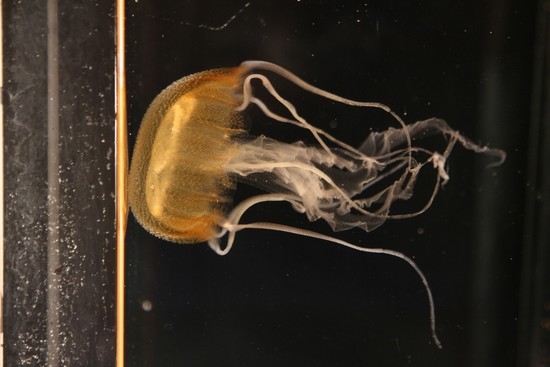
Why Do Only Males of Mawia benovici (Pelagiidae: Semaeostomeae: Scyphozoa) Seem to Inhabit the Northern Adriatic Sea?
Abstract
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Avian, M.; Ramšak, A.; Tirelli, V.; D’Ambra, I.; Malej, A. Redescription of Pelagia benovici into a new jellyfish genus, Mawia, gen. nov. and its Phylogenetic Position within Pelagiidae (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa: Semaeostomeae). Invertebr. Syst. 2016, 30, 523–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piraino, S.; Aglieri, G.; Martell, L.; Mazzoldi, C.; Melli, V.; Milisenda, G.; Scorrano, S.; Boero, F. Pelagia benovici sp. nov. (Cnidaria, Scyphozoa): A new jellyfish in the Mediterranean Sea. Zootaxa 2014, 3794, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokes, M.; Andreou, V.; Bakiu, R.; Bonanomi, S.; Camps, J.; Christidis, G.; Crocetta, F.; Giovos, I.; Gori, A.; Juretić, T.; et al. New Mediterranean Biodiversity Records (November 2018). Med. Mar. Sci. 2018, 19, 678. [Google Scholar]
- Bayha, K.M.; Collins, A.G.; Gaffney, P.M. Multiple phylogeny of the scyphozoan jellyfish family Pelagiidae reveals that the common U.S. Atlantic sea nettle comprises two distinct species (Chrysaora quinquecirrha and C. chesapeakei). Peer J. 2017, 5, e3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chartosia, N.; Anastasiadis, D.; Bazairi, H.; Crocetta, F.; Deidun, A.; Despalatović, M.; Di Martino, V.; Dimitriou, N.; Dragičević, B.; Dulčić, J.; et al. New Mediterranean Biodiversity Records (July 2018). Med. Mar. Sci. 2018, 19, 406–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardent, P. Sex and Sex Determination in Coelenterates. In Intersexuality in the Animal Kingdom; Reinboth, R., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1975; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Siebert, S.; Juliano, C.E. Sex, Polyps and Medusae: Determination and Maintenance of Sex in Cnidaria. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2017, 84, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Gu, Z.; Xing, M.; Sun, Y.; Chen, S.; Chen, Z. Sex determination and differentiation in Aurelia sp.1: The absence of temperature dependence. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2018, 36, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiariti, A.; Morandini, A.C.; Jarms, G.; von Glehn Paes, R.; Franke, S.; Mianzan, H.W. Asexual reproduction strategies and blooming potential in Scyphozoa. Mar. Ecol. Progr. Ser. 2014, 510, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avian, M.; Motta, G.; Prodan, M.; Tordoni, E.; Macaluso, V.; Beran, A.; Goruppi, A.; Bacaro, G.; Tirelli, V. Asexual reproduction and strobilation of Sanderia malayensis (Scyphozoa, Pelagiidae) in relation to temperature: Experimental evidence and implications. Diversity 2021, 13, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tirelli, V.; Kogovšek, T.; Rogelja, M.; Paliaga, P.; Avian, M.; Malej, A. Why Do Only Males of Mawia benovici (Pelagiidae: Semaeostomeae: Scyphozoa) Seem to Inhabit the Northern Adriatic Sea? Diversity 2021, 13, 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13060222
Tirelli V, Kogovšek T, Rogelja M, Paliaga P, Avian M, Malej A. Why Do Only Males of Mawia benovici (Pelagiidae: Semaeostomeae: Scyphozoa) Seem to Inhabit the Northern Adriatic Sea? Diversity. 2021; 13(6):222. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13060222
Chicago/Turabian StyleTirelli, Valentina, Tjaša Kogovšek, Manja Rogelja, Paolo Paliaga, Massimo Avian, and Alenka Malej. 2021. "Why Do Only Males of Mawia benovici (Pelagiidae: Semaeostomeae: Scyphozoa) Seem to Inhabit the Northern Adriatic Sea?" Diversity 13, no. 6: 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13060222
APA StyleTirelli, V., Kogovšek, T., Rogelja, M., Paliaga, P., Avian, M., & Malej, A. (2021). Why Do Only Males of Mawia benovici (Pelagiidae: Semaeostomeae: Scyphozoa) Seem to Inhabit the Northern Adriatic Sea? Diversity, 13(6), 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13060222