Meiotic Analysis of Gomphidae Species Sheds Light on the Large X Chromosome of the Family (Anisoptera, Odonata)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
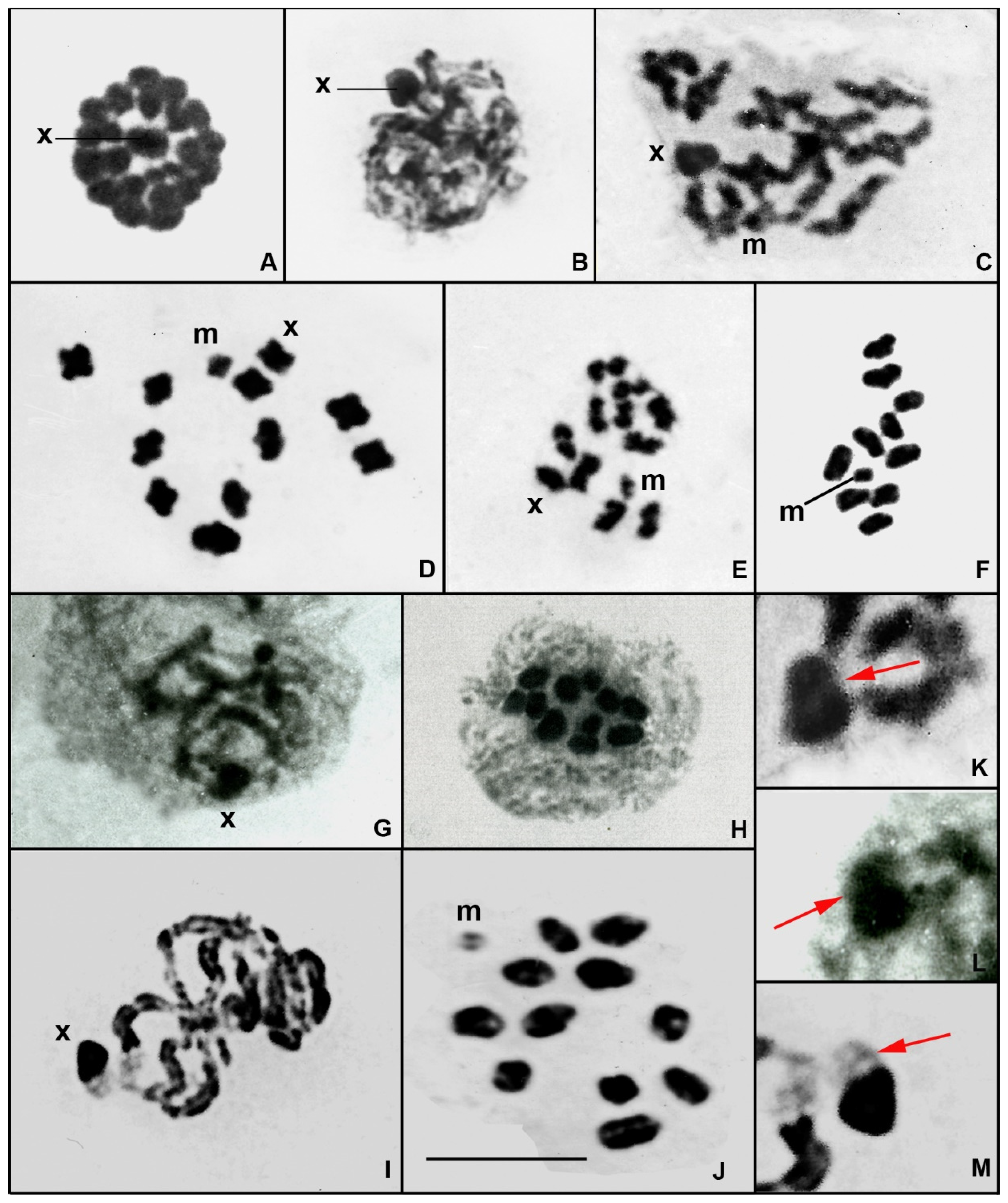
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Ancestral Chromosome Number of Gomphidae
4.2. Characterisation of the Large X Chromosome of Gomphidae
4.3. Derived Sex-Determining Systems
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Novelo-Gutiérrez, R.; Ramírez, A.; González-Soriano, E. Chapter 14.2—Superfamily Gomphoidea. In Thorp and Covich’s Freshwater Invertebrates, 4th ed; Hamada, N., Thorp, J.H., Rogers, D.C., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; Volume 3, pp. 377–397. [Google Scholar]
- Mola, L.M. Cytogenetics of American Odonata. In Odonata: Biology of Dragonflies, 1st ed.; Tyagi BK. Scientific Publishers: Jodhpur, India, 2007; pp. 153–173. [Google Scholar]
- Nokkala, S.; Laukkanen, A.; Nokkala, C. Mitotic and meiotic chromosomes in Somatochlora metallica (Corduliidae, Odonata). The absence of localized centromeres and inverted meiosis. Hereditas 2002, 136, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznetsova, V.G.; Golub, N.V. A checklist of chromosome numbers and a review of karyotype variation in Odonata of the world. Comp. Cytogenet. 2020, 14, 501–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumming, R.B. Cytogenetic Studies in the Order Odonata. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Texas, Austin, TX, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Mola, L.M.; Fourastié, M.F.; Agopian, S.S. High karyotypic variation in Orthemis Hagen, 1861 species, with insights about the neo-XY in Orthemis ambinigra Calvert, 1909 (Libellulidae, Odonata). Comp. Cytogenet. 2021, 15, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asana, J.J.; Makino, S. A comparative study of the chromosomes in the Indian dragonflies. J. Fac. Sci. Hokkaido Univ. Zool. 1935, 4, 67–86. [Google Scholar]
- Oksala, T. Zytologische Studien an Odonaten. III. Die Ovogenese. Ann. Acad. Sci. Fenn. 1945, 9, 1–132. [Google Scholar]
- Omura, T. The spermatogenesis of an Indian dragonfly, Ictinus rapax (Rambur) with special reference to the behaviour of the spermatozoa in the cyst. Biol. J. Okayama Univ. 1952, 1, 103–146. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta, B. Morphology and kinetic behaviour of the odonate sex chromosomes, with a review of the distribution of sex determining mechanisms in the order. Genen. Phaenen. 1968, 12, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta, B. Sex chromosomes and sex determining mechanisms in Odonata, with a review of the cytological conditions in the family Gomphidae, and reference to the karyotypic evolution in the order. Genetica 1969, 40, 127–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, B.K. Cytogenetics, karyosystematics and cytophylogeny of the Indian Odonata. Indian Rev. Life Sci. 1986, 6, 215–229. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, A.; Kiauta, B.; Zaha, A. Male germ cell chromosomes of thirty-two Brazilian dragonflies. Odonatologica 1979, 8, 5–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta, B.; Kiauta, M. List of species, with chromosome number and preliminary notes on the karyotypes of the Odonata, collected in May, 1979 and August, 1980 by the members of the Kansai Research Group of Odonatology. Personal Communication, Utrecht, Holland, 14 July 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, K.J.; Saitoh, K. Germ-line chromosomes of two species of Dadivíus with special reference to the sex chromosomes (Anisoptera, Gomphidae). Odonatologica 1988, 17, 275–280. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, K.J.; Saitoh, K. A revised chromosome study of Japanese Odonates (I). Chromosomes of 14 species belonging to nine families. Sci. Rep. Hirosaki Univ. 1990, 37, 38–49. [Google Scholar]
