Abstract
Tunisia is one of the world’s largest producers of olive oil, and it preserves pools of olive genetic diversity that are still unexplored. A recent prospection and collection program of the National Gene Bank of Tunisia (NGBT) focused on the vast oasis of Degache, in the south west part of Tunisia, where 47 samples were collected and genetically characterized through simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers. Identification and authentication of genotypes were obtained through comparison with reference cultivars belonging to the Olive National Collection of Tunisia (IOC) and with cultivars from Algeria, Italia, Syria and Lebanon. Degache olive genotypes showed large genetic variability, a significant diversity from the reference germplasm, and a clear differentiation from modern varieties. The population structure analysis identified four gene pools characterizing genotypes from different area of origin. Two gene pools appear to be more represented in germplasm from southern Tunisia, where environmental conditions at critical plant development phases, are harsher. This suggests that this germplasm might present traits of adaptation useful for breeding to improve resilience to abiotic stresses. Our results will support ex situ and in situ conservation activities of Tunisian olive germplasm pursued by the National Gene Bank of Tunisia.
1. Introduction
Olive growing is progressively increasing in Tunisia, with an actual cultivated surface of about 1.8 million ha, which corresponds to 30 percent of the North African cultivated land [1]. Olive cultivation in Tunisia can be traced back to the Phoenicians colonization of islands (Cyraunis, now called Kerkennah, Djerba, etc.) and coasts (Cap Bon, Sousse, etc.), followed by Greek, Roman and Arab civilizations [2]. During the centuries, varietal introductions from all over the Mediterranean basin, France, Spain, Morocco, Greece, have further enriched the Tunisian olive germplasm. Nevertheless, the current olive cultivation mostly relies on only two highly productive varieties, CHEMLALI SFAX and CHETOUI for oil production, and MESKI for table olives, neglecting much of the Tunisian olive heritage [3]. Trigui and Msallem [4] morphologically characterized 56 local varieties and ecotypes, but the real number of genotypes in Tunisia is still underestimated, because many minor varieties are still cultivated, although at a very small scale, in marginal areas of the country [5,6,7].
Genetic resources are the bases of crop adaptation. They allow crops to respond to environmental challenges such as those produced by the ongoing climate changes, helping to sustain the production in marginal lands, and enhancing food security and quality [8,9,10]. In this regard, in several Mediterranean countries there has been an increased interest in safeguarding crop resources for a sustainable agriculture [11,12]. In this area, actions for protecting genetic resources of many crops have multiplied, with the aim of enriching the existing collections with new genotypes useful for breeding programs, as well as to improve their identification, conservation and exploitation [13,14]. In Tunisia, some researches have been carried out to prospect and analyze the olive germplasm, but most of these investigations have focused on the main cultivars and on the consolidation of the existing ex situ collections [6,15], despite the importance of identifying the minor varieties and the amount of genetic variability present in restricted marginal areas of the country.
In order to cover region’s gaps for exploring new olive germplasm, a governental program of the Olive Institute, the Oasis Regional Center of Research of Degache and the National Genebank of Tunisia has been focused on the continental Saharan oasis of Degache (Tozeur), in the south-west of Tunisia. It is located north-west of Chott El Jerid, thus it is part of the upper Saharan bioclimatic area, with dry and arid climate and a rainfall <100 mm/year. The oasis is dominated by the palm groves, forages and legumes, but several fruit trees are cultivated, such as apricot, fig, vines and olive. The oasis still holds ancient olive trees that ensure small typical olive oil productions. The existence of traditional and ancient oil mills testifies to the antiquity of the culture of olives in this region. Previous researches has been conducted at phenotypical level on morphological and pomological characters, highlighting a wide variability among the Degache olive germplasm [16]. The identification, characterization and evaluation of such genotypes could be useful to develop new olive oils characterized by high quality, historical memory and connection with the local culture label such as the Controlled Designation of Origin (AOC) and Indication of Provenance (IP). The valorization of the traditional products would have a beneficial economic impact on the marginal regions of Tunisia, sustaining the socio-economic development of the region, ensuring an additional source of incomes for local populations, enhancing on-farm conservation strategies, and protecting the oasis from deforestation.
To reach the right valorization of Degache olive genotypes, it is necessary to ensure their varietal correspondence. The use of molecular markers is a good option for crop genotyping since they are highly polymorphic, almost unlimited in number, and not affected by plant tissue types, developmental stages, and environmental factors. In particular, simple sequence repeats (SSR) markers still represent a useful option, having high information content, codominant inheritance, locus specificity and high reproducibility. The easiness and low cost have made the use of standardized sets of SSR markers a routine for the variety identification and product traceability in many species [17,18,19].
The olive scientific community still lacks standardized methods for molecular analyses to be shared among research centers, but it is possible to use a standard set of SSR markers that is widely validated by researchers and could guarantee results more comparable between laboratories [20,21,22]. Thus, the main objectives of this study were: (i) the molecular characterization and identification of 47 olive accessions grown in the oasis of Degache, in south west of Tunisia; (ii) the validation of results in comparison with cultivars from official collections of the National Gene Bank of Tunisia; (iii) the exploration of the relationships between Degache genotypes and other Mediterranean germplasm; (iv) the enrichment of reference collections of Tunisian olive varieties.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
In 2018, surveys were made on 26 farms of the oasis of Degache in the south west of Tunisia (Figure 1, Supplementary Table S1), collecting a sample from each olive tree existing in the oasis. According to the morphological characterization by Ben Maachia and Ben Amar [16], each tree was considered a single genotype, thus a total of 47 olive trees were sampled, tagged as Degache 1 to 47 (DG), and submitted to the genetic characterization.
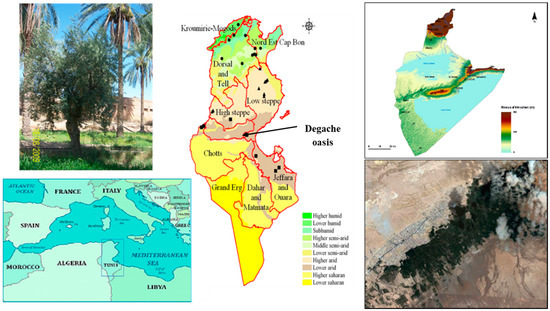
Figure 1.
