Animal Forest Mortality: Following the Consequences of a Gorgonian Coral Loss on a Mediterranean Coralligenous Assemblage
Abstract
1. Introduction
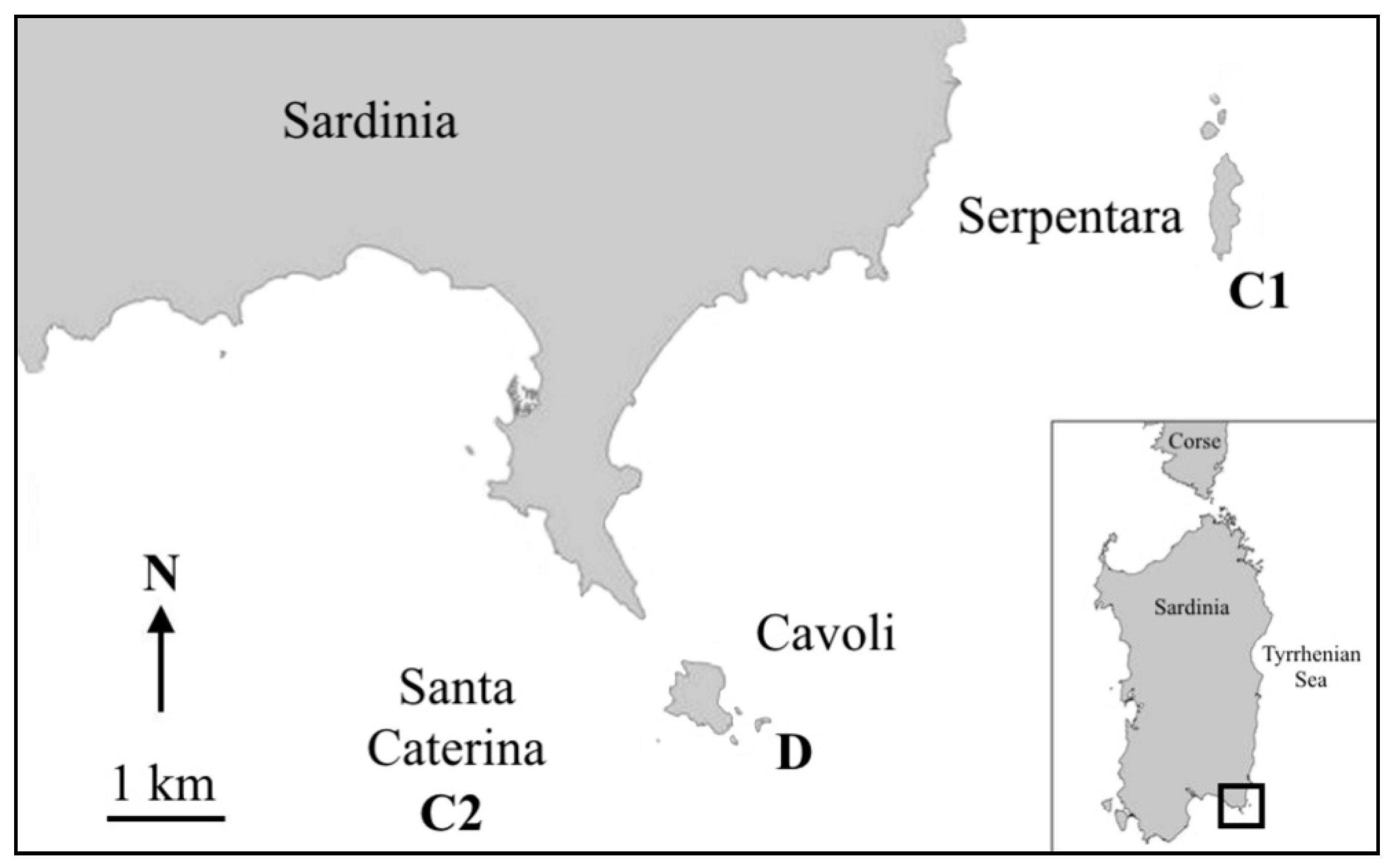
2. Material and Methods
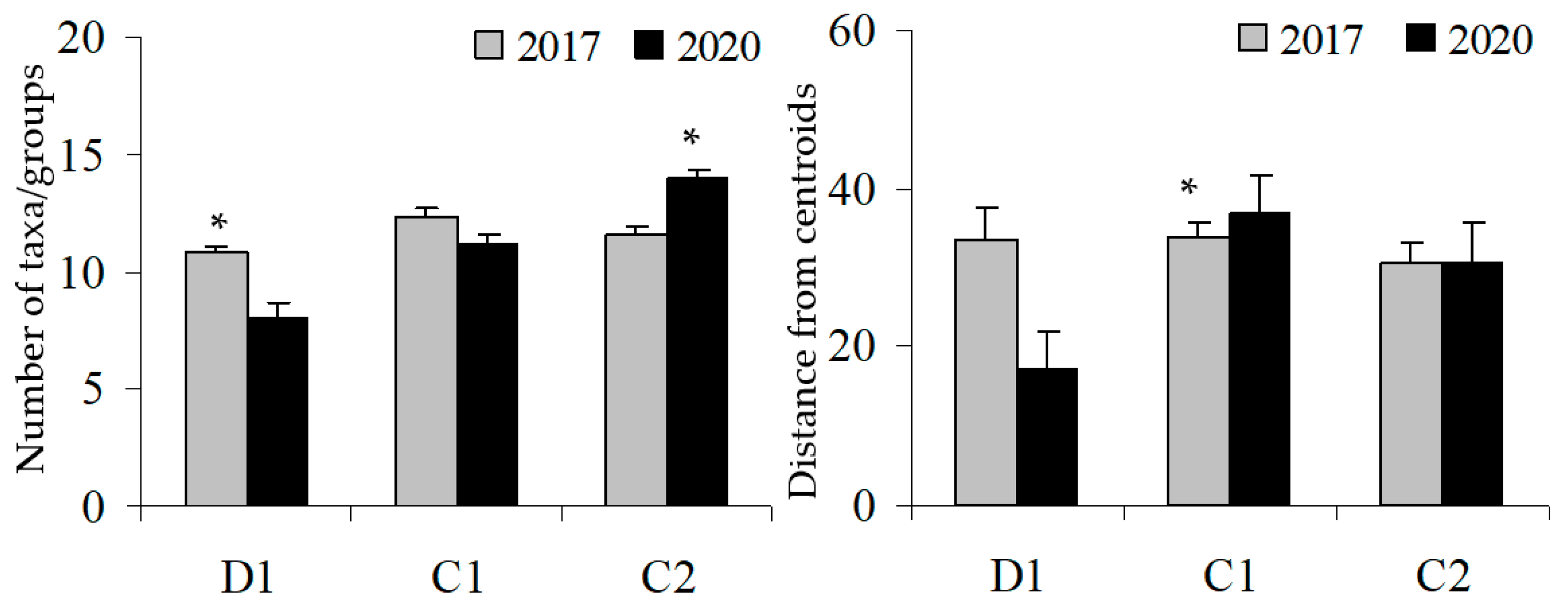
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crisci, C.; Bensoussan, N.; Romano, J.C.; Garrabou, J. Temperature anomalies and mortality events in marine communities: Insights on factors behind differential mortality impacts in the NW Mediterranean. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eakin, M.; Liu, G.; Gomez, A.; De la Cour, J.; Heron, S.; Skirving, W. Global coral bleaching 2014–2017: Status and an appeal for observations. Reef Encount. 2016, 31, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Ereskovsky, A.; Ozerov, D.A.; Pantyulin, A.N.; Tzetlin, A.B. Mass mortality event of White Sea sponges as the result of high temperature in summer 2018. Polar Biol. 2019, 42, 2313–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, T.P.; Kerry, J.T.; Baird, A.H.; Sean, R.; Connolly, S.R.; Dietzel, A.; Eakin, C.M.; Heron, S.F.; Hoey, A.S.; Hoogenboom, M.O.; et al. Global warming transforms coral reef assemblages. Nature 2018, 556, 492–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, N.P.; Figueiredo, J.; Gilliam, D.S. Thermal stress-related spatiotemporal variations in high-latitude coral reef benthic communities. Coral Reefs 2020, 39, 1661–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morri, C.; Montefalcone, M.; Lasagna, R.; Gatti, G.; Rovere, A.; Parravicini, V.; Baldelli, G.; Colantoni, P.; Bianchi, C.N. Through bleaching and tsunami: Coral reef recovery in the Maldives. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2015, 98, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montefalcone, M.; Morri, C.; Bianchi, C.N. Influence of local pressures on Maldivian coral reef resilience following repeated bleaching events, and recovery perspectives. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.P.W.; Wilson, S.K.; Graham, N.A.J. Abiotic and biotic controls on coral recovery 16 years after mass bleaching. Coral Reefs 2019, 38, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercelloni, J.; Mengersen, K.; Ruggeri, F.; Caley, M.J. Improved coral population estimation reveals trends at multiple scales on Australia’s Great Barrier Reef. Ecosystems 2017, 20, 1337–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavestrello, G.; Boero, F. Necrosi e rigenerazione in Eunicella cavolinii (Anthozoa, Cnidaria) in Mar Ligure. Bollet. Mus. Ist. Biol. Univ. Genova 1986, 52, 295–300. [Google Scholar]
- Gaino, E.; Pronzato, R. Ultrastructural evidence of bacterial damage to Spongia officinalis fibres (Porifera, Demospongiae). Diseases Aquat. Organ. 1989, 6, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voultsiadou, E.; Dailianis, T.; Antoniadou, C.; Vafidis, D.; Dounas, C.; Chintiroglou, C.C. Aegean bath sponges: Historical data and current status. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2011, 19, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrano, C.; Bavestrello, G.; Bianchi, C.N.