Antarctic Special Protected Area 161 as a Reference to Assess the Effects of Anthropogenic and Natural Impacts on Meiobenthic Assemblages
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
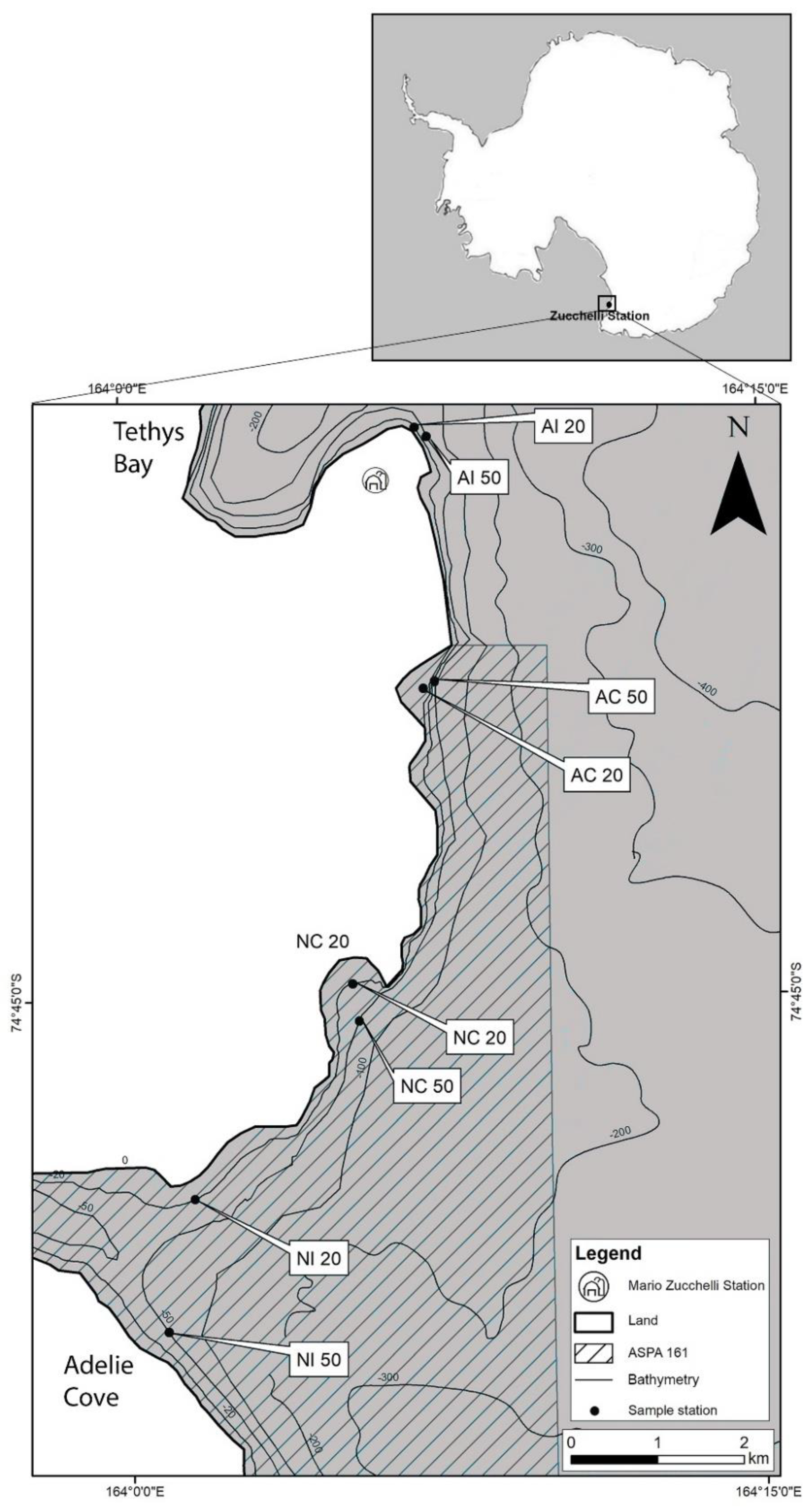
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Sites
2.2. Environmental Parameters Analyses
2.3. Meiobenthic Assemblage Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
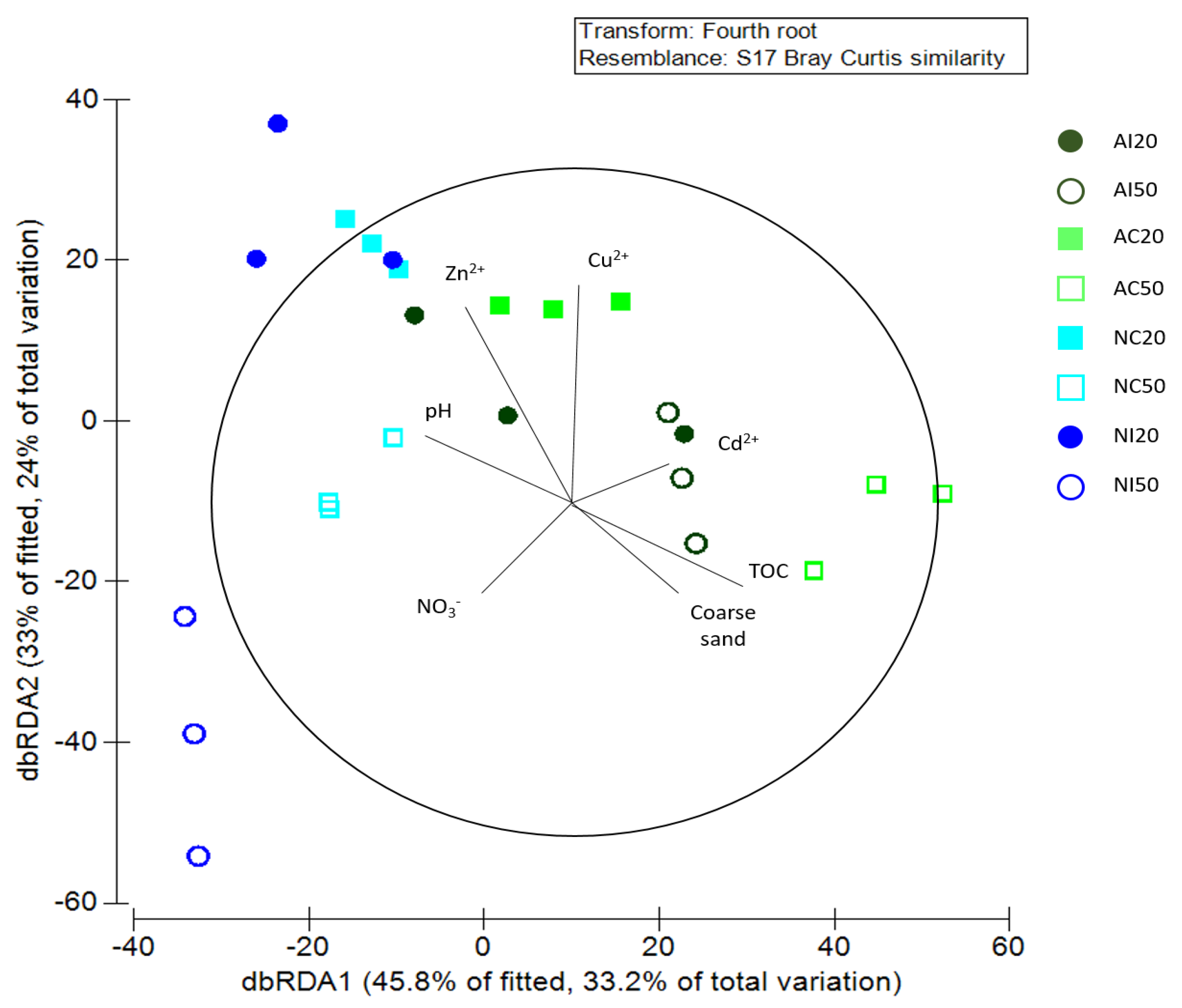
3.1. Environmental Data
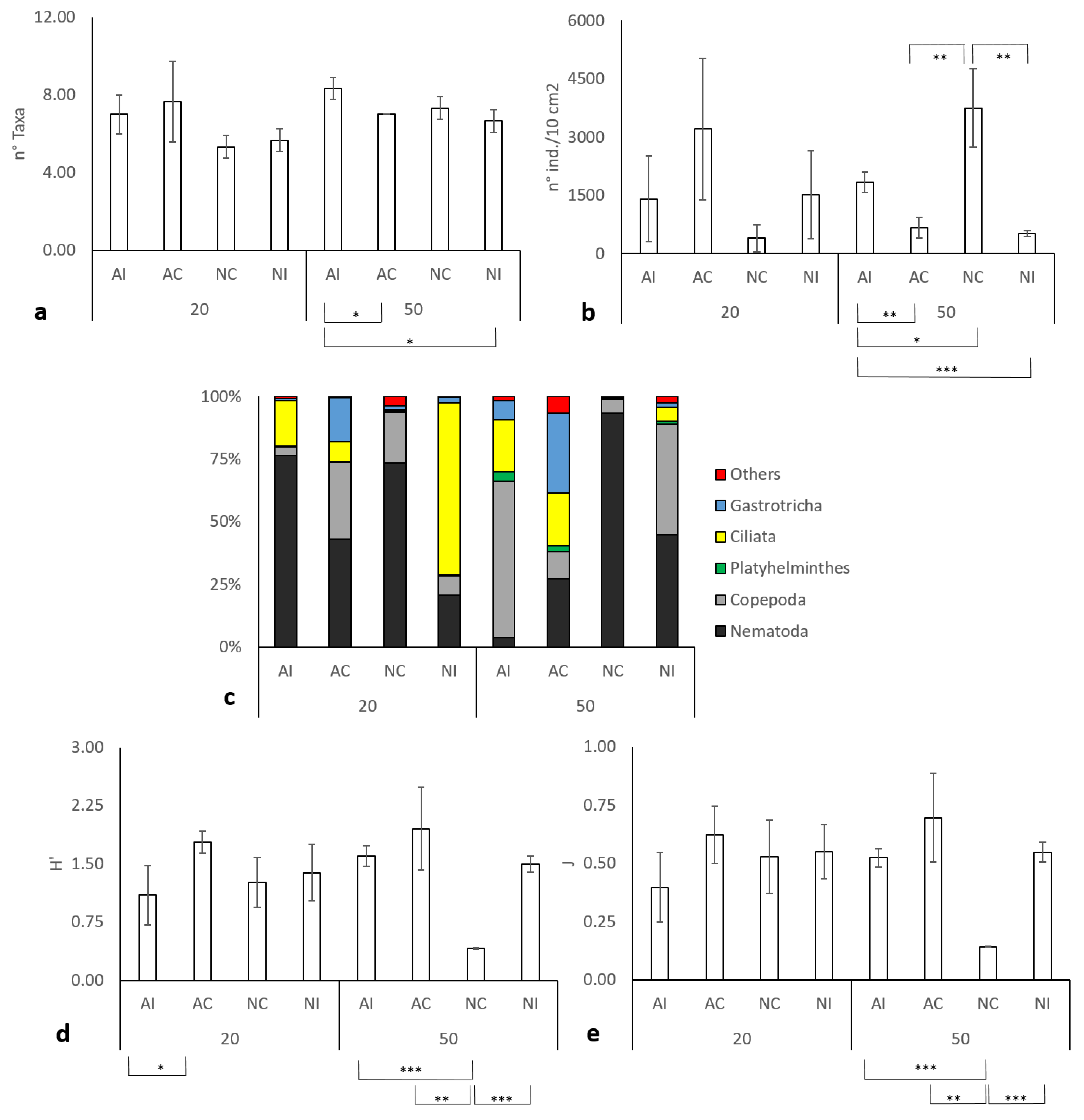
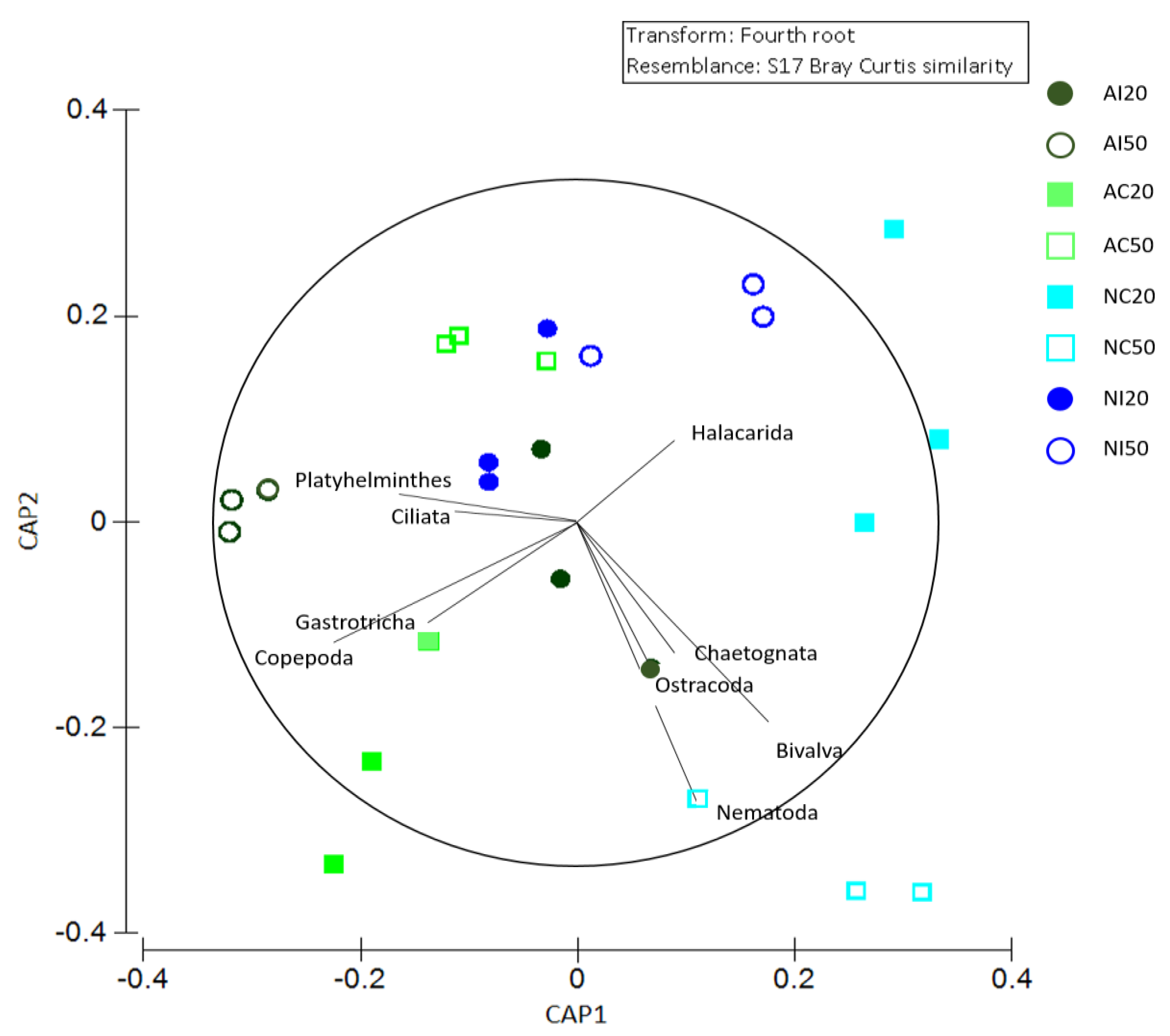
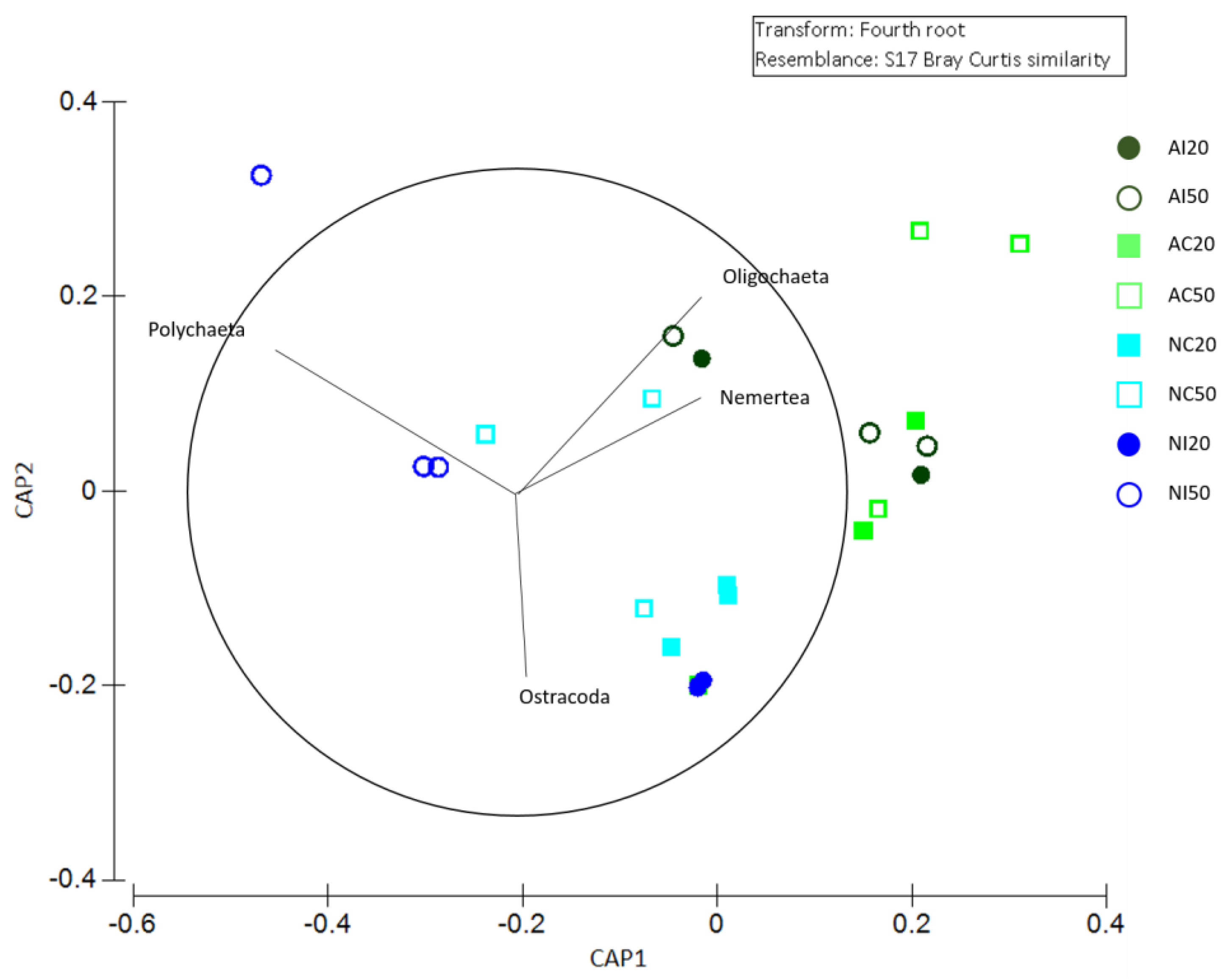
3.2. Meiobenthic Assemblage Analysis
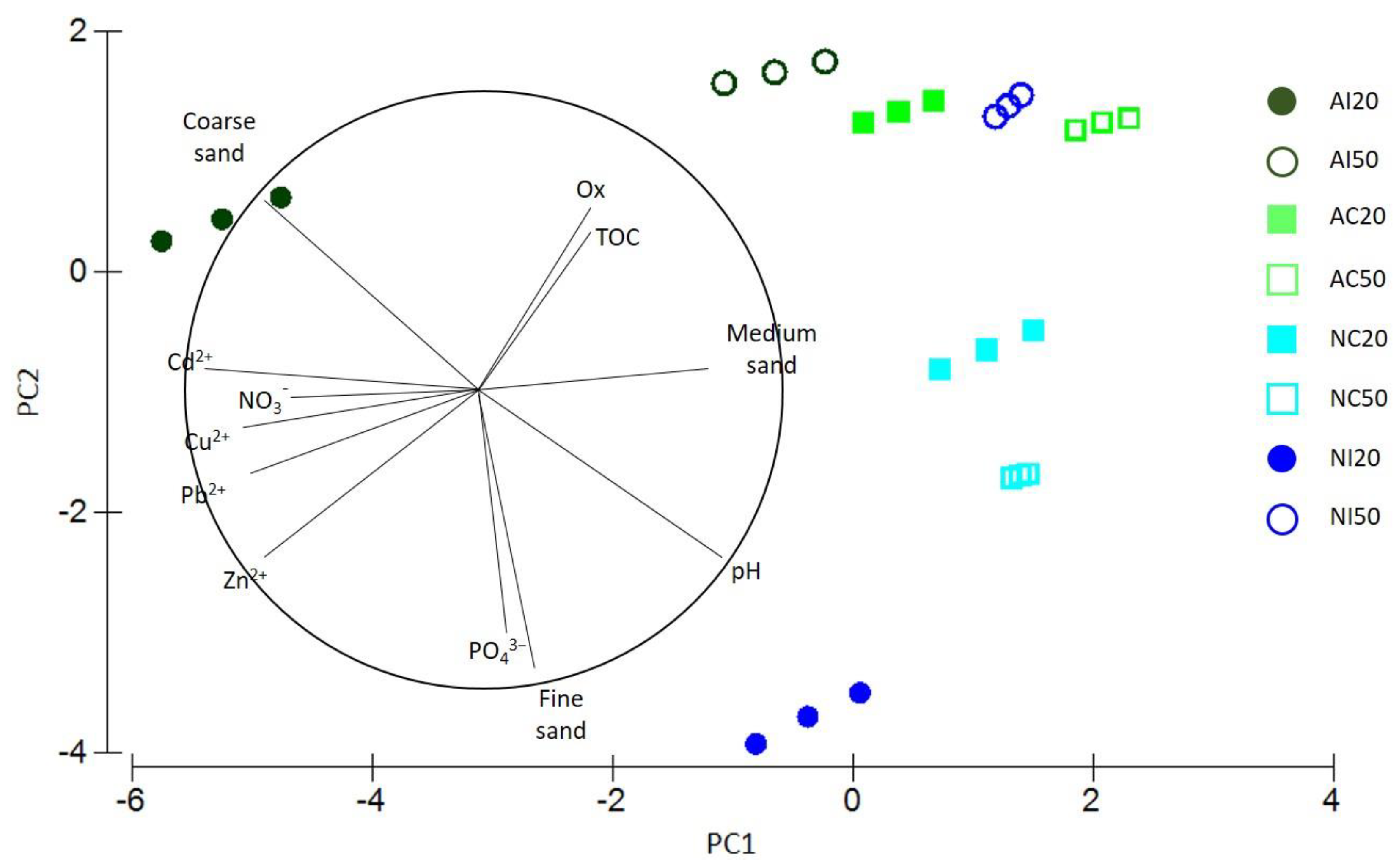
3.3. Interaction between Environmental and Biological Data
4. Discussion
4.1. Environmental Characterization of the Study Area
4.2. Meiobenthic Assemblage Structure
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cook, W.M.; Yao, J.; Foster, B.L.; Holt, R.D.; Patrick, L.B. Secondary succession in an experimentally fragmented landscape: Community patterns across space and time. Ecology 2005, 86, 1267–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fabiano, M.; Danovaro, R. Meiofauna distribution and mesoscale variability in two sites of the Ross Sea (Antarctica) with contrasting food supply. Polar Biol. 1999, 22, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, V.G.; Sinniger, F.; Gaspar, J.M.; Quince, C.; Creer, S.; Power, D.M.; Peck, L.S.; Clark, M.S. Revealing higher than expected meiofaunal diversity in Antarctic sediments: A metabarcoding approach. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchelli, S.; Nizzoli, D.; Bartoli, M.; Viaroli, P.; Rastelli, E.; Pusceddu, A. Sedimentary organic matter, prokaryotes, and meiofauna across a river-lagoon-sea gradient. Diversity 2020, 12, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schratzberger, M.; Ingels, J. Meiofauna matters: The roles of meiofauna in benthic ecosystems. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2018, 502, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsamo, M.; Semprucci, F.; Frontalini, F.; Coccioni, R. Meiofauna as a tool for marine ecosystem biomonitoring. Mar. Ecosyst. 2012, 4, 77–104. [Google Scholar]
- Semprucci, F.; Balsamo, M.; Appolloni, L.; Sandulli, R. Assessment of ecological quality status along the Apulian coasts (eastern Mediterranean Sea) based on meiobenthic and nematode assemblages. Mar. Biodivers. 2018, 48, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boufahja, F.; Semprucci, F.; Beyrem, H. An experimental protocol to select nematode species from an entire community using progressive sedimentary enrichment. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 292–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontalini, F.; Semprucci, F.; Di Bella, L.; Caruso, A.; Cosentino, C.; Maccotta, A.; Scopelliti, G.; Sbrocca, C.; Bucci, C.; Balsamo, M. The response of cultured meiofaunal and benthic foraminiferal communities to lead exposure: Results from mesocosm experiments. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 2439–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appolloni, L.; Zeppilli, D.; Donnarumma, L.; Baldrighi, E.; Chianese, E.; Russo, G.F.; Sandulli, R. Seawater Acidification Affects Beta-Diversity of Benthic Communities at a Shallow Hydrothermal Vent in a Mediterranean Marine Protected Area (Underwater Archaeological Park of Baia, Naples, Italy). Diversity 2020, 12, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldrighi, E.; Zeppilli, D.; Appolloni, L.; Donnarumma, L.; Chianese, E.; Russo, G.F.; Sandulli, R. Meiofaunal communities and nematode diversity characterizing the Secca delle Fumose shallow vent area (Gulf of Naples, Italy). PeerJ 2020, 8, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semprucci, F.; Cesaroni, L.; Guidi, L.; Balsamo, M. Do the morphological and functional traits of free-living marine nematodes mirror taxonomical diversity? Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 135, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnarumma, L.; Appolloni, L.; Chianese, E.; Bruno, R.; Baldrighi, E.; Guglielmo, R.; Russo, G.F.; Zeppilli, D.; Sandulli, R. Environmental and Benthic Community Patterns of the Shallow Hydrothermal Area of Secca Delle Fumose (Baia, Naples, Italy). Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, J.-H.; Semprucci, F.; Jeong, R.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.; Jeon, D.; Yoo, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Yeom, J. Meiobenthic nematodes in the assessment of the relative impact of human activities on coastal marine ecosystem. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahraeian, N.; Sahafi, H.H.; Mosallanejad, H.; Ingels, J.; Semprucci, F. Temporal and spatial variability of free-living nematodes in a beach system characterized by domestic and industrial impacts (Bandar Abbas, Persian Gulf, Iran). Ecol. Indic. 2020, 118, 106697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchelli, S.; Gambi, C.; Zeppilli, D.; Danovaro, R. Metazoan meiofauna in deep-sea canyons and adjacent open slopes: A large-scale comparison with focus on the rare taxa. Deep. Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2010, 57, 420–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusceddu, A.; Bianchelli, S.; Gambi, C.; Danovaro, R. Assessment of benthic trophic status of marine coastal ecosystems: Significance of meiofaunal rare taxa. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 93, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losi, V.; Grassi, E.; Balsamo, M.; Rocchi, M.; Gaozza, L.; Semprucci, F. Changes in taxonomic structure and functional traits of nematodes as tools in the assessment of port impact. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 260, 107524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coull, B.C.; Chandler, G.T. Pollution and meiofauna: Field, laboratory, and mesocosm studies. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 1992, 30, 191–271. [Google Scholar]
