Extracellular RNAs as Messengers and Early Biomarkers in Neurodegeneration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Biology of Extracellular RNAs
| Disease | Metabolic Abnormalities | Representative Gene and Pathway | Cellular Effects of Transcriptional Dysregulation | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alzheimer’s disease (AD) | Hypometabolism in the hippocampus and posterior cingulate cortex (low FDG-PET uptake); impaired neuronal insulin signaling | PGC-1α, IRS1, IDE, APP, MAPT | Mitochondrial dysfunction, energy deficiency, enhanced Tau phosphorylation | [21,23,24,28,29,40,43,44] |
| Parkinson’s disease (PD) | Reduced oxidative phosphorylation and complex I activity in substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons; altered lipid metabolism in basal ganglia | PINK1, PARKIN, DJ-1, LRRK2 | Impaired mitophagy, oxidative stress accumulation, neuronal death | [30,31,39,50,98] |
| Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) | Metabolic imbalance in motor cortex and spinal motor neurons; disrupted glucose and lipid utilization within corticospinal tracts | SOD1, TARDBP, FUS, C9orf72 | RNA metabolic dysregulation, mitochondrial deformation, stress-induced neuronal death | [34,35,36,48,52,99,100,101] |
| Carrier Type | Composition & Physical Features | Biological Roles/Interpretive Meaning | Isolation Method Bias | Key Considerations | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small EVs (30–150 nm) (commonly enriched for exosomes) | Lipid bilayer vesicles; contain miRNA, lncRNA, circRNA, mRNA, proteins | Reflect regulated endosomal secretion; can mediate targeted intercellular communication | Ultracentrifugation, density gradients, SEC, immunoaffinity capture | Size cannot define exosomes; population is heterogeneous | [118,119,120] |
| Microvesicles (100–1000 nm) | Shed from the plasma membrane; carry cytosolic RNA and signaling molecules | Indicate cellular stress, inflammation, activation, or injury | Low-/medium-speed centrifugation, SEC, density separation | Highly heterogeneous; cargo varies by cell state | [121,122,123] |
| RBP-associated RNAs (e.g., Ago2-miRNA complexes) | Non-vesicular ribonucleoprotein complexes; major component of circulating miRNAs | Reflect basal RNA export or passive release from damaged cells | Enriched in post-EV supernatants; protein affinity purification | Do not represent EV biology; dominate plasma miRNA pools | [4,5,124,125] |
| Lipoprotein-associated RNAs (HDL, LDL) | RNAs bound to apolipoproteins; abundant in plasma | Link lipid metabolism with RNA transport; prevalent in circulation | Density flotation, precipitation reagents; present in “EV-free” fractions | Strongly influenced by metabolic state; interpret with lipid context | [116,117,126,127,128,129] |
| Total mixed exRNA (unfractionated plasma) | Combination of vesicular and non-vesicular RNAs | Reflects global RNA shifts but lacks cellular specificity | Commercial precipitation kits, low-speed pelleting | Interpretation difficult; usually dominated by non-vesicular RNA | [4,118,125,129] |
| Immuno-captured EV subsets (e.g., neuron-derived EVs) | EVs isolated via cell-type-specific surface markers | Highest interpretability for CNS diseases; enriched in cell-type-specific RNAs | Depends on antibody specificity and epitope exposure | Lower yield; potential nonspecific binding; high specificity | [69,70,71,74] |
| Platform | Principle | Main Strengths | Main Limitations | Typical Role in exRNA Studies | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small RNA/total RNA next-generation sequencing (NGS) | Library prep from total or size-selected RNA followed by high-throughput sequencing | Unbiased, genome-wide profiling; wide dynamic range; detects novel RNAs, splice variants, fusions | Higher cost; longer turnaround; higher input requirement; complex bioinformatics and batch effects | Discovery-phase profiling of EV and non-vesicular exRNA (miRNA, lncRNA, circRNA, mRNA) in plasma/CSF; construction of disease signatures and pathway maps | [134,135,136,137] |
| RT-qPCR | Reverse transcription followed by quantitative PCR with sequence-specific primers/probes | High sensitivity for moderate–high abundance targets; inexpensive; fast; widely available | Requires a priori target selection; relative (not absolute) quantification; normalization difficulties in biofluids; limited multiplexing | Validation of miRNA/lncRNA biomarkers; small targeted panels for longitudinal monitoring | [134] |
| Droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) | Partitioning RT-PCR reactions into thousands of droplets, end-point fluorescence counting for absolute quantification | Very high analytical sensitivity and precision; absolute copy-number detection; ideal for rare exRNAs | Specialized equipment; higher cost per sample; low multiplexing capacity | Precise quantification of rare EV-miRNAs or lncRNAs; low-copy CNS exRNAs in plasma/CSF; EV-mRNA mutation detection | [138,139,140] |
| miRNA/mRNA microarrays | Hybridization of labeled cDNA/cRNA to probe panels; fluorescence-based detection | Medium–high multiplex capacity; relatively inexpensive; simpler workflow than NGS | Limited to known targets; lower sensitivity and narrower dynamic range than NGS and ddPCR; cross-hybridization background | High-throughput screening of predefined miRNA/mRNA panels; large-cohort exRNA biomarker screening | [134] |
| NanoString nCounter/barcode hybridization panels | Probe hybridization with color-coded barcodes, direct digital counting (no amplification) | High reproducibility; medium–high multiplexing; tolerates low or partially degraded input; no PCR bias | Sensitivity lower than NGS and ddPCR; restricted to panel design; platform-specific normalization needed | EV-miRNA or EV-mRNA analysis from low-input EV RNA; cohort screening with targeted panels | [141,142] |
| Single-EV/single-particle RNA methods (microfluidic or droplet-based) | Isolation or barcoding of individual EVs, followed by cDNA synthesis and sequencing or targeted RNA assays | Resolves heterogeneity between EV subpopulations; links RNA cargo to EV size/phenotype | Technically demanding; expensive; low throughput; not standardized | Mechanistic studies of EV cargo selection; exploratory single-EV diagnostics | [143,144,145] |
| Biosensor-based exRNA detection (electrochemical, SERS, etc.) | Surface-immobilized probes capture specific RNAs; electrical or Raman-based signal detection | Ultrafast detection; tiny sample requirement; potential for point-of-care devices | Limited to few targets; lacks broad clinical validation; mainly proof-of-concept | On-chip detection of selected EV miRNAs or tumor exRNAs; potential POCT applications | [146,147,148,149,150] |
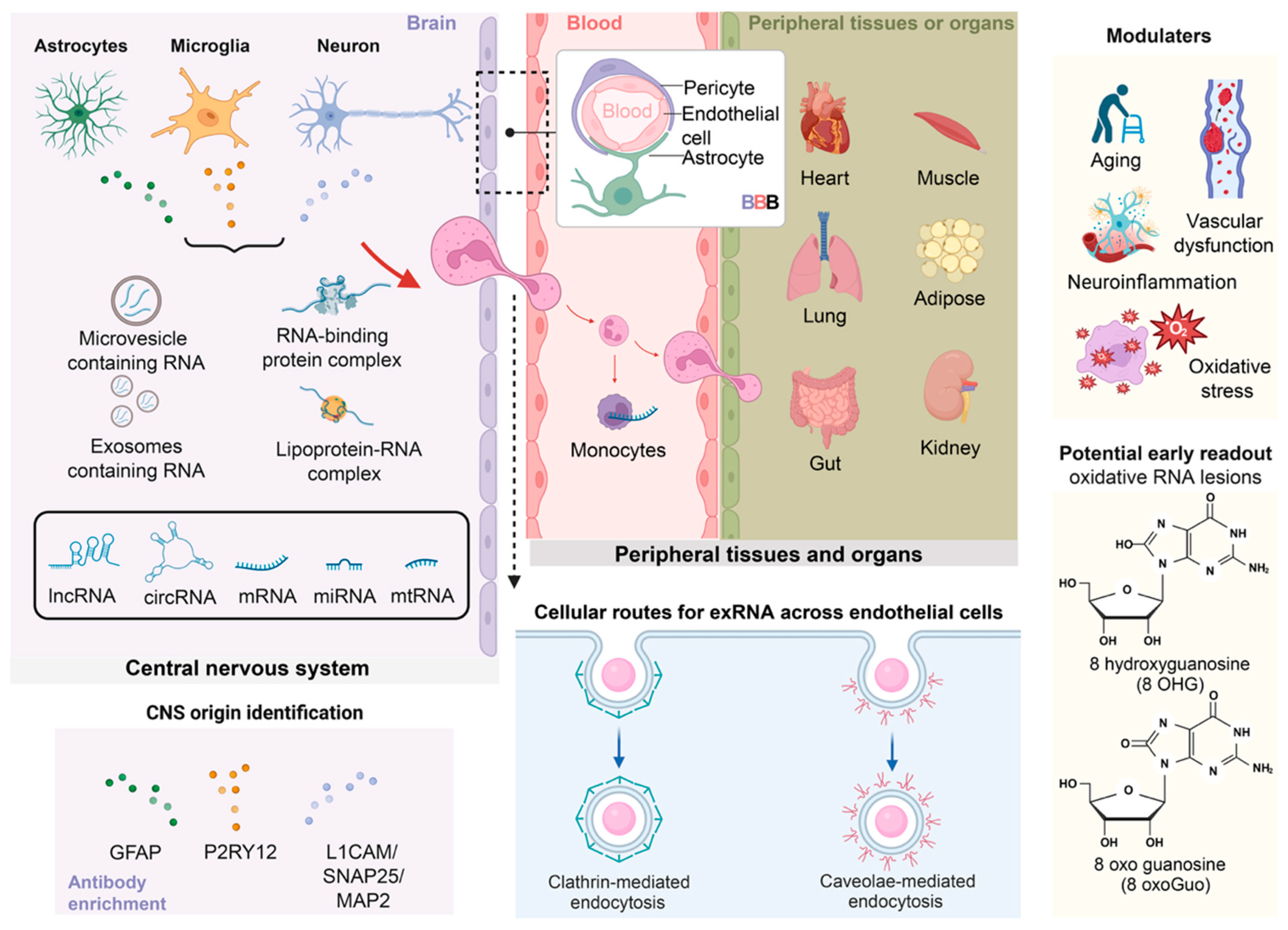
3. Extracellular RNA Trafficking and the Blood–Brain Barrier
| Disease | Neuroimaging Diagnostic Indicators | CSF Biomarkers | Diagnostic Stage | Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alzheimer’s disease (AD) | FDG-PET hypometabolism, MRI-detected cortical atrophy | Aβ42 ↓/Tau ↑ | Mostly diagnosed at middle to late stages | Cannot reflect early transcriptional or metabolic alterations | [43,161] |
| Parkinson’s disease (PD) | DAT-SPECT imaging | α-synuclein oligomers, DJ-1 | Diagnosed after symptom onset | Lacks indicators of early neuronal metabolic abnormalities | [49,50,51] |
| Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) | MRI-detected cortical atrophy, electromyography (EMG) | NfL | At the stage of neuronal injury | Unable to monitor early metabolic imbalance or RNA regulatory dysfunction | [48,52] |
4. Functional Roles of Extracellular RNAs in Neural Physiology
| Axis | Representative EV-miRNAs | Associated CNS Effects/Diseases | Potential Biomarker or Therapeutic Relevance | Validation | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gut–Brain | miR-146a, miR-206-3p, miR-155-5p | Dysbiosis-linked neuroinflammation; anxiety, depression, AD, PD, ASD | Candidate biomarkers for gut–brain disorders; therapeutic modulation of dysregulated miRNAs | Observational/correlative; limited mechanistic linkage for specific miRNAs | [208,209,210,211,212] |
| Lung-Brain | miR-21, miR-145, miR-217, miR-374a-5p | Lung cancer-derived EVs promote brain metastasis; TBI-associated inflammation | Circulating EV-miRNAs as markers for metastasis risk; possible targets to block BBB disruption | In vivo model support (causal evidence for EV-miRNA in brain metastasis); plus human biomarker validation in cohorts | [213,214,215,216] |
| Heart-Brain | miR-1, miR-27a, miR-29b, miR-340, miR-424, miR-17-92 cluster | Post-MI EV-miR-1 induces hippocampal microtubule damage; EV-miR-27a linked to oxidative stress in heart failure; overlapping EV-miRNAs in stroke and MI | Diagnostic candidates for cardiogenic dementia and stroke; therapeutic miRNA delivery (e.g., MSC-EVs) | In vivo model support (exosome-mediated heart-to-brain transfer demonstrated) | [217,218,219,220,221,222,223,224,225] |
| Muscle-Brain | MyomiRs (miR-1, miR-133a, miR-206, miR-499, miR-486, miR-29b-3p) | Exercise-induced neuroprotection; traumatic brain injury (TBI); regulation of BDNF, neuroplasticity, neuropathic pain | Serum exosomal myomiRs as biomarkers for neurodegeneration and TBI prognosis | Observational/correlative (circulating/exosomal myomiRs); mechanistic CNS effects remain limited/indirect | [226,227,228] |
| Adipose-Brain | miR-155, miR-21, miR-425, miR-29a, miR-9-3p, miR-33 | Obesity/diabetes-induced neuroinflammation; cognitive decline; altered hypothalamic signaling | Adipose-derived EV-miRNAs as liquid biopsy markers for obesity-associated cognitive impairment | In vivo model support (adipose EVs/miRNA cargo modulate brain outcomes in obesity/metabolic disease models) | [229,230,231,232] |
| Kidney-Brain | miR-29a, miR-223, miR-27a, miR-326, miR-34a, miR-17, miR-126 | Chronic kidney disease (CKD) linked to cognitive impairment; ischemic brain injury; EV-miR-34a shared between brain and kidney | Novel liquid biopsy markers to monitor CNS complications in CKD | Observational/correlative (CKD biofluid EV-miRNAs as biomarkers); limited direct kidney-to-brain causal EV-miRNA evidence | [233,234,235,236,237] |
| Immune-Brain | miR-146a, miR-155, miR-124, miR-21-5p, miR-409-3p | Neuroinflammation in AD, PD, MS, TBI; microglial activation or polarization | Targets for EV-based immunomodulation (e.g., engineered EV-miR-124 delivery for neuroprotection) | In vivo model support (EV-miRNA therapy/functional modulation of neuroinflammation and recovery) | [210,238,239,240,241,242] |
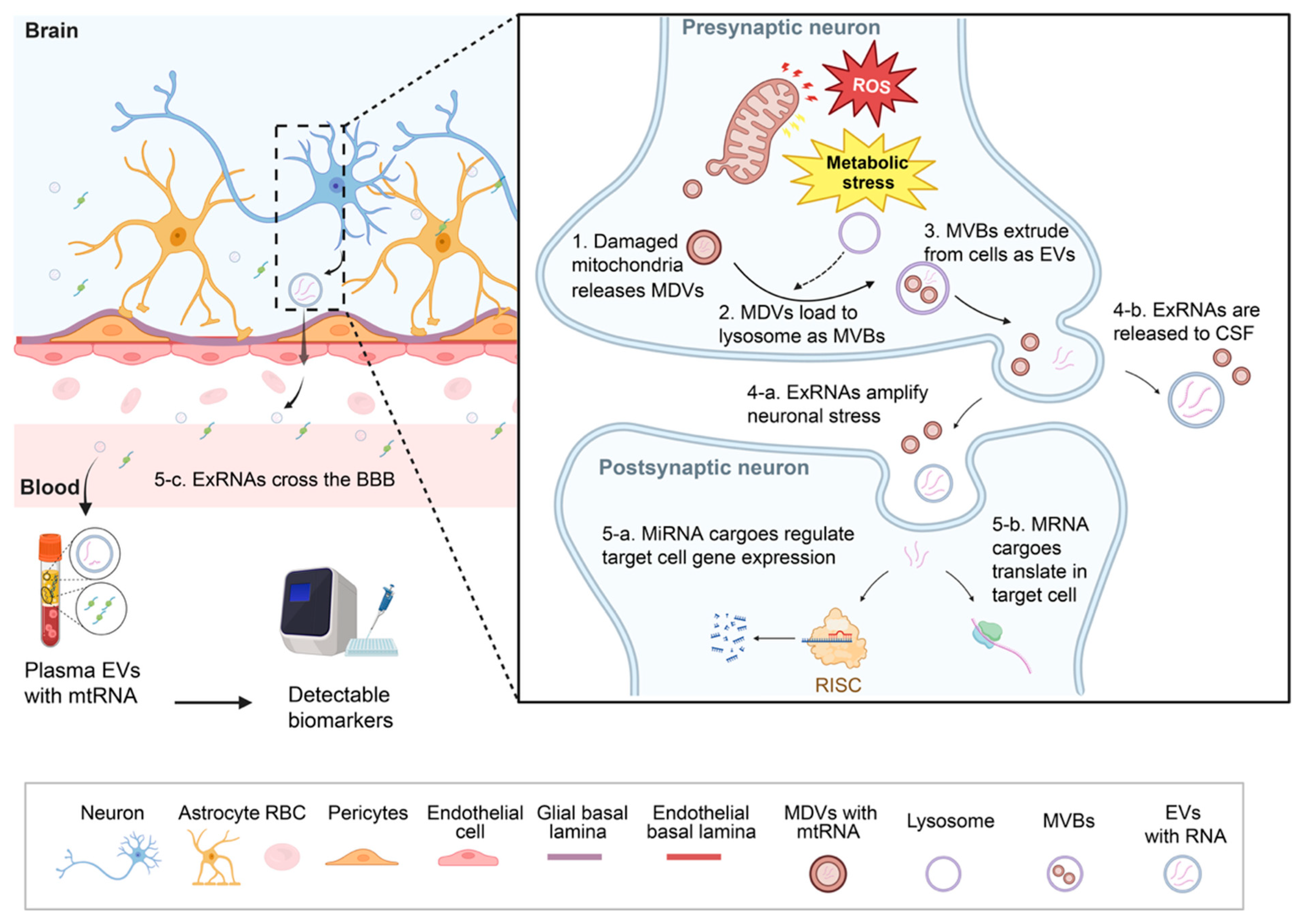
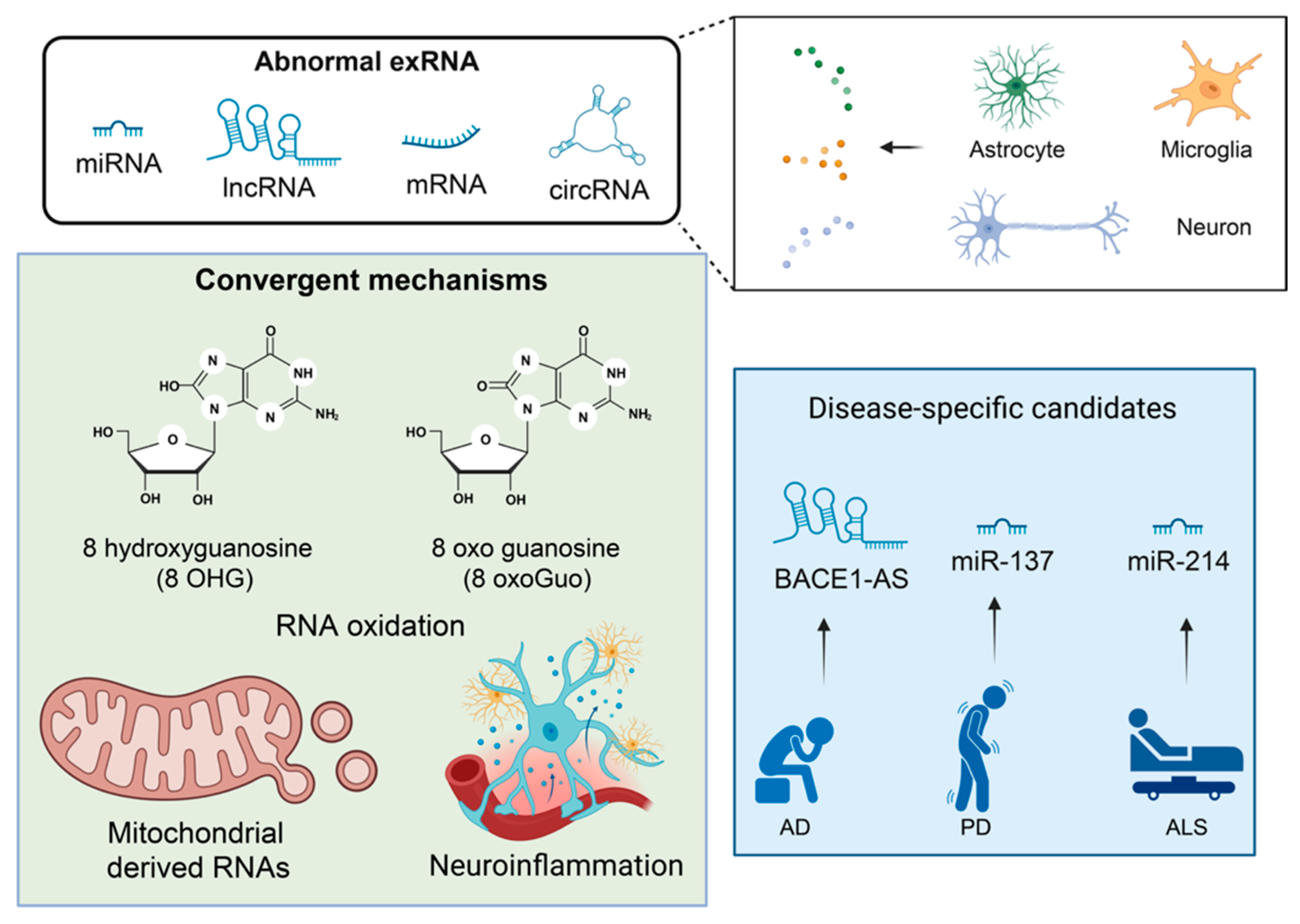
5. Altered exRNA Signaling in Neurodegeneration
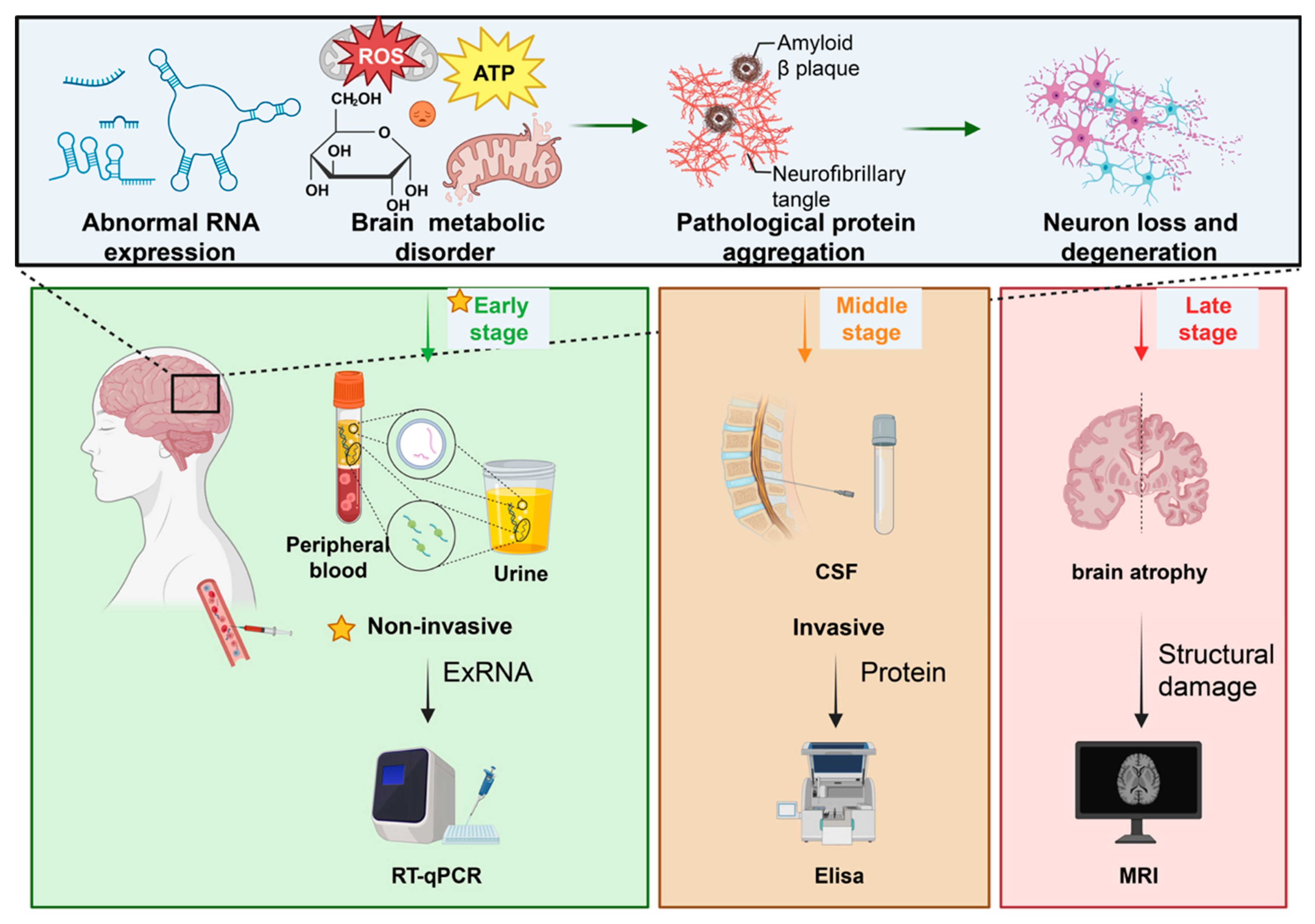
6. Extracellular RNAs as Biomarkers: Technical and Conceptual Considerations
7. Disease-Specific Evidence
7.1. Alzheimer’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment
7.2. Parkinson’s Disease
7.3. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
7.4. Frontotemporal Dementia and Huntington’s Disease
7.5. Multiple Sclerosis and Traumatic Brain Injury
7.6. Glioblastoma and Other Brain Tumors
7.7. Cross-Disease Patterns and Shared Pathways
7.8. Vascular Dementia and Other Underrepresented Conditions
8. Translational Potential and Therapeutic Applications
9. Limitations, Gaps and Recommendations
10. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tkach, M.; Théry, C. Communication by Extracellular Vesicles: Where We Are and Where We Need to Go. Cell 2016, 164, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruner, H.N.; McManus, M.T. Examining the Evidence for Extracellular RNA Function in Mammals. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021, 22, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosar, J.P.; Witwer, K.; Cayota, A. Revisiting Extracellular RNA Release, Processing, and Function. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2021, 46, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, J.D.; Chevillet, J.R.; Kroh, E.M.; Ruf, I.K.; Pritchard, C.C.; Gibson, D.F.; Mitchell, P.S.; Bennett, C.F.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Stirewalt, D.L.; et al. Argonaute2 Complexes Carry a Population of Circulating microRNAs Independent of Vesicles in Human Plasma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5003–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhu, D.; Huang, L.; Zhang, J.; Bian, Z.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Zen, K. Argonaute 2 Complexes Selectively Protect the Circulating MicroRNAs in Cell-Secreted Microvesicles. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampetaki, A.; Willeit, P.; Drozdov, I.; Kiechl, S.; Mayr, M. Profiling of Circulating microRNAs: From Single Biomarkers to Re-Wired Networks. Cardiovasc. Res. 2012, 93, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Kang, M.-H.; Kim, J.-H. A Comprehensive Review on Factors Influences Biogenesis, Functions, Therapeutic and Clinical Implications of Exosomes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 1281–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratajczak, M.Z.; Ratajczak, J. Extracellular Microvesicles/Exosomes: Discovery, Disbelief, Acceptance, and the Future? Leukemia 2020, 34, 3126–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular Vesicles: Exosomes, Microvesicles, and Friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurung, S.; Perocheau, D.; Touramanidou, L.; Baruteau, J. The Exosome Journey: From Biogenesis to Uptake and Intracellular Signalling. Cell Commun. Signal. 2021, 19, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricarico, C.; Clancy, J.; D’Souza-Schorey, C. Biology and Biogenesis of Shed Microvesicles. Small GTPases 2017, 8, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadi, H.; Ekström, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lötvall, J.O. Exosome-Mediated Transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs Is a Novel Mechanism of Genetic Exchange between Cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chausse, B.; Malorny, N.; Lewen, A.; Poschet, G.; Berndt, N.; Kann, O. Metabolic Flexibility Ensures Proper Neuronal Network Function in Moderate Neuroinflammation. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulica, P.; Grünewald, A.; Pereira, S.L. Astrocyte-Neuron Metabolic Crosstalk in Neurodegeneration: A Mitochondrial Perspective. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 668517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shichkova, P.; Coggan, J.S.; Markram, H.; Keller, D. Brain Metabolism in Health and Neurodegeneration: The Interplay Among Neurons and Astrocytes. Cells 2024, 13, 1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sertbaş, M.; Ülgen, K.; Çakır, T. Systematic Analysis of Transcription-Level Effects of Neurodegenerative Diseases on Human Brain Metabolism by a Newly Reconstructed Brain-Specific Metabolic Network. FEBS Open Bio 2014, 4, 542–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yelamanchili, S.V.; Lamberty, B.G.; Rennard, D.A.; Morsey, B.M.; Hochfelder, C.G.; Meays, B.M.; Levy, E.; Fox, H.S. MiR-21 in Extracellular Vesicles Leads to Neurotoxicity via TLR7 Signaling in SIV Neurological Disease. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005032, Erratum in PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005131. Erratum in PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamptey, R.N.L.; Chaulagain, B.; Trivedi, R.; Gothwal, A.; Layek, B.; Singh, J. A Review of the Common Neurodegenerative Disorders: Current Therapeutic Approaches and the Potential Role of Nanotherapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toader, C.; Tataru, C.P.; Munteanu, O.; Serban, M.; Covache-Busuioc, R.-A.; Ciurea, A.V.; Enyedi, M. Decoding Neurodegeneration: A Review of Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Advances in Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and ALS. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribarič, S. Detecting Early Cognitive Decline in Alzheimer’s Disease with Brain Synaptic Structural and Functional Evaluation. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwman, M.M.A.; Frigerio, I.; Reijner, N.; van de Berg, W.D.J.; Jonkman, L.E. Synaptic Density in the Hippocampal and Parahippocampal Subregions and Its Association with the Severity of Axonal Damage and Cognitive Decline in Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2025, 20, e092170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, G.M.; Walsh, D.M. Alzheimer’s Disease: Synaptic Dysfunction and Aβ. Mol. Neurodegener. 2009, 4, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessandro, M.C.B.; Kanaan, S.; Geller, M.; Praticò, D.; Daher, J.P.L. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 2025, 107, 102713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Kim, S.-H.; Bishayee, K. Dysfunctional Glucose Metabolism in Alzheimer’s Disease Onset and Potential Pharmacological Interventions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, W.-I.; Bormann, M.K.; Shen, M.; Kim, D.; Forester, B.; Park, Y.; So, J.; Seo, H.; Sonntag, K.-C.; Cohen, B.M. Brain Cells Derived from Alzheimer’s Disease Patients Have Multiple Specific Innate Abnormalities in Energy Metabolism. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 5702–5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonsungsan, P.; Aimauthon, S.; Sriwichai, N.; Namchaiw, P. Unveiling Mitochondria as Central Components Driving Cognitive Decline in Alzheimer’s Disease through Cross-Transcriptomic Analysis of Hippocampus and Entorhinal Cortex Microarray Datasets. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.-W.; Al-Ouran, R.; Mangleburg, C.G.; Perumal, T.M.; Lee, T.V.; Allison, K.; Swarup, V.; Funk, C.C.; Gaiteri, C.; Allen, M.; et al. Meta-Analysis of the Alzheimer’s Disease Human Brain Transcriptome and Functional Dissection in Mouse Models. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 107908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, T.; Li, Y.I.; Wong, G.; Humphrey, J.; Wang, M.; Ramdhani, S.; Wang, Y.-C.; Ng, B.; Gupta, I.; Haroutunian, V.; et al. Integrative Transcriptome Analyses of the Aging Brain Implicate Altered Splicing in Alzheimer’s Disease Susceptibility. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1584–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magistri, M.; Velmeshev, D.; Makhmutova, M.; Faghihi, M.A. Transcriptomics Profiling of Alzheimer’s Disease Reveal Neurovascular Defects, Altered Amyloid-β Homeostasis, and Deregulated Expression of Long Noncoding RNAs. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2015, 48, 647–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masato, A.; Plotegher, N.; Boassa, D.; Bubacco, L. Impaired Dopamine Metabolism in Parkinson’s Disease Pathogenesis. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Ponce, X.; Velasco, I. Dopaminergic Neuron Metabolism: Relevance for Understanding Parkinson’s Disease. Metabolomics 2024, 20, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wei, L.; Wu, F.; Hu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, W. Advances with microRNAs in Parkinson’s Disease Research. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2013, 7, 1103–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nies, Y.H.; Mohamad Najib, N.H.; Lim, W.L.; Kamaruzzaman, M.A.; Yahaya, M.F.; Teoh, S.L. MicroRNA Dysregulation in Parkinson’s Disease: A Narrative Review. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 660379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragagnin, A.M.G.; Shadfar, S.; Vidal, M.; Jamali, M.S.; Atkin, J.D. Motor Neuron Susceptibility in ALS/FTD. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grad, L.I.; Rouleau, G.A.; Ravits, J.; Cashman, N.R. Clinical Spectrum of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2017, 7, a024117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butti, Z.; Patten, S.A. RNA Dysregulation in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Front. Genet. 2019, 9, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, J.; Guerrero, E.N.; Hegde, P.M.; Liachko, N.F.; Wang, H.; Vasquez, V.; Gao, J.; Pandey, A.; Taylor, J.P.; Kraemer, B.C.; et al. Motor Neuron Disease-Associated Loss of Nuclear TDP-43 Is Linked to DNA Double-Strand Break Repair Defects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 4696–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suk, T.R.; Rousseaux, M.W.C. The Role of TDP-43 Mislocalization in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Mol. Neurodegener. 2020, 15, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schapira, A.H.V. Evidence for Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease—A Critical Appraisal. Mov. Disord. 1994, 9, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schapira, A.H.V. Human Complex I Defects in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Bioenerg. 1998, 1364, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Li, L.; Perry, G.; Lee, H.; Zhu, X. Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 1240–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistur, R.; Mosconi, L.; Santi, S.D.; Guzman, M.; Li, Y.; Tsui, W.; de Leon, M.J. Current Challenges for the Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease: Brain Imaging and CSF Studies. J. Clin. Neurol. 2009, 5, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosconi, L.; McHugh, P.F. FDG- and Amyloid-PET in Alzheimer’s Disease: Is the Whole Greater than the Sum of the Parts? Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2011, 55, 250–264. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhao, G.; Zhao, Y. Dysregulation of Energy Metabolism in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurol. 2025, 272, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, N.; Shaheen, A.; Osama, M.; Nashwan, A.J.; Bharmauria, V.; Flouty, O. MicroRNAs Regulation in Parkinson’s Disease, and Their Potential Role as Diagnostic and Therapeutic Targets. npj Park. Dis. 2024, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falduti, A.; Giovinazzo, A.; Lo Feudo, E.; Rocca, V.; Brighina, F.; Messina, A.; Conforti, F.L.; Iuliano, R. The Role of Non-Coding RNAs in ALS. Genes 2025, 16, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziff, O.J.; Harley, J.; Wang, Y.; Neeves, J.; Tyzack, G.; Ibrahim, F.; Skehel, M.; Chakrabarti, A.M.; Kelly, G.; Patani, R. Nucleocytoplasmic mRNA Redistribution Accompanies RNA Binding Protein Mislocalization in ALS Motor Neurons and Is Restored by VCP ATPase Inhibition. Neuron 2023, 111, 3011–3027.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmins, H.C.; Thompson, A.E.; Kiernan, M.C. Diagnostic Criteria for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2024, 37, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waragai, M.; Sekiyama, K.; Sekigawa, A.; Takamatsu, Y.; Fujita, M.; Hashimoto, M. α-Synuclein and DJ-1 as Potential Biological Fluid Biomarkers for Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 4257–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Z.; Shi, M.; Chung, K.A.; Quinn, J.F.; Peskind, E.R.; Galasko, D.; Jankovic, J.; Zabetian, C.P.; Leverenz, J.B.; Baird, G.; et al. DJ-1 and α-Synuclein in Human Cerebrospinal Fluid as Biomarkers of Parkinson’s Disease. Brain 2010, 133, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höglinger, G.; Trenkwalder, C. Diagnosis and Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease (Guideline of the German Society for Neurology). Neurol. Res. Pract. 2024, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, K.E.; Sheth, U.; Wong, P.C.; Gendron, T.F. Fluid Biomarkers for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Review. Mol. Neurodegener. 2024, 19, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, P.S.; Parkin, R.K.; Kroh, E.M.; Fritz, B.R.; Wyman, S.K.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Peterson, A.; Noteboom, J.; O’Briant, K.C.; Allen, A.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as Stable Blood-Based Markers for Cancer Detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10513–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creemers, E.E.; Tijsen, A.J.; Pinto, Y.M. Circulating microRNAs: Novel Biomarkers and Extracellular Communicators in Cardiovascular Disease? Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchinovich, A.; Weiz, L.; Langheinz, A.; Burwinkel, B. Characterization of Extracellular Circulating microRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 7223–7233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Pol, J.; Gosselet, F.; Duban-Deweer, S.; Pottiez, G.; Karamanos, Y. Targeting and Crossing the Blood-Brain Barrier with Extracellular Vesicles. Cells 2020, 9, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y. Extracellular Vesicles in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Insights and New Perspectives. Genes Dis. 2021, 8, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.A.; Baba, S.K.; Sadida, H.Q.; Marzooqi, S.A.; Jerobin, J.; Altemani, F.H.; Algehainy, N.; Alanazi, M.A.; Abou-Samra, A.-B.; Kumar, R.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles as Tools and Targets in Therapy for Diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombo, T.B.; Ganguly, A.; Tagle, D.A. Diagnostic Potential of Extracellular RNA from Biofluids. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2016, 16, 1135–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosaka, T.; Yamashita, T.; Tamaoka, A.; Kwak, S. Extracellular RNAs as Biomarkers of Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Other Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Q.; Wittens, M.M.J.; Engelborghs, S.; van Herwijnen, M.H.M.; Tsamou, M.; Roggen, E.; Smeets, B.; Krauskopf, J.; Briedé, J.J. Beyond CSF and Neuroimaging Assessment: Evaluating Plasma miR-145-5p as a Potential Biomarker for Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2024, 15, 1042–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhenaky, A.; Alhazmi, S.; Alamri, S.H.; Alkhatabi, H.A.; Alharthi, A.; Alsaleem, M.A.; Abdelnour, S.A.; Hassan, S.M. Exosomal MicroRNAs in Alzheimer’s Disease: Unveiling Their Role and Pioneering Tools for Diagnosis and Treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, P.; Bian, X.; Xu, S.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, M.; Han, M.; Huang, L.; Bi, J.; et al. Elevated Plasma Levels of Exosomal BACE1-AS Combined with the Volume and Thickness of the Right Entorhinal Cortex May Serve as a Biomarker for the Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, L.H.P.; Chang, C.; Tuchez, K.; Liu, F.; Chen, Y. Assessing Alzheimer’s Disease via Plasma Extracellular Vesicle–Derived mRNA. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 16, e70006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, Q.; Chen, Z.B.; Koo, E.H.; Zhong, S. Presymptomatic Increase of an Extracellular RNA in Blood Plasma Associates with the Development of Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, 1771–1782.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currim, F.; Brown-Leung, J.; Syeda, T.; Corson, M.; Schumann, S.; Qi, W.; Baloni, P.; Shannahan, J.H.; Rochet, J.-C.; Singh, R.; et al. Rotenone Induced Acute miRNA Alterations in Extracellular Vesicles Produce Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Cell Death. npj Park. Dis. 2025, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, G.; Lin, Z.; Du, S.; Fu, Z.; Chen, T.; Qin, Y.; et al. Serum Secreted miR-137-Containing Exosomes Affects Oxidative Stress of Neurons by Regulating OXR1 in Parkinson’s Disease. Brain Res. 2019, 1722, 146331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prada, I.; Gabrielli, M.; Turola, E.; Iorio, A.; D’Arrigo, G.; Parolisi, R.; De Luca, M.; Pacifici, M.; Bastoni, M.; Lombardi, M.; et al. Glia-to-Neuron Transfer of miRNAs via Extracellular Vesicles: A New Mechanism Underlying Inflammation-Induced Synaptic Alterations. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 135, 529–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eitan, E.; Thornton-Wells, T.; Elgart, K.; Erden, E.; Gershun, E.; Levine, A.; Volpert, O.; Azadeh, M.; Smith, D.G.; Kapogiannis, D. Synaptic Proteins in Neuron-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease: Novel Methodology and Clinical Proof of Concept. Extracell. Vesicles Circ. Nucleic Acids 2023, 4, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agliardi, C.; Guerini, F.R.; Zanzottera, M.; Bianchi, A.; Nemni, R.; Clerici, M. SNAP-25 in Serum Is Carried by Exosomes of Neuronal Origin and Is a Potential Biomarker of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 5792–5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapic, M.; Eitan, E.; Werner, J.K.; Berkowitz, S.T.; Lazaropoulos, M.P.; Tran, J.; Goetzl, E.J.; Kapogiannis, D. Plasma Extracellular Vesicles Enriched for Neuronal Origin: A Potential Window into Brain Pathologic Processes. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.M.; Meng, Q.; Perez de Acha, O.; Mustapic, M.; Cheng, A.; Eren, E.; Kundu, G.; Piao, Y.; Munk, R.; Wood, W.H.; et al. Mitochondrial RNA in Alzheimer’s Disease Circulating Extracellular Vesicles. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 581882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Sun, S.; Tan, H. Different Contributions of Clathrin- and Caveolae-Mediated Endocytosis of Vascular Endothelial Cadherin to Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Vascular Hyperpermeability. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Y.; Muraoka, S.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Hu, J.; McQuade, A.K.; Young-Pearse, T.; Aslebagh, R.; Shaffer, S.A.; Gygi, S.P.; Blurton-Jones, M.; et al. Human Neural Cell Type-Specific Extracellular Vesicle Proteome Defines Disease-Related Molecules Associated with Activated Astrocytes in Alzheimer’s Disease Brain. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2022, 11, e12183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouillard, M.E.; Sutter, P.A.; Durham, O.R.; Willis, C.M.; Crocker, S.J. Astrocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicles (ADEVs): Deciphering Their Influences in Aging. Aging Dis. 2021, 12, 1462–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roseborough, A.D.; Myers, S.J.; Khazaee, R.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Iorio, E.; Elahi, F.M.; Pasternak, S.H.; Whitehead, S.N. Plasma Derived Extracellular Vesicle Biomarkers of Microglia Activation in an Experimental Stroke Model. J. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 20, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, L.; Oberländer, J.; Mateos-Maroto, A.; Schunke, J.; Fichter, M.; Krämer-Albers, E.; Landfester, K.; Mailänder, V. Uptake of Extracellular Vesicles into Immune Cells Is Enhanced by the Protein Corona. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2023, 12, e12399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, A.M.; Leicaj, M.L.; Fabiano, M.P.; Cabrerizo, G.; Bannoud, N.; Croci, D.O.; Witwer, K.W.; Remes Lenicov, F.; Ostrowski, M.; Pérez, P.S. Extracellular Vesicles from Human Plasma Dampen Inflammation and Promote Tissue Repair Functions in Macrophages. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2023, 12, 12331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.-C.; Zhang, Y.; Song, E. Extracellular RNA: Mechanisms of It’s Transporting into Target Cells. ExRNA 2019, 1, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, S.K. The Generation of Neuronal Diversity in the Central Nervous System. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1991, 14, 269–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, N.J.; Patabendige, A.A.K.; Dolman, D.E.M.; Yusof, S.R.; Begley, D.J. Structure and Function of the Blood–Brain Barrier. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 37, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obermeier, B.; Daneman, R.; Ransohoff, R.M. Development, Maintenance and Disruption of the Blood-Brain Barrier. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1584–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Ye, W.; Ding, H.; Li, P.; Aung, L.H.H. Role of RNA Oxidation in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rufino-Ramos, D.; Leandro, K.; Perdigão, P.R.L.; O’Brien, K.; Pinto, M.M.; Santana, M.M.; van Solinge, T.S.; Mahjoum, S.; Breakefield, X.O.; Breyne, K.; et al. Extracellular Communication between Brain Cells through Functional Transfer of Cre mRNA. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valles, S.L.; Singh, S.K.; Campos-Campos, J.; Colmena, C.; Campo-Palacio, I.; Alvarez-Gamez, K.; Caballero, O.; Jorda, A. Functions of Astrocytes under Normal Conditions and after a Brain Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Park, J.; Choi, Y.K. The Role of Astrocytes in the Central Nervous System Focused on BK Channel and Heme Oxygenase Metabolites: A Review. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharbi, T.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, G.-Y. The Function of Astrocyte Mediated Extracellular Vesicles in Central Nervous System Diseases. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 568889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordillo-Sampedro, S.; Antounians, L.; Wei, W.; Mufteev, M.; Lendemeijer, B.; Kushner, S.A.; de Vrij, F.M.S.; Zani, A.; Ellis, J. iPSC-Derived Healthy Human Astrocytes Selectively Load miRNAs Targeting Neuronal Genes into Extracellular Vesicles. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2024, 129, 103933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Wu, X.; Guo, C.; Wang, T.; Guo, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, B.; Cui, W.; Bai, H.; Zhou, J.; et al. Astrocyte–Neuron Crosstalk through Extracellular Vesicle-Shuttled miRNA-382-5p Promotes Traumatic Brain Injury. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 2642–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.; Pearse, D.D. The Yin and Yang of Microglia-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in CNS Injury and Diseases. Cells 2024, 13, 1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccarelli, L.; Giacomelli, C.; Marchetti, L.; Martini, C. Microglia Extracellular Vesicles: Focus on Molecular Composition and Biological Function. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2021, 49, 1779–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemaire, Q.; Raffo-Romero, A.; Arab, T.; Van Camp, C.; Drago, F.; Forte, S.; Gimeno, J.-P.; Begard, S.; Colin, M.; Vizioli, J.; et al. Isolation of Microglia-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Towards miRNA Signatures and Neuroprotection. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 17, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philips, T.; Rothstein, J.D. Oligodendroglia: Metabolic Supporters of Neurons. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 3271–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, M.; Nave, K.-A. Oligodendrocytes: Myelination and Axonal Support. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a020479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nave, K.-A.; Asadollahi, E.; Sasmita, A. Expanding the Function of Oligodendrocytes to Brain Energy Metabolism. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2023, 83, 102782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistono, C.; Bister, N.; Stanová, I.; Malm, T. Glia-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Role in Central Nervous System Communication in Health and Disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 623771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frühbeis, C.; Kuo-Elsner, W.P.; Müller, C.; Barth, K.; Peris, L.; Tenzer, S.; Möbius, W.; Werner, H.B.; Nave, K.-A.; Fröhlich, D.; et al. Oligodendrocytes Support Axonal Transport and Maintenance via Exosome Secretion. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramaniam, S.R.; Chesselet, M.-F. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress in Parkinson’s Disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2013, 106–107, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masrori, P.; Van Damme, P. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Clinical Review. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 1918–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kmetzsch, V.; Anquetil, V.; Saracino, D.; Rinaldi, D.; Camuzat, A.; Gareau, T.; Jornea, L.; Forlani, S.; Couratier, P.; Wallon, D.; et al. Plasma microRNA Signature in Presymptomatic and Symptomatic Subjects with C9orf72-Associated Frontotemporal Dementia and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2021, 92, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha-Oliveira, T.; Montezinho, L.; Mendes, C.; Firuzi, O.; Saso, L.; Oliveira, P.J.; Silva, F.S.G. Oxidative Stress in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Pathophysiology and Opportunities for Pharmacological Intervention. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 5021694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target Recognition and Regulatory Functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statello, L.; Guo, C.-J.; Chen, L.-L.; Huarte, M. Gene Regulation by Long Non-Coding RNAs and Its Biological Functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 96–118, Erratum in Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchese, F.P.; Raimondi, I.; Huarte, M. The Multidimensional Mechanisms of Long Noncoding RNA Function. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Joseph, S.; Xia, M.; Teng, F.; Chen, X.; Huang, R.; Zhai, L.; Deng, W. Circular RNAs Acting as miRNAs’ Sponges and Their Roles in Stem Cells. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akat, K.M.; Lee, Y.A.; Hurley, A.; Morozov, P.; Max, K.E.A.; Brown, M.; Bogardus, K.; Sopeyin, A.; Hildner, K.; Diacovo, T.G.; et al. Detection of Circulating Extracellular mRNAs by Modified Small-RNA-Sequencing Analysis. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e127317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Mauro, S.; Scamporrino, A.; Filippello, A.; Di Marco, M.; Di Martino, M.T.; Scionti, F.; Di Pino, A.; Scicali, R.; Malaguarnera, R.; Purrello, F.; et al. Mitochondrial RNAs as Potential Biomarkers of Functional Impairment in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deus, C.M.; Tavares, H.; Beatriz, M.; Mota, S.; Lopes, C. Mitochondrial Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns Content in Extracellular Vesicles Promotes Early Inflammation in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Cells 2022, 11, 2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picca, A.; Guerra, F.; Calvani, R.; Coelho-Junior, H.J.; Bossola, M.; Landi, F.; Bernabei, R.; Bucci, C.; Marzetti, E. Generation and Release of Mitochondrial-Derived Vesicles in Health, Aging and Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, T.; McBride, H.M. Mitochondrial-Derived Vesicles in Metabolism, Disease, and Aging. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akers, J.C.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Kim, R.; Skog, J.; Nakano, I.; Pingle, S.; Kalinina, J.; Hua, W.; Kesari, S.; Mao, Y.; et al. miR-21 in the Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) of Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF): A Platform for Glioblastoma Biomarker Development. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluchino, S.; Smith, J.A. Explicating Exosomes: Reclassifying the Rising Stars of Intercellular Communication. Cell 2019, 177, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastoridis, S.; Bertolino, G.M.; Whitehouse, G.; Dazzi, F.; Sanchez-Fueyo, A.; Martinez-Llordella, M. Multiparametric Analysis of Circulating Exosomes and Other Small Extracellular Vesicles by Advanced Imaging Flow Cytometry. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luisotti, L.; Germelli, L.; Piccarducci, R.; Giacomelli, C.; Marchetti, L.; Martini, C. Extracellular Vesicles as Vehicles for Small Non-Coding RNA Therapeutics: Standardization Challenges for Clinical Translation. Extracell. Vesicles Circ. Nucleic Acids 2025, 6, 403–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, T.C.; Godfrey, C.; McClorey, G.; Vader, P.; Briggs, D.; Gardiner, C.; Aoki, Y.; Sargent, I.; Morgan, J.E.; Wood, M.J.A. Extracellular microRNAs Are Dynamic Non-Vesicular Biomarkers of Muscle Turnover. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 9500–9513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Wong, D.K.; Luk, F.S.; Kim, R.Y.; Raffai, R.L. Isolation of Plasma Lipoproteins as a Source of Extracellular RNA. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1740, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castleberry, M.; Raby, C.A.; Ifrim, A.; Shibata, Y.; Matsushita, S.; Ugawa, S.; Miura, Y.; Hori, A.; Miida, T.; Linton, M.F.; et al. High-Density Lipoproteins Mediate Small RNA Intercellular Communication between Dendritic Cells and Macrophages. J. Lipid Res. 2023, 64, 100328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A Position Statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and Update of the MISEV2014 Guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, J.A.; Goberdhan, D.C.I.; O’Driscoll, L.; Buzas, E.I.; Blenkiron, C.; Bussolati, B.; Cai, H.; Di Vizio, D.; Driedonks, T.A.P.; Erdbrügger, U.; et al. Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles (MISEV2023): From Basic to Advanced Approaches. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12404, Erratum in J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repici, A.; Piraino, G.; Wolfe, V.; Kaplan, J.; Nakamura, T.; Zingarelli, B. Role of Extracellular Vesicles as Mediators of Cell Communication and Novel Biomarkers in Sepsis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słomka, A.; Urban, S.K.; Lukacs-Kornek, V.; Żekanowska, E.; Kornek, M. Large Extracellular Vesicles: Have We Found the Holy Grail of Inflammation? Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Benny, M.; Duara, J.; Williams, K.; Tan, A.; Schmidt, A.; Young, K.C. Extracellular Vesicles: Pathogenic Messengers and Potential Therapy for Neonatal Lung Diseases. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1205882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ståhl, A.; Johansson, K.; Mossberg, M.; Kahn, R.; Karpman, D. Exosomes and Microvesicles in Normal Physiology, Pathophysiology, and Renal Diseases. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2019, 34, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geekiyanage, H.; Rayatpisheh, S.; Wohlschlegel, J.A.; Brown, R.; Ambros, V. Extracellular microRNAs in Human Circulation Are Associated with miRISC Complexes That Are Accessible to Anti-AGO2 Antibody and Can Bind Target Mimic Oligonucleotides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 24213–24223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boon, R.A.; Vickers, K.C. Intercellular Transport of MicroRNAs. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickers, K.C.; Palmisano, B.T.; Shoucri, B.M.; Shamburek, R.D.; Remaley, A.T. MicroRNAs Are Transported in Plasma and Delivered to Recipient Cells by High-Density Lipoproteins. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 423–433, Erratum in Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michell, D.L.; Vickers, K.C. Lipoprotein Carriers of microRNAs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1861, 2069–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, K.J.; Hennessy, E.J. Extracellular Communication via microRNA: Lipid Particles Have a New Message. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 1174–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuana, Y.; Levels, J.; Grootemaat, A.; Sturk, A.; Nieuwland, R. Co-Isolation of Extracellular Vesicles and High-Density Lipoproteins Using Density Gradient Ultracentrifugation. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 23262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Grady, T.; Njock, M.-S.; Lion, M.; Bruyr, J.; Mariavelle, E.; Galvan, B.; Boeckx, A.; Struman, I.; Dequiedt, F. Sorting and Packaging of RNA into Extracellular Vesicles Shape Intracellular Transcript Levels. BMC Biol. 2022, 20, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbiano, F.; Corsi, J.; Gurrieri, E.; Trevisan, C.; Notarangelo, M.; D’Agostino, V.G. RNA Packaging into Extracellular Vesicles: An Orchestra of RNA-Binding Proteins? J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 10, e12043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Kawasaki, Y. A Novel Sorting Signal for RNA Packaging into Small Extracellular Vesicles. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matias-Garcia, P.R.; Wilson, R.; Mussack, V.; Reischl, E.; Waldenberger, M.; Gieger, C.; Anton, G.; Peters, A.; Kuehn-Steven, A. Impact of Long-Term Storage and Freeze-Thawing on Eight Circulating microRNAs in Plasma Samples. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestdagh, P.; Hartmann, N.; Baeriswyl, L.; Andreasen, D.; Bernard, N.; Chen, C.; Cheo, D.; D’Andrade, P.; DeMayo, M.; Dennis, L.; et al. Evaluation of Quantitative miRNA Expression Platforms in the microRNA Quality Control (miRQC) Study. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 809–815, Erratum in Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-A.; Park, C.; Sung, J.-J.; Seo, D.-J.; Choi, S.-J.; Hong, Y.-H. Small RNA Sequencing of Circulating Small Extracellular Vesicles microRNAs in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldez, M.; Spengler, R.; Etheridge, A.; Godoy, P.; Barczak, A.; Srinivasan, S.; De Hoff, P.; Tanriverdi, K.; Courtright, A.; Lu, S.; et al. Comprehensive Multi-Center Assessment of Accuracy, Reproducibility and Bias of Small RNA-Seq Methods for Quantitative miRNA Profiling. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 746–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeri, A.; Courtright, A.; Danielson, K.; Hutchins, E.; Alsop, E.; Carlson, E.; Hsieh, M.; Ziegler, O.; Das, A.; Shah, R.V.; et al. Evaluation of Commercially Available Small RNASeq Library Preparation Kits Using Low Input RNA. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ding, Q.; Plant, P.; Basheer, M.; Yang, C.; Tawedrous, E.; Krizova, A.; Boulos, C.; Farag, M.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Droplet Digital PCR Improves Urinary Exosomal miRNA Detection Compared to Real-Time PCR. Clin. Biochem. 2019, 67, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das Gupta, S.; Ndode-Ekane, X.E.; Puhakka, N.; Pitkänen, A. Droplet Digital Polymerase Chain Reaction-Based Quantification of Circulating microRNAs Using Small RNA Concentration Normalization. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevillet, J.R.; Kang, Q.; Ruf, I.K.; Briggs, H.A.; Vojtech, L.N.; Hughes, S.M.; Cheng, H.H.; Arroyo, J.D.; Meredith, E.K.; Gallichotte, E.N.; et al. Quantitative and Stoichiometric Analysis of the microRNA Content of Exosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 14888–14893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamova, P.; Powell, A.K.; Dykes, I.M. Assessment of NanoString Technology as a Tool for Profiling Circulating miRNA in Maternal Blood during Pregnancy. Extracell. Vesicles Circ. Nucleic Acids 2024, 5, 471–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossland, R.E.; Albiero, A.; Sanjurjo-Rodríguez, C.; Reis, M.; Resteu, A.; Anderson, A.E.; Dickinson, A.M.; Pratt, A.G.; Birch, M.; McCaskie, A.W.; et al. MicroRNA Profiling of Low Concentration Extracellular Vesicle RNA Utilizing NanoString nCounter Technology. J. Extracell. Biol. 2023, 2, e72, Erratum in J. Extracell. Biol. 2025, 4, e70070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Li, B.; Guo, J.; Mai, X.; Yu, H.; Pan, W.; Wu, B.; Liu, W.; Zhong, M.; Liao, T.; et al. Simultaneous Detection of Membrane Protein and mRNA at Single Extracellular Vesicle Level by Droplet Microfluidics for Cancer Diagnosis. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 73, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Ji, Y.; Deng, J.; Li, L.; Bai, X.; Liu, X.; Lin, B.; Lu, Y. Microfluidics-Based Technologies for the Analysis of Extracellular Vesicles at the Single-Cell Level and Single-Vesicle Level. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 2893–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, A.A.; Duraivel, S.; Jiang, J.; Fischer, J.; Greenberg, Z.F.; He, M.; Angelini, T.E.; Schmittgen, T.D. RNA Sequencing at Single Vesicle Resolution via 3D Printed Embedded Droplet Arrays. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 17, 53110–53121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhu, H.; Li, X. Advances in Electrochemical Biosensors for the Detection of Tumor-Derived Exosomes. Front. Chem. 2025, 13, 1556595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Gu, J.; Xu, W.; Cai, H.; Fang, X.; Zhang, X. Exosomes as a New Frontier of Cancer Liquid Biopsy. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Huang, C.; Zheng, J.; Tang, J.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Yang, R. Quantitative Detection of Exosomal microRNA Extracted from Human Blood Based on Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 101, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Li, Q.; Wang, C.; Pang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Xiao, R. In Situ Exosomal MicroRNA Determination by Target-Triggered SERS and Fe3O4@TiO2-Based Exosome Accumulation. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 852–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Tu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, D.; Li, T.; Li, J.; Ni, W.; Xiao, M.-M.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Zhang, G.-J. Ultrasensitive Detection of Exosomal miRNA with PMO-Graphene Quantum Dots-Functionalized Field-Effect Transistor Biosensor. iScience 2022, 25, 104522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, N.; Pu, J.; Zhang, C.; Xu, K.; Wang, W.; Liu, L.; Gao, L.; Xu, X.; Tan, J. The Plasma Derived Exosomal miRNA-483-5p/502-5p Serve as Potential MCI Biomarkers in Aging. Exp. Gerontol. 2024, 186, 112355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, M.-Y.; Kwon, M.-S.; Oh, K.; Nahm, M.; Park, J.; Jin, H.K.; Bae, J.; Son, B.; Kim, S.H. miRNA-214 to Predict Progression and Survival in ALS. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2025, 96, e335177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banack, S.A.; Dunlop, R.A.; Mehta, P.; Mitsumoto, H.; Wood, S.P.; Han, M.; Cox, P.A. A microRNA Diagnostic Biomarker for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Brain Commun. 2024, 6, fcae268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marangon, D.; Castro e Silva, J.H.; Lecca, D. Neuronal and Glial Communication via Non-Coding RNAs: Messages in Extracellular Vesicles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saugstad, J.A.; Lusardi, T.A.; Van Keuren-Jensen, K.R.; Phillips, J.I.; Lind, B.; Harrington, C.A.; McFarland, T.J.; Courtright, A.L.; Reiman, R.A.; Yeri, A.S.; et al. Analysis of Extracellular RNA in Cerebrospinal Fluid. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2017, 6, 1317577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, D.; Lorenz, D.R.; Misra, V.; Chettimada, S.; Morgello, S.; Gabuzda, D. Proteomic Analysis of Cerebrospinal Fluid Extracellular Vesicles Reveals Synaptic Injury, Inflammation, and Stress Response Markers in HIV Patients with Cognitive Impairment. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Ineichen, B.V.; Detmar, M.; Proulx, S.T. Outflow of Cerebrospinal Fluid Is Predominantly through Lymphatic Vessels and Is Reduced in Aged Mice. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margetis, K.; Baker, S. Physiology, Cerebral Spinal Fluid. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, F.; Lv, S.; Zong, Z.; Wu, L.; Tang, X.; Kuang, W.; Zhang, P.; Li, X.; Fu, J.; Xiao, M.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers for Brain Tumor Detection: Clinical Roles and Current Progress. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 1379–1396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anoop, A.; Singh, P.K.; Jacob, R.S.; Maji, S.K. CSF Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis. Int. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2010, 2010, 606802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerson, B.C.; Atri, A.; Clevenger, C.; Karlawish, J.; Knopman, D.; Lin, P.-J.; Norman, M.; Onyike, C.; Sano, M.; Scanland, S.; et al. The Alzheimer’s Association Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnostic Evaluation, Testing, Counseling, and Disclosure of Suspected Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Disorders (DETeCD-ADRD): Executive Summary of Recommendations for Specialty Care. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2025, 21, e14337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, W.A.; Sharma, P.; Bullock, K.M.; Hansen, K.M.; Ludwig, N.; Whiteside, T.L. Transport of Extracellular Vesicles across the Blood-Brain Barrier: Brain Pharmacokinetics and Effects of Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morad, G.; Carman, C.V.; Hagedorn, E.J.; Perlin, J.R.; Zon, L.I.; Mustafaoglu, N.; Park, T.-E.; Ingber, D.E.; Daisy, C.C.; Moses, M.A. Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Breach the Intact Blood-Brain Barrier via Transcytosis. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 13853–13865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Li, Q.; Ruan, Y.; Xia, Y.; Fang, Z. Caveolae-Mediated Transcytosis and Its Role in Neurological Disorders. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowa, G. Caveolae, Caveolins, Cavins, and Endothelial Cell Function: New Insights. Front. Physiol. 2012, 2, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabian, A.; Dadpour, S.; Mashreghi, M.; Zarqi, J.; Askarizadeh, A.; Badiee, A.; Arabi, L.; Moosavian, S.A.; Jaafari, M.R. The Comparison of Biodistribution of Glutathione PEGylated Nanoliposomal Doxorubicin Formulations Prepared by Pre-insertion and Post-insertion Methods for Brain Delivery in Normal Mice. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 17, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powter, E.E.; Coleman, P.R.; Tran, M.H.; Lay, A.J.; Bertolino, P.; Parton, R.G.; Vadas, M.A.; Gamble, J.R. Caveolae Control the Anti-Inflammatory Phenotype of Senescent Endothelial Cells. Aging Cell 2015, 14, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terao, J. Caveolae and Caveolin-1 as Targets of Dietary Polyphenols for Protection against Vascular Endothelial Dysfunction. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2024, 75, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Stoppani, E.; Volonte, D.; Galbiati, F. Caveolin-1, Cellular Senescence and Age-Related Diseases. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2011, 132, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shihata, W.A.; Michell, D.L.; Andrews, K.L.; Chin-Dusting, J.P.F. Caveolae: A Role in Endothelial Inflammation and Mechanotransduction? Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louveau, A.; Plog, B.A.; Antila, S.; Alitalo, K.; Nedergaard, M.; Kipnis, J. Understanding the Functions and Relationships of the Glymphatic System and Meningeal Lymphatics. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 3210–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Cao, Y.; Tang, X.; Huang, J.; Cai, L.; Zhou, L. The Meningeal Lymphatic Vessels and the Glymphatic System: Potential Therapeutic Targets in Neurological Disorders. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2022, 42, 1364–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formolo, D.A.; Yu, J.; Lin, K.; Tsang, H.W.H.; Ou, H.; Kranz, G.S.; Yau, S.