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R.; Bava, S.; Morganti, C.; Morri, C.; Pico, P.; Sarà, G.; Schiaparelli, S.; et al. A catastrophic mass-mortality episode of gorgonians and other organisms in the Ligurian Sea (Northwestern Mediterranean), summer 1999. Ecol. Lett. 2000, 3, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, T.; Garrabou, J.; Sartoretto, S.; Harmelin, J.G.; Francour, P.; Vacelet, J. Mass mortality of marine invertebrates: An unprecedent event in the North Occidental Mediterranean. CR Acad. Sci. Paris 2000, 323, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrabou, J.; Coma, R.; Bensoussan, N.; Bally, M.; Chevaldonné, P.; Cigliano, M.; Diaz, D.; Harmelin, J.G.; Gambi, M.C.; Kersting, D.K.; et al. Mass mortality in Northwestern Mediterranean rocky benthic communities: Effects of the 2003 heat wave. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 1090–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivetti, I.; Fraschetti, S.; Lionello, P.; Zambianchi, E.; Boero, F. Global warming and mass mortalities of benthic invertebrates in the Mediterranean Sea. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marbà, N.; Gabriel, J.; Agusti, S.; Girard, C.; Duarte, C.M. Footprints of climate change on Mediterranean Sea biota. Front. Mar. Sci. 2015, 2, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersting, D.K.; Bensoussan, N.; Linares, C. Long-term responses of the endemic reef-builder Cladocora caespitosa to Mediterranean warming. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turicchia, E.; Abbiati, M.; Sweet, M.; Ponti, M. Mass mortality hits gorgonian forests at Montecristo Island. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2018, 131, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensoussan, N.; Chiggiato, J.; Buongiorno Nardelli, B.; Pisano, A.; Garrabou, J. Insights on 2017 Marine Heat Waves in the Mediterranean Sea. In Copernicus Marine Service Ocean State, Report 3. J. Operat. Oceanogr. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrabou, J.; Gómez-Gras, D.; Ledoux, J.-B.; Linares, C.; Bensoussan, N.; López-Sendino, P.; Bazairi, H.; Espinosa, F.; Ramdani, M.; Grimes, S.; et al. Collaborative database to track mass mortality events in the Mediterranean Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özalp, H.B.; Kersting, D.K. A pan-Mediterranean extinction? Pinna nobilis mass mortality has reached the Turkish straits system. Mar. Biodivers. 2020, 50, 81. [Google Scholar]
- Kruzic, P.; Rodic, P. Impact of climate changes on coralligenous community in the Adriatic Sea. In Proceedings of the Second Mediterranean Symposium of Coralligenous and Other Calcareous Bioconcretions, Portoroz, Slovenia, 29–30 October 2014; RACSPA: Tunis, Tunisia, 2014; pp. 100–105. [Google Scholar]
- Ballesteros, E. Mediterranean coralligenous assemblages: A synthesis of present knowledge. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. 2006, 44, 123–195. [Google Scholar]
- Ezzat, L.; Merle, P.L.; Furla, P.; Buttler, A.; Ferrier-Pagès, C. The response of the Mediterranean gorgonian Eunicella singularis to thermal stress is independent of its nutritional regime. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S.; Cohu, S.; Vignot, C.; Zimmerman, G.; Gattuso, J.P. One-year experiment on the physiological response of the Mediterranean crustose coralline alga, Lithophyllum cabiochae, to elevated pCO2 and temperature. Ecol. Evol. 2013, 3, 676–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Prieto, C. Light and temperature requirements for survival, growth and reproduction of the crustose coralline Lithophyllum stictaeforme from the Mediterranean Sea. Bot. Mar. 2016, 59, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagès-Escolà, M.; Hereu, B.; Garrabou, J.; Montero-Serra, I.; Gori, A.; Gómez-Gras, D.; Figuerola, B.; Linares, C. Divergent responses to warming of two common co-occurring Mediterranean bryozoans. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Gras, D.; Linares, C.; de Caralt, S.; Cebrian, E.; Frleta-Valić, M.; Montero-Serra, I.; Pagès-Escolà, M.; López-Sendino, P.; Garrabou, J. Response diversity in Mediterranean coralligenous assemblages facing climate change: Insights from a multispecific thermotolerance experiment. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 4168–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrabou, J.; Perez, T.; Sartoretto, S.; Harmelin, J.G. Mass mortality event in red coral Corallium rubrum populations in the Provence Region (France, NW Mediterranean). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 217, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebrian, E.; Uriz, M.J.; Garrabou, J.; Ballesteros, E. Sponge mass mortalities in a warming Mediterranean Sea: Are Cyanobacteria harboring species worse off? PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20211. [Google Scholar]
- Cocito, S.; Sgorbini, S. Long-term trend in substratum occupation by a clonal, carbonate bryozoan in a temperate rocky reef in times of thermal anomalies. Mar. Biol. 2013, 161, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hereu, B.; Kersting, D.K. Diseases of coralline algae in the Mediterranean Sea. Coral Reefs 2016, 35, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrano, C.; Bavestrello, G. Medium-term effects of die-off of rocky benthos in the Ligurian Sea. What can we learn from gorgonians? Chem. Ecol. 2008, 24, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coma, R.; Linares, C.; Ribes, M.; Diaz, D.; Garrabou, J.; Ballesteros, E. Consequences of a mass mortality in populations of Eunicella singularis (Cnidaria:Octocorallia) in Menorca (NW Mediterranean). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 327, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete-Stauffer, C.; Vielmini, I.; Palma, M.; Navone, A.; Panzalis, P.; Vezzulli, L.; Misic, C.; Cerrano, C. Paramuricea clavata (Anthozoa, Octocorallia) loss in the Marine Protected Area of Tavolara (Sardinia, Italy) due to a mass mortality event. Mar. Ecol. Evol. Persp. 2011, 32, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixido, N.; Casas, E.; Cebrian, E.; Linares, C.; Garrabou, J. Impacts on coralligenous outcrop biodiversity of a dramatic coastal storm. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavestrello, G.; Cerrano, C.; Zanzi, D.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R. Damage by fishing activities in the gorgonian coral Paramuricea clavata in the Ligurian Sea. Aquat. Conserv. 1997, 7, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coma, R.; Pola, E.; Ribes, M.; Zabala, M. Long-term assessment of temperate octocoral mortality patterns, protected vs. unprotected areas. Ecol. Appl. 2004, 14, 1466–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebrian, E.; Linares, C.; Marschal, C.; Garrabou, J. Exploring the effects of invasive algae on the persistence of gorgonian populations. Biol. Invasions 2012, 14, 2647–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, C.N.; Azzola, A.; Bertolino, M.; Betti, F.; Bo, M.; CattaneoVietti, R.; Cocito, S.; Montefalcone, M.; Morri, C.; Oprandi, A.; et al. Consequences of the marine climate and ecosystem shift of the 1980–90s on the Ligurian Sea biodiversity (NW Mediterranean). Eur. Zool. J. 2019, 86, 458–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdura, J.; Linares, C.; Ballesteros, E.; Coma, R.; Uriz, M.J.; Bensoussan, N.; Cebrian, E. Biodiversity loss in a Mediterranean ecosystem due to an extreme warming event unveils the role of an engineering gorgonian species. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mistri, M.; Ceccherelli, V.U. Effects of a mucilage event on the Mediterranean gorgonian Paramuricea clavata. 1. Short term impacts at the population and colony levels. It. J. Zool. 1996, 63, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, S.; Virno Lamberti, C.; Sonni, C.; Pellegrini, D. Mucilage impact on gorgonians in the Tyrrhenian Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 353, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazzi, L.; Atzori, F.; Cadoni, N.; Cinti, M.F.; Frau, F.; Ceccherelli, G. Benthic mucilage blooms threaten coralligenous reefs. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 140, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, Y.; Bonnefort, J.L.; Chancerelle, L. Gorgonians mass mortality during the 1999 late summer in french Mediterranean coastal waters: The bacterial hypothesis. Water Res. 2002, 36, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzulli, L.; Previati, M.; Pruzzo, C.; Marchese, A.; Bourne, D.G.; Cerrano, C. Vibrio infections triggering mass mortality events in a warming Mediterranean Sea. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 2007–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzulli, L.; Pezzati, E.; Huete-Stauffer, C.; Pruzzo, C.; Cerrano, C. 16SrDNA pyrosequencing of the Mediterranean gorgonian Paramuricea clavata reveals a link among alterations in bacterial holobiont members, anthropogenic influence and disease outbreaks. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistri, M.; Ceccherelli, V.U. Effects of a mucilage event on the Mediterranean gorgonian Paramuricea clavata. 2. Population recovery after two years. It. J. Zool. 1996, 63, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, C.; Coma, R.; Diaz, D.; Zabala, M.; Hereu, B.; Dantart, L. Immediate and delayed effects of a mass mortality event on gorgonian population dynamics and benthic community structure in the NW Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 305, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupido, R.; Cocito, S.; Sgorbini, S.; Bordone, A.; Santangelo, G. Response of a gorgonian (Paramuricea clavata) population to mortality events: Recovery or loss? Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2008, 18, 984–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramanti, L.; Bendetti, M.C.; Cupido, S.; Priori, C.; Erra, F.; Iannelli, M.; Santangelo, G. Demography of animal forests: The example of Mediterranean gorgonians. In Marine Animal Forests; Rossi, S., Bramanti, L., Gori, A., Orejas Saco del Valle, C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrano, C.; Danovaro, R.; Gambi, C.; Pusceddu, A.; Riva, A.; Schiaparelli, S. Gold coral (Savalia savaglia) and gorgonian forests enhance benthic biodiversity and ecosystem functioning in the mesophotic zone. Biodivers. Conserv. 