- Mirto, S.; La Rosa, T.; Danovaro, R.; Mazzola, A. Microbial and meiofaunal response to intensive mussel-farm biodeposition in coastal sediments of the Western Mediterranean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 40, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzulli, L.; Moreno, M.; Marin, V.; Pezzati, E.; Bartoli, M.; Fabiano, M. Organic waste impact of capture-based Atlantic bluefin tuna aquaculture at an exposed site in the Mediterranean Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 78, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grego, M.; De Troch, M.; Forte, J.; Malej, A. Main meiofauna taxa as an indicator for assessing the spatial and seasonal impact of fish farming. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1178–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dal Zotto, M.; Santulli, A.; Simonini, R.; Todaro, M.A. Organic enrichment effects on a marine meiofauna community, with focus on Kinorhyncha. Zool. Anzeiger-A J. Comp. Zool. 2016, 265, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espejo, W.; Celis, J.E.; Sandoval, M.; González-Acuña, D.; Barra, R.; Capulín, J. The impact of penguins on the content of trace elements and nutrients in coastal soils of North Western Chile and the Antarctic Peninsula area. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emslie, S.D. Ancient Adélie penguin colony revealed by snowmelt at Cape Irizar, Ross Sea, Antarctica. Geology 2021, 49, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batalla Salvarrey, A.V.; Kotzian, C.B.; Spies, M.R.; Braun, B. The influence of natural and anthropic environmental variables on the structure and spatial distribution along longitudinal gradient of macroinvertebrate communities in southern Brazilian streams. J. Insect Sci. 2014, 14, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, C.; Brugnoli, E.; Bergamino, L.; Muniz, P.; García-Rodríguez, F.; Figueira, R. Anthropogenic and natural variability in the composition of sedimentary organic matter of the urbanised coastal zone of Montevideo (Río de la Plata). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 126, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermand, R.; Salen-Picard, C. Responses of a Macrobenthic Mediterranean Community Submitted to Allochtonous Natural or Anthropic Sedimentary Inputs; Universite de l a Mediterranee, Centre d’Oceanologie de Marseille, Station Marine d’Endoume: Marseille, France, 2008; Volume 33, p. 18. [Google Scholar]