-Y. Leveraging the Glymphatic and Meningeal Lymphatic Systems as Therapeutic Strategies in Alzheimer’s Disease: An Updated Overview of Nonpharmacological Therapies. Mol. Neurodegener. 2023, 18, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershenhouse, K.S.; Shauly, O.; Gould, D.J.; Patel, K.M. Meningeal Lymphatics: A Review and Future Directions from a Clinical Perspective. Neurosci. Insights 2019, 14, 1179069519889027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hablitz, L.M.; Plá, V.; Giannetto, M.; Vinitsky, H.S.; Stæger, F.F.; Metcalfe, T.; Nguyen, R.; Benrais, A.; Nedergaard, M. Circadian Control of Brain Glymphatic and Lymphatic Fluid Flow. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestre, H.; Mori, Y.; Nedergaard, M. The Brain’s Glymphatic System: Current Controversies. Trends Neurosci. 2020, 43, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.; Liu, J.; Liang, C.; Yang, L.; Wang, G. Aquaporin-4 in Glymphatic System, and Its Implication for Central Nervous System Disorders. Neurobiol. Dis. 2023, 179, 106035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Zaldívar, H.M.; Polakovicova, I.; Salas-Huenuleo, E.; Corvalán, A.H.; Kogan, M.J.; Yefi, C.P.; Andia, M.E. Extracellular Vesicles through the Blood–Brain Barrier: A Review. Fluids Barriers CNS 2022, 19, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandau, U.S.; Magaña, S.M.; Costa, J.; Nolan, J.P.; Ikezu, T.; Vella, L.J.; Jackson, H.K.; Moreira, L.R.; Palacio, P.L.; Hill, A.F.; et al. Recommendations for Reproducibility of Cerebrospinal Fluid Extracellular Vesicle Studies. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, 12397, Erratum in J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Xi, W.; Liu, C.; Zhou, X.; Yuan, M.; Yu, X.; Li, L.; et al. Integrating Spatial and Single-Cell Transcriptomics to Characterize the Molecular and Cellular Architecture of the Ischemic Mouse Brain. Sci. Transl. Med. 2024, 16, eadg1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Prieto, D.M.; Murrieta-Coxca, J.M.; Stojiljkovic, M.; Diezel, C.; Streicher, P.E.; Henao-Restrepo, J.A.; Röstel, F.; Lindner, J.; Witte, O.W.; Weis, S.; et al. Small Extracellular Vesicles from Peripheral Blood of Aged Mice Pass the Blood-Brain Barrier and Induce Glial Cell Activation. Cells 2022, 11, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; He, B. Insight into Endothelial Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Cardiovascular Disease: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 207, 107309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, F.; Li, Q.; Pfeifer, A.; Werner, N. Endothelial- and Immune Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in the Regulation of Cardiovascular Health and Disease. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2017, 2, 790–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.D.; Linville, R.M.; Guo, Z.; Ye, R.; Jha, R.; Grifno, G.N.; Searson, P.C. Effects of Acute and Chronic Oxidative Stress on the Blood–Brain Barrier in 2D and 3D in Vitro Models. Fluids Barriers CNS 2022, 19, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, K.K.; Coleman, P.; Kim, H.J.; Zhao, Y.; Mulangala, J.; Cheng, N.C.; Li, W.; Gunatilake, D.; Johnstone, D.M.; Loo, L.; et al. Vascular Senescence and Leak Are Features of the Early Breakdown of the Blood–Brain Barrier in Alzheimer’s Disease Models. GeroScience 2023, 45, 3307–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadry, H.; Noorani, B.; Cucullo, L. A Blood–Brain Barrier Overview on Structure, Function, Impairment, and Biomarkers of Integrity. Fluids Barriers CNS 2020, 17, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janigro, D.; Bailey, D.M.; Lehmann, S.; Badaut, J.; O’Flynn, R.; Hirtz, C.; Marchi, N. Peripheral Blood and Salivary Biomarkers of Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability and Neuronal Damage: Clinical and Applied Concepts. Front. Neurol. 2021, 11, 577312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, P.L.H.; Garic, D.; Shen, M.D.; Lundgaard, I.; Schwichtenberg, A.J. Sleep, Cerebrospinal Fluid, and the Glymphatic System: A Systematic Review. Sleep Med. Rev. 2022, 61, 101572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, O.C.; van der Werf, Y.D. The Sleeping Brain: Harnessing the Power of the Glymphatic System through Lifestyle Choices. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hablitz, L.M.; Nedergaard, M. The Glymphatic System: A Novel Component of Fundamental Neurobiology. J. Neurosci. 2021, 41, 7698–7711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Stowell, M.H.B.; Shen, J. Progress and Gaps of Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Intercellular Cargo Transfer in the Central Nervous System. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchette, C.R.; Rodal, A.A. Mechanisms for Biogenesis and Release of Neuronal Extracellular Vesicles. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2020, 63, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, A.; Auderset, L.; Kaurani, L.; Sebastian, E.; Zeng, Y.; Allahham, M.; Cases-Cunillera, S.; Schoch, S.; Gründemann, J.; Fischer, A.; et al. Neuronal Extracellular Vesicles and Associated microRNAs Induce Circuit Connectivity Downstream BDNF. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Tian, X.; Schekman, R. Extracellular Vesicles from Neurons Promote Neural Induction of Stem Cells through Cyclin D1. J. Cell Biol. 2021, 220, e202101075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chivet, M.; Javalet, C.; Laulagnier, K.; Blot, B.; Hemming, F.J.; Sadoul, R. Exosomes Secreted by Cortical Neurons upon Glutamatergic Synapse Activation Specifically Interact with Neurons. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 24722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frühbeis, C.; Fröhlich, D.; Kuo, W.P.; Krämer-Albers, E.-M. Extracellular Vesicles as Mediators of Neuron-Glia Communication. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, D.M.; Wang, C.; Mohamud Yusuf, A.; Herz, J.; Doeppner, T.R.; Giebel, B. Extracellular Vesicles Lay the Ground for Neuronal Plasticity by Restoring Mitochondrial Function, Cell Metabolism and Immune Balance. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2025, 0271678X251325039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikezu, T.; Yang, Y.; Verderio, C.; Krämer-Albers, E.-M. Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Neuron–Glia Communications in the Central Nervous System. J. Neurosci. 2024, 44, e1170242024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Tian, C.; Xiong, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J. Extracellular Vesicles: New Horizons in Neurodegeneration. eBioMedicine 2025, 113, 105605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnatz, A.; Müller, C.; Brahmer, A.; Krämer-Albers, E. Extracellular Vesicles in Neural Cell Interaction and CNS Homeostasis. FASEB BioAdv. 2021, 3, 577–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.R.; Weaver, A.M. Astrocyte-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Promote Synapse Formation via Fibulin-2-Mediated TGF-β Signaling. Cell Rep. 2021, 34, 108829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filannino, F.M.; Panaro, M.A.; Benameur, T.; Pizzolorusso, I.; Porro, C. Extracellular Vesicles in the Central Nervous System: A Novel Mechanism of Neuronal Cell Communication. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabrielli, M.; Raffaele, S.; Fumagalli, M.; Verderio, C. The Multiple Faces of Extracellular Vesicles Released by Microglia: Where Are We 10 Years After? Front Cell Neurosci. 2022, 16, 984690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogaki, A.; Ikegaya, Y.; Koyama, R. Extracellular Vesicles Taken up by Astrocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhao, L.; Mao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M. Bidirectional Communication Between the Brain and Other Organs: The Role of Extracellular Vesicles. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 43, 2675–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busatto, S.; Morad, G.; Guo, P.; Moses, M.A. The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in the Physiological and Pathological Regulation of the Blood–Brain Barrier. FASEB BioAdv. 2021, 3, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, J.; Miao, X.; Schlüter, D.; Lin, L.; Wang, X. Extracellular Vesicles in Neuroinflammation: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Therapy. Mol. Ther. 2021, 29, 1946–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyanar, M.P.; Vijayan, M. A Review on Gut Microbiota and miRNA Crosstalk: Implications for Alzheimer’s Disease. GeroScience 2024, 47, 339–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, J.S.; Mak, W.Q.; Tan, L.K.S.; Ng, C.X.; Chan, H.H.; Yeow, S.H.; Foo, J.B.; Ong, Y.S.; How, C.W.; Khaw, K.Y. Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis and Its Therapeutic Applications in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Yang, B.; Liu, W.; Tan, C.; Chen, H.; Wang, X. Emerging Role of Non-Coding RNAs in Neuroinflammation Mediated by Microglia and Astrocytes. J. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 20, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, G.; Carista, A.; Manna, O.M.; Paladino, L.; Picone, D.; Sarullo, S.; Sausa, M.; Cappello, F.; Vitale, A.M.; Caruso Bavisotto, C. Brain–Periphery Axes: The Potential Role of Extracellular Vesicles-Delivered miRNAs. Biology 2024, 13, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, J. Gut Microbiota-Induced microRNA-206-3p Increases Anxiety-like Behaviors by Inhibiting Expression of Cited2 and STK39. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 176, 106008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudet, A.D.; Fonken, L.K.; Watkins, L.R.; Nelson, R.J.; Popovich, P.G. microRNAs: Roles in Regulating Neuroinflammation. Neuroscientist 2018, 24, 221–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Espinosa, I.; Serrato, J.A.; Ortiz-Quintero, B. The Role of Exosome-Derived microRNA on Lung Cancer Metastasis Progression. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiong, T.-Y.; Chan, M.-L.; Wang, C.-H.; Yadav, V.K.; Pikatan, N.W.; Fong, I.-H.; Yeh, C.-T.; Kuo, K.-T.; Huang, W.-C. Exosomal miR-21 Determines Lung-to-Brain Metastasis Specificity through the DGKB/ERK Axis within the Tumor Microenvironment. Life Sci. 2023, 329, 121945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, N.; Solár, P.; Hašanová, K.; Zamani, A.; Akbar, M.S.; Mrázová, K.; Bartošík, M.; Kazda, T.; Hrstka, R.; Joukal, M. Breaking Boundaries: Role of the Brain Barriers in Metastatic Process. Fluids Barriers CNS 2025, 22, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.-L.; Duan, M.-J.; Ma, J.-C.; Xu, L.; Mao, M.; Biddyut, D.; Wang, Q.; Yang, C.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Y.; et al. Myocardial Infarction-Induced Hippocampal Microtubule Damage by Cardiac Originating microRNA-1 in Mice. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2018, 120, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, M.-J.; Yan, M.-L.; Wang, Q.; Mao, M.; Su, D.; Sun, L.-L.; Li, K.-X.; Qu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, X.-Y.; et al. Overexpression of miR-1 in the Heart Attenuates Hippocampal Synaptic Vesicle Exocytosis by the Posttranscriptional Regulation of SNAP-25 through the Transportation of Exosomes. Cell Commun. Signal. 2018, 16, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Hu, G.; Gao, L.; Hackfort, B.T.; Zucker, I.H. Extracellular Vesicular MicroRNA-27a* Contributes to Cardiac Hypertrophy in Chronic Heart Failure. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2020, 143, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lyu, X.; Tan, S.; Zhang, X. Research Progress of Exosomal Non-Coding RNAs in Cardiac Remodeling. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 20, 1469–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlacu, C.-C.; Ciobanu, D.; Badulescu, A.-V.; Chelaru, V.-F.; Mitre, A.-O.; Capitanescu, B.; Hermann, D.M.; Popa-Wagner, A. Circulating MicroRNAs and Extracellular Vesicle-Derived MicroRNAs as Predictors of Functional Recovery in Ischemic Stroke Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-Z.; Wang, J.; Xu, F. Circulating miR-29b and miR-424 as Prognostic Markers in Patients with Acute Cerebral Infarction. Clin. Lab. 2017, 63, 1667–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vavassori, C.; Cipriani, E.; Colombo, G.I. Circulating MicroRNAs as Novel Biomarkers in Risk Assessment and Prognosis of Coronary Artery Disease. Eur. Cardiol. 2022, 17, e06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Ziegler, J.N.; Zucker, I.H. Extracellular Vesicle MicroRNAs in Heart Failure: Pathophysiological Mediators and Therapeutic Targets. Cells 2023, 12, 2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Song, J.; Huang, X.; Pan, Z.; Goldbrunner, R.; Stavrinou, L.; Lin, S.; Hu, W.; Zheng, F.; Stavrinou, P. Exosomes Derived From Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Novel Effects in the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 899887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchelson, K.R.; Qin, W.-Y. Roles of the Canonical myomiRs miR-1, -133 and -206 in Cell Development and Disease. World J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 6, 162–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Liu, G.; Wang, B.; Momeni, M.R. Exosomes and microRNAs as Mediators of the Exercise. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2025, 30, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Bai, F.; Liu, C.; Huang, X. Serum Exosomes miR-206 and miR-549a-3p as Potential Biomarkers of Traumatic Brain Injury. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10082, Erratum in Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdoncin, M.; Konrad, A.; Wyner, J.R.; Lohana, S.; Pillai, S.S.; Pereira, D.G.; Lakhani, H.V.; Sodhi, K. A Review of miRNAs as Biomarkers and Effect of Dietary Modulation in Obesity Associated Cognitive Decline and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 756499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, P.; Yu, M.; Tian, W. Diverse RNAs in Adipose-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Their Therapeutic Potential. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 26, 665–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaguarnera, M.; Cauli, O.; Cabrera-Pastor, A. Obesity and Adipose-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Implications for Metabolic Regulation and Disease. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Deng, L.; Xu, X.; Chang, H.; Liu, C.; Wu, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, R.; Gao, R.; Chen, H.; et al. Astrocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicular NFIA Mediates Obesity-Associated Cognitive Impairment. J. Neuroinflamm. 2025, 22, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motshwari, D.D.; Matshazi, D.M.; Erasmus, R.T.; Kengne, A.P.; Matsha, T.E.; George, C. MicroRNAs Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease in the General Population and High-Risk Subgroups—A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Lee, C.M.; Kwon, S.-H. Extracellular Vesicle microRNA in the Kidney. Compr. Physiol. 2023, 13, 4833–4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Cunha, R.S.; Azevedo, C.A.B.; Miniskiskosky, G.; Gregório, P.C.; Stinghen, A.E.M. MicroRNAs and Vascular Damage in Chronic Kidney Disease: Advances and Clinical Implications. Braz. J. Nephrol. 2025, 47, e20240223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Lv, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Leng, Y. MircoRNA-29a in Astrocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Suppresses Brain Ischemia Reperfusion Injury via TP53INP1 and the NF-κB/NLRP3 Axis. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 42, 1487–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Shi, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Chen, R.; Liao, W.; Zhu, J.; Yang, D.; Wu, X.; Han, S. Mesenchymal Cell-Derived Exosomes and miR-29a-3p Mitigate Renal Fibrosis and Vascular Rarefaction after Renal Ischemia Reperfusion Injury. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2025, 16, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Hong, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, P.; Körner, H.; Tu, J.; Wei, W. MicroRNAs in Microglia: How Do MicroRNAs Affect Activation, Inflammation, Polarization of Microglia and Mediate the Interaction Between Microglia and Glioma? Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, D.-Q.; Zhao, Y.-J.; Li, T.-T.; Ke, H.-F.; Gai, C.-C.; Guo, X.-F.; Chen, W.-Q.; Liu, D.-X.; Wang, Z. The Delivery of miR-21a-5p by Extracellular Vesicles Induces Microglial Polarization via the STAT3 Pathway Following Hypoxia-Ischemia in Neonatal Mice. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 2238–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, Z.; He, T.; Qu, M.; Jiang, L.; Li, W.; Shi, X.; Pan, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; et al. M2 Microglia-Derived Exosomes Protect the Mouse Brain from Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Exosomal miR-124. Theranostics 2019, 9, 2910–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ye, Y.; Kong, C.; Su, X.; Zhang, X.; Bai, W.; He, X. MiR-124 Enriched Exosomes Promoted the M2 Polarization of Microglia and Enhanced Hippocampus Neurogenesis After Traumatic Brain Injury by Inhibiting TLR4 Pathway. Neurochem. Res. 2019, 44, 811–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, L.; Yin, Z.; Han, Z.; Ge, X.; Li, M.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, S.; Zuo, Y.; et al. Exosomes Derived from Microglia Overexpressing miR-124-3p Alleviate Neuronal Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Damage after Repetitive Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Neural Regen. Res. 2024, 19, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonul, C.P.; Karacicek, B.; Genc, S. Neuron-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Emerging Biomarkers and Functional Mediators in Alzheimer’s Disease, with Comparative Insights Into Neurodevelopment and Aging. Dev. Neurobiol. 2025, 85, e22984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, D.M.; Peruzzotti-Jametti, L.; Giebel, B.; Pluchino, S. Extracellular Vesicles Set the Stage for Brain Plasticity and Recovery by Multimodal Signalling. Brain 2024, 147, 372–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghav, A.; Singh, M.; Jeong, G.-B.; Giri, R.; Agarwal, S.; Kala, S.; Gautam, K.A. Extracellular Vesicles in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Systematic Review. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 1061076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, B.; Gong, H.; Zhang, K.; Lin, Y.; Sun, M. Extracellular Vesicles: Biological Mechanisms and Emerging Therapeutic Opportunities in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Transl. Neurodegener. 2024, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.F. Extracellular Vesicles and Neurodegenerative Diseases. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 9269–9273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shen, L.; Wan, M.; Xie, H.; Wang, Z. Peripheral Extracellular Vesicles in Neurodegeneration: Pathogenic Influencers and Therapeutic Vehicles. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanadgol, N.; Mousavi, P.; Sadri, F.; Voelz, C.; Scheld, M.; Khalseh, R.; Amini, J.; Karimi, E.; Rahi, A.; Sepand, M.-R.; et al. Role of Extracellular Vesicle-Carried ncRNAs in the Interactive ‘Dialogue’ within the Brain and beyond: Emerging Theranostic Epigenetic Modifiers in Brain-Derived Nanoplatforms. Transl. Neurodegener. 2025, 14, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canseco-Rodriguez, A.; Masola, V.; Aliperti, V.; Meseguer-Beltran, M.; Donizetti, A.; Sanchez-Perez, A.M. Long Non-Coding RNAs, Extracellular Vesicles and Inflammation in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Qu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, L.; Han, Y.; Zhao, W.; Yu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Microarray microRNA Profiling of Urinary Exosomes in a 5XFAD Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Anim. Models Exp. Med. 2021, 4, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Lin, L.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, X. Microglia-Derived Exosomes Selective Sorted by YB-1 Alleviate Nerve Damage and Cognitive Outcome in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, R.; Alcibahy, Y.; Bucheeri, S.; Albishtawi, A.; Tama, M.; Shetty, J.; Butler, A.E. The Role of Hypothalamic Microglia in the Onset of Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes: A Neuro-Immune Perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, C.; Yuan, J. Metabolic Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease: A Mini Review. Metab. Transl. Med. 2023, 1, 0409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharan, P.; Vellapandian, C. Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) Axis: Unveiling the Potential Mechanisms Involved in Stress-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease and Depression. Cureus 2024, 16, e67595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kuraishy, H.M.; Jabir, M.S.; Albuhadily, A.K.; Al-Gareeb, A.I.; Rafeeq, M.F. The Link between Metabolic Syndrome and Alzheimer Disease: A Mutual Relationship and Long Rigorous Investigation. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 91, 102084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadimitriou, A.; Priftis, K.N. Regulation of the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis. Neuroimmunomodulation 2009, 16, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumani, H.; Petereit, H.F.; Gerritzen, A.; Gross, C.C.; Huss, A.; Isenmann, S.; Jesse, S.; Khalil, M.; Lewczuk, P.; Lewerenz, J.; et al. S1 Guidelines “Lumbar Puncture and Cerebrospinal Fluid Analysis” (Abridged and Translated Version). Neurol. Res. Pract. 2020, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingle, S.C.; Lin, F.; Anekoji, M.S.; Patro, C.P.K.; Datta, S.; Jones, L.D.; Kesari, S.; Ashili, S. Exploring the Role of Cerebrospinal Fluid as Analyte in Neurologic Disorders. Future Sci. OA 2023, 9, FSO851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelibter, S.; Marostica, G.; Mandelli, A.; Siciliani, S.; Podini, P.; Finardi, A.; Furlan, R. The Impact of Storage on Extracellular Vesicles: A Systematic Study. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2022, 11, e12162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Schueren, C.; Decruyenaere, P.; Avila Cobos, F.; Bult, J.; Deleu, J.; Dipalo, L.L.; Helsmoortel, H.H.; Hulstaert, E.; Morlion, A.; Ramos Varas, E.; et al. Subpar Reporting of Pre-Analytical Variables in RNA-Focused Blood Plasma Studies. Mol. Oncol. 2025, 19, 1968–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Rames, M.J.; Tassi Yunga, S.; Armstrong, R.; Morita, M.; Ngo, A.T.P.; McCarty, O.J.T.; Civitci, F.; Morgan, T.K.; Ngo, T.T.M. Irreversible Alteration of Extracellular Vesicle and Cell-Free Messenger RNA Profiles in Human Plasma Associated with Blood Processing and Storage. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaly, S.; Ramberg, C.; Olsen, R.; Latysheva, N.; Webster, P.; Sovershaev, T.; Brækkan, S.K.; Hansen, J.-B. Impact of Preanalytical Conditions on Plasma Concentration and Size Distribution of Extracellular Vesicles Using Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witwer, K.W.; Buzás, E.I.; Bemis, L.T.; Bora, A.; Lässer, C.; Lötvall, J.; Nolte-‘t Hoen, E.N.; Piper, M.G.; Sivaraman, S.; Skog, J.; et al. Standardization of Sample Collection, Isolation and Analysis Methods in Extracellular Vesicle Research. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 20360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeri, A.; Courtright, A.; Reiman, R.; Carlson, E.; Beecroft, T.; Janss, A.; Siniard, A.; Richholt, R.; Balak, C.; Rozowsky, J.; et al. Total Extracellular Small RNA Profiles from Plasma, Saliva, and Urine of Healthy Subjects. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holcar, M.; Ferdin, J.; Sitar, S.; Tušek-Žnidarič, M.; Dolžan, V.; Plemenitaš, A.; Žagar, E.; Lenassi, M. Enrichment of Plasma Extracellular Vesicles for Reliable Quantification of Their Size and Concentration for Biomarker Discovery. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wei, S.; Zhou, C.; Yu, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, W.; Zhao, L. Extracellular Vesicles Isolated by Size-Exclusion Chromatography Present Suitability for RNomics Analysis in Plasma. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabús, L.; Lagarde, J.; Curado, J.; Lizano, E.; Pérez-Boza, J. Current Challenges and Best Practices for Cell-Free Long RNA Biomarker Discovery. Biomark. Res. 2022, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryzgunova, O.; Konoshenko, M.; Zaporozhchenko, I.; Yakovlev, A.; Laktionov, P. Isolation of Cell-Free miRNA from Biological Fluids: Influencing Factors and Methods. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, P.; Bai, L.; Hong, M.; Ouyang, J.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X.; Chen, P. A Comprehensive Review on Circulating cfRNA in Plasma: Implications for Disease Diagnosis and Beyond. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Extracellular RNA Communication Consortium; Ansel, K.M.; Bitzer, M.; Breakefield, X.O.; Charest, A.; Galas, D.J.; Gerstein, M.B.; Gupta, M.; Milosavljevic, A.; et al. The Extracellular RNA Communication Consortium: Establishing Foundational Knowledge and Technologies for Extracellular RNA Research. Cell 2019, 177, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miceli, R.T.; Chen, T.; Nose, Y.; Tichkule, S.; Brown, B.; Fullard, J.F.; Saulsbury, M.D.; Heyliger, S.O.; Gnjatic, S.; Kyprianou, N.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles, RNA Sequencing, and Bioinformatic Analyses: Challenges, Solutions, and Recommendations. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e70005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grätz, C.; Schuster, M.; Brandes, F.; Meidert, A.S.; Kirchner, B.; Reithmair, M.; Schelling, G.; Pfaffl, M.W. A Pipeline for the Development and Analysis of Extracellular Vesicle-Based Transcriptomic Biomarkers in Molecular Diagnostics. Mol. Asp. Med. 2024, 97, 101269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, J.F.; Patel, T.; Wong, D.; Das, S.; Freedman, J.E.; Laurent, L.C.; Carter, B.S.; Hochberg, F.; Keuren-Jensen, K.V.; Huentelman, M.; et al. Extracellular RNAs: Development as Biomarkers of Human Disease. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, C.E.; Kimble, L.; Bayoumy, S.; Bolsewig, K.; Burtscher, F.; Coppens, S.; Das, S.; Gogishvili, D.; Fernandes Gomes, B.; Gómez de San José, N.; et al. Methods to Discover and Validate Biofluid-Based Biomarkers in Neurodegenerative Dementias. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2023, 22, 100629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, J.D.; Kadukhina, E.; Aiello, I.; Finkielstein, C.V. Circadian Regulation of Extracellular Vesicle Biogenesis, Composition, and Release. npj Biol. Timing Sleep 2025, 2, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mareboina, M.; Deng, E.; Mouratidis, I.; Yee, N.S.; Pitteloud, N.; Georgakopoulos-Soares, I.; Chartoumpekis, D.V. A Review on Cell-Free RNA Profiling: Insights into Metabolic Diseases and Predictive Value for Bariatric Surgery Outcomes. Mol. Metab. 2024, 87, 101987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.T.; Kim, H.J.; Johnson-Camacho, K.C.; Kelley, T.; Newell, L.F.; Spellman, P.T.; Ngo, T.T.M. Diurnal Stability of Cell-Free DNA and Cell-Free RNA in Human Plasma Samples. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, R. Clinical Trial Designs for Evaluating the Medical Utility of Prognostic and Predictive Biomarkers in Oncology. Pers. Med. 2010, 7, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, D.F. Biomarker Validation and Testing. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Provenzano, F.A.; Small, S.A.; For the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. A Deep Learning MRI Approach Outperforms Other Biomarkers of Prodromal Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2022, 14, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yoshizawa, J.M.; Kim, K.-M.; Kanjanapangka, J.; Grogan, T.R.; Wang, X.; Elashoff, D.E.; Ishikawa, S.; Chia, D.; Liao, W.; et al. Discovery and Validation of Salivary Extracellular RNA Biomarkers for Noninvasive Detection of Gastric Cancer. Clin. Chem. 2018, 64, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogishvili, D.; Vromen, E.M.; Koppes-den Hertog, S.; Lemstra, A.W.; Pijnenburg, Y.A.L.; Visser, P.J.; Tijms, B.M.; Del Campo, M.; Abeln, S.; Teunissen, C.E.; et al. Discovery of Novel CSF Biomarkers to Predict Progression in Dementia Using Machine Learning. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellomo, G.; Indaco, A.; Chiasserini, D.; Maderna, E.; Paolini Paoletti, F.; Gaetani, L.; Paciotti, S.; Petricciuolo, M.; Tagliavini, F.; Giaccone, G.; et al. Machine Learning Driven Profiling of Cerebrospinal Fluid Core Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Neurological Disorders. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 647783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshehri, R.S.; Abuzinadah, A.R.; Alrawaili, M.S.; Alotaibi, M.K.; Alsufyani, H.A.; Alshanketi, R.M.; AlShareef, A.A. A Review of Biomarkers of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Pathophysiologic Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juganavar, A.; Joshi, A.; Shegekar, T. Navigating Early Alzheimer’s Diagnosis: A Comprehensive Review of Diagnostic Innovations. Cureus 2023, 15, e44937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweingruber, C.; Nijssen, J.; Mechtersheimer, J.; Reber, S.; Lebœuf, M.; O’Brien, N.L.; Mei, I.; Hedges, E.; Keuper, M.; Benitez, J.A.; et al. Single-Cell RNA-Sequencing Reveals Early Mitochondrial Dysfunction Unique to Motor Neurons Shared across FUS- and TARDBP-ALS. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, Q.; Ping, D.; Wang, Y.; Wu, W.; Lin, X.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shao, A. The Role of Exosomal microRNAs and Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 3232869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellison, T.J.; Stice, S.L.; Yao, Y. Therapeutic and Diagnostic Potential of Extracellular Vesicles in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Extracell. Vesicle 2023, 2, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petracci, I.; Bellini, S.; Goljanek-Whysall, K.; Quinlan, L.R.; Fiszer, A.; Cakmak, A.; Njume, C.M.; Borroni, B.; Ghidoni, R. Exploring the Role of microRNAs as Blood Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease and Frontotemporal Dementia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.Q.; Michelle Luk, K.H.; Lee, K.Y.; Nurul, N.; Loh, S.J.; Yeow, Z.X.; Wong, Q.X.; Daniel Looi, Q.H.; Chong, P.P.; How, C.W.; et al. Small Extracellular Vesicles’ miRNAs: Biomarkers and Therapeutics for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, M.; Piscopo, P.; Talarico, G.; Ricci, L.; Crestini, A.; Tosto, G.; Gasparini, M.; Bruno, G.; Denti, M.A.; Confaloni, A. Plasma microRNA Profiling Distinguishes Patients with Frontotemporal Dementia from Healthy Subjects. Neurobiol. Aging 2019, 84, 240.e1–240.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoss, A.G.; Lagomarsino, V.N.; Frank, S.; Hadzi, T.C.; Myers, R.H.; Latourelle, J.C. Study of Plasma-Derived miRNAs Mimic Differences in Huntington’s Disease Brain. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1961–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoss, A.G.; Labadorf, A.; Latourelle, J.C.; Kartha, V.K.; Hadzi, T.C.; Gusella, J.F.; MacDonald, M.E.; Chen, J.-F.; Akbarian, S.; Weng, Z.; et al. miR-10b-5p Expression in Huntington’s Disease Brain Relates to Age of Onset and the Extent of Striatal Involvement. BMC Med. Genom. 2015, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.T.; Chu, K.; Jung, K.H.; Kim, J.H.; Huh, J.Y.; Yoon, H. miR-206 Regulates Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Alzheimer Disease Model. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 72, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimkhani, S.; Vafaee, F.; Young, P.E.; Hur, S.S.J.; Hawke, S.; Devenney, E.; Beadnall, H.; Barnett, M.H.; Suter, C.M.; Buckland, M.E. Exosomal microRNA Signatures in Multiple Sclerosis Reflect Disease Status. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, R. miRNA in Multiple Sclerosis: Search for Novel Biomarkers. Mult. Scler. J. 2015, 21, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagot, F.; Davoust, N. Is It Worth Considering Circulating microRNAs in Multiple Sclerosis? Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, R.M.; Kahn, D.; Gibson, W.S.J.; Round, J.L.; Scholz, R.L.; Chaudhuri, A.A.; Kahn, M.E.; Rao, D.S.; Baltimore, D. MicroRNA-155 Promotes Autoimmune Inflammation by Enhancing Inflammatory T Cell Development. Immunity 2010, 33, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Cui, W.; Li, M.; Li, B.; Guo, L. MicroRNA-155 Modulates Th1 and Th17 Cell Differentiation and Is Associated with Multiple Sclerosis and Experimental Autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2014, 266, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asl, E.R.; Hosseini, S.E.; Tahmasebi, F.; Bolandi, N.; Barati, S. MiR-124 and MiR-155 as Therapeutic Targets in Microglia-Mediated Inflammation in Multiple Sclerosis. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2025, 45, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, R.; Yu, J.; Liu, R.; Jin, X.; Zhao, Y. Plasma Exosome-Derived MicroRNAs as Novel Biomarkers of Traumatic Brain Injury in Rats. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 17, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.; Hemphill, M.; Yang, Z.; Sewell, E.; Na, Y.J.; Sandsmark, D.K.; Haber, M.; Fisher, S.A.; Torre, E.A.; Svane, K.C.; et al. Diagnosis of Traumatic Brain Injury Using miRNA Signatures in Nanomagnetically Isolated Brain-Derived Extracellular Vesicles. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 3617–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beylerli, O.; Tamrazov, R.; Gareev, I.; Ilyasova, T.; Shumadalova, A.; Bai, Y.; Yang, B. Role of Exosomal ncRNAs in Traumatic Brain Injury. Non-Coding RNA Res. 2023, 8, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magee, R.; Shen, J.; Walter, A.E.; Schneider, A.L.C.; Puccio, A.M.; Lynch, C.E.; Diaz-Arrastia, R.; Sandsmark, D.K. MicroRNAs Detected in Whole Blood Following Traumatic Brain Injury Are Associated with Recovery 6 Months after Injury. Neurotrauma Rep. 2025, 6, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, E.B.; Hochfelder, C.G.; Lamberty, B.G.; Meays, B.M.; Morsey, B.M.; Kelso, M.L.; Fox, H.S.; Yelamanchili, S.V. Traumatic Brain Injury Increases Levels of miR-21 in Extracellular Vesicles: Implications for Neuroinflammation. FEBS Open Bio 2016, 6, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Lu, Y.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, P.; Zou, D.; Wei, F.; Chen, X. miR-29a-5p Alleviates Traumatic Brain Injury- (TBI-) Induced Permeability Disruption via Regulating NLRP3 Pathway. Dis. Markers 2021, 2021, 9556513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, J.M.; Skog, J.; Akers, J.; Li, H.; Komotar, R.; Jensen, R.; Ringel, F.; Yang, I.; Kalkanis, S.; Thompson, R.; et al. Detection of Wild-Type EGFR Amplification and EGFRvIII Mutation in CSF-Derived Extracellular Vesicles of Glioblastoma Patients. Neuro-oncology 2017, 19, 1494–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rennert, R.C.; Hochberg, F.H.; Carter, B.S. ExRNA in Biofluids as Biomarkers for Brain Tumors. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cela, I.; Capone, E.; Trevisi, G.; Sala, G. Extracellular Vesicles in Glioblastoma: Biomarkers and Therapeutic Tools. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2024, 101, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skog, J.; Würdinger, T.; van Rijn, S.; Meijer, D.H.; Gainche, L.; Sena-Esteves, M.; Curry, W.T.; Carter, B.S.; Krichevsky, A.M.; Breakefield, X.O. Glioblastoma Microvesicles Transport RNA and Proteins That Promote Tumour Growth and Provide Diagnostic Biomarkers. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 1470–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, S.M.; Muralidharan, K.; Hsia, T.; Falotico, S.; Gamblin, A.S.; Rosenfeld, Y.B.; Khanna, S.K.; Balaj, L.; Carter, B.S. Highly Sensitive EGFRvIII Detection in Circulating Extracellular Vesicle RNA of Glioma Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 4070–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, W.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.; Wei, C.; Sun, L. MicroRNA-Based Diagnosis and Therapeutics for Vascular Cognitive Impairment and Dementia. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 895316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zheng, D.; Nao, J. Circulating Exosome microRNAs as Diagnostic Biomarkers of Dementia. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 580199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar, P.; Chandra, S.R.; Christopher, R. Circulating microRNAs as Potential Biomarkers for the Identification of Vascular Dementia Due to Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Age Ageing 2017, 46, 861–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titze-de-Almeida, S.S.; Marina, C.L.; Ramos, M.V.; Silva, L.D.; Brandão, P.R.; Bispo, D.D.; Von Glehn, F. Exosomal Non-Coding RNAs as Potential Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease: Advances and Perspectives in Translational Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palade, J.; Alsop, E.; Courtright-Lim, A.; Hsieh, M.; Whitsett, T.G.; Galasko, D.; Van Keuren-Jensen, K. Small RNA Changes in Plasma Have Potential for Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease before Symptom Onset. Cells 2024, 13, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhen, H.; Guo, M.; Ye, J.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X. Differential Expression of Plasma Exo-miRNA in Neurodegenerative Diseases by Next-Generation Sequencing. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandau, U.S.; Wiedrick, J.T.; McFarland, T.J.; Galasko, D.R.; Fanning, Z.; Quinn, J.F.; Saugstad, J.A. Analysis of the Longitudinal Stability of Human Plasma miRNAs and Implications for Disease Biomarkers. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Hefu, Z.; Li, B.; Lifang, W.; Zhijie, S.; Zhou, L.; Deng, Y.; Zhili, L.; Ding, J.; Li, T.; et al. Plasma Extracellular Vesicle MicroRNA Analysis of Alzheimer’s Disease Reveals Dysfunction of a Neural Correlation Network. Research 2023, 6, 0114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryja, A.; Zadka, Ł.; Farzaneh, M.; Zehtabi, M.; Ghasemian, M.; Dyszkiewicz-Konwińska, M.; Mozdziak, P.; Zabel, M.; Podhorska-Okołów, M.; Dzięgiel, P.; et al. Small Extracellular Vesicles—A Host for Advanced Bioengineering and “Trojan Horse” of Non-Coding RNAs. Life Sci. 2023, 332, 122126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menjivar, N.G.; Oropallo, J.; Gebremedhn, S.; Souza, L.A.; Gad, A.; Puttlitz, C.M.; Tesfaye, D. MicroRNA Nano-Shuttles: Engineering Extracellular Vesicles as a Cutting-Edge Biotechnology Platform for Clinical Use in Therapeutics. Biol. Proced. Online 2024, 26, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Wu, F.; Mao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, X.; Hong, K.; Li, B.; Qiu, X.; Wen, C. The Role of Microglia in Neurological Diseases with Involvement of Extracellular Vesicles. Neurobiol. Dis. 2024, 202, 106700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shams, S.G. Decoding the Secrets of Small Extracellular Vesicle Communications: Exploring the Inhibition of Vesicle-Associated Pathways and Interception Strategies for Cancer Treatment. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2024, 14, 1957–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarkson, B.D.S.; Grund, E.; David, K.; Johnson, R.K.; Howe, C.L. ISGylation Is Induced in Neurons by Demyelination Driving ISG15-Dependent Microglial Activation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Han, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tian, S.; Shang, Z.; Yuan, Z.; He, L. Extracellular Vesicles for Targeted Drug Delivery: Advances in Surface Modification Strategies and Therapeutic Applications. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brillante, S.; Volpe, M.; Indrieri, A. Advances in MicroRNA Therapeutics: From Preclinical to Clinical Studies. Hum. Gene Ther. 2024, 35, 628–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avendaño-Portugal, C.; Montaño-Samaniego, M.; Guttman-Bazbaz, R.; Bravo-Estupiñan, D.M.; Ibáñez-Hernández, M. Therapeutic Applications of Poly-miRNAs and miRNA Sponges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, A.; Shrivastava, S.; Supramaniam, A.; Ray, R.M.; Shevchenko, G.; Acharya, D.; McMillan, N.A.J.; Morris, K.V. Extracellular Vesicles Loaded with Long Antisense RNAs Repress Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2024, 34, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Kim, Y.; MacLeod, A.R. Targeting Long Noncoding RNA with Antisense Oligonucleotide Technology as Cancer Therapeutics. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1402, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.-W.; Liu, C.