Geographical localization of the Degache oasis from where the 47 olive samples were collected: map of the Mediterranean Basin, Agro-ecological map of Tunisia (redrawn from CNEA, 2007) and the geographical borders of Tozeur governorate where Degache oasis is located.
For the authentication of the Degache genotypes, a panel of 37 varieties representative of the overall Tunisian olive germplasm, maintained at the National Gene Bank of Tunisia (NGBT), was used in this study. In addition, the analysis was extended to 103 olive genotypes largely cultivated in different Mediterranean countries, comprising 20 Algerian varieties maintained at the Institut Technique de l’Arboriculture Fruitière et de la Vigne, ITAFV, Takarietz, Bejaia, Algeria; 43 Italian varieties maintained at the Dipartimento di Scienze del Suolo, della Pianta e degli Alimenti, DISSPA, Università di Bari, Italy; 17 Syrian varieties maintained at the General Commission for Scientific Agricultural Research, GCSAR, Aleppo, and 23 Lebanese varieties furnished by the Lebanese agriculture institute (Table S1).
2.2. DNA Extraction and SSR Assays
Three young leaves of each olive sample were washed with distilled water, lyophilized and finely ground, and stored at −80 °C until analysis. Fifty milligrams of leaf tissue were used to extract the total genomic DNA according to Spadoni et al., [23]. DNA quality and concentration were assessed on 1% agarose gel and Nano Drop TM ND2000 (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) spectrophotometer. DNA was reduced to the concentration of 50 ng/µL and stored at −20 °C until use.
A standardized set of 10 preselected microsatellite markers was used (Table S2) [24,25,26,27]. PCR reactions were performed in a final volume of 12.0 µL including 1.25 µL of 10× Dream Taq Buffer, 0.6 µL of 2M dNTP, 1.25 µL of 2.5 µM mix of primers, 0.2 µL of 5 U/µL Dream Taq (Thermo Scientific), 7.7 µL H2O, and 50 ng of DNA. A C1000TM Thermal Cycler (Bio-Rad, Hercules, Foster City, CA, USA) was used for the amplification, and PCR products were detected by the automatic capillary sequencer ABI PRISM 3100 Avant Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). Sample analyses were carried out with GeneMapper genotyping software v3.7 (Applied Biosystems), with the internal molecular size standard GeneScan 600 LIZ (Applied Biosystems).
2.3. Authentication of Degache genotypes and Relationships with Other Mediterranean germplasm
The authentication of Degache accessions was obtained by comparing their molecular profiles obtained with the 10 SSRs with those of 37 widely cultivated Tunisian varieties (37), available at the (NGB, Tunisia) and DISSPA-UNIBA (Italy) database (Supplementary Table S1). In addition, to explore the relationships with other Mediterranean germplasm, the genetic profiles of Degache genotypes were compared with molecular data of varieties originated from other Mediterranean countries, namely Algeria (20), Italy (43), Syria (17), and Lebanon (23) collected in a common dataset at the DISSPA-UNIBA (Italy) (Table S1).
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. Genetic Diversity
GenAlEx software v.6.5 (h [28] was used to estimate the following genetic indices: number of alleles (Na), effective number of alleles (Ne), Shannon’s diversity index (I) [29], observed (Ho) and expected (He) heterozygosity, and fixation index (F) [30]. The same software was also used for the multilocus genotype (MLG) analysis, and to estimate the number of private alleles [31] and the probability of identity (PI) [32]. The informativeness of the primers as the polymorphic information content (PIC) [33] and the frequency of null alleles (F null) were calculated by using Cervus v 2.0 software [34].
2.4.2. Genetic Relationships and Population Structure
The genetic relationships between the 177 olive accessions were estimated. A principal coordinate analysis (PCoA), based on inter-individual relationship using Nei’s unbiased genetic distance pairwise population matrix, was carried out with GenALEx, followed by an analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA) among and within populations. In addition, a dendrogram was obtained using the Ward’s hierarchical clustering method based on the dissimilarity matrix, using the software DARWIN v. 6.0.010 (http://darwin.cirad.fr). To determine the support for each node, a 1000 replicate bootstrapping was performed [35]. The visualization of the dendrogram was elaborated with FigTree software v.1.4.3 (http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/).
The population genetic structure was assessed by using the Bayesian model-based clustering analysis implemented in STRUCTURE software (version 2.3.4 [36]. The number of sub-populations (K) that best fit with the olive analyzed collection, was obtained performing 10 independent runs for each K (from 1 to 10), with 100,000 Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) repetitions and 100,000 burn-in periods. The resulting data were analyzed by Structure Harvester software [37] based on ad hoc statistic ∆K test [38]. Accessions were assigned to defined groups if the value of the corresponding membership coefficient (qi) was higher than 0.8; otherwise they were considered to be admixed.
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Diversity of Degache Genotypes
The multilocus genotype analysis individuated 5 synonymy groups: A (including DC26-DC20-DC15), B (including DC29-DC27-DC19), C (including DC43-DC47), D (including DC42-DC44-DC30-DC18) and E (including DC45-DC12-DC10) (Figure S1). For each group, only one genotype was retained, thus 37 samples were further used for subsequent analyses (Table S1). Within the 37 Degache samples, a total of 42 alleles were obtained (4.2 alleles/locus), with a minimum of 2 alleles for DCA05 and a maximum of 8 alleles for DCA16 (Table 1).

Table 1.
Genetic diversity indices number of alleles (Na), effective number of alleles (Ne), Shannon’s diversity index (I), observed heterozygosity (Ho), expected heterozygosity (He), fixation index (F), and PIC values revealed in the 37 olive Degache accessions analyzed with 10 SSR markers.