- Danovaro, R.; Chiantore, M.; Pusceddu, A.; Cattaneo Vietti, R.; Manini, E.; Fabiano, M. Sediment organic matter, bacteria and protozoans in Terra Nova bay, Ross Sea, Antarctica, during austral summer 1993/1994. In National Programme for Antarctic Research—ROSSMIZE (Ross Sea Marginal Ice Zone Ecology); Faranda, F.M., Guglielmo, L., Povero, P., Eds.; G.Lang Editor: Genoa, Italy, 1997; pp. 423–430. [Google Scholar]
- Bargagli, R. Antarctic Ecosystems: Environmental Contamination, Climate Change, and Human Impact; Czeschlik, D., Ed.; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; Volume 175, ISBN 3540264655. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, K.A.; Thompson, A. Distribution of sewage pollution around a maritime Antarctic research station indicated by faecal coliforms, Clostridium perfringens and faecal sterol markers. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 127, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.S.; Smith, J.; King, C.K.; Lindsay, M.; Stark, S.; Palmer, A.S.; Snape, I.; Bridgen, P.; Riddle, M. Physical, chemical, biological and ecotoxicological properties of wastewater discharged from Davis Station, Antarctica. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2015, 113, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.S.; Corbett, P.A.; Dunshea, G.; Johnstone, G.; King, C.; Mondon, J.A.; Power, M.L.; Samuel, A.; Snape, I.; Riddle, M. The environmental impact of sewage and wastewater outfalls in Antarctica: An example from Davis station, East Antarctica. Water Res. 2016, 105, 602–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbett, P.A.; King, C.K.; Stark, J.S.; Mondon, J.A. Direct evidence of histopathological impacts of wastewater discharge on resident Antarctic fish (Trematomus bernacchii) at Davis Station, East Antarctica. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 87, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tin, T.; Fleming, Z.L.; Hughes, K.A.; Ainley, D.G.; Convey, P.; Moreno, C.A.; Pfeiffer, S.; Scott, J.; Snape, I. Impacts of local human activities on the Antarctic environment. Antarct. Sci. 2009, 21, 3–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stark, J.S.; Snape, I.; Riddle, M.J. The effects of petroleum hydrocarbon and heavy metal contamination of marine sediments on recruitment of Antarctic soft-sediment assemblages: A field experimental investigation. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2003, 283, 21–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancora, S.; Volpi, V.; Olmastroni, S.; Focardi, S.; Leonzio, C. Assumption and elimination of trace elements in Adélie penguins from Antarctica: A preliminary study. Mar. Environ. Res. 2002, 54, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espejo, W.; Celis, J.E.; Acuna, D.G.; Jara, S.; Barra, R. Concentration of trace metals in excrements of two species of penguins from different locations of the Antarctic Peninsula. Polar Biol. 2014, 37, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.S.; Mohammad, M.; McMinn, A.; Ingels, J. Diversity, Abundance, Spatial Variation, and Human Impacts in Marine Meiobenthic Nematode and Copepod Communities at Casey Station, East Antarctica. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlan, K.E.; Kim, S.L.; Thurber, A.R.; Hendrycks, E. Benthic changes at McMurdo Station, Antarctica following local sewage treatment and regional iceberg-mediated productivity decline. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenihan, H.S.; Peterson, C.H.; Kim, S.L.; Conlan, K.E.; Fairey, R.; McDonald, C.; Grabowski, J.H.; Oliver, J.S. Variation in marine benthic community composition allows discrimination of multiple stressors. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 261, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlan, K.E.; Kim, S.L.; Lenihan, H.S.; Oliver, J.S. Benthic changes during 10 years of organic enrichment by McMurdo Station, Antarctica. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 49, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, S.; Cavanagh, R.; Knowland, C.; Grant, S.; Downie, R. Bridging the Krill Divide: Understanding Cross-Sector Objectives for Krill Fishing and Conservation; WWF Living Planet Centre: Woking, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Stark, J.S.; Mohammad, M.; McMinn, A.; Ingels, J. The effects of hydrocarbons on meiofauna in marine sediments in Antarctica. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2017, 496, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.S.; Bridgen, P.; Dunshea, G.; Galton-fenzi, B.; Hunter, J.; Johnstone, G.; King, C.; Leeming, R.; Palmer, A.; Smith, J.; et al. Chemosphere Dispersal and dilution of wastewater from an ocean outfall at Davis Station, Antarctica, and resulting environmental contamination. Chemosphere 2016, 152, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.S.; Kim, S.L.; Oliver, J.S. Anthropogenic disturbance and biodiversity of marine benthic communities in Antarctica: A regional comparison. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povero, P.; Chiantore, M.; Misic, C.; Budillon, G.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R. Land forcing controls pelagic-benthic coupling in Adelie Cove (Terra Nova Bay, Ross Sea). Polar Biol. 2001, 24, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianese, E.; Tirimberio, G.; Riccio, A. PM2.5 and PM10 in the urban area of Naples: Chemical composition, chemical properties and influence of air masses origin. J. Atmos. Chem. 2019, 76, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentworth, C.K. A Scale of Grade and Class Terms for Clastic Sediments. Published by The University of Chicago Press. J. Geol. 1922, 30, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, B.A. Methods for the Determination of Total Organic Carbon (TOC) in Soils and Sediments, NCEA-C-1282, 1st ed.; Schumacher, B.A., Ed.; US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development: Washington, DC, USA, 2002.
