Synthesis of γ-Glutamyl Derivatives of Sulfur-Containing Amino Acids in a Multigram Scale via a Two-Step, One-Pot Procedure
Abstract
1. Introduction
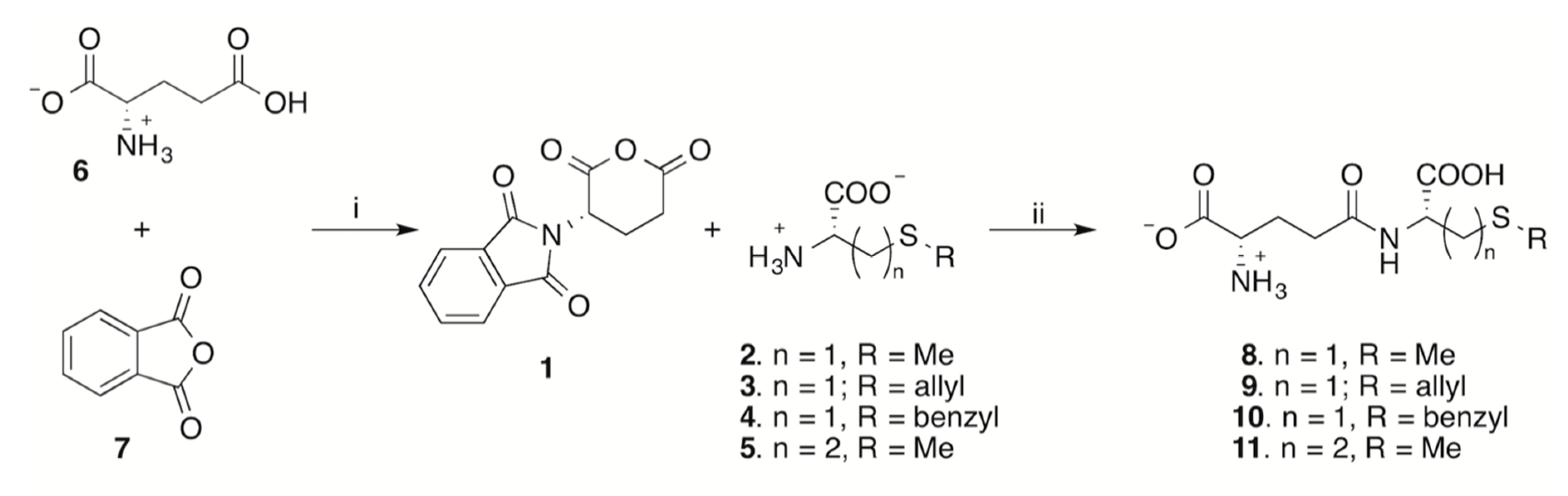
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
3.2. Synthesis of N-Phtaloyl-l-glutamic Acid Anhydride 1
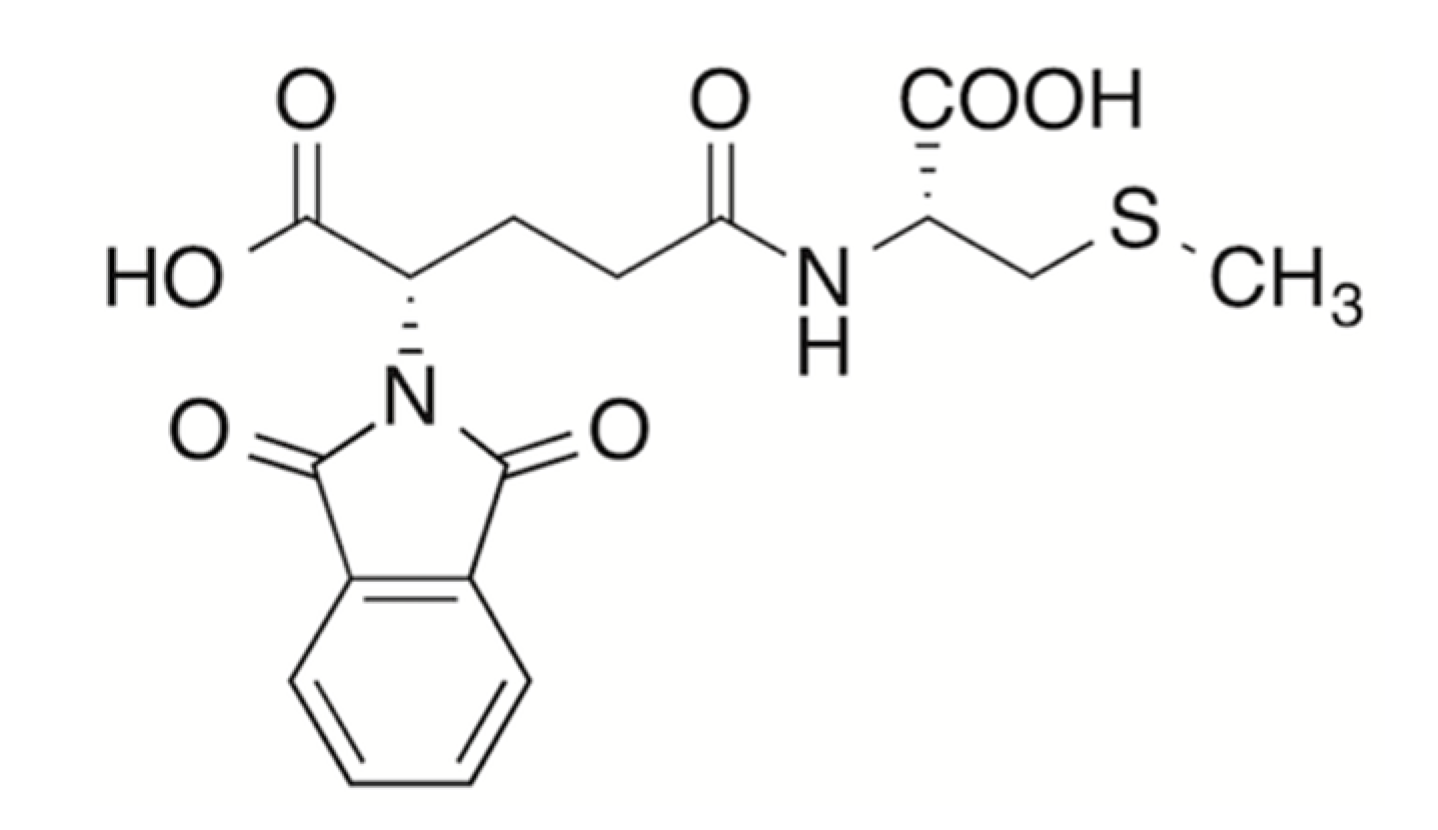
3.3. Synthesis of N-Phtaloyl-γ-glutamyl-S-methyl-l-cysteine 12
3.4. One-Pot Synthesis of γ-Glutamyl Derivatives of Sulfur Amino Acids.
3.4.1. General Procedure
3.4.2. γ-Glutamyl-S-methyl-l-cysteine 8
3.4.3. γ-Glutamyl-S-allyl-l-cysteine 9
3.4.4. γ-Glutamyl-S-benzyl-l-cysteine 10
3.4.5. γ-Glutamyl-l-methionine 11
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kasai, T.; Shiroshita, Y.; Sakamura, S. gamma-Glutamyl peptides of Vigna radiata seeds. Phytochemistry 2013, 25, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muetsch-Eckner, M.; Meier, B.; Wright, A.D.; Sticher, O. γ-Glutamyl peptides from Allium sativum bulbs. Phytochemistry 1992, 31, 2389–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giada, M.D.L.R.; Miranda, M.T.M.; Marquez, U.M.L. Sulfur γ-glutamyl peptides in mature seeds of common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Food Chem. 1998, 61, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubec, R.; Musah, R.A. γ-Glutamyl dipeptides in Petiveria alliacea. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 2494–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Lisk, D.; Block, E.; Ip, C. Characterization of the biological activity of γ-glutamyl-Se-methylselenocysteine. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 2923–2928. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.J.; Schieber, A.; Gänzle, M.G. Formation of taste-active amino acids, amino acid derivatives and peptides in food fermentations—A review. Food Res. Int. 2016, 89, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amino, Y.; Wakabayashi, H.; Akashi, S.; Ishiwatari, Y. Structural analysis and taste evaluation of γ-glutamyl peptides comprising sulfur-containing amino acids. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2018, 82, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, Y.; Yasuda, R.; Kuroda, M.; Eto, Y. Kokumi substances, enhancers of basic tastes, induce responses in calcium-sensing receptor expressing taste cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Bai, W.; Zeng, X.; Cui, C. g-Glutamyl peptides: The food source, enzymatic synthesis, kokumi-active and the potential functional properties—A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 91, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetli, H.A.; Brenneisen, R.; Tschudi, I.; Langos, M.; Bigler, P.; Sprang, T.; Schuerch, S.; Muehlbauer, R.C. A γ-Glutamyl peptide isolated from onion (Allium cepa L.) by bioassay-guided fractionation inhibits resorption activity of osteoclasts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 3408–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Sun, D.; Cui, C.; Dong, K.; Zhao, M. γ-Glu-Met synthesised using a bacterial glutaminase as a potential inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase IV. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 1166–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, M.; Ide, N.; Ono, K. Changes in organosulfur compounds in garlic cloves during storage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 4849–4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Hu, D.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, F.; Hu, X.; Zhao, G. Relationship between γ-glutamyl transpeptidase activity and garlic greening, as controlled by temperature. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 941–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Yamada, C.; Kato, K. γ-Glutamyl compounds and their enzymatic production using bacterial γ-glutamyltranspeptidase. Amino Acids 2007, 32, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-Y.; Lo, H.-F.; Wang, T.-F.; Lin, M.-G.; Lin, L.-L.; Chi, M.-C. Enzymatic synthesis of γ-l-glutamyl-S-allyl-l-cysteine, a naturally occurring organosulfur compound from garlic, by Bacillus licheniformis γ-glutamyltranspeptidase. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2015, 75, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, C.F.; Calvio, C.; Biagiotti, M.; Speranza, G. pH-Dependent hydrolase, glutaminase, transpeptidase and autotranspeptidase activities of Bacillus subtilis γ-glutamyltransferase. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, J.C.; Bolhofer, W.A. The structure of hydroxylysine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1950, 72, 2469–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speranza, G.; Morelli, C.F. γ-Glutamyl transpeptidase-catalyzed synthesis of naturally occurring flavor enhancers. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2012, 84, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Jiang, Y. A practical preparation of N,N-Phthalyl-l-glutamic 1,5-anhydride. Org. Prep. Proc. Int. 2004, 36, 479–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipson, S.R. N,N-Phtaloyl-l-glutamic acid and some derivatives. J. Org. Chem. 1956, 21, 1353–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnan, S.D.J.; Shirota, F.N.; Nagasawa, H.T. Drug latentiation by gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. J. Med. Chem. 1982, 25, 1018–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menard, A.; Castonguay, R.; Lherbet, C.; Rivard, C.; Roupioz, Y.; Keillor, J.W. Nonlinear free energy relationship in the general-acid-catalyzed acylation of rat kidney γ-glutamyl transpeptidase by a series of γ-glutamyl anilide substrate analogues. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 12678–12685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feigl, F. Detection of characteristic functional groups in organic compounds. In Spots Tests in Organic Analysis, 7th ed.; Elsevier Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1966; pp. 277–279. [Google Scholar]
- Goudreau, N.; Brochu, C.; Cameron, D.R.; Duceppe, J.-S.; Faucher, A.-M.; Ferland, J.-M.; Grand-Maître, C.; Poirier, M.; Simoneau, B.; Tsantrizos, Y.S. Potent inhibitors of the hepatitis C virus NS3 protease: Design and synthesis of macrocyclic substrate-based β-strand mimics. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 6185–6201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, J.F.; Wong, F.F. Preparation of γ-glutamyl dipeptides of sulfur-containing amino-acids. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1974, 1, 685–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Speranza, G.; Rabuffetti, M.; Vidović, N.; Morelli, C.F. Synthesis of γ-Glutamyl Derivatives of Sulfur-Containing Amino Acids in a Multigram Scale via a Two-Step, One-Pot Procedure. Molbank 2020, 2020, M1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1147
Speranza G, Rabuffetti M, Vidović N, Morelli CF. Synthesis of γ-Glutamyl Derivatives of Sulfur-Containing Amino Acids in a Multigram Scale via a Two-Step, One-Pot Procedure. Molbank. 2020; 2020(3):M1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1147
Chicago/Turabian StyleSperanza, Giovanna, Marco Rabuffetti, Nikolina Vidović, and Carlo F. Morelli. 2020. "Synthesis of γ-Glutamyl Derivatives of Sulfur-Containing Amino Acids in a Multigram Scale via a Two-Step, One-Pot Procedure" Molbank 2020, no. 3: M1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1147
APA StyleSperanza, G., Rabuffetti, M., Vidović, N., & Morelli, C. F. (2020). Synthesis of γ-Glutamyl Derivatives of Sulfur-Containing Amino Acids in a Multigram Scale via a Two-Step, One-Pot Procedure. Molbank, 2020(3), M1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1147






