Are Wildland Fires Increasing Large Patches of Complex Early Seral Forest Habitat?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quayle, B. Calibration and Validation of Immediate Post-Fire Satellite-Derived Data to Three Severity Metrics. Fire Ecol. 2015, 11, 12–30. [Google Scholar]
- Lydersen, J.M.; Collins, B.M.; Miller, J.D.; Fry, D.L.; Stephens, S.L. Relating fire-caused change in forest structure to remotely sensed estimates of fire severity. Fire Ecol. 2016, 12, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellasala, D.A.; Bond, M.L.; Hanson, C.T.; Hutto, R.L.; Odion, D.C. Complex Early Seral Forests of the Sierra Nevada: What are They and How Can They Be Managed for Ecological Integrity? Nat. Areas J. 2014, 34, 310–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odion, D.C.; Hanson, C.T.; Arsenault, A.; Baker, W.L.; Dellasala, D.A.; Hutto, R.L.; Klenner, W.; Moritz, M.A.; Sherriff, R.L.; Veblen, T.T.; et al. Examining Historical and Current Mixed-Severity Fire Regimes in Ponderosa Pine and Mixed-Conifer Forests of Western North America. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odion, D.C.; Hanson, C.T.; Baker, W.L.; Dellasala, D.A.; Williams, M.A. Areas of Agreement and Disagreement Regarding Ponderosa Pine and Mixed Conifer Forest Fire Regimes: A Dialogue with Stevens et al. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, J.T.; Safford, H.D.; North, M.P.; Fried, J.S.; Gray, A.N.; Brown, P.M.; Dolanc, C.R.; Dobrowski, S.Z.; Falk, D.A.; Farris, C.A.; et al. Average stand age from forest inventory plots does not describe historical fire regimes in ponderosa pine and mixed-conifer forests of western North America. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, C.T.; Odion, D.C.; Dellasala, D.A.; Baker, W.L. Overestimation of Fire Risk in the Northern Spotted Owl Recovery Plan. Conserv. Boil. 2009, 23, 1314–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, W.L. Historical forest structure and fire in Sierran mixed-conifer forests reconstructed from General Land Office survey data. Ecosphere 2014, 5, 1–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, W.L. Are High-Severity Fires Burning at Much Higher Rates Recently than Historically in Dry-Forest Landscapes of the Western USA? PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136147. [Google Scholar]
- Law, B.; Waring, R. Carbon implications of current and future effects of drought, fire and management on Pacific Northwest forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 355, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyser, A.; Westerling, A. Climate drives inter-annual variability in probability of high severity fire occurrence in the western United States. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 65003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, G.K.; Holden, Z.A.; Morgan, P.; Crimmins, M.A.; Heyerdahl, E.K.; Luce, C.H. Both topography and climate affected forest and woodland burn severity in two regions of the western US, 1984 to 2006. Ecosphere 2011, 2, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.D.; Safford, H.D.; Crimmins, M.; Thode, A.E. Quantitative evidence for increasing forest fire severity in the Sierra Nevada and Southern Cascade Mountains, California and Nevada, USA. Ecosystems 2009, 12, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallek, C.; Safford, H.D.; Viers, J.; Miller, J.D. Modern departures in fire severity and area vary by forest type, Sierra Nevada and Southern Cascades, USA. Ecosphere 2013, 4, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, C.T.; Odion, D.C. Is fire severity increasing in the Sierra Nevada, California, USA? Int. J. Wildland Fire 2014, 23, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, C.T.; Odion, D.C. Sierra Nevada fire severity conclusions are robust to further analysis: A reply to Safford et al. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2015, 24, 294–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, S.L. Forest fire causes and extent on United States Forest Service lands. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2005, 14, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, S.L.; Agee, J.K.; Fulé, P.Z.; North, M.P.; Romme, W.H.; Swetnam, T.W.; Turner, M.G. Managing Forests and Fire in Changing Climates. Science 2013, 342, 41–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lydersen, J.M.; North, M.P.; Collins, B.M. Severity of an uncharacteristically large wildfire, the Rim Fire, in forests with relatively restored frequent fire regimes. For. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 328, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessburg, P.F.; Churchill, D.J.; Larson, A.J.; Haugo, R.D.; Miller, C.; Spies, T.A.; North, M.P.; Povak, N.A.; Belote, R.T.; Singleton, P.H.; et al. Restoring fire-prone Inland Pacific landscapes: Seven core principles. Landsc. Ecol. 2015, 30, 1805–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, M.J.; Dunn, C.J.; Meigs, G.W.; Spies, T.A.; Kennedy, R.E.; Bailey, J.D.; Briggs, K. Contemporary patterns of fire extent and severity in forests of the Pacific Northwest, USA (1985–2010). Ecosphere 2017, 8, e01695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessburg, P.F.; Spies, T.A.; Perry, D.A.; Skinner, C.N.; Taylor, A.H.; Brown, P.M.; Stephens, S.L.; Larson, A.J.; Churchill, D.J.; Povak, N.A.; et al. Tamm review: Management of mixed-severity fire regime forests in Oregon, Washington, and Northern California. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 366, 221–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, S.A.; Miller, C.; Abatzoglou, J.T.; Holsinger, L.M.; Parisien, M.-A.; Dobrowski, S.Z. How will climate change affect wildland fire severity in the western US? Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 35002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DellaSala, D.A.; Hanson, C.T. Ecological and biodiversity benefits of mega-fires. In The Ecological Importance of Mixed-Severity Fires: Nature’s Phoenix; DellaSala, D.A., Hanson, C.T., Eds.; Elsevier: Waltham, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 23–54. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, W.L. Accommodating Mixed-Severity Fire to Restore and Maintain Ecosystem Integrity with a Focus on the Sierra Nevada of California, USA. Fire Ecol. 2017, 13, 148–171. [Google Scholar]
- Donato, D.C.; Fontaine, J.B.; Robinson, W.D.; Kauffman, J.B.; Law, B.E. Vegetation response to a short interval between high-severity wildfires in a mixed-evergreen forest. J. Ecol. 2009, 97, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, J.B.; Donato, D.C.; Robinson, W.D.; Law, B.E.; Kauffman, J.B. Bird communities following high-severity fire: Response to single and repeat fires in a mixed-evergreen forest, Oregon, USA. For. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 257, 1496–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutto, R.L.; Bond, M.L.; Dellasala, D.A. Using Bird Ecology to Learn About the Benefits of Severe Fire. In The Ecological Importance of Mixed-Severity Fires: Nature’s Phoenix; DellaSala, D.A., Hanson, C.T., Eds.; Elsevier: Waltham, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 55–88. [Google Scholar]
- Bond, M.L. Mammals and Mixed- and High-severity Fire. In The Ecological Importance of Mixed-Severity Fires: Nature’s Phoenix; DellaSala, D.A., Hanson, C.T., Eds.; Elsevier: Waltham, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 89–117. [Google Scholar]
- Buchalski, M.R.; Fontaine, J.B.; Heady, P.A., III; Hayes, J.P.; Frick, W.F. Bat response to differing fire severity in mixed-conifer forest, California, USA. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulakowski, D.; Veblen, T.T. Bark Beetles and High-Severity Fires in Rocky Mountain Subalpine Forests. In The Ecological Importance of Mixed-Severity Fires: Nature’s Phoenix; DellaSala, D.A., Hanson, C.T., Eds.; Elsevier: Waltham, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 149–174. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, B.K.; Sullivan, S.M.P.; Baxter, C.V.; Malison, R.L. Stream-Riparian Ecosystems and Mixed- and High-Severity Fire. In The Ecological Importance of Mixed-Severity Fires: Nature’s Phoenix; DellaSala, D.A., Hanson, C.T., Eds.; Elsevier: Waltham, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 118–148. [Google Scholar]
