Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Schiff Bases of Isoniazid and Evaluation of Their Anti-Proliferative and Antibacterial Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
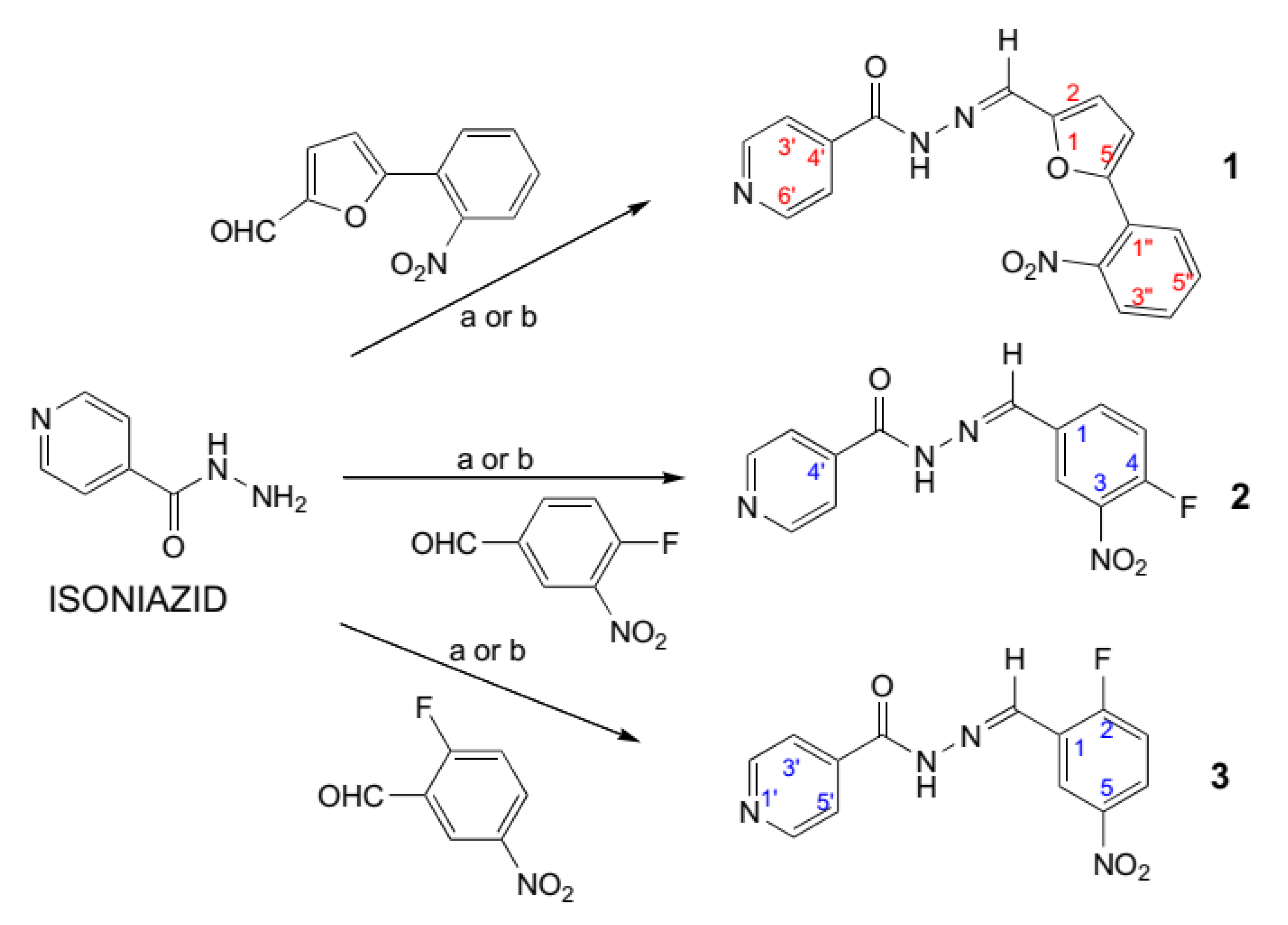
2.1. Chemical Section
2.2. Biological Studies
2.2.1. Antiproliferative Activity
2.2.2. Antibacterial Screening
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
General Procedure for the Synthesis of Schiff Bases of Isoniazid
3.2. Chemicals and Cell Lines
3.2.1. Antiproliferative Activity
3.2.2. Antibacterial Screening
3.3. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aboul-Fadl, T.; Mohammed, F.A.; Hassan, E.A. Synthesis, antitubercular activity and pharmacokinetic studies of some Schiff bases derived from 1-alkylisatin and isonicotinic acid hydrazide (INH). Arch. Pharm. Res. 2003, 26, 778–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearn, M.J.; Cynamon, M.H.; Chen, M.F.; Coppins, R.; Davis, J.; Joo-On Kang, H.; Noble, A.; Tu-Sekine, B.; Terrot, M.S.; Trombino, D.; et al. Preparation and antitubercular activities in vitro and in vivo of novel Schiff bases of isoniazid. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 4169–4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazim, U.; Ali, S.I.; Ishrat, G.; Hassan, A.; Ahmed, M.; Ali, M.; Ali, Z.; Noori, M.Y. Synthesis, characterization and SEM studies of novel 1-indanyl isoniazid and hydrazide Schiff base derivatives as new anti-tubercular agents. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 33, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar]
- Chohan, Z.H.; Arif, M.; Shafiq, Z.; Yaqub, M.; Supuran, C.T. In vitro antibacterial, antifungal & cytotoxic activity of some isonicotinoylhydrazide Schiff’s bases and their cobalt (II), copper (II), nickel (II) and zinc (II) complexes. J Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2006, 21, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habala, L.; Varényi, S.; Bilková, A.; Herich, P.; Valentová, J.; Kožíšek, J.; Devínsky, F. Antimicrobial Activity and Urease Inhibition of Schiff Bases Derived from Isoniazid and Fluorinated Benzaldehydes and of Their Copper(II) Complexes. Molecules 2016, 21, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, N.; Rashid, F.; Ali, S.; Tirmizi, S.A.; Ahmad, I.; Zaib, S.; Zubair, M.; Diaconescu, P.L.; Tahir, M.N.; Iqbal, J.; et al. Synthesis, characterization, and anticancer activity of Schiff bases. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 38, 3246–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Bhat, M.A.; Shakeel, F. Development and validation of UHPLC-MS/MS assay for rapid determination of a carvone Schiff base of isoniazid (CSB-INH) in rat plasma: Application to pharmacokinetic study. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2015, 29, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Jia, Z.L.; Ma, R.J.; Wang, X.F.; Chen, W.Y.; Liu, K.C. Isoniazid promotes the anti-inflammatory response in zebrafish associated with regulation of the PPARgamma/NF-kappaB/AP-1 pathway. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2020, 316, 108928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, F.A.; Oliveira, A.C.; Cavalcanti, B.C.; Pessoa, C.; Pinheiro, A.C.; de Souza, M.V. Biological evaluation of isoniazid derivatives as an anticancer class. Sci. Pharm. 2014, 82, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firmino, G.S.; de Souza, M.V.; Pessoa, C.; Lourenco, M.C.; Resende, J.A.; Lessa, J.A. Synthesis and evaluation of copper(II) complexes with isoniazid-derived hydrazones as anticancer and antitubercular agents. Biometals 2016, 29, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, P.S.; Kasare, S.L.; Haval, N.B.; Khedkar, V.M.; Dixit, P.P.; Rekha, E.M.; Sriram, D.; Haval, K.P. Novel isoniazid embedded triazole derivatives: Synthesis, antitubercular and antimicrobial activity evaluation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardosh, H.H.; Patel, M.P. Design and synthesis of biquinolone-isoniazid hybrids as a new class of antitubercular and antimicrobial agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 65, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigorita, M.G.; Ottana, R.; Maccari, R.; Monforte, F.; Bisignano, G.; Pizzimenti, F.C. Synthesis and in vitro antimicrobial and antitumoral screening of novel lipophilic isoniazid analogues. VI. Boll. Chim. Farm. 1998, 137, 267–276. [Google Scholar]
- Volynets, G.P.; Tukalo, M.A.; Bdzhola, V.G.; Derkach, N.M.; Gumeniuk, M.I.; Tarnavskiy, S.S.; Yarmoluk, S.M. Novel isoniazid derivative as promising antituberculosis agent. Future Microbiol. 2020, 15, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozycka, D.; Korycka-Machala, M.; Zaczek, A.; Dziadek, J.; Gurda, D.; Orlicka-Plocka, M.; Wyszko, E.; Biniek-Antosiak, K.; Rypniewski, W.; Olejniczak, A.B. Novel Isoniazid-Carborane Hybrids Active in Vitro Against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, A.; Johansen, M.D.; Roquet-Baneres, F.; Kremer, L.; Awolade, P.; Ebenezer, O.; Singh, P.; Sumanjit; Kumar, V. Design and synthesis of 4-Aminoquinoline-isoindoline-dione-isoniazid triads as potential anti-mycobacterials. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaraman, P.; Alagarraj, A.; Natarajan, R. In silico and in vitro studies of transition metal complexes derived from curcumin-isoniazid Schiff base. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 38, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.C.; Henriques, R.R.; Junior, M.; Farias, A.B.; Nogueira, T.; Quimas, J.V.F.; Romeiro, N.C.; Silva, L.L.D.; Souza, A.L.F. Acylhydrazones as isoniazid derivatives with multi-target profiles for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: Radical scavenging, myeloperoxidase/acetylcholinesterase inhibition and biometal chelation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. Ca. Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.B.; Tupe, P.N.; Badhe, R.V.; Nanda, R.K.; Kothapalli, L.P.; Paradkar, O.D.; Sharma, P.A.; Deshpande, A.D. Green route synthesis of Schiff’s bases of isonicotinic acid hydrazide. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2009, 2, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elagbar, Z.A.; Naik, R.R.; Shakya, A.K.; Bardaweel, S.K. Fatty Acids Analysis, Antioxidant and Biological Activity of Fixed Oil of Annona muricata L. Seeds. J. Chem. 2016, 2016, 6948098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardaweel, S.K.; Tawaha, K.A.; Hudaib, M.M. Antioxidant, antimicrobial and antiproliferative activities of Anthemis palestina essential oil. BMC Complementary Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenover, F.C. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing☆. In Encyclopedia of Microbiology, 4th ed.; Schmidt, T.M., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2019; pp. 166–175. [Google Scholar]
| Compound | Anti-Proliferative Activity *, µM | Antibacterial Activity (Zone of Inhibition, mm) @ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MCF-7 Cell Lines | S. aureus ATCC 6538 | E. coli ATCC 8739 | |
| 1 | 276 ± 3 | 18 | 15 |
| 2 | 125 ± 3 | 13 | 14 |
| 3 | 253 ± 3 | 14 | 14 |
| Vincristine sulfate | 0.05 ± 0.001 | − | − |
| Amoxicillin (25 μg) | − | 30 | 30 |
| Gentamycin (10 μg) | − | 25 | 25 |
| Tobramycin (30 μg) | − | 35 | 20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Hiyari, B.A.; Shakya, A.K.; Naik, R.R.; Bardaweel, S. Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Schiff Bases of Isoniazid and Evaluation of Their Anti-Proliferative and Antibacterial Activities. Molbank 2021, 2021, M1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1189
Al-Hiyari BA, Shakya AK, Naik RR, Bardaweel S. Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Schiff Bases of Isoniazid and Evaluation of Their Anti-Proliferative and Antibacterial Activities. Molbank. 2021; 2021(1):M1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1189
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Hiyari, Bayan Ahed, Ashok K. Shakya, Rajashri R. Naik, and Sanaa Bardaweel. 2021. "Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Schiff Bases of Isoniazid and Evaluation of Their Anti-Proliferative and Antibacterial Activities" Molbank 2021, no. 1: M1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1189
APA StyleAl-Hiyari, B. A., Shakya, A. K., Naik, R. R., & Bardaweel, S. (2021). Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Schiff Bases of Isoniazid and Evaluation of Their Anti-Proliferative and Antibacterial Activities. Molbank, 2021(1), M1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1189








