28-O-Acetyl-3-O′-(prop-2-enoyl)betulin
Abstract
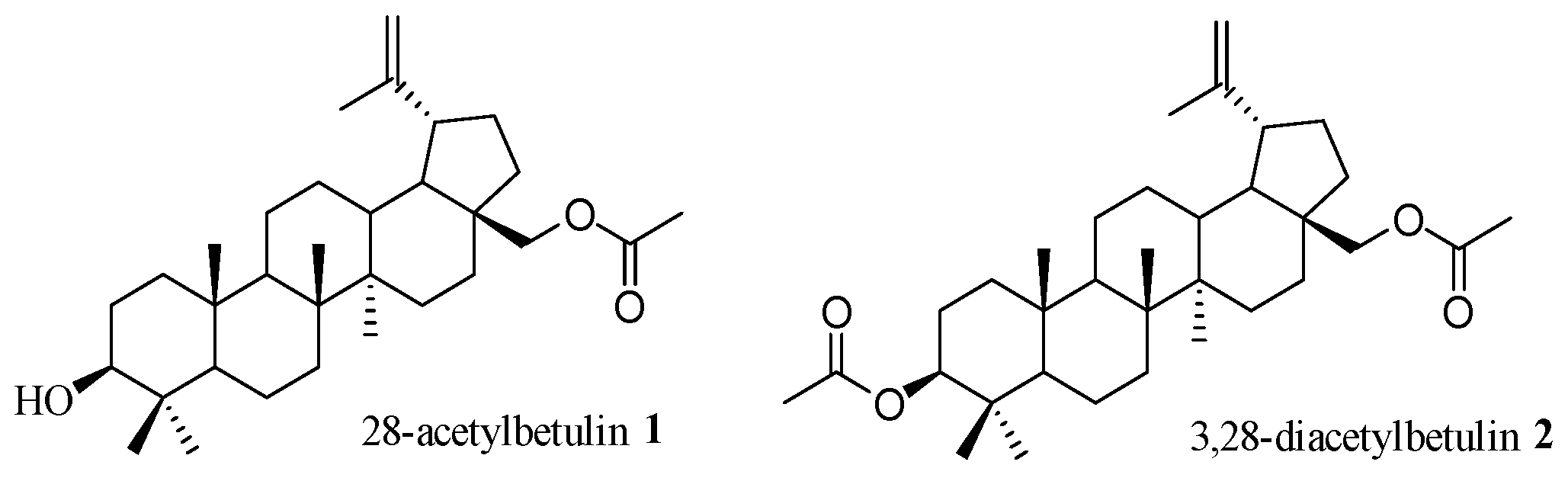
1. Introduction
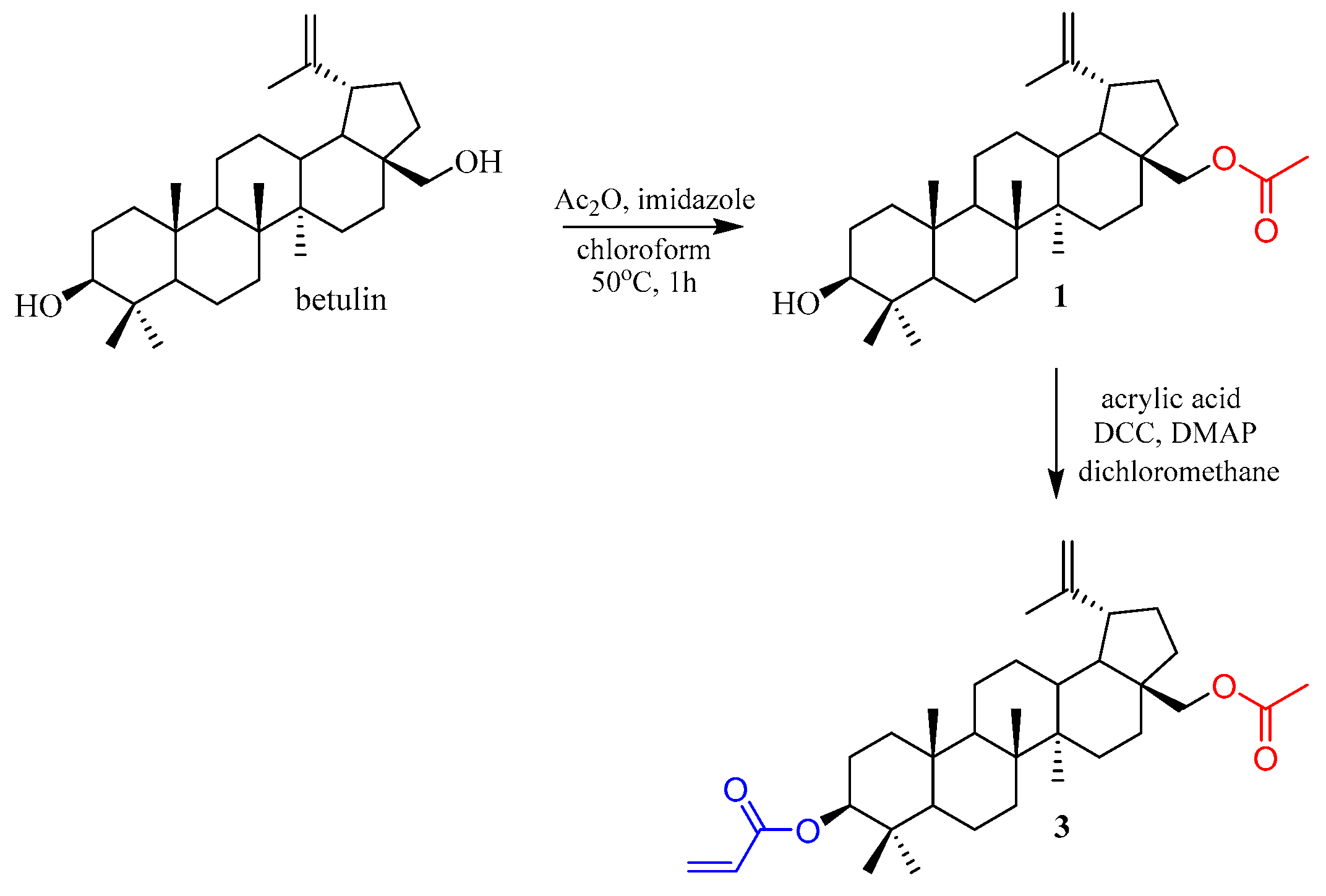
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
3.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 28-O-Acetyl-3-O′-(prop-2-enoyl)betulin 3
3.3. In Silico Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bernardini, S.; Tiezzi, A.; Laghezza Masci, V.; Ovidi, E. Natural products for human health: An historical overview of the drug discovery approaches. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 1926–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hordyjewska, A.; Ostapiuk, A.; Horecka, A.; Kurzepa, J. Betulin and betulinic acid: Triterpenoids derivatives with a powerful biological potential. Phytochem. Rev. 2019, 18, 929–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, A.; Chaudhuri, S.K.; Panda, S.K. Betulin-3-caffeate from Quercus suber. 13C-NMR spectra of some lupenes. J. Nat. Prod. 1988, 51, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.; Hafeez, F.; Begum, S.; Siddiqui, B.S. Oleanderol, a new pentacyclic triterpene from the leaves of Nerlum oleander. J. Nat. Prod. 1988, 51, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Snyder, J.K. Preparation of a 24-nor-1,4-dien-3-one triterpene derivative from betulin: A new route to 24-nortriterpene analogues. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 2864–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tietze, L.F.; Heinzen, H.; Moyna, P.; Rischer, M.; Neunaber, H. Synthesis of [13C]- and [2H]betulin for biological transformations. Lieb. Ann. Chem. 1991, 1991, 1245–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kommera, H.; Kaluderović, G.N.; Dittrich, S.; Kalbitz, J.; Dräger, B. Carbamate derivatives of betulinic acid and betulin with selective cytotoxic activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 3409–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohjala, L.; Alakurtti, S.; Ahola, T.; Yli-Kauhaluoma, J.; Tammela, P. Betulin-derived compounds as inhibitors of alphavirus replication. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1917–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salin, O.; Alakurtti, S.; Pohjala, L.; Siiskonen, A.; Maass, V.; Matthias, M.; Yli-Kauhaluoma, J.; Vuorela, P. Inhibitory effect of the natural product betulin and its derivatives against the intracellular bacterium Chlamydia pneumoniae. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 1141–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boryczka, S.; Bębenek, E.; Wietrzyk, J.; Kempińska, K.; Jastrzębska, M.; Kusz, J.; Nowak, M. Synthesis, structure and cytotoxic activity of new acetylenic derivatives of betulin. Molecules 2013, 18, 4526–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sut, S.; Poloniato, G.; Malagoli, M.; Dall’Acqua, S. Fragmentation of the main triterpene acids of apple by LC-APCI-MSn. J. Mass. Spectrom. 2018, 53, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, P.; Alheety, M.A.; Srivastava, V. Molecular docking and ADMET study of spice-derived potential phytochemicals against human DNA topoisomerase III alpha. Macromol. Symp. 2023, 407, 2200108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, P.L.; Renu, K.; Gopalakrishnan, A.V. New molecular and biochemical insights of doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity. Life Sci. 2020, 250, 117599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, D.E.; Tom, L.; Blundell, T.L.; Ascher, D.B. pkCSM: Predicting small-molecule pharmacokinetic and toxicity properties using graph-based signatures. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 4066–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameters | Compound 3 | Doxorubicin |
|---|---|---|
| Absorption | ||
| Caco-2 permeability (logPapp) a | 1.27 | 0.48 |
| Skin permeability (logKp) b | −2.56 | −2.73 |
| Human intestinal absorption (HIA) c | 100% | 55% |
| Distribution | ||
| BBB permeability (logBB) | −0.64 | −1.27 |
| CNS permeability (logPS) | −1.09 | −4.29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bębenek, E.; Chrobak, E.; Kadela-Tomanek, M. 28-O-Acetyl-3-O′-(prop-2-enoyl)betulin. Molbank 2023, 2023, M1696. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1696
Bębenek E, Chrobak E, Kadela-Tomanek M. 28-O-Acetyl-3-O′-(prop-2-enoyl)betulin. Molbank. 2023; 2023(3):M1696. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1696
Chicago/Turabian StyleBębenek, Ewa, Elwira Chrobak, and Monika Kadela-Tomanek. 2023. "28-O-Acetyl-3-O′-(prop-2-enoyl)betulin" Molbank 2023, no. 3: M1696. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1696
APA StyleBębenek, E., Chrobak, E., & Kadela-Tomanek, M. (2023). 28-O-Acetyl-3-O′-(prop-2-enoyl)betulin. Molbank, 2023(3), M1696. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1696