The values of Shannon information index (I) ranged from 0.69 (DCA5) to 1.64 (DCA16) (mean 1.08). High values of observed (Ho) and expected (He) heterozygosity were observed: Ho values ranged from 0.378 for DCA17, to 1 for DCA15 (0.77 on average); He ranged between 0.42 (DCA15) and 0.75 (DCA16) (average 0.60). For 8 out of the 10 loci analyzed, the observed heterozygosity was significantly higher than the expected values (Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium) with a mean inbreeding coefficient F = −0.115. The likelihood of null alleles incidence ranged from −0.102 to 0.201.
PIC values, which indicate the informativeness of a microsatellite marker, had, for the 10 SSRs considered, a mean value of 0.536, ranging from the lowest value of DCA15 (0.364) to the highest value of DCA17 (0.723).
The value of the total probability of identity for the 10 SSRs analyzed, which indicates the probability that two unrelated genotypes randomly chosen have the same profile, was low (1.4 × 10−13), (Figure S2), confirming the efficiency of the microsatellites used for genotypes fingerprinting, and indicating that identical profiles correspond to synonyms.
The genetic indices calculated within each of the six geographical groups of genotypes were remarkably different (Table 2).

Table 2.
Genetic diversity indices Na, Ne, I, Ho, He, F and private Alleles obtained with 10 SSR markers in the 6 groups of genotypes of different geographical origin (number of samples in parentheses).
The Italian and Tunisian collections were the richest in alleles (105 and 91, respectively), followed by Algeria (76), Syria (64), Lebanon (44) and Degache (42) collections. The high genetic variability was confirmed also by the Shannon index which was ≥1 in all the collections except the Lebanese one, which showed also a negative F value, together with the Syrian and Degache collections. The Italian and Tunisian collections had the highest number of private alleles (16 and 15, respectively), while the Degache collection showed only 2 private alleles (Table 2, Table S3, Figure S3).
3.2. Genetic Relationships of Degache Genotypes with Other Mediterranean Germplasm
The genetic relationships of Degache genotypes with Tunisian cultivars and varieties from other Mediterranean countries were investigated through a principal coordinate analysis based on Nei’s unbiased genetic distance matrix (Figure 2).
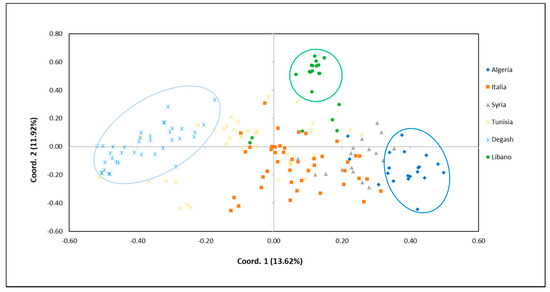
Figure 2.
Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) based on genetic distance between Degache olive samples and 140 varieties deriving from different geographical areas. Circles are drawn arbitrarily to emphasize the prominent groups of genotypes from Degache oasis (light blue), Algeria (blue), and Lebanon (green).
The first two components of the PCoA explained only the 13.62% and the 11.92% of the total variance for component PCo1 and component PCo2, respectively (Figure 2).
The AMOVA analysis carried out on the six groups of olive genotypes, assigned 86% of the molecular variance to differences among individuals, and only 14% to differences between groups (Table 3), but the calculation of the pairwise FST distances among the six groups indicated a great genetic differentiation between Algeria and Lebanon (FST = 0.251), and between Algeria and Degache (FST = 0.247) (Table 4). Conversely, the lowest FST distances were found between Italy and Tunisia (0.055) and between Degache and Tunisia (0.062).

Table 3.
The partitioning of genetic variation within and among groups obtained with AMOVA analysis on the six olive groups having different geographical origin.

Table 4.
Genetic differentiation (Pairwise population Fst) between the six groups of genotypes of different geographic origin.
The genetic relationships among olive samples were further investigated by using the similarity matrix to produce a Ward’s dendrogram (Figure 3).
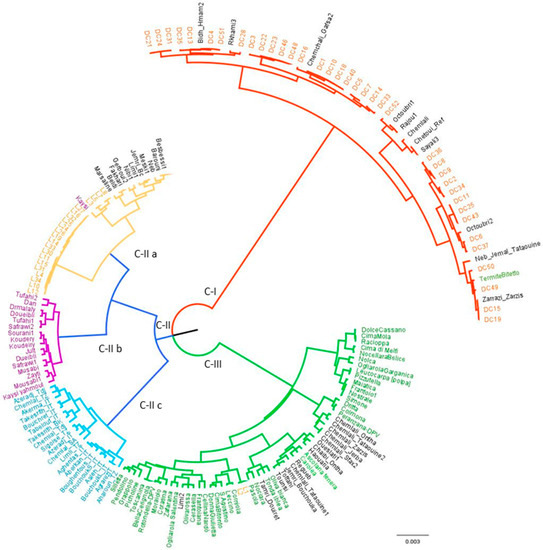
Figure 3.
Dendrogram generated by Ward clustering method using 10 SSR markers, illustrating the phylogenetic relationships among the analyzed olive genotypes originated from Degache oasis (orange, C-I), Lebanon (yellow, C-II a), Syria (purple, C-II b), Algeria (blue, C-II c), Italy and Tunisia (green, C-III).
The dendrogram clearly separated the genotypes according to their geographical origin. In detail, we observed three clusters (C-I, C-II and C-III). Cluster C-I included all the Degache genotypes with 11 Tunisian varieties and the Italian TERMITE DI BITETTO. Cluster C-II included three sub-clusters; C-II a, including all Lebanese genotypes (except L1 and L2, in cluster C-III), 11 Tunisian and 1 Syrian variety; C-II b, including all the Syrian varieties; C-II c, comprising the Algerian varieties. Cluster C-III included all the Italian varieties, together with two groups of Tunisian varieties. One group comprised five CHEMLAL variants (ZARZIS, ONTHA, JERBA, SFAX2, TATAOUINE2) with the Italian cultivars DRITTA, CULMONA and PERANZANA_DPV. A second group included the varieties OUESLATI1, CHAIBI_ONTHA, HAOUARIA, REGUEB, CHEMLALI_TATAOUINE1, JEMRI-BOUCHOUKA, TOFFAHI, TOUNSI, OLIVA BIANCA, TONDA IBLEA, TAMRI_DOUIRET, and NOCIARA E PASOLA.
