2-(2-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-4,9-dimethyl-7-oxo-7H-furo[2,3-f]chromen-3-yl)acetic Acid
Abstract
1. Introduction
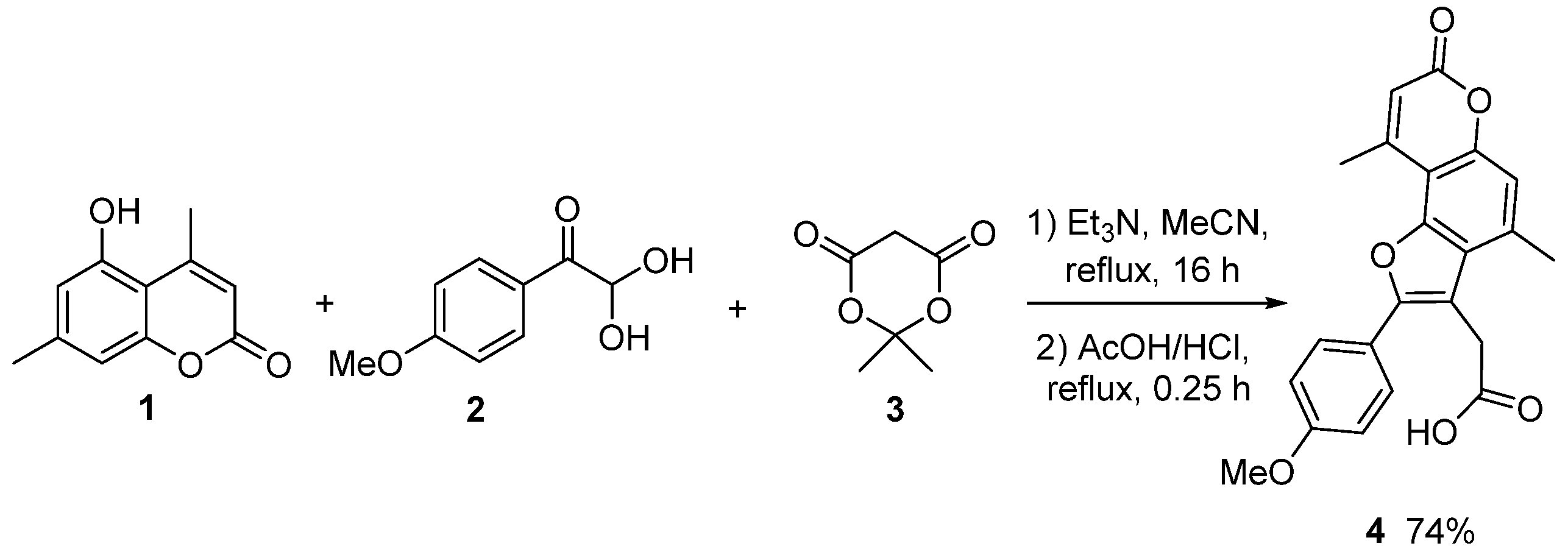
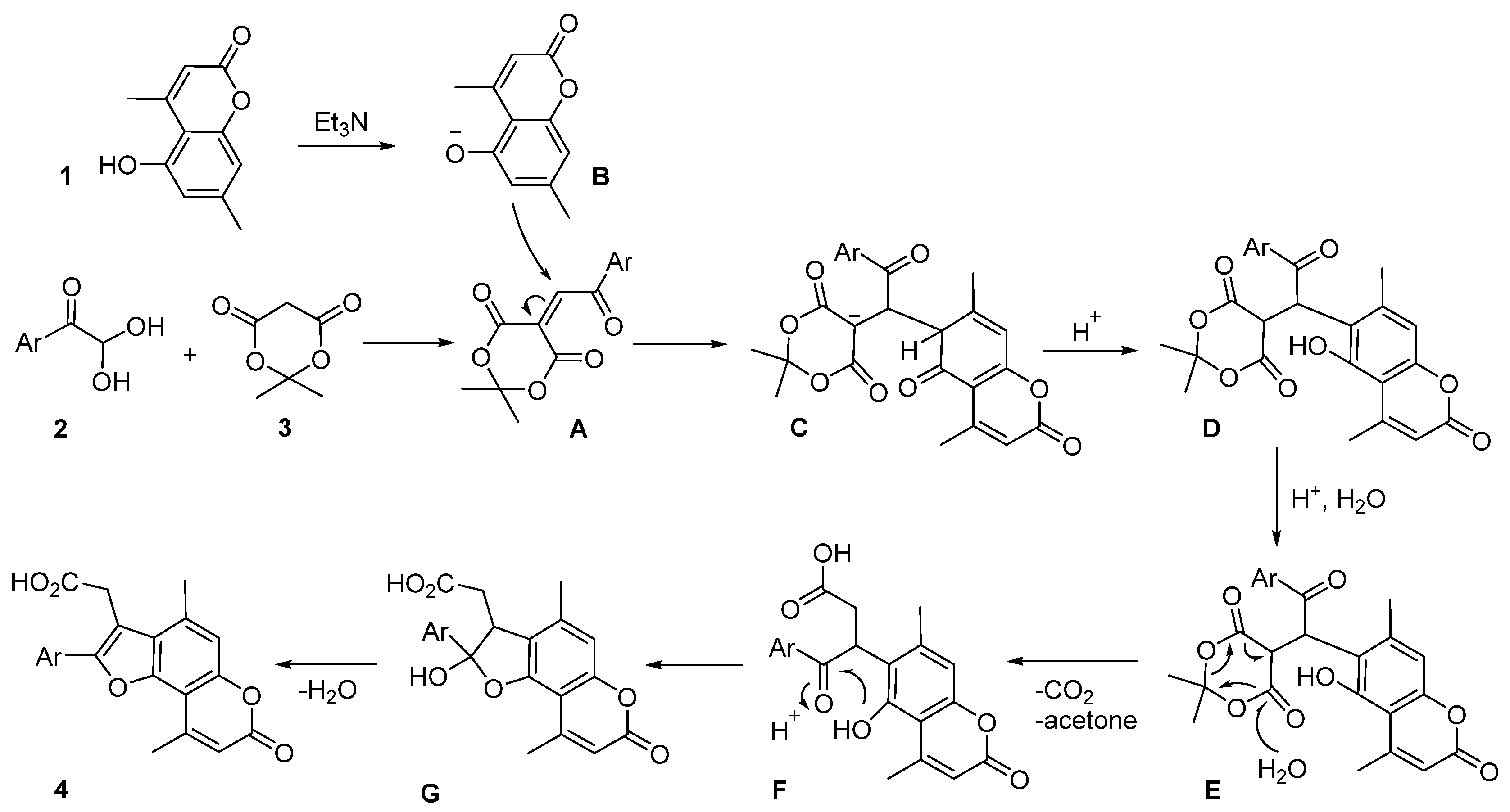
2. Results
3. Materials and Methods
Experimental Procedure for the Synthesis of 2-(2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4,9-dimethyl-7-oxo-7H-furo[2,3-f]chromen-3-yl)acetic Acid 4
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matos, M.J.; Santana, L.; Uriarte, E.; Abreu, O.A.; Molina, E.; Yordi, E.M.A.E.G. Coumarins—An Important Class of Phytochemicals. In Phytochemicals—Isolation, Characterisation and Role in Human Health; Rao, A.V., Rao, L.G., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2015; pp. 113s–140s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopala, K.N.; Rashmi, V.; Odhav, B. Review on Natural Coumarin Lead Compounds for Their Pharmacological Activity. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordin, F.; Dall’Acqua, F.; Guiotto, A. Angelicins, angular analogs of psoralens: Chemistry, photochemical, photobiological and phototherapeutic properties. Pharmacol. Ther. 1991, 52, 331–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, S.K.; Ceska, O.; Warrington, P.J.; Ashwood-Smith, M.J. Increased furocoumarin content of celery during storage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1985, 33, 1153–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-H.; Hwang, T.-L.; Chen, L.-C.; Chang, T.-H.; Wei, C.-S.; Chen, J.-J. Isoflavones and anti-inflammatory constituents from the fruits of Psoralea corylifolia. Phytochemistry 2017, 143, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugrand-Judek, A.; Olry, A.; Hehn, A.; Costantino, G.; Ollitrault, P.; Froelicher, Y.; Bourgaud, F. The Distribution of Coumarins and Furanocoumarins in Citrus Species Closely Matches Citrus Phylogeny and Reflects the Organization of Biosynthetic Pathways. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melough, M.M.; Cho, E.; Chun, O.K. Furocoumarins: A review of biochemical activities, dietary sources and intake, and potential health risks. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 113, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadaček, F.; Müller, C.; Werner, A.; Greger, H.; Proksch, P. Analysis, isolation and insecticidal activity of linear furanocoumarins and other coumarin derivatives fromPeucedanum (Apiaceae: Apioideae). J. Chem. Ecol. 1994, 20, 2035–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wangchuk, P.; Pyne, S.; Keller, P.; Taweechotipatr, M.; Kamchonwongpaisan, S. Phenylpropanoids and Furanocoumarins as Antibacterial and Antimalarial Constituents of the Bhutanese Medicinal Plant Pleurospermum amabile. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2014, 9, 1934578X1400900719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souri, E.; Farsam, H.; Sarkheil, P.; Ebadi, F. Antioxidant Activity of Some Furanocoumarins Isolated fromHeracleum persicum. Pharm. Biol. 2004, 42, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, W.-L.; Suh, J.H.; Wang, Y. Chemistry and health effects of furanocoumarins in grapefruit. J. Food Drug Anal. 2016, 25, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, R.; Barreca, D.; Protti, M.; Brighenti, V.; Righetti, L.; Anceschi, L.; Mercolini, L.; Benvenuti, S.; Gattuso, G.; Pellati, F. Botanical Sources, Chemistry, Analysis, and Biological Activity of Furanocoumarins of Pharmaceutical Interest. Molecules 2019, 24, 2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dongfack, M.D.J.; Lallemand, M.-C.; Kuete, V.; Mbazoa, C.D.; Wansi, J.-D.; Trinh-Van-Dufat, H.; Michel, S.; Wandji, J. A New Sphingolipid and Furanocoumarins with Antimicrobial Activity from Ficus exasperata. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 60, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Schuler, M.A.; Berenbaum, M.R. Diversification of furanocoumarin-metabolizing cytochrome P450 monooxygenases in two papilionids: Specificity and substrate encounter rate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100 (Suppl. S2), 14593–14598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, C.; Lu, X.; Aisa, H.A. Preparation of novel 1,2,3-triazole furocoumarin derivatives via click chemistry and their anti-vitiligo activity. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.; Yin, L.; Aisa, H.A. Novel Furocoumarin Derivatives Stimulate Melanogenesis in B16 Melanoma Cells by Up-Regulation of MITF and TYR Family via Akt/GSK3β/β-Catenin Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Anderson, T.F. Psoralen photochemotherapy. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1987, 17, 703–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honig, B.; Morison, W.L.; Karp, D. Photochemotherapy beyond psoriasis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1994, 31, 775–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurshid, K.; Haroon, T.S.; Hussain, I.; Pal, S.S.; Jahangir, M.; Zaman, T. Psoralen-ultraviolet A therapy vs. psoralen-ultraviolet B therapy in the treatment of plaque-type psoriasis: Our experience with fitzpatrick skin type IV. Int. J. Dermatol. 2000, 39, 865–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, P. Psoralen–ultraviolet A endures as one of the most powerful treatments in dermatology: Reinforcement of this ‘triple-product therapy’ by the 2016 British guidelines. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 174, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farahnik, B.; Nakamura, M.; Singh, R.K.; Abrouk, M.; Zhu, T.H.; Lee, K.M.; Jose, M.V.; Dalovisio, R.; Koo, J.; Bhutani, T.; et al. The Patient’s Guide to Psoriasis Treatment. Part 2: PUVA Phototherapy. Dermatol. Ther. 2016, 6, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez, R.; Jacobe, H. Phototherapy for sclerosing skin conditions. Expert Rev. Dermatol. 