Neurotoxicity of Chronic Alcohol Exposure: Mechanistic Insights, Cellular Disruption, and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies
Abstract
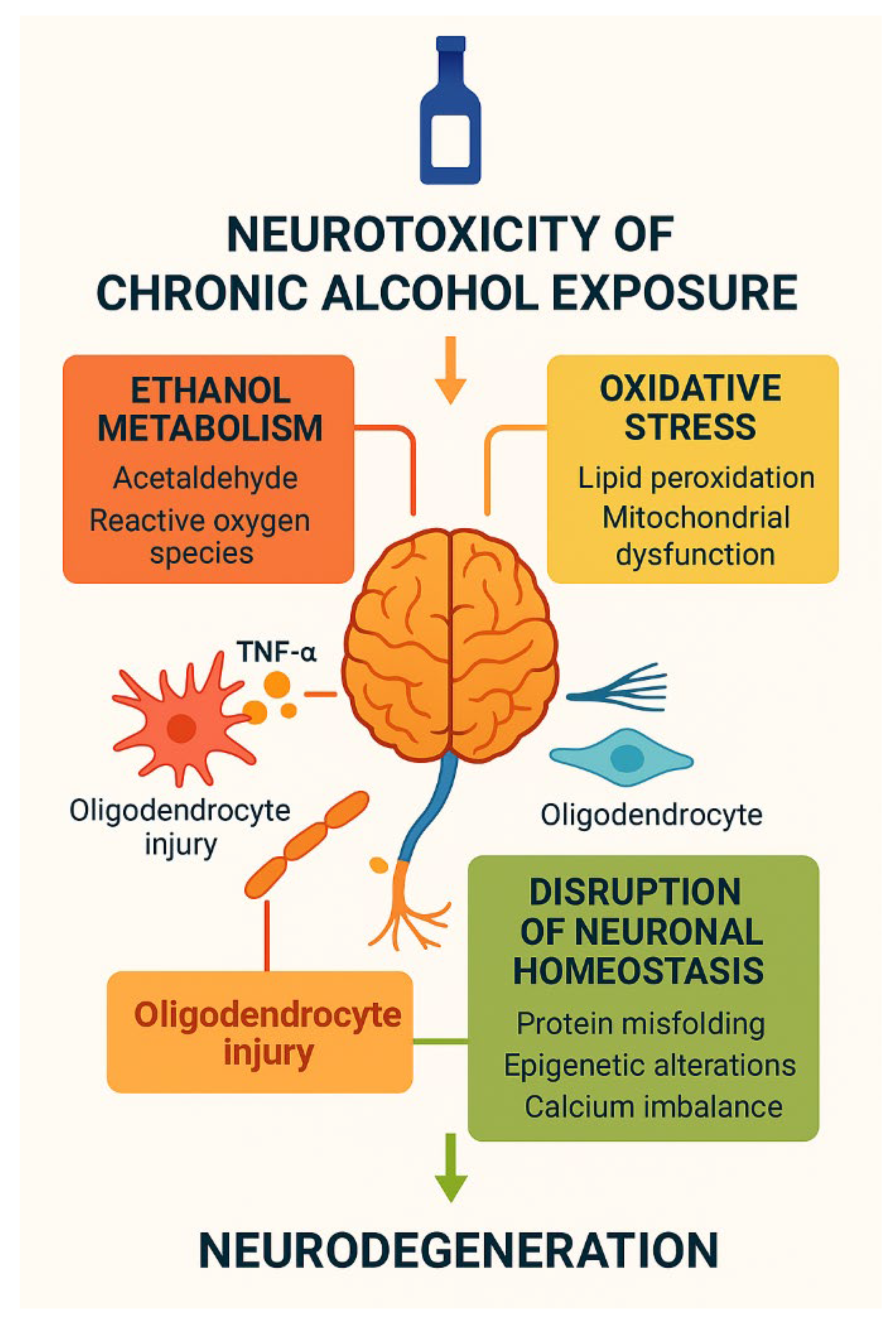
1. Introduction
2. Ethanol Metabolism and Its Neurotoxic Intermediates
2.1. Oxidative Metabolism and Acetaldehyde
2.2. Salsolinol and Dopaminergic Toxicity
2.3. Non-Oxidative Pathways and Membrane-Targeting Metabolites
2.4. Implications
3. Disruption of Protein Homeostasis in Neurons
3.1. Oxidative Protein Damage and ER Stress
3.2. Impairment of Protein Degradation Pathways
3.3. Chaperone Dysfunction and Loss of Proteostasis
4. Mitochondrial Impairment and Bioenergetic Failure
4.1. Structural Damage and Cytochrome c Release
4.2. Oxidative Injury and Mitophagy Dysfunction
4.3. Mitochondrial Dynamics and Energetic Failure
5. Alcohol-Induced Neuroinflammation
5.1. Microglial Activation and TLR4 Signaling
5.2. Astrocytic Dysfunction and Excitotoxicity
5.3. Glial Priming and Persistent Inflammation
6. Calcium Dysregulation and Synaptic Dysfunction
6.1. Ethanol-Induced Calcium Influx and Signaling
6.2. ER Calcium Depletion and Unfolded Protein Response
6.3. Mitochondrial Calcium Overload and Neuronal Death
7. Epigenetic Remodeling in Alcohol-Induced Neurotoxicity
7.1. DNA Methylation
7.2. Histone Modifications
7.3. microRNAs and Post-Transcriptional Regulation
8. Apoptotic Pathways and PI3K/Akt/mTOR Dysregulation
8.1. Intrinsic Apoptotic Cascade
8.2. Suppression of PI3K/Akt/mTOR Survival Signaling
8.3. BDNF Downregulation and Synaptic Vulnerability
9. Alcohol-Induced White Matter Injury and Oligodendrocyte Vulnerability
10. GABAergic Dysregulation in Chronic Alcohol Exposure
11. Sex Differences in Alcohol-Induced Neurotoxicity
12. Neuroprotective and Therapeutic Strategies in Alcohol-Induced Neurotoxicity
12.1. Targeting Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction
12.2. Modulating Neuroinflammation and Microglial Activation
12.3. Stabilising Calcium Homeostasis and Limiting Excitotoxicity
12.4. Epigenetic Therapeutic Strategies
12.5. Enhancing Neurotrophic and Pro-Survival Signalling
12.6. Multimodal and Translational Considerations
13. Limitations of Current Research and Translational Gaps
14. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Airapetov, M.; Eresko, S.; Lebedev, A.; Bychkov, E.; Shabanov, P. The role of Toll-like receptors in neurobiology of alcoholism. Biosci. Trends 2021, 15, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helander, A.; Beck, O. Ethyl sulfate: A metabolite of ethanol in humans and a potential biomarker of acute alcohol intake. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2005, 29, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, I.; Henriksen, A.; Gamsby, J.; Gulick, D. Impact of Alcohol Abuse on Susceptibility to Rare Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 643273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeri, L.; Izzo, L.; Sardelli, L.; Tunesi, M.; Albani, D.; Giordano, C. Advanced Organ-on-a-Chip Devices to Investigate Liver Multi-Organ Communication: Focus on Gut, Microbiota and Brain. Bioengineering 2019, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, S.; Ramesh, V.; Locasale, J.W. Acetate Metabolism in Physiology, Cancer, and Beyond. Trends Cell Biol. 2019, 29, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandt, M.; Garlapati, V.; Oelze, M.; Sotiriou, E.; Knorr, M.; Kröller-Schön, S.; Kossmann, S.; Schönfelder, T.; Morawietz, H.; Schulz, E.; et al. NOX2 amplifies acetaldehyde-mediated cardiomyocyte mitochondrial dysfunction in alcoholic cardiomyopathy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Ke, Z.; Xu, M.; Liao, M.; Wang, X.