Abstract
A nickel complex with a Schiff base Ni(3-tert-butyl-salophen) was synthesized and structurally characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction, 1H, 13C{1H}, 1H–13C HMQC, 1H–13C HMBC, 1H-1H dqf-COSY and 1H-1H NOESY NMR spectroscopy, and IR and UV-vis spectroscopy.
1. Introduction
Schiff bases are compounds containing an imine or azomethine functional group formed by the reaction of a primary amine with an aldehyde or ketone [,,]. They form stable complexes with various metal ions. They are commonly used as ligands in coordination chemistry due to their ability to form stable complexes with metal ions. Schiff base complexes have a wide range of applications, including catalysis [,,,,], energy storage devices [], sensors [], and medicinal chemistry [,,,]. The catalytic activity strongly depends on the structure and properties of the complexes, particularly the presence of substituents in the ligand part of the molecule and the nature of the metal ion. One example of a Schiff base ligand is salophen, a tetradentate ligand containing a central aromatic ring substituted with two phenolic groups via the azomethine linkers. Salophen ligands have been extensively studied due to their unique properties, including high selectivity and catalytic activity. Recently, there has been increasing interest in the synthesis and characterization of sterically hindered Schiff base complexes [,,,]. The introduction of bulky tert-butyl groups into the ortho- and para-positions of the ligand rings provides efficient enantioselective catalysis, affects the coordination geometry of the metal center, and can change the properties of the formed complex []. Crystal structure determination is an important tool for the characterization of sterically hindered Schiff base complexes, because it provides valuable information on the impact of steric hindrance on the structure and properties of metal complexes. The structures of tert-butyl-substituted salophen complexes reported previously include relatively simple ortho- and para-di-tert-butyl- or ortho-tert-butyl- and other functional groups para-substituted complexes [,,,,,], di-tert-butyl-substituted crown ethers bearing complexes [,], as well as more sophisticated supramolecular structures [,,,,,]. The structures of complexes containing tert-butyl-substituents in the ortho- and para-positions of the phenyl rings of the ligand and various substituents the bridge, such as HOOC-, CH3-, CH3O-, N(CH3)2-, have also been described [,,,]. Introduction of N(CH3)2 substituent in the para-position of the ligand moiety leads to monoclinic packing [], while the complex with CH3- groups in phenyl bridge leads to triclinic packing []. Meanwhile, the simplest ortho-tert-butyl-salophen Ni complex has not been structurally characterized yet. In this article, we will focus on the synthesis and NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance), FTIR (Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy), and UV-VIS (ultraviolet and visible) characterization of a new Ni(salophen) complex that contains a sterically hindered Schiff base ligand. This study will contribute to our understanding of the properties of sterically hindered Schiff base complexes and may have important implications for the design of new catalysts and materials.
2. Results
2.1. X-Ray Structural Analysis
The crystal structure of the Ni(3-tert-butyl-salophen) was determined by X-ray diffraction. Brick red needle-like crystals were grown from a saturated acetonitrile solution by slow solvent evaporation.
The title compound crystallizes in the orthorhombic space group Pbca. Figure 1 presents the molecular structures of Ni(3-tert-butyl-salophen). Nickel with two oxygen and two nitrogen atoms form a square-planar coordination skeleton. The distortion of the square-planar geometry for the Ni(3-t-butyl-salophen) is low and can be characterized by torsion angles Ni1-O1-C24-C19 (1.5(2)°) and Ni1-N2-C7-C8 (10.9(2)°) and by valence angles O1-Ni1-N2 (176.05(6)°) and N1-Ni1-O2 (175.57(6)°).
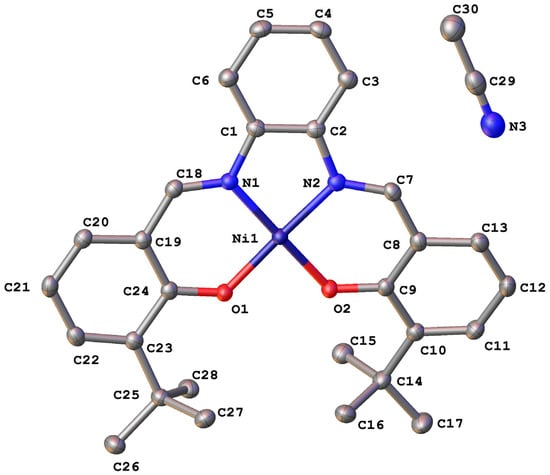
Figure 1.
Molecular view of the Ni(3-tert-butyl-salophen) × CH3CN in representation of atoms with thermal ellipsoids (p = 50%).
