Revisiting the Coordination Chemistry of Molybdenum(V): Novel Complexes with Pyrazinoate and Picolinate Ligands
Abstract
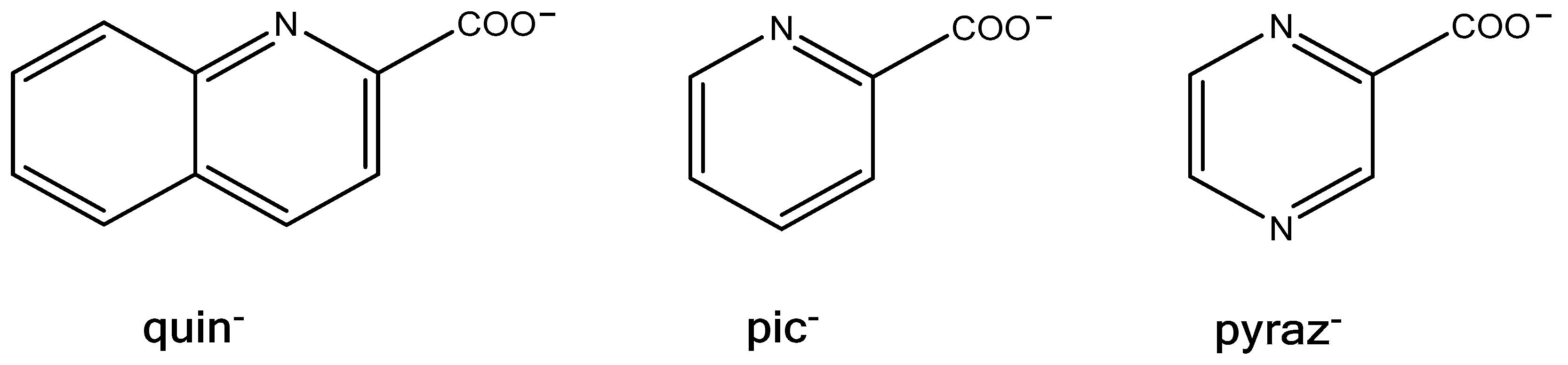
1. Introduction
2. Discussion
2.1. Synthetic Considerations
2.2. Crystal Structures
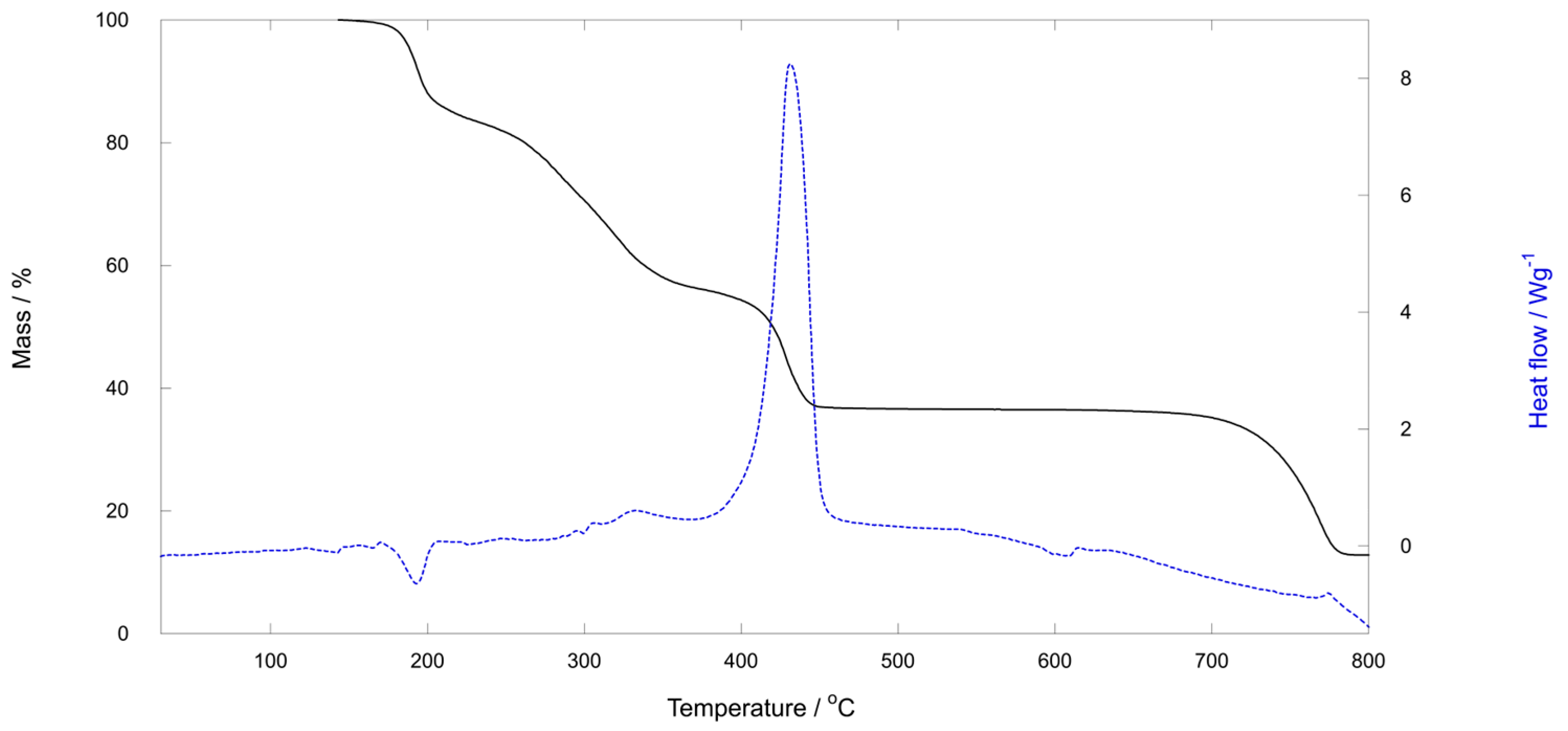
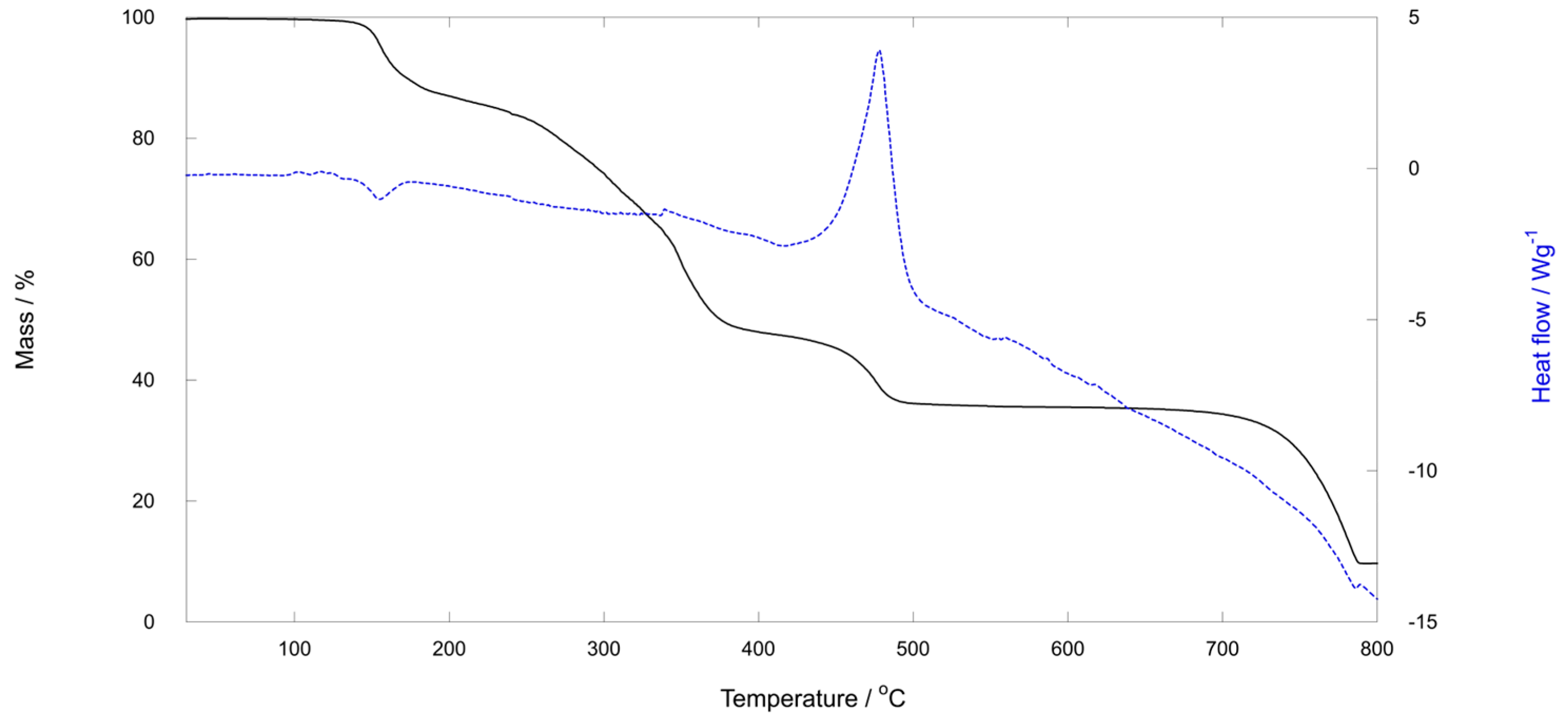
2.3. TG Analysis
3. Experimental
3.1. General Remarks
3.2. X-Ray Crystallography
3.3. Preparation of (pyH)2[Mo2O4Cl2(pic)2]·CH3CN (1)
3.4. Preparation of (pyH)2[Mo2O4Cl2(pic)2]·CH3CH2CN (2)
3.5. Preparation of (pyH)2[Mo2O4Cl2(pyraz)2]·CH3CN (3)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Modec, B.; Podjed, N.; Šturm, J. Oxidation vs. coordination chemistry of the {MoV2O4}2+ species: A structural study. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1253, 132246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, H.K.; Klemperer, W.G.; Marquart, T.A. High-nuclearity oxomolybdenum(V) complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1993, 128, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, M.; Patra, S.K.; Bera, J.K. Oxidative route to polyoxomolybdates