The dendrogram allowed also observing that few Degache genotypes were very similar to Tunisian varieties, such as for DC4 and DC51 with BIDH HAMAM2; DC1, DC10, DC18 and DC40 with CHEMLALI GAFSA2; DC15 and DC19 with ZARRASI.
3.3. Genetic Structure
The application of the Bayesian clustering method implemented by the software STRUCTURE, indicated K = 2 as the number of sub-populations (SP) which best fits the overall analyzed collection, followed by K = 4 and K = 7 (Figure 4A; Supplementary Figure S4).
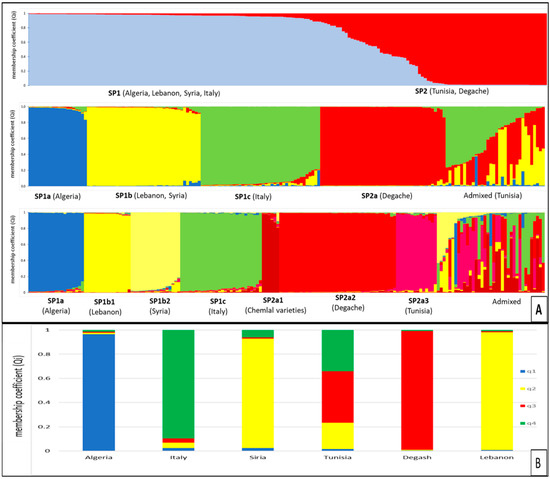
Figure 4.
(A) Bayesian inference of population structure based on 10 microsatellite loci in 177 olive accessions, for K = 2 (the most probable genetic structure model), K = 4, and K = 7, inferred with a model-based clustering method implemented in STRUCTURE v.2.3.4. q is the membership coefficient. (B) The stacked bar plots showing, for olive populations originating from different geographical areas, the estimated membership coefficient (qi) relative to the subpopulations identified by STRUCTURE for K = 4.
At K = 2, the olive germplasm was divided into SP1 and SP2; SP1 includes Italian, Lebanese, Syrian and Algerian cultivars, while SP2 includes Tunisian cultivars with Degache genotypes.
At K = 4, the SP1 was split into three subgroups, SP1a, SP1b and SP1c. The subgroup SP1a includes Algerian cultivars, SP1b includes Lebanese and Syrian genotypes, and SP1c includes Italian genotypes. The subgroup SP2 includes all the Degache genotypes and part of the Tunisian varieties, while the remaining Tunisian genotypes comprise the admixed group.
At K = 7, the SP1b group further split Lebanese (SP1b1) from the Syrian (SP1b2) germplasm, and SP2a further split into SP2a1, SP2a2 and SP2a3, including, respectively, six CHEMLALI variants (SP2a1), the Degache genotypes (SP2a2) and 14 Tunisian cultivars (SP2a3); most of the Tunisian genotypes fell in the admixed group (Figure 4A).
For the six olive collections of different geographical origin, the estimated mean membership coefficient (qi) relative to the subpopulations identified by STRUCTURE for K = 4, was calculated. The results, illustrated in Figure 4B, indicated a different genetic stratification in the groups. While Algerian, Italian, Syrian, Degache and Lebanese collections showed an estimated membership coefficient qi greater than 0.85, the Tunisian collection confirmed the presence of different proportions of qi.
4. Discussion
Sustainable management of genetic resources plays a fundamental role in achieving the objectives of preservation of plant biodiversity encouraged by the Convention on Biological Diversity of United Nations and Food Organization and Agriculture [39]. Crop genetic resources are primary in the traditional cropping systems, which largely rely on the use of local varieties that are better adapted to the local environments [40,41,42]. Moreover, they are an important tool for crop breeding plans to increase yield, quality and resistance to a wide range of biotic and abiotic stresses, in the frame of the ongoing climate changes, particularly the agricultural systems in southern Europe [43,44,45].
The Tunisian Government, through the National Gene Bank of Tunisia (NGBT), has recently implemented a program for the collection of new olive germplasm in marginal areas of the country, focusing particular attention on the ancient continental Saharan oasis of Degache (Tozeur), in the south-west of Tunisia. This oasis holds a wide genetic diversity for several fruit trees, particularly date palm, fig, apricot, vine and olive. These plant genetic resources should be of great interest since they are adapted to severe conditions of the upper Saharan climate and arid regions. Moreover, local populations have conserved a traditional way of cultivation, preserving unique and rare genotypes.
The main goal of this program was to characterize molecularly the olive Degache germplasm, understanding its relationships with other Mediterranean varieties, and possibly shedding light on the origin of this germplasm. A deep survey was conducted on 26 farmers located in the area of the oasis, in partnership with several research institutions and agricultural regional authorities. Forty-seven olive samples were collected, and they were submitted to the molecular characterization by using a standardized set of 10 SSRs markers. The multilocus genotype analysis of the Degache germplasm revealed the presence of 10 genotypes sharing identity; these redundant genotypes were discarded, and 37 samples were used for further investigation. The obtained profiles were compared with those of cultivars representative of the olive germplasm of Tunisia itself and other Mediterranean countries, Italy, Algeria, Syria and Lebanon.
The genetic analysis highlighted a wide genetic diversity among the studied genotypes, confirming the evidence obtained in studies conducted at phenotypical level [17]. The Degache germplasm displayed high values for the number of alleles, Shannon information index, and both observed (Ho) and expected (He) heterozygosity. The observed heterozygosity exceeded the expected heterozygosity, indicating an excess of heterozygosity not expected in isolated germplasm such as that of this remote oasis. This can be due to the process of olive cultivation carried out during the centuries, through the selection of interesting morphological variants in the wild and/or imported plants; then, the maintenance of these elite genotypes through the vegetative propagation has preserved this heterozygosity or even increased it by mutation over the generations [46,47,48,49].
