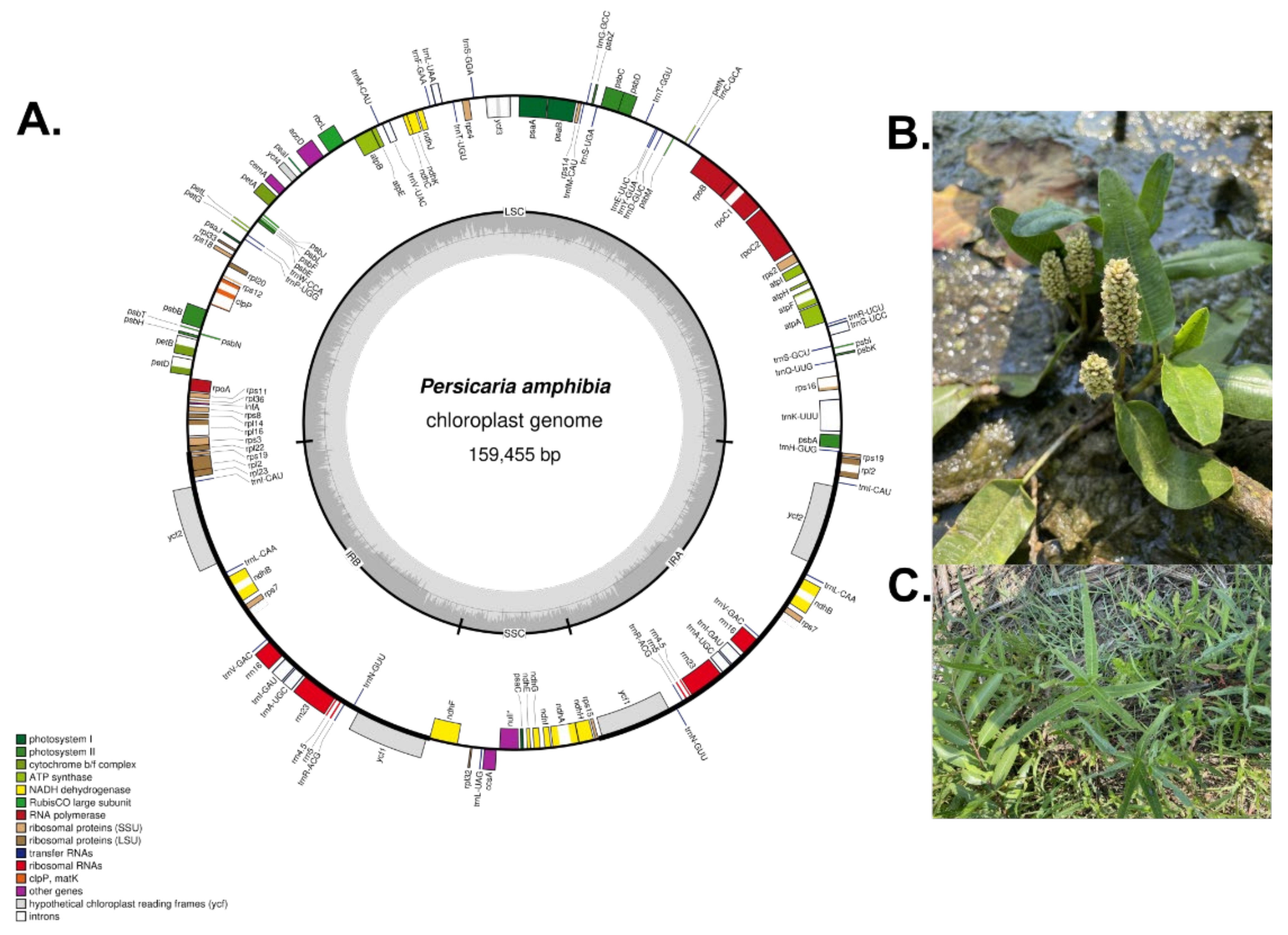
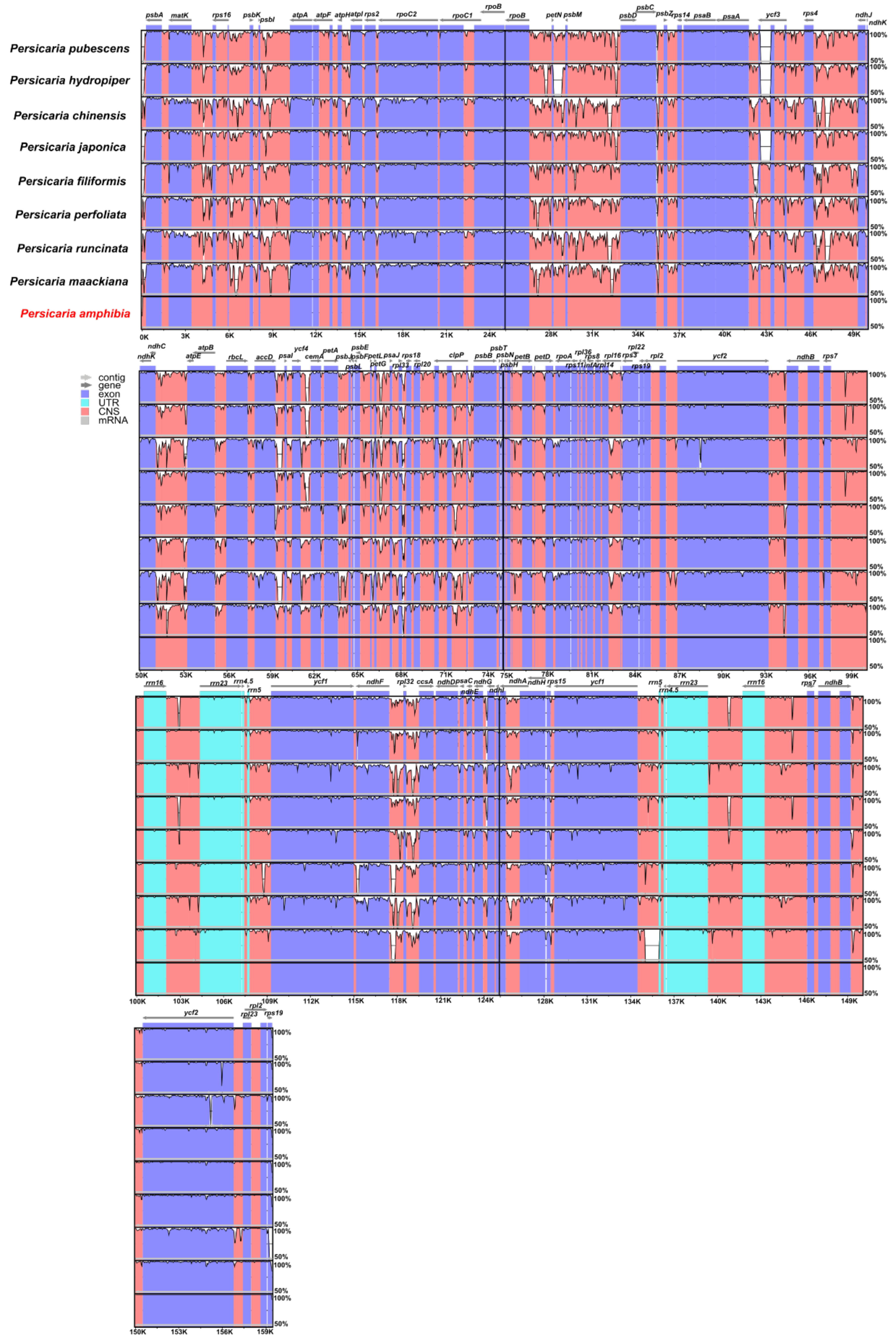

| Persicaria amphibia | Persicaria pubescens | Persicaria hydropiper | Persicaria chienesis | Persicaria japonica | Persicaria filiformis | Persicaria perfoliata | Persicaria runcinata | Persicaria maackiana | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length | |||||||||
| Total | 159,455 bp | 159,502 bp | 159,054 bp | 159,981 bp | 159,747 bp | 159,741 bp | 160,585 bp | 159,220 bp | 160,595 bp |
| LSC | 84,281 bp | 84,555 bp | 83,835 bp | 84,347 bp | 85,013 bp | 84,432 bp | 85,439 bp | 84,461 bp | 85,376 bp |
| SSC | 13,258 bp | 13,385 bp | 13,357 bp | 12,890 bp | 13,178 bp | 13,073 bp | 12,879 bp | 12,807 bp | 13,055 bp |
| IR | 30,956 bp | 30,781 bp | 30,931 bp | 30,872 bp | 30,778 bp | 31,118 bp | 31,135 bp | 30,884 bp | 31,082 bp |
| Genes | |||||||||
| Total | 113 | 113 | 113 | 113 | 113 | 113 | 113 | 113 | 113 |
| Protein-coding genes | 79 | 79 | 79 | 79 | 79 | 79 | 79 | 79 | 79 |
| tRNA | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 |
| rRNA | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| GC contents | 38.2% | 38.2% | 38.2% | 38.0% | 38.1% | 37.8% | 37.5% | 37.9% | 37.9% |
| Accession number | This study (ON938209) | MK234901 | MK234902 | NC_050358 | NC_056952 | NC_058319 | NC_060649 | NC_061176 | NC_061657 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, K.; Hwang, Y.; Hong, J.-K. Comparative Chloroplast Genomics and Phylogenetic Analysis of Persicaria amphibia (Polygonaceae). Diversity 2022, 14, 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14080641
Choi K, Hwang Y, Hong J-K. Comparative Chloroplast Genomics and Phylogenetic Analysis of Persicaria amphibia (Polygonaceae). Diversity. 2022; 14(8):641. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14080641
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, KyoungSu, Yong Hwang, and Jeong-Ki Hong. 2022. "Comparative Chloroplast Genomics and Phylogenetic Analysis of Persicaria amphibia (Polygonaceae)" Diversity 14, no. 8: 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14080641
APA StyleChoi, K., Hwang, Y., & Hong, J.-K. (2022). Comparative Chloroplast Genomics and Phylogenetic Analysis of Persicaria amphibia (Polygonaceae). Diversity, 14(8), 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14080641