- Dudley, J.G.; Saab, V.A. Home Range Size of Black-Backed Woodpeckers in Burned Forests of Southwestern Idaho. West. N. Am. Nat. 2007, 67, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saab, V.A.; Russell, R.E.; Dudley, J.G. Nest Densities of Cavity-Nesting Birds in Relation to Postfire Salvage Logging and Time Since Wildfire. Condor 2007, 109, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, C.T.; North, M.P. Postfire Woodpecker Foraging in Salvage-Logged and Unlogged Forests of the Sierra Nevada. Condor 2008, 110, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saab, V.A.; Russell, R.E.; Dudley, J.G. Nest-site selection by cavity-nesting birds in relation to postfire salvage logging. For. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 257, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, M.; Lee, D.E.; Siegel, R.B.; Ward, J.P. Habitat Use and Selection by California Spotted Owls in a Postfire Landscape. J. Wildl. Manag. 2009, 73, 1116–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, M.L.; Bradley, C.; Lee, D.E.; Lee, D. Foraging habitat selection by California spotted owls after fire. J. Wildl. Manag. 2016, 80, 1290–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, W.L. Restoring and managing low-severity fire in dry-forest landscapes of the western USA. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, C.M.; Hanson, C.T.; DellaSala, D.A. Does increased forest protection correspond to higher fire severity in frequent-fire forests of the western USA? Ecosphere 2016, 7, e01492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.D.; Thode, A.E. Quantifying burn severity in a heterogeneous landscape with a relative version of the delta Normalized Burn Ratio (dNBR). Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 109, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, Z.A.; Morgan, P.; Hudak, A.T. Burn severity of areas reburned by wildfires in the Gila National Forest, New Mexico, USA. Fire Ecol. 2010, 6, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cansler, C.A.; McKenzie, D. How Robust Are Burn Severity Indices When Applied in a New Region? Evaluation of Alternate Field-Based and Remote-Sensing Methods. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 456–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.D. Patterns and Trends in Burned Area and Fire Severity from 1984 to 2010 in the Sierra De San Pedro Mártir, Baja California, Mexico. Fire Ecol. 2016, 12, 52–72. [Google Scholar]
- Kemp, K.B.; Higuera, P.E.; Morgan, P. Fire legacies impact conifer regeneration across environmental gradients in the U.S. northern Rockies. Landsc. Ecol. 2016, 31, 619–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steel, Z.L.; Koontz, M.J.; Safford, H.D. The changing landscape of wildfire: Burn pattern trends and implications for California’s yellow pine and mixed conifer forests. Landsc. Ecol. 2018, 33, 1159–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens-Rumann, C.; Kemp, K.B.; Higuera, P.E.; Harvey, B.J.; Rother, M.T.; Donato, D.C.; Morgan, P.; Veblen, T.T. Evidence for declining forest resilience to wildfires under climate change. Ecol. Lett. 2018, 21, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picotte, J.J.; Peterson, B.; Meier, G.; Howard, S.M. 1984–2010 trends in fire burn severity and area for the conterminous US. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2016, 25, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis, 5th ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Shatford, J.P.A.; Hibbs, D.E.; Puettmann, K.J. Conifer regeneration after forest fire in the Klamath-Siskiyous: How much, how soon? J. For. 2007, 105, 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Haire, S.L.; McGarigal, K. Effects of landscape patterns of fire severity on regenerating ponderosa pine forests (Pinus ponderosa) in New Mexico and Arizona, USA. Landsc. Ecol. 2010, 25, 1055–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, M.E.; Fornwalt, P.J.; Malone, S.L.; Battaglia, M.A. Patterns of conifer regeneration following high severity wildfire in ponderosa pine—Dominated forests of the Colorado Front Range. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 378, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, C.T. Landscape heterogeneity following high-severity fire in California’s forests. Wildl. Soc. Bull. 2018, 42, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiberg, J.B. Forest Conditions in the Northern Sierra Nevada, California. USDI Geological Survey; Professional Paper No. 8; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1902.
