Abstract
The mullets are a widespread group of ecologically and economically important fishes of disputed taxonomy due to their uniform external morphology. Barcoding and phylogenetic studies from various locations around the world largely highlighted the species diversity underestimation using morphological criteria used to establish the taxonomy of the family. Here, we investigated the mullet species diversity from Pakistan, a biogeographic area where nearly no mullet species were genetically characterized. Morphological examination of 40 mullets reveals 6 known species (Planiliza macrolepis, P. klunzingeri, P. subviridis, Crenimugil seheli, Ellochelon vaigiensis, and Mugil cephalus). Using a references DNA barcode library, the DNA barcode-based species identification flagged eight molecular operational taxonomic units (MOTUs) belonging to five genera (Crenimugil, Ellochelon, Mugil, Osteomugil, and Planiliza). Among these MOTUs, only one was already present in Barcode of Life Data system, all other representing new Barcode Index Numbers (BIN). These results emphasize the importance of the recognition of cryptic species and the necessity to re-evaluate the overall diversity by the genetic characterization of different species of this family. DNA barcoding is an effective tool to reveal cryptic species that need to be considered in conservation and management measures of fisheries in Pakistan.
1. Introduction
It is largely acknowledged that the current fish taxonomy based on the variation of morpho-anatomical characters greatly underestimated the species diversity [1,2]. Numerous phylogeographic, phylogenetic, and DNA barcoding studies flagged independent evolutionary lineages in widely geographically distributed species that are more and more recognized as cryptic species or at least as candidate species pending further taxonomic investigations [1,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. The proper delineation of species is essential not only for better management and conservation of biodiversity [10,11] but also helps us to understand the causes of different evolutionary processes [12]. From a more pragmatic perspective, incorrect identification of commercially important species may lead to overexploitation and contribute to fish stock depletion [13].
In this context, the DNA barcoding method proved to be a useful and independent approach based on the variation of morphometric and meristic characters for species identification [14]. Instead of observable and definite morphological differences, mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (COI) gene has been used to resolve many taxonomic ambiguities [15,16].
The family Mugilidae currently consists of about 27 genera and 77 recognized species [17]. Mullets are important in marine fisheries and aquaculture in many temperate and tropical countries [18]. Owing to the significant morphological conservatism, the delimitation of mullet species is arduous, as a result, mullet species are often inadequately represented in field guides [19]. For this reason, several studies have been carried out to solve the phylogenetic relationship and identification of mullet species using different molecular methods [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27]. Over the past decades, molecular phylogenetic studies have evidenced the presence of many species complexes within the Mugilidae family [2,19,28,29,30,31,32]. These species complex, often presented as complex of cryptic species due to the absence of evident diagnostic morphometric and meristic characters, are usually sibling species and thus with much more limited distribution range than described for the morpho-species [2]. Among those species Mugil cephalus Linnaeus, 1758, is a good example as the morpho species present in nearly all tropical, subtropical, and temperate waters of the world [33] consists of 14 molecular operational taxonomic units (MOTU’s) with a distribution range generally limited to a biogeographic province [18]. In this context, it is important to better estimate the species diversity of the Mugilidae family and their distribution range to barcode most mullet species in the different biogeographic provinces. While some DNA barcoding or phylogenetic studies have been realized in various regions of the world such as Europe [21,22,23,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42], Africa [43], South America [32,44], Asia [20,26,31], and India [45,46], no studies have been considered species diversity present in Pakistan or, more generally, in the Arabian sea.
Based on morphological variations, a variable number of mullet species have previously been reported from Pakistan: 6 species by Qureshi [47], 12 by Bianchi [48], 7 by Fahmida [49], 10 by Froese and Pauly [50], and 12 species by Psomadakis et al. [51]. Since DNA barcodes are not available for Pakistani mullet species, it is not possible to know if these morpho-species belong to already identified MOTU’s (such as those listed in [29]) or represent cryptic diversity.
The present study was designed to evaluate the divergence threshold and barcoding gap for the accurate molecular delimitation of mullet species present in Pakistan and flag new MOTU’s using sequences of the mitochondrial COI gene. The results will significantly contribute to BOLD systems and GenBank databases with new DNA barcodes and provide an overview of species diversity of mullets from Pakistan in comparison with species elsewhere.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. DNA Barcode Reference Library and Taxonomical Nomenclature
The reference library used in this study originates from Durand et al. [28], Shen and Durand [29], and Delrieu-Trottin et al. [31]. This library consists of 76 DNA barcode records trimmed to 556 base pairs representing all the species and BIN diversity of genera Planiliza, Ellochelon, Crenimugil, Osteomugil, and Mugil. These DNA barcodes have been selected as reference for the DNA barcode-based species identification since most of specimens barcoded are stored in museum and have been identified by taxonomic experts of the Mugilidae family [2,19,28] (Table S1). They have been used in a number of phylogenetic studies dealing with the taxonomy of the Mugilidae family by several authors [2,19,29,30,31,32]. The nomenclature proposed by Durand et al. [52] and Xia et al. [30] was used for genera while cryptic or unidentified species followed the interim taxonomical nomenclatures established by Durand and Borsa [2]. However, in a state of clarity and traceability, we also mentioned the Barcode Index Numbers (BINs) that can also represent an interim taxonomical nomenclature when no clear species name can be assigned to a barcode. The two interim taxonomical nomenclatures are largely redundant since Durand et al. [19] demonstrated a large overlap of barcode gaps recovered with COI marker (used to establish the BIN by the BOLD system) or a longer marker composed of COI, 16S, and cytochrome b fragment (such as in Durand et al. [28] used by Durand et al. [2] for their interim taxonomical nomenclature). However, the advantage of BIN is to have using the BOLD system with a direct and dynamic vision of the distribution range of the putative species.