- Danovaro, R.; Gambi, C.; Mirto, S.; Sandulli, R.; Ceccherelli, V. Meiofauna. In Mediterranean Marine Benthos: A Manual of Methods for Its Sampling and Study; Gambi, M.C., Dappiano, M., Eds.; S.I.B.M-Società Italiana di Biologia Marina: Genova, Italy, 2004; pp. 55–97. [Google Scholar]
- Heip, C.; Vincx, M.; Vranken, G. The Ecology of Marine Nematodes; Aberdeen University Press: Aberdeen, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Appolloni, L.; Bevilacqua, S.; Sbrescia, L.; Sandulli, R.; Terlizzi, A.; Russo, G.F. Does full protection count for the maintenance of β-diversity patterns in marine communities? Evidence from Mediterranean fish assemblages. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2017, 27, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azzurro, E.; Matiddi, M.; Fanelli, E.; Guidetti, P.; La Mesa, G.; Scarpato, A.; Axiak, V. Sewage pollution impact on Mediterranean rocky-reef fish assemblages. Mar. Environ. Res. 2010, 69, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Underwood, A.J. Beyond BACI: Experimental Designs for Detecting Human Environmental Impacts on Temporal Variations in Natural Populations. Aust. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1991, 42, 569–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.; Gorley, R.N.; Clarke, K.R. PERMANOVA + for PRIMER User Manual; PRIMER-E Ltd.: Plymouth, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.J. A new method for non parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral. Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. Permutation tests for univariate or multivariate analysis of variance and regression. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2001, 58, 626–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; Willis, T.J. Canonical Analysis of Principal Coordinates: A Useful Method of Constrained Ordination for Ecology. Ecology 2003, 84, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.; Sommerfield, P.J.; Warwick, R.M. Change in Marine Communities—An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation, 3rd ed.; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Terlizzi, A.; Anderson, M.J.; Fraschetti, S.; Benedetti-Cecchi, L. Scales of spatial variation in Mediterranean subtidal sessile assemblages at different depths. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 332, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, M.J. DISTLM v. 5: A FORTRAN computer program to calculate a distance-based multivariate analysis for a linear model. Dep. Stat. Univ. Auckl. N. Z. 2004, 10, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Legendre, P.; Anderson, M.J. Distance-based redundancy analysis: Testing multispecies responses in multifactorial ecological experiments. Ecol. Monogr. 1999, 69, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larner, B.L.; Seen, A.J.; Snape, I. Evaluation of diffusive gradients in thin film (DGT) samplers for measuring contaminants in the Antarctic marine environment. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.-L.; Dang, N.-L.; Kok, Y.-Y.; Yap, K.-S.I.; Phang, S.-M.; Convey, P. Heavy metal pollution in Antarctica and its potential impacts on algae. Polar Sci. 2019, 20, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Yang, W.; Yang, L.; Gao, Y. Assessment of heavy metal contamination from penguins and anthropogenic activities on fildes peninsula and ardley island, antarctic. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcheva, R.; Yurukova, L.; Teodorova, S.E. Biogenic and toxic elements in feathers, eggs, and excreta of Gentoo penguin (Pygoscelis papua ellsworthii) in the Antarctic. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 182, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA Ambient Aquatic Life Water Quality Criteria for Dissolved Oxygen (Saltwater): Cape Cod to Cape Hatteras; Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water, Office of Science and Technology: Washington, DC, USA, 2000.
- Dimitrakakis, E.; Hahladakis, J.; Gidarakos, E. The “Sea Diamond” shipwreck: Environmental impact assessment in the water column and sediments of the wreck area. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 1421–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, T.; Yang, L.; Chu, Z.; Sun, L.; Yin, X. Geochemical record of high emperor penguin populations during the Little Ice Age at Amanda Bay, Antarctica. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 1185–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monien, P.; Lettmann, K.A.; Monien, D.; Asendorf, S.; Wölfl, A.-C.; Lim, C.H.; Thal, J.; Schnetger, B.; Brumsack, H.-J. Redox conditions and trace metal cycling in coastal sediments from the maritime Antarctic. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 141, 26–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.B.; Kurtz, D.D.; Domack, E.W.; Balshaw, K.M. Glacial and glacial marine sediments of the antarctic continental shelf. J. Geol. 1980, 88, 399–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusceddu, A.; Dell’Anno, A.; Fabiano, M. Organic matter composition in coastal sediments at Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea) during summer 1995. Polar Biol. 2000, 23, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasotti, F.; De Troch, M.; Raes, M.; Vanreusel, A. Feeding ecology of shallow water meiofauna: Insights from a stable isotope tracer experiment in Potter Cove, King George Island, Antarctica. Polar Biol. 2012, 35, 1629–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradinger, R. Integrated abundance and biomass of sympagic meiofauna in Arctic and Antarctic pack ice. Polar Biol. 1999, 22, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhove, S.; Beghyn, M.; Van Gansbeke, D.; Bullough, L.W.; Vincx, M. A seasonally varying biotope at Signy Island, Antarctic: Implications for meiofaunal structure. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 202, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Vanhove, S.; Peck, L.S.; Vincx, M. Recolonisation of meiofauna after catastrophic iceberg scouring in shallow Antarctic sediments. Polar Biol. 2001, 24, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veit-Köhler, G.; Durst, S.; Schuckenbrock, J.; Hauquier, F.; Suja, L.D.; Dorschel, B.; Vanreusel, A.; Arbizu, P.M. Oceanographic and topographic conditions structure benthic meiofauna communities in the Weddell Sea, Bransfield Strait and Drake Passage (Antarctic). Prog. Oceanogr. 2018, 162, 240–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ehrlich, J.; Schaafsma, F.L.; Bluhm, B.A.; Peeken, I.; Castellani, G.; Brandt, A.; Flores, H. Sympagic fauna in and under Arctic pack ice in the annual sea-ice system of the new Arctic. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leasi, F.; Sevigny, J.L.; Hassett, B.T. Meiofauna as a valuable bioindicator of climate change in the polar regions. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouili, S.; Essid, N.; Semprucci, F.; Boufahja, F.; Nasri, A.; Beyrem, H.; Mahmoudi, E. Environmental quality assessment of El Bibane lagoon (Tunisia) using taxonomic and functional diversity of meiofauna and nematodes. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. United Kingdom 2017, 97, 1593–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsamo, M.; Albertelli, G.; Ceccherelli, V.U.; Coccioni, R.; Colangelo, M.A.; Curini-Galletti, M.; Danovaro, R.; D’Addabbo, R.; Leonardis, C.; Fabiano, M.; et al. Meiofauna of the Adriatic Sea: Current state of knowledge and future perspectives. Chem. Ecol. 2010, 26, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrigno, F.; Russo, G.F.; Semprucci, F.; Sandulli, R. Unveiling the state of some underexplored deep coralligenous banks in the Gulf of Naples (Mediterranean Sea, Italy). Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2018, 22, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapp, H.; Giere, O. Spadella interstitialis sp. nov., a meiobenthic chaetognath from Mediterranean calcareous sands. Meiofauna Mar. 2005, 14, 109–114. [Google Scholar]
- Casanova, J.P.; Hernández, F.; Jiménez, S. Spadella lainezi n. sp., the first cave chaetognath from the Eastern Atlantic Ocean. Vieraea 2006, 34, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Curini-Galletti, M.; Artois, T.; Di Domenico, M.; Fontaneto, D.; Jondelius, U.; Jörger, K.M.; Leasi, F.; Martínez, A.; Norenburg, J.L.; Sterrer, W. Contribution of soft-bodied meiofaunal taxa to Italian marine biodiversity. Eur. Zool. J. 2020, 87, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semprucci, F.; Colantoni, P.; Baldelli, G.; Rocchi, M.; Balsamo, M. The distribution of meiofauna on back-reef sandy platforms in the Maldives (Indian Ocean). Mar. Ecol. 2010, 31, 592–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semprucci, F.; Frontalini, F.; Losi, V.; du Chatelet, E.A.; Cesaroni, L.; Sandulli, R.; Coccioni, R.; Balsamo, M. Biodiversity and distribution of the meiofaunal community in the reef slopes of the Maldivian archipelago (Indian Ocean). Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 139, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

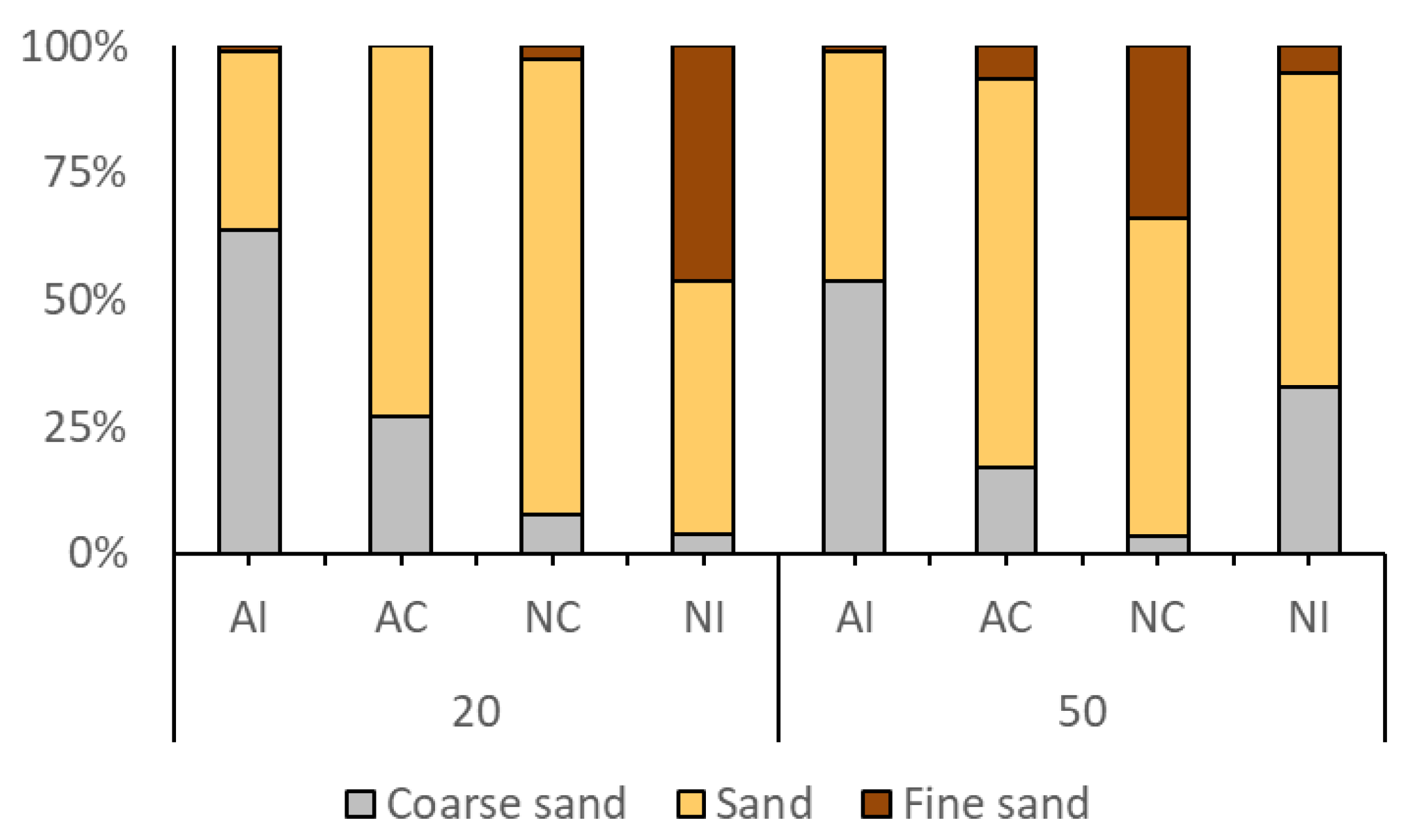

| Station | Zn2+ | Cd2+ | Pb2+ | Cu2+ | pH | O2 | NO3− | PO43− | SO42− | Coarse Sand | Sand | Fine Sand | TOC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (nM) | (nM) | (nM) | (nM) | (mg/L) | (mM) | (mM) | (mM) | % | % | % | % | ||
