Abstract
The measurement of stable isotopes in ‘bulk’ animal and plant tissues (e.g., muscle or leaf) has become an important tool for studies of functional diversity from organismal to continental scales. In consumers, isotope values reflect their diet, trophic position, physiological state, and geographic location. However, interpretation of bulk tissue isotope values can be confounded by variation in primary producer baseline values and by overlapping values among potential food items. To resolve these issues, biologists increasingly use compound-specific isotope analysis (CSIA), in which the isotope values of monomers that constitute a macromolecule (e.g., amino acids in protein) are measured. In this review, we provide the theoretical underpinnings for CSIA, summarize its methodology and recent applications, and identify future research directions. The key principle is that some monomers are reliably routed directly from the diet into animal tissue, whereas others are biochemically transformed during assimilation. As a result, CSIA of consumer tissue simultaneously provides information about an animal’s nutrient sources (e.g., food items or contributions from gut microbes) and its physiology (e.g., nitrogen excretion mode). In combination, these data clarify many of the confounding issues in bulk analysis and enable novel precision for tracing nutrient and energy flow within and among organisms and ecosystems.
1. Stable Isotope Analysis of Bulk Tissues
The measurement of the abundance of naturally-occurring stable isotopes within animal and plant tissues has proven to be a powerful and cost-effective tool for a wide range of ecological and physiological studies [1]. Here, we use δ notation to describe isotope values, defined as the measure of the heavy (e.g., 13C) to light (e.g., 12C) isotope relative to an internationally accepted standard. The key premises of isotope ecology are that: (1) carbon isotope (δ13C) values vary among primary producers, and this variation persists in higher trophic-level consumers [2]; (2) nitrogen isotope (δ15N) values increase systematically moving up a food chain with consumers having higher δ15N values than their food [3,4]; and (3) hydrogen (δ2H) and oxygen (δ18O) isotope values of consumer tissues are influenced by local precipitation as well as food, allowing them to be used to characterize animal movement [5,6]. Other isotope systems (e.g., sulfur: δ34S) also have ecological applications, although here we focus on carbon, nitrogen, and hydrogen. An implicit assumption behind these three key premises is that isotope values are also influenced by organismal physiology, namely the biochemical reactions that control the assimilation, synthesis, and degradation of macromolecules (protein, lipid, carbohydrate) required by producers and consumers for homeostasis. In other words, after accounting for physiology, “you are what you eat” isotopically.
δ13C and δ15N values of whole animals such as small invertebrates, or of ‘bulk’ animal tissues such as muscle therefore reflect their diet, trophic position, and physiological state [7]. These values can also be used to calculate dietary niche metrics of individuals and populations, as well as community measures of food chain length and food web structure [8,9,10]. Analysis of metabolically active tissues with different turnover rates (e.g., liver versus muscle) or inert tissues that continuously grow (e.g., whiskers, baleen) can provide inferences reflecting varying time periods [11,12,13]. Bulk tissue isotope analysis complements traditional methods such as gut content analysis, with the benefits of illustrating the assimilated diet integrated over time [2,7]. In addition, because tissue δ2H and δ18O values are influenced by drinking and food water that is ultimately sourced from local precipitation, they can be used to study habitat selection and migration at regional and continental spatial scales [6]. Although here we focus on animals, there is also a rich history of applying bulk tissue isotope analysis to plant tissue in ecological and physiological studies; see [14,15,16] for reviews.
Bulk tissue isotope analysis is appealing for a variety of reasons including the ease of sample preparation, low cost, and quick analysis time. Sample preparation can be as simple as drying and homogenizing a specimen and then carefully weighing it into tin or silver capsules. Some samples may need to be demineralized to remove inorganic carbon, or lipid-extracted because lipids have lower δ13C values than protein—the dominant macromolecule in animal tissue [17,18]—and thus are commonly removed to avoid biasing measurements. Access to stable isotope laboratories in many regions is readily available because universities or government agencies have centralized facilities for both internal and external sample submission. Sample analysis is also quick—with modern instrumentation, the δ13C and δ15N values of a sample can be measured in <10 min.
Although there are many benefits to bulk tissue isotope analysis, there are also limitations. The most prevalent is that isotope values of primary producers at the base of the food web (i.e., baseline values) can vary across space and time, confounding interpretations of the values of organisms at higher trophic levels. To account for this variation, researchers must sample potential dietary items from appropriate locations and times, after careful consideration of the turnover rates of the consumer tissue(s) being analyzed [19,20]. Another limitation is isotopic overlap among co-occurring dietary resources. For example, terrestrial C3 plants and freshwater aquatic algae can have overlapping δ13C values [21], making it impossible to determine whether a consumer primarily relies on terrestrial-derived (allochthonous) or algal-derived (autochthonous) energy, a key question in many aquatic food web studies [22].
In addition, interpretations of bulk tissue isotope data often must assume that macromolecules in the diet are routed directly into consumer tissue; e.g., prey protein is directly incorporated into predator protein. However, some macromolecules are extensively synthesized by consumers de novo using carbon and nitrogen from alternative dietary macromolecules. For example, animals can synthesize protein components such as non-essential amino acids (AANESS) using carbon from dietary carbohydrates or lipids, creating differences between the δ13C values of protein in consumer tissues and their diet items [23]. Even if dietary macromolecules are directly routed, there can be offsets in isotope values between a consumer and its diet because of the metabolic processing of nutrients during routing. These offsets, known as trophic discrimination factors (TDF), reflect isotopic fractionation caused by physiological processes. One prominent example is that excretion of waste nitrogen often favors 14N, causing consumers to have higher δ15N values than their food [3,24].
2. Principles of Compound-Specific Isotope Analysis (CSIA)
To help reveal shifts in baseline isotope values, resolve overlapping isotope values of diet items, and explicitly address the potential routing of dietary nutrients, biologists are increasingly using compound-specific stable isotope analysis, or CSIA. In this approach, the isotope values of individual monomers that constitute a macromolecule (e.g., amino acids, or AA, in protein) are measured and interpreted in biochemical and ecological contexts. The basic premise is the same as in bulk tissue isotope analysis: after accounting for physiology, “you are what you eat” isotopically. However, because many monomers have unique anabolic and catabolic biochemical pathways that are well understood, CSIA has the potential to provide much greater information than bulk tissue isotope analysis of the same sample.
Bulk tissue and CSIA studies both frequently focus on protein because it constitutes >50% of the organic matter in most consumers [25]. All proteins are made of the same monomers, 20 standard AA, each containing three primary functional groups: an amine (-NH2), a carboxyl (-COOH), and a unique side chain that creates distinct biochemical properties (R-group; [26]). AA fall into three categories based on an organism’s ability to synthesize the sequence of carbon atoms (i.e., the carbon skeleton) bonded to the α-carbon that links these functional groups (Table 1). First, AA can be essential (AAESS), meaning that an organism cannot synthesize them at all, or rapidly enough to meet their basic needs. Second, AA can be conditionally essential, meaning that the rate of de novo synthesis becomes inadequate under some physiological conditions. Third, AA can be non-essential (AANESS), meaning that organismal needs can be fully met with de novo synthesis. All 20 standard AA are non-essential for bacteria, fungi, plants, and many protists, but some AA are essential for animals and some protists because the enzymes required for de novo synthesis were lost during their evolution [27].

Table 1.
Classification of 15 standard amino acids (AA) for which stable isotope carbon (δ13C) or nitrogen (δ15N) values have been measured. Classifications based on data from invertebrates, fish, mammals, and birds [26,28,29,30,31,32,33].
Based on a consumer’s ability to synthesize AA de novo, general relationships between the δ13C values of consumers and their diets (δ13CConsumer − δ13CDiet or Δ13CC-D) can be predicted for essential and non-essential AA (Figure 1A). For the AAESS of eukaryotic consumers, Δ13CC-D values should be near 0‰ because these organisms must route them directly from their diet into their tissues, leading to minimal isotopic fractionation [34]. However, recent research has highlighted that AAESS may be assimilated from symbiotic gut microbes, causing Δ13CC-D values to deviate from 0‰ ([35]; see “CSIA applications” below). For AANESS, Δ13CC-D values can differ from zero as a result of de novo synthesis because the biosynthetic steps may cause fractionation and because the carbon substrate (e.g., lipids or carbohydrates) may vary in isotopic composition [35,36]. Similar to AAESS, Δ13CC-D values close to 0‰ for AANESS likely indicate direct routing of these molecules from the diet into endogenous tissue with minimal isotopic alteration. For example, gentoo penguins (Pygoscelis papua) eating a known diet had Δ13CC-D values that were ~0‰ for AAESS (−0.1‰ to 0.3‰), but their Δ13CC-D values for AANESS were larger and more variable (−0.5‰ to 2.4‰), reflecting a combination of direct routing and de novo synthesis from non-protein dietary macromolecules [34].