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, T.; Frank, J.A.; Bower, K.A.; Shi, X.; et al. Autophagy is a protective response to ethanol neurotoxicity. Autophagy 2012, 8, 1577–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Ma, C.; Bower, K.A.; Shi, X.; Ke, Z.; Luo, J. Ethanol promotes endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced neuronal death: Involvement of oxidative stress. J. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 86, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heier, C.; Xie, H.; Zimmermann, R. Nonoxidative ethanol metabolism in humans-from biomarkers to bioactive lipids. IUBMB Life 2016, 68, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Zentella, M.L.; Villalobos-García, D.; Hernández-Muñoz, R. Ethanol Metabolism in the Liver, the Induction of Oxidant Stress, and the Antioxidant Defense System. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, F.T.; Coleman, L.G.; Macht, V.A.; Vetreno, R.P. Targeting Persistent Changes in Neuroimmune and Epigenetic Signaling in Adolescent Drinking to Treat Alcohol Use Disorder in Adulthood. Pharmacol. Rev. 2023, 75, 380–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crews, F.T.; Zou, J.; Coleman, L.G. Extracellular microvesicles promote microglia-mediated pro-inflammatory responses to ethanol. J. Neurosci. Res. 2021, 99, 1940–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Liu, Y.; Chang, X.; Gou, W.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zuo, D. Acetaldehyde Induces Neurotoxicity In Vitro via Oxidative Stress- and Ca2+ Imbalance-Mediated Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 2593742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahim, M.; Rafiee Zadeh, A.; Shoureshi, P.; Ghadimi, K.; Cheshmavar, M.; Sheikhinia, N.; Afzali, M. Alcohol and multiple sclerosis: An immune system-based review. Int. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. Pharmacol. 2020, 12, 58–69. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, N.; Li, J.; Li, M.R.; Qi, B.; Wang, Z.; Wang, G.J.; Gao, J.; Qiao, H.L. Higher Activity of Alcohol Dehydrogenase Is Correlated with Hepatic Fibrogenesis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2018, 367, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getachew, B.; Csoka, A.B.; Bhatti, A.; Copeland, R.L.; Tizabi, Y. Butyrate Protects Against Salsolinol-Induced Toxicity in SH-SY5Y Cells: Implication for Parkinson’s Disease. Neurotox. Res. 2020, 38, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, G.I.; Alvear, T.F.; Roa, D.A.; Farias-Pasten, A.; Vergara, S.A.; Mellado, L.A.; Martinez-Araya, C.J.; Prieto-Villalobos, J.; García-Rodríguez, C.; Sánchez, N.; et al. Cx43 hemichannels and panx1 channels contribute to ethanol-induced astrocyte dysfunction and damage. Biol. Res. 2024, 57, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heit, C.; Dong, H.; Chen, Y.; Thompson, D.C.; Deitrich, R.A.; Vasiliou, V.K. The role of CYP2E1 in alcohol metabolism and sensitivity in the central nervous system. In Cytochrome P450 2E1: Its Role in Disease and Drug Metabolism; Subcellular Biochemistry; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 67, pp. 