Marinobacterium sedimentorum sp. nov., Isolated from the Bottom Sediments of the Okhotsk Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. Phenotypic Characterization
2.3. Chemotaxonomic Characterization
2.4. 16S rRNA Gene Sequence and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Genome-Based Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
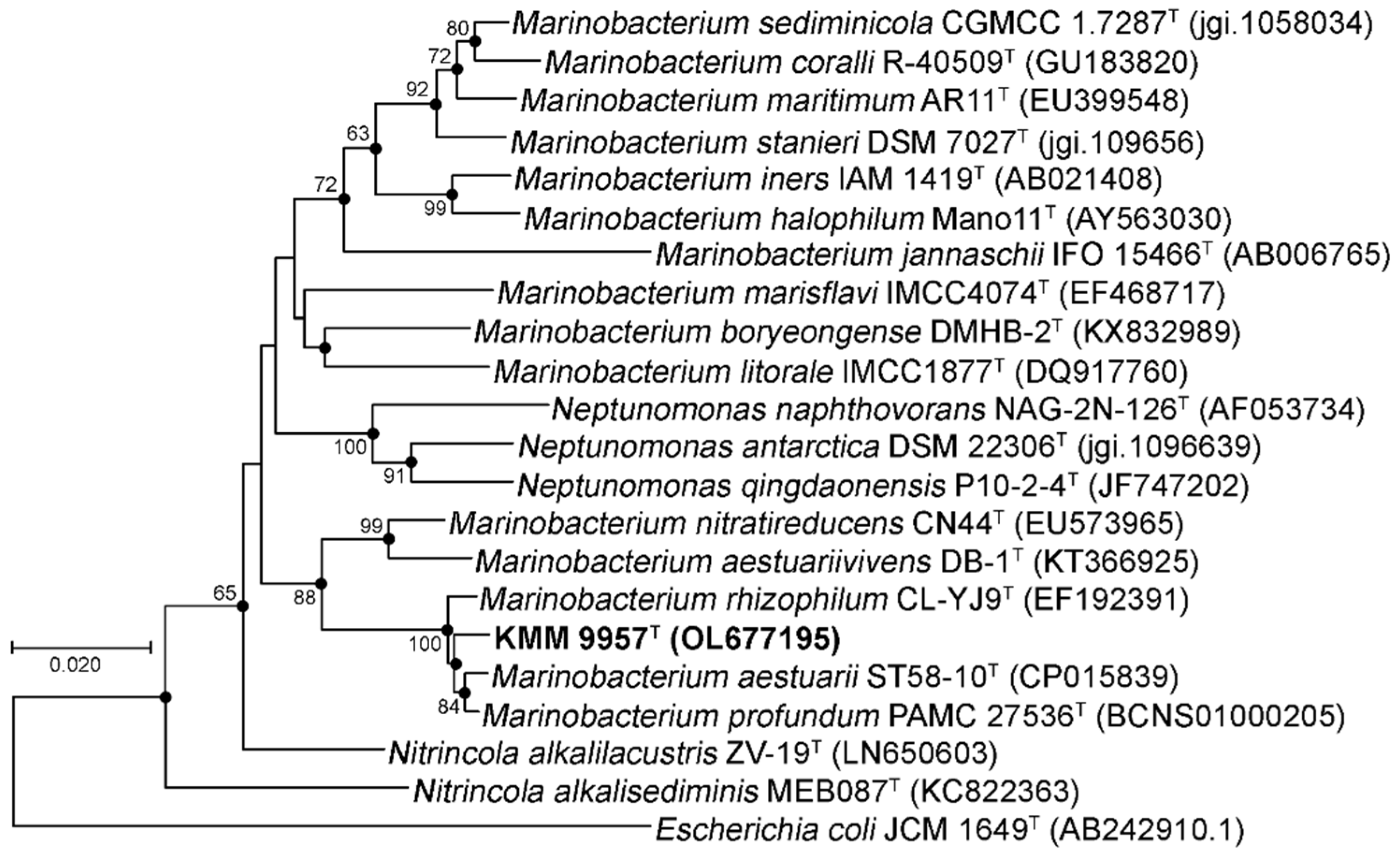
3.1. Phylogenetic and Phylogenomic Analyses
3.2. Genomic Characteristics
3.3. Morphological, Physiological, and Biochemical Characteristics
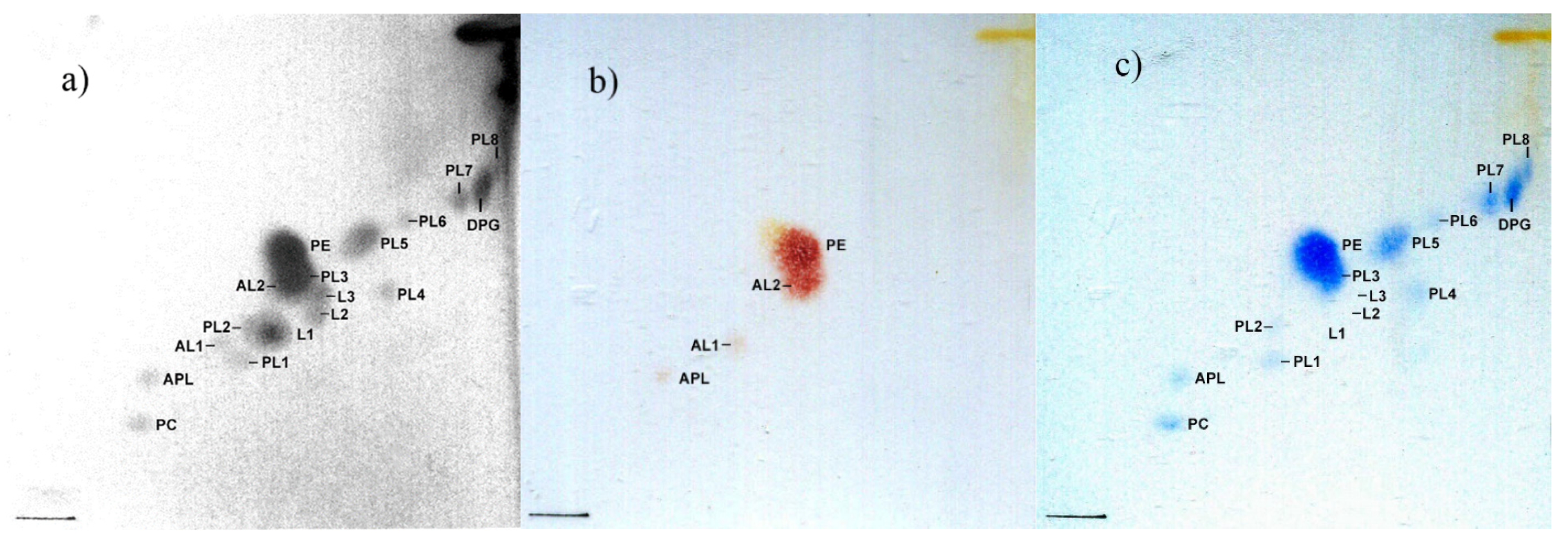
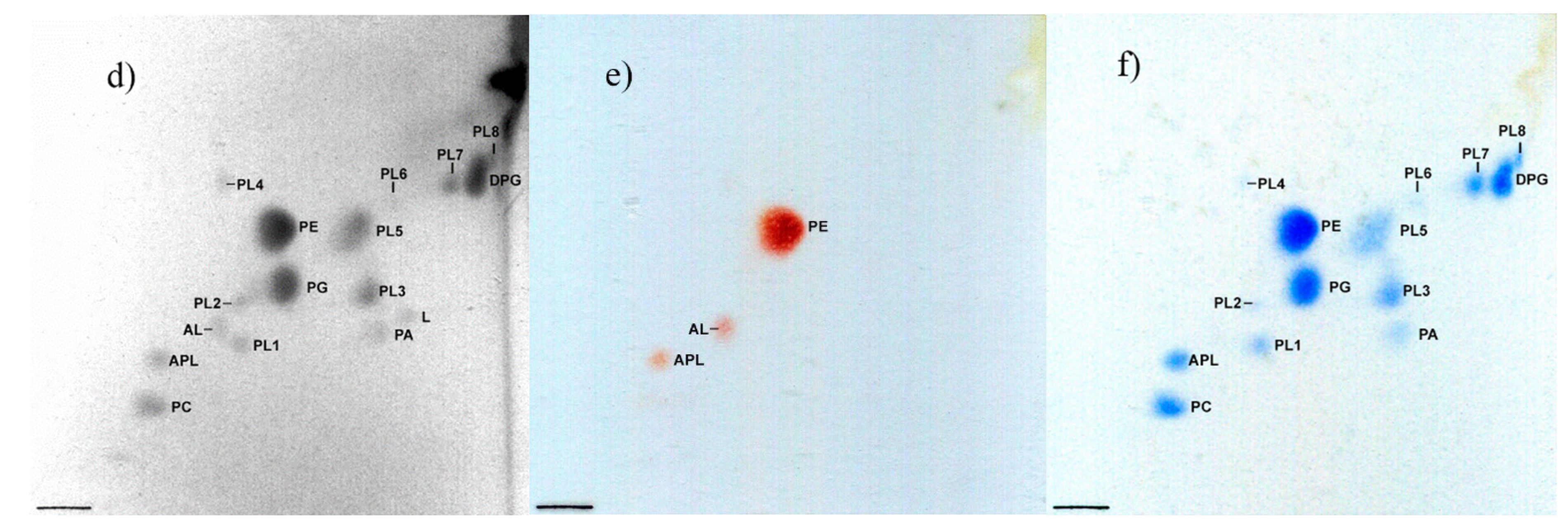
3.4. Chemotaxonomy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- González, J.M.; Mayer, F.; Moran, M.A.; Hodson, R.E.; Whitman, W.B. Microbulbifer hydrolyticus gen. nov., sp. nov., and Marinobacterium georgiense gen. nov., sp. nov., two marine bacteria from a lignin-rich pulp mill waste enrichment community. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1997, 47, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.S.; Jung, J.; Chung, D.; Baek, K. Marinobacterium aestuarii sp. nov., a benzene-degrading marine bacterium isolated from estuary sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Chun, J.; Son, K.P.; Jahng, K.Y. Marinobacterium boryeongense sp. nov., isolated from seawater. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán-Viseras, A.; Castro, D.J.; Reina, J.C.; Béjar, V.; Martínez-Checa, F. Taxogenomic and metabolic insights into Marinobacterium ramblicola sp. nov., a new slightly halophilic bacterium isolated from Rambla Salada, Murcia. Microorganisms. 2021, 9, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.B.; Wang, R.J.; Yu, X.Y.; Su, Y.; Sun, C.; Fu, G.Y.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zhu, X.F.; Wu, M. Marinobacterium zhoushanense sp. nov., isolated from surface seawater. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 3437–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.W.; Nam, Y.D.; Kwon, H.Y.; Park, J.R.; Lee, J.S.; Yoon, J.H.; An, K.G.; Bae, J.W. Marinobacterium halophilum sp. nov., a marine bacterium isolated from the Yellow Sea. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Park, S.J.; Yoon, D.N.; Park, B.J.; Choi, B.R.; Lee, D.H.; Roh, Y.; Rhee, S.K. Marinobacterium maritimum sp. nov., a marine bacterium isolated from Arctic sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 3030–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.Y.; Xu, X.W.; Cao, Y.; Wang, C.S.; Zhu, X.F.; Oren, A.; Wu, M. Marinobacterium nitratireducens sp. nov. and Marinobacterium sediminicola sp. nov., isolated from marine sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Lee, S.H.; Jung, J.Y.; Jeon, C.O. Marinobacterium lutimaris sp. nov., isolated from a tidal flat. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 1828–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.Y.; Yoon, S.J.; Lee, I.; Baek, K.; Lee, Y.M.; Yoo, K.C.; Yoon, H.I.; Lee, H.K. Marinobacterium profundum sp. nov., a marine bacterium from deep-sea sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1561–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Jung, Y.T.; Kim, S.; Yoon, J.H. Marinobacterium aestuariivivens sp. nov., isolated from a tidal flat. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1718–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimetto, L.A.; Cleenwerck, I.; Brocchi, M.; Willems, A.; De Vos, P.; Thompson, F.L. Marinobacterium coralli sp. nov., isolated from mucus of coral (Mussismilia hispida). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.G.; Jin, Y.A.; Hwang, C.Y.; Cho, B.C. Marinobacterium rhizophilum sp. nov., isolated the rhizosphere of the coastal tidal-flat plant Suaeda japonica. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Alfaro-Espinoza, G.; Ullrich, M.S. Marinobacterium mangrovicola sp. nov., a marine nitrogen-fixing bacterium isolated from mangrove roots of Rhizophora mangle. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 3988–3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhardt, P.; Murray, R.G.E.; Wood, W.A.; Krieg, N.R. Methods for General and Molecular Bacteriology; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Romanenko, L.A.; Tanaka, N.; Svetashev, V.I.; Falsen, E. Description of Cobetia amphilecti sp. nov., Cobetia litoralis sp. nov. and Cobetia pacifica sp. nov., classification of Halomonas halodurans as a later heterotypic synonym of Cobetia marina and emended descriptions of the genus Cobetia and Cobetia marina. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane Stanley, G. A simple method of isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.D.; Shah, H.N. Fatty acid, menaquinone and polar lipid composition of Rothia dentocariosa. Arch. Microbiol. 1984, 137, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.D.; Goodfellow, M.; Minnikin, D.E. Fatty acid, isoprenoid quinone and polar lipid composition in the classification of Curtobacterium and related taxa. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1980, 118, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, K.; Fallon, R.J. The determination of ubiquinone profiles by reversed-phase high-performance thin-layer chromatography as an aid to the speciation of Legionellaceae. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1990, 136, 2035–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasser, M. Identification of Bacteria by Gas Chromatography of Cellular Fatty Acids; MIDI Technical Note 101; MIDI Inc.: Newark, DE, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Romanenko, L.A.; Kurilenko, V.V.; Guzev, K.V.; Svetashev, V.I. Characterization of Labrenzia polysiphoniae sp. nov. isolated from red alga Polysiphonia sp. Arch. Microbiol. 2019, 201, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.H.; Ha, S.M.; Kwon, S.; Lim, J.; Kim, Y.; Seo, H.; Chun, J. Introducing EzBioCloud: A taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rate of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics. 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, A.; Saveliev, V.; Vyahhi, N.; Tesler, G. QUAST: Quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics. 2013, 29, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.H.; Imelfort, M.; Skennerton, C.T.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM: Assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatusova, T.; DiCuccio, M.; Badretdin, A.; Chetvernin, V.; Nawrocki, E.P.; Zaslavsky, L.; Lomsadze, A.; Pruitt, K.D.; Borodovsky, M.; Ostell, J. NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 6614–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, R.K.; Bartels, D.; Best, A.A.; DeJongh, M.