The second target of this study was to understand the relationships of the Degache germplasm with other olive Mediterranean varieties, and possibly obtain information about its origin. To this aim, the genetic analysis was extended to a collection of 140 largely cultivated varieties as representative of the olive germplasm of Tunisia and other Mediterranean countries such as Italy, Algeria, Syria and Lebanon. The obtained results confirmed a remarkable genetic variation of olive germplasm in all the countries, as already observed by several authors [50,51,52,53]. In particular, Italian, Algerian and Tunisian germplasm stood out for a higher number of alleles, Shannon index, heterozygosity and number of private alleles, with respect to Syrian and Lebanese germplasm, suggesting, for the genetic background of the germplasm of these countries, an important contribution of the local wild olive through the crosses [54,55,56]. A high number of private alleles was observed in all the collections, underlining the large diversity of olive germplasm in the Mediterranean region, while Degache genotypes had only two, which could be explained by the sharing of their gene pool with the Tunisian varieties cultivated in the region.
The PCo analysis remarked the genetic distance of Degache germplasm from all the others, confirming its distinctiveness, although it appeared to have strong relationships with the contemporary Tunisian germplasm. Indeed, the pairwise distance calculated between the groups indicated a great genetic differentiation of the Degache from the Algerian (FST = 0.251) and the Lebanese (FST = 0.228) germplasm. These two groups of genotypes formed well-separated clusters, while the Italian, Syrian and part of Tunisian germplasm were more overlapped.
These results were confirmed by the Ward’s dendrogram, which clustered the genotypes according to their geographical origin. Degache genotypes grouped well apart from the other germplasm; Lebanese, Syrian and Algerian cultivars comprised a second cluster, and Italian genotypes a third cluster. Interestingly, Tunisian varieties appeared to belong to the three different clusters, indicating a multi-origin genetic background.
Out of 37 different Degache genotypes identified, only eight had a genetic profile very similar to that of contemporary Tunisian cultivars: DC4 and DC51 were very similar to BIDH HAMAM2; which is known as a table olive; indeed, they presented a high weight of fruit, respectively 9.64 g and 5.11g. Likewise, DC28 was very similar to RKHAMI, another table olive, as confirmed by the pomological description [57]. Both RKHAMI and BIDH HAMAM are varieties very well appreciated in Tunisia as table olives and they are in great demand for cultivation. In addition, DC1, DC10, DC18 and DC40 were very similar to CHEMCHALI GAFSA2, and DC15 along with DC19 clustered with ZARRASI, both largely cultivated in this region [58]. These genotypes differed from the corresponding varieties for one to three alleles; thus, they can be considered local variants of these varieties. The intra-varietal polymorphism is well described in several olive cultivars, with differences in up to 15% of the analyzed alleles [29]. A great intra-varietal diversity is particularly usual in regionally selected varieties that are at the base of typical local productions. It probably derives by somatic mutations occurring in the process of vegetative propagation and that accumulate during generations without phenotypic changes in crop morphology and agronomic performances [59,60]. In our study, this intra-varietal variability was observed especially in cultivar CHEMLALI, thus confirming that it is a polyclonal mixture of closely related genotypes [3,61]. Most of CHEMLALI variants clustered near other Tunisian varieties, but in the same cluster of Italian germplasm, indicating a relationship between the germplasm of the two countries. On the contrary, almost all Degache accessions found no match with any reference varieties neither from Tunisia, nor from Algeria, Italy, Syria, and Lebanon, thus confirming their potential as candidates of putative new varieties.
Bayesian inference of population structure implemented in STRUCTURE indicated 2 as the number of sub-populations which best fits the overall analyzed collection. One subpopulation included the Degache germplasm and part of Tunisian varieties, as indication of common ancestry, while the second subpopulation included the remaining germplasm At K = 4, the 177 analyzed genotypes split into four subpopulations according to their geographical origin: Algerian germplasm, Lebanese and Syrian germplasm, Italian germplasm, Degache germplasm, while Tunisian genotypes fell in the admixed group. Interestingly, this subdivision mimics the pattern of occurrence of the olive’s three distinct genetic pools hypothesized by several authors in the Mediterranean Basin: Q1 for the west, Q2 for centre, and Q3 for the east [62,63,64]. Our results suggest this distribution of the analyzed germplasm, distinguishing the Algerian germplasm (west basin) from Tunisian (included Degache) and Italian germplasm (Central basin), and from Syrian and Lebanese germplasm (eastern basin). While western (Algerian) and eastern (Lebanese and Syrian) cultivars were strongly assigned to one specific gene pool, Italian and Tunisian (but not Degache) germplasm showed a high level of admixture. This is in accord with the hypothesis of the Near East as olive center of origin, followed by the spread of the crop towards the west, which ultimately resulted in genotypes derived from different routes of variation generated through the crossing with local genotypes [65,66,67]. The population structure analysis showed, for Degache germplasm, a specific gene pool that appeared underrepresented in the modern varieties. This suggests that Degache germplasm, which is adapted to harsh environmental conditions at the critical plant development phases, might possess traits of adaptation that could be useful for breeding varieties more resilient to drought, thus is worth being better studied and preserved.
In conclusion, this work allowed giving some valuable insight into the Tunisian olive germplasm biodiversity, highlighting the richness in new genetic variability preserved in the germplasm of the oasis of Degache. The strong differences among the Degache and all the other germplasm, including the Tunisian ones, suggests that it can be considered an exclusive genetic core, selected and developed in this area during the centuries.