- Perepelov, E.; Bugrov, A.G. C-heterochromatin in chromosomes of Ophiogomphus cecilia cecilia (Four.) (Anisoptera: Gomphidae) with notes on the sex chromosome origin in the species. Caryologia 2001, 54, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mola, L.M.; Papeschi, A.G.; Carrillo, E.T. Cytogenetics of seven species of dragonflies. Hereditas 1999, 131, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perepelov, E.A.; Bugrov, A.G.; Warchałowska-Śliwa, E. C banded karyotypes of some dragonfly species from Russia. Folia Biol. 1998, 46, 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Perepelov, E.A.; Bugrov, A.G.; Warchalowska-Sliwa, E. C-banded karyotypes of some dragonfly species from Russia. II. The families Cordulegasteridae, Corduliidae and Gomphidae. Folia Biol. 2001, 49, 175–178. [Google Scholar]
- Perepelov, E.; Bugrov, A.G. Constitutive heterochromatin in chromosomes of some Aeshnidae, with notes on the formation of the neo-XY/neo-XX mode of sex determination in Aeshna (Anisoptera). Odonatologica 2002, 31, 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Walia, G.K.; Chahal, S.S. Distribution of constitutive heterochromatin and nucleolar organizer regions in two species of family Gomphidae (Odonata: Anisoptera). Nucleus 2014, 57, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, V.G.; Maryańska-Nadachowska, A.; Shapoval, N.A.; Anokhin, B.A.; Shapoval, A.P. Cytogenetic characterization of eight Odonata species originating from the Curonian Spit (the Baltic Sea, Russia) using C-banding and FISH with 18S rDNA and telomeric (TTAGG)n probes. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2018, 153, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walia, G.K.; Devi, M. Distribution of constitutive heterochromatin in four species of genus Copera of family Platycnemididae (Odonata: Zygoptera) from India. Int. J. Life Sci. 2018, 6, 457–461. [Google Scholar]
- Garrison, R.W.; von Ellenrieder, N.; Louton, J.A. Dragonfly Genera of the New World. An illustrated and Annotated Key to the Anisoptera, 1st ed.; The Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2006; 368p. [Google Scholar]
- De Gennaro, D. Análisis Meiótico y Caracterización de la Heterocromatina en Especies Argentinas de Anizoptera (Odonata). Licenciatura´s Thesis, Universidad de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Das, C. Studies on the association between non-homologous chromosomes during meiosis in four species of the Indian dragonflies (Odonata). J. Zool. Soc. India 1956, 8, 119–132. [Google Scholar]
- Walia, G.K.; Chahal, S.S. Linear differentiation of chromosomes of Anisogomphus bivittatus Selys, 1854 from India (Odonata: Anisoptera: Gomphidae). Int. J. Entomol. 2020, 5, 120–122. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta, B. Cytotaxonomy of Dragonflies, with Special Reference to the Nepalese Fauna; Lectures Delivered at the Tribhuvan University, Kathmandu, II; Nepal Research Center: Kathmandu, Nepal, 1975; 78p. [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi, B.K. Studies on the Chromosomes of Odonata of Dun Valley (Dehradun, India). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Garhwal, Srinagar, 1978. In Tyagi 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta, B.; van Brink, J.M. Male chromosome complements of some Florida dragonflies, United States. Odonatologica 1978, 7, 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Cruden, R.W. Chromosome numbers of some North American dragonflies (Odonata). Can. J. Genet. Cytol. 1968, 10, 200–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyoshima, H.; Hirai, H. Studies on chromosomes of four dragonflies from Kagawa Prefecture. Kagawa Biol. 1953, 1, 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Hirai, H. Chromosomes of six species of dragonflies. Zool. Mag. 1956, 65, 198–202. [Google Scholar]
