Genetic Differentiation of an Endangered Megalobrama terminalis Population in the Heilong River within the Genus Megalobrama
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and DNA Extraction
2.2. Mitochondrial Sequencing and Analysis
2.3. SRAP Primer, PCR Amplification and Analysis
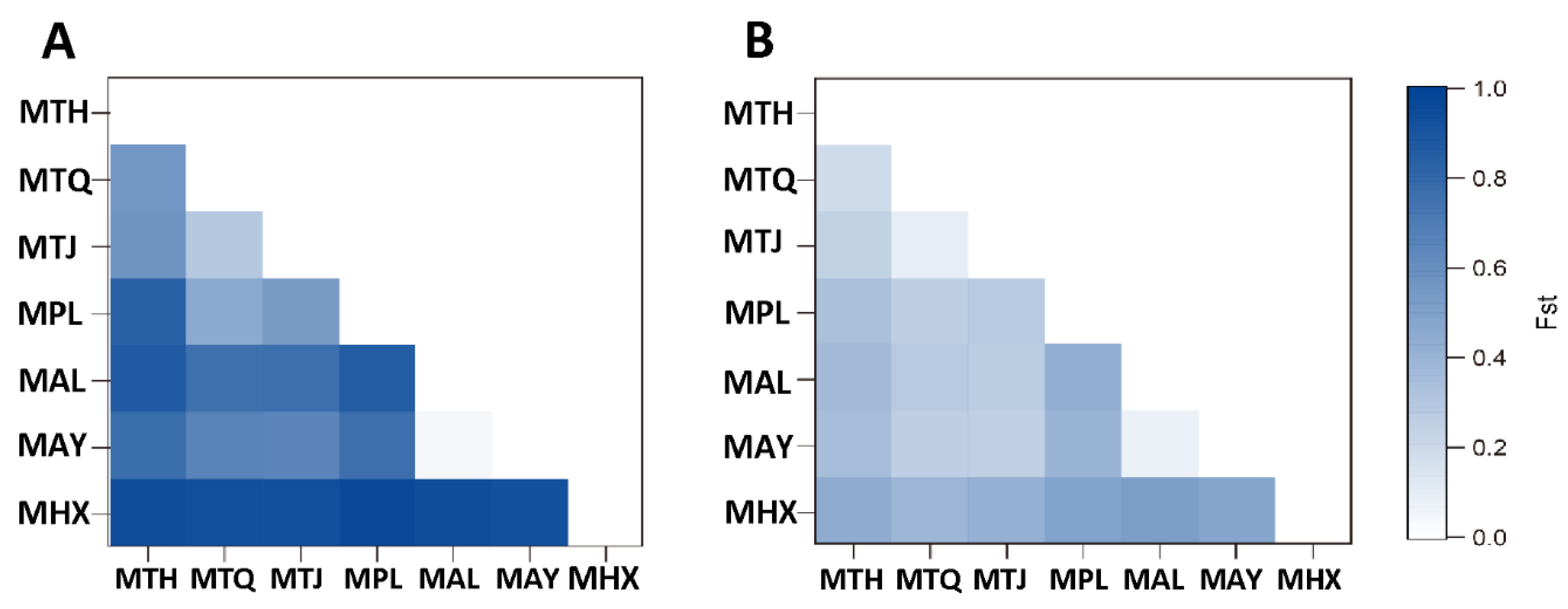
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Variability
3.2. Population Genetic Structure and Differentiation
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, X.Y.; Xie, N.; Ma, H.J.; Feng, X.Y. An overview of the germplasm characteristics of four fish species in the genus Megalobrama. H. Z. Agr. Sci. Tech. 2016, 6, 41–43. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yi, P.L. Notes on Megalobrama amblycephala, sp. Nov., a distinct species from M. terminalis (Richardson). Hydribiol. Anthol. 1955, 2, 115–122, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.S.; Shi, L.Y. Research progress on germplasm resource of black bream (Megalobrama terminalis) in China. Chin. J. Fish. 2020, 3, 84–89, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.X.; Wang, W.M.; Jiang, E.M.; Chen, B.X. Research advances on germplasm resources and genetic improvement of blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala). J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2014, 33, 138–144, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.Y. Research progress, demonstration and expansion of Megalobrama terminalis in Zhejiang Province. Sci. Fish Farming 2009, 10, 40–41. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liang, K.X.; Li, M.B. Developing now breeds and large-scale culturing Megalobrama terminalis. J. Hydroecol. 1994, 6, 37–38. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.M. Ichthyography of the Heilongjiang Province, 1st ed.; Heilongjiang Science and Technology Press: Harbin, China, 1995; p. 120. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Yang, D.Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Ma, X.Z.; Jin, X.; Hu, C.X. The preliminary study on Megalobrama skolkovii Dybowsky from Heilong River. Fish Heilongjiang 1993, 10–13. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Novomodny, G.; Sharov, P.; Zolotukhin, S. Amur Fish: Wealth and Crisis, 1st ed.; WWF RFE: Vladivostok, Russia, 2004; p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.S.; Luan, P.X.; Cao, C.H.; Li, C.T.; Jia, Z.Y.; Ge, Y.L.; Shang, M.; Wang, S.H.; Meng, Z.N.; Tong, J.G.; et al. Characterization of the mitochondrial genome of Megalobrama terminalis in the Heilong River and a clearer phylogeny of the genus Megalobrama. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.S.; Xu, C.X. Artificial breeding of Faluo fish has been successful. Fish. Sci. Tech. Inform. 2019, 46, 236–237. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.F.; Cai, W.Q.; Zhou, B.Y. Morphology and biochemical genetic variations among populations of blunt snout bream (Megalobrama abmlycephala). J. Fish. China 1991, 15, 204–211, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.C. Study on genetic diversity of bluntnose black bream from Yunihu and Liangzihu Lakes. J. Chin. Three Gorges Univ. 2001, 23, 282–284, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.H. MtDNA sequence variation and genetic structure of the Megalobrama amblycephala from Yuni Lake, Liangzi Lake and Poyang Lake. Freshw. Fish. 2008, 38, 63–65, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ji, W.; Zhang, G.R.; Ran, W.; Gardner, J.P.A.; Wei, K.J.; Wang, W.M.; Zou, G.W. Genetic diversity of and differentiation among five populations of blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala) revealed by SRAP markers: Implations for conservation and management. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Wang, Y.Z.; Zhu, D.M.; Nie, Z.L.; Wang, W.M. Morphological variation and discriminant analysis of three geographical populations of freshwater bream Megalobrama skolkovii. Chin. J. Fish. 2013, 26, 1–7, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.F.; Zhu, Z.W.; Zou, S.M.; Zhao, J.L.; Cai, W.Q. Interspicific phylogenesis and intraspecific genetic differences of genus Megalobrama: Bluntnose black bream (M. amblycephala), Guangdong black bream (M. hoffmanni) and black bream (M. terminalis). Acta Zool. Sin. 2002, 48, 339–345, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Robarts, D.W.H.; Wolfe, A.D. Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) markers: A potential resource for studies in plant molecular biology. Appl. Plant Sci. 2014, 2, 1400017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Quiros, C.F. Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP), a new marker system based on a simple PCR reaction: Its application to mapping and gene tagging in Brassica. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2001, 103, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budak, H.; Shearman, R.C.; Parmaksiz, I.; Dweikat, I. Comparative analysis of seeded and vegetative biotypes buffalograsses based on phylogenetic relationship using ISSRs, SSRs, RAPDs and SRAPs. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 109, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, Z.J.; Yang, F.; Fu, Q.W.; Liu, H.S.; Wang, D.D.; Yang, Y.C.; Yang, R.Y. Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) for studying genetic diversity and population structure of plants and other living organisms: A protocol. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2014, 24, 1478–1486. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.H.; Xu, J.Z.; Wang, Y.B.; Chai, X.J. SRAP analysis of genetic variation between female and male swimming carb (Portunus trituberculatus). J. Shanghai Ocean Univ. 2010, 19, 734–738, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ding, W.D.; Cao, Z.M.; Cao, L.P. Molecular analysis of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) by SRAP and SCAR molecular markers. Aquacult. Int. 2010, 18, 575–587, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; He, M.X. Segregation pattern of SRAP marker in F1 generation of Pinctada martensii family. Mar. Sci. Bull. 2009, 28, 50–56, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.W.; Han, Y.P.; Zhong, X.M.