Synthesis of a Hydrogen Isotope-Labeled SGLT1 C-Glucoside Ligand for Distribution and Metabolic Fate Studies
Abstract
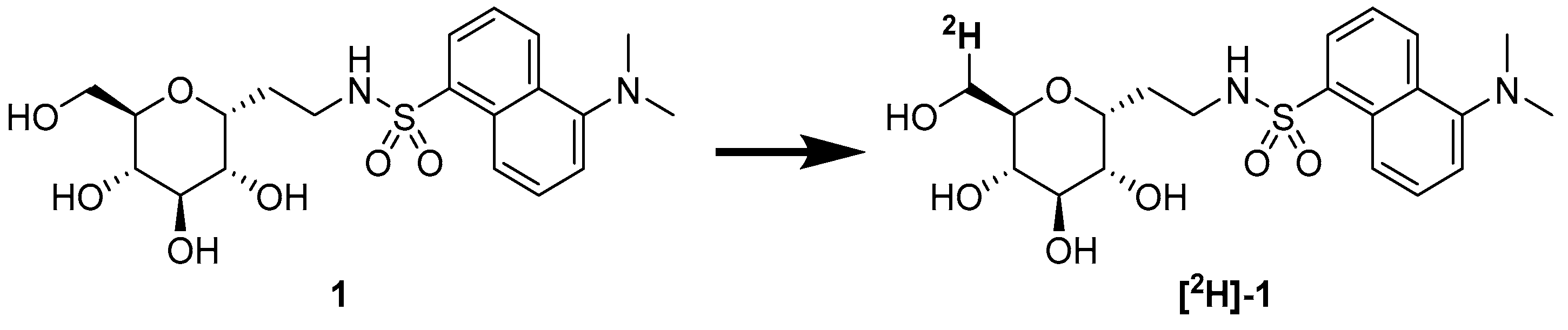
1. Introduction
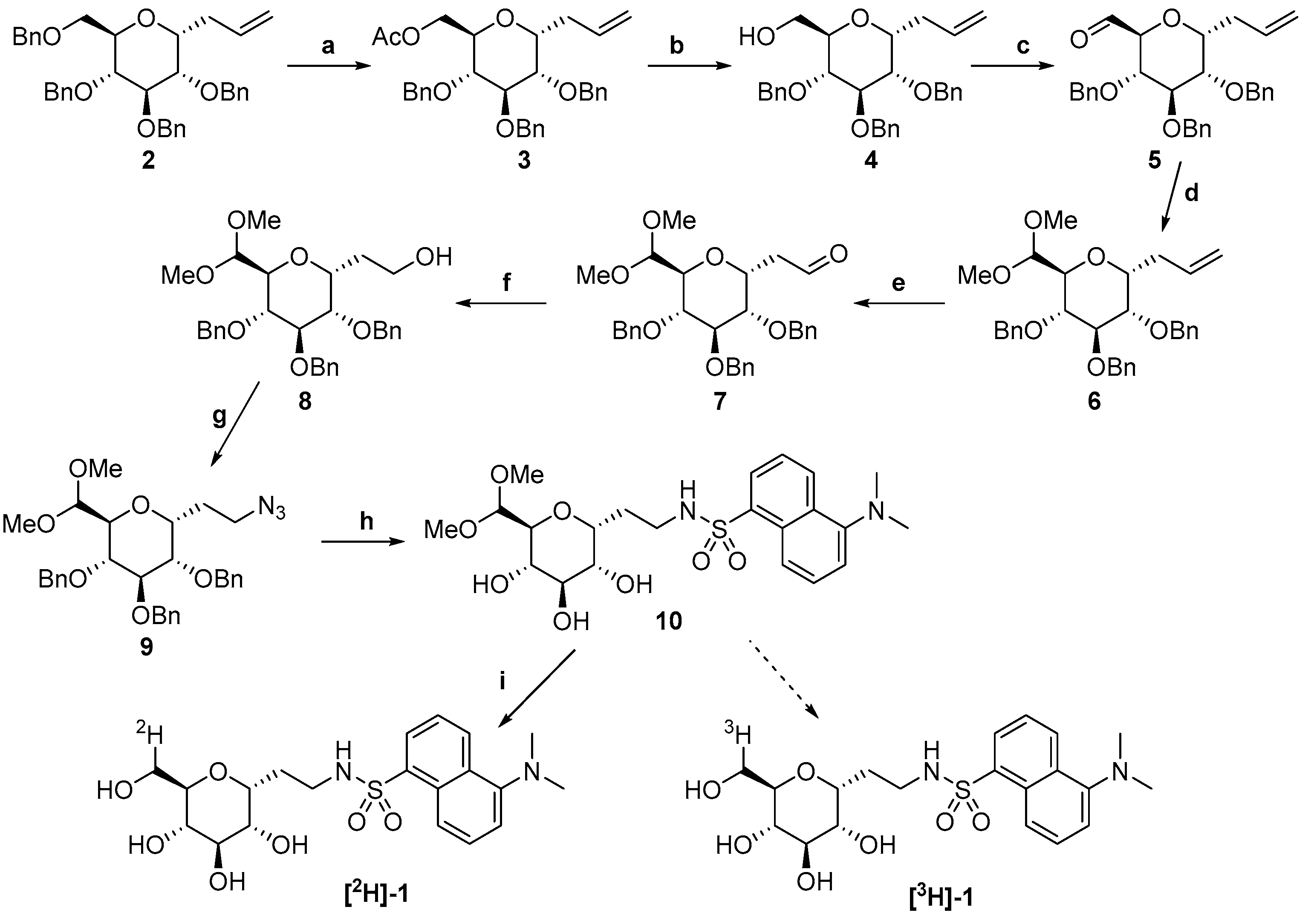
2. Results
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Remarks
3.2. Synthetic Procedures
3.2.1. 2,3,4-Tri-O-benzyl-6-O-acetyl-C-allyl-α-d-glucopyranoside 3
3.2.2. 2,3,4-Tri-O-benzyl-C-allyl-α-d-glucopyranoside 4
3.2.3. 2,3,4-Tri-O-benzyl-6-oxo-C-allyl-α-d-glucopyranoside 5
3.2.4. 2,3,4-Tri-O-benzyl-6-deoxy-6,6-dimethoxy-C-allyl-α-d-glucopyranoside 6
3.2.5. 2-(2,3,4-Tri-O-benzyl-6-deoxy-6,6-dimethoxy-α-d-glucopyranosyl)-ethanal 7
3.2.6. 2-(2,3,4-Tri-O-benzyl-6-deoxy-6,6-dimethoxy-α-d-glucopyranosyl)-ethanol 8
3.2.7. 1-C-(2′-azidoethyl)-2,3,4-tri-O-benzyl-6-deoxy-6,6-dimethoxy-α-d-glucopyranoside 9
3.2.8. 1-C-[(1′-ethylen-(N,N-dimethylamino)-N-naphthalensulfonamidyl]-6-deoxy-6,6-dimethoxy-α-d-glucopyranoside 10
3.2.9. 6-[2H]-1-C-[(1′-ethylen-(N,N-dimethylamino)-N-naphthalensulfonamidyl]-α-d-glucopyranoside [2H]-1
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wright, E.M.; Hirayama, B.A.; Loo, D.F. Active Sugar Transport in Health and Disease. J. Intern. Med. 2007, 261, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koepsell, H. Glucose Transporters in the Small Intestine in Health and Disease. Pflugers Arch. 2020, 472, 1207–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorboulev, V.; Schürmann, A.; Vallon, V.; Kipp, H.; Jaschke, A.; Klessen, D.; Friedrich, A.; Scherneck, S.; Rieg, T.; Cunard, R.; et al. Na+-Glucose Cotransporter SGLT1 Is Pivotal for Intestinal Glucose Absorption and Glucose-Dependent Incretin Secretion. Diabetes 2012, 61, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, E.M.; Loo, D.D.F.; Hirayama, B.A.; Turk, E. Surprising Versatility of Na+-Glucose Cotransporters: SLC5. Physiology 2004, 19, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koepsell, H. The Na+-D-Glucose Cotransporters SGLT1 and SGLT2 Are Targets for the Treatment of Diabetes and Cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 170, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimihodimos, V.; Filippas-Ntekouan, S.; Elisaf, M. SGLT1 Inhibition: Pros and Cons. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 838, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Li, N.; Zhou, H. SGLT1: A Potential Drug Target for Cardiovascular Disease. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2023, 17, 2011–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.C.H.; Turner, J.R.; Buret, A.G. LPS/CD14 Activation Triggers SGLT-1-Mediated Glucose Uptake and Cell Rescue in Intestinal Epithelial Cells via Early Apoptotic Signals Upstream of Caspase-3. Exp. Cell Res. 2006, 312, 3276–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.C.H.; Flynn, A.N.; Turner, J.R.; Buret, A.G. SGLT-1-mediated