- Omura, T. A comparative study of the spermatogenesis in the Japanese dragonfly II: Family Aeschnidae, Gomphidae and Calopterygidae. Biol. J. Okayama Univ. 1957, 3, 1–86. [Google Scholar]
- Walia, G.K.; Chahal, S.S.; Singh, N. Cytogenetic studies on three species of genus Burmagomphus of family Gomphidae (Odonata: Anisoptera) from India. Intern. J. Zool. Investig. 2021, 7, 272–277. [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi, B.K. A note on the karyotypes of Burmagomphus pytamidalis Laidlow and Onychogomphus saundersi duaricus Faser (Anizoptera; Gomphidae). Odonatologica 1977, 6, 277–282. [Google Scholar]
- Kichijo, H. Chromosomes of Tachopteryx pryeri and Gomphus hakiensis (Odonata, Aeshnidae). Jpn. J. Genet. 1939, 15, 287–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiauta, B. The chromosomes of four Neotropical dragonflies from Mexico. CIS 1970, 11, 8–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta, B. Notes on new or little known dragonfly karyotypes IV. Spermatocyte chromosomes of Calopterix splendens splendens (Harris) (Zygoptera. Calopterygidae), Gomphus pulchellus Selys, and Libellula depressa Linnaeus (Anisoptera: Gomphidae, Libellulidae) from Northern France. Genen. Phaenen. 1973, 16, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta, B.; Kiauta, M. The chromosome numbers of eleven dragonfly species from Singapore. Not Odonatol. 1982, 1, 164–165. [Google Scholar]
- Makino, S.A. comparative study of the chromosomes in the Indian dragonflies. Jpn. J. Genet. 1935, 11, 234–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kichijo, H. Insect chromosomes. IV. Order of dragonflies, Pt. 2. Nagasaki Med. J. 1942, 10, 1639–1648, In Kuznetsova & Golub 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta, J. Cytological studies of some Indian dragonflies. II: A study of the chromosomes during meiosis in thirty species of Indian Odonata (Insecta). Proc. Zool. Soc. 1957, 10, 1–65, In Kuznetsova & Golub 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bagga, S. Cytology and Cytochemistry of Gametogenesis of India Dragonflies. Ph.D. Thesis, Delhi University, Delhi, India, 1961. In Tyagi 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Walia, G.K.; Sandhu, R.; Goyal, S. Cytogenetical analysis of Nepogomphus modestus from Palampur area of Himachal Pradesh, India (Gomphidae: Anisoptera). Chromosome Sci. 2006, 9, 99–100. [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi, B.K. Cytotaxonomy of the genus Onychogomphus Selys (Odonata: Anisoptera, Gomphidae), with a Special Reference to the Evolution of the Sex-Determining Mechanism and Reduced Chromosome Number in the family Gomphidae. In Proceedings of the First Indian Symposium of Odonatology; Mathavan, S., Ed.; Madurai Kamaraj University: India, 1985; pp. 217–228. [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi, B.K. The chromosome numbers and sex-determining mechanisms newly recorded in thirteen Indian dragonflies (Odonata). CIS 1978, 25, 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Perepelov, E.; Bugrov, A.G. The constituent geterochromatin in karyotypes of dragonflies. Belyshevia 2001, 1, 10–13, In Kuznetsova & Golub 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Wu, J. Notes on the male germ cell karyotypes of some Odonata from the Shanxi Province, China. Not. Odonatol. 1986, 2, 118–120. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta, B.; Kiauta, M.A.J.E. The chromosome numbers of some Odonata from Thailand. Not. Odonatol. 1983, 2, 27–28. [Google Scholar]