2.2. Sample Collection and Identification
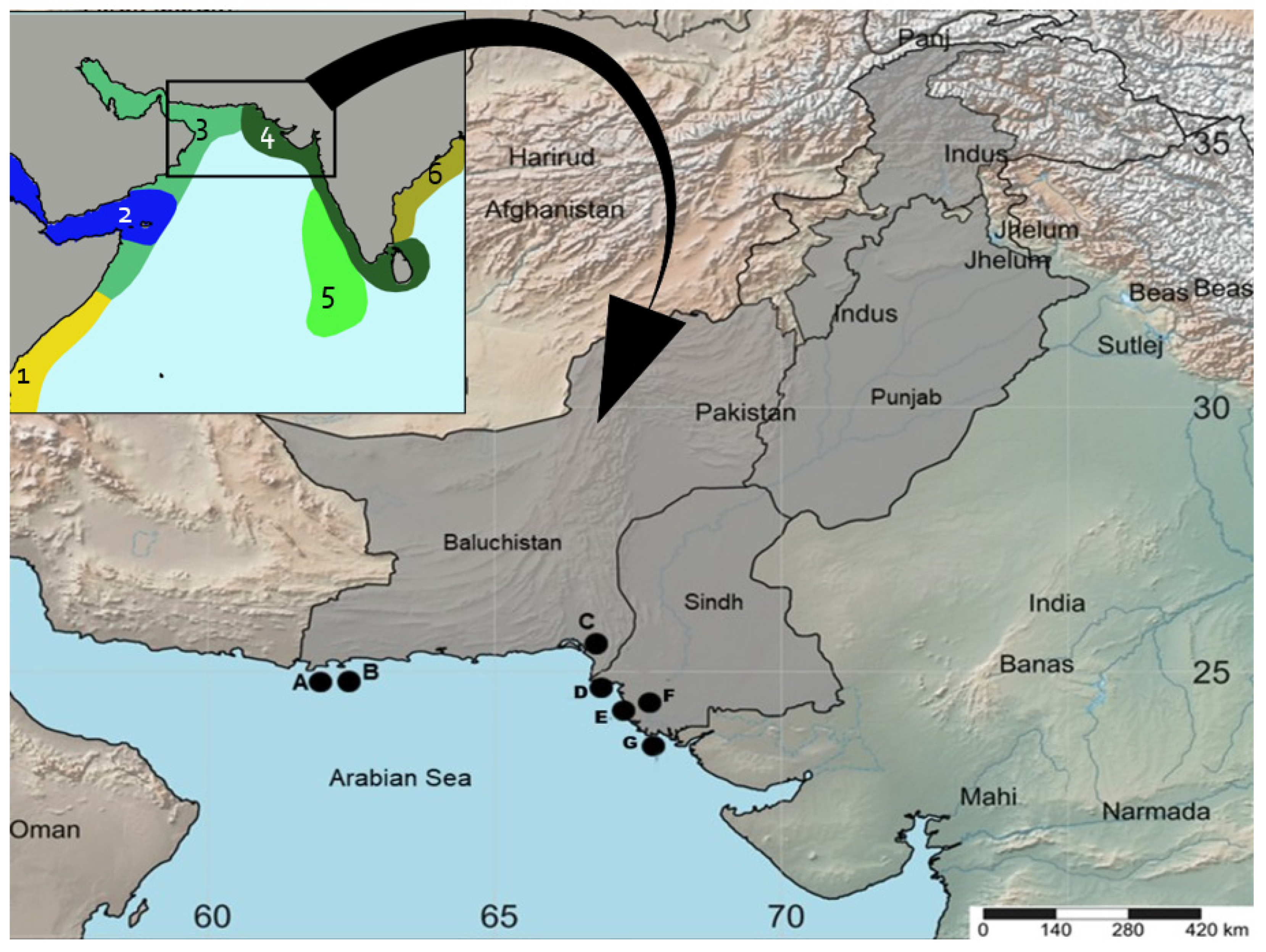
Mullet fish samples were collected from the landing sites and fish markets of Pakistan located along with Sindh (Karachi Fish Harbor, Kakapir, and Keti Bunder) and Baluchistan coasts (Somniani, Pasni, Gwadar, and Jiwani) (Figure 1). All samples were morphologically identified using different identification keys [48,51] and other available literature [53,54]. Each specimen was photographed and fin clipped; then, all the samples were stored individually in an Eppendorf vial with 70% ethanol, and later, they were stored at −20 °C.
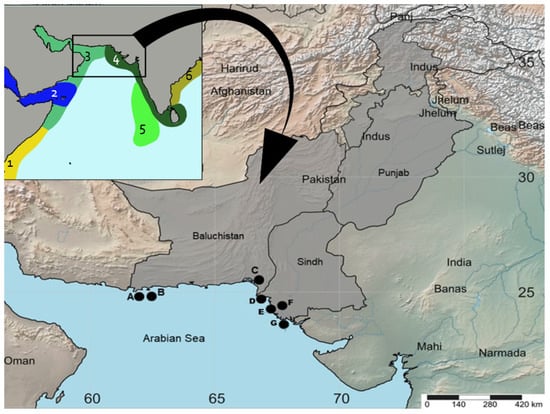
Figure 1.
Biogeographic provinces present and surrounding the Pakistan marine region [55]: 1 = Western Indian Ocean, 2 = Red Sea and Gulf of Aden, 3 = Somali/Arabian, 4 = West and South Indian Shelf, 5 = Central Indian Ocean Islands, and 6 = Bay of Bengal. (B) Map showing the sampling locations of mullets analyzed in this study. A = Jiwani; B = Gwadar, C = Somniani, D = French Beach, E = Kakapir, F = Karachi Fish Harbor, G = Ibrahim Haideri and H = Keti Bunder.
2.3. DNA Amplification and Sequencing
Genomic DNA was isolated from fins using the G-Spin Total DNA extraction mini kit (iNtRON Biotechnology, Jungwon-gu, Gyeonggi, Korea) following the manufacturer’s recommendations. Approximately, 652 base pairs (bp) of the cytochrome oxidase subunit I (COI) were amplified using primers FishF1+ FishF2/FishR1 [56]. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) was conducted in the total volume of 40 µL containing 20 µL of MyTaq PCR Mastermix (Bioline, London, UK), 16 µL of ultrapure water, 0.8 µL of BSA (Euromedex, Souffelweyersheim, France), 0.6 µL of each primer (3 µM), and 2 µL of DNA template. The conditions used during PCR reaction were as follows: initial denaturation temperature at 92 °C for 5 min followed by 35 cycles of strand denaturation at 92 °C for 1 min, primer annealing at 52 °C for 45 s, primer extension at 72 °C for 1.5 min, and a final extension at 72 °C for 5 min. Sequencing was performed by Macrogen Inc. (Seoul, Korea). All nucleotide sequences were deposited in GenBank. The accession numbers are given in Table 1.

Table 1.
List of mullet species (names inferred from morpho-anatomical keys), code numbers, locality information and GenBank’s accession numbers.
2.4. DNA Barcode-Based Species Identification
Species identification based on specimen morphology was confronted to an independent species identification using DNA barcodes. All DNA barcodes generated in this study were uploaded on the BOLD system that assigned these barcodes to molecular operational taxonomic units, (MOTUs) called Barcode Index Numbers (BINs) using the RESL algorithm. [57]
This algorithm flag MOTU’s boundaries by clustering DNA barcodes with high sequence similarity and connectivity using all DNA barcodes of the BOLD’s library. BINs are used to confirm the concordance between species designations and barcode sequence clusters [57].
The composition and variations of nucleotides were analyzed by Mega V. 7.0 [58]. For the calculation of genetic distances between and within the species of mullets, Kimura-2-parameter (K2P) model was used [59]. A Neighbor-Joining tree was constructed with bootstrap analysis (500 replicates) to evaluate the reciprocal monophyly of species. To reveal and discriminate various species present in our sampling, we constructed phylogenetic tree using all COI barcodes generated in this study and secondarily with mullet reference barcodes. All trees were rooted using as outgroup a sequence of Abudefduf vaigiensis (Perciformes: Pomacentridae).