- Hanson, C.T. Post-Fire Management of Snag Forest Habitat in the Sierra Nevada. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California at Davis, Davis, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, D.A.; Hessburg, P.F.; Skinner, C.N.; Spies, T.A.; Stephens, S.L.; Taylor, A.H.; Franklin, J.F.; McComb, B.; Riegel, G. The ecology of mixed severity fire regimes in Washington, Oregon, and Northern California. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2011, 262, 703–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, W.L. Implications of spatially extensive historical data from surveys for restoring dry forests of Oregon’s eastern Cascades. Ecosphere 2012, 3, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiberg, J.B. Southern part of Cascade Range Forest Reserve. In Forest Conditions in the Cascade Range Forest Reserve, Oregon; Langille, H.D., Plummer, F.G., Dodwell, A., Rixon, T.F., Leiberg, J.B., Eds.; Professional Paper No. 9; U.S. Geological Survey; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1903; pp. 229–289. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, M.A.; Baker, W.L. Spatially extensive reconstructions show variable-severity fire and heterogeneous structure in historical western United States dry forests. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2012, 21, 1042–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodge, I.R. The Black Hills: A Minute Description of the Routes, Scenery, Soil, Climate, Timber, Gold, Geology, Zoology, etc.; Miller, J., Ed.; Kessinger Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 1876. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, P.; Heyerdahl, E.K.; Miller, C.; Wilson, A.M.; Gibson, C.E. Northern Rockies pyrogeography: An example of fire atlas utility. Fire Ecol. 2014, 10, 14–30. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, P.; Hudak, A.T.; Wells, A.; Parks, S.A.; Baggett, L.S.; Bright, B.C.; Green, P. Multidecadal trends in area burned with high severity in the Selway-Bitterroot Wilderness Area 1880–2012. Inter. J. Wildland Fire 2017, 26, 930–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, B.J.; Donato, D.C.; Turner, M.G. Drivers and trends in landscape patterns of stand-replacing fire in forests of the US Northern Rocky Mountains (1984–2010). Landsc. Ecol. 2016, 31, 2367–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, S.M.; Sieg, C.H.; Meador, A.J.S.; Fulé, P.Z.; Iniguez, J.M.; Baggett, L.S.; Fornwalt, P.J.; Battaglia, M.A. Ponderosa pine regeneration in high-severity burn patches. For. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 405, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Mickley, L.J.; Logan, J.A.; Kaplan, J.O. Ensemble projections of wildfire activity and carbonaceous aerosol concentrations over the western United States in the mid-21st century. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 767–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, D.; Littell, J.S. Climate change and the eco-hydrology of fire: Will area burned increase in a warming western USA? Ecol. Appl. 2017, 27, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, S.A.; Holsinger, L.M.; Miller, C.; Parisien, M.A. Analog-based fire regime and vegetation shifts in mountainous regions of the western US. Ecography 2018, 41, 910–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, J.T.; Collins, B.M.; Miller, J.D.; North, M.P.; Stephens, S.L. Changing spatial patterns of stand-replacing fire in California conifer forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 406, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, B.M.; Stevens, J.T.; Miller, J.D.; Stephens, S.L.; Brown, P.M.; North, M.P. Alternative characterization of forest fire regimes: Incorporating spatial patterns. Landsc. Ecol. 2017, 32, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, D.C.; Campbell, J.L.; Franklin, J.F. Multiple successional pathways and precocity in forest development: Can some forests be born complex? J. Veg. Sci. 2012, 23, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.D.; Safford, H.D.; Welch, K.R. Using one year post-fire fire severity assessments to estimate longer-term effects of fire in conifer forests of northern and eastern California, USA. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 382, 168–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, M.; Mast, J.N. How resilient are southwestern ponderosa pine forests after crown fires? Can. J. For. Res. 2005, 35, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepley, A.J.; Thompson, J.R.; Epstein, H.E.; Anderson-Teixeira, K.J.; Anderson-Teixeira, K.J. Vulnerability to forest loss through altered postfire recovery dynamics in a warming climate in the Klamath Mountains. Glob. Chang. Boil. 2017, 23, 4117–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, M.E.; Franklin, J.F.; Beschta, R.L.; Crisafulli, C.M.; DellaSala, D.A.; Hutto, R.L.; Lindenmayer, D.B.; Swanson, F.J. The forgotten stage of forest succession: Early-successional ecosystems on forested sites. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 9, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DellaSala, D.A.; Hanson, C.T. (Eds.) The Ecological Importance of Mixed Severity Fire: Nature’s Phoenix; Elsevier: Waltham, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Phalan, B.T.; Northrup, J.M.; Yang, Z.; Deal, R.L.; Rousseau, J.S.; Spies, T.A.; Betts, M.G. Impacts of the Northwest Forest Plan on Forest Composition and Bird Populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 3322–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Preventing disaster: Home ignitability in the wildland-urban interface. J. For. 2000, 98, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritz, M.A.; Batllori, E.; Bradstock, R.A.; Gill, A.M.; Handmer, J.; Hessburg, P.F.; Leonard, J.; McCaffrey, S.; Odion, D.C.; Schoennagel, T.; et al. Learning to coexist with wildfire. Nature 2014, 515, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoennagel, T.; Balch, J.K.; Brenkert-Smith, H.; Dennison, P.E.; Harvey, B.J.; Krawchuk, M.A.; Mietkiewicz, N.; Morgan, P.; Moritz, M.A.; Rasker, R.; et al. Adapt to more wildfire in western North American forests as climate changes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 4582–4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