- Souza Bueno, A.M. Estudios Vromosomicos na Ordem Odonata. Master’s Thesis, Universidad Estatal Paulista, São Paulo, Brazil, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta, B. The karyotypes of some Anisoptera from Surinam. Odonatologica 1979, 2, 267–283. [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi, B.K. Cytotaxonomy of Indian dragonflies. Indian Rev. Life Sci. 1982, 2, 149–161. [Google Scholar]
- Oguma, K. A comparative study of the spermatocyte chromosome in allied species of the dragonfly. J. Fac. Sci. Hokkaido Univ. Zool. 1930, 6, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, B.K. Male reproductive organs of Crocothemis servilia servilia Drury (Libellulidae: Odonata). Zool. Anz. 1963, 170, 386–392. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta, B. Studies on the germ cell chromosome cytology of some cytotaxonomically interesting or hitherto not studied Odonata from the autonomous region Friuli-Venezia Giulia (northern Italy). Atti. Mus. Civ. Stor. Nat. Trieste 1971, 27, 65–127. [Google Scholar]
- Mola, L.M. Post-reductional meiosis in Aeshna (Aeshnidae, Odonata). Hereditas 1995, 122, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mola, L.M.; Papeschi, A.G. Holokinetic chromosomes at a glance. J. Basic Appl. Genet. 2006, 17, 17–33. [Google Scholar]
- Oksala, T. Zytologische Studien an Odonaten: 1. Chromosomenverhältnisse bei der Gattung Aeschna, mit Besonderer Berücksichtigung der Postreduktionellen Teilung der Bivalente, 1st ed.; Suomalainen Tiedeakatemia: Helsinki, Finland, 1943; Volume 4, p. 64. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchsówna, J.; Sawczyńska, J. Observations on the heterochromosomes during the spermatogenesis in dragonflies (Odonata). Pt. I. Aeschna grandis L. and Libellula quadrimaculata L. Arch. Sci. Soc. 1928, 9, 177–197. [Google Scholar]
- Makalowskaja, W.N. Comparative karyological studies of dragonflies (Odonata). Arch. Russes. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 1940, 25, 24–39. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta, B. Considerations on the evolution of the chromosome complement in Odonata. Genetica 1967, 38, 430–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seshachar, B.R.; Bagga, S. Chromosome number and sex-determining mechanism in dragonfly Hemianax ephippiger (Burmeister). Cytologia 1962, 27, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiauta, B. Notes on new or little known dragonfly karyotypes, 2. Male germ cell chromosomes of four East Mediterranean species: Lestes barbarus (Fabricius), Calopteryx splendens amasina Bartenev (Zygoptera: Lestidae, Calopterygidae), Caliaeschna microstigma (Schneider) and Orthetrum taeniolatum (Schneider) (Anisoptera: Aeshnidae, Libellulidae). Genen. Phaenen. 1972, 15, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Mola, L.M.; Papeschi, A.G. Karyotype evolution in Aeshna (Aeshnidae: Odonata). Hereditas 1994, 121, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray Chaudhuri, S.P.; Dasgupta, J. Cytological studies on the Indian dragonflies I. Structure and behaviour of chromosomes in six species of dragonflies (Odonata). Proc. Zool. Soc. Bengal. 1949, 2, 81–93. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta, B.; Kiauta, M.A.J.E. The chromosome numbers of sixteen dragonfly species from the Arun Valley, Eastern Nepal. Not. Odonatol. 1982, 9, 143–146. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta, B. The status of the Japanese Crocothemis servilia (Drury) as revealed by karyotypic morphology (Anisoptera: Libellulidae). Odonatologica 1983, 12, 381–388. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, J.S. A note on the karyotypic variability in Crocothemis erythraea (Brullé) and C. servilia (Drury) (Anisoptera, Libellulidae). Not. Odonatol. 1979, 1, 77–79. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta, B.; Kiauta, M.A.J.E. On a small collection of dragonfly karyotypes from the Philippines. Odonatologica 1980, 9, 237–245. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta, B.; Kiauta, M. Further notes on Philippine odonate karyotypes. Not. Odonatol. 1983, 2, 14–15. [Google Scholar]
