AFLP-Based Analysis of Variation and Population Structure in Mutagenesis Induced Faba Bean
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials, Phenotypic Characterization, and DNA Extraction
2.2. AFLP
2.3. Running the AFLP Gel on the ABI 3130xl Genetic Analyzer
2.4. AFLP-Fragment Analysis
2.5. Genetic Diversity Parameters and Analysis of Molecular Variance (AMOVA)
2.6. Population Structure
3. Results
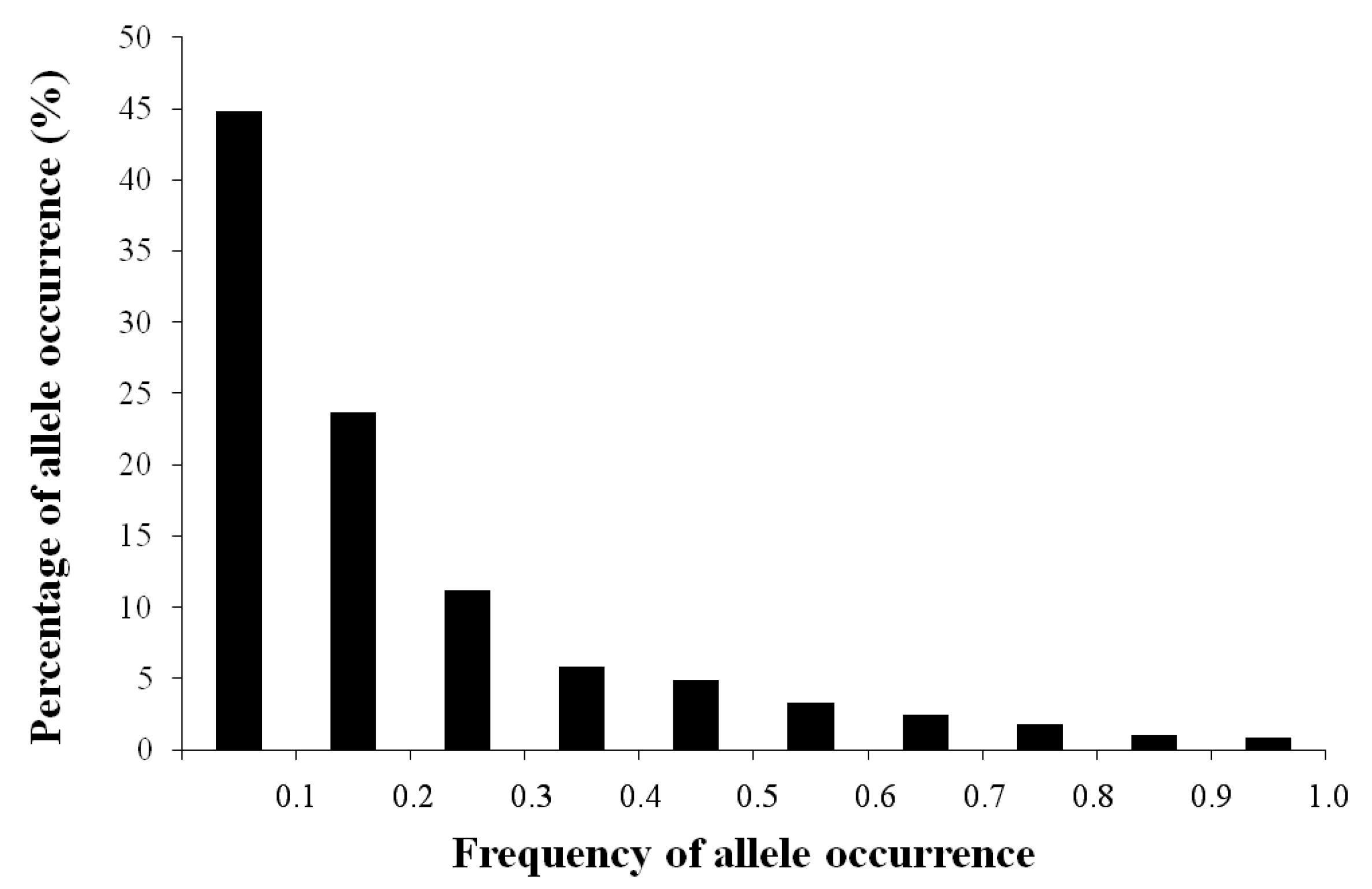
3.1. AFLP Polymorphism
3.2. AFLP Band Abundance
3.3. Genetic Diversity Parameters and Analysis of Molecular Variance (AMOVA)
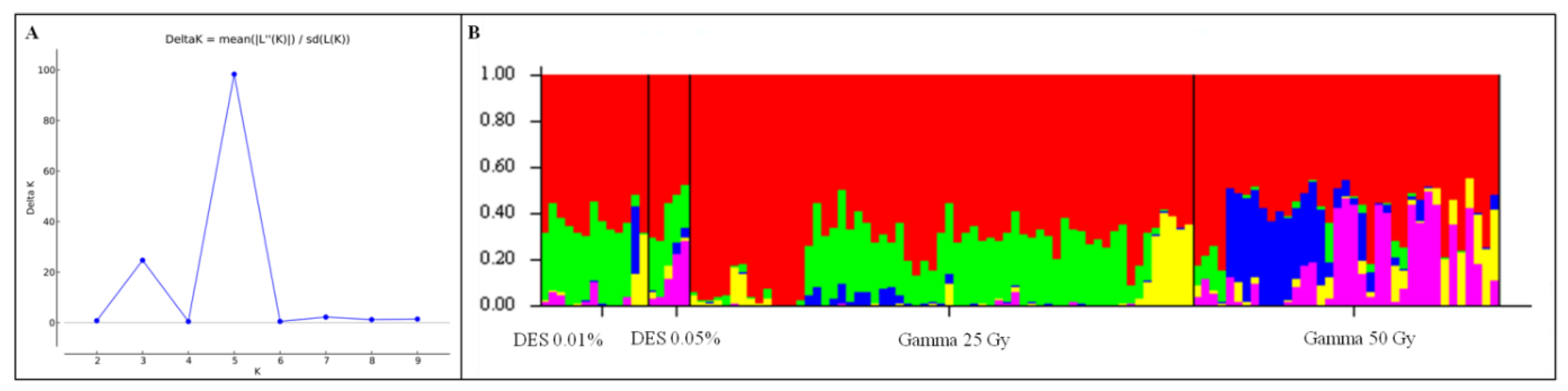
3.4. Population Structure
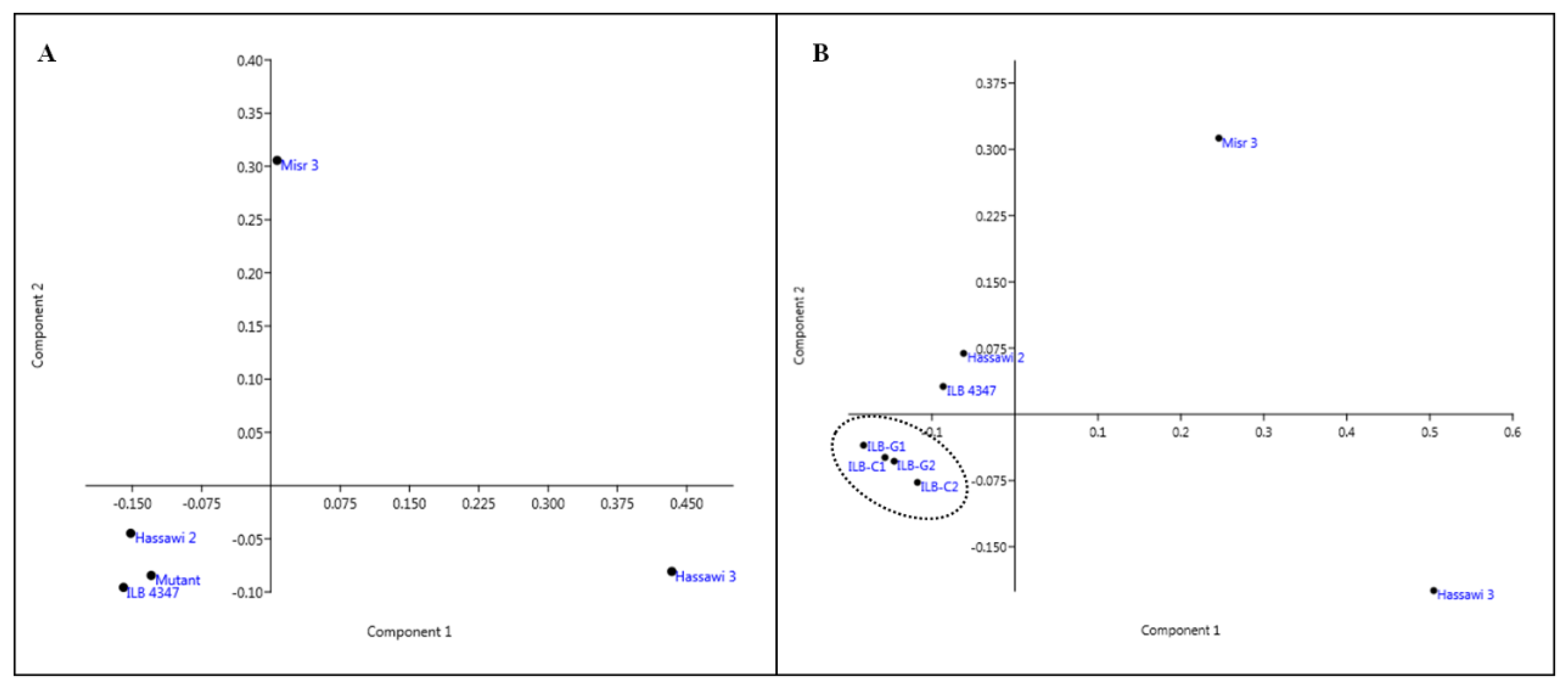
3.5. Genetic Relatedness
3.6. Relationship between Molecular and Phenotypic Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) of the United Nations. Declaration of the World Summit on Food Security; Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2009; Available online: http://www.fao.org/fileadmin/templates/wsfs/Summit/Docs/Declaration/WSFS09_Draft_Declaration.pdf (accessed on 11 June 2020).
- Tester, M.; Langridge, P. Breeding technologies to increase crop production in a changing world. Science 2010, 320, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.B.; Peterson, G.W.; Scoles, G.; Rossnagel, B.; Schoen, D.J.; Richards, K.W. Allelic diversity changes in 96 Canadian oat genotypes released from 1886 to 2001. Crop Sci. 2013, 43, 1989–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.B.; Peterson, G.W.; Richards, K.W.; Somers, D.; DePauw, R.M.; Clarke, J.M. Allelic reduction and genetic shift in the Canadian hard red spring wheat germplasm released from 1845 to 2004. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2005, 110, 1505–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussell, V.; Koenig, J.; Bechert, M.; Balfourier, F. Molecular diversity in French bread wheat accessions related to temporal trends and breeding programmes. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 108, 920–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.B.; Peterson, G.W.; Yu, J.K.; Gao, L.; Jia, J.; Richards, K.W. Impact of plant breeding on genetic diversity of the Canadian hard red spring wheat germplasm as revealed by EST-derived SSR markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2006, 112, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Chen, L.; Zhang, S.; Hu, F.; Wang, Z.; Lyu, J.; Wang, B.; Xiang, H.; Zhao, R.; Tian, Z.; et al. Decrease of gene expression diversity during domestication of animals and plants. BMC Evol. Biol. 2019, 19, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, S.; Da Silva, J.A.T.; Khan, A.A.; Naveed, A. Consequences of plant breeding on genetic diversity. Int. J. Plant Breed. 