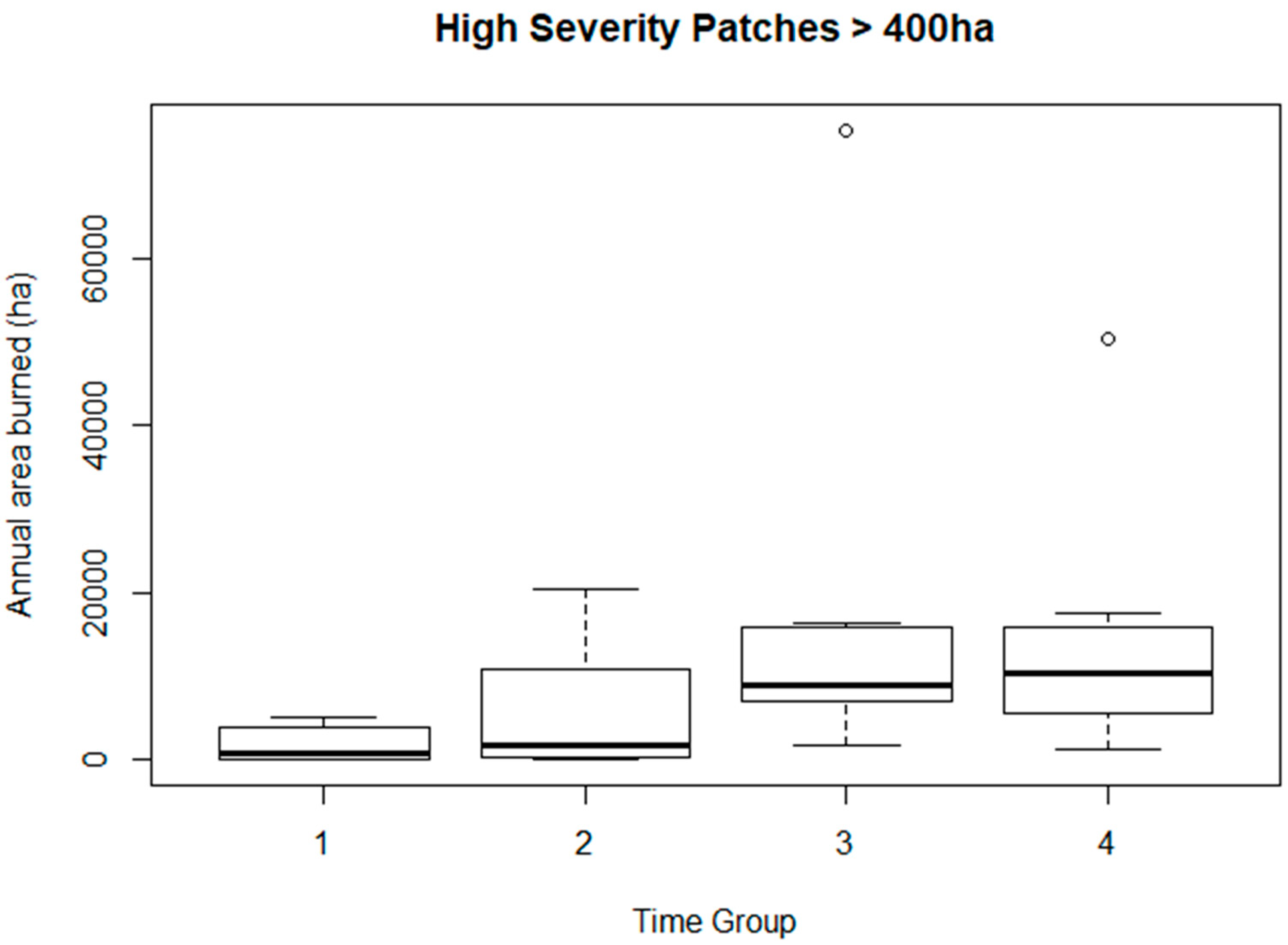
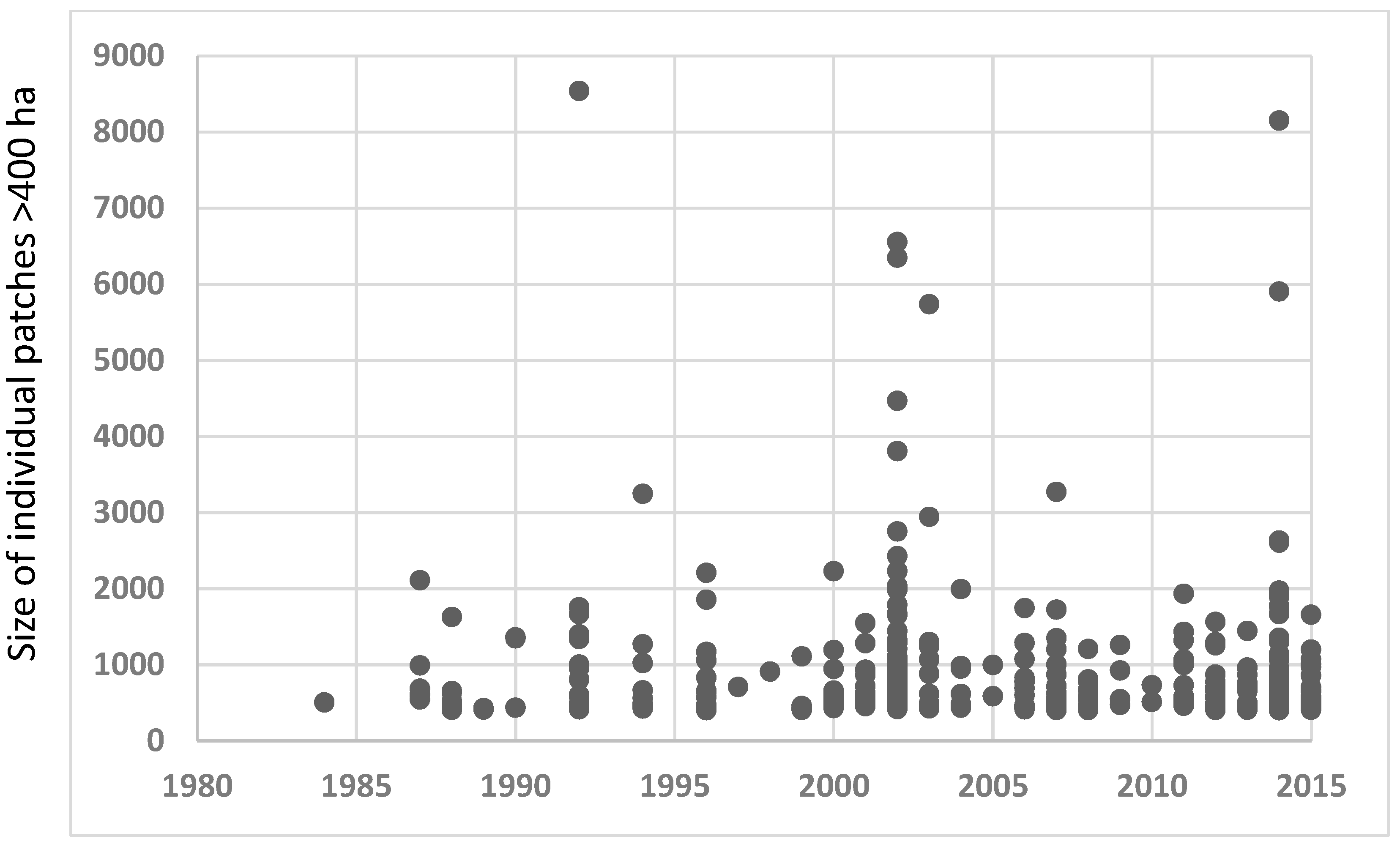
| Time Group Comparison | q0.05,4 | |RA-RB| | SE | q | Significant? (Is q > q0.05,4 ?) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1–2 | 3.63 | 45.0 | 26.53 | 1.70 | N |
| 1–3 | 3.63 | 108.0 | 26.53 | 4.07 | Y |
| 1–4 | 3.63 | 107.0 | 26.53 | 4.03 | Y |
| 2–3 | 3.63 | 63.0 | 26.53 | 2.37 | N |
| 2–4 | 3.63 | 62.0 | 26.53 | 2.34 | N |
| 3–4 | 3.63 | 1.00 | 26.53 | 0.04 | N |
| Time Group Comparison | Q0.05,4 | |A-B| | SE | Q | Significant? (Is Q > Q0.05,4?) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1–2 | 2.64 | 2.73 | 26.91 | 0.10 | N |
| 1–3 | 2.64 | 26.50 | 24.37 | 1.09 | N |
| 1–4 | 2.64 | 15.08 | 24.42 | 0.62 | N |
| 2–3 | 2.64 | 23.77 | 16.23 | 1.46 | N |
| 2–4 | 2.64 | 12.35 | 16.29 | 0.76 | N |
| 3–4 | 2.64 | 11.42 | 11.60 | 0.98 | N |
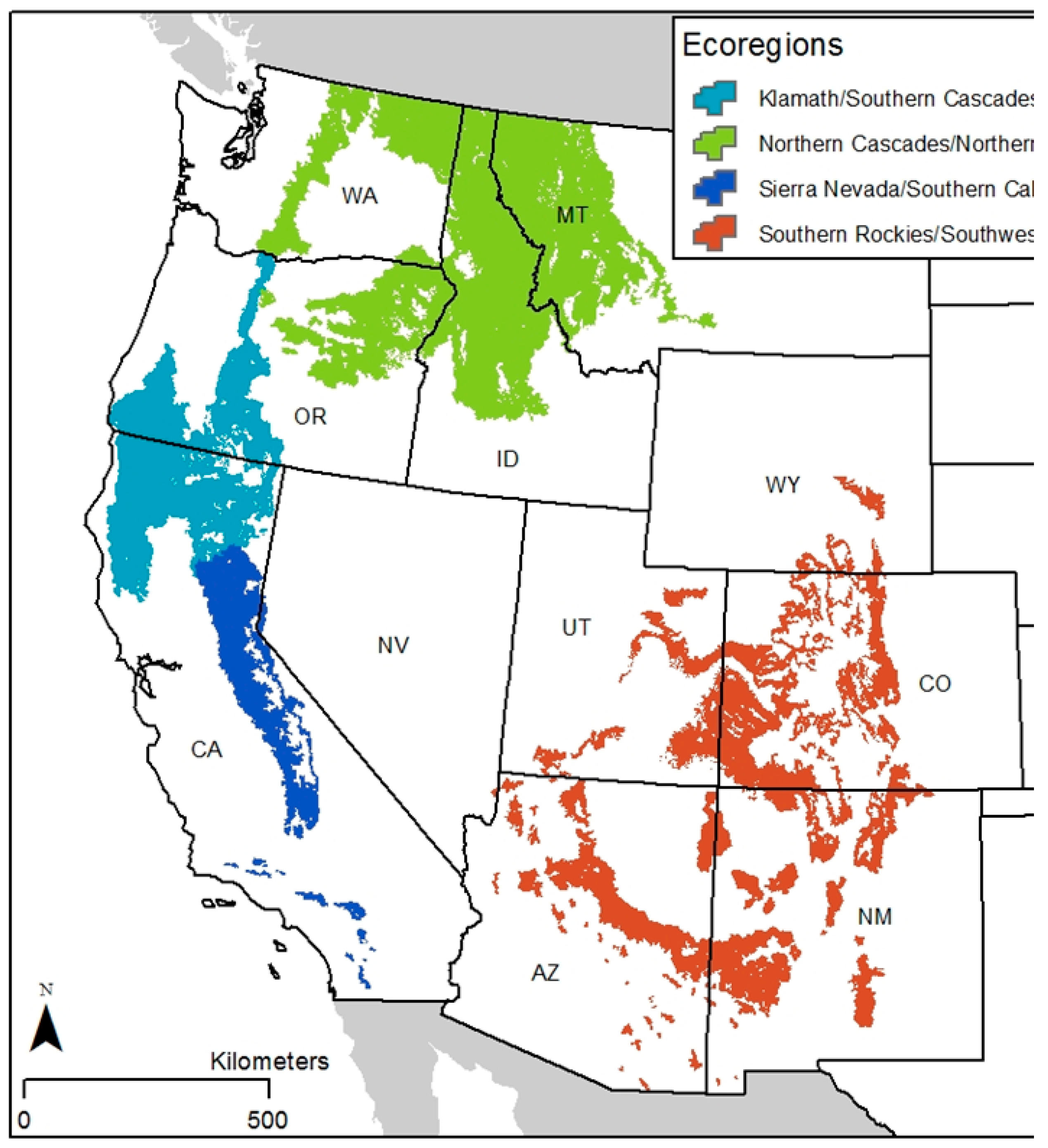
| Region | Area of Forest (ha) | Area (ha) of Patches >400 ha (% of Ecoregion) | Rotation Interval 1 (Years) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sierra Nevada/Southern California | 2,395,288 | 64,895 (2.709) | 1181 |
| Klamath/Southern Cascades | 5,741,930 | 100,112 (1.744) | 1835 |
| Northern Cascades/Northern Rockies | 10,057,451 | 73,936 (0.735) | 4354 |
| Southern Rockies/Southwest | 6,956,201 | 72,851 (1.047) | 3056 |
| Distance (m) | Sierra-Nevada/ Southern-California | Klamath/ Southern-Cascades | Northern-Cascades/ Northern-Rockies | Southern-Cascades/ Southwest |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <100 | 49.3 | 55.6 | 46.8 | 54.7 |
| 101–200 | 27.6 | 25.5 | 25.2 | 26.0 |
| 201–300 | 13.5 | 11.2 | 12.8 | 10.6 |
| >300 | 9.6 | 7.7 | 15.3 | 8.7 |
| Source | Region | Forest Type | Evidence Type | Patch Size/s (ha) | Time Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [54,55] | Northern Sierra Nevada | Mixed-conifer and ponderosa pine | Historical USGS mapping, and current GIS analysis | 400–~9000 | 19th century |
| [8] | Sierra Nevada | Mixed-conifer and ponderosa pine | Reconstruction, using 19th-century General Land Office data | Largest = 8050 (northern) and 9400 (southern) | 19th century |