- Katatani, N. On the chromosomes of dragonflies, 1. Synopsis on the studies in some Japanese dragonflies. Aeschna 1987, 20, 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- Higashi, K.; Kayano, H. The distribution of distinct karyomorphs of Crocothemis servilia Drury (Anisoptera, Libellulidae) in Kyushu and the south-western islands of Japan. Jpn. J. Entomol. 1993, 61, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Higashi, K.; Lee, C.E.; Kayano, H.; Kayano, A. Korea strait delimiting distribution of distinct karyomorphs of Crocothemis servilia (Drury) (Anisoptera: Libellulidae). Odonatologica 2001, 30, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Omura, T. A comparative study of the spermatogenesis in the Japanese dragonflies. I. Family Libellulidae. Biol. J. Okayama Univ. 1955, 2, 95–135. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta, B.; Boyes, J.W. Cytology of ten South American Libellulidae, with cytophylogenetic consideration of the genera Orthemis Hagen and Erythrodipax Brauer (Odonata, Anisoptera). Genetica 1972, 43, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mola, L.M. Meiotic studies in nine species of Erythrodiplax (Libellulidae, Odonata). Neo-XY sex chromosome system in Erythrodiplax media. Cytologia 1996, 61, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agopian, S.S.; Mola, L.M. Intra and interspecific karyotype variability in five species of Libellulidae (Odonata, Anisoptera). Caryologia 1988, 41, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agopian, S.S.; Mola, L.M. Bandeo C en Odonata. In Proceedings of the XV Congreso de la Sociedad Argentina de Genética, Corrientes, Argentina, 16–21 September 1984; p. 17. [Google Scholar]
- Oguma, K.; Asana, J.J. Additional data to our knowledge on the dragonfly chromosome with a note on the occurrence of X-Y chromosome in the ant-lion (Neuroptera). J. Fac. Sci. Hokkaido Univ. Zool. 1932, 1, 133–142. [Google Scholar]
- Grozeva, S.M.; Marinov, M.G. Cytogenetic study of Somatochlora borisi Marinov, 2001 (Odonata: Corduliidae), and three relative species. Acta Zool. Bulg. 2007, 59, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta, B. The karyotype of the damselfly, Leptagrion macrurum (Burmeister, 1839), and its possible origin, with a note on the cytotaxonomic affinities of the genus (Zygoptera: Coenagrionidae). Odonatologica 1972, 1, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
| Species | n (Male) | X Size in Mitosis | X Size in Meiosis | Locality | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Anisogomphus bivittatus (Selys, 1854) | 11 + X 11 + X 11 + X | - LL - | S S S | India India Nepal | [27] [28] [29] as Temnogomphus bivittatus (Selys, 1854) |
| 2 | A. occipitalis (Selys, 1854) | 11 + X | - | S - | Nepal India | [29] [30] |
| 3 | Aphylla cf. distinguenda (Campion, 1920) | 11 + X | LL | M | Argentina | [2] this work |
| 4 | A. edentata Selys, 1869 | 11 + X | - | - | Bolivia | [5] |
| 5 | A. producta Selys, 1854 | 11 + X | - | - | Bolivia | [5] |
| 6 | A. theodorina (Navas, 1933) | 11 + X | LL | LL | Brazil | [13] |
| 7 | A. williamsoni (Gloyd, 1936) | 11 + X | M | M | USA | [31] |
| 8 | Arigomphus lentulus (Needham, 1902) | 11 + X | - | - | USA | [32] as Gomphus lentulus Needham, 1902 |
| 9 | A. pallidus (Rambur, 1842) | 11 + X | - | - | USA | [5] as Gomphus pallidus Rambur, 1842 |
| 10 | A. submedianus (Williamson, 1914) | 11 + X | - | - | USA | [32] as Gomphus submedianus Williamson, 1914 |
| 11 | Asiagomphus melaenops (Selys, 1854) | 9 + X 9 + X 11 + X 11 + X | - - LL LL | - M L L | Japan Japan Japan Japan | [33] [34] [35] [14] all as Gomphus melaenops Selys, 1854 |
| 12 | Burmagomphus cf. arboreus Lieftinck, 1940 | 11 + X | - | - | India | [30] |