2011, 6, 595–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Traven, V.F. New Synthetic Routes to Furocoumarins and Their Analogs: A Review. Molecules 2004, 9, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gogary, S.; Hashem, N.; Khodeir, M.N. Synthesis and photooxygenation of angular furocoumarins: Isopsedopsoralen and allopsoralen. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2013, 41, 1591–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Via, L.D.; Mammi, S.; Uriarte, E.; Santana, L.; Lampronti, I.; Gambari, A.R.; Gia, O. New Furan Side Tetracyclic Allopsoralen Derivatives: Synthesis and Photobiological Evaluation. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 4317–4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uriarte, E.; González-Gómez, J.C.; Santana, L. Regioselective Synthesis of Linear and Angular Pyridazine Furocoumarins. Synthesis 2002, 2002, 0043–0046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamalis, J.; Yusof, F.S.M.; Chander, S.; Wahab, R.A.; Bhagwat, D.P.; Sankaranarayanan, M.; Almalki, F.; Ben Hadda, T. Psoralen Derivatives: Recent Advances of Synthetic Strategy and Pharmacological Properties. Anti-Inflamm. Anti-Allergy Agents Med. Chem. 2020, 19, 222–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garazd, M.M.; Garazd, Y.L.; Shilin, S.V.; Khilya, V.P. Modified Coumarins. I. Synthesis of 5-Phenyl-7H-furo[2, 3-g]chromen-7-ones and 9-Phenyl-7H-furo-[2, 3-f]chromen-7-ones. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2000, 36, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touré, B.B.; Hall, D. Natural Product Synthesis Using Multicomponent Reaction Strategies. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 4439–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaczyk-Lesanko, A.; Hall, D.G. Wanted: New multicomponent reactions for generating libraries of polycyclic natural products. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2005, 9, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dömling, A.; Wang, W.; Wang, K. Chemistry and Biology Of Multicomponent Reactions. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 3083–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, S.E.; Gulati, S.; Shankaraiah, N. Recent advances in multi-component reactions and their mechanistic insights: A triennium review. Org. Chem. Front. 