2010, 19, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas-Güell, E.; Teixidó, N.; Garrabou, J.; Cebrian, E. Structure and biodiversity of coralligenous assemblages over broad spatial and temporal scales. Mar. Biol. 2015, 162, 901–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponti, M.; Grech, D.; Mori, M.; Perlini, R.A.; Ventra, V.; Panzalis, P.A.; Cerrano, C. The role of gorgonians on the diversity of vagile benthic fauna in Mediterranean rocky habitats. Mar. Biol. 2016, 163, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponti, M.; Turicchia, E.; Ferro, F.; Cerrano, C.; Abbiati, M. The understorey of gorgonian forests in mesophotic temperate reefs. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2018, 28, 1153–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gori, A.; Bavestrello, G.; Grinyó, J.; Dominguez-Carrió, C.; Ambroso, S.; Bo, M. Animal forests in deep coastal bottoms and continental shelf of the Mediterranean Sea. In Marine Animal Forests; Rossi, S., Bramanti, L., Gori, A., Orejas, C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Bramanti, L.; Gori, A.; Orejas, C. An overview of the animal forests of the world. In Marine Animal Forests; Rossi, S., Bramanti, L., Gori, A., Orejas, C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponti, M.; Perlini, R.A.; Ventra, V.; Grech, D.; Abbiati, M.; Cerrano, C. Ecological shifts in Mediterranean coralligenous assemblages related to gorgonian forest loss. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerrano, C.; Arillo, A.; Azzini, F.; Calcinai, B.; Castellano, L.; Muti, C.; Valisano, L.; Zega, G.; Bavestrello, G. Gorgonian population recovery after a mass mortality event. Aquat. Conserv. 2005, 15, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santangelo, G.; Cupido, R.; Cocito, S.; Bramanti, L.; Priori, C.; Erra, F.; Iannelli, M. Effects of increased mortality on gorgonian corals (Cnidaria, Octocorallia): Different demographic features may lead affected populations to unexpected recovery and new equilibrium points. Hydrobiologia 2015, 759, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, A.J. On beyond BACI: Sampling designs that might reliably detect environmental disturbances. Ecol. Appl. 1994, 4, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti-Cecchi, L. Beyond BACI: Optimization of environmental sampling designs through monitoring and simulation. Ecol. Appl. 2001, 11, 783–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzi, L.; Gennaro, P.; Montefalcone, M.; Bianchi, C.N.; Cecchi, E.; Morri, C.; Serena, F. STAR: An integrated and standardized procedure to evaluate the ecological status of coralligenous reefs. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosys. 2019, 29, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchi, E.; Gennaro, P.; Piazzi, L.; Ricevuto, E.; Serena, F. Development of a new biotic index for ecological status assessment of Italian coastal waters based on coralligenous macroalgal assemblages. Eur. J. Phycol. 2014, 49, 298–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzi, L.; Gennaro, P.; Cecchi, E.; Serena, F.; Bianchi, C.N.; Morri, C.; Montefalcone, M. Integration of ESCA index through the use of sessile invertebrates. Sci. Mar. 2017, 81, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.J.; Ellingsen, K.E.; McArdle, B.H. Multivariate dispersion as a measure of beta diversity. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M.J. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar]