| 13 | B. divaricatus Lieftinck, 1964 | 11 + X | - | M | India | [36] |
| 14 | B. pyramidalis Laidlaw, 1922 | 11 + X 11 + X | - | S-M M | India India | [30,37] [36] |
| 15 | B. sivalikensis Laidlaw, 1922 | 11 + X | - | M | India | [36] |
| 16 | B. williamsoni Förster, 1914 | 11 + X | - | M | India | [36] |
| 17 | Davidius fujiama Fraser, 1936 | 11 + X 2n = 24 F | H | LL | Japan | [15] |
| 18 | D. moiwanus (Okumura, 1935) | 11+X | H | M | Japan | [15] as D. m. moiwanus (Okumura) |
| 19 | D. nanus (Selys, 1869) | 11 + X 11 + X 11 + X | - - M | S M M | Japan Japan Japan | [38] as Gomphus hakiensis Oguma, 1926 [14] [16] |
| 20 | Dromogomphus spinosus (Selys, 1854) | 11 + X | - | - | USA | [32] |
| 21 | D. spoliatus (Hagen, 1857) | 11 + X | - | - | USA | [32] |
| 22 | Epigomphus llama Calvert, 1903 | 9 + X | - | - | Bolivia | [5] |
| 23 | Erpetogomphus designatus Hagen, 1857 | 11 + X | - | - | USA | [5] |
| 24 | E. diadophis Calvert, 1905 | 11 + X | - | - | USA | [5] |
| 25 | E. ophibolus Calvert, 1905 | 11 + X | - | M | Mexico | [39] |
| 26 | Gomphoides sp. | 11 + X | - | - | Bolivia | [5] |
| 27 | Gomphus confraternus Selys, 1873 | 11 + X | - | - | USA | [32] |
| 28 | G. exilis Selys, 1854 | 11 + X 2n = 24F | - | - - | USA Canada | [32] [11] |
| 29 | G. graslini Rambur, 1842 | 11 + X | LL | - | France | [10] [11] |
| 30 | G. pulchellus Selys, 1840 | 11 + X | - | M-L | France | [40] |
| 31 | G. vulgatissimus (Linnaeus, 1758) | 11 + X | - | s | Russia | [20] |
| 32 | Ictinogomphus decoratus (Selys, 1854) | 11 + X | LL | M-L | Singapur | [41] as I. decoratus melaenops |
| 33 | I. pertinax (Hagen in Selys, 1854) | 11 + X | - | M | Japan | [14] |
| 34 | I. rapax (Rambur, 1942) | 11 + X 11 + X 11 + X | H - LL | LL - LL | India India India | [7] as Ictinus rapax [42,43,44,45] [9] as Ictinus rapax Omura 1949 |
| 35 | Nepogomphus modestus (Selys, 1878) | 11 + X 11 + X | - M | M M | India India | [46] [22] |
| 36 | Nihonogomphus ruptus (Selys, 1858) | 11 + X | - | S | Russia | [20] |
| 37 | N. viridis Oguma, 1926 | 11 + X 11 + X | - H | L L | Japan Japan | [35] [16] |
| 38 | Octogomphus specularis (Hagen, 1859) | 11 + X | - | - | USA | [32] |
| 39 | Onychogomphus forcipatus (Linnaeus, 1758) | 11 + neo-XY | Austria | [11] | ||
| 40 | O. saundersii Selys, 1854 | 11 + neo-XY | India | [12,30,37,47] as O. s. duaricus Fraser, 1924 | ||
| 41 | O schmidti Fraser, 1937 | 11 + neo-XY | India | [12,30,47,48] | ||
| 42 | Ophiogomphus bison Selys, 1873 | 11 + X/12 + X | - | - | USA | [32] |
| 43 | O. cecilia (Fourcroy, 1785) | 12 F 11 + X 11 + X | - - H | LL LL LL | Finland Russia Russia | [8] as O. serpentinus Charp. Syn Aeschna serpentina Charpentier, 1825 [19] [17] as O. c. cecilia (Four.) |
| 44 | O. colubrinus Selys, 1854 | 11 + X | - | - | USA | [32] |
| 45 | O. obscurus Bartenev, 1909 | 11 + X | - | - | Russia | [49] |
| 46 | O. occidentalis Hagen, 1882 | 11 + X | - | - | USA | [32] |
| 47 | O. rupinsulensis (Walsh, 1862) | 11 + X | - | S-M | USA | [32] |
| 48 | O spinicornis Selys, 1878 | 11 + X | - | LL | China | [50] as O. spinicorne |
| 49 | Paragomphus capricornis (Förster, 1914) | 11 + X | - | L | Thailand | [51] |
| 50 | P. lineatus (Selys, 1850) | 11 + X 11 + X 11 + X | - - L | M - M | Nepal India India | [29] [30] [22] |
| 51 | Phanogomphus lividus (Selys, 1854) | 11 + X | - | - | USA | [32] as Gomphus lividus Selys, 1854 |
| 52 | Ph. militaris (Hagen, 1858) | 11 + X | - | - | USA | [32] as Gomphus militaris Hagen, 1858 |
| 53 | Ph. spicatus (Selys, 1854) | 11 + X | - | - | USA | [32] as Gomphus spicatus Selys, 1854 |
| 54 | Phyllocycla propinqua Belle, 1972 | 10 + X | - | M | Argentina | [51] this work |
| 55 | Phyllocycla sp. | 11 + X | - | - | Bolivia | [5] |
| 56 | Phyllocycla sp. | 11 | - | - | Brazil | [52] |