2010, 4, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Nedumaran, S.; Abinaya, P.; Jyosthnaa, P.; Shraavya, B.; Rao, P.; Bantilan, C. Grain Legumes Production, Consumption and Trade Trends in Developing Countries; Working Paper Series No. 60; ICRISAT Research Program, Markets, Institutions and Policies: Patancheru, India, 2015; 64p. [Google Scholar]
- Maalouf, F.; Hu, J.; O’Sullivan, D.M.; Zong, X.; Hamwieh, A.; Kumar, S.; Baum, M. Breeding and genomics status in faba bean (Vicia faba). Plant Breed. 2019, 138, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Xu, S.; Mao, W.; Li, Z.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, G.; Ding, J. Genetic diversity analysis of faba bean (Vicia faba L.) based on EST-SSR markers. Agric. Sci. China 2011, 10, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babay, E.; Khamassi, K.; Sabetta, W.; Miazzi, M.M.; Montemurro, C.; Pignone, D.; Danzi, D.; Finetti-Sialer, M.M.; Mangini, G. Serendipitous in situ conservation of faba bean landraces in Tunisia: A case study. Genes 2020, 11, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mba, C. Induced mutations unleash the potentials of plant genetic resources for food and agriculture. Agronomy 2013, 3, 200–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjodin, J. Induced morphological variation in Vicia faba L. Hereditas 1971, 67, 155–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khursheed, S.; Khan, S. Genetic improvement of two cultivars of Vicia faba L. using gamma irradiation and ethyl methane sulphonate mutagenesis. Legume Res. 2017, 40, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmansyah; Alghamdi, S.S.; Migdadi, H.M.; Farooq, M. Novel inflorescence architecture in gamma radiation-induced faba bean mutant populations. Int. J. Rad. Biol. 2019, 95, 1744–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, S.S.; Migdadi, H.M. Morphological diversity of faba bean (Vicia faba L.) M2 mutant populations induced by gamma radiation and diethyl sulfate. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2020, 32, 1647–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Ven, M.; Powell, W.; Ramsay, G.; Waugh, R. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms as genetic markers in Vicia. Heredity 1990, 65, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, W.; Dixkens, C.; Singh, M.; Schwall, M.; Melchinger, A.E. Genetic diversity in European and Mediterranean faba bean germplasm revealed by RAPD markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1995, 90, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, A.M.; Gonzalez, S.G.; Syed, N.H.; Suso, M.J.; Saldana, C.C.; Flavell, A.J. Genetic diversity analysis in Vicia species using retrotransposon-based SSAP markers. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2007, 278, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.; Ren, J.; Guan, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, Q.; Paull, J.G.; Redden, R. Molecular variation among Chinese and global germplasm in spring faba bean areas. Plant Breed. 2010, 129, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zong, X.; Guan, J.; Yang, T.; Sun, X.; Ma, Y.; Redden, R. Genetic diversity and relationship of global faba bean (Vicia faba L.) germplasm revealed by ISSR markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2012, 124, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, S.S.; Al-Faifi, S.A.; Migdadi, H.M.; Khan, M.A.; EL-Harty, E.H.; Ammar, M.H. Molecular diversity assessment using Sequence Related Amplified Polymorphism (SRAP) markers in Vicia faba L. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 16457–16471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, S.; Cogan, N.O.I.; Forster, J.W.; Paull, J.G. Assessment of genetic diversity in faba bean based on single nucleotide polymorphism. Diversity 2014, 6, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gӧl, S.; Doganlar, S.; Frary, A. Relationship between geographical origin, seed size and genetic diversity in faba bean (Vicia faba L.) as revealed by SSR markers. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2017, 292, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorkheh, K.; Shiran, B.; Aranzana, M.J.; Mohammadi, S.A.; Martinez-Gomez, P. Application of amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLPs) analysis to plant breeding and genetics: Procedures, applications and prospects. J. Food. Agric. Environ. 2007, 5, 197–204. [Google Scholar]
- Kurowska, M.; Labocha-Pawłowska, A.; Gnizda, D.; Maluszynski, M.; Szarejko, I. Molecular analysis of point mutations in a barley genome exposed to MNU and gamma rays. Mutant Res. 2012, 738–739, 52–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, A.; Garcia-Pereira, M.J.; Quesda, H. Genomic distribution of AFLP markers relative to gene locations for different eukaryotic species. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmansyah; Alghamdi, S.S.; Migdadi, H.M.; Farooq, M. Morphological and chromosomal abnormalities in gamma radiation-induced faba bean mutant populations. Int. J. Rad. Biol. 2018, 94, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, M.; Bonnes, B.; Ficetola, G.F.; Poncet, B.N.; Després, L. Amplified fragment length homoplasy: In silico analysis for model and non-model species. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, M.; Milligan, B.G. Analysis of population genetic structure with RAPD markers. Mol. Ecol. 1994, 3, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khierallah, H.S.M.; Bader, S.M.; Baum, M.; Hamwieh, A. Assessment of genetic diversity of some Iraqi date palms (Phoenix dactylifera L.) using AFLP markers. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 9570–9575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6.5: Genetic Analysis in Excel. Population Genetic Software for Teaching and Research—An Update. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, Ø.; David, A.T.; Ryan, P.D. Past: Paleontological Statistics Software Package for Education and Data Analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 4–9. [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P.J. Inference of population Structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Falush, D.M.; Stephens, M.; Pritchard, J.K. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: Linked loci and correlated allele frequencies. Genetics 2003, 164, 1567–1587. [Google Scholar]
- Falush, D.M.; Stephens, M.; Pritchard, J.K. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: Dominant markers and null alleles. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubisz, M.J.D.; Falush, D.M.; Stephens, M.; Pritchard, J.K. Inferring weak population structure with the assistance of sample group information. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earl, D.A.; vonHoldt, B.M. STRUCTURE HARVESTER: A website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv. Genet. Res. 2012, 4, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, H.R.; Tomás, D.; Silva, M.; Lopes, S.; Viegas, W.; Veloso, M.M. Genetic diversity and population structure in Vicia faba L. landraces and wild related species assessed by nuclear SSRs. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, S.S.; Al-Faifi, S.A.; Migdadi, H.M.; Ammar, M.H.; Siddique, K.M. Inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR)-based diversity assessment among faba bean genotypes. Crop Pasture Sci. 2011, 62, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Jain, R.; Chern, M.; Pham, N.T.; Martin, J.A.; Wei, T.; Schackwitz, W.S.; Lipzen, A.M.; Duong, P.Q.; Jones, K.C.; et al. The sequence of 1504 mutant in the model rice variety Kitaake facilitate rapid functional genomic studies. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 1218–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Luo, W.; Zhang, J.; Yan, X.; Du, Y.; Zhou, L.; Li, W.; Wang, H.; Chen, Z.; Guo, T. Genome-wide coparisons of mutations induced by carbon-ion beam and gamma-rays irradiation in rice via resequencing multiple mutants. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Esawi, M.A. SSR analysis of genetic diversity and structure of the germplasm of faba bean (Vicia faba L.). CR Biol. 2017, 340, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebaa, F.; Abid, G.; Aouida, M.; Abdelkarim, S.; Aroua, I.; Muhovski, Y.; Baudoin, J.; M’hamdi, M.; Sassi, K.; Jebara, M. Genetic variability in Tunisian populations of faba bean (Vicia faba L. var. major) assessed by morphological and SSR markers. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2017, 23, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Primer Combination Eco R1/Mse 1 | Total Alleles | Total No. of Bands | Average Bands per Allele (Range) | Polymorphism Rate (%) | DP (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TG/CTT | 268 | 7549 | 28.17 (4–118) | 100 | 15.89 |
| TA/CCA | 185 | 4182 | 22.61 (4–105) | 100 | 10.97 |
| TC/CCA | 175 | 3993 | 22.82 (4–110) | 100 | 10.37 |
| AA/CCC | 168 | 3968 | 23.62 (4–112) | 100 | 9.96 |
| TC/CAC | 151 | 2937 | 19.45 (4–116) | 100 | 8.95 |
| AA/CCT | 149 | 3584 | 24.05 (4–105) | 100 | 8.83 |
| TC/CAG | 149 | 2416 | 16.21 (4–100) | 100 | 8.83 |
| TA/CAG | 137 | 3575 | 26.09 (4–113) | 100 | 8.12 |
| TT/CAC | 132 | 3080 | 23.33 (4–137) | 100 | 7.82 |
| CC/CCA | 95 | 2127 | 22.39 (4–109) | 100 | 5.63 |
| TT/CTT | 78 | 1951 | 25.01 (4–112) | 100 | 4.62 |
| Total | 1687 | - | - | - | |
| Average | 153.36 | 3578.36 | 23.33 | 100 | 9.09 |
| Population | No. of Samples | AFLP Band Observed | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Range | Lowest | Highest | ||
| Reference genotypes | 4 | 334.50 | 161.21 | 320 | 195 | 515 |
| All mutant plants | 116 | 327.79 | 108.22 | 428 | 117 | 545 |
| DES 0.01% | 13 | 354.54 | 48.45 | 149 | 305 | 454 |
| DES 0.05% | 5 | 401.20 | 96.14 | 210 | 295 | 505 |
| Gamma 25 Gy | 61 | 271.97 | 85.84 | 352 | 117 | 469 |
| Gamma 50 Gy | 37 | 400.51 | 107.69 | 357 | 188 | 545 |
| Population | No. of Samples | No. of Alleles | Na | Ne | I | He | % P | Private Alleles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference genotypes | 4 | 867 | 1.008 | 1.232 | 0.234 | 0.150 | 49.38 | 0 |
| ILB4347 | 116 | 1687 | 2.000 | 1.236 | 0.283 | 0.164 | 100.00 | 820 |