- Benedetti-Cecchi, L.; Pannacciulli, F.; Bulleri, F.; Moschella, P.; Airoldi, L.; Relini, G.; Cinelli, F. Predicting the consequences of anthropogenic disturbance: Large-scale effects of loss of canopy algae on rocky shores. Mar. Ecol. Progr. Ser. 2001, 214, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montefalcone, M.; Vassallo, P.; Gatti, G.; Parravicini, V.; Paoli, C.; Morri, C.; Bianchi, C.N. The exergy of a phase shift: Ecosystem functioning loss in seagrass meadows of the Mediterranean Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 156, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carugati, L.; Gatto, B.; Rastelli, E.; Lo Martire, M.; Coral, C.; Greco, S.; Danovaro, R. Impact of mangrove forests degradation on biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valisano, L.; Notari, F.; Mori, M.; Cerrano, C. Temporal variability of sedimentation rates and mobile fauna inside and outside a gorgonian garden. Mar. Ecol. 2016, 37, 1303–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, C.; Cebrian, E.; Coma, R. Effects of turf algae on recruitment and juvenile survival of gorgonian corals. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 452, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birrell, C.L.; McCook, L.J.; Willis, B.L. Effects of algal turfs and sediment on coral settlement. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 51, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, S.N.; Steneck, R.S.; Mumby, P.J. Running the gauntlet: Inhibitory effects of algal turfs on the processes of coral recruitment. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 414, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzi, L.; Atzori, F.; Cadoni, N.; Cinti, M.F.; Frau, F.; Ceccherelli, G. Monitoring non-indigenous macroalgae in a Mediterranean MPA: Lessons from a short-temporal variability of pristine habitats invasion. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzi, L.; Gennaro, P.; Cecchi, E.; Bianchi, C.N.; Cinti, F.; Gatti, G.; Guala, I.; Morri, C.; Sartoretto, F.; Serena, F.; et al. Ecological Status of Coralligenous Assemblages: Ten years of application of the ESCA index from local to wide scale validation. Ecol. Ind. 2021, 121, 107077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S. The destruction of the ‘animal forests’ in the oceans: Towards an over-simplification of the benthic ecosystems. Ocean Coast Manag. 2013, 84, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudouresque, C.F.; Blanfuné, A.; Personnic, S.; Ruitton, S.; Thibaut, T.; Verlaque, M. Where seaweed forests meet animal forests: The examples of macroalgae in coral reefs and the Mediterranean coralligenous ecosystem. In Marine Animal Forests; Rossi, S., Bramanti, L., Gori, A., Orejas, C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, G.; Bianchi, C.N.; Morri, C.; Montefalcone, M.; Sartoretto, S. Coralligenous reefs state along anthropized coasts: Application and validation of the COARSE index, based on a rapid visual assessment (RVA) approach. Ecol. Ind. 2015, 52, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrigno, F.; Russo, G.F.; Sandulli, R. Coralligenous Bioconstructions Quality Index (CBQI): A synthetic indicator to assess the status of different types of coralligenous habitats. Ecol. Ind. 2017, 82, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enrichetti, F.; Bo, M.; Morri, C.; Montefalcone, M.; Toma, M.; Bavestrello, G.; Tunesi, L.; Canese, S.; Giusti, M.; Salvati, E.; et al. Assessing the environmental status of temperate mesophotic reefs: A new, integrated methodological approach. Ecol. Ind. 2019, 102, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Taxa/Group | Pseudo-F4,8 | P (Perm) | Pair-Wise Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multivariate analysis | 4.44 | 0.003 | 2016 = 2017 = 2018 ≠ 2019 ≠ 2020 |