Glucose Uptake Protects Intestinal Epithelial Cells against LPS-induced Apoptosis and Barrier Defects: A Novel Cellular Rescue Mechanism? FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1822–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzo, M.; Gariboldi, S.; Zanobbio, L.; Selleri, S.; Dusio, G.F.; Mauro, V.; Rossini, A.; Balsari, A.; Rumio, C. Sodium-Dependent Glucose Transporter-1 as a Novel Immunological Player in the Intestinal Mucosa. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 3126–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanobbio, L.; Palazzo, M.; Gariboldi, S.; Dusio, G.F.; Cardani, D.; Mauro, V.; Marcucci, F.; Balsari, A.; Rumio, C. Intestinal Glucose Uptake Protects Liver from Lipopolysaccharide and D-Galactosamine, Acetaminophen, and Alpha-Amanitin in Mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 175, 1066–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Ferla, B.; Spinosa, V.; D’Orazio, G.; Palazzo, M.; Balsari, A.; Foppoli, A.A.; Rumio, C.; Nicotra, F. Dansyl C-Glucoside as a Novel Agent Against Endotoxic Shock. ChemMedChem 2010, 5, 1677–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Airoldi, C.; Palmioli, A. Synthesis of C- and S-Glycosides. In Comprehensive Glycoscience; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 160–199. [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda, S.; Kobashi, Y.; Oi, T.; Amada, H.; Okumura-Kitajima, L.; Io, F.; Yamamto, K.; Kakinuma, H. Discovery of a Potent, Low-Absorbable Sodium-Dependent Glucose Cotransporter 1 (SGLT1) Inhibitor (TP0438836) for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 3534–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Luo, X.; Chen, M.; Lu, J.; Liu, J.J. Investigational Agents Targeting SGLT1 and SGLT2 in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Curr. Drug Targets 2023, 24, 648–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deswal, N.; Takkar, P.; Kaur, L.; Ojha, H.; Kumar, R. Synthesis and Bio-Evaluation of Newer Dihydropyridines and Tetrahydropyridines Based Glycomimetic Azasugars. Bioorg. Chem. 2024, 145, 107224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decroocq, C.; Rodríguez-Lucena, D.; Russo, V.; Mena Barragán, T.; Ortiz Mellet, C.; Compain, P. The Multivalent Effect in Glycosidase Inhibition: Probing the Influence of Architectural Parameters with Cyclodextrin-based Iminosugar Click Clusters. Chem.—A Eur. J. 2011, 17, 13825–13831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orazio, G.; Martorana, A.M.; Filippi, G.; Polissi, A.; De Gioia, L.; Ferla, B. La N-Spirofused Bicyclic Derivatives of 1-Deoxynojirimycin: Synthesis and Preliminary Biological Evaluation. ChemistrySelect 2016, 1, 2444–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thépaut, M.; Luczkowiak, J.; Vivès, C.; Labiod, N.; Bally, I.; Lasala, F.; Grimoire, Y.; Fenel, D.; Sattin, S.; Thielens, N.; et al. DC/L-SIGN Recognition of Spike Glycoprotein Promotes SARS-CoV-2 Trans-Infection and Can Be Inhibited by a Glycomimetic Antagonist. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, R.; Wagner, S.; Rox, K.; Varrot, A.; Hauck, D.; Wamhoff, E.-C.; Schreiber, J.; Ryckmans, T.; Brunner, T.; Rademacher, C.; et al. Glycomimetic, Orally Bioavailable LecB Inhibitors Block Biofilm Formation of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 2537–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonini, G.; Bernardi, A.; Gillon, E.; Dal Corso, A.; Civera, M.; Belvisi, L.; Varrot, A.; Mazzotta, S. Achieving High Affinity for a Bacterial Lectin with Reversible Covalent Ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 67, 19546–19560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecioni, S.; Imberty, A.; Vidal, S. Glycomimetics versus Multivalent Glycoconjugates for the Design of High Affinity Lectin Ligands. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 525–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leusmann, S.; Ménová, P.; Shanin, E.; Titz, A.; Rademacher, C. Glycomimetics for the Inhibition and Modulation of Lectins. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 3663–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Orazio, G.; Parisi, G.; Policano, C.; Mechelli, R.; Codacci Pisanelli, G.; Pitaro, M.; Ristori, G.; Salvetti, M.; Nicotra, F.; La Ferla, B. Arsenical C-Glucoside Derivatives with Promising Antitumor Activity. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 2015, 4620–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiotta, A.; D’Orazio, G.; Palorini, R.; Ricciardiello, F.; Zoia, L.; Votta, G.; De Gioia, L.; Chiaradonna, F.; La Ferla, B. Design, Synthesis, and Preliminary Biological Evaluation of GlcNAc-6P Analogues for the Modulation of Phosphoacetylglucosamine Mutase 1 (AGM1/PGM3). Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 2018, 1946–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Ye, X. Synthetic Glycans and Glycomimetics: A Promising Alternative to Natural Polysaccharides. Chem.—A Eur. J. 2018, 24, 6696–6704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Büll, C.; Boltje, T.J.; van Dinther, E.A.W.; Peters, T.; de Graaf, A.M.A.; Leusen, J.H.W.; Kreutz, M.; Figdor, C.G.; den Brok, M.H.; Adema, G.J. Targeted Delivery of a Sialic Acid-Blocking Glycomimetic to Cancer Cells Inhibits Metastatic Spread. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Tejada, A.; Cañada, F.J.; Jiménez-Barbero, J. Recent Developments in Synthetic Carbohydrate-Based Diagnostics, Vaccines, and Therapeutics. Chem.—A Eur. J. 2015, 21, 10616–10628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hevey, R. Strategies for the Development of Glycomimetic Drug Candidates. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburrini, A.; Colombo, C.; Bernardi, A. Design and Synthesis of Glycomimetics: Recent Advances. Med. Res. Rev. 2020, 40, 495–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, B.; Magnani, J.L. From Carbohydrate Leads to Glycomimetic Drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 661–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Ferla, B.; D’Orazio, G. Pyranoid Spirosugars as Enzyme Inhibitors. Curr. Org. Synth. 2021, 18, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Orazio, G.; Colombo, L.; Salmona, M.; La Ferla, B. Synthesis and Preliminary Biological Evaluation of Fluorescent Glycofused Tricyclic Derivatives of Amyloid Β-Peptide Ligands. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 2016, 1660–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardani, D.; Sardi, C.; La Ferla, B.; D’Orazio, G.; Sommariva, M.; Marcucci, F.; Olivero, D.; Tagliabue, E.; Koepsell, H.; Nicotra, F.; et al. Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 1 Ligand BLF501 as a Novel Tool for Management of Gastrointestinal Mucositis. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumio, C.; Dusio, G.; Cardani, D.; La Ferla, B.; D’Orazio, G. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of SGLT1 Synthetic Ligand in In Vitro and In Vivo Models of Lung Diseases. Immuno 2024, 4, 502–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orazio, G.; Marradi, M.; La Ferla, B. Dual-Targeting Gold Nanoparticles: Simultaneous Decoration with Ligands for Co-Transporters SGLT-1 and B0AT1. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orazio, G.; La Ferla, B. Synthesis of a Small Library of Glycoderivative Putative Ligands of SGLT1 and Preliminary Biological Evaluation. Molecules 2024, 29, 5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orazio, G. Glycoderivatives: Drug Candidates and Molecular Tools. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Milano-Bicocca, Milan, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kopf, S.; Bourriquen, F.; Li, W.; Neumann, H.; Junge, K.; Beller, M. Recent Developments for the Deuterium and Tritium Labeling of Organic Molecules. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 6634–6718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Salem, N.; Corn, D.J.; Erokwu, B.; Tian, H.; Wang, F.; Lee, Z. Transport and Metabolism of Radiolabeled Choline in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 2077–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zona, C.; La Ferla, B. Synthesis of Labeled Curcumin Derivatives as Tools for in Vitro Blood Brain Barrier Trafficking Studies. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2011, 54, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, A.; Iijima, K.; Sakamoto, R.; Mizumoto, Y.; Iwaki, M.; Takiwaki, M.; Kikutani, Y.; Fukuzawa, S.; Odagi, M.; Tera, M.; et al. Synthesis of Deuterium-Labeled Vitamin D Metabolites as Internal Standards for LC-MS Analysis. Molecules 2022, 27, 2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimers, N.; Do, Q.; Zhang, R.; Guo, A.; Ostrander, R.; Shoji, A.; Vuong, C.; Xu, L. Tracking the Metabolic Fate of Exogenous Arachidonic Acid in Ferroptosis Using Dual-Isotope Labeling Lipidomics. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2023, 34, 2016–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, Y.; Yang, H.; Tian, Y. The Development and Application of Tritium-Labeled Compounds in Biomedical Research. Molecules 2024, 29, 4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenna, E.; Fuganti, C.; Grasselli, P.; Serra, S.; Zambotti, S. A Novel General Route for the Synthesis of C-Glycosyl Tyrosine Analogues. Chem.—A Eur. J. 2002, 8, 1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarvey, G.J.; LeClair, C.A.; Schmidtmann, B.A. Studies on the Stereoselective Synthesis of C-Allyl Glycosides. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 4727–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z. Zemplén Deacetylation. In Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 3123–3128. [Google Scholar]
- Zemplén, G.; Kunz, A. Studien Über Amygdalin, IV: Synthese Des Natürlichen l-Amygdalins. Berichte Dtsch. Chem. Ges. (A B Ser.) 1924, 57, 1357–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dess, D.B.; Martin, J.C. Readily Accessible 12-I-5 Oxidant for the Conversion of Primary and Secondary Alcohols to Aldehydes and Ketones. J. Org. Chem. 1983, 48, 4155–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleuze, A.; Sollogoub, M.; Blériot, Y.; Marrot, J.; Sinaÿ, P. Synthesis of Methoxy-Substituted Exocyclic (E)- and (Z)-Unsaturated Methyl Pyranosides and a Study of Their Reactivity towards Lewis Acids. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 2003, 2678–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D’Orazio, G.; La Ferla, B. Synthesis of a Hydrogen Isotope-Labeled SGLT1 C-Glucoside Ligand for Distribution and Metabolic Fate Studies. Molbank 2025, 2025, M1982. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1982
D’Orazio G, La Ferla B. Synthesis of a Hydrogen Isotope-Labeled SGLT1 C-Glucoside Ligand for Distribution and Metabolic Fate Studies. Molbank. 2025; 2025(1):M1982. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1982
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’Orazio, Giuseppe, and Barbara La Ferla. 2025. "Synthesis of a Hydrogen Isotope-Labeled SGLT1 C-Glucoside Ligand for Distribution and Metabolic Fate Studies" Molbank 2025, no. 1: M1982. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1982
APA StyleD’Orazio, G., & La Ferla, B. (2025). Synthesis of a Hydrogen Isotope-Labeled SGLT1 C-Glucoside Ligand for Distribution and Metabolic Fate Studies. Molbank, 2025(1), M1982. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1982