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Cao, Z.M.; Wu, T.T. Genetic structure analysis of grass carp populations between wild and cultured ones. J. Fish. Sci. China 2007, 14, 720–725, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xin, W.T.; Sun, Z.W.; Yin, H.B.; Sun, Y. Identification of sex-associated SRAP markers in Pelteobagrus fulvidraco. J. Northeast For. Univ. 2009, 37, 112–113, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, Z.W.; Liu, W.; Yin, H.B. Orthogonal design and optimization of SRAP amplification system for Oncorhynchus keta. Chin. J. Fish. 2010, 23, 6–10, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Fadly, G.E.; Khatab, I.; Rehan, M.; Kalboush, A. Genetic diversity in Egyptian populations of Tilapia species using RAPD and SRAP markers. J. Bio. Env. Sci. 2016, 8, 231–243. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E.L. Arlequin suite ver 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassam, B.J.; Caetano-Anollés, G.; Gresshoff, P.M. Fast and sensitive silver staining of DNA in polyacrylamide gels. Anal. Biochem. 1991, 196, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riek, J.D.; Calsyn, E.; Everaert, I.; Bockstaele, E.V.; Loose, M.D. AFLP based alternatives for the assessment of distinctness, uniformity and stability of sugar beet varieties. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2001, 103, 1254–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6.5: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research-an update. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Falush, D.; Stephens, M.; Prichard, J.K. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: Dominant markers and null alleles. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2005, 13, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.J.; Tong, J.G.; Zhang, Y.G.; Peng, Z.G. Study on the genetic diversity of two wild populations of Megalobrama Pellegrini (Teleostei, Cyprinidae). Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2014, 38, 975–979, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Brunner, P.C.; Douglas, M.R.; Bernatchez, L. Microsatellite and mitochondrial DNA assessment of population structure and stocking effects in Arctic charr Salvelinus alpinus (Teleostei: Salmonidae) from central alpine lakes. Mol. Ecol. 1998, 7, 209–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Nakajima, M.; Taniguchi, N. Loss of genetic variation and increased population differentiation in geographically peripheral populations of Japanese char Salvelinus leucomaenis. Aquaculture 2010, 308, S20–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höglund, J.; Morrison, D.A.; Mattsson, J.G.; Engström, A. Population genetic of the bovine/cattle lungworm (Dictyocaulus viviparus) based on mtDNA and AFLP marker techniques. Parasitology 2006, 133, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omote, K.; Nishida, C.; Takenaka, T.; Saito, K.; Shimura, R.; Fujimoto, S.; Sato, T.; Masuda, R. Recent fragmentation of the endangered Blakiston′s fish owl (Bubo blakistoni) population on Hokkaido island, Northern Japan, revealed by mitochondrial DNA and microsatellite analysis. Zool. Lett. 2015, 1, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbi, S.R.; Cipriano, F.; Hare, M.P. Predicting nuclear gene coalescence from microchondrial data: Three-times rule. Evolution 2001, 55, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.L. Ichthyofauna of the Heilongjiang River. Chin. J. Fish. 1994, 7, 1–14, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Geng, L.W.; Jiang, H.F.; Tong, G.X. Exploitation and utilization of fish stocks in Heilongjiang River Basin. Chin. J. Fish. 2017, 30, 50–53, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