| 57 | Phyllocycla sp. | 11 + X | - | M | Argentina | [2] this work |
| 58 | Phyllogomphoides undulatus (Needham, 1944) | 11 + X | - | S | Surinam | [53] |
| 59 | Progomphus borealis McLachlan, 1873 | 11 + X | - | - | USA | [32] |
| 60 | P. intricatus (Hagen, 1857) | 11 + X 11 + neo-XY | - - | - - | Bolivia Brazil | [5] [52] |
| 61 | P. obscurus (Rambur, 1842) | 11 + X | - | - | USA | [32] |
| 62 | P. phyllochromus Ris, 1918 | 11 + X | - | - | Bolivia | [5] |
| 63 | Scalmogomphus bistrigatus (Hagen, 1854) | 11 + X 11 + X | - - | LL LL | Nepal India | [29] [30,54] both as Onychogomphus bistrigatus (Hagen, 1854) |
| 64 | Shaogomphus postocularis (Selys, 1869) | 11 + X 11 + X | - - | - S | Japan Russia | [16,35] both as Gomphus postocularis Selys,1869 [20] as Gomphus epophtalmus Selys, 1872 |
| 65 | Sieboldius albardae Selys, 1886 | 11 + X 11 + X 11 + X | - H H | LL LL LL | Japan Japan Japan | [35] [14] [16] |
| 66 | Sinictinogomphus clavatus (Fabricius, 1775) | 11 + X | LL | M | Japan | [14] as Ictinogomphus clavatus (Fabricius, 1775) |
| 67 | Stylogomphus suzukii (Oguma, 1926) | 11 + X | - - | S - | Japan Japan | [55] [42] both as Gomphus suzukii Oguma, 1926 |
| 68 | Stylurus flavipes (Charpentier, 1825) | 11 + X | - | - | Russia | [48] |
| 69 | S. plagiatus (Selys, 1854) | 11 + X | - | - | USA | [32] as Gomphus plagiatus Selys, 1854 |
| 70 | S. scudderi (Selys, 1873) | 11 + X | - | - | USA | [32] as Gomphus scudderi Selys, 1873 |
| 71 | S. townesi Gloyd, 1936 | 11 + neo-XY | USA | [31] as Gomphus townesi Gloyd, 1936 | ||
| 72 | Trigomphus citimus (Needham, 1931) | 10 + X 10 + X 10 + X | - - - | - S L | Japan Japan Japan | [33] [34] [14] all as Gomphus citimus tabei Asahina, 1949 |
| 73 | T. interruptus (Selys, 1854) | 9 + X | - | L | Japan | [14] |
| 74 | T. melampus (Selys, 1869) | 9 + X 10 + X 9 + X 11 + X 10 + X | - - - - LL | M L M-L S M-S | Japan Japan Japan Japan Japan | [55] as Gomphus melampus Selys, 1869 [55] as Gomphus unifasciatus Oguma, 1926 [35] as Gomphus melampus bifasciatus Asahina [34] as Gomphus m. bifasciatus Asahina [16] |
| 75 | T. ogumai Asahina, 1949 | 10 + X | - | s | Japan | [14] |
| 76 | Zonophora callipus Selys, 1869 | 11 + X | LL | M | Surinam | [53] |
| Family Suborder | 2n Male | n Male | H | SBS | N | Locality | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | |||||||
| Anisoptera | |||||||
| Aeshnidae | |||||||
| Aeshna caerulea (Ström, 1783) | 11 + neo-XY | Y | SS | 2 | Finland | [60] | |
| A. grandis (Linnaeus, 1758) | 27 25 25 26 26F 26 | 13 + X 12 + X X 12 + neo-XY 12 + neo-XX 12 + neo-XY 12 + neo-XY | Y Y Y | LL LL LL | - - - 23 - 8 - | USSR USSR Finland Finland Netherlands Russia | [61] [62] [20] [8,60] [10,11,63] [21] |
| A. juncea (Linnaeus, 1758) | 26 26F 26 | 12 + X 12 + neo-XY 12 + neo-XY 12 + neo-XY | N - D Y ‡ | - - L L | - 14 3 6 4 | USSR Finland Italy Russia | [62] [60] [57] [21] |
| A.serrata Hagen, 1856 | 12 + neo-XY | N | - | 1 | Finland | [60] as A.osiliensis fennica | |
| A. viridis Eversmann, 1836 | - 26F 26 | 12 + neo-XY 12 + neo-XY | N - D ‡ | - - LL | 3 2 2 | Finland Russia | [60] [19] |
| Anax ephippiger (Burmeister, 1839) | 14 14F | 6 + neo-XY | D | M | - | India | [64] as Hemianax ephippiger |
| Caliaeschna microstigmata (Schneider, 1845) | 6 + neo-XY | N | - | 1 | Greece | [65] | |
| Gynacanta interioris Williamson, 1923 | 26 | 12 + neo-XY | D | M | 2 | Brazil | [13] |
| Rhionaeschna bonariensis (Rambur, 1842) | 26 | 12 + neo-XY | Y Y | LL LL | 5 2 | Argentina Uruguay | [58,66] both as Aeschna bonariensis |
| R. planaltica (Calvert, 1845) | 16 | 7 + neo-XY | Y | SS | 2 | Argentina | [58,66] both as Aeschna cornigera planaltica |
| Gomphidae | |||||||
| Onychogomphus forcipatus (Linnaeus, 1758) | 24 | 11 + neo-XY | Y | LL | - | Austria | [11] |
| † O. saundersii Selys, 1854 | 22? 23? | 11 + neo-XY | Y | LL | 10 | India | [37] as O. saundersi duaricus |