The substantial diversity observed in these genotypes could be used to support the national breeding programs for olive improvement and conservation. Human activities and the replacement of traditional olive cultivations into intensive orchards with introduced cultivars, threatens the preservation of the local olive germplasm. Consequently, the characterization and preservation of this primeval Tunisian olive gene pool should be considered mandatory. These results will support the activities of in situ (on-farm) conservation of Tunisian olive germplasm, promoted by the National Gene Bank of Tunisia along with the ex situ approach. A better knowledge of this genetic material will allow a better valorization of it, thus helping to obtain the labelling for olive oil to be exported internationally and promoting the full exploitation of its potential financial value in the high-quality local production.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/1424-2818/12/9/358/s1. Figure S1: Multilocus Genotypes analysis using 10 SSR on 47 olive genotypes from the Degache Oasis (Tunisia); Figure S2: Probability of identity for the 6 groups of olive genotypes considered in this study. A minimum of 4 microsatellite loci were needed to meet the PID threshold of P 0.01 (Waits et al., 2001); Figure S3: Allelic patterns across the six groups of olive genotypes having different geographic origin; Figure S4: (a) Mean of estimation ln probabilistic data of analysed olive samples; (b) Graph of Delta K values to determine the best number of populations present in the analysed olive germplasm. The best K was at K = 2, followed by K = 4 and K = 7; Table S1. List of olive genotypes analysed: country of origin, genotype, sampling site, and prevalent use; Table S2. List of the 10 microsatellite markers (SSR) used for molecular characterization of olive accessions. For each SSR, the identification code (SSR ID), repeat motif, primer sequence, bibliographic reference and annealing temperature (Ta) are reported; Table S3: Number of private alleles found in the six group of genotypes originating from different Mediterranean countries (number of accessions in parentheses).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, O.S.D., C.M. and M.M.M.; Data curation, M.E.R., A.C., M.S. and S.B.; Formal analysis, O.S.D. and M.M.M.; Funding acquisition, O.S.D. and C.M.; Investigation, O.S.D., S.B.M., F.B.A., V.F. and S.G.; Methodology, O.S.D. and M.M.M.; Resources, O.S.D. and C.M.; Supervision, M.M.M.; Writing—original draft, O.S.D. and M.M.M.; Writing—review & editing, O.S.D., C.M. and M.M.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research and the publication fee for this work were supported by a grant from the Republic of Italy to the Republic of Tunisia, Project “Tunisian plant genetic resources better conserved and valued” coordinated by CIHEAM-Bari and the National Genebank of Tunisia. The characterization of Lebanese germplasm was supported by *Olio Del Libano III* Project funded by the Italian Government through the Italian Agency for Development Cooperation (AICS).
Acknowledgments
V.F. has been supported by MIUR-PON Ricerca e Innovazione 2014–2020 (project AIM1809249-attività 2, linea 1).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tunisian Agriculture Ministry-General Direction of Agricultural Production. Available online: http://www.agriculture.tn (accessed on 20 February 2020).
- Wolff, S. Oleoculture and Olive Oil Presses in Phoenician North Africa. In Olive Oil in Antiquity; Eitam, D., Heltzer, M., Eds.; Sargon: Padova, Italy, 1996; pp. 129–136. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Mohamed, M.; Zelasco, S.; Ben Ali, S.; Guasmi, F.; Triki, T.; Conforti, F.L.; Kamoun Naziha, G. Exploring olive trees genetic variability in the South East of Tunisia. Genet. Mol. Res. 2017, 16, gmr16039850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigui, A.; Msallem, M. Oliviers de Tunisie: Catalogue des Variétés Autochtones and Types Locaux: Identification Variétale and Caractérisation Morpho-Pomologique des Ressources Génétiques Oléicoles de Tunisie; Institution de la Recherche et de l’Enseignement Supérieur Agricoles: Tunis, Tunisia, 2002; Volume 1, p. 159. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Mohamed, M.; Ben Ali, S.; Boussora, F.; Guasmi, F.; Triki, T. Polymorphism of microsatellite (SSR) Markers in tunisian olive (Olea Europaea L.) cultivars. J. Multidisc. Eng. Sci. Stud. 2017, 3, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Abdelaali, S.; Saddoud Debbabi, O.; Ben Abdelaali, N.; Hajlaoui, M.R.; Mars, M. Fingerprinting of on-farm conserved local Tunisian orange cultivars (Citrus sinensis (L.) osbeck) using microsatellite markers. Acta Biol. Cracov. Bot. 2018, 60, 83–93. [Google Scholar]
- Saddoud Debbabi, O.M.M.; Miazzi, O.; Elloumi, M.; Fendri, F.; Ben Amar, M.; Savoia, S.; Sion, H.; Souabni, S.; Rahmani Mnasri, S. Recovery, assessment, and molecular characterization of minor olive genotypes in Tunisia. Plants 2020, 9, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucheffa, S.; Tamendjari, A.; Sanchez-Gimeno, A.C.; Rovellini, P.; Venturini, S.; di Rienzo, V.; Miazzi, M.M.; Montemurro, C. Diversity Assessment of Algerian Wild and cultivated Olives (Olea europaea L.) by molecular; morphological and chemical traits. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2019, 121, 1800302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Rienzo, V.; Miazzi, M.M.; Fanelli, V.; Sabetta, W.; Montemurro, C. The preservation and characterization of Apulian olive germplasm biodiversity. Acta Hort. 2018, 1199, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sion, S.; Taranto, F.; Montemurro, C.; Mangini, G.; Camposeo, S.; Falco, V.; Gallo, A.; Mita, G.; Saddoud Debbabi, O.; Ben Amar, F.; et al. Genetic characterization of apulian olive germplasm as potential source in new breeding programs. Plants 2019, 8, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fendri, M.; Trujillo, I.; Trigui, A.; Rodríguez-García, M.I.; Alché Ramírez, J.D. Simple sequence repeat identification and endocarp characterization of olive tree accessions in a Tunisian germplasm collection. Hort. Sci. 2010, 45, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miazzi, M.M.; D’Agostino, N.; Gadaleta, S.; Montemurro, C.; Taranto, F. Genotyping-by-sequencing-derived single-nucleotide polymorphism catalog from a grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) germplasm collection that includes the most representative Apulian autochthonous cultivars. Acta Hortic. 