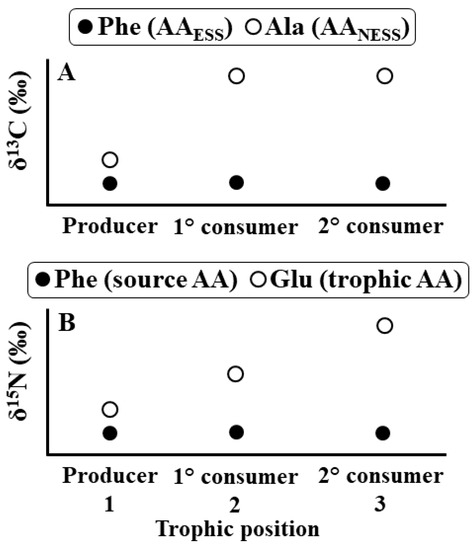
Figure 1.
Idealized isotope values are shown for two amino acids (AA) in tissue from three different organisms, including a primary producer, a primary consumer (1°), and a secondary consumer (2°)—note that these are hypothetical data to illustrate trends. (A) shows carbon isotope values. For phenylalanine, an essential AA, the value of Δ13CC-D (δ13CConsumer − δ13CDiet) was 0‰ for both consumers. As a result, δ13CPhe values were the same for all organisms. For alanine, a non-essential AA, the primary consumer synthesized substantial amounts of this AA de novo, causing it to have a higher δ13CAla value than its diet (i.e., the producer). In contrast, the secondary consumer extensively routed alanine from its diet (i.e., the primary consumer) directly into its tissues, causing both consumers to have the same δ13CAla value. (B) shows nitrogen isotope values. The values of Δ15NC-D for phenylalanine, a source AA, were 0‰ for both consumers. As a result, δ15NPhe values were the same for all organisms. In contrast, the values of Δ15NC-D for glutamic acid, a trophic AA, were similarly positive for both consumers. As a result, δ15NGlu values steadily increased from the producer to each consumer.
Predictions for Δ15NC-D values are not based on the essential versus non-essential classifications used for carbon, but instead rely on the categories of source versus trophic AA (Table 1; [32]) that refer to the lability of the nitrogen atom in the amine group (Figure 1B). This classification was initially empirically-derived but recent studies provide a sound biochemical basis for identifying AA as trophic or source [31,32,37]. The amine nitrogen atom can be replaced during transamination reactions in which the AA carbon skeleton is left intact, leading to a dissociation between changes in δ13C and δ15N values of AA and by extension, between the classifications of essential versus non-essential and source versus trophic (Table 1). Source AA generally do not participate in reactions involving deamination and transamination, thus their δ15N values remain largely unaltered during assimilation by consumers and their Δ15NC-D values are ~0‰. In contrast, trophic AA frequently undergo deamination and transamination reactions which result in 15N-enrichment, reflecting preferential deamination and ultimate excretion of light nitrogen (14N). This causes the Δ15NC-D values for trophic AA to be ~2–8‰ [31]. Several AA do not consistently fall into either category. Glycine and serine readily exchange nitrogen with each other but participate in few transaminations with other AA. As a result, the Δ15NC-D values of these two AA are frequently similar within an organism but vary widely between organisms, depending on diet and physiological status. Threonine is apparently often involved with transaminations that cause its δ15N value to decrease rather than increase with each trophic level, leading to negative Δ15NC-D values, although the biochemical mechanism remains unclear [38]. Overall, the primary benefit of CSIA is that the measurement of trophic AA, source AA, AAESS, and AANESS from a single sample can enable multiple, interwoven inferences about consumer physiology and ecology.
CSIA can also be applied to fatty acids (FA) in lipids, however, thus far this approach is less common than AA isotope analysis. Values of Δ13CC-D for individual FA have been assessed in controlled feeding experiments for birds [39,40] and invertebrates [41,42]. It is more difficult to predict Δ13CC-D for FA than for AA because of the greater diversity of FA structure, the variety of potential post-assimilation FA modifications, and the prominent dual roles of FA as structural molecules and as metabolic fuel [40]. However, these challenging dynamics also provide a wealth of potential hypotheses under which to evaluate Δ13CC-D, thus we anticipate that the application of CSIA to FA will continue to expand.
3. CSIA Methods
3.1. Sample Collection and Storage
Following field collection, samples for AA isotopic analysis should be stored frozen at ≤−20 °C or lyophilized, while it is best to store samples for FA analysis at ≤−80 °C and possibly with antioxidants (see [43]). Oxidation is less problematic for AA than for FA analysis because of the stability of the strong peptide bonds within proteins. For samples that have been stored with liquid preservative, the effects on AA and FA isotope values have not been comprehensively studied to our knowledge. Studies are available, however, for storage effects on AA composition and bulk stable isotope values. Up to 22 years of storage of delphinid skin samples in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) did not alter the tissue AA composition [44]. In contrast, six months of storage of muscle samples from elasmobranchs and marine teleosts in 95% ethanol led to small decreases in bulk δ13C values and C:N ratios, suggesting a loss of small AA [45,46]. However, a previous study found that eight weeks of storage in 70% ethanol did not appear to significantly influence bulk δ13C and δ15N values [47]. Until results are available for AA and FA isotopic analyses, we suggest using these and other bulk stable isotope studies as a guide for evaluating the potential effects of sample preservation techniques.
For both AA and FA analyses, plastic storage containers should be avoided because of potential contamination from plastic hydrocarbons. Best practice involves collecting, drying, and storing samples in glassware that has been pre-combusted in a muffle furnace at 500 °C for ≥8 h to burn off any organic residue. Caps for glassware should be either Teflon or foil-lined and cleaned of surface contaminants via acid washes (typically 0.1 N HCl) followed by rinses in deionized H2O. If feasible, tissues can also be stored in pre-combusted aluminum foil.
3.2. Chemical Preparation for AA Isotope Analysis
Methods to prepare a sample for AA δ13C and δ15N analysis vary among tissues, although three general steps apply to all samples: (1) the isolation and purification of protein from other organic compounds within a sample (e.g., lipids, carbohydrates), (2) the breakdown of the protein structure via hydrolysis to produce free AA, and (3) the derivatization of free AA to more volatile forms that can be readily separated via gas chromatography (GC), combusted or pyrolyzed to gas, and analyzed in an isotope ratio mass spectrometer (IRMS). Derivatization is the most complex process and typically involves a full day of laboratory work, although some methods require considerably less time [48]. Alternatively, liquid chromatography can also be used to separate individual AA which then undergo standard isotope analysis in an elemental analyzer interfaced to an IRMS (e.g., [49]), although this approach is less common.
For lipid-rich tissue or whole animal samples (e.g., liver or small invertebrates), fats must be removed prior to hydrolysis, typically with multi-day solvent rinses [50,51]. Samples can be soaked in a 2:1 mixture of chloroform:methanol for 72 h, with the solvent changed every 24 h. Alternatively, samples can be soaked in petroleum ether for 72–96 h—this milder solution is advantageous for delicate samples such as invertebrate tissue because more polar solvent mixtures like chloroform:methanol may leach nitrogen from whole body samples (e.g., [52]). Following the final solvent soak, samples should be rinsed 5–7 times in deionized water and then lyophilized.