from quadruply bonded [MoIIMoII] precursor: Structural characterization of a tetranuclear cluster [Mo4Cl5O8(pyNP)2] (pyNP=(2-(2-pyridyl)1,8-naphthyridine)). Polyhedron 2007, 26, 1597–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguado, R.; Escribano, J.; Pedrosa, M.R.; De Cian, A.; Sanz, R.; Arnáiz, F.J. Binuclear oxomolybdenum(V) chlorides: Molecular structure of Mo2O4Cl2(DMF)4 and Mo2O4Cl2(bipy)2·DMF. Polyhedron 2007, 26, 3842–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyashenko, G.; Herbst-Irmer, R.; Jancik, V.; Pal, A.; Mösch-Zanetti, N.C. Molybdenum oxo and imido complexes of β-diketiminate ligands: synthesis and structural aspects. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modec, B.; Dolenc, D.; Kasunič, M. Complexation of molybdenum(V) with glycolic acid: An unusual orientation of glycolato ligand in {Mo2O4}2+ complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 3625–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compain, J.-D.; Dolbecq, A.; Marrot, J.; Mialane, P.; Sécheresse, F. Characterization of tetra, dodeca and tetradeca MoV polyoxometalate wheels structured by etidronate ligands. C. R. Chimie 2010, 13, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota Merelo de Aguiar, S.R.; Stöger, B.; Weil, M.; Kirchner, K. Tetrakis(μ2-diphenylphosphinato-κ2O,O′)tetra-μ3-oxido-tetraoxidohexamolybdenum(V). IUCrData 2016, 1, x160036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.C.; Neves, P.; Cunha-Silva, L.; Valente, A.A.; Gonçalves, I.S.; Pillinger, M. Oxidomolybdenum complexes for acid catalysis using alcohols as solvents and reactants. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 5207–5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-Y.; Jin, W.-T.; Chen, H.-B.; Zhou, Z.-H. Comparison of hydroxycarboxylato imidazole molybdenum(IV) complexes and nitrogenase protein structures: Indirect evidence for the protonation of homocitrato FeMo-cofactors. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 7412–7421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, F.A.; Morehouse, S.M. The molecular structure of a diamagnetic, doubly oxygen-bridged, binuclear complex of molybdenum(V) containing a metal-metal bond. Inorg. Chem. 