3. Results
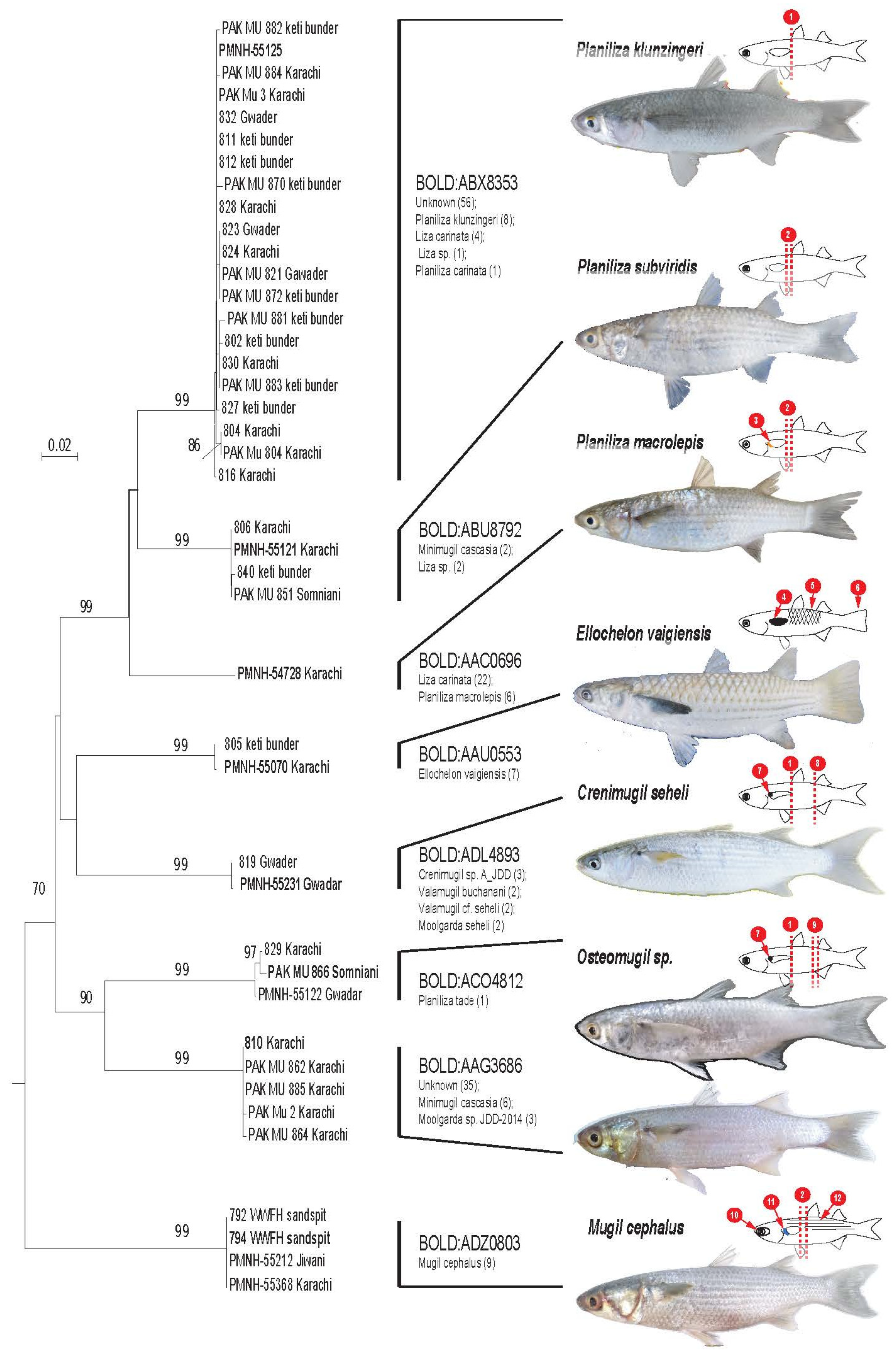
A total of 41 specimens were successfully barcoded. All data relative to these specimens as well as their DNA barcodes were uploaded in BOLD’s project PAKF. Among these specimens, 33 were morphologically identified at the species level. (Figure 2). These species are Planiliza macrolepis, P. klunzingeri, P. subviridis, Crenimugil seheli, Ellochelon vaigiensis, and Mugil cephalus (Table 1). The remaining eight specimens were identified at the genus level only: the Osteomugil genus. At exception of Osteomugil species, they were easily distinguishable using following criteria: length of the pectoral fin in regard to the birth of the first dorsal fin, presence of dot or blotch at the birth of the pectoral fin, presence and importance of adipose eyelid, color of the pectoral fin, position of the second dorsal in regard to the anal fin, form of the caudal fin, and scale margin (Figure 2).
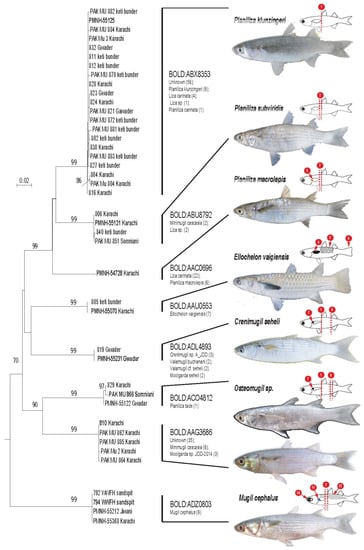
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic relationships among Mugilidae specimens collected along Pakistan shores recovered using 622 bp of the COI and the Neighbor-Joining method. The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (500 replicates) are shown next to the branches [2]. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree. The evolutionary distances were computed using the Kimura 2-parameter method [3] and are in the units of the number of base substitutions per site. Each leaf of the tree corresponds to an individual sampled in Pakistani water, and leaves in bold correspond to the specimen’s picture on the right. BINs provided from BOLD is mentioned for each clade as well as species name of specimen belonging to the BIN (in parentheses number of specimen). Species identified using morpho-anatomical criteria are indicated on the right of the figure. Fish draws highlight main morphometrical criteria that discriminate species collected in Pakistan. 1. Tip the pectoral fin at vertical of the birth of the first dorsal fin, 2. Tip the pectoral fin not reaching vertical of the birth of the first dorsal fin, 3. Presence of a golden blotch at the birth of the pectoral fin, 4. Pectoral fin black, 5. Scales with black margin, 6. Fin tail truncated, 7. Presence of a black dot at the birth of the pectoral fin, 8. Birth of the second dorsal fin at vertical of the birth of the birth of the anal fin, 9. Birth of the second dorsal fin not at vertical of the birth of the anal fin, 10. Large adipose eyelid, 11. Presence of a blue blotch at the birth of the pectoral fin, and 12. Black stripes on flank. Pictures provided by Ariba Hasan & Shabir Ali Amir (copyright).
All barcodes obtained in this study have been assigned in BOLD to 8 BINs (Figure 2). For specimens identified at the species taxonomic level, only one BIN has been recovered. The generated COI sequences were compared with the available COI sequences [2,19] and BOLD system revealed the presence of at least seven unknown candidate species.