2019, 1248, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnasri, S.; Saddoud Debbabi, O.; Ben Salah, M.; Ferchichi, A. Morphological and molecular characterization of the main varieties cultivated in the region of Hbebsa (North West of Tunisia). Int. J. Agron. Agric. Res. 2014, 5, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- Laabidi, I.; Gouta, H.; Mezghani, A.; Ayachi, M.; Labidi, F.; Mars, M. Combination of morphological and molecular markers for the characterization of ancient native olive accessions in Central-Eastern Tunisia. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2017, 340, 287–297. [Google Scholar]
- Taamalli, W.; Geuna, F.; Banfi, R.; Bassi, D.; Daoud, D.; Zarrouk, M. Agronomic and molecular analyses for the characterisation of accessions in Tunisian olive germplasm collections. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 9, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Maachia, S.; Ben Amar, F. Prospection, morphological and Pomological identification of olive ecotypes (Olea europaea L.) in the Degache oasis (Tozeur, Tunisia). J. New Sci. Agric. Biotechnol. 2016, 33, 1892–1900. [Google Scholar]
- Muzzalupo, I.; Vendramin, G.G.; Chiappetta, A. Genetic biodiversity of Italian olives (Olea europaea) germplasm analyzed by SSR markers. Sci. World J. 2014, 296590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasqualone, A.; di Rienzo, V.D.; Miazzi, M.M.; Fanelli, V.; Caponio, F.; Montemurro, C. High resolution melting analysis of DNA microsatellites in olive pastes and virgin olive oils obtained by talc addition. Eur. J. Lip. Sci. Technol. 2015, 117, 2044–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Rienzo, V.; Fanelli, V.; Miazzi, M.M.; Sabetta, W.; Montemurro, C. A reliable analytical procedure to discover table grape DNA adulteration in industrial wines and musts. Acta Hortic. 2017, 1188, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldoni, L.; Cultrera, N.G.; Mariotti, R.; Ricciolini, C.; Arcioni, S.; Vendramin, G.G. A consensus list of microsatellite markers for olive genotyping. Mol. Breed. 2009, 24, 213–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimonti, A.; Simone, V.; Cesari, G.; Lamaj, F.; Cattivelli, L.; Perri, E.; Desiderio, F.; Fanizzi, F.P.; Del Coco, L.; Zelasco, S. A first molecular investigation of monumental olive trees in Apulia region. Sci. Hort. 2013, 162, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabetta, W.; Miazzi, M.M.; di Rienzo, V.; Fanelli, V.; Pasqualone, A.; Montemurro, C. Development and application of protocols to certify the authenticity and the traceability of Apulian typical products in olive sector. Riv. Ital. Delle Sostanze Grasse 2017, 94, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Spadoni, A.; Sion, S.; Gadaleta, S.; Savoia, M.; Piarulli, L.; Fanelli, V.; di Rienzo, V.; Taranto, D.; Miazzi, M.; Montemurro, C.; et al. Simple and rapid method for genomic DNA extraction and microsatellite analysis in tree plants. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2019, 21, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Carriero, F.; Fontanazza, G.; Cellini, F.; Giorio, G. Identification of simple sequence repeats (SSRs) in olive (Olea europaea L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2002, 104, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipriani, G.; Marrazzo, M.T.; Marconi, R.; Cimato, A.; Testolin, R. Microsatellite markers isolated in olive (Olea europaea L.) are suitable for individual finger-printing and reveal polymorphism within ancient cultivars. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2002, 104, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Rosa, R.; James, C.M.; Tobutt, K.R. Isolation and characterization of polymorphic microsatellites in olive (Olea europaea L.) and their transferability to other genera in the Oleaceae. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2002, 2, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefc, K.M.; Lopes, M.S.; Mendonica, D.; Rodrigues Dos Santos, M.; Laimer Da Camara Machado, M.; Da Camara Machado, A. Identification of microsatellite loci in olive (Olea europaea L.) and their characterization in Italian and Iberian olive trees. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2000, 9, 1171–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenALEx 6.5: Genetic analysis in excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research an update. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E.; Weaver, W. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S. The genetical structure of populations. Ann. Eugen. 1949, 15, 323–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowski, S.T. Counting alleles with rarefaction: Private alleles and hierarchical sampling designs. Conserv. Genet. 2004, 5, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waits, L.P.; Luikart, G.; Taberlet, P. Estimating the probability of identity among genotypes in natural populations: Cautions and guidelines. Mol. Ecol. 2001, 10, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botstein, D.; White, R.L.; Skolnick, M.; Davis, R.W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am. J. Hum. Gen. 1980, 32, 314–331. [Google Scholar]
- Kalinowski, S.T.; Taper, M.L.; Marshall, T.C. Revising how the computer program Cervus accommodates genotyping error increases success in paternity assignment. Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar]
- Earl, D.A.; Von Holdt, B.M. Structure Harvester: A website and program for visualizing Structure output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv. Gen. Res. 2012, 4, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software Structure: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faostat. 2019. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/?#data/QC (accessed on 20 December 2019).