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Formsma, K.; Gerdes, S.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; et al. The RAST Server: Rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattam, A.R.; Abraham, D.; Dalay, O.; Disz, T.L.; Driscoll, T.; Gabbard, J.L.; Gillespie, J.J.; Gough, R.; Hix, D.; Kenyon, R.; et al. PATRIC, the bacterial bioinformatics database and analysis resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D581–D591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-R, L.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T. The enveomics collection: A toolbox for specialized analyses of microbial genomes and metagenomes. PeerJ Prepr. 2016, 4, e1900v1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Göker, M. TYGS is an automated high-throughput platform for state-of-the-art genome-based taxonomy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnicar, F.; Thomas, A.M.; Beghini, F.; Mengoni, C.; Manara, S.; Manghi, P.; Zhu, Q.; Bolzan, M.; Cumbo, F.; May, U.; et al. Precise phylogenetic analysis of microbial isolates and genomes from meta-genomes using PhyloPhlAn 3.0. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchholz, P.C.F.; Feuerriegel, G.; Zhang, H.; Perez-Garcia, P.; Nover, L.L.; Chow, J.; Streit, W.R.; Pleiss, J. Plastics degradation by hydrolytic enzymes: The plastics-active enzymes database—PAZy. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Genet. 2022, 90, 1443–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, J.; Oren, A.; Ventosa, A.; Christensen, H.; Arahal, D.R.; da Costa, M.S.; Rooney, A.P.; Yi, H.; Xu, X.W.; De Meyer, S.; et al. Proposed minimal standards for the use of genome data for the taxonomy of prokaryotes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, M.; Rosselló-Móra, R. Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19126–19131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinidis, K.T.; Rosselló-Móra, R.; Amann, R. Uncultivated microbes in need of their own taxonomy. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2399–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNA G+C content (%) * | 58.4 | 58.8 | 57.2 | 58.5 |