1965, 4, 1377–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modec, B.; Brenčič, J.V. From small {Mo2O4}2+ aggregates to infinite solids. J. Cluster Sci. 2002, 13, 279–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groom, C.R.; Bruno, I.J.; Lightfoot, M.P.; Ward, S.C. The Cambridge Structural Database. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B 2016, 72, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modec, B.; Dolenc, D.; Brenčič, J.V. New molybdenum(V) complexes based on the {Mo2O4}2+ structural core with esters or anions of malonic and succinic acid. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2007, 360, 663–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Hu, F.; Wang, J.; Niu, J. Carboxylate covalently modified polyoxometalates: From synthesis, structural diversity to applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 378, 281–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaporte, S.; Abánades Lázaro, I.; López-Cabrelles, J.; Mazarakioti, E.C.; Chebourou, S.; Vitórica-Yrezábal, I.J.; Giménez-Marqués, M.; Mínguez Espallargas, G. Imparting structural robustness of metal–organic cages based on oxo-dimolybdenum clusters. Dalton Trans. 2023, 52, 15682–15687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modec, B.; Brenčič, J.V. Novel methanol-containing oxomolybdate(V) complexes: Synthesis and structural characterisation of intermediates in the formation of {Mo2O4}2+ clusters from [MoOCl4(H2O)]− and [MoOBr4]− precursors. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 2005, 1698–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, G.B.; Phillips, R.J. Relationships between the carbon-oxygen stretching frequencies of carboxylato complexes and the type of carboxylate coordination. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1980, 33, 227–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinze, K.; Fischer, A. Polymer-supported dioxido-MoVI complexes as truly functional molybdenum oxotransferase model systems. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 2007, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, H.E.; Kotlyar, V.; Nudelman, A. NMR chemical shifts of common laboratory solvents as trace impurities. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 7512–7515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willcott, M.R. MestRe Nova. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 13180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agilent. CrysAlis PRO; Agilent Technologies Ltd.: Yarnton, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourhis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.K.; Puschmann, H. Olex2: A complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT—Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C.F.; Sovago, I.; Cottrell, S.J.; Galek, P.T.A.; McCabe, P.; Pidcock, E.; Platings, M.; Shields, G.P.; Stevens, J.S.; Towler, M.; et al. Mercury 4.0: From visualization to analysis, design and prediction. J. Appl. Cryst. 2020, 53, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
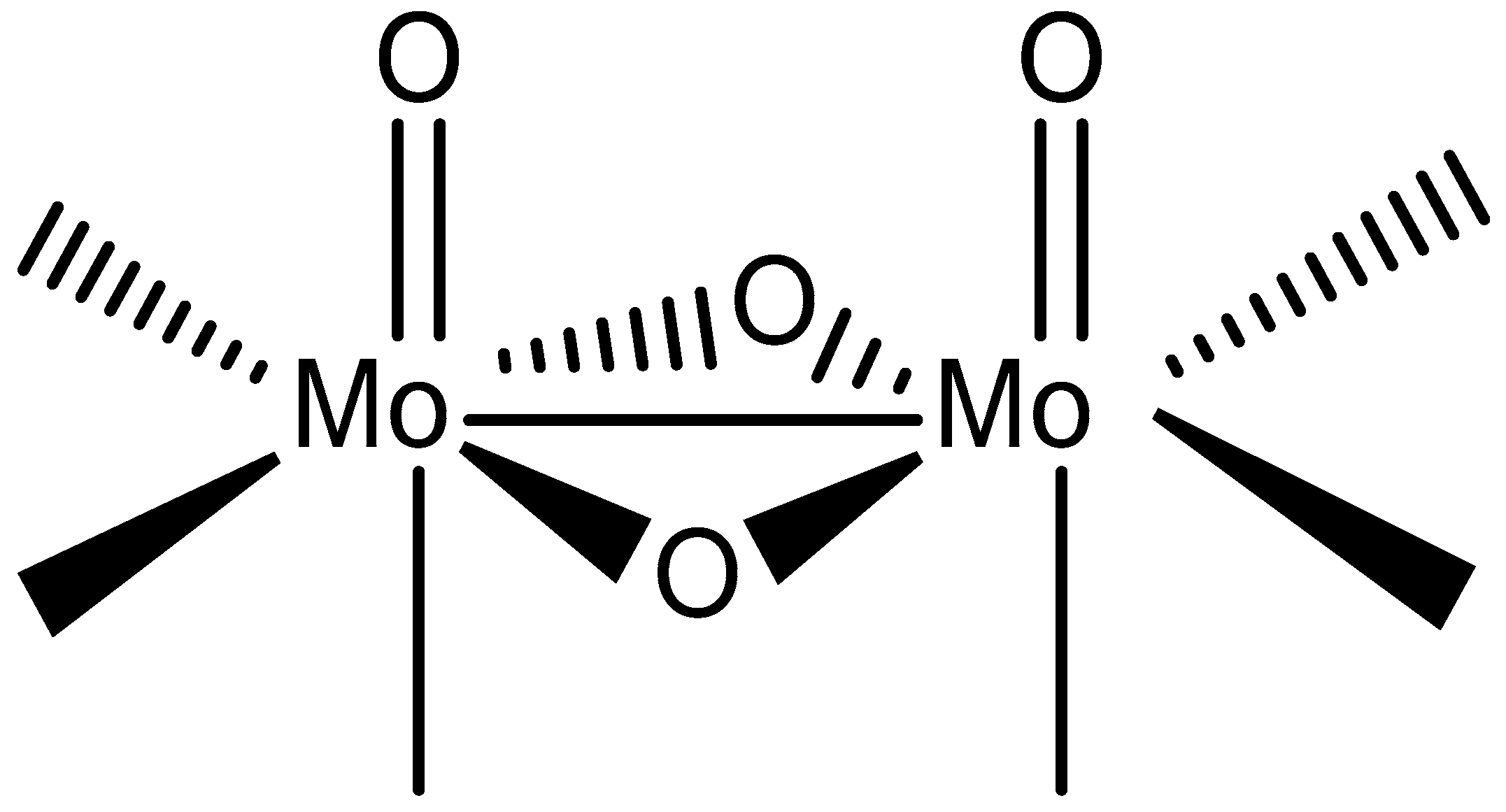
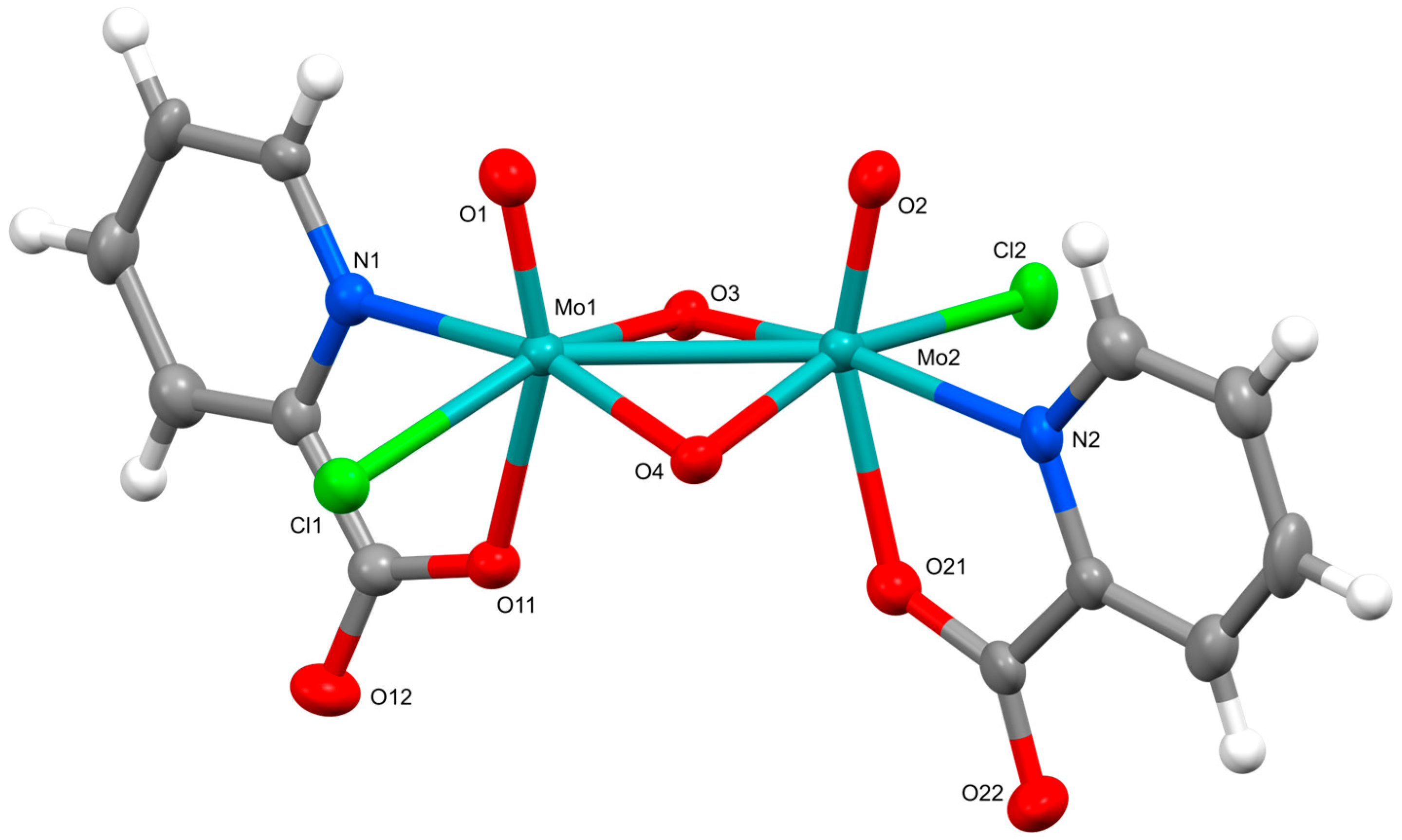
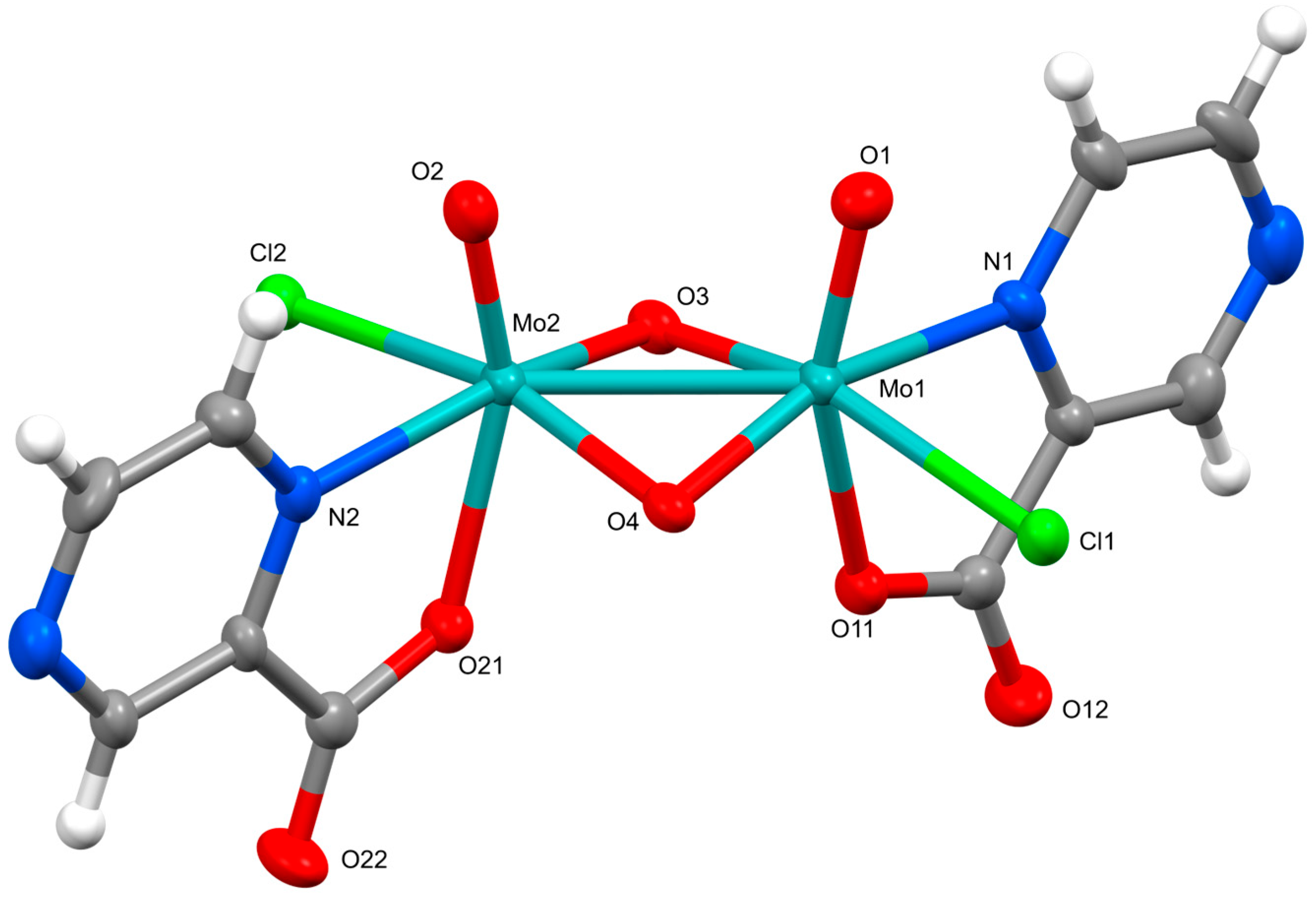
| [Mo2O4Cl2(pic)2]2− in 1 | [Mo2O4Cl2(pyraz)2]2− in 3 | |
|---|---|---|
| Mo–Mo | 2.5704(6) | 2.5592(6) |