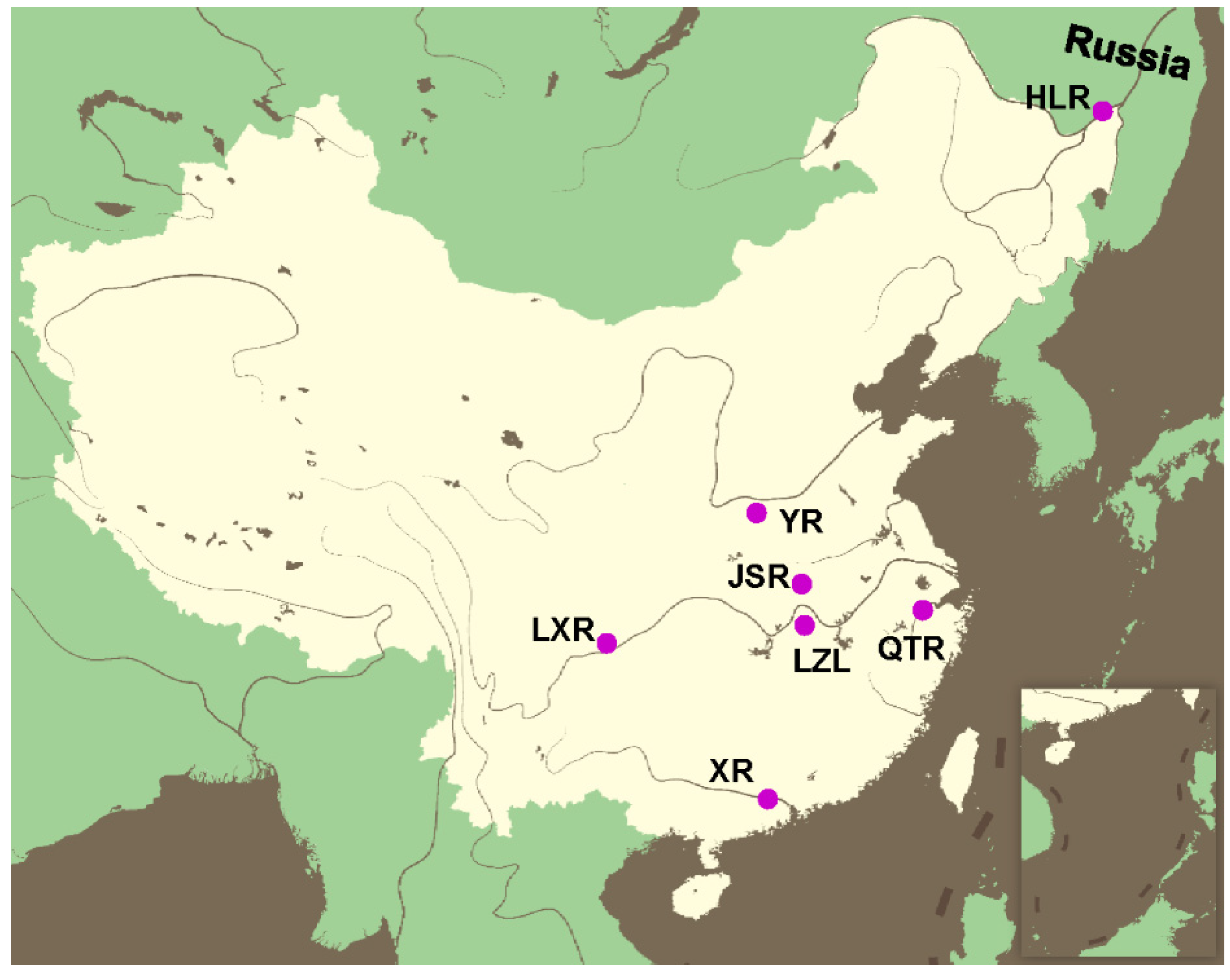
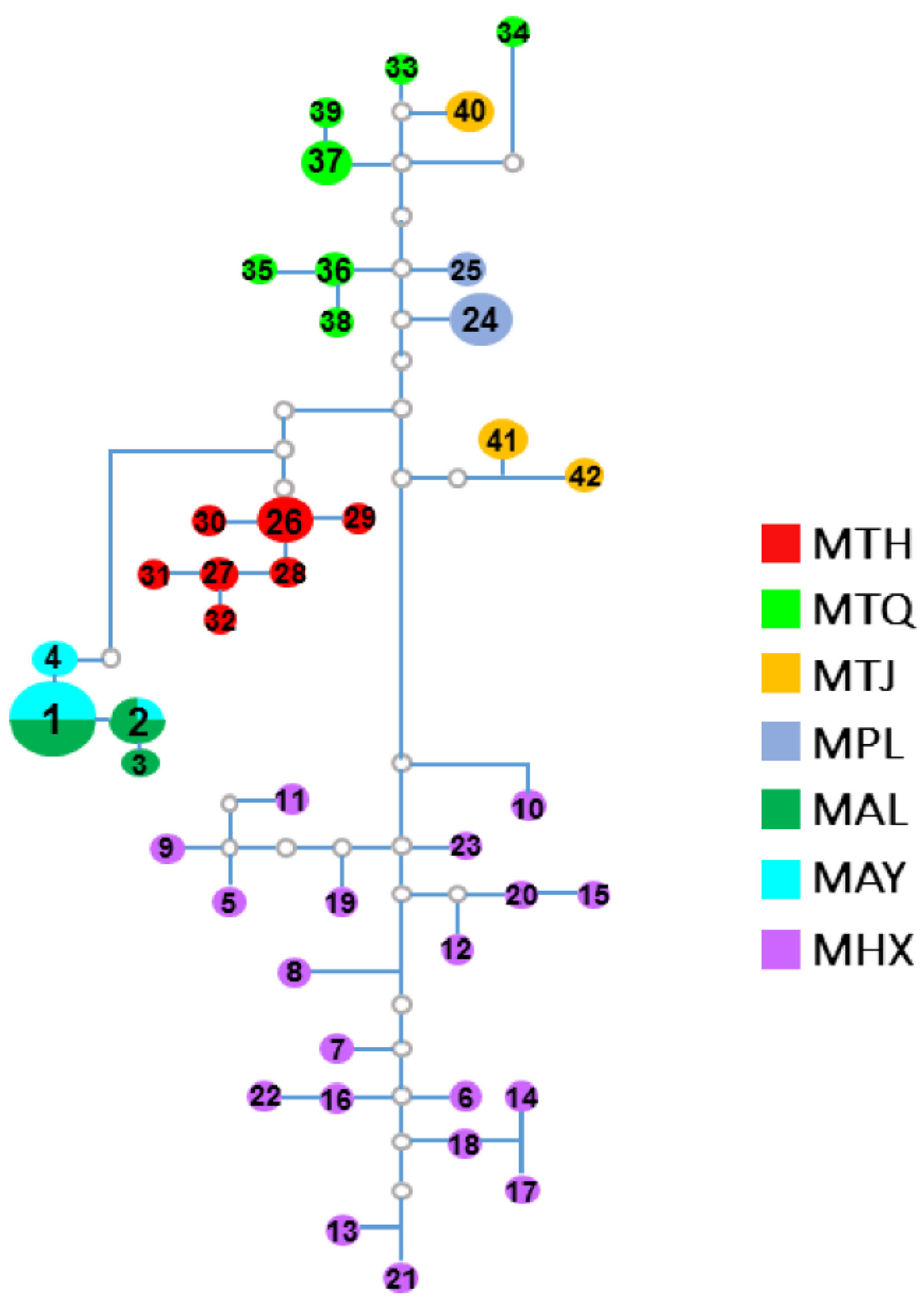
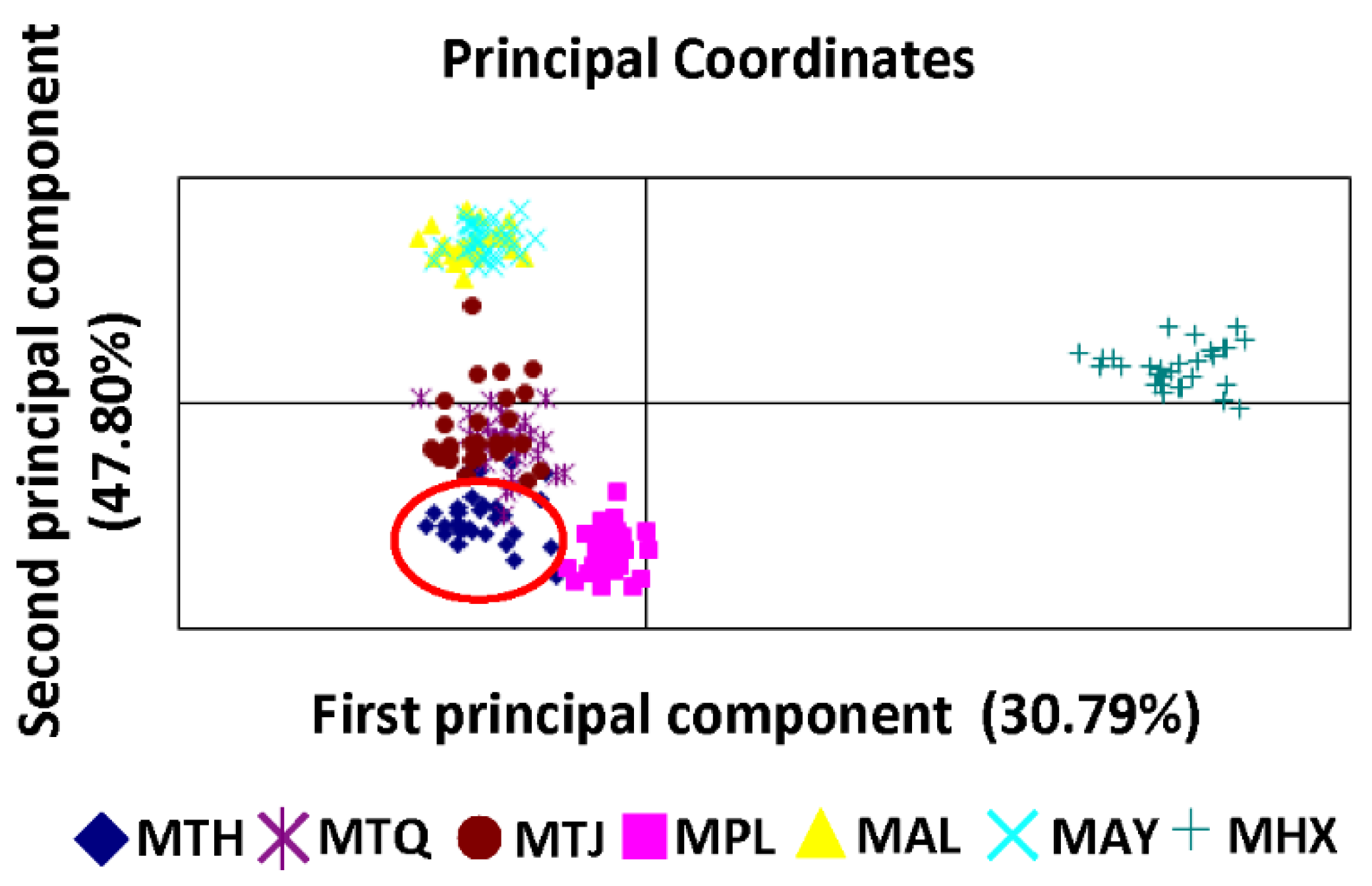
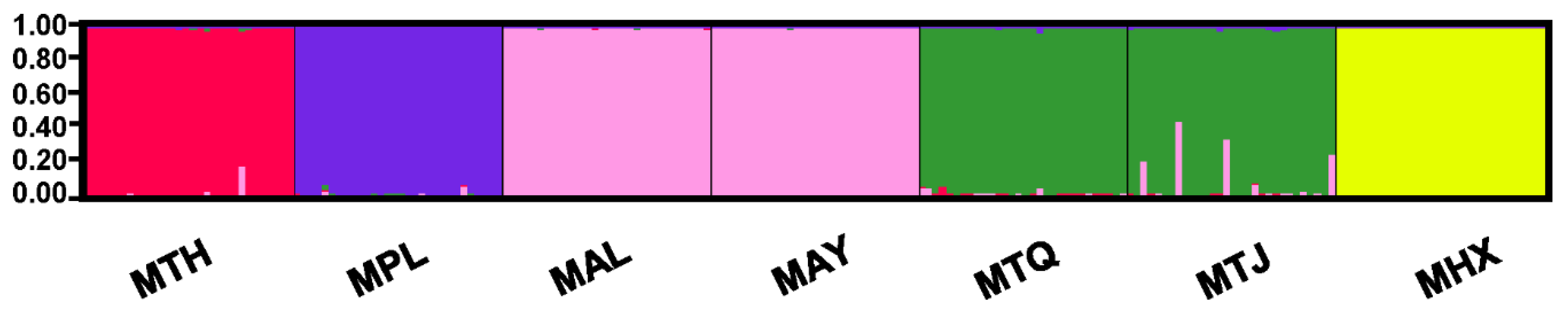
| Population | Sample Size | No. of Haplotypes | No. of Variable Sites | Percent Variable Sites (%) | Haplotype Diversity (Hd) (±SD) | Nucleotide Diversity (π) (±SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MTH | 26 | 7 | 8 | 0.26 | 0.683 ± 0.087 | 0.00045 ± 0.00009 |
| MTQ | 20 | 8 | 57 | 1.83 | 0.784 ± 0.084 | 0.00330 ± 0.00104 |
| MTJ | 15 | 3 | 25 | 0.8 | 0.686 ± 0.061 | 0.00363 ± 0.00039 |
| MPL | 20 | 2 | 12 | 0.39 | 0.189 ± 0.108 | 0.00073 ± 0.00042 |
| MAL | 18 | 3 | 2 | 0.06 | 0.601 ± 0.080 | 0.00023 ± 0.00004 |
| MAY | 16 | 3 | 2 | 0.06 | 0.567 ± 0.109 | 0.00020 ± 0.00005 |
| MHX | 20 | 19 | 61 | 1.96 | 0.995 ± 0.018 | 0.00437 ± 0.00033 |
| Total | 135 | 42 | 167 |
| Primer Pair ID | Total Bands | Polymorphic Bands | Percent Polymorphic Bands (%) | PIC Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1f2r | 14 | 13 | 93 | 0.320 |
| 1f5r | 11 | 10 | 91 | 0.352 |
| 1f17r | 14 | 14 | 100 | 0.412 |
| 2f5r | 12 | 12 | 100 | 0.309 |
| 2f9r | 11 | 11 | 100 | 0.349 |
| 4f20r | 17 | 17 | 100 | 0.278 |
| 7f8r | 13 | 13 | 100 | 0.340 |
| 7f19r | 21 | 20 | 95 | 0.262 |
| 7f20r | 22 | 22 | 100 | 0.265 |
| 10f13r | 13 | 12 | 100 | 0.298 |
| 10f18r | 11 | 11 | 85 | 0.293 |
| 10f20r | 15 | 15 | 100 | 0.282 |
| 12f3r | 20 | 17 | 100 | 0.352 |
| 12f4r | 17 | 17 | 97 | 0.286 |
| 12f5r | 10 | 10 | 97 | 0.273 |
| Total | 221 | 214 | \ | \ |
| Mean | 14.73 | 14.27 | 97 | 0.311 |
| Population | Number of Polymorphic Bands (NPB) | Percent of Polymorphic Bands (PPB, %) | Nei’s Gene Diversity (h) (±SD) | Shannon’s Information Index (I) (±SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MTH | 113 | 51.13 | 0.177 ± 0.205 | 0.263 ± 0.291 |
| MTQ | 115 | 52.04 | 0.173 ± 0.196 | 0.261 ± 0.281 |
| MTJ | 112 | 50.68 | 0.168 ± 0.198 | 0.252 ± 0.283 |
| MPL | 76 | 34.39 | 0.125 ± 0.191 | 0.185 ± 0.274 |
| MAL | 82 | 37.10 | 0.109 ± 0.167 | 0.169 ± 0.246 |