4. Discussion
BOLD:AAC0696/Planiliza macrolepis (morphology)
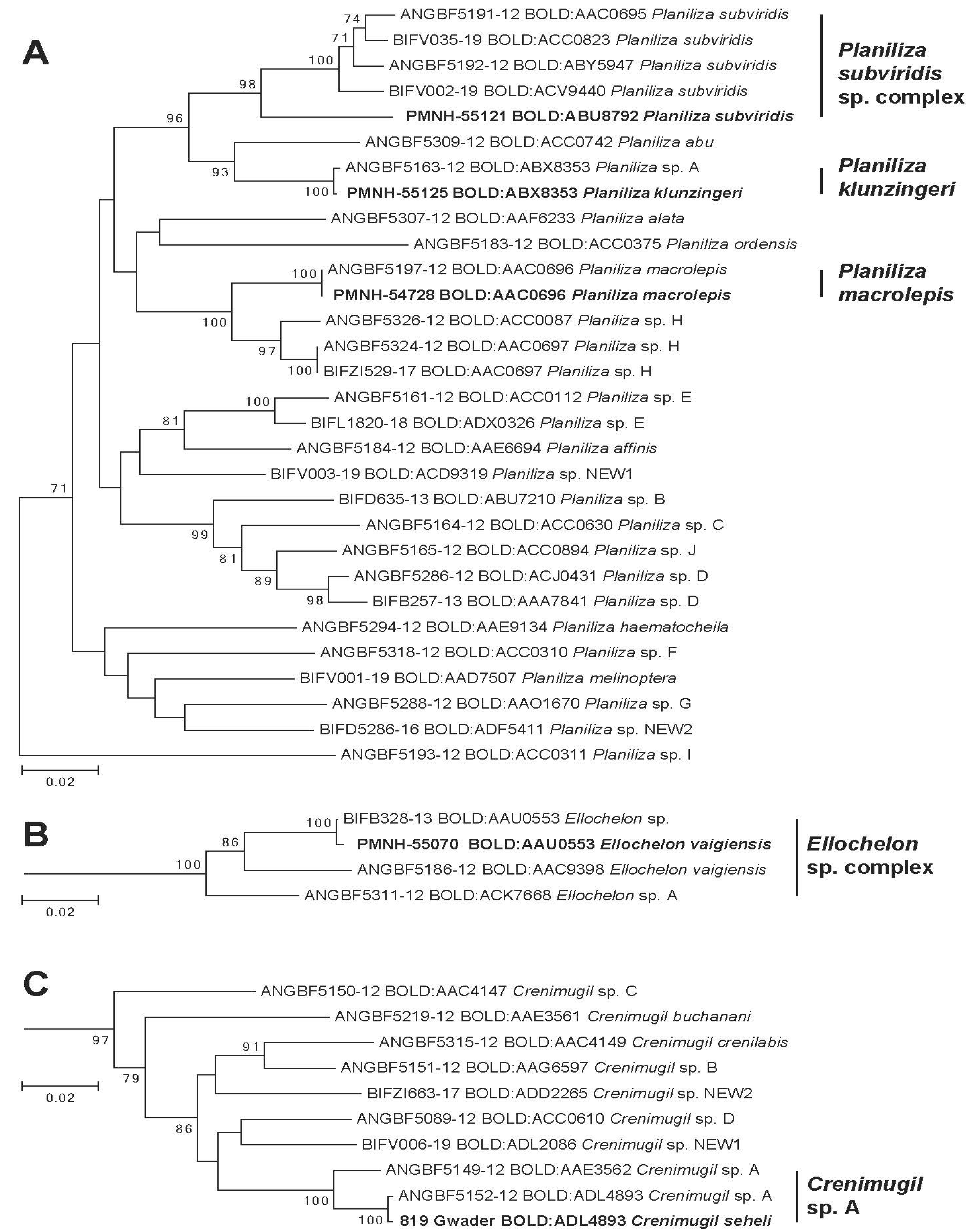
Specimen from Pakistan identified morphologically as Planiliza macrolepis belongs to this BIN as well as Durand and Borsa’s [2] reference sequences of Planiliza macrolepis (Figure 3A). Specimens identified morphologically as P. macrolepis belongs to two lineages with parapatric geographic distribution: one located in the East Indian Ocean (South Africa, Seychelles, and Oman) and one from the Central Indian Ocean to the Pacific Ocean (Maldives, Sri Lanka, Taiwan, Japan, New Caledonia, and Fiji) [28]. However, because the type locality of P. macrolepis Smith 1948 is in South Africa, Durand and Borsa [2] proposed to keep this name only for the NW Indian lineage, the second one being provisionally designated as Planiliza sp. H. Present data precise P. macrolepis (BOLD:AAC0696) distribution range eastward and, more importantly, its geographic limit with its sibling species Planiliza sp. H, to date, situated in India [29].
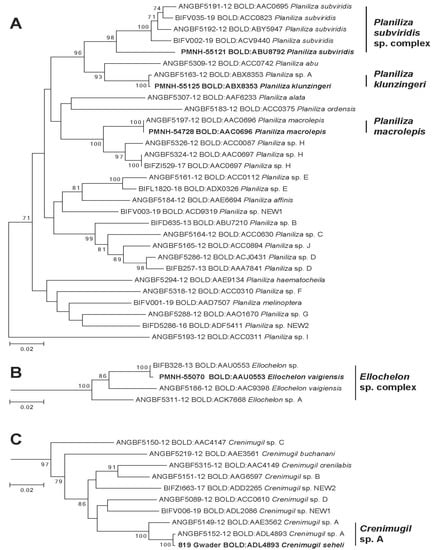
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic tree of species in Genera Planiliza (A), Ellochelon (B), and Crenimugil (C). Leaves in bold represent a representative MOTU/BIN identified in Pakistan waters.
BOLD:ABX8353/Planiliza klunzingeri (morphology)
Specimens from Pakistan identified morphologically as Planiliza klunzingeri assigned to the BIN BOLD:ABX8353 that also included reference sequences of Planiliza sp. A of Durand and Borsa [2] (Figure 3A). There is no doubt that mullet specimens collected in the Persian Gulf and named “Planiliza sp. A” by Durand and Borsa [2] is actually Planiliza klunzingeri considering morphological characters records on our specimen as well as previous barcoding studies [29,60] The distribution range of Planiliza klunzingeri encompasses the Persian Gulf eastward to the coast of Karachi and Bombay [61]. Eastward distribution limits have been confirmed by [62], which provided DNA barcodes of P. klunzingeri (BOLD:ABX8353) collected in the Narmada River (NW India). Interestingly, P. klunzingeri (BOLD:ABX8353) and P. macrolepis (BOLD:AAC0696) probably shared the same eastward distribution limit, which suggests the presence of a biogeographic barrier in NW India and not along Pakistani shores as suggested by Spalding et al. [55] (Figure 1).
BOLD:ABU8792/Planiliza subviridis (morphology)
Pakistani specimens assigned to this BIN have been morphologically identified as Planiliza subviridis but does not correspond to any reference sequences nor Planiliza subviridis sensu Durand and Borsa [2] that are assigned in BOLD to 4 different BINs (Figure 3A). If specimens from Pakistan share a common ancestor with P. subviridis sensu Durand and Borsa [2], the divergence of Pakistani specimen with other P. subviridis specimen (6.9% K2P) largely exceeds divergence observed among P. subviridis sensu Durand and Borsa [2] (1.8% K2P).
