Phylogenomic Reconstruction Sheds Light on New Relationships and Timescale of Rails (Aves: Rallidae) Evolution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Sequence Assembly and Alignment
2.3. Phylogenetic Analyses and Divergence Time Estimates
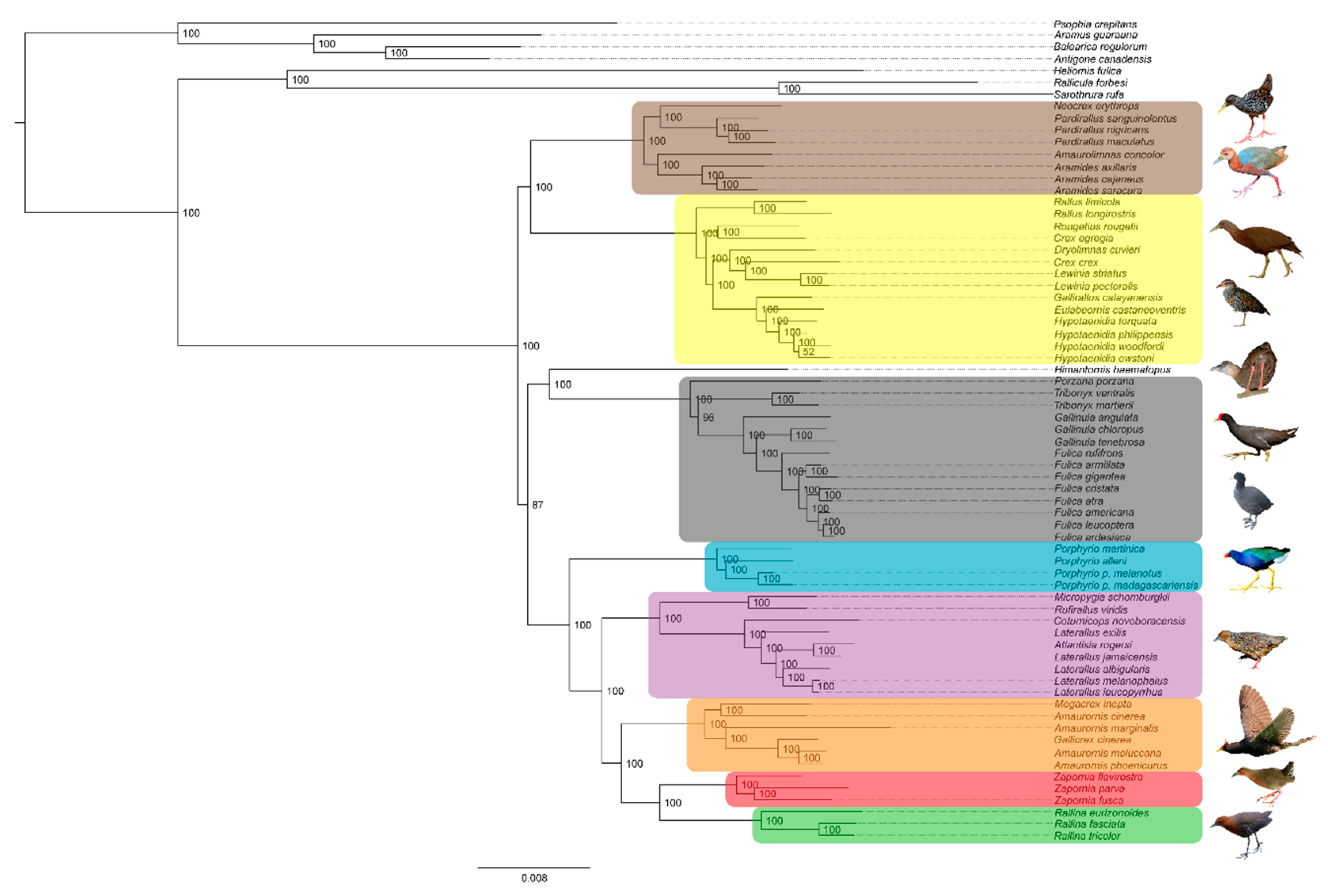
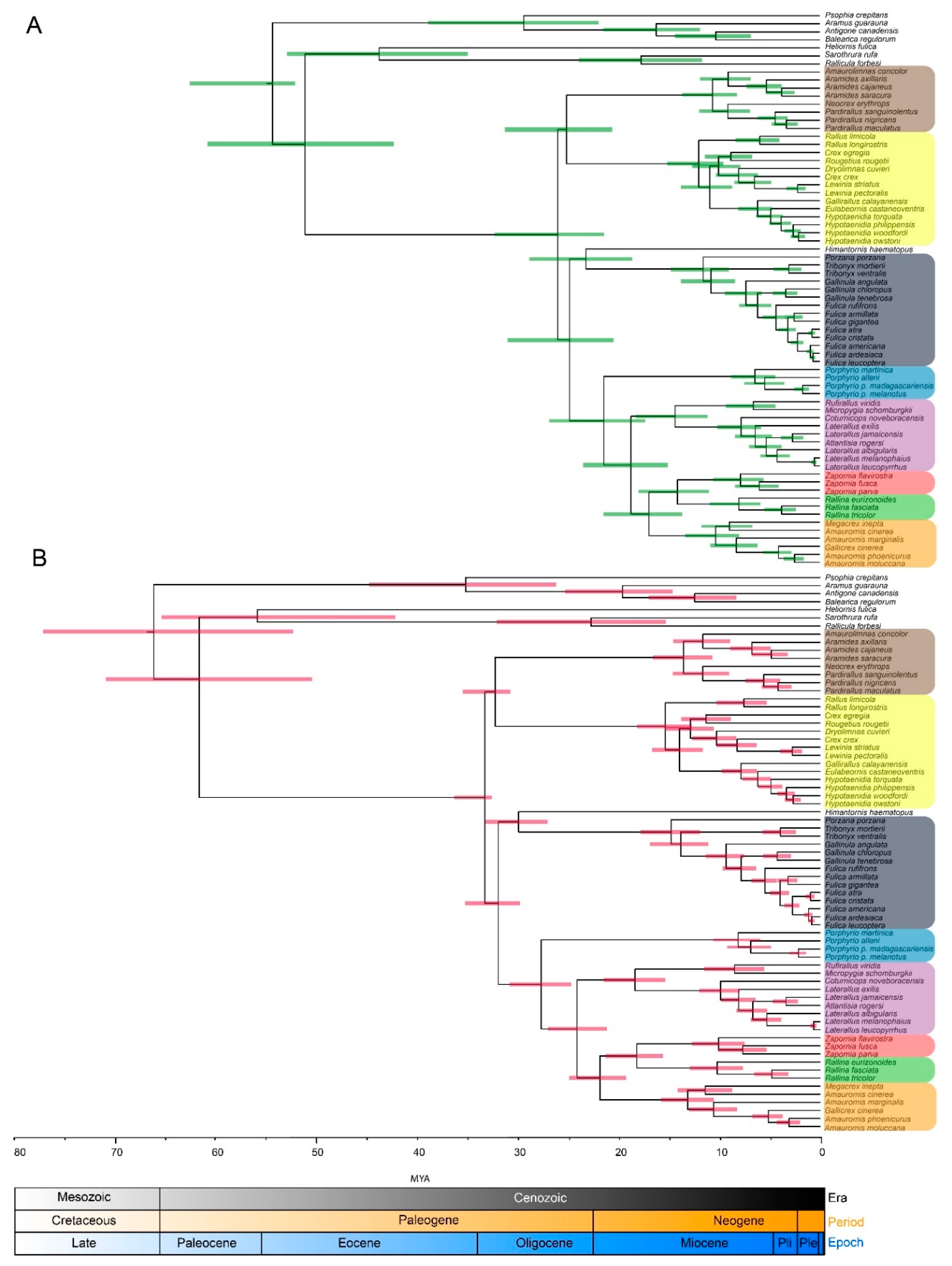
3. Results
3.1. Phylogenetics
3.2. Molecular Dating
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garcia-R, J.C.; Elliott, G.; Walker, K.; Castro, I.; Trewick, S.A. Trans-equatorial range of a land bird lineage (Aves: Rallidae) from tropical forests to subantarctic grasslands. J. Avian Biol. 2016, 47, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-R, J.C.; Joseph, L.; Adcock, G.; Reid, J.; Trewick, S.A. Interisland gene flow among populations of the buff-banded rail (Aves: Rallidae) and its implications for insular endemism in Oceania. J. Avian Biol. 2017, 48, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-R, J.C.; Trewick, S.A. Dispersal and speciation in purple swamphens (Rallidae: Porphyrio). The Auk 2015, 132, 140–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-R, J.C.; Gonzalez-Orozco, C.E.; Trewick, S.A. Contrasting patterns of diversification in a bird family (Aves: Gruiformes: Rallidae) are revealed by analysis of geospatial distribution of species and phylogenetic diversity. Ecography 2019, 42, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livezey, B.C. A phylogenetic analysis of the Gruiformes (Aves) based on morphological characters, with an emphasis on the rails (Rallidae). Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 1998, 353, 2077–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slikas, B.; Olson, S.L.; Fleischer, R.C. Rapid, independent evolution of flightlessness in four species of Pacific Island rails (Rallidae): An analysis based on mitochondrial sequence data. J. Avian Biol. 2002, 33, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, L.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Ouyang, Y. Polyphyletic origin of the genus Amaurornis inferred from molecular phylogenetic analysis of rails. Biochem. Genet. 2012, 50, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Han, Y.; Zhu, C.; Gao, B.; Ruan, L. Complete mitochondrial genome of Porzana fusca and Porzana pusilla and phylogenetic relationship of 16 Rallidae species. Genetica 2017, 145, 559–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Zhao, R.; Huang, Q.; Sun, X.; Huang, L.; Jing, M. Two mitogenomes in Gruiformes (Amaurornis akool/A. phoenicurus) and the phylogenetic placement of Rallidae. Genes Genom. 2017, 39, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchman, J.J. Speciation of flightless rails on islands: A DNA-based phylogeny of the typical rails of the Pacific. The Auk 2012, 129, 56–69. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-R, J.C.; Gibb, G.C.; Trewick, S.A. Eocene diversification of crown group rails (Aves: Gruiformes: Rallidae). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-R, J.C.; Gibb, G.C.; Trewick, S.A. Deep global evolutionary radiation in birds: Diversification and trait evolution in the cosmopolitan bird family Rallidae. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2014, 81, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangster, G.; Garcia-R, J.C.; Trewick, S.A. A new genus for the Lesser Moorhen Gallinula angulata Sundevall, 1850 (Aves, Rallidae). Eur. J. Taxon. 2015, 153, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boast, A.P.; Chapman, B.; Herrera, M.B.; Worthy, T.H.; Scofield, R.P.; Tennyson, A.J.D.; Houde, P.; Bunce, M.; Cooper, A.; Mitchell, K.J. Mitochondrial Genomes from New Zealand’s Extinct Adzebills (Aves: Aptornithidae: Aptornis) Support a Sister-Taxon Relationship with the Afro-Madagascan Sarothruridae. Diversity 2019, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stervander, M.; Ryan, P.G.; Melo, M.; Hansson, B. The origin of the world’s smallest flightless bird, the Inaccessible Island Rail Atlantisia rogersi (Aves: Rallidae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2019, 130, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.Y.W.; Duchêne, S. Molecular-clock methods for estimating evolutionary rates and timescales. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 5947–5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.W.; Payne, R.B.; Mindell, D.P. Nuclear DNA does not reconcile ‘rocks’ and ‘clocks’ in Neoaves: A comment on Ericson et al. Biol. Lett. 2007, 3, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ksepka, D.T.; Ware, J.L.; Lamm, K.S. Flying rocks and flying clocks: disparity in fossil and molecular dates for birds. P. Roy. Soc. B: Bio. Sci. 2014, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cranston, K.; Rannala, B. Molecular clocks: Closing the gap between rocks and clocks. Heredity 2005, 94, 461–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cracraft, J.; Houde, P.; Ho, S.Y.W.; Mindell, D.P.; Fjeldså, J.; Lindow, B.; Edwards, S.V.; Rahbek, C.; Mirarab, S.; Warnow, T.; et al. Response to Comment on “Whole-genome analyses resolve early branches in the tree of life of modern birds”. Science 2015, 349, 1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, K.J.; Cooper, A.; Phillips, M.J. Comment on “Whole-genome analyses resolve early branches in the tree of life of modern birds”. Science 2015, 349, 1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prum, R.O.; Berv, J.S.; Dornburg, A.; Field, D.J.; Townsend, J.P.; Lemmon, E.M.; Lemmon, A.R. A comprehensive phylogeny of birds (Aves) using targeted next-generation DNA sequencing. Nature 2015, 526, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claramunt, S.; Cracraft, J. A new time tree reveals Earth history’s imprint on the evolution of modern birds. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1501005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steadman, D.W. Extinction and Biogeography of Tropical Pacific Birds; The University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hume, J.P.; Walters, M. Extinct Birds; Bloomsbury: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- De Pietri, V.L.; Mayr, G. Reappraisal of early Miocene rails (Aves, Rallidae) from central France: diversity and character evolution. J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 2014, 52, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, G. A rail (Aves, Rallidae) from the early Oligocene of Germany. Ardea 2006, 94, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Mayr, G.; Smith, R. Ducks, rails, and limicoline waders (Aves: Anseriformes, Gruiformes, Charadriiformes) from the lowermost Oligocene of Belgium. Geobios 2001, 34, 547–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, G.; Bochenski, Z.M. A skeleton of a small rail from the Rupelian of Poland adds to the diversity of early Oligocene Ralloidea. Neues Jahrb. Geol. Paläontol. - Abhandlungen 2016, 282, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericson, P.G.P.; Anderson, C.L.; Britton, T.; Elzanowski, A.; Johansson, U.S.; Kallersjo, M.; Ohlson, J.I.; Parsons, T.J.; Zuccon, D.; Mayr, G. Diversification of Neoaves: Integration of molecular sequence data and fossils. Biol. Lett. 2006, 2, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fain, M.G.; Krajewski, C.; Houde, P. Phylogeny of ‘‘core Gruiformes’’ (Aves: Grues) and resolution of the Limpkin–Sungrebe problem. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2007, 43, 515–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lemmon, A.R.; Lemmon, E.M.; Alexander Pyron, R.; Burbrink, F.T. Using phylogenomics to understand the link between biogeographic origins and regional diversification in ratsnakes. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2017, 111, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmon, A.; Emme, S.; Lemmon, E. Anchored hybrid enrichment for massively high-throughput phylogenomics. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, M.; Kircher, M. Illumina sequencing library preparation for highly multiplexed target capture and sequencing. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2010, 2010, pdb.prot5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rokyta, D.R.; Lemmon, A.R.; Margres, M.J.; Aronow, K. The venom-gland transcriptome of the eastern diamondback rattlesnake (Crotalus adamanteus). BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruane, S.; Raxworthy, C.J.; Lemmon, A.R.; Lemmon, E.M.; Burbrink, F.T. Comparing species tree estimation with large anchored phylogenomic and small Sanger-sequenced molecular datasets: an empirical study on Malagasy pseudoxyrhophiine snakes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2015, 15, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, C.A.; Lemmon, A.R.; Lemmon, E.M.; Bond, J.E. Expanding anchored hybrid enrichment to resolve both deep and shallow relationships within the spider tree of life. BMC Evol. Biol. 2016, 16, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirarab, S.; Warnow, T. ASTRAL-II: Coalescent-based species tree estimation with many hundreds of taxa and thousands of genes. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, i44–i52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadi, S.; Azouri, D.; Pupko, T.; Mayrose, I. Model selection may not be a mandatory step for phylogeny reconstruction. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouckaert, R.; Heled, J.; Kühnert, D.; Vaughan, T.; Wu, C.-H.; Xie, D.; Suchard, M.A.; Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J. BEAST 2: A Software Platform for Bayesian Evolutionary Analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musser, G.; Ksepka, D.T.; Field, D.J. New Material of Paleocene-Eocene Pellornis (Aves: Gruiformes) Clarifies the Pattern and Timing of the Extant Gruiform Radiation. Diversity 2019, 11, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertelli, S.; Chiappe, L.M.; Mayr, G. A new Messel rail from the Early Eocene Fur Formation of Denmark (Aves, Messelornithidae). J. Syst. Palaeontol. 2011, 9, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, J.; Hedges, S.B. Undersampling Genomes has Biased Time and Rate Estimates Throughout the Tree of Life. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, msy103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: more models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Battistuzzi, F.U.; Billing-Ross, P.; Murillo, O.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. Estimating divergence times in large molecular phylogenies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 19333–19338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, S.L. A classification of the Rallidae. Wilson Bull. 1973, 85, 381–416. [Google Scholar]
- Ripley, S.D. Rails of the world: A monograph of the Family Rallidae; David, R., Ed.; Godine Publisher: Boston, MA, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Bourne, W.R.P.; Ashmole, N.P.; Simmons, K.E.L. A New Subfossil Night Heron and a New Genus for the Extinct Rail from Ascension Island, Central Tropical Atlantic Ocean. Ardea 2003, 91, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Mayr, G. Avian Evolution: The Fossil Record of Birds and its Paleobiological Significance; Wiley: West Sussex, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Irisarri, I.; Singh, P.; Koblmüller, S.; Torres-Dowdall, J.; Henning, F.; Franchini, P.; Fischer, C.; Lemmon, A.R.; Lemmon, E.M.; Thallinger, G.G.; et al. Phylogenomics uncovers early hybridization and adaptive loci shaping the radiation of Lake Tanganyika cichlid fishes. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Tao, Q.; Kumar, S. Theoretical Foundation of the RelTime Method for Estimating Divergence Times from Variable Evolutionary Rates. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1770–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Fernandez, J.; dos Reis, M.; Donoghue, P.C.J.; Pisani, D. RelTime Rates Collapse to a Strict Clock When Estimating the Timeline of Animal Diversification. Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 1320–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battistuzzi, F.U.; Tao, Q.; Jones, L.; Tamura, K.; Kumar, S. RelTime Relaxes the Strict Molecular Clock throughout the Phylogeny. Genome Biol. Evol. 2018, 10, 1631–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ericson, P.G.P.; Anderson, C.L.; Mayr, G. Hangin’on to our rocks’n clocks: a reply to Brown et al. Biol. Lett. 2007, 3, 260–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, E.K.; Tennyson, A.J.D.; Scofield, R.P.; De Pietri, V.L.; Hand, S.J.; Archer, M.; Handley, W.D.; Worthy, T.H. Flightless rails (Aves: Rallidae) from the early Miocene St Bathans Fauna, Otago, New Zealand. J. Syst. Palaeontol. 2018, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukoschek, V.; Scott Keogh, J.; Avise, J.C. Evaluating Fossil Calibrations for Dating Phylogenies in Light of Rates of Molecular Evolution: A Comparison of Three Approaches. Syst. Biol. 2011, 61, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauquet, H.; Ho, S.Y.W.; Gandolfo, M.A.; Jordan, G.J.; Wilf, P.; Cantrill, D.J.; Bayly, M.J.; Bromham, L.; Brown, G.K.; Carpenter, R.J.; et al. Testing the Impact of Calibration on Molecular Divergence Times Using a Fossil-Rich Group: The Case of Nothofagus (Fagales). Syst. Biol. 2011, 61, 289–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, C.R. Using the Fossil Record to Evaluate Timetree Timescales. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.; Kimball, R.T.; Pandey, A.; Hosner, P.A.; Braun, M.J.; Hackett, S.J.; Han, K.-L.; Harshman, J.; Huddleston, C.J.; Kingston, S.; et al. Why Do Phylogenomic Data Sets Yield Conflicting Trees? Data Type Influences the Avian Tree of Life more than Taxon Sampling. Syst. Biol. 2017, 66, 857–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimball, R.T.; Oliveros, C.H.; Wang, N.; White, N.D.; Barker, F.K.; Field, D.J.; Ksepka, D.T.; Chesser, R.T.; Moyle, R.G.; Braun, M.J.; et al. A Phylogenomic Supertree of Birds. Diversity 2019, 11, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garcia-R, J.C.; Lemmon, E.M.; Lemmon, A.R.; French, N. Phylogenomic Reconstruction Sheds Light on New Relationships and Timescale of Rails (Aves: Rallidae) Evolution. Diversity 2020, 12, 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12020070
Garcia-R JC, Lemmon EM, Lemmon AR, French N. Phylogenomic Reconstruction Sheds Light on New Relationships and Timescale of Rails (Aves: Rallidae) Evolution. Diversity. 2020; 12(2):70. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12020070
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcia-R, Juan C., Emily Moriarty Lemmon, Alan R. Lemmon, and Nigel French. 2020. "Phylogenomic Reconstruction Sheds Light on New Relationships and Timescale of Rails (Aves: Rallidae) Evolution" Diversity 12, no. 2: 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12020070
APA StyleGarcia-R, J. C., Lemmon, E. M., Lemmon, A. R., & French, N. (2020). Phylogenomic Reconstruction Sheds Light on New Relationships and Timescale of Rails (Aves: Rallidae) Evolution. Diversity, 12(2), 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12020070