| O. schmidti Fraser, 1937 | 22 | 11 + neo-XY | - | LL | - | India | [47,48] |
| Progomphus intricatus (Hagen in Selys, 1858) | 23 24 | 11 + X 11 + neo-XY | - N | - - | - 3 | Bolivia Brazil | [5] [52] |
| Stylurus townesi Gloyd, 1936 | 23? | 11 + neo-XY | Y | LL | 1 | USA | [31] as Gomphus townesi |
| Libellulidae | |||||||
| Crocothemis servilia (Hagen, 1857) servilia | 25 | 12 + X | India, Nepal, China, Philippines, Japan Singapore, Korea, Thailand | [7,29,30,42,43,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75] | |||
| C. servilia mariannae ssp. n. | 24 | 11 + neo-XY 11 + neo-XY 11 + neo-XY 11 + neo-XY | N D Y Y | - S SS SS | 3 5 - 25 | Japan Japan Japan Japan | [76] [69] [74] [75] |
| Elasmothemis williamsoni (Ris, 1919) | 22 | 11 + neo-XY | N | - | 2 | Surinam | [53] as Dythemis williamsoni |
| Erythrodiplax media Borror, 1942 | 22F 22 | 10 + X 11 10 + neo-XY | D | L | - 1 8 | Bolivia, Brazil Brazil Argentina | [5,13,52] [77] [78] |
| Macrothemis hemichlora (Burmeister,1839) | 6 | 2 + neo-XY | N | - | - | Bolivia | [5] |
| Micrathyria longifasciata Calvert, 1909 | 24 | 11 + neo-XY | Y | LL | 8 | Argentina | [79] |
| M. ungulata Foerster, 1907 | 23 | 10 + X1X2Y | Y | M | 2 | Argentina | [18] |
| Neurothemis tulia (Drury, 1773) | 28 | 13 + neo-XY 12 + X | Y | U | - 4 | India Thailand | [54,67] [73] all as N.t.tulia |
| Orthemis aequilibris Calvert, 1909 | 12 | 5 + neo-XY | N | - | 1 | Surinam | [53] |
| O.ambinigra Calvert, 1909 | 12 | 5 + neo-XY | N | - | 19 | Argentina | [2,6,80] |
| O. discolor (Burmeister, 1839) | 23 25 23 24 F | 11 + X 11 + neo-XY 10 + neo-XY 11 + X | 4 | Surinam Perú, Surinam, Brazil, Argentina Argentina | [53] as O. ferruginea [2,13,52,53,77] all as O. ferruginea [6] | ||
| O. levis Calvert, 1906 | 7 | 2II + III | N | - | 2 | Bolivia | [5] |
| Orthemis sp. | 10 | 4 + neo-XY | N | - | 4 | Bolivia | [5] as O. ferrugínea |
| Pseudothemis zonata (Burmeister, 1839) | - | 11 + neo-XY | Y | LL | 6 | Japan | [76] |
| Trithemis aurora (Burmeister, 1839) | 25 | 12 + X 9 + neo-XY | - | - | 4 | India Nepal | [30,81] [29] |
| Corduliidae | |||||||
| Somatochlora borisi Marinov, 2001 | 10 + neo-XY | N | - | 7 | Bulgaria | [82] | |
| Zygoptera | |||||||
| Coenagrionidae | |||||||
| Ischnura lobata Needham, 1930 | 13 + neo-XY | Y | LL | 5 | China | [50] | |
| Leptagrion macrurum (Burmeister, 1839) | 30 | neo-XY | - | - | 2 | Brazil | [83] |
| Mecistogaster sp.2 | 12 | 5 + neo-XY | N | - | - | Bolivia | [5] |
| Lestidae | |||||||
| Lestes vigilax Selys, 1862 | 9II + III | - | - | 1 | USA | [31] | |
| Megapodagrionidae | |||||||
| Heteragrion sp. b | 26 | 12 + neo-XY | D | M | 2 | Brazil | [52] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mola, L.M.; Rebagliati, P.J.; Fourastié, M.F.; Agopian, S.S. Meiotic Analysis of Gomphidae Species Sheds Light on the Large X Chromosome of the Family (Anisoptera, Odonata). Diversity 2022, 14, 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14100874
Mola LM, Rebagliati PJ, Fourastié MF, Agopian SS. Meiotic Analysis of Gomphidae Species Sheds Light on the Large X Chromosome of the Family (Anisoptera, Odonata). Diversity. 2022; 14(10):874. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14100874
Chicago/Turabian StyleMola, Liliana M., Pablo J. Rebagliati, María F. Fourastié, and Silvia S. Agopian. 2022. "Meiotic Analysis of Gomphidae Species Sheds Light on the Large X Chromosome of the Family (Anisoptera, Odonata)" Diversity 14, no. 10: 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14100874
APA StyleMola, L. M., Rebagliati, P. J., Fourastié, M. F., & Agopian, S. S. (2022). Meiotic Analysis of Gomphidae Species Sheds Light on the Large X Chromosome of the Family (Anisoptera, Odonata). Diversity, 14(10), 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14100874