In BOLD, the BIN BOLD: ABU8792 consists of only 4 specimens (ANGEN 113-115, DBFN284-12, DBFN295-12, and GBMINI126937-17) collected at two localities: Gujarat, India, and the Persian Gulf, Iran. These barcodes are labeled as Liza sp. or Minimugil cascasia, which indicate nomenclature mistake, i.e., Liza is no longer considered as valid [52], or misidentification, Minimugil cascasia is endemic to rivers of northern Bengal and present a very different phylogenetic position [63]. However, the barcode’s geographic distribution origins describe a geographic distribution for this MOTU (BOLD: ABU8792) similar to P. klunzingeri, from the Persian Gulf to NW India. This distribution is fully parapatric to the distribution of P. subviridis sensu Durand and Borsa [2] as BIN assigned to this last species consists of specimen sampled from West to East in India (Maharashtra and Kochi to Puducherry, (BOLD:AAC0695); Indonesia and Malaysia (BOLD:ACC0823); Indonesia and Papua New Guinea (BOLD:ACV9440); Philippines, Taiwan, and China (BOLD:ABY5947). Considering the type locality of P. subviridis, Valenciennes 1836 Ganges River, Malabar, India, the name subviridis should be maintained only for the BIN BOLD: AAC0695, the other close candidate species being named “Planiliza cf. subviridis”. In the case of the MOTU present in Pakistan, we assigned provisional species name Planiliza cf. subviridis (BOLD:ABU8792) pending further morpho-anatomical investigation to determine potential diagnostic feature.
BOLD:AAU0553/Ellochelon vaigiensis (morphology)
Pakistani specimens assigned to the BIN BOLD:AAU0553 have been identified morphologically as Ellochelon vaigiensis. This BIN also includes the reference sequence from Indonesia labeled as Ellochelon sp. by Delrieu-Trottin et al. [31] but none of those depicted in Durand et al. [28] that identified two MOTUs in Ellochelon vaigiensis morpho species (Figure 3B). Later, based on the level of divergence that largely exceeds interspecific diversity, Durand et al. [2] proposed to provisionally name these MOTUs as Ellochelon sp. A for the lineage (BOLD:ACK7668) observed only in Australian specimens and maintained the name for the lineage (BOLD:AAC9398) present from Indonesia to French Polynesia. Following this logic, this third lineage corresponding to the BIN BOLD:AAU0553 with the divergence of 6.2% and 5.8% with Ellochelon sp. A and by Ellochelon vaigiensis, respectively, and is temporarily designated as Ellochelon cf. vaigiensis (BOLD:AAU0553). This MOTU is observed in specimens collected in Pakistan, as well as Iran, Malaysia, and Indonesia (BOLD, consultation 01/20/21). No significant phylogenetic relationship has been recovered in the COI phylogenetic tree; all MOTUs corresponding to Ellochelon vaigiensis sensu [2] descended from the same common ancestor (Figure 3B). A larger sampling scheme in the Indo-Pacific targeting Ellochelon spp. is necessary to better delineate the geographic structure of this species complex as well as its evolutionary history.
BOLD:ADL4893/Crenimugil seheli (morphology)
Specimen from Pakistan identified morphologically as Crenimugil seheli is assigned to the BIN BOLD:ADL4893 also included reference sequences of Crenimugil sp. A of Durand and Borsa [2] (Figure 3C). [28] Durand et al. [28] identified in Crenimugil seheli three lineages that occur sympatrically in the Indo-West Pacific; Crenimugil sp. A sensu Durand and Borsa [2] is one of this lineages. In BOLD, barcodes identified as Crenimugil sp. A by Durand and Borsa [2] are assigned to two BINs; BOLD:ADL4893 and BOLD:AAE3562 (Figure 3C). In BOLD, the BIN BOLD:ADL4893 is composed of barcodes observed in 9 specimens collected in the NW Indian Ocean (Iran, Saudi Arabia, Oman, and Seychelles), while BOLD:AAE3562 is composed of 50 specimens collected in the Indo-Pacific region (Reunion Island, Maldives, West Papua, China, Taiwan, Saipan, Australia, New Caledonia, and Fiji). Geographic distribution of these two MOTUs appears parapatric suggesting that these three are sibling species; the species present in Pakistan being assigned to provisional species name Crenimugil cf. seheli (BOLD:ADL4893).
BOLD: ACO4812/Osteomugil sp. (morphology)
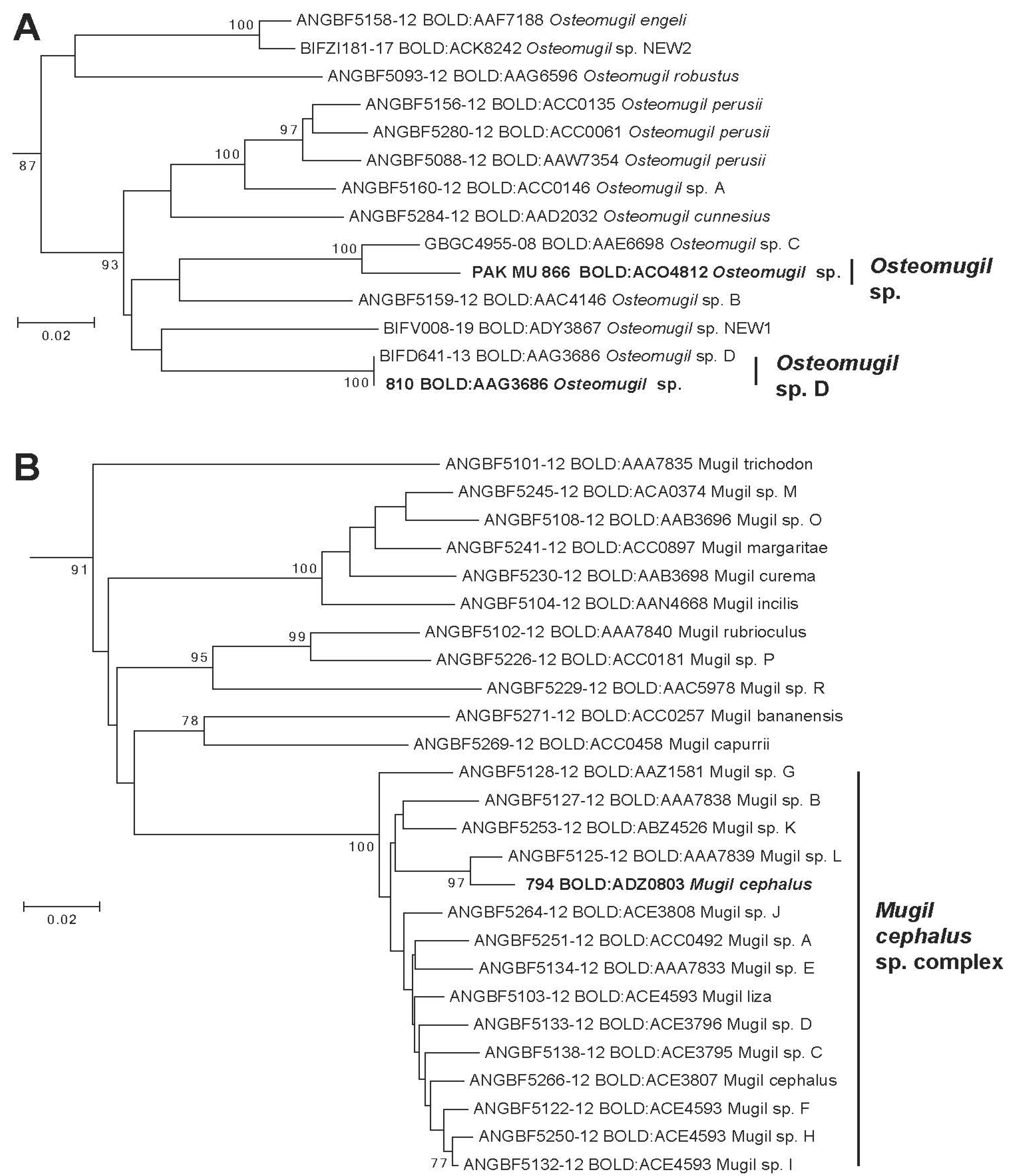
Pakistani specimens assigned to this BIN have been morphologically identified as an Osteomugil species but their barcode does not correspond to any reference sequences. BIN BOLD:ACO4812 is associated with only one public specimen (LQDWL-TIS-31-12-2013-011) collected in India, Gujarat, close to Pakistan’s border.