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendler, R.A.; Ramchandani, V.A.; Gilman, J.; Hommer, D.W. Stimulant and sedative effects of alcohol. In Behavioral Neurobiology of Alcohol Addiction; Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 13, pp. 489–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez, F.; Montesinos, J.; Ureña-Peralta, J.R.; Guerri, C.; Pascual, M. TLR4 participates in the transmission of ethanol-induced neuroinflammation via astrocyte-derived extracellular vesicles. J. Neuroinflammation 2019, 16, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Yang, Q.; BJoshi, R.; Liu, Y.; Akbar, M.; Song, B.J.; Zhou, S.; Wang, X. Role of Alcohol Drinking in Alzheimer’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease, and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimatkin, S.M.; Buben, A.L. Ethanol oxidation in the living brain. Alcohol Alcohol. 2007, 42, 529–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiter-Lopez, L.; Khan, M.A.S.; Wang, X.; Song, B.J. Roles of Oxidative Stress and Autophagy in Alcohol-Mediated Brain Damage. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimatkin, S.M.; Pronko, S.P.; Vasiliou, V.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Deitrich, R.A. Enzymatic mechanisms of ethanol oxidation in the brain. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2006, 30, 1500–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.A.; Hopkinson, R.J. The biochemistry of the carcinogenic alcohol metabolite acetaldehyde. DNA Repair 2024, 144, 103782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Jee, Y.M.; Yang, K.; Ryu, T. Alcohol-Induced Oxidative Stress and Gut-Liver-Brain Crosstalk: Expanding the Paradigm from ALD to MetALD. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, M.R.; Molina-Castro, M.; Etkins, J.C.; Koide, T.L.; Ramchandani, V.A.; Plawecki, M.H.; Mennella, J.A.; Pepino, M.Y. Recent advances in alcohol metabolism: From the gut to the brain. Physiol. Rev. 2025, 105, 2501–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, K.; Ueno, Y.; Mizoi, Y.; Tatsuno, Y. Genetic polymorphism of alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenase and the effects on alcohol metabolism. Arukoru Kenkyuto Yakubutsu Ison 1993, 28, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Q.; Zheng, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Deng, Y.; Zhong, R.; Wang, J.; Chen, X. Sal synthase induced cytotoxicity of PC12 cells through production of the dopamine metabolites salsolinol and N-methyl-salsolinol. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2022, 21, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Li, Q.; Lang, W.; Li, W.; Jiang, X.; Wan, Z.; Sun, H.; Wang, H. Salsolinol Induces Parkinson’s Disease Through Activating NLRP3-Dependent Pyroptosis and the Neuroprotective Effect of Acteoside. Neurotox. Res. 2022, 40, 1948–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Krnjević, K.; Ye, J.H. Salsolinol modulation of dopamine neurons. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hipólito, L.; Sánchez-Catalán, M.J.; Martí-Prats, L.; Granero, L.; Polache, A. Revisiting the controversial role of salsolinol in the neurobiological effects of ethanol: Old and new vistas. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2012, 36, 362–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurnik-Łucka, M.; Panula, P.; Bugajski, A.; Gil, K. Salsolinol: An Unintelligible and Double-Faced Molecule-Lessons Learned from In Vivo and In Vitro Experiments. Neurotox. Res. 2018, 33, 485–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rommelspacher, H.; Sllström Baum, S.; Dufeu, P.; Schmidt, L.G. Determination of (R)- and (S)-salsolinol sulfate and dopamine sulfate levels in plasma of nonalcoholics and alcoholics. Alcohol 1995, 12, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrea, E.M.; Hernandez, J.D.; Bielawski, D.M.; Kan, J.M.; Leonardo, G.M.; Abela, M.B.; Church, M.W.; Hannigan, J.H.; Janisse, J.J.; Ager, J.W.; et al. Fatty acid ethyl esters in meconium: Are they biomarkers of fetal alcohol exposure and effect? Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2006, 30, 1152–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelner, I.; Kenna, K.; Brien, J.F.; Bocking, A.; Harding, R.; Walker, D.; Koren, G. Meconium fatty acid ethyl esters as biomarkers of late gestational ethanol exposure and indicator of ethanol-induced multi-organ injury in fetal sheep. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viel, G.; Boscolo-Berto, R.; Cecchetto, G.; Fais, P.; Nalesso, A.; Ferrara, S.D. Phosphatidylethanol in blood as a marker of chronic alcohol use: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 14788–14812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perilli, M.; Toselli, F.; Franceschetto, L.; Cinquetti, A.; Ceretta, A.; Cecchetto, G.; Viel, G. Phosphatidylethanol (PEth) in Blood as a Marker of Unhealthy Alcohol Use: A Systematic Review with Novel Molecular Insights. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teschke, R. Alcoholic Liver Disease: Alcohol Metabolism, Cascade of Molecular Mechanisms, Cellular Targets, and Clinical Aspects. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Xiong, Q.; Tian, X.; Liu, W.; Sun, B.; Ru, Q.; Shu, X. Alcohol Exposure Induces Depressive and Anxiety-like Behaviors via Activating Ferroptosis in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, M.; Rubin, C.S. A Calcium- and Diacylglycerol-Stimulated Protein Kinase C (PKC), Caenorhabditis elegans PKC-2, Links Thermal Signals to Learned Behavior by Acting in Sensory Neurons and Intestinal Cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2017, 37, e00192-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.Z.; Chen, N.H. Connexin 43: An Interface Connecting Neuroinflammation to Depression. Molecules 2023, 28, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Li, D.; Huang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, X. Role of Ferroptosis Regulation by Nrf2/NQO1 Pathway in Alcohol-Induced Cardiotoxicity In Vitro and In Vivo. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2024, 37, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.C.; Namkoong, K. Alcohol: Intoxication and poisoning—Diagnosis and treatment. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2014, 125, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemasters, J.J. Evolution of Voltage-Dependent Anion Channel Function: From Molecular Sieve to Governator to Actuator of Ferroptosis. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Cederbaum, A.I. Alcohol, oxidative stress, and free radical damage. Alcohol Res. Health 2003, 27, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mailloux, R.J. An Update on Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species Production. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Daré, B.; Lagente, V.; Gicquel, T. Ethanol and its metabolites: Update on toxicity, benefits, and focus on immunomodulatory effects. Drug Metab. Rev. 2019, 51, 545–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Zhao, Y. Acetaldehyde induces phosphorylation of dynamin-related protein 1 and mitochondrial dysfunction via elevating intracellular ROS and Ca2+ levels. Redox Biol. 2020, 28, 101381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugarte-Uribe, B.; Prévost, C.; Das, K.K.; Bassereau, P.; García-Sáez, A.J. Drp1 polymerization stabilizes curved tubular membranes similar to those of constricted mitochondria. J. Cell Sci. 2018, 132, jcs208603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Rojas, C.; Carvajal, F.J.; Mira, R.G.; Arce, C.; Lerma-Cabrera, J.M.; Orellana, J.A.; Cerpa, W.; Quintanilla, R.A. Adolescent Binge Alcohol Exposure Affects the Brain Function Through Mitochondrial Impairment. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 4473–4491, Erratum in Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 8216–8217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendeln, A.C.; Degenhardt, K.; Kaurani, L.; Gertig, M.; Ulas, T.; Jain, G.; Wagner, J.; Häsler, L.M.; Wild, K.; Skodras, A.; et al. Innate immune memory in the brain shapes neurological disease hallmarks. Nature 2018, 556, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, F.T.; Macht, V.; Vetreno, R.P. Epigenetic regulation of microglia and neurons by proinflammatory signaling following adolescent intermittent ethanol (AIE) exposure and in human AUD. Adv. Drug Alcohol Res. 2024, 4, 12094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Qin, C.; Hu, Z.W.; Zhou, L.Q.; Yu, H.H.; Chen, M.; Bosco, D.B.; Wang, W.; Wu, L.J.; Tian, D.S. Microglia reprogram metabolic profiles for phenotype and function changes in central nervous system. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 152, 105290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.K.; Ahmad, M.H.; Sahu, M.R.; Subba, R.; Mondal, A.C. Detrimental Effects of Alcohol-Induced Inflammation on Brain Health: From Neurogenesis to Neurodegeneration. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 43, 1885–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Kracht, L.; Lerario, A.M.; Dubbelaar, M.L.; Brouwer, N.; Wesseling, E.M.; Boddeke, E.W.G.M.; Eggen, B.J.L.; Kooistra, S.M. Epigenetic regulation of innate immune memory in microglia. J. Neuroinflammation 2022, 19, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.-H.; Zuo, W.; Chaudhry, F.; Chinn, L. Neuroimmune Mechanisms in Alcohol Use Disorder: Microglial Modulation and Therapeutic Horizons. Psychoactives 2025, 4, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, P.P.; Morel, C.; Ambade, A.; Iracheta-Vellve, A.; Kwiatkowski, E.; Satishchandran, A.; Furi, I.; Cho, Y.; Gyongyosi, B.; Catalano, D.; et al. Chronic alcohol-induced neuroinflammation involves CCR2/5-dependent peripheral macrophage infiltration and microglia alterations. J. Neuroinflammation 2020, 17, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Luo, J. Role of MCP-1 and CCR2 in alcohol neurotoxicity. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 139, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, D.; Pan, F.; Ho, C.S.H.; Ho, R.C.M. Ethanol Exposure Induces Microglia Activation and Neuroinflammation through TLR4 Activation and SENP6 Modulation in the Adolescent Rat Hippocampus. Neural Plast. 2019, 2019, 1648736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guizzetti, M.; Mangieri, R.A.; Ezerskiy, L.A.; Hashimoto, J.G.; Bajo, M.; Farris, S.P.; Homanics, G.E.; Lasek, A.W.; Mayfield, R.D.; Messing, R.O.; et al. Astrocytes and Alcohol Throughout the Lifespan. Biol. Psychiatry 2026, 99, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadler, E.; Kish, S.J.; Tong, J.; Lê, A.D.; Boileau, I. Astrocyte alterations and dysfunction in alcohol use disorder: A comprehensive scoping review of clinical postmortem and preclinical evidence. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2025, 142, 111509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tizabi, Y.; Getachew, B.; Aschner, M.; Collins, M.A. Role of glial cells in neurotoxicological effects of alcohol. Adv. Neurotoxicol. 2025, 14, 41–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Lindström, C.L.; Donahue, A.; Miller, M.W. Differential effects of ethanol on the expression of cyclo-oxygenase in cultured cortical astrocytes and neurons. J. Neurochem. 2001, 76, 1354–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Kusumo, H.; Sakharkar, A.J.; Pandey, S.C.; Guizzetti, M. Regulation of DNA methylation by ethanol induces tissue plasminogen activator expression in astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 2014, 128, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangaunchom, P.; Dharmasaroja, P. Caffeine Potentiates Ethanol-Induced Neurotoxicity Through mTOR/p70S6K/4E-BP1 Inhibition in SH-SY5Y Cells. Int. J. Toxicol. 2020, 39, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, A.; Kim, H.; Thomas, D.; Biggs, P.; Ara, R.; Bosomtwi, A.; Kang, S. Glutamatergic dysfunction of astrocytes in paraventricular nucleus of thalamus contributes to adult anxiety susceptibility in adolescent ethanol exposed mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-González, D.; Romero-Llopis, B.; Roldán-Lázaro, M.; Baquero, L.; Noverques, R.; Pallardó, F.V.; Navarro, J.A.; González-Cabo, P. Regulatory drugs of Glutamate Transporter 1 (EAAT2/GLT-1) expression and activity: Role in quenching oxidative damage. Redox Exp. Med. 2024, 2024, e240004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najim, S.M.; Sadeq, Z.A.; Sabri, L.A. Glutamate as a target therapy for alcohol dependence disorder. Mil. Med Sci. Lett. 2024, 93, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, A.; Bhowmik, K.K.; Wong, W.; Mohammed, A.S.; Abou-Gharbia, M.; Childers, W.; Sari, Y. Modulatory effects of GLT-1 enhancer, MC-100093, on glutamate uptake and associated signaling pathways in female and male alcohol preferring rats exposed to ethanol. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2025, 28, pyaf075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Zou, J.; Barnett, A.; Vetreno, R.P.; Crews, F.T.; Coleman, L.G. TRAIL Mediates Neuronal Death in AUD: A Link between Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friske, M.M.; Torrico, E.