The packing of Ni(3-tert-butyl-salophen) is quite compact (Figure 2) with the closest Ni-Ni distance of 4.706 Å. As anticipated, the bulky complex is packed into a crystal without any stacking motif. The steric bulkiness induced by the tert-butyl groups in the phenol rings prevents close molecular contacts in the crystal.
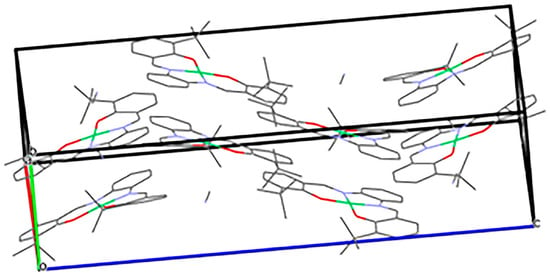
Figure 2.
Packing of the Ni(3-tert-butyl-Salophen) × CH3CN in crystals.
Crystallographic data, experimental parameters, and refinement of the complex structure are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Crystallographic data, experimental parameters, and refinement of the Ni(3-tert-butyl-Salophen) × CH3CN complex structure.
2.2. Infrared Spectroscopic and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Studies
IR spectra (Figure S1) were registered on a Shimadzu IR Prestige-21 spectrometer with samples in KBr pellets. The main experimental IR bands and their assignment are given in Table S1. 1H, 13C NMR spectra (Figures S2 and S3), 1H–13C HMQC (Figure S4), 1H–13C HMBC (Figure S5), 1H-1H dqf-COSY (Figure S6), as well as NOESY (mixing time from 0.5 to 2 s) (Figure S7) experiments were performed on a Jeol ECX400A spectrometer (400 MHz for 1H nuclei and 100 MHz for 13C nuclei) in DMSO-d6. Residual solvent signals (DMSO-d6: 2.50 ppm for 1H nuclei and 39.6 ppm for 13C nuclei) were used as an internal standard.
1H NMR: 1.36 (9H, s, 3CH3), 6.58 (1H, t, H4, 3J 7.6 Hz), 7.23 (1H, dd, H5, 3J 7.2, 4J 1.5 Hz), 7.28 (1H, dd, H3′, 3J 6.2, 4J 3.2 Hz), 7.47 (1H, dd, H3, 3J 7.9, 4J 1.5 Hz), 8.12 (1H, dd, H2′, 3J 6.2, 4J 3.2 Hz), 8.78 (1H, s, CH=N) (Atom labeling is shown in Figure 3).
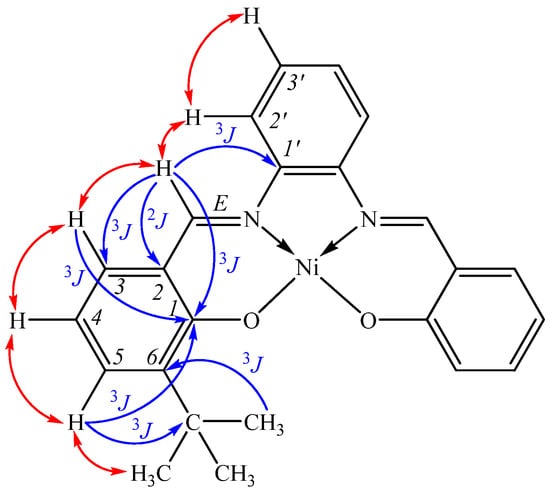
Figure 3.
Key correlations in 1H-13C HMBC (blue arrows) and 1H-1H NOESY (red double-edged arrows) spectra.
13C{1H} NMR: 30.06 [C(CH3)3], 35.77 [C(CH3)3], 115.40 (C4), 116.51 (C2′), 121.12 (C2), 127.80 (C3′), 131.88 (C5), 133.44 (C3), 140.31 (C6), 142.93 (C1′), 157.32 (C=N), 165.11 (C1).
The assignment of signals of protons and carbon atoms in 1H and 13C NMR spectra was carried out using homonuclear (1H-1H COSY, 1H-1H NOESY) and heteronuclear (1H-13C HMQC, 1H-13C HMBC) experiments. Noteworthy is the presence of cross peaks in the 1H-1H COSY spectrum due to long-range spin-spin interactions through five bonds (CH3/H5, CH=N/H2′, CH=N/H3), as well as the characteristic of ortho-substituted benzene ring J-coupling constant (4J 1.5 Hz) through four bonds (H3/H5). The key cross peaks used for interpretation in the 1H-13C HMBC spectra were 1.36 (CH3)/140.31 (C6); 8.78 (CH=N)/142.93 (C1′)/121.12 (C2)/133.44 (C3)/165.11 (C1); 7.47 (H3)/157.32 (C=N); 7.23 (H5), 7.47 (H3)/165.11 (C1); 7.23 (H5)/35.77 [C(CH3)3] (Figure 3).