To break down protein structure and obtain free AA, lipid-free samples are hydrolyzed in strong acid at high temperature. Samples are added to 0.5–1.5 mL of 6 N HCl in pre-combusted glass vials which are then flushed with N2 gas before sealing to prevent oxidation. Samples are then held at either 150 °C for 70 min [48] or 110 °C for 20–24 h [53]; this process coverts glutamine and asparagine into glutamic acid and aspartic acid respectively due to cleavage of the terminal amine group. Following hydrolysis, samples are dried down under N2 gas. The remaining solids form a film on the interior of the glass vial which consists of pure AA and, if present, contaminants such as hydrolyzed carbohydrates or lipids. This film is stable and can be safely stored at −20 °C for at least six months. For carbohydrate-rich samples such as primary producers and whole invertebrates an additional purification step is required post-hydrolysis to remove carbohydrates and other contaminants, leaving isolated AA for derivatization. The most common method calls for hydrolyzed samples to be resuspended in weak acid, passed through a Dowex resin (50WX8 100–200 mesh) that retains AA while allowing other molecules to pass through, then eluting the AA with a base [54]. Samples are then dried again to a film under N2 gas.
AA are not easily converted into gas phase; to be separated on a GC column, they must be transformed into more volatile forms with a low boiling point. This transformation is termed ‘derivatization’ and includes adding functional groups to each AA after their purification; three methods are prevalent in the AA literature. The most common method was developed by Silfer et al. [53] and it derivatizes AA into N-trifluoroacetyl isopropyl esters in two steps. First, esterification of the carboxyl terminus of each AA is achieved by adding a 4:1 isopropanol:acetyl chloride mixture to the hydrolyzed film and reacting at 110 °C for one hour. Following this, the solvent is dried down under N2 gas, and the sample is rinsed twice with a neutral dichloromethane solution to remove excess isopropanol:acetyl chloride (after each rinse, the sample is again dried down under N2 gas). Second, acetylation of the amine terminus is achieved by adding 1:1 trifluoroacetic anhydride:dichloromethane and reacting at 110 °C for 10 min. Following these steps, derivatized samples may be stored at −20 °C in a freezer designed to accommodate flammable or explosive reagents. However, derivatized AA slowly dissociate into their non-derivatized forms, affecting their isotopic composition [55], and thus samples should be analyzed as soon as feasible. For analysis, derivatized samples are dried under N2 gas, rinsed twice with dichloromethane, then dissolved in dichloromethane for injection on a GC column.
A second method derivatizes AA to N-pivaloyl isopropyl esters [56,57]. Hydrolysates are first reacted at 110 °C for two hours with a 4:1 mixture of isopropanol:thionyl chloride, dried under N2 gas and rinsed three times with dichloromethane, and then reacted again at 110 °C for two hours with 4:1 mixture of dichloromethane:pivaloyl chloride. A third technique, modified by Walsh et al. [48] from GC-MS procedures [58], involves a single-step derivatization which simultaneously modifies both the carboxyl and amine terminus. The derivatizing agent, methyl chloroformate, is added to a hydrolyzed sample which has been resuspended in 0.1 N HCl. This mixture sits for ~1–2 min before being vortexed, after which an organic layer containing derivatized AA forms and is removed for GC injection.
Each derivatization method described above adds carbon to AA and thus the measured AA δ13C values reflect a combination of intrinsic AA carbon from the original molecule and reagent carbon added during derivatization. Researchers account for this by derivatizing each batch of unknown samples alongside a standard that contains AA in known concentrations and of known isotopic values. Correction equations are then used to calculate the δ13C values of the intrinsic carbon alone in each AA, as described in detail in [48,53,59]. Nitrogen is not added to AA during derivatization in any of these methods, thus measured δ15N values need only standard IRMS corrections (e.g., linearity or drift corrections). The N-pivaloyl isopropyl ester methods [56,57] have only been used for AA δ15N analysis and thus to our knowledge, their application to δ13C measurements has not been experimentally validated. Ultimately, deciding which derivatization method to use depends on the scientific question of interest, as each technique better resolves certain AA with specific GC protocols [48,53,59]. In addition, where possible, researchers should consider which technique has been used in generating previous datasets on similar questions. This is important because without direct comparisons of materials derivatized with each method, raw AA δ13C and δ15N values are not directly comparable between methods [60].
3.3. Chemical Preparation for FA Isotope Analysis
As with AA analysis, individual FA must be made more volatile before GC separation and isotopic analysis, however, this process is simpler than the derivatization for AA. To extract and save lipids for FA analysis, researchers typically use variants of the methods of Folch et al. [50] or Bligh and Dyer [51]. Several grams of wet tissue are homogenized in a mixture of 2:1 chloroform:methanol. Samples are then centrifuged and rinsed with a salt solution to remove aqueous solutes. The remaining organic phase is dried under N2 gas and typically resuspended in chloroform. After extraction, FA can be converted to methyl esters (FAME) by the addition of 1M acetyl chloride in methanol and reacting at 90 °C for two hours. Once this solution is dried, FAME can be resuspended in dichloromethane or hexane and injected directly onto a GC column for analysis. As with AA derivatization, producing FAME adds carbon to the original molecules, and each batch of unknown samples must be esterified and analyzed alongside a standard for which the intrinsic δ13C is known to account for the addition of the methyl group.
3.4. Isotopic Analysis of Individual AA and FA
Once samples have been chemically prepared, they can be analyzed via a GC coupled to a combustion/reduction and pyrolysis unit that is interfaced with an IRMS system (i.e., GC-C-IRMS). A small aliquot of sample (~1–5 µL) is injected into a small heated space where it is volatilized at high temperature into a gas phase, and then the sample enters the GC column. The GC temperature ramps following a protocol designed to separate the monomers (AA or FA) by mass and polarity. Individual AA or FA elute from the column at particular times based on their size and chemical properties. To separate the elements, monomers are then oxidized and reduced into CO2 or N2, or pyrolyzed into H2 gas, in a high temperature reactor and these reaction products are delivered to the IRMS. Each AA or FA is then detected as a voltage increase, represented by a distinct peak in a chromatogram (Figure 2), from which isotopic ratios are calculated. Individual AA and FA always elute in the same order unless the GC temperature ramping protocol is changed. The final result is measurement of δ13C, δ15N or δ2H for 10–14 AA, or δ13C for multiple FA (depending on sample type), from a single injection of a single sample. This data richness is a main reason that CSIA is rapidly becoming a powerful tool in physiological and ecological studies.
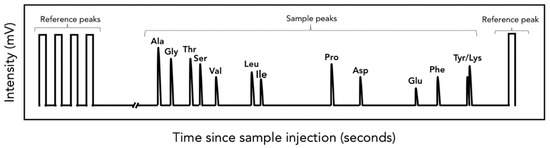
Figure 2.
A typical amino acid (AA) chromatogram of a sample prepared with the Silfer et al. [53] derivatization method. Here the X axis has been broken for clarity; typical injections take ~1 h. Included are peaks of reference gas (square) and individual AA from the sample (rounded). AA with simpler molecular structures tend to elute earlier (e.g., Gly and Ser) whereas more complex AA require more time to pass through the GC column (e.g., Phe, Lys). Although a single line is shown for clarity, chromatograms have multiple lines representing different atomic masses that are then integrated to calculate isotopic ratios. During carbon analysis, lines represent atomic masses 44, 45, 46; during nitrogen analysis, masses 28, 29, 30; and during hydrogen analysis, masses 1 and 2.
Best GC-C-IRMS practices involve running duplicate or triplicate injections of every sample and bracketing them with standard injections, to account for any temporal drift in isotope values caused by variation in instrument performance. Quality control processes involve examining chromatograms and assessing peak shape (symmetrical peaks are ideal), baseline gas levels, and the degree of separation between AA peaks because coelution can affect isotope values. These assessments are where expertise becomes critical, because chromatograms require time and experience for accurate interpretation, producing the highest degree of data quality control.
4. CSIA Applications to Date
Thus far, CSIA studies have provided important insights at molecular, organismal, and ecological scales. Physiological applications have illustrated that in addition to AA classifications (essential or non-essential for carbon; source or trophic for nitrogen), expectations for Δ13CC-D and Δ15NC-D should consider factors such as diet composition (e.g., quality and content of protein), mode of nitrogen excretion, and if possible, previously published ΔC-D values for species with similar physiologies [31,36,61,62]. Ecological applications have demonstrated that variation in baseline isotope values can produce misleading results when using bulk tissue isotope analysis, which can be resolved with CSIA. CSIA has also enabled the tracing of nutrient and energy flow within and among ecosystems, providing a new approach to assessing species interactions and the relative importance of different sources of primary production to consumers across trophic levels.