| MAY | 83 | 37.56 | 0.128 ± 0.184 | 0.192 ± 0.267 |
| MHX | 80 | 36.20 | 0.120 ± 0.182 | 0.181 ± 0.263 |
| Source of Variation | Degrees of Freedom | Sum of Squares | Percentage Variation (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Based on mtDNA sequences | ||||
| Among groups | 3 | 3646.435 | 88.48 | < 0.01 |
| Among populations within groups | 6 | 129.304 | 5.00 | < 0.01 |
| Within populations | 128 | 356.276 | 6.52 | < 0.01 |
| Total | 134 | 4132.015 | 100 | \ |
| Based on SRAP loci | ||||
| Among groups | 3 | 170.656 | 8.00 | < 0.01 |
| Among populations within groups | 6 | 83.906 | 9.78 | < 0.01 |
| Within populations | 203 | 1242.700 | 82.22 | < 0.01 |
| Total | 209 | 1497.262 | 100 | \ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, X.; Ma, B.; Li, C.; Jia, Z.; Jiang, X.; Ge, Y.; Tong, J.; Shi, L. Genetic Differentiation of an Endangered Megalobrama terminalis Population in the Heilong River within the Genus Megalobrama. Diversity 2020, 12, 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12100404
Hu X, Ma B, Li C, Jia Z, Jiang X, Ge Y, Tong J, Shi L. Genetic Differentiation of an Endangered Megalobrama terminalis Population in the Heilong River within the Genus Megalobrama. Diversity. 2020; 12(10):404. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12100404
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Xuesong, Bo Ma, Chitao Li, Zhiying Jia, Xiaona Jiang, Yanlong Ge, Jingou Tong, and Lianyu Shi. 2020. "Genetic Differentiation of an Endangered Megalobrama terminalis Population in the Heilong River within the Genus Megalobrama" Diversity 12, no. 10: 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12100404
APA StyleHu, X., Ma, B., Li, C., Jia, Z., Jiang, X., Ge, Y., Tong, J., & Shi, L. (2020). Genetic Differentiation of an Endangered Megalobrama terminalis Population in the Heilong River within the Genus Megalobrama. Diversity, 12(10), 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12100404