Analysis of the 1H-1H NOESY spectrum (mixing time variation) indicates the planar structure of the complex. Thus, the cross peaks CH=N/H2′ (a very important cross peak for identifying the H2′ proton) and CH=N/H3, due to the nuclear Overhauser effect, indicate the spatial proximity of the azomethine proton simultaneously with two protons of different aromatic rings, which is possible with the coplanar organization of the (E)-azomethine block.
2.3. UV-Vis Spectroscopic Studies
The spectrum of the Ni(3-tert-butyl-Salophen) complex (Figure S8) contains three main bands: 263, 378, and 475 nm (Table S2). The absorption band of the complex at 263 nm is due to the π → π* transition of benzene. Another band at 378 nm is attributed to the n → π* transition of the non-bonding electron located on the azomethine nitrogen atom of the ligand. The bands 475 nm and the weakly resolved band at 563 nm correspond to π-d and d-d transitions in the nickel center [,].
3. Materials and Methods
All reagents were of commercial grade and were used without purification.
The complex Ni(3-tert-butyl-salophen) was prepared according to previously published procedures []. The ligand N,N′-1,2-phenylene-bis(3-tert-butylsalicylideneamine) was obtained by condensation of o-phenylenediamine with 3-tert-butylbenzaldehyde []. The nickel (II) complex Ni(3-tert-butyl-Salophen) was prepared by refluxing ethanolic solutions of Ni(II) acetate (Aldrich) with the ligand. The obtained complex was recrystallized from acetonitrile and dried at 60 °C for 12 h (70% yield).
X-ray diffraction analysis was performed at 100 K on a Rigaku XtaLAB Synergy-S diffractometer equipped with a HyPix-6000HE CCD detector with CuKα radiation (λ 1.54184 Å). The structure was solved using the ShelXT software package [] and refined using the ShelXL package [] included in the OLEX2 interface []. The crystallographic parameters were deposited in the Cambridge X-ray Database (CCDC 2236037).
4. Conclusions
N,N′-1,2-phenylene-bis(3-tert-butylsalicylideneiminato)nickel (II) was synthesized and characterized by NMR and by IR and UV-vis spectroscopy.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded online. Figure S1: IR spectrum of N,N′-1,2-phenylene-bis(3-tert-butyl-salicylideneiminato)nickel (II) in KBr; Table S1: The main experimental IR bands of the metal complexes Ni(3-tert-butyl-Salophen) and their assignment; Figure S2: 1H NMR spectrum of N,N′-1,2-phenylene-bis(3-tert-buty—salicylideneiminato)nickel (II) in DMSO-d6; Figure S3: 1H{13C} NMR spectrum of N,N′-1,2-phenylene-bis(3-tert-butyl-salicylideneiminato)nickel (II) in DMSO-d6; Figure S4: 1H-13C HMQC spectrum of N,N′-1,2-phenylene-bis(3-tert-butyl-salicylideneiminato)nickel (II) in DMSO-d6; Figure S5: 1H-13C HMBC spectrum of N,N′-1,2-phenylene-bis(3-tert-butyl-salicylideneiminato)nickel (II) in DMSO-d6; Figure S6: 1H-1H dqf-COSY spectrum of N,N′-1,2-phenylene-bis(3-tert-butyl-salicylideneiminato)nickel (II) in DMSO-d6; Figure S7: 1H-1H NOESY spectrum of N,N′-1,2-phenylene-bis(3-tert-butyl-salicylideneiminato)nickel (II) in DMSO-d6. Figure S8: UV-vis spectrum of N,N′-1,2-phenylene-bis(3-tert-butyl-salicylideneiminato)nickel (II) in acetonitrile; Table S2: The main experimental UV-vis spectra maximums of the metal complexes [Ni(3-tert-butyl-Salophen)] and their assignment. CCDC 2236037contains the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data can be obtained free of charge from The Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre via http://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/structures, accessed on 19 June 2023 (or from the CCDC, 12 Union Road, Cambridge CB2 1EZ, UK; Fax: +44 1223 336033; E-mail: deposit@ccdc.cam.ac.uk).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.N. and J.P.; synthesis, M.N. and J.P.; methodology, M.K.; investigation, R.B. and D.S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.N., J.P. and R.B.; writing—review and editing, M.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
NMR and IR spectral studies were performed at the Center for Collective Use «Physico-chemical methods for the study of nitro compounds, coordination compounds, biologically active substances, and nanostructured materials» of the Interdisciplinary Resource Center for Collective Use «Modern physico-chemical methods of formation and research of materials for the needs of industry, science, and education» of the Herzen State Pedagogical University of Russia. The structural studies were carried out using the equipment of the Research Centre for X-ray Diffraction Studies of the Research Park of St. Petersburg State University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Al Zoubi, W.; Al-Hamdani, A.A.S.; Kaseem, M. Synthesis and Antioxidant Activities of Schiff Bases and Their Complexes: A Review. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2016, 30, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, J.L.; Mancheño, M.J.; Zamora, F. Covalent Organic Frameworks Based on Schiff-Base Chemistry: Synthesis, Properties and Potential Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 5635–5671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeiffer, P.; Breith, E.; Lübbe, E.; Tsumaki, T. Tricyclische Orthokondensierte Nebenvalenzringe. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1933, 503, 84–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.C.; Sutar, A.K. Catalytic Activities of Schiff Base Transition Metal Complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2008, 252, 1420–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karvembu, R.; Hemalatha, S.; Prabhakaran, R.; Natarajan, K. Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activities of Ruthenium Complexes Containing Triphenylphosphine/Triphenylarsine and Tetradentate Schiff Bases. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2003, 6, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalia, S.A.; Afsan, F.; Hossain, M.S.; Khan, M.N.; Zakaria, C.; Zahan, M.K.E.; Ali, M. A Short Review on Chemistry of Schiff Base Metal Complexes and Their Catalytic Application. Int. Journal. Chem. Stud. 2018, 6, 2859–2866. [Google Scholar]
- Cozzi, P.G. Metal–Salen Schiff Base Complexes in Catalysis: Practical Aspects. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2004, 33, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Linert, W. Schiff Base-Derived Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Palladium Catalysts for the Suzuki–Miyaura Reaction. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 311, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łępicka, K.; Pieta, P.; Francius, G.; Walcarius, A.; Kutner, W. Structure-Reactivity Requirements with Respect to Nickel-Salen Based Polymers for Enhanced Electrochemical Stability. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 315, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Li, Z.; Shi, R.; Yan, L.; Zhu, Y.; Li, H. Schiff Base-Modified Nanomaterials for Ion Detection: A Review. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 13998–14020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, N.K.; Guragain, B.; Chaudhary, S.K.; Mishra, P. Schiff Base Metal Complex as a Potential Therapeutic Drug in Medical Science: A Critical Review. Bibechana 2021, 18, 214–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.N.; Ahmed, S.S.; Alam, S.M.R. REVIEW: Biomedical Applications of Schiff Base Metal Complexes. J. Coord. Chem. 2020, 73, 3109–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avaji, P.G.; Vinod Kumar, C.H.; Patil, S.A.; Shivananda, K.N.; Nagaraju, C. Synthesis, Spectral Characterization, In-Vitro Microbiological Evaluation and Cytotoxic Activities of Novel Macrocyclic Bis Hydrazone. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 3552–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Rhodes, J. Schiff Base Forming Drugs: Mechanisms of Immune Potentiation and Therapeutic Potential. J. Mol. Med. 1996, 74, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, F. Ligand-Centred Oxidative Chemistry in Sterically Hindered Salen Complexes: An Interesting Case with Nickel. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 10866–10877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, R.A.; Germino, J.C.; Fazolo, B.R.; Thaines, E.H.N.S.; Ferraro, F.; Santana, A.M.; Ramos, R.J.; de Souza, G.L.C.; Freitas, R.G.; Vazquez, P.A.M.; et al. Electronic and Magnetic Properties of the [Ni(Salophen)]: An Experimental and DFT Study. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 9, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-X.; Tang, L.-Z.; Deng, Y.-F.; Zhan, S.-Z. Synthesis and Electrocatalytic Function for Hydrogen Generation of Cobalt and Nickel Complexes Supported by Phenylenediamine Ligand. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2016, 72, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotthaus, O.; Jarjayes, O.; Thomas, F.; Philouze, C.; Perez Del Valle, C.; Saint-Aman, E.; Pierre, J.-L. Fine Tuning of the Oxidation Locus, and Electron Transfer, in Nickel Complexes of Pro-Radical Ligands. Chem.—A Eur. J. 2006, 12, 2293–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecarme, L.; Chiang, L.; Philouze, C.; Jarjayes, O.; Storr, T.; Thomas, F. Detailed Geometric and Electronic Structures of a One-Electron-Oxidized Ni Salophen Complex and Its Amido Derivatives. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 2014, 3479–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Shi, Y.; Chen, J.; Yang, S.; Qi, C.; Jiang, H. Ni(Salphen)-Based Metal–Organic Framework for the Synthesis of Cyclic Carbonates by Cycloaddition of CO2 to Epoxides. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bellefeuille, D.; Askari, M.S.; Lassalle-Kaiser, B.; Journaux, Y.; Aukauloo, A.; Orio, M.; Thomas, F.; Ottenwaelder, X. Reversible Double Oxidation and Protonation of the Non-Innocent Bridge in a Nickel(II) Salophen Complex. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 12796–12804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schley, M.; Lönnecke, P.; Hey-Hawkins, E. Monometallic and Heterobimetallic Complexes Derived from Salen-Type Ligands. J. Organomet. Chem. 2009, 694, 2480–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotthaus, O.; Jarjayes, O.; Perez Del Valle, C.; Philouze, C.; Thomas, F. A Versatile Electronic Hole in One-Electron Oxidized NiIIbis-Salicylidene Phenylenediamine Complexes. Chem. Commun. 2007, 43, 4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benisvy, L.; Kannappan, R.; Song, Y.; Milikisyants, S.; Huber, M.; Mutikainen, I.; Turpeinen, U.; Gamez, P.; Bernasconi, L.; Baerends, E.J.; et al. A Square-Planar Nickel(II) Monoradical Complex with a Bis(Salicylidene) Diamine Ligand (Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 5/2007). Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 2007, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, J.D.; Rosa, D.T.; Coucouvanis, D. Lipophilic Metal−Salicylideneimine−Crown Ether Hybrids—Ditopic Carriers in the Facilitated Transport of Amphiphilic Molecules Across Bulk Liquid Membranes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 2001, 761–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosaand, D.T.; Coucouvanis, D. Crown-Ether-Functionalized Nickel Salicylaldimine Complexes. Structural Characterization of Their Potassium, Cesium, and Hexylammonium Derivatives and Their Use in the Transport of Amino Acids. Inorg. Chem. 1998, 37, 2328–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doistau, B.; Benda, L.; Cantin, J.-L.; Chamoreau, L.-M.; Ruiz, E.; Marvaud, V.; Hasenknopf, B.; Vives, G. Six States Switching of Redox-Active Molecular Tweezers by Three Orthogonal Stimuli. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 9213–9220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhrmacher, F.; Elbert, S.M.; Rominger, F.; Mastalerz, M. Synthesis of Large [2+3] Salicylimine Cages with Embedded Metal-Salphen Units. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 2022, e202100864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselmo, D.; Salassa, G.; Escudero-Adán, E.C.; Martin, E.; Kleij, A.W. Merging Catalysis and Supramolecular Aggregation Features of Triptycene Based Zn(Salphen)s. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 7962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotthaus, O.; Jarjayes, O.; Philouze, C.; Del Valle, C.P.; Thomas, F. One-Electron Oxidized Nickel(II) Complexes of Bis and Tetra(Salicylidene) Phenylenediamine Schiff Bases: From Monoradical to Interacting Ni(III) Ions. Dalton Trans. 2009, 10, 1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schley, M.; Fritzsche, S.; Lönnecke, P.; Hey-Hawkins, E. Soluble Monometallic Salen Complexes Derived from O-Functionalised Diamines as Metalloligands for the Synthesis of Heterobimetallic Complexes. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chichak, K.; Jacquemard, U.; Branda, N.R. The Construction of (Salophen)Ruthenium(II) Assemblies Using Axial Coordination. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2002, 2002, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asraf, M.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Kabiraz, D.C.; Ansary, R.H.; Hossen, M.F.; Haque, M.F.; Zakaria, C.M. Structural Elucidation, 3D Molecular Modeling and Antibacterial Activity of Ni (II), Co (II), Cu (II) and Mn (II) Complexes Containing Salophen Ligand. Asian J. Appl. Chem. Res. 2019, 3, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Wei, K.; Ma, X.; Zhou, X.; Xiang, H. Synthesis and Photophysical Properties of Colorful Salen-Type Schiff Bases. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 16552–16563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, R.H.; Everett, G.W.; Chakravorty, A. Metal Complexes of Schiff Bases and β-Ketoamines. In Progress in Inorganic Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1966; Volume 7, pp. 83–214. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT—Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Crystallogr. A Found. Adv. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C Struct. Chem. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourhis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).