| [56] | Eastern Washington Cascades | Mixed-conifer | Reconstructions of past high-severity from historical aerial photos | 400–10,500 | 19th century, and early 20th |
| [57] | Eastern Oregon Cascades | Mixed-conifer and ponderosa pine | Reconstruction from 19th-century General Land Office data | 400–~5000 | 19th century |
| [58] | Oregon Klamath | Mostly ponderosa pine | Historical account, early 20th century U.S. Geological Survey report | ~14,000 | 19th century |
| [59] | Colorado Front Range | Mostly ponderosa pine | Reconstruction from 19th-century General Land Office data | 400–~22,000 | 19th century |
| [59] | Blue Mountains, Oregon | Ponderosa pine | Reconstruction from 19th-century General Land Office data | 400–~12,000 | 19th century |
| [59] | Central/eastern Arizona | Ponderosa pine | Reconstruction from 19th-century General Land Office data | 400–~40,000 | 19th century |
| [60] | Black Hills, South Dakota | Ponderosa pine, some lodgepole pine | Historical account | ~19,000 | mid-19th century |
| [61,62] | Northern Rockies | Ponderosa pine, some Douglas-fir | Reconstruction from historical aerial photos | ~35,000 | 1910 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
DellaSala, D.A.; Hanson, C.T. Are Wildland Fires Increasing Large Patches of Complex Early Seral Forest Habitat? Diversity 2019, 11, 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11090157
DellaSala DA, Hanson CT. Are Wildland Fires Increasing Large Patches of Complex Early Seral Forest Habitat? Diversity. 2019; 11(9):157. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11090157
Chicago/Turabian StyleDellaSala, Dominick A., and Chad T. Hanson. 2019. "Are Wildland Fires Increasing Large Patches of Complex Early Seral Forest Habitat?" Diversity 11, no. 9: 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11090157
APA StyleDellaSala, D. A., & Hanson, C. T. (2019). Are Wildland Fires Increasing Large Patches of Complex Early Seral Forest Habitat? Diversity, 11(9), 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11090157