| Mean | 60 | 1.504 | 1.234 | 0.259 | 0.157 | 74.69 | ||
| Reference genotypes | 4 | 867 | 1.008 | 1.232 | 0.234 | 0.150 | 49.38 | 0 |
| ILB4347 (Gamma Radiation) | 98 | 1684 | 1.996 | 1.231 | 0.277 | 0.161 | 99.82 | 164 |
| ILB4347 (DES) | 18 | 1437 | 1.697 | 1.256 | 0.284 | 0.171 | 84.47 | 1 |
| Mean | 40 | 1.567 | 1.240 | 0.265 | 0.160 | 77.89 | ||
| Reference genotypes | 4 | 867 | 1.008 | 1.232 | 0.234 | 0.150 | 49.38 | 0 |
| ILB4347 (25 Gy Gamma) | 61 | 1570 | 1.861 | 1.195 | 0.238 | 0.136 | 93.06 | 30 |
| ILB4347 (50 Gy Gamma) | 37 | 1504 | 1.781 | 1.289 | 0.304 | 0.186 | 88.97 | 26 |
| ILB4347 (0.01% DES) | 13 | 1227 | 1.434 | 1.231 | 0.250 | 0.152 | 70.66 | 0 |
| ILB4347 (0.05% DES) | 5 | 992 | 1.153 | 1.281 | 0.272 | 0.176 | 56.49 | 0 |
| Mean | 24 | 1.447 | 1.246 | 0.260 | 0.160 | 71.71 |
| Source | df | Sum of Square | Mean Square | Estimated Variance | % | φPT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Among populations | 4 | 2457.808 | 614.452 | 22.530 | 11% | 0.107 ** |
| Within populations | 115 | 21,541.825 | 187.320 | 187.320 | 89% | |
| Total | 119 | 23,999.633 | 209.850 | 100% |
| Mutant Population | No. of Sample | No. of Phenotypic Variation | No. of Phenotypic Variation/Sample | Correlation Phenotype vs. Shannon’s Index | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p | ||||
| 25 Gy Gamma | 61 | 114 | 1.87 | 0.801 ns | 0.199 |
| 50 Gy Gamma | 37 | 102 | 2.76 | ||
| 0.01% DES | 11 | 14 | 1.27 | ||
| 0.05% DES | 5 | 9 | 1.80 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nurmansyah; Alghamdi, S.S.; Migdadi, H.M.; Khan, M.A.; Afzal, M. AFLP-Based Analysis of Variation and Population Structure in Mutagenesis Induced Faba Bean. Diversity 2020, 12, 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12080303
Nurmansyah, Alghamdi SS, Migdadi HM, Khan MA, Afzal M. AFLP-Based Analysis of Variation and Population Structure in Mutagenesis Induced Faba Bean. Diversity. 2020; 12(8):303. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12080303
Chicago/Turabian StyleNurmansyah, Salem S. Alghamdi, Hussein M. Migdadi, Muhammad A. Khan, and Muhammad Afzal. 2020. "AFLP-Based Analysis of Variation and Population Structure in Mutagenesis Induced Faba Bean" Diversity 12, no. 8: 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12080303
APA StyleNurmansyah, Alghamdi, S. S., Migdadi, H. M., Khan, M. A., & Afzal, M. (2020). AFLP-Based Analysis of Variation and Population Structure in Mutagenesis Induced Faba Bean. Diversity, 12(8), 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12080303






