N2-tert-Butoxycarbonyl-N5-[N-(9-fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl)-2-aminoethyl]-(S)-2,5-diaminopentanoic Acid
Abstract
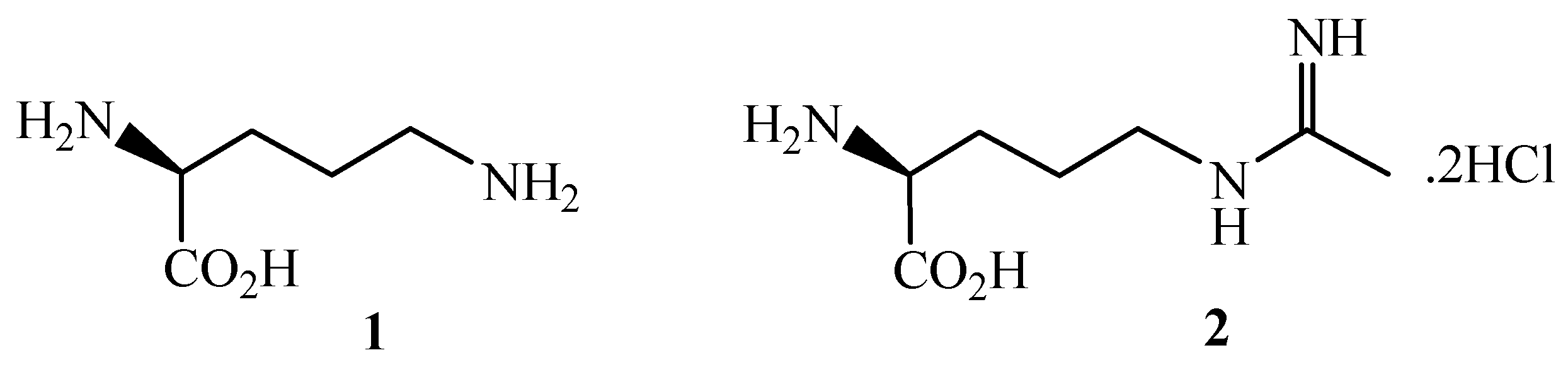
:Introduction
Experimental
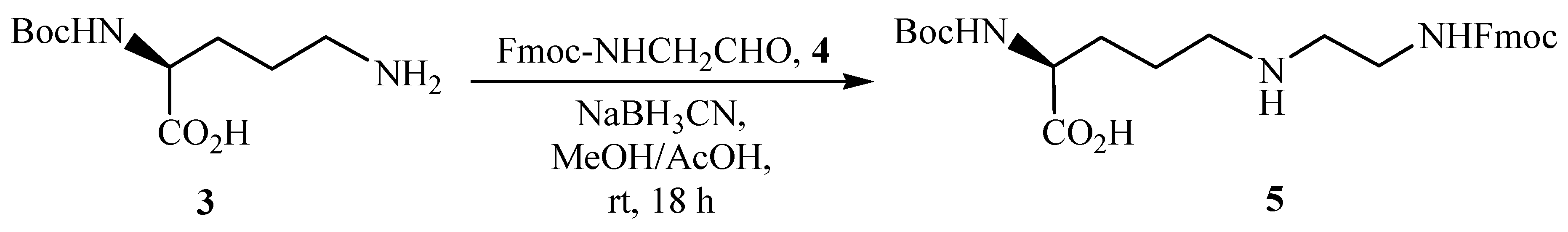
N2-tert-Butoxycarbonyl-N5-[N-(9-fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl)-2-aminoethyl]-(S)-2,5-diaminopentanoic acid (5)
Supplementary materials
Supplementary File 1Supplementary File 2Supplementary File 3Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sugino, T.; Shiri, T.; Kajimoto, Y.; Kajimoto, O. L-Ornithine supplementation attenuates physical fatigue in healthy volunteers by modulation lipid and amino acid metabolism. Nutr. Res. 2008, 28, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demura, S.; Yamada, T.; Yamaji, S.; Komatsu, M.; Morishita, K. The effect of L-ornithine hydrochloride ingestion on performance during incremental exhaustive ergometer bicycle exercise and ammonia metabolism during and after exercise. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 1166–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kottirsch, G.; Zerwes, H.-G.; Cook, N.S.; Tapparelli, C. Beta-amino acid derivatives as orally active non-peptide fibrinogen receptor antagonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1997, 7, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, K.; Tanaka, A.; Fujii, N.; Takasugi, H.; Tenda, Y.; Tomita, M.; Nakazato, S.; Nakano, K.; Kato, Y.; Kono, Y.; et al. Discovery of diphenyloxazole and Nδ-Z-ornithine derivatives as highly potent and selective human prostaglandin EP4 receptor antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 3103–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson, T.; Andersson, P.; Bodelsson, M.; Laurell, M.; Malm, J.; Egesten, A. Bactericidal activity of human eosinophilic granucytes against Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 3591–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, R.P.; Verma, S.S.; Pandey, J.; Tiwati, V.K. Recent development on catalytic reductive amination and applications. Curr. Org. Chem. 2008, 12, 1093–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumori, N.; Masuda, R.; Murata, M. Amphoteric B covalent dimers bearing a tartarate linkage. Chem. Biodivers. 2004, 1, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Maity, J.; Stromberg, R. N2-tert-Butoxycarbonyl-N5-[N-(9-fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl)-2-aminoethyl]-(S)-2,5-diaminopentanoic Acid. Molbank 2014, 2014, M833. https://doi.org/10.3390/M833
Maity J, Stromberg R. N2-tert-Butoxycarbonyl-N5-[N-(9-fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl)-2-aminoethyl]-(S)-2,5-diaminopentanoic Acid. Molbank. 2014; 2014(3):M833. https://doi.org/10.3390/M833
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaity, Jyotirmoy, and Roger Stromberg. 2014. "N2-tert-Butoxycarbonyl-N5-[N-(9-fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl)-2-aminoethyl]-(S)-2,5-diaminopentanoic Acid" Molbank 2014, no. 3: M833. https://doi.org/10.3390/M833
APA StyleMaity, J., & Stromberg, R. (2014). N2-tert-Butoxycarbonyl-N5-[N-(9-fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl)-2-aminoethyl]-(S)-2,5-diaminopentanoic Acid. Molbank, 2014(3), M833. https://doi.org/10.3390/M833