This specimen LGEN074-14 has been identified as Planiliza tade but the picture of specimen available in BOLD System (consultation 05/23/2021) indicates that it is an Osteomugil species: presence of a black dot at the birth of the pectoral fin, pectoral fin long reaching to the first dorsal fin vertically, and birth of second dorsal fin not to the birth of anal fin vertically. The phylogenetic position in the tree of this BIN also confirms that it is an Osteomugil species with a sister relationship with Osteomugil sp. C also collected in India. (Figure 4A). This MOTU is assigned to a provisional species name Osteomugil sp. (BOLD:ACO4812).
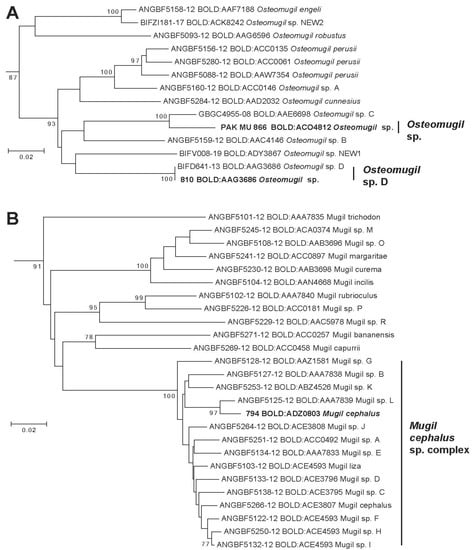
Figure 4.
Phylogenetic tree of species in Genera Osteomugil (A) and Mugil (B). Leaves in bold represent a representative MOTU/BIN identified in Pakistan waters.
Pakistani specimen assigned to the BIN BOLD:AAG3686 present morphological characters of an Osteomugil species but the exact species was not identified. This BIN includes a reference sequence labeled as Osteomugil sp. D by Shen et al. [29] and Delrieu-Trottin et al. [31] but none depicted in Durand and Borsa [2] (Figure 4A). These reference sequences have been observed in a specimen collected in India and Indonesia. In BOLD, this BIN is associated with some additional barcodes obtained from India, Bangladesh, and Malaysia. This species provisionally named “Osteomugil sp. D” (BOLD: AAG3686) appear to be endemic to the Indian Ocean largely distributed from Pakistan to Indonesia. More taxonomical investigations are necessary to identify this species among all the Osteomugil species diversity described in the past.
BOLD: ADZ0803/Mugil cephalus (morphology)
Pakistani specimens assigned to this BIN BOLD: ADZ0803 have been identified morphologically as Mugil cephalus. No reference sequences have been observed in this BIN, while Durand et al. [28] and later Durand et al. [52] depicted in this morpho-species up to 13 and 14 MOTUs, respectively. In BOLD, this BIN is composed of 3 public specimens, collected in Bangladesh (GBMNB8388-20), India (GBGC9983-09), and one from unknown origin but the sequence produced from a laboratory in India (ANGBF54236-19). Within the Mugil cephalus species complex, these new MOTUs presents significant phylogenetic relationships with Mugil sp. L (BOLD:AAA7893) (Figure 4B) observed in the Pacific Ocean [2,18,64]. Mugil cephalus is considered as a species complex consisting of 15 candidate species including Mugil liza in the West Atlantic [2,18]. In some parts of the world, most of these species present parapatric distribution ranges such as the present new species provisionally named “Mugil cf. cephalus” (BOLD:ADZ0803) which is, to date, limited to the North Indian Ocean where no other M. cephalus MOTUs have been identified. When sympatry occurred, such as in the NW Pacific where three MOTU are present, reproductive isolation has been demonstrated, which confirms the validity of their species status [27,65]. No clear phylogenetic structure has been observed in the phylogenetic tree (Figure 4B) as well as a previous phylogenetic tree that included more molecular markers [28]. The diversification of M. cephalus sensu lato occurred during 5 million years (MYA) [32]. The divergence between the Indian Mugil cf. cephalus (BOLD:ADZ0803) and Pacific Mugil sp. L probably has rating of less than 2 MYA, considering its low level of divergence (1.7% K2P) by comparing to other lineages (mean distance 2.9% K2P).
More taxonomic and phylogenetic investigations are necessary to highlight the evolutionary history of this species complex present on a worldwide scale.
5. Conclusions
DNA barcoding appears to be the most efficient method for species identification and its advantage in the detection of cryptic species, an appealing application for many taxonomists [66]. The increasing number of new species detected through DNA barcoding suggests that the biodiversity level is greatly underestimated using solely the classical system of morphology-based identification.
In the present study, the COI gene was successfully used for species identification. Delimitation of MOTUs within the members of family Mugilidae found along the Pakistani waters was determined for the first time. Here, we morphologically characterized six species, although our specimens correspond genetically to eight MOTUs. The comparison of COI sequences generated in this study with the sequences available from different geographical regions [2,19] and BOLD system uncovered the existence of at least seven unknown candidate species from as much as a species complex. Analysis of the geographic distribution of Planiliza species present in Pakistan in light of the genetic diversity stressed the importance of Pakistan as a biogeographic border or transition between the NW Indian fauna and the rest of the Indo-Pacific region. This study calls for more taxonomic and phylogenetic investigations to describe Pakistani species and highlight the biogeographic component of Pakistan ichthyofauna in the Indo-Pacific area. This study will help in the development of DNA barcode reference data for the mullets of Pakistan which in turn would help in the management and conservation of fisheries. Furthermore, the novel sequences generated in this study and deposited in BOLD/GenBank will be available for future reference and research.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/d13060232/s1: Table S1: Mullet specimens list used as species reference from genera Planiliza, Ellochelon, Crenimugil, Osteomugil and Mugil.