2021, 8, 4237–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younus, H.A.; Al-Rashida, M.; Hameed, A.; Uroos, M.; Salar, U.; Rana, S.; Khan, K.M. Multicomponent reactions (MCR) in medicinal chemistry: A patent review (2010–2020). Expert Opin. Ther. Patents 2021, 31, 267–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komogortsev, A.N.; Lichitsky, B.V.; Melekhina, V.G. Straightforward One-Step Approach towards Novel Derivatives of 9-Oxo-5,6,7,9-Tetrahydrobenzo[9,10]Heptaleno[3,2-b]Furan-12-yl)Acetic Acid Based on the Multicomponent Reaction of Colchiceine, Arylglyoxals and Meldrum’s Acid. Tetrahedron Lett. 2021, 78, 153292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbunov, Y.O.; Lichitsky, B.V.; Komogortsev, A.N.; Mityanov, V.S.; Dudinov, A.A.; Krayushkin, M.M. Synthesis of Condensed Furylacetic Acids Based on Multicomponent Condensation of Heterocyclic Enols with Arylglyoxals and Meldrum’s Acid. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 2018, 54, 692–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komogortsev, A.N.; Lichitsky, B.V.; Tretyakov, A.D.; Dudinov, A.A.; Krayushkin, M.M. Investigation of the multicomponent reaction of 5-hydroxy-2-methyl-4H-pyran-4-one with carbonyl compounds and Meldrum’s acid. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 2019, 55, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichitsky, B.V.; Melekhina, V.G.; Komogortsev, A.N.; Minyaev, M.E. A new multicomponent approach to the synthesis of substituted furan-2(5H)-ones containing 4H-chromen-4-one fragment. Tetrahedron Lett. 2020, 61, 152602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichitsky, B.V.; Tretyakov, A.D.; Komogortsev, A.N.; Mityanov, V.; Dudinov, A.A.; Gorbunov, Y.O.; Daeva, E.D.; Krayushkin, M.M. Synthesis of substituted benzofuran-3-ylacetic acids based on three-component condensation of polyalkoxyphenols, arylglyoxals and Meldrum’s acid. Mendeleev Commun. 2019, 29, 587–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lichitsky, B.V.; Komogortsev, A.N.; Melekhina, V.G. 2-(2-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-4,9-dimethyl-7-oxo-7H-furo[2,3-f]chromen-3-yl)acetic Acid. Molbank 2021, 2021, M1304. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1304
Lichitsky BV, Komogortsev AN, Melekhina VG. 2-(2-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-4,9-dimethyl-7-oxo-7H-furo[2,3-f]chromen-3-yl)acetic Acid. Molbank. 2021; 2021(4):M1304. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1304
Chicago/Turabian StyleLichitsky, Boris V., Andrey N. Komogortsev, and Valeriya G. Melekhina. 2021. "2-(2-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-4,9-dimethyl-7-oxo-7H-furo[2,3-f]chromen-3-yl)acetic Acid" Molbank 2021, no. 4: M1304. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1304
APA StyleLichitsky, B. V., Komogortsev, A. N., & Melekhina, V. G. (2021). 2-(2-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-4,9-dimethyl-7-oxo-7H-furo[2,3-f]chromen-3-yl)acetic Acid. Molbank, 2021(4), M1304. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1304