| Growth in NaCl (%) | 0.5–5 | 0.5–7 | 1–4 | 1–5 |
| Growth at 35 °C | + | + | − | − |
| Hydrolysis of: | ||||
| DNA | + | − | ND | ND |
| Tween-80 | − | − | + | + |
| Enzyme activity (API ZYM): | ||||
| Esterase C4 | − | − | + | + |
| Esterase lipase C8 | − | + | (+) | − |
| Valine arylamidase | − | − | + | − |
| Acid phosphatase | − | − | + | + |
| α-glucosidase | − | − | − | + |
| Fatty Acid | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C10:0 | 1.4 | 3.8 | 4.8 | 3.9 |
| C10:0 3-OH | 14.8 | 16.1 | 7.7 | 7.1 |
| C12:0 | 2.0 | 2.8 | 3.9 | 4.0 |
| C14:0 | 6.6 | 8.1 | Tr | - |
| C16:1ω7c | 14.1 | 19.4 | 42.2 a | 40.3 b |
| C16:0 | 14.7 | 17.4 | 19.1 | 16.6 |
| C18:1ω9c | 5.0 | 0.6 | - | - |
| C18:1ω7c | 12.1 | 19.9 | 20.9 c | 26.6 |
| C18:0 | 2.9 | 1.1 | - | - |
| C20:4ω6 | 1.7 | - | - | - |
| C20:5ω3 | 5.8 | - | - | - |
| C20:1 | 2.0 | 0.4 | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romanenko, L.; Otstavnykh, N.; Kurilenko, V.; Velansky, P.; Baldaev, S.; Mikhailov, V.; Isaeva, M. Marinobacterium sedimentorum sp. nov., Isolated from the Bottom Sediments of the Okhotsk Sea. Diversity 2022, 14, 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14110944
Romanenko L, Otstavnykh N, Kurilenko V, Velansky P, Baldaev S, Mikhailov V, Isaeva M. Marinobacterium sedimentorum sp. nov., Isolated from the Bottom Sediments of the Okhotsk Sea. Diversity. 2022; 14(11):944. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14110944
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomanenko, Lyudmila, Nadezhda Otstavnykh, Valeriya Kurilenko, Peter Velansky, Sergey Baldaev, Valery Mikhailov, and Marina Isaeva. 2022. "Marinobacterium sedimentorum sp. nov., Isolated from the Bottom Sediments of the Okhotsk Sea" Diversity 14, no. 11: 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14110944
APA StyleRomanenko, L., Otstavnykh, N., Kurilenko, V., Velansky, P., Baldaev, S., Mikhailov, V., & Isaeva, M. (2022). Marinobacterium sedimentorum sp. nov., Isolated from the Bottom Sediments of the Okhotsk Sea. Diversity, 14(11), 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14110944