Author Contributions
A.H., P.J.A.S. and S.A.A. collected the samples and performed morphological analysis. Molecular analysis was performed by J.-D.D. J.-D.D., A.H., and S.A.A. wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The molecular analysis was funded by IRD, France.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset generated/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
References
- Hubert, N.; Meyer, C.P.; Bruggemann, H.J.; Guerin, F.; Komeno, R.J.; Espiau, B.; Causse, R.; Williams, J.T.; Planes, S. Cryptic diversity in Indo-Pacific coral-reef fishes revealed by DNA-barcoding provides new support to the centre-of-overlap hypothesis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e28987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand, J.D.; Borsa, P. Mitochondrial phylogeny of grey mullets (Acanthopterygii: Mugilidae) suggest high proportion of cryptic species. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2015, 338, 226–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, R.D.; Holmes, B.H.; Yearsley, G.K. DNA barcoding reveals a likely second species of Asian sea bass (barramundi) (Lates calcarifer). J. Fish Biol. 2008, 72, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.D.; Holmes, B.H.; White, W.T.; Last, P.R. DNA barcoding Australasian chondrichthyans: Results and potential uses in conservation. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2008, 59, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, A.; PONCE de LEÓN, J.L.; Rodriguez, R.; Casane, D.; Cote, G.; Bernatchez, L.; Garcíamachado, E.R.I.K. DNA barcoding of Cuban freshwater fishes: Evidence for cryptic species and taxonomic conflicts. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriwattanarothai, N.; Steinke, D.; Ruenwongsa, P.; Hanner, R.; Panijpan, B. Molecular and morphological evidence supports the species status of the Mahachai fighter Betta sp. Mahachai and reveals new species of Betta from Thailand. J. Fish Biol. 2010, 77, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.L.; Harmon, L.J.; Shoo, L.P.; Melville, J. Evidence of constrained phenotypic evolution in a cryptic species complex of agamid lizards. Evolution 2011, 65, 976–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puckridge, M.; Last, P.R.; White, W.T.; Andreakis, N. Phylogeography of the Indo West Pacific maskrays (Dasyatidae, Neotrygon): A complex example of chondrichthyan radiation in the Cenozoic. Ecol. Evol. 2013, 3, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsa, P.; Arlyza, I.S.; Hoareau, T.B.; Shen, K.N. Diagnostic description and geographic distribution of four new cryptic species of the blue-spotted maskray species complex (Myliobatoidei: Dasyatidae; Neotrygon spp.) based on DNA sequences. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2018, 36, 827–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsa, P.; Fauvelot, C.; Tiavouane, J.; Grulois, D.; Wabnitz, C.; Naguit, M.A. Andrefouet S Distribution of Noah’s giant clam, Tridacna noae. Mar. Biodivers. 2015, 45, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pante, E.; Puillandre, N.; Viricel, A.; Arnaud-Haond, S.; Aurelle, D.; Castelin, M.; Viard, F. Species are hypotheses: Avoid connectivity assessments based on pillars of sand. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 525–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struck, T.H.; Cerca, J. Cryptic species and their evolutionary significance. Encycl. Life Sci. 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, C.; Taylor, M.I.; Pereyra, R.; Rico, C. Mapping of the spawning grounds of Irish Sea gadoids using genetic identification of planktonic eggs. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, N.; Hanner, R.; Holm, E.; Mandrak, N.E.; Taylor, E.; Burridge, M.; Zhang, J. Identifying Canadian freshwater fishes through DNA barcodes. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bickford, D.; Lohman, D.J.; Sodhi, N.S.; Ng, P.K.L.; Meier, R.; Winker, K.; Das, I. Cryptic species as a window on diversity and conservation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyde, J.R.; Underkoffler, K.E.; Sundberg, M.A. DNA barcoding provides support for a cryptic species complex within the globally distributed and fishery important opah (Lampris guttatus). Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2014, 14, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froese, R.; Pauly, D. FishBase. 2021. Available online: www.fishbase.org (accessed on 5 March 2021).
- Whitfield, A.K.; Panfili, J.; Durand, J.D. A global review of the cosmopolitan flathead mullet Mugil cephalus Linnaeus 1758 (Teleostei: Mugilidae), with emphasis on the biology, genetics, ecology and fisheries aspects of this apparent species complex. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2012, 22, 641–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, J.D.; Hubert, N.; Shen, K.N.; Borsa, P. DNA barcoding grey mullets. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2017, 27, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Chang, J.T.; Tsu, Y.Y. Genetic relationships of four Taiwan mullets (Pisces: Perciformes: Mugilidae). J. Fish Biol. 1995, 46, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papasotiropoulos, V.; Klossa-Kilia, E.; Kilias, G.; Alahiotis, S. Genetic divergence and phylogenetic relationships in grey mullets (Teleostei: Mugilidae) using allozyme data. Biochem. Genet. 2001, 39, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papasotiropoulos, V.; Klossa-Kilia, E.; Alahiotis, S.N.; Kilias, G. Molecular phylogeny of grey mullets (Teleostei: Mugilidae) in Greece: Evidence from sequence analysis of mtDNA segments. Biochem. Genet. 2007, 45, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, C.; Caliskan, M.; Kucuktas, H. Phylogenetic relationships of nine mullet species (Mugilidae) in the Mediterranean Sea. Hydrobiologia 2005, 532, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, E.; Schneider, H.; Nirchio, M.; Santa-Brigida, E.; Rodrigues-Filho, L.F.; Sampaio, I. Molecular phylogenetic analyses of mullets (Mugilidae, Mugiliformes) based on two mitochondrial genes. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2007, 23, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erguden, D.; Gurlek, M.; Yaglioglu, D.; Turan, C. Genetic Identification and Taxonomic Relationship of Mediterranean Mugilid Species Based on Mitochondrial 168 rDNA Sequence Data. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2010, 9, 336–341. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.Y.; Brown, C.L.; Yang, T.B. Phylogenetic relationships of mullets (Mugilidae) in China Seas based on partial sequences of two mitochondrial genes. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2010, 38, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.N.; Jamandre, B.W.; Hsu, C.C.; Tzeng, W.N.; Durand, J.D. Plio Pleistocene sea level and temperature fluctuations in the northwestern Pacific promoted speciation in the globally distributed flathead mullet Mugil cephalus. BMC Evol. Biol. 2011, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Durand, J.D.; Shen, K.N.; Chen, W.J.; Jamandre, B.W.; Blel, H.; Diop, K.; Borsa, P. Systematics of the grey mullets (Teleostei: Mugiliformes: Mugilidae): Molecular phylogenetic evidence challenges two centuries of morphology-based taxonomy. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2012, 64, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.; Durand, J.D. The biogeography of Mugilidae in India, South-East and East Asia. In Biology, Ecology and Culture of Grey Mullets (Mugilidae); Crosetti, D., Blaber, S., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Racon, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, R.; Durand, J.D.; Fu, C. Multilocus resolution of Mugilidae phylogeny (Teleostei: Mugiliformes) implications for the family’s taxonomy. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 96, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delrieu-Trottin, E.; Durand, J.D.; Limmon, G.; Sukmono, T.; Sugeha, H.Y.; Chen, W.J.; Fitriana, Y. Biodiversity inventory of the grey mullets (Actinopterygii:Mugilidae) of the Indo Australian Archipelago through the iterative use of DNA based species delimitation and specimen assignment methods. Evol. Appl. 2020, 13, 1451–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, J.M.; Almeida, J.P.; Sturaro, M.J.; FabrÉ, N.N.; Pereira, R.J.; Mott, T. Deep genetic divergence and paraphyly in cryptic species of Mugil fishes (Actinopterygii: Mugilidae). Syst. Biodivers. 2020, 18, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, J.C. Fishes of worldwide (circumtropical) distribution. Copeia 1960, 3, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autem, M.; Bonhomme, F. Eléments de systématique biochimique chez les Mugilidés de Méditerranée. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1980, 8, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldara, F.; Bargelloni, L.; Ostellari, L.; Penzo, E.; Colombo, L.; Patarnello, T. Molecular phylogeny of grey mullets based on mitochondrial DNA sequence analysis: Evidence of a differential rate of evolution at the intrafamily level. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 1996, 6, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.R.; Capula, M.; Crosetti, D.; Campton, D.E.; Sola, L. Genetic divergence and phylogenetic inferences in five species of Mugilidae (Pisces: Perciformes). Mar. Biol. 1998, 131, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.R.; Ungaro, A.; De Innocentiis, S.; Crosetti, D.; Sola, L. Phylogenetic analysis of Mediterranean Mugilids by allozymes and 16S mt-rRNA genes investigation: Are the Mediterranean species of Liza monophyletic? Biochem. Genet. 2004, 42, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murgia, R.; Tola, G.; Archer, S.N.; Vallerga, S.; Hirano, J. Genetic identification of grey mullet species (Mugilidae) by analysis of mitochondrial DNA sequence: Application to identify the origin of processed ovary products (bottarga). Mar. Biotechnol. 2002, 4, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gornungm, E.; Colangelo, P.; Annesi, F. 5S ribosomal RNA genes in six species of Mediterranean grey mullets: Genomic organization and phylogenetic inference. Genome 2007, 50, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imsiridou, A.; Minos, G.; Katsares, V.; Karaiskou, N.; Tsiora, A. Genetic identification and phylogenetic inferences in different Mugilidae species using 5S rDNA markers. Aquac. Res. 2007, 38, 1370–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semina, A.V.; Polyakova, N.E.; Makhotkin, M.A.; Brykov, V.A. Mitochondrial DNA divergence and phylogenetic relationships in mullets (Pisces: Mugilidae) of the Sea of Japan and the Sea of Azov revealed by PCR-RFLP-analysis. Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2007, 33, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blel, H.; Chatti, N.; Besbes, R.; Farjallah, S.; Elouaer, A.; Guerbej, H.; Said, K. Phylogenetic relationships in grey mullets (Mugilidae) in a Tunisian lagoon. Aquac. Res. 2008, 39, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, J.D.; Whitfield, A.K. Biogeography and Distribution of Mugilidae in the Western, Central and Southern Regions of Africa. In Biology, Ecology and Culture of Grey Mullets (Mugilidae); Crosetti, D., Blaber, S., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Racon, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, N.A.; Nirchio, M.; Oliveira, C.D.; Siccharamirez, R. Taxonomic review of the species of Mugil (Teleostei: Perciformes: Mugilidae) from the Atlantic South Caribbean and South America, with integration of morphological, cytogenetic and molecular data. Zootaxa 2015, 3918, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, M.R.; Martins, M.; Naik, S. Interspecific genetic divergence in grey mullets from the Goa region. Aquaculture 1992, 105, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.U.; Khan, S.A.; Lyla, P.S.; Kumar, C.P. DNA barcoding resolves taxonomic ambiguity in mugilidae of Parangipettai waters (Southeast Coast of India). Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2013, 13, 321–330. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, M.R. Marine Fishes of Karachi and the Coast of Sindh and Makran; Government of Pakistan Ministry of Food Agriculture; Government of Pakistan Press: Karachi, Pakistan, 1955; p. 80.
- Bianchi, G. Field Guide to the Commercial Marine and Brackish-Water Species of Pakistan; FAO species identification sheets for fishery purposes; prepared with the support of PAK/77/033 and FAO (FIRM) Regular Programme; FAO: Italy, Rome, 1985; p. 200. [Google Scholar]
- Fahmida, I. Mullets of Korangi Creek Karachi. Zool. Surv. Rec. Pak. 2002, 14, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Froese, R.; Pauly, D. Fish Base. World Wide Web Electronic Publication. 2010. Available online: www.fishbase.org (accessed on 10 September 2010).
- Psomadakis, P.N.; Osmany, H.B.; Moazzam, M. Field Identification Guide to the Living Marine Resources of Pakistan; FAO Species Identification Guide for Fishery Purposes; FAO: Italy, Rome, 2015; 386p. [Google Scholar]
- Durand, J.D.; Chen, W.J.; Shen, K.N.; Borsa, P. Genus-level taxonomic changes imposed by the mitochondrial phylogene.y of grey mullets (Teleostei: Mugilidae). Comptes Rendus Biol. 2012, 335, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, J.M. The Mugilidae of the world. Mem. Qld. Mus. 1997, 41, 457–562. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemzadeh, J. Phylogeny and Systematics of Indo-Pacific Mullets (Teleostei: Mugilidae) with Special Reference to the Mullets of Australia. Ph.D. Thesis, Macquarie University, Sydney, Australia, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Spalding, M.D.; Fox, H.E.; Allen, G.R.; Davidson, N.; Ferdaña, Z.A.; Finlayson, M.A.X.; Robertson, J. Marine eco regions of the world: A bio regionalization of coastal and shelf areas. BioScience 2007, 57, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.D.; Zemlak, T.S.; Innes, B.H.; Last, P.R.; Hebert, P.D. DNA barcoding of Australia’s fish species. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1847–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D. A DNA-based registry for all animal species: The Barcode Index Number (BIN) system. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senou, H.; Yoshino, T.; Okiyama, M. A review of the mullets with a keel on the back, Liza carinata complex (Pisces: Mugilidae). Publ. Seto Mar. Biol. Lab. 1987, 32, 303–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Panhwar, S.K.; Gao, T.; Han, Z.; Li, C.; Sun, D.; Song, N. New genetic evidence from three keel-backed liza species based on DNA Barcoding confirms morphology-based identification. Pak. J. Zool. 2017, 49, 1901–1907. [Google Scholar]
- Khedkar, G.D.; Jamdade, R.; Naik, S.; David, L.; Haymer, D. DNA barcodes for the fishes of the Narmada, one of India’s longest rivers. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand, J.D. Implications of Molecular Phylogeny for the Taxonomy of Mugilidae. In Biology, Ecology and Culture of Grey Mullets (Mugilidae); Crosetti, D., Blaber, S., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Racon, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 22–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viet Tran, T.T.; Ke Phan, L.; Durand, J.D. Diversity and distribution of cryptic species within the Mugil cephalus species complex in Vietnam. Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2017, 28, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, K.N.; Chang, C.W.; Durand, J.D. Spawning segregation and philopatry are major prezygotic barriers in sympatric cryptic Mugil cephalus species. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2015, 338, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knebelsberger, T.; Landi, M.; Neumann, H.; Kloppmann, M.; Sell, A.F.; Campbell, P.D.; Laakmann, S.; Raupach, M.J.; Carvalho, G.R.; Costa, F.O. A reliable DNA barcode reference library for the identification of the North European shelf fish fauna. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2014, 14, 1060–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).