| “fold” angle * | 151.1(2) | 151.4(3) |
| Mo–Cl | 2.4653(19), 2.4750(18) | 2.4678(19), 2.469(2) |
| Mo–N | 2.238(6), 2.254(6) | 2.256(7), 2.271(7) |
| Mo–O(COO–) | 2.155(5), 2.180(5) | 2.154(6), 2.202(6) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Modec, B.; Podjed Rihtaršič, N. Revisiting the Coordination Chemistry of Molybdenum(V): Novel Complexes with Pyrazinoate and Picolinate Ligands. Molbank 2025, 2025, M2079. https://doi.org/10.3390/M2079
Modec B, Podjed Rihtaršič N. Revisiting the Coordination Chemistry of Molybdenum(V): Novel Complexes with Pyrazinoate and Picolinate Ligands. Molbank. 2025; 2025(4):M2079. https://doi.org/10.3390/M2079
Chicago/Turabian StyleModec, Barbara, and Nina Podjed Rihtaršič. 2025. "Revisiting the Coordination Chemistry of Molybdenum(V): Novel Complexes with Pyrazinoate and Picolinate Ligands" Molbank 2025, no. 4: M2079. https://doi.org/10.3390/M2079
APA StyleModec, B., & Podjed Rihtaršič, N. (2025). Revisiting the Coordination Chemistry of Molybdenum(V): Novel Complexes with Pyrazinoate and Picolinate Ligands. Molbank, 2025(4), M2079. https://doi.org/10.3390/M2079