| AI20 | 41.994 | 7.894 | 17.556 | 50.177 | 8.33 | 5.7 | 0.494 | nd. | 23.002 | 63.618 | 35.426 | 0.956 | 1.732 |
| ±SD | 8.344 | 1.150 | 0.741 | 2.083 | 0.013 | 0.045 | 0.983 | 0.144 | 0.398 | 0.008 | |||
| AC20 | 13.735 | 1.031 | 12.700 | 14.838 | 8.70 | 6.2 | nd. | nd. | 18.362 | 26.844 | 73.142 | 0.014 | 4.043 |
| ±SD | 3.181 | 0.581 | 1.091 | 1.629 | 0.036 | 0.923 | 0.689 | 0.006 | 0.008 | ||||
| NC20 | 21.939 | nd. | 7.269 | 11.024 | 8.85 | 5.7 | nd. | nd. | 20.411 | 7.800 | 89.740 | 2.460 | 1.263 |
| ±SD | 2.686 | 4.184 | 2.457 | 0.064 | 0.674 | 0.965 | 0.893 | 0.001 | |||||
| NI20 | 45.453 | 2.033 | 14.802 | 13.976 | 8.86 | 5.9 | nd. | 1.864 | 24.183 | 3.814 | 50.015 | 46.172 | 2.348 |
| ±SD | 8.680 | 0.598 | 1.913 | 1.176 | 0.012 | 0.052 | 0.380 | 0.501 | 0.138 | 0.006 | |||
| AI50 | 11.482 | 2.639 | 5.698 | 9.727 | 8.55 | 6.2 | nd. | nd. | 24.770 | 53.867 | 45.075 | 1.057 | 2.800 |
| ±SD | 3.643 | 1.395 | 1.540 | 0.825 | 0.031 | 0.251 | 0.255 | 0.041 | 0.009 | ||||
| AC50 | 7.423 | 2.106 | nd. | 1.938 | 8.70 | 6.2 | nd. | 0.569 | 23.907 | 17.025 | 76.701 | 6.275 | 5.711 |
| ±SD | 2.681 | 0.807 | 0.710 | 0.014 | 0.048 | 0.876 | 0.019 | 0.818 | 0.010 | ||||
| NC50 | 6.942 | 0.706 | nd. | 0.642 | 8.85 | 5.7 | 0.313 | 0.438 | 24.465 | 3.341 | 62.875 | 33.784 | 1.153 |
| ±SD | 0.873 | 0.331 | 0.115 | 0.017 | 0.009 | 0.056 | 0.595 | 0.636 | 0.740 | 0.007 | |||
| NI50 | 11.722 | nd. | nd. | 1.484 | 8.71 | 6.2 | 0.205 | nd. | 24.342 | 32.872 | 61.760 | 5.369 | 3.867 |
| ±SD | 4.413 | 0.176 | 0.014 | 0.043 | 0.965 | 0.595 | 0.099 | 0.007 |
| (a) | (b) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Station Pair | t | p | Station Pair | t | p |
| AI vs. AC | 1.4662 | 0.147 | AI vs. AC | 1.8175 | 0.0718 |
| AI vs. NC | 1.6671 | 0.105 | AI vs. NC | 3.989 | 0.0032 |
| AI vs. NI | 1.0871 | 0.356 | AI vs. NI | 4.0749 | 0.0018 |
| AC vs. NC | 2.5469 | 0.0244 | AC vs. NC | 3.1563 | 0.012 |
| AC vs. NI | 2.2636 | 0.028 | AC vs. NI | 2.4701 | 0.0208 |
| NC vs. NI | 1.9268 | 0.0544 | NC vs. NI | 2.7836 | 0.0136 |
| (a) | (b) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Station Pair | t | p | Station Pair | t | p |
| AI vs. AC | 0.46728 | 0.8484 | AI vs. AC | 0.72994 | 0.6404 |
| AI vs. NC | 1.3267 | 0.2092 | AI vs. NC | 2.0195 | 0.0548 |
| AI vs. NI | 1.4224 | 0.1976 | AI vs. NI | 3.1182 | 0.019 |
| AC vs. NC | 1.3719 | 0.1856 | AC vs. NC | 2.1586 | 0.043 |
| AC vs. NI | 1.5315 | 0.1794 | AC vs. NI | 2.9999 | 0.0152 |
| NC vs. NI | 2.136 | 0.0586 | NC vs. NI | 2.5334 | 0.0396 |
| Variable | Adj. r2 | Pseudo-F | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| +Cd2+ | 0.27427 | 3.9724 | 0.0018 |
| +NO3− | 0.35437 | 3.6054 | 0.0032 |
| +Coarse sand | 0.46235 | 2.4745 | 0.051 |
| +pH | 0.52549 | 3.2622 | 0.019 |
| +PO43− | 0.56052 | 2.2752 | 0.0832 |
| Variable | Adj. r2 | Pseudo-F | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| +TOC | 0.1047 | 3.6896 | 0.0112 |
| +Cu2+ | 0.19544 | 3.4813 | 0.0146 |
| +pH | 0.27149 | 3.1921 | 0.0302 |
| +NO3− | 0.29641 | 1.7084 | 0.1804 |
| +Coarse sand | 0.4142 | 4.7817 | 0.003 |
| +Zn2+ | 0.48903 | 2.2048 | 0.1056 |
| +Cd2+ | 0.50471 | 1.2803 | 0.3088 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Semprucci, F.; Appolloni, L.; Grassi, E.; Donnarumma, L.; Cesaroni, L.; Tirimberio, G.; Chianese, E.; Di Donato, P.; Russo, G.F.; Balsamo, M.; et al. Antarctic Special Protected Area 161 as a Reference to Assess the Effects of Anthropogenic and Natural Impacts on Meiobenthic Assemblages. Diversity 2021, 13, 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13120626
Semprucci F, Appolloni L, Grassi E, Donnarumma L, Cesaroni L, Tirimberio G, Chianese E, Di Donato P, Russo GF, Balsamo M, et al. Antarctic Special Protected Area 161 as a Reference to Assess the Effects of Anthropogenic and Natural Impacts on Meiobenthic Assemblages. Diversity. 2021; 13(12):626. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13120626
Chicago/Turabian StyleSemprucci, Federica, Luca Appolloni, Eleonora Grassi, Luigia Donnarumma, Lucia Cesaroni, Giuseppina Tirimberio, Elena Chianese, Paola Di Donato, Giovanni Fulvio Russo, Maria Balsamo, and et al. 2021. "Antarctic Special Protected Area 161 as a Reference to Assess the Effects of Anthropogenic and Natural Impacts on Meiobenthic Assemblages" Diversity 13, no. 12: 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13120626
APA StyleSemprucci, F., Appolloni, L., Grassi, E., Donnarumma, L., Cesaroni, L., Tirimberio, G., Chianese, E., Di Donato, P., Russo, G. F., Balsamo, M., & Sandulli, R. (2021). Antarctic Special Protected Area 161 as a Reference to Assess the Effects of Anthropogenic and Natural Impacts on Meiobenthic Assemblages. Diversity, 13(12), 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13120626