| encrusting coralline | 2.88 | 0.090 | |
| Peyssonnelia spp. | 0.33 | 0.810 | |
| algal turf | 49.02 | 0.001 | 2016 = 2017 = 2018 < 2019 = 2020 |
| encrusting sponges | 0.10 | 0.981 | |
| massive sponges | 2.90 | 0.073 | |
| erect bryozoans | 14.36 | 0.004 | 2016 = 2017 = 2018 = 2019 > 2020 |
| Paramuricea clavata | 17.07 | 0.003 | 2016 = 2017 > 2018 = 2019 = 2020 |
| Eunicella cavolini | 4.98 | 0.028 | 2016 = 2017 = 2018 = 2019 > 2020 |
| Source | df | MS | Pseudo-F | P (Perm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time = T | 1 | 10,175 | 5.59 | 0.007 |
| Site = S | 2 | 53,273 | 28.66 | 0.003 |
| Plot(S) = P(S) | 6 | 1858 | 4.13 | 0.001 |
| TxS | 2 | 13,359 | 7.34 | 0.002 |
| TxP(S) | 6 | 1818 | 4.04 | 0.001 |
| Residual | 162 | 449 | ||
| Pair-wise test (TxS) | D: | T1 ≠ T2 | ||
| C1: | T1 = T2 | |||
| C2: | T1 = T2 |
| Source | df | MS | Pseudo-F | P (Perm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time = T | 1 | 12.8 | 9.4 | 0.028 |
| Site = S | 2 | 175.5 | 13.21 | 0.011 |
| Plot(S) = P(S) | 6 | 13.2 | 2.9 | 0.013 |
| TxS | 2 | 96.2 | 70.72 | 0.001 |
| TxP(S) | 6 | 1.3 | 0.29 | 0.941 |
| Residual | 162 | 4.5 | ||
| Pair-wise test (TxS) | D: | T1 > T2 | ||
| C1: | T1 = T2 | |||
| C2: | T1 < T2 |
| Source | df | MS | Pseudo-F | P (Perm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time = T | 1 | 95.6 | 5.37 | 0.028 |
| Site = S | 2 | 150.7 | 8.47 | 0.009 |
| TxS | 2 | 164.2 | 9.24 | 0.004 |
| Residual | 12 | 17.7 | ||
| Pair-wise test (TxS) | D: | T1 > T2 | ||
| C1: | T1 = T2 | |||
| C2: | T1 = T2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piazzi, L.; Atzori, F.; Cadoni, N.; Cinti, M.F.; Frau, F.; Pansini, A.; Pinna, F.; Stipcich, P.; Ceccherelli, G. Animal Forest Mortality: Following the Consequences of a Gorgonian Coral Loss on a Mediterranean Coralligenous Assemblage. Diversity 2021, 13, 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13030133
Piazzi L, Atzori F, Cadoni N, Cinti MF, Frau F, Pansini A, Pinna F, Stipcich P, Ceccherelli G. Animal Forest Mortality: Following the Consequences of a Gorgonian Coral Loss on a Mediterranean Coralligenous Assemblage. Diversity. 2021; 13(3):133. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13030133
Chicago/Turabian StylePiazzi, Luigi, Fabrizio Atzori, Nicoletta Cadoni, Maria Francesca Cinti, Francesca Frau, Arianna Pansini, Federico Pinna, Patrizia Stipcich, and Giulia Ceccherelli. 2021. "Animal Forest Mortality: Following the Consequences of a Gorgonian Coral Loss on a Mediterranean Coralligenous Assemblage" Diversity 13, no. 3: 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13030133
APA StylePiazzi, L., Atzori, F., Cadoni, N., Cinti, M. F., Frau, F., Pansini, A., Pinna, F., Stipcich, P., & Ceccherelli, G. (2021). Animal Forest Mortality: Following the Consequences of a Gorgonian Coral Loss on a Mediterranean Coralligenous Assemblage. Diversity, 13(3), 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13030133