-G.; Kirby, J.A.; Chu, C.; Zang, D.; Chen, J. The Emerging Role of Extracellular Vesicle-Derived lncRNAs and circRNAs in Tumor and Mesenchymal Stem Cells: The Biological Functions and Potential for Clinical Application. Cancers 2025, 17, 2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirani, N.; Abdi, N.; Chehelgerdi, M.; Yaghoobi, H.; Chehelgerdi, M. Investigating the Role of Exosomal Long Non-Coding RNAs in Drug Resistance within Female Reproductive System Cancers. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2025, 13, 1485422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, M.; O’Driscoll, L. Inhibiting Extracellular Vesicles Formation and Release: A Review of EV Inhibitors. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 9, 1703244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, C.-H.; Baek, M.-C. Dissecting Exosome Inhibitors: Therapeutic Insights into Small-Molecule Chemicals against Cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 1833–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, A.; Kim, H.; McGee, L.; Johnson, A.E.; Talwar, S.; Marugan, J.; Southall, N.; Hu, X.; Lal, M.; Mondal, D.; et al. High-Throughput Screening Identified Selective Inhibitors of Exosome Biogenesis and Secretion: A Drug Repurposing Strategy for Advanced Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Xiong, Y.; Chopp, M.; Zhang, Y. Engineered Exosomes Enriched with Select microRNAs Amplify Their Therapeutic Efficacy for Traumatic Brain Injury and Stroke. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1376601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Erviti, L.; Seow, Y.; Yin, H.; Betts, C.; Lakhal, S.; Wood, M.J.A. Delivery of siRNA to the Mouse Brain by Systemic Injection of Targeted Exosomes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanez Arteta, M.; Kjellman, T.; Bartesaghi, S.; Wallin, S.; Wu, X.; Kvist, A.J.; Dabkowska, A.; Székely, N.; Radulescu, A.; Bergenholtz, J.; et al. Successful Reprogramming of Cellular Protein Production through mRNA Delivered by Functionalized Lipid Nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E3351–E3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Ma, L.; Du, X.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, J.; Fan, Z.; Zheng, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, G. M2 Microglia-Derived Exosomes Protect Against Glutamate-Induced HT22 Cell Injury via Exosomal miR-124-3p. Mol. Neurobiol. 2024, 61, 7845–7861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, L.; Wang, H.; Wei, D.; Yi, M.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L. Exosomal microRNAs: Implications in the Pathogenesis and Clinical Applications of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1300864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-T.; Im, W.; Ban, J.-J.; Lee, M.; Jung, K.-H.; Lee, S.K.; Chu, K.; Kim, M. Exosome-Based Delivery of miR-124 in a Huntington’s Disease Model. J. Mov. Disord. 2017, 10, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiklander, O.P.B.; Nordin, J.Z.; O’Loughlin, A.; Gustafsson, Y.; Corso, G.; Mäger, I.; Vader, P.; Lee, Y.; Sork, H.; Seow, Y.; et al. Extracellular Vesicle in Vivo Biodistribution Is Determined by Cell Source, Route of Administration and Targeting. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 26316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driedonks, T.; Jiang, L.; Carlson, B.; Han, Z.; Liu, G.; Queen, S.E.; Shirk, E.N.; Gololobova, O.; Liao, Z.; Nyberg, L.H.; et al. Pharmacokinetics and Biodistribution of Extracellular Vesicles Administered Intravenously and Intranasally to Macaca Nemestrina. J. Extracell. Biol. 2022, 1, e59, Erratum in J. Extracell. Biol. 2022, 1, e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.; Jordan, V.; Blenkiron, C.; Chamley, L.W. Biodistribution of Extracellular Vesicles Following Administration into Animals: A Systematic Review. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.; Choi, Y.; Yim, H.Y.; Mirzaaghasi, A.; Yoo, J.-K.; Choi, C. Biodistribution of Exosomes and Engineering Strategies for Targeted Delivery of Therapeutic Exosomes. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2021, 18, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onohuean, H.; Naik Bukke, S.P.; Thalluri, C.; Abass, K.S.; Choonara, Y.E. Exosome Engineering for Targeted Therapy of Brain-Infecting Pathogens: Molecular Tools, Delivery Platforms, and Translational Advances. Front. Med. Technol. 2025, 7, 1655471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanadgol, N.; Abedi, M.; Hashemzaei, M.; Kamran, Z.; Khalseh, R.; Beyer, C.; Voelz, C. Exosomes as Nanocarriers for Brain-Targeted Delivery of Therapeutic Nucleic Acids: Advances and Challenges. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2025, 23, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, B.W.S.; Tan, M.; Gao, C.; Pham, T.T.; Tran, L.T.N.; Nguyen, L.N.; Sidik, H.; Lim, M.B.H.; Le, A.H.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Administered via Intrathecal Injection Mediate Safe Delivery of Nucleic Acids to the Central Nervous System for Gene Therapy. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2025, 14, e70116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Guo, C.; Zhou, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Chen, J.; Li, F. Exosome-Mediated miRNA Delivery: A Molecular Switch for Reshaping Neuropathic Pain Therapy. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2025, 18, 1625943, Erratum in Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2025, 18, 1668038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, M.S.; Etzioni, R.; Feng, Z.; Potter, J.D.; Thompson, M.L.; Thornquist, M.; Winget, M.; Yasui, Y. Phases of Biomarker Development for Early Detection of Cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2001, 93, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karikari, T.K.; Pascoal, T.A.; Ashton, N.J.; Janelidze, S.; Benedet, A.L.; Rodriguez, J.L.; Chamoun, M.; Savard, M.; Kang, M.S.; Therriault, J.; et al. Blood Phosphorylated Tau 181 as a Biomarker for Alzheimer’s Disease: A Diagnostic Performance and Prediction Modelling Study Using Data from Four Prospective Cohorts. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.B.; Sundaram, R.; Martins, R.N. Multiplex Biomarkers in Blood. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2013, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Pepe, M.S. Adding Rigor to Biomarker Evaluations—EDRN Experience. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2020, 29, 2575–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couch, Y. Challenges Associated with Using Extracellular Vesicles as Biomarkers in Neurodegenerative Disease. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2023, 23, 1091–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Rodosthenous, R.S.; Kashanchi, F.; Gingeras, T.; Gould, S.J.; Kuo, L.S.; Kurre, P.; Lee, H.; Leonard, J.N.; Liu, H.; et al. Advances, Challenges, and Opportunities in Extracellular RNA Biology: Insights from the NIH exRNA Strategic Workshop. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e98942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarova, J.; Maltseva, D.; Tonevitsky, A. Challenges in Characterization of Transcriptomes of Extracellular Vesicles and Non-Vesicular Extracellular RNA Carriers. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1327985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wijerathne, H.; Godwin, A.K.; Soper, S.A. Isolation and Analysis Methods of Extracellular Vesicles (EVs). Extracell. Vesicles Circ. Nucleic Acids 2021, 2, 80–103, Erratum in Extracell. Vesicles Circ. Nucleic Acids 2021, 2, 222–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, K.P.; Rossi, I.; Abdullahi, M.; Ramirez, M.I.; Stratton, D.; Inal, J.M. Isolation and Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles and Future Directions in Diagnosis and Therapy. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 15, e1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Lausted, C.; Scherler, K.; Ng, A.H.C.; Lu, Y.; Lee, I.; Hood, L.; Wang, K. Approaches and Challenges in Characterizing the Molecular Content of Extracellular Vesicles for Biomarker Discovery. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badhwar, A.; Hirschberg, Y.; Valle-Tamayo, N.; Iulita, M.F.; Udeh-Momoh, C.T.; Matton, A.; Tarawneh, R.M.; Rissman, R.A.; Ledreux, A.; Winston, C.N.; et al. Assessment of Brain-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Enrichment for Blood Biomarker Analysis in Age-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases: An International Overview. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 20, 4411–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, A.M.; Khawar, M.B.; Afzal, A.; Hassan, A.; Ali, A. Multifaceted Roles of Extracellular RNAs in Different Diseases. Mil. Med. Res. 2022, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, E.; Milne, R.; Curlewis, K. Ethical Issues When Using Digital Biomarkers and Artificial Intelligence for the Early Detection of Dementia. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2023, 13, e1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiaki, E.M.; Falasca, M. Comparative Analysis of the Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles Guidelines: Advancements and Implications for Extracellular Vesicle Research. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2024, 101, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Arauzo, M.; Reymond, S.; Gruaz, L.; Schvartz, D.; Civic, N.; Docquier, M.; Deffert, C.; Colosetti, P.; Sanchez, J.; Bridel, C. Cerebrospinal Fluid-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: A Proteomic and Transcriptomic Comparative Analysis of Enrichment Protocols. J. Extracell. Biol. 2025, 4, e70076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hicks, D.A. Extracellular RNA in Alzheimer’s Disease. ExRNA 2021, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanirati, G.; dos Santos, P.G.; Alcará, A.M.; Bruzzo, F.; Ghilardi, I.M.; Wietholter, V.; Xavier, F.A.C.; Gonçalves, J.I.B.; Marinowic, D.; Shetty, A.K.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles: The Next Generation of Biomarkers and Treatment for Central Nervous System Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roudi, S.; Rädler, J.A.; El Andaloussi, S. Therapeutic Potential of Extracellular Vesicles in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2023, 193, 243–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, N.; Chen, L.; Hu, G.; Ma, R. Advancements in Extracellular Vesicle Therapy for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Explor. Neuroprot. Ther. 2025, 5, 1004104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Bao, Q.; Xu, W.; Zhai, X. Extracellular Particles: Emerging Insights into Central Nervous System Diseases. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2025, 23, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemunto, G.; Ghadami, S.; Dellinger, K. Advancing Extracellular Vesicle Research: A Review of Systems Biology and Multiomics Perspectives. Proteomics 2025, 25, e70066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigdel, S.; Swenson, S.; Wang, J. Extracellular Vesicles in Neurodegenerative Diseases: An Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.A.; Ludwig, R.G.; Garcia-Martin, R.; Brandão, B.B.; Kahn, C.R. Extracellular miRNAs: From Biomarkers to Mediators of Physiology and Disease. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 656–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kioko, M.; Mwangi, S.; Pance, A.; Ochola-Oyier, L.I.; Kariuki, S.; Newton, C.; Bejon, P.; Rayner, J.C.; Abdi, A.I. The mRNA Content of Plasma Extracellular Vesicles Provides a Window into Molecular Processes in the Brain during Cerebral Malaria. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadl2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, M.; Bayat, A.-H.; Pearse, D.D. Small Extracellular Vesicles in Neurodegenerative Disease: Emerging Roles in Pathogenesis, Biomarker Discovery, and Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirmast, P.; Shahri, M.A.; Brent, A.; Idris, A.; McMillan, N.A.J. Delivering Therapeutic RNA into the Brain Using Extracellular Vesicles. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2024, 35, 102373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muskan, M.; Abeysinghe, P.; Cecchin, R.; Branscome, H.; Morris, K.V.; Kashanchi, F. Therapeutic Potential of RNA-Enriched Extracellular Vesicles: The next Generation in RNA Delivery via Biogenic Nanoparticles. Mol. Ther. 2024, 32, 2939–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tielking, K.; Fischer, S.; Preissner, K.T.; Vajkoczy, P.; Xu, R. Extracellular RNA in Central Nervous System Pathologies. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkozhayev, A.M.; Al-Yozbaki, M.; George, A.; Niyazova, R.Y.; Sharipov, K.O.; Byrne, L.J.; Wilson, C.M. Extracellular Vesicles, Stem Cells and the Role of miRNAs in Neurodegeneration. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2022, 20, 1450–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Lu, K.; Koziol, M.J. Extracellular RNAs as Messengers and Early Biomarkers in Neurodegeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2026, 27, 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010320
Lu K, Koziol MJ. Extracellular RNAs as Messengers and Early Biomarkers in Neurodegeneration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2026; 27(1):320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010320
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Kaidong, and Magdalena J. Koziol. 2026. "Extracellular RNAs as Messengers and Early Biomarkers in Neurodegeneration" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 27, no. 1: 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010320
APA StyleLu, K., & Koziol, M. J. (2026). Extracellular RNAs as Messengers and Early Biomarkers in Neurodegeneration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 27(1), 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010320





