N,N′-Bis-(4-nitrophenylcarbamothioyl)phthalamide
Abstract
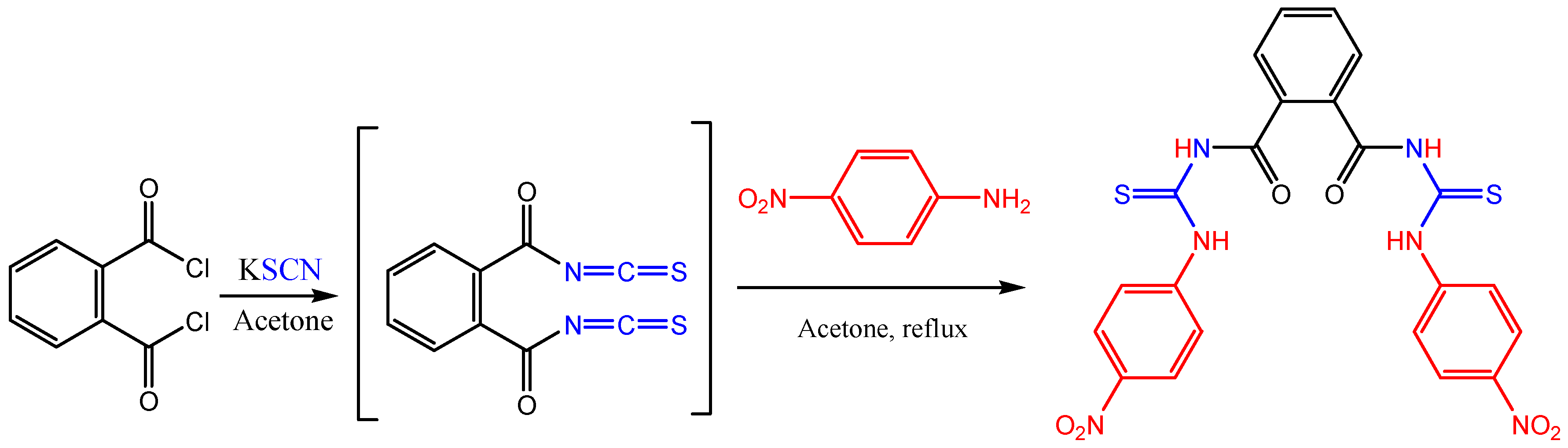
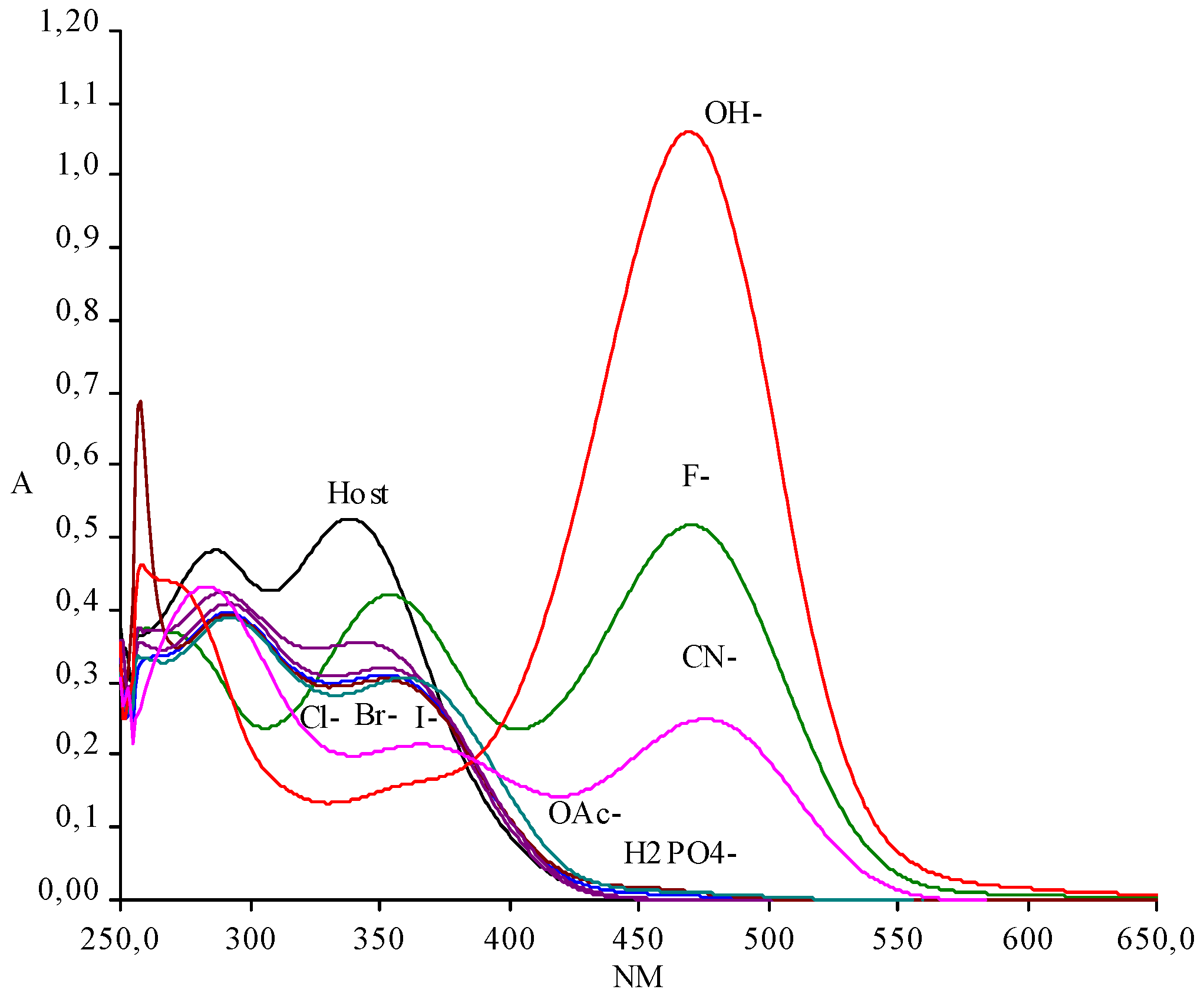
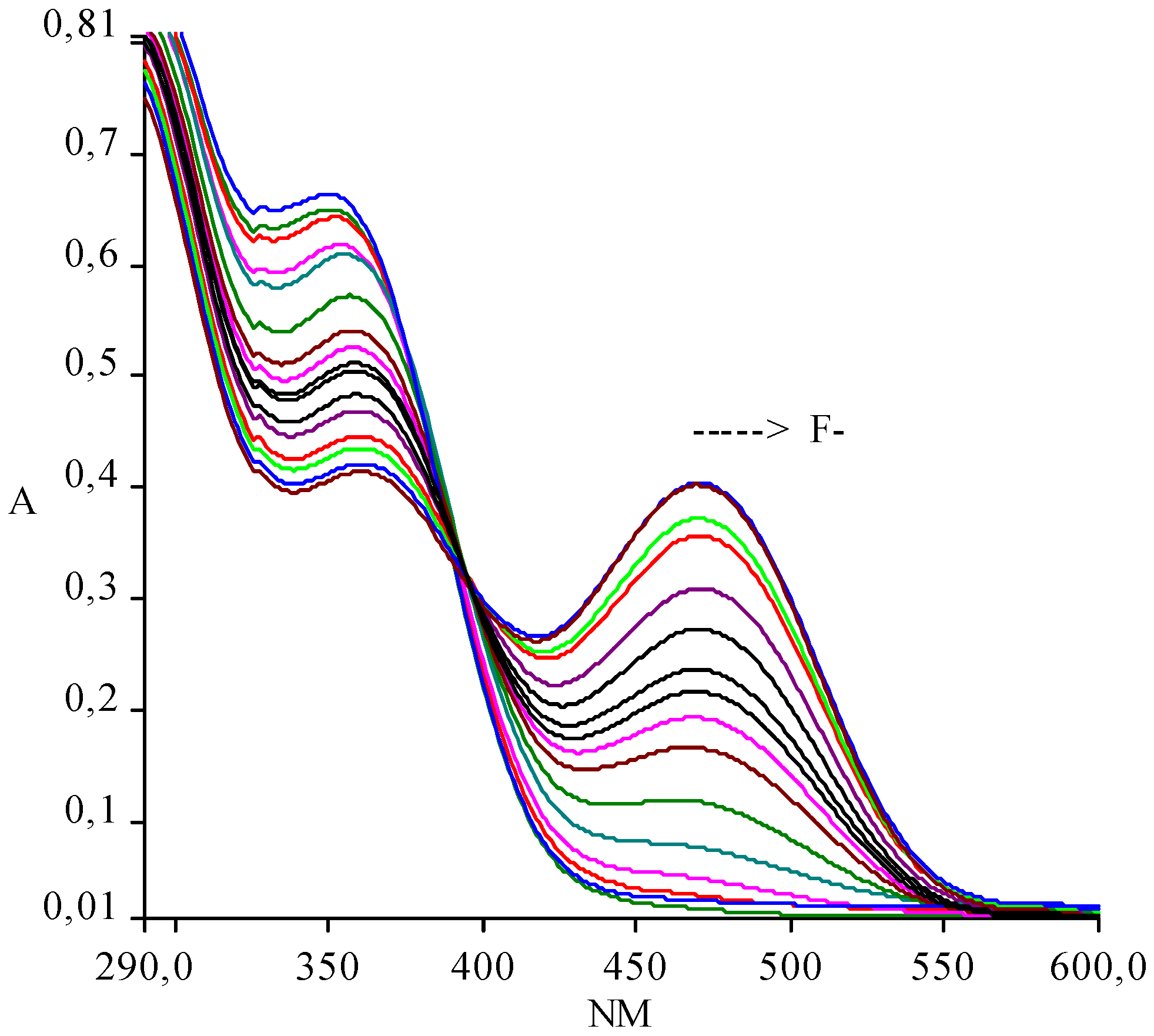
:Results and Discussion
Experimental
Materials and Measurements
Synthesis and Characterization of N,N′-Bis-(4-nitrophenylcarbamothioyl)phthalamide
Supplementary materials
Supplementary File 1Supplementary File 2Supplementary File 3Supplementary File 4Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Voet, D.; Voet, J.G. Biochemistry, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Sessler, J.L.; Gale, P.A.; Cho, W.S. Anion Receptor Chemistry; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gimeno, N.; Vilar, R. Anions as templates in coordination and supramolecular chemistry. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2006, 250, 3161–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.O.; Begum, R.A.; Bowman-James, K. Amide-Based Ligands for Anion Coordination. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 7882–7894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, F.; Tunoglu, N.; Aykac, D. Synthesis of two novel aroyl thioureas and their use as anion binding receptors. Asian J. Chem. 2013, 25, 2455–2458. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Qin, J.; Lin, Q.; Wei, T. Convenient synthesis and anion recognition properties of N-flurobenzoyl-N′-phenylthioureas in water-containing media. J. Fluorine Chem. 2006, 127, 1222–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmiatowski, B.; Mroczynska, K.; Kolehmainen, E.; Kowalska, M.; Volkonen, A.; Pietrzak, M. Association of N-(Pyridin-2-yl),N′-substituted ureas with 2-amino-1,8-naphthyridines and benzoates: NMR and quantum chemical studies of the substituent effect on complexation. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 7582–7593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dydio, P.; Lichosyt, D.; Jurczak, J. Amide- and urea-functionalized pyrroles and benzopyrroles as synthetic, neutral anion receptors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 2971–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Kang, J. Chromogenic anion receptors based on 4-nitrophenylhydrazone and phenylhydrozone. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, H.; Shao, J.; Cai, Z.-S.; Lin, H.-K. A phenylhydrazone-based indole receptor for sensing acetate. Talanta 2008, 74, 1122–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, F.; Tunoglu, N.; Aykac, D.; Arslan, N.B.; Kazak, C. Synthesis and structural X-ray analysis of 1,1′-(naphthalene-1,8-diyl)-3,3′-dibenzoyl-bisthiourea and its use as anion-binding receptor. Turk. J. Chem. 2012, 36, 764–777. [Google Scholar]
- Arslan, H.; Duran, N.; Börekci, G.; Koray, Ö.; Akbay, C. Antimicrobial activity of some thiourea derivatives and their nickel and copper complexes. Molecules 2009, 14, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.H.; Xu, L.; Wang, J.; Wei, T.-B. Studies on the crystal structure and properties of N-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-N′-(4-ethoxybenzoyl)-thiourea. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2008, 183, 1584–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, K.R. New chemistry with old ligands: N-alkyl- and N,N-dialkyl-N′-acyl(aroyl)thioureas in co-ordination, analytical and process chemistry of the platinum group metals. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2001, 216–217, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, N.B.; Kazak, C.; Aydin, F. Synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, X-ray structure and DFT studies on N-(4-nitrobenzoyl)-N′-(1,5-dimethyl-3-oxo-2-phenyl-1H-3(2H)-pyrazolyl)-thiourea. Spectrachim. Acta part A 2012, 89, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, J.; Lin, H.; Lin, H.K. Rational design of a colorimetric and ratiometric fluorescent chemosensor based on intramolecular charge transfer (ICT). Talanta 2008, 77, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Aydin, F.; Dagci, E. N,N′-Bis-(4-nitrophenylcarbamothioyl)phthalamide. Molbank 2013, 2013, M809. https://doi.org/10.3390/M809
Aydin F, Dagci E. N,N′-Bis-(4-nitrophenylcarbamothioyl)phthalamide. Molbank. 2013; 2013(4):M809. https://doi.org/10.3390/M809
Chicago/Turabian StyleAydin, Fatma, and Erdogan Dagci. 2013. "N,N′-Bis-(4-nitrophenylcarbamothioyl)phthalamide" Molbank 2013, no. 4: M809. https://doi.org/10.3390/M809
APA StyleAydin, F., & Dagci, E. (2013). N,N′-Bis-(4-nitrophenylcarbamothioyl)phthalamide. Molbank, 2013(4), M809. https://doi.org/10.3390/M809