- Dridi, J.; Fendri, M.; Breton, C.M.; Msallem, M. Characterization of olive progenies derived from a Tunisian breeding program by morphological traits and SSR markers. Sci. Hort. 2018, 236, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taranto, F.; D’Agostino, N.; Fanelli, V.; di Rienzo, V.; Miazzi, M.M.; Pavan, S.; Zelasco, S.; Perri, E.; Montemurro, C. SNP diversity in an olive germplasm collection. Acta Hortic. 2018, 1199, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miazzi, M.M.; di Rienzo, V.; Mascio, I.; Montemurro, C.; Sion, S.; Sabetta, W.; Vivaldi, G.A.; Camposeo, S.; Caponio, F.; Squeo, G.; et al. Re.Ger.O.P.: An Integrated Project for the Recovery of Ancient and Rare Olive Germplasm. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanasijevica, M.; Todorovica, L.S.; Pereira, C.; Pizzigalli, P.; Lionello, S. Impacts of climate change on olive crop evapotranspiration and irrigation requirements in the Mediterranean region. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 144, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, H.; Pinto, J.G.; Viola, F.; Santos, J.A. Climate change projections for olive yields in the Mediterranean Basin. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 40, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, W.; Guiot, J.; Fader, M.; Garrabou, J.; Gattuso, J.-P.; Iglesias, A.; Lange, M.A.; Lionello, P.; Llasat, M.C.; Paz, S.; et al. Climate change and interconnected risks to sustainable development in the Mediterranean. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balloux, F.; Lehmann, L.; de Meeus, T. The population genetics of clonal and partially clonal diploids. Genetics 2003, 164, 1635–1644. [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckel, S.; Grange, J.; Fernández-Manjarres, J.F.; Bilger, I.; Frascaria-Lacoste, N.; Mariette, S. Heterozygote excess in a self-incompatible and partially clonal forest tree species—Prunus avium L. Mol. Ecol. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez, C.M.; Barrio, I.; Belaj, A.; Barranco, D.; Rallo, L. Centennial olive trees as a reservoir of genetic diversity. Ann. Bot. 2011, 108, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí i Fernández, A.; Forcada i Font, C.; Rubio-Cabetas, M.J.; Socias i Company, R. Genetic relationships and population structure of local olive tree accessions from Northeastern Spain revealed by SSR markers. Acta Physiol. Plant 2015, 37, 1726–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, S.; Gouta, H.; Gharsallaoui, M.; Ghrab, M. A Review on Current Status of Olive and Olive Oil Production in Tunisia. J. Korean Soc. Int. Agric. 2013, 25, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalak, L.; Haouane, H.; Essalouh, L.; Santoni, S.; Besnard, G.; Khadari, B. Extent of the genetic diversity in Lebanese olive (Olea europaea L.) trees: A mixture of an ancient germplasm with recently introduced varieties. Gen. Res. Crop Evol. 2015, 62, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucheffa, S.; Miazzi, M.M.; di Rienzo, V.; Mangini, G.; Fanelli, V.; Tamendjari, A.; Pignone, D.; Montemurro, C. The coexistence of oleaster and traditional varieties affects genetic diversity and population structure in Algerian olive (Olea europaea) germplasm. Gen. Res. Crop Evol. 2017, 64, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Rienzo, V.; Sion, S.; Taranto, F.; Zammit-Mangion, M.; Miazzi, M. Genetic flow among olive populations within the Mediterranean basin. PeerJ 2018, 18, e5260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannachi, H.; Breton, C.; Msallem, M.; Ben El Hadj, S.; El Gazzzah, M.; Bervillé, A. Genetic relationships between cultivated and wild olive trees (Olea europaea L. var. europaea and var. sylvestris) based on nuclear and Chloroplast SSR markers. Nat. Res. 2010, 1, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, B.; Gristina, A.S.; Mercati, F.; Saadi, A.E.; Aiter, N.; Martorana, A.; Sharaf, A.; Carimi, F. Molecular analysis of the official algerian olive collection highlighted a hotspot of biodiversity in the central mediterranean basin. Genes 2020, 11, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anestiadou, K.; Nikoloudakis, N. Monumental olive trees of Cyprus contributed to the establishment of the contemporary olive germplasm. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Amar, F.; Ben Maachia, S.; Yengui, A. Catalogue des Ressources Génétiques de 431 L’Olivier Dans L’Oasis de Degache (Tunisie); FAO and Ministry of Agriculture of Tunisia: Rome, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Grati-Kamoun, N.; Lamy Mahmoud, F.; Rebai, A.; Gargouri, A.; Panaud, O.; Saar, A. Genetic diversity of Tunisian olive tree (Olea europaea L.) cultivars assessed by AFLP markers. Gen. Res. Crop Evol. 2006, 53, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, I.; Ojeda, M.A.; Urdiroz, N.M.; Potter, D.; Barranco, D.; Rallo, L. Identification of the Worldwide Olive Germplasm Bank of Córdoba (Spain) using SSR and morphological markers. Tree Genet Genomes 2014, 10, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez, C.M.; Trujillo, I.; Martinez-Urdiroz, N.; Barranco, D.; Rallo, L.; Marfil, P. Olive domestication and diversification in the Mediterranean Basin. New Phytol. 2015, 206, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, S.; Omri, A.; Grati-Kamoun, N.; Marra, F.P.; Caruso, T. Molecular characterization and genetic relationships of cultivated Tunisian olive varieties (Olea europaea L.) using SSR markers. J. New Sci. Agric. Biotechnol. 2017, 40, 2175–2185. [Google Scholar]
- Haouane, H.; El Bakkali, A.; Moukhli, A.; Tollon, C.; Santoni, S.; Oukabli, A. Genetic structure and core collection of the World Olive Germplasm Bank of Marrakech: Towards the optimized management and use of Mediterranean olive genetic resources. Genetica 2011, 139, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugini, E.; Baldoni, L.; Muleo, R.; Sebastiani, L. The Olive Tree Genome. In Compendium of Plant Genomes; Rugini, E., Baldoni, L., Muleo, R., Sebastiani, L., Eds.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 27–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besnard, G.; Terral, J.F.; Cornille, A. On the origins and domestication of the olive: A review and perspectives. Ann. Bot. 2018, 121, 385–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besnard, G.; El Bakkali, A.; Haouane, H.; Baali-Cherif, D.; Moukhli, A.; Khadari, B. Population genetics of Mediterranean and Saharan olives: Geographic patterns of differentiation and evidence for early-generations of admixture. Ann. Bot. 2013, 112, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, C.; Lorre, C.; Sauvage, C.; Ivorra, S.; Terral, J.-F. On the origins and spread of Olea europaea L. (olive) domestication: Evidence for shape variation of olive stones at Ugarit, Late Bronze Age, Syria—A window on the Mediterranean Basin and on the westward diffusion of olive varieties. Veg. Hist. Archaeobotany 2013, 23, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, N.; Taranto, F.; Camposeo, S.; Mangini, G.; Fanelli, V.; Gadaleta, S.; Miazzi, M.M.; Pavan, S.; Di Rienzo, V.; Sabetta, W.; et al. GBS-derived SNP catalogue unveiled wide genetic variability and geographical relationships of Italian olive cultivars. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).