One prominent research focus has been the carbon sources for AA synthesis. Regarding de novo synthesis of AANESS, the use of carbon from non-protein dietary macromolecules (i.e., carbohydrates and lipids) can be extensive when consumers consume diets that contain inadequate amounts of the protein required for growth or homeostasis. For example, O’Brien et al. [59] showed that adult hawkmoths (Amphion floridensis) fed on a sugar solution synthesized ~60–95% of the AANESS used to build their bodies from dietary carbohydrates; in contrast, all the AAESS in their tissues were sourced from the plant diet that they consumed as larvae, which contained low but sufficient amounts of protein. Differential use of dietary nutrients to synthesize AA has also been observed in pigs (Sus domesticus; [63]), rats (Rattus norvegicus; [64]), and mice (Mus musculus; [36]). For example, a feeding experiment revealed that mice synthesized a significant portion of the AANESS used to build their tissues from dietary lipids, even when fed diets containing as little as 10% fat by weight [36]. As expected, AANESS synthesized from intermediaries in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle were more sensitive to dietary fat content than those synthesized from glycolytic intermediaries, because the TCA cycle is more closely linked to the metabolic processing of lipids. These results also call into question the benefits of removing lipids from potential food sources before bulk tissue δ13C analyses, as is common in studies of foraging ecology [65]. Combined, these controlled feeding studies using CSIA show that (1) herbivorous and omnivorous animals are quite flexible in their ability to maintain AANESS homeostasis when fed diets containing insufficient amounts of protein, and (2) that complete, direct routing of dietary AANESS into tissues is a poor assumption when animals consume diets rich in carbohydrates and lipids that exceed energy requirements.
Regarding AAESS, recent studies on invertebrates [66,67,68] and vertebrates [35,69] show that dietary protein is not the sole source of AAESS used to build and maintain animal tissues. Because eukaryotic consumers cannot synthesize AAESS de novo, they should directly route dietary AAESS into their tissues, resulting in Δ13CC-D values of ~0‰; however, this fundamental expectation has not always been met in controlled experiments. Because animals in these feeding experiments were consuming known diets with carefully measured AA isotopic composition, there are two feasible explanations. First, animals can assimilate a substantial portion of their AAESS from symbiotic gut microbes (e.g., bacteria and fungi) that use carbon from dietary carbohydrates or lipids to synthesize the carbon skeletons of AAESS, which would result in non-zero Δ13CC-D values. There is evidence for this phenomenon for a limited suite of AAESS using other methodologies [70]. Second, it is possible that extensive catabolism of AAESS immediately upon their absorption into cells lining the gut [71] causes fractionation. This would alter the δ13C values of the remaining AAESS that are incorporated into consumer tissue. This second pathway could feasibly occur without gut microbe activity; however, the relevant study [71] occurred prior to the recognition that gut microbes make appreciable contributions to the protein balance of their eukaryotic hosts. To our knowledge, isotopic fractionation related to AAESS catabolism by the gut microbiome or by eukaryotic hosts has not been experimentally explored. Overall, a summary of current literature highlights the fact that while AAESS are more likely than AANESS to have Δ13CC-D values near 0‰, there is considerable variation (Figure 3; Table S1), and a principal cause is likely the increasingly-recognized role of the gut microbiome in host protein homeostasis.
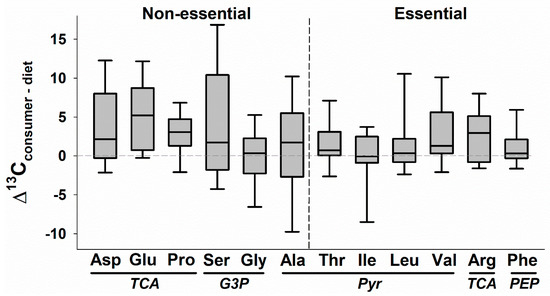
Figure 3.
Median values (solid line; boxes and error bars represent 25th and 10th percentiles) of the carbon isotope discrimination factors (Δ13CC-D, or δ13CConsumer tissue − δ13CDiet item) for individual amino acids (AA) across nine species of animals consuming a total of 24 different diets in controlled experiments. AA that are essential tend to have reduced variation and values closer to 0‰ in comparison to those that are non-essential. Note that Arg is conditionally essential, and Gly is essential for birds. AA are also grouped by the source of precursor molecules for biosynthesis: TCA = intermediates of the tricarboxylic acid cycle; G3P = glycerate-3-phosphate of glycolysis; Pyr = pyruvate; PEP = phosphoenolpyruvate of glycolysis. Note that of the 20 standard AA, four are excluded here because they are usually not measured (histidine, methionine, tryptophan, cysteine) and two are excluded because they have been reported in only one study of which we are aware (lysine, tyrosine; [72]). In addition, during sample preparation, glutamine is converted to glutamic acid and asparagine to aspartic acid. Studies were located by (1) searching the references cited in a recent review of AA Δ15NC-D [31]; (2) searching “Web of Science” electronic database for “carbon isotope” and “amino acid”; and (3) searching citations of relevant publications. Studies are listed in Table S1.
There is also substantial variation in published Δ15NC-D values (Figure 4); for a comprehensive review see [31]. Some of this variation can be attributed to dietary protein content and quality [31,61,73]. Consumers eating diets that are high in protein with AA compositions that closely match their requirements (i.e., high biological quality) generally have lower Δ15NC-D values, suggestive of little metabolic processing and extensive direct protein routing [62]. In addition, consumers that excrete nitrogen as ammonia rather than as urea or uric acid have higher Δ15NC-D values [74], possibly because the relatively greater toxicity of ammonia requires this molecule to be excreted rapidly, which can cause substantial fractionation [37,75]. Values of Δ15NC-D can also vary among tissues [76,77] with the highest values occurring in tissues with very active metabolic processing of AA, such as liver [73]. Unique physiological processes can also affect Δ15NC-D. A recent study of captive leopard sharks (Triakis semifasciata) found surprisingly low Δ15NC-D values for trophic AA [72], likely related to the ability of elasmobranchs to retain and recycle urea nitrogen into newly-synthesized AA [31,76]. Importantly, the distinction between trophic and source AA applies to microbial consumers as well as animals [78].
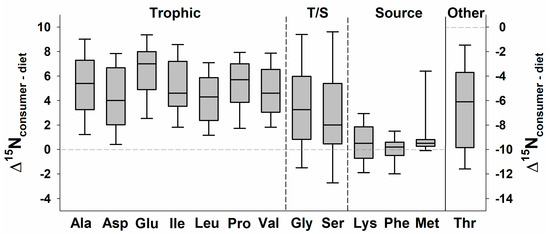
Figure 4.
Median values (solid line; boxes and error bars represent 25th and 10th percentiles) of the nitrogen isotope discrimination factors (Δ15NC-D, or δ15NConsumer tissue − δ15NDiet item) for individual amino acids (AA) across 58 species of consumers in controlled experiments and well-constrained field studies. AA that are trophic tend to have greater Δ15NC-D values in comparison to source AA. Note that T/S indicates AA that can be classified as either trophic or source, and that threonine has a separate y-axis. Of the 20 standard AA, five are excluded here because they are rarely reported (arginine, cysteine, histidine, tryptophan, tyrosine). In addition, during sample preparation, glutamine is converted to glutamic acid and asparagine to aspartic acid. Studies were located (1) in Supplement 1 of [31]; and (2) by repeating the literature search described in [31] to add more recent studies. Studies are listed in Table S2.
CSIA studies have also yielded important ecological advances, particularly for resolving resource use and trophic level for consumers. Trophic level can be estimated by comparing the δ15N values between trophic and source AA [79,80]. The most common pairing in published studies is δ15NGlu − δ15NPhe [31,32,37]. Because trophic AA experience fractionation at each trophic level, their δ15N values increase proportionately with trophic steps, and consequently larger δ15NGlu − δ15NPhe offsets indicate higher trophic positions. The inference of trophic level can also be formalized by the equation [57,81]
Trophic Level = 1 + [δ15NTrophic AA − δ15NSourceAA − β] × TDFTrophic AA−1,
Here, β is the offset between trophic and source δ15N in primary producers at the base of the food web, thus this term assigns primary producers to trophic level 1. TDF is the trophic discrimination factor which represents the magnitude of the increase in the δ15N value which occurs with a single trophic step. Recent research has emphasized that values of both β and TDF can vary among biological systems [31], and such variability should be considered in the application of Equation (1) (see CSIA limitations below).
In several studies, CSIA revealed that ecological inferences based on bulk tissue isotope analyses were misleading. Dale et al. [82] found that when brown stingrays (Dasyatis lata) sampled inshore reached a body size indicative of sexual maturity, bulk muscle tissue δ15N values declined, suggesting that large stingrays were feeding almost one trophic level lower than smaller individuals [4]. Values of source AA δ15N were surprisingly lower for the larger stingrays, however, indicating that the cause of the decrease in their bulk tissue δ15N values was not feeding at a lower trophic level, but instead feeding on prey which originated in offshore waters with lower δ15N values at the base of the food web. Similarly, Seminoff et al. [83] showed that leatherback sea turtles (Dermochelys coriacea) departing nesting beaches in Indonesia could be divided into groups with bulk skin tissue δ15N values of 13–18‰ and 10–12‰. However, rather than feeding at different trophic levels, this difference was attributed to lower δ15N values for source AA resulting from varying oceanographic characteristics among foraging regions.
In addition to nitrogen isotope values, δ13C values are also informative for understanding animal feeding ecology. For example, Ruiz-Cooley et al. [84] reported a striking temporal trend in sperm whales (Physeter macrocephalus) feeding in the California Current off the western coast of North America. Bulk skin tissue δ13C and δ15N values of the whales declined by 1.1‰ and 1.7‰ from 1993 to 2005; a single sample from 1972 suggested that the decline had been occurring for decades. These trends were paralleled by decreases of similar magnitude in the AAESS δ13C and source AA δ15N values. This pattern indicates that the whales likely did not change their diet over time, but rather that the California Current food web likely experienced changes in biogeochemical cycling, primary production rates, or primary producer species composition that affected the baseline stable isotope composition of the food web.
Analysis of AAESS δ13C values have been particularly useful for studying community ecology, food web structure, and energy flow. Scott et al. [85] and Larsen et al. [86,87] found that patterns of the relative AAESS δ13C values in producers such as plants, bacteria, and fungi consistently differed among groups defined by physiology or CO2 sources. These patterns can be distilled via multivariate statistical techniques such as principal component analysis (PCA) and linear discriminant analysis (LDA), leading to the identification of distinct ‘fingerprints’ or patterns in δ13C values among individual AAESS. These fingerprints can provide resolution among types of primary producers that often do not differ in bulk tissue isotope values; e.g., fingerprints can distinguish between phytoplankton and understory macroalgae [88], and between seagrass and mangroves [89]. Importantly, because isotope values of AAESS are shaped by biochemical processes that are conserved across taxa, these fingerprints are not thought to change with growth rates, seasons or locales, which provides a tremendous advantage over bulk tissue isotope studies [88,90,91]. Furthermore, because AAESS δ13C values are generally not altered by consumers, AAESS δ13C fingerprints appear to persist across trophic levels and to be identifiable in top consumers [87,88,91]. We note, however, that the previously-discussed potential contribution of AAESS from the gut microbiome to host protein metabolism should be considered when interpreting δ13C fingerprints.
To date, fingerprinting has been primarily utilized in marine ecology. The first application assessed the relative importance of terrestrial, marine, and microbial production to consumers living in a mangrove ecosystem [89]. Fingerprinting was also used by Larsen et al. [90] to quantify the amino acid contribution from bacteria to organic carbon in ancient Peruvian marine sediments and to infer historical ecosystem processes. McMahon et al. [91] measured producer fingerprints in coral reef fishes to demonstrate that shelf vs. oceanic reefs differ in the degree to which consumers use benthic, pelagic, or recycled carbon. Most recently, Elliott Smith et al. [88] applied this approach to test for connectivity between inter- and subtidal components of a nearshore ecosystem in south central Alaska, finding differences among trophic levels in the degree of subtidal kelp-derived nutrients. Outside of marine ecosystems, this approach has been used to evaluate the importance of terrestrial versus instream primary production for freshwater fishes [92] and the sources of AAESS for detritus feeders in terrestrial soils [68,93].
5. CSIA Limitations
To fully achieve the promise of CSIA in addressing a variety of ecological and physiological questions, further technical refinement is needed via both laboratory experiments and field studies. In particular, the values of β and TDF in Equation (1) require attention. Based on a limited amount of published data for a combination of cultivated and wild-collected primary producers, β values appear to vary among marine phytoplankton, C3 plants, and C4 plants [37]; however, the paucity of available data does not allow for an estimate of how β varies within these general classes of producers. Furthermore, we currently lack β values for many important groups of producers, including marine and freshwater macroalgae, seagrass, aquatic macrophytes, and CAM plants.
In regard to TDF values, some reviews have suggested that they are approximately constant. For example, δ15NGlu − δ15NPhe for consumers in marine ecosystems were reported to be ~7.5‰ for each trophic level increase [37]. However, more recent meta-analyses that include data from a larger number of laboratory and field-based studies show that TDF values are quite variable and are correlated to consumer physiology [31,62,94], especially differences in how animals excrete nitrogen. Surprisingly, the fact that ammonia requires few steps for biosynthesis and is rapidly excreted, while urea production requires additional steps and may be retained or recycled, has been used to explain opposite patterns: that the TDF of ammonia-excreting animals are lower than urea-excreting animals in bulk tissue analyses [3], and higher for trophic AA in CSIA [74]. This inconsistency has yet to be explained; δ15N values for arginine, a nitrogen-rich AA that is not commonly measured in nitrogen-focused CSIA studies, would potentially be informative. Indeed, for all CSIA studies, researchers should bear in mind that dynamics of carbon, nitrogen, and hydrogen can be influenced by AA that are not commonly measured. Some CSIA studies have also suggested that multiple pairs of trophic-source AA (e.g., Glu-Phe and Pro-Phe) should be used to address the issue of inherent variation in physiologically-mediated discrimination and to provide more tailored taxon-specific estimates of trophic level based on AA δ15N analysis [74,94]. In general, CSIA data from a greater variety of species and ecosystems will enable comparative analyses that will help reveal the mechanisms driving variation in isotope values.
Similar to AA-based estimates of trophic level, AA fingerprinting requires additional data collected from wild contexts in addition to controlled feeding experiments on a wider range of taxa. Currently, not enough information is available to broadly assess the uniqueness of fingerprints across time and space among the organisms—plants, algae, bacteria, and fungi—that synthesize AAESS de novo. To our knowledge, only a single study has examined AAESS δ13C fingerprints among primary producers at local scales [88]; other studies have used global compilations of fingerprints from various AAESS synthesizers (e.g., [85,87,89,90]). It is also unclear at what taxonomic and functional scales fingerprints become indistinguishable. Furthermore, no study has validated via controlled feeding experiments the persistence of AAESS fingerprints from dietary protein into consumer tissue. Eliminating these gaps in our understanding will require greater inclusion of physiological and biochemical mechanisms, which offers tremendous opportunities for refining and expanding this approach to address fundamental questions regarding energy flow in community and ecosystem ecology.
Another limitation and potential research opportunity are estimates of the isotopic incorporation rates for individual AA and FA, which are fundamental to applications of this approach to wild animal populations because it is paramount to understand the timeframe over which isotope values integrate ecological information. There is extensive literature on isotopic incorporation in bulk tissues (e.g., [12,95,96]) in which the isotopic composition of a consumer diet is changed in a feeding experiment and tissues are collected at regular intervals to quantify the incorporation rate, residence time, and half-life of isotopes. Studies of bluefin tuna (Thunnus orientalis; [97]), white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei; [98]), and zebra finches (Taeniopygia guttata; [40]) indicate that there is substantial variation among AA and FA in incorporation rates, and that rates can be altered by demands such as increased muscular activity. Additional studies should test if this variation is consistent across taxa and through time. Results will allow ecologists and physiologists to better understand the time reflected in the isotopic composition of compounds mediated by physiological processes associated with nutrient assimilation and tissue synthesis. Such information from controlled settings is essential for the physiological and ecological interpretations of CSIA data collected from wild animals.
Lastly, as CSIA becomes more widely adopted, it is important that researchers standardize sample preparation protocols and share internal reference materials. This is especially important for derivatization [53] and methylation [39] techniques which add carbon and/or hydrogen to AA and FA, and which require careful post analysis corrections and data reduction. In addition, because CSIA data for AA have been generated using multiple derivatization techniques [48], meta-analyses will require direct comparisons of materials prepared with each technique so that differences resulting from methodology alone can be reconciled.
6. CSIA Future Directions
In addition to the opportunities highlighted in the section above, several recent technical advances in the application of CSIA to ecological and physiological questions have opened new avenues of research. Fogel et al. [99] were the first to report hydrogen isotope data for individual AA, using experiments on cultured E. coli to show that the incorporation of hydrogen from environmental water into both AANESS and AAESS during de novo synthesis varied with media protein content. As expected, E. coli used a higher proportion of environmental water to synthesize AA when supplied media did not contain protein. In the treatment containing protein, the degree of direct routing of hydrogen from media into E. coli was higher for AAESS than for AANESS, even though as prokaryotes E. coli can synthesize all forms de novo. Lastly, the proportion of water used to synthesize alanine (AANESS) was high (40–50%) regardless of media treatment. Collectively, these patterns suggest that AA hydrogen isotope analysis may enable ecologists to simultaneously trace both dietary and environmental water sources of hydrogen to an individual animal.
A second technical advance that promises to broaden the use of CSIA is position-specific isotope analysis. Using a high-pressure liquid chromatography system interfaced with an IRMS, Fry et al. [100] automated a ninhydrin-based method for separating the carboxyl carbon atom and measuring its carbon isotope composition at a level of analytical precision (<0.5‰) that will likely make it very useful for tracing key biochemical reactions. While the carboxyl carbon represents a single atom in an AA skeleton containing up to nine carbons (i.e., in Phe), it is arguably the most labile carbon because it is directly involved in a number of (de)carboxylation reactions involving AA precursors in the Calvin cycle, glycolysis, and the TCA cycle [101]. This relatively high degree of mobility likely produces significant isotopic fractionation that can be now traced with position-specific isotope analysis. Additional methods are being developed for measuring the δ13C of carbon in specific positions and sections of AA, and over the next decade this capability will likely open new frontiers for isotope ecology, enabling ecologists and physiologists to address novel questions.
In many respects, the development of CSIA is analogous to that of bulk tissue isotope analysis. In the early stages of widespread adoption of bulk tissue analysis in animal biology, Gannes et al. [102] predicted explosive growth in the use of this method and exhorted researchers to complement their field applications with controlled experimental studies to validate key assumptions. A decade later, Martínez del Rio et al. [7] were pleased to report that bulk tissue isotope analysis had indeed flourished and was now supported by a broader suite of experimental evidence for the mechanisms driving observed patterns. Here, we echo this prediction and exhortation for CSIA. In the last five years, there has been a dramatic increase in the number of studies using CSIA to answer biological questions (e.g., [31]) and this tool is poised to make significant contributions to ecology and physiology. In addition to novel applications, we urge researchers to continue developing theoretical and experimental validations of the processes that shape AA and FA isotope values.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at http://www.mdpi.com/1424-2818/11/1/8/s1, Table S1: Published studies of controlled feeding experiments which present carbon isotope discrimination factors (Δ13CC-D, or δ13CConsumer tissue − δ13CDiet item) for consumers which were thought to be in steady state with their known diet, Table S2: Published studies of controlled feeding experiments and well-constrained field collections which present nitrogen isotope discrimination factors (Δ15NC-D, or δ15NConsumer tissue − δ15NDiet item) for consumers which were thought to be in steady state with their known diet.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and data curation, J.P.W.; Writing—original draft preparation, J.P.W., E.A.E.S, A.C.B., and S.D.N.; Writing—review and editing, J.P.W., E.A.E.S, A.C.B., and S.D.N.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
We are deeply grateful to Marilyn Fogel for her intellectual and technical contributions to develop the field of compound-specific isotope analysis, and for her input to many of our research projects.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Michener, R.; Lajtha, K. (Eds.) Stable Isotopes in Ecology and Environmental Science, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Malden, MA, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-1-4051-2680-9. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, J.F. Stable isotopes of carbon and nitrogen in the study of avian and mammalian trophic ecology. Can. J. Zool. 2000, 78, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderklift, M.A.; Ponsard, S. Sources of variation in consumer-diet 15N enrichment: A meta-analysis. Oecologia 2003, 136, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minagawa, M.; Wada, E. Stepwise enrichment of N-15 along food-chains—Further evidence and the relation between delta-N-15 and animal age. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1984, 48, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobson, K.A.; Atwell, L.; Wassenaar, L.I. Influence of drinking water and diet on the stable-hydrogen isotope ratios of animal tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 8003–8006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, G.J.; Wassenaar, L.I.; Hobson, K.A. Global application of stable hydrogen and oxygen isotopes to wildlife forensics. Oecologia 2005, 143, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez del Rio, C.M.; Wolf, N.; Carleton, S.A.; Gannes, L.Z. Isotopic ecology ten years after a call for more laboratory experiments. Biol. Rev. 2009, 84, 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Layman, C.A.; Arrington, D.A.; Montana, C.G.; Post, D.M. Can stable isotope ratios provide for community-wide measures of trophic structure? Ecology 2007, 88, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsome, S.D.; Martinez del Rio, C.; Bearhop, S.; Phillips, D.L. A niche for isotopic ecology. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2007, 5, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, M.J.; McDonald, R.A.; van Veen, F.J.F.; Kelly, S.D.; Rees, G.; Bearhop, S. Application of nitrogen and carbon stable isotopes (δ15N and δ13C) to quantify food chain length and trophic structure. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsome, S.D.; Tinker, M.T.; Monson, D.H.; Oftedal, O.T.; Ralls, K.; Staedler, M.M.; Fogel, M.L.; Estes, J.A. Using stable isotopes to investigate individual diet specialization in California sea otters (Enhydra lutris nereis). Ecology 2009, 90, 961–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez del Rio, C.; Carleton, S.A. How fast and how faithful: The dynamics of isotopic incorporation into animal tissues. J. Mammal. 2012, 93, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busquets-Vass, G.; Newsome, S.D.; Calambokidis, J.; Serra-Valente, G.; Jacobsen, J.K.; Aguíñiga-García, S.; Gendron, D. Estimating blue whale skin isotopic incorporation rates and baleen growth rates: Implications for assessing diet and movement patterns in mysticetes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farquhar, G.D.; O’Leary, M.H.; Berry, J.A. On the relationship between carbon isotope discrimination and the intercellular carbon dioxide concentration in leaves. Functional Plant Biol. 1982, 9, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, M.H. Carbon isotopes in photosynthesis. BioScience 1988, 38, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, T.E.; Mambelli, S.; Plamboeck, A.H.; Templer, P.H.; Tu, K.P. Stable isotopes in plant ecology. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2002, 33, 507–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrose, S.H. Preparation and characterization of bone and tooth collagen for isotopic analysis. J. Archaeol. Sci. 1990, 17, 431–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniro, M.J.; Epstein, S. Mechanism of carbon isotope fractionation associated with lipid synthesis. Science 1977, 197, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabana, G.; Rasmussen, J.B. Comparison of aquatic food chains using nitrogen isotopes. PNAS 1996, 93, 10844–10847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, C.; Jennings, J.T.; Barry, S. Environmental correlates of large-scale spatial variation in the δ13C of marine animals. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 81, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlay, J.C. Stable-carbon-isotope ratios of river biota: Implications for energy flow in lotic food webs. Ecology 2001, 82, 1052–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershey, A.E.; Northington, R.M.; Finlay, J.C.; Peterson, B.J. Stable isotopes in stream food webs. In Methods in Stream Ecology; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Newsome, S.D.; Clementz, M.T.; Koch, P.L. Using stable isotope biogeochemistry to study marine mammal ecology. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2010, 26, 509–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.N.; Buck, C.L.; Barnes, B.M.; O’Brien, D.M. A test of alternative models for increased tissue nitrogen isotope ratios during fasting in hibernating arctic ground squirrels. J. Exp. Biol. 2012, 215, 3354–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, R.W.; Wyse, G.A.; Anderson, M. Animal Physiology, 2nd ed.; Sinauer Associates, Inc.: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G. Amino acids: Metabolism, functions, and nutrition. Amino Acids 2009, 37, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, S.H.; Loomis, W.F. Retention and loss of amino acid biosynthetic pathways based on analysis of whole-genome sequences. Eukaryot Cell 2006, 5, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austic, R.E. Nutritional and metabolic interrelationships of arginine, glutamic acid and proline in the chicken. Fed. Proc. 1976, 35, 1914–1916. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koutsos, E.A.; Matson, K.D.; Klasing, K.C. Nutrition of birds in the order Psittaciformes: A review. J. Avian Med. Surg. 2001, 15, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, A.; Teshima, S. Essential amino acids of the prawn. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1981, 47, 1375–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, K.W.; McCarthy, M.D. Embracing variability in amino acid δ15N fractionation: Mechanisms, implications, and applications for trophic ecology. Ecosphere 2016, 7, e01511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, T.C. ‘Trophic’ and ‘source’ amino acids in trophic estimation: A likely metabolic explanation. Oecologia 2017, 184, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, E.J.; Nott, H.M.R.; Earle, K.E. Dietary glycine: Its importance in growth and development of the budgerigar (Melopsittacus undulatus). J. Nutr. 1994, 124, 2555S–2558S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, K.W.; Polito, M.J.; Abel, S.; McCarthy, M.D.; Thorrold, S.R. Carbon and nitrogen isotope fractionation of amino acids in an avian marine predator, the gentoo penguin (Pygoscelis papua). Ecol. Evol. 2015, 5, 1278–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newsome, S.D.; Fogel, M.L.; Kelly, L.; Martínez del Rio, C. Contributions of direct incorporation from diet and microbial amino acids to protein synthesis in Nile tilapia. Funct. Ecol. 2011, 25, 1051–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsome, S.D.; Wolf, N.; Peters, J.; Fogel, M.L. Amino acid δ13C analysis shows flexibility in the routing of dietary protein and lipids to the tissue of an omnivore. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2014, 54, 890–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chikaraishi, Y.; Steffan, S.A.; Ogawa, N.O.; Ishikawa, N.F.; Sasaki, Y.; Tsuchiya, M.; Ohkouchi, N. High-resolution food webs based on nitrogen isotopic composition of amino acids. Ecol. Evol. 2014, 4, 2423–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, B.T.; Petzke, K.J. The dietary protein paradox and threonine 15N-depletion: Pyridoxal-5′-phosphate enzyme activity as a mechanism for the δ15N trophic level effect. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 31, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budge, S.M.; Wang, S.W.; Hollmén, T.E.; Wooller, M.J. Carbon isotopic fractionation in eider adipose tissue varies with fatty acid structure: Implications for trophic studies. J. Exp. Biol. 2011, 214, 3790–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, W.A.; Whiteman, J.P.; Cooper-Mullin, C.; Newsome, S.D.; McWilliams, S.R. The dynamics of individual fatty acids in muscle fat stores and membranes of a songbird are affected by exercise and have functional and ecological importance. Physiol. Biochem. Zool. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain, P.M.; Bull, I.D.; Black, H.I.J.; Ineson, P.; Evershed, R.P. Lipid content and carbon assimilation in Collembola: Implications for the use of compound-specific carbon isotope analysis in animal dietary studies. Oecologia 2004, 139, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruess, L.; Chamberlain, P.M. The fat that matters: Soil food web analysis using fatty acids and their carbon stable isotope signature. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1898–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budge, S.M.; Iverson, S.J.; Koopman, H.N. Studying trophic ecology in marine ecosystems using fatty acids: A primer on analysis and interpretation. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2006, 22, 759–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsome, S.D.; Chivers, S.J.; Berman Kowalewski, M. The influence of lipid-extraction and long-term DMSO preservation on carbon (δ13 C) and nitrogen (δ15 N) isotope values in cetacean skin. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2018, 34, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.L.; Koch, P.L. Methods to collect, preserve, and prepare elasmobranch tissues for stable isotope analysis. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2012, 95, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, B.; Dempson, J.B.; Power, M. The effects of preservation on fish tissue stable isotope signatures. J. Fish Biol. 2006, 69, 1595–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobson, K.A.; Gloutney, M.L.; Gibbs, H.L. Preservation of blood and tissue samples for stable-carbon and stable-nitrogen isotope analysis. Can. J. Zool. 1997, 75, 1720–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, R.G.; He, S.; Yarnes, C.T. Compound-specific δ13C and δ15N analysis of amino acids: A rapid, chloroformate-based method for ecological studies. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2014, 28, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCullagh, J.S.O.; Juchelka, D.; Hedges, R.E.M. Analysis of amino acid 13C abundance from human and faunal bone collagen using liquid chromatography/isotope ratio mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 2761–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Stanley, G.H.S. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 497–509. [Google Scholar]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiropoulos, M.A.; Tonn, W.M.; Wassenaar, L.I. Effects of lipid extraction on stable carbon and nitrogen isotope analyses of fish tissues: Potential consequences for food web studies. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2004, 13, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silfer, J.A.; Engel, M.H.; Macko, S.A.; Jumeau, E.J. Stable carbon isotope analysis of amino acid enantiomers by conventional isotope ratio mass spectrometry and combined gas chromatography/isotope ratio mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 1991, 63, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelung, W.; Zhang, X. Determination of amino acid enantiomers in soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, K.W.; Fogel, M.L.; Johnson, B.J.; Houghton, L.A.; Thorrold, S.R. A new method to reconstruct fish diet and movement patterns from δ13C values in otolith amino acids. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 68, 1330–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metges, C.C.; Petzke, K.J.; Hennig, U. Gas chromatography/combustion/isotope ratio mass spectrometric comparison of N-acetyl- and N-pivaloyl amino acid esters to measure 15N isotopic abundances in physiological samples: A pilot study on amino acid synthesis in the upper gastro-intestinal tract of minipigs. J. Mass Spectrom. 1996, 31, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chikaraishi, Y.; Kashiyama, Y.; Ogawa, N.O.; Kitazato, H.; Ohkouchi, N. Metabolic control of nitrogen isotope composition of amino acids in macroalgae and gastropods: Implications for aquatic food web studies. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 342, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hušek, P. Rapid derivatization and gas chromatographic determination of amino acids. J. Chromatogr. A 1991, 552, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, D.M.; Fogel, M.L.; Boggs, C.L. Renewable and nonrenewable resources: Amino acid turnover and allocation to reproduction in Lepidoptera. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 4413–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarnes, C.T.; Herszage, J. The relative influence of derivatization and normalization procedures on the compound-specific stable isotope analysis of nitrogen in amino acids. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 31, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chikaraishi, Y.; Steffan, S.A.; Takano, Y.; Ohkouchi, N. Diet quality influences isotopic discrimination among amino acids in an aquatic vertebrate. Ecol. Evol. 2015, 5, 2048–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, K.W.; Thorrold, S.R.; Elsdon, T.S.; McCarthy, M.D. Trophic discrimination of nitrogen stable isotopes in amino acids varies with diet quality in a marine fish: Trophic discrimination of amino acids. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2015, 60, 1076–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howland, M.R.; Corr, L.T.; Young, S.M.M.; Jones, V.; Jim, S.; Van Der Merwe, N.J.; Mitchell, A.D.; Evershed, R.P. Expression of the dietary isotope signal in the compound-specific δ13C values of pig bone lipids and amino acids. Int. J. Osteoarchaeol. 2003, 13, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jim, S.; Jones, V.; Ambrose, S.H.; Evershed, R.P. Quantifying dietary macronutrient sources of carbon for bone collagen biosynthesis using natural abundance stable carbon isotope analysis. Br. J. Nutr. 2006, 95, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarroux, A.; Ehrich, D.; Lecomte, N.; Jardine, T.D.; Bety, J.; Berteaux, D. Sensitivity of stable isotope mixing models to variation in isotopic ratios: Evaluating consequences of lipid extraction. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2010, 1, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayayee, P.A.; Jones, S.C.; Sabree, Z.L. Can 13C stable isotope analysis uncover essential amino acid provisioning by termite-associated gut microbes? PeerJ 2015, 3, e1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayayee, P.A.; Larsen, T.; Sabree, Z. Symbiotic essential amino acids provisioning in the American cockroach, Periplaneta americana (Linnaeus) under various dietary conditions. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, T.; Ventura, M.; Maraldo, K.; Triadó-Margarit, X.; Casamayor, E.O.; Wang, Y.V.; Andersen, N.; O’Brien, D.M. The dominant detritus-feeding invertebrate in Arctic peat soils derives its essential amino acids from gut symbionts. J. Anim. Ecol. 2016, 85, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newsome, S.D.; Feeser, K.L.; Bradley, C.J.; Wolf, C.; Takacs-Vesbach, C.; Fogel, M.L. Quantifying the role of the gut microbiome in host essential amino acid metabolism. ISME J. in review.
- Metges, C.C. Contribution of microbial amino acids to amino acid homeostasis of the host. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1857S–1864S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G. Intestinal mucosal amino acid catabolism. J. Nutr. 1998, 128, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteman, J.P.; Kim, S.L.; McMahon, K.W.; Koch, P.L.; Newsome, S.D. Amino acid isotope discrimination factors for a carnivore: Physiological insights from leopard sharks and their diet. Oecologia 2018, 188, 977–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuche-Pascual, M.T.; Lazo, J.P.; Ruiz-Cooley, R.I.; Herzka, S.Z. Amino acid-specific δ5N trophic enrichment factors in fish fed with formulated diets varying in protein quantity and quality. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 9192–9217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.M.; Popp, B.N.; Winder, M. Meta-analysis of amino acid stable nitrogen isotope ratios for estimating trophic position in marine organisms. Oecologia 2015, 178, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randall, D.J.; Tsui, T.K.N. Ammonia toxicity in fish. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 45, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, L.R.; Koch, P.L.; Harvey, J.; McCarthy, M.D. Nitrogen isotope fractionation in amino acids from harbor seals: Implications for compound-specific trophic position calculations. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Series 2013, 482, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto-Curiel, F.; Focken, U.; D’Abramo, L.R.; Viana, M.T. Metabolism of Seriola lalandi during starvation as revealed by fatty acid analysis and compound-specific analysis of stable isotopes within amino acids. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffan, S.A.; Chikaraishi, Y.; Currie, C.R.; Horn, H.; Gaines-Day, H.R.; Pauli, J.N.; Zalapa, J.E.; Ohkouchi, N. Microbes are trophic analogs of animals. PNAS 2015, 112, 15119–15124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClelland, J.W.; Montoya, J.P. Trophic relationships and the nitrogen isotopic composition of amino acids in plankton. Ecology 2002, 83, 2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffan, S.A.; Chikaraishi, Y.; Horton, D.R.; Ohkouchi, N.; Singleton, M.E.; Miliczky, E.; Hogg, D.B.; Jones, V.P. Trophic hierarchies illuminated via amino acid isotopic analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chikaraishi, Y.; Ogawa, N.O.; Ohkouchi, N. Further evaluation of the trophic level estimation based on nitrogen isotopic composition of amino acids. In Earth, Life, and Isotopes; Kyoto University Press: Kyoto, Janpan, 2010; Volume 415, pp. 37–51. [Google Scholar]
- Dale, J.; Wallsgrove, N.; Popp, B.; Holland, K. Nursery habitat use and foraging ecology of the brown stingray Dasyatis lata determined from stomach contents, bulk and amino acid stable isotopes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Series 2011, 433, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seminoff, J.A.; Benson, S.R.; Arthur, K.E.; Eguchi, T.; Dutton, P.H.; Tapilatu, R.F.; Popp, B.N. Stable isotope tracking of endangered sea turtles: Validation with satellite telemetry and δ15N analysis of amino acids. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Cooley, R.I.; Koch, P.L.; Fiedler, P.C.; McCarthy, M.D. Carbon and nitrogen isotopes from top predator amino acids reveal rapidly shifting ocean biochemistry in the outer California Current. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.H.; O’Brien, D.M.; Emerson, D.; Sun, H.; McDonald, G.D.; Salgado, A.; Fogel, M.L. An examination of the carbon isotope effects associated with amino acid biosynthesis. Astrobiology 2006, 6, 867–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, T.; Taylor, D.L.; Leigh, M.B.; O’Brien, D.M. Stable isotope fingerprinting: A novel method for identifying plant, fungal, or bacterial origins of amino acids. Ecology 2009, 90, 3526–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, T.; Ventura, M.; Andersen, N.; O’Brien, D.M.; Piatkowski, U.; McCarthy, M.D. Tracing carbon sources through aquatic and terrestrial food webs using amino acid stable isotope fingerprinting. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott Smith, E.A.; Harrod, C.; Newsome, S.D. The importance of kelp to an intertidal ecosystem varies by trophic level: Insights from amino acid δ13C analysis. Ecosphere 2018, 9, e02516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, T.; Wooller, M.J.; Fogel, M.L.; O’Brien, D.M. Can amino acid carbon isotope ratios distinguish primary producers in a mangrove ecosystem? Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 26, 1541–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, T.; Bach, L.T.; Salvatteci, R.; Wang, Y.V.; Andersen, N.; Ventura, M.; McCarthy, M.D. Assessing the potential of amino acid 13C patterns as a carbon source tracer in marine sediments: Effects of algal growth conditions and sedimentary diagenesis. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 4979–4992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, K.W.; Thorrold, S.R.; Houghton, L.A.; Berumen, M.L. Tracing carbon flow through coral reef food webs using a compound-specific stable isotope approach. Oecologia 2016, 180, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorp, J.H.C.; Bowes, R.E. Carbon sources in riverine food webs: New evidence from amino acid isotope techniques. Ecosystems 2016, 20, 1029–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, T.; Pollierer, M.M.; Holmstrup, M.; D’Annibale, A.; Maraldo, K.; Andersen, N.; Eriksen, J. Substantial nutritional contribution of bacterial amino acids to earthworms and enchytraeids: A case study from organic grasslands. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 99, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, C.J.; Wallsgrove, N.J.; Choy, C.A.; Drazen, J.C.; Hetherington, E.D.; Hoen, D.K.; Popp, B.N. Trophic position estimates of marine teleosts using amino acid compound specific isotopic analysis. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2015, 13, 476–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieszen, L.L.; Boutton, T.W.; Tesdahl, K.G.; Slade, N.A. Fractionation and turnover of stable carbon isotopes in animal tissues: Implications for 13C analysis of diet. Oecologia 1983, 57, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerling, T.E.; Ayliffe, L.K.; Dearing, M.D.; Ehleringer, J.R.; Passey, B.H.; Podlesak, D.W.; Torregrossa, A.-M.; West, A.G. Determining biological tissue turnover using stable isotopes: The reaction progress variable. Oecologia 2007, 151, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, C.J.; Madigan, D.J.; Block, B.A.; Popp, B.N. Amino acid isotope incorporation and enrichment factors in Pacific Bluefin Tuna, Thunnus orientalis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downs, E.; Popp, B.; Holl, C. Nitrogen isotope fractionation and amino acid turnover rates in the Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 516, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogel, M.L.; Griffin, P.L.; Newsome, S.D. Hydrogen isotopes in individual amino acids reflect differentiated pools of hydrogen from food and water in Escherichia coli. PNAS 2016, 113, E4648–E4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, B.; Carter, J.F.; Yamada, K.; Yoshida, N.; Juchelka, D. Position-specific 13C/12C analysis of amino acid carboxyl groups—Automated flow-injection analysis based on reaction with ninhydrin. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2018, 32, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, D.L.; Cox, M.M. Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry, 5th ed.; W. H. Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 2008; ISBN 978-0-7167-7108-1. [Google Scholar]
- Gannes, L.Z.; O’Brien, D.M.; Martinez del Rio, C.M. Stable isotopes in animal ecology: Assumptions, caveats, and a call for more laboratory experiments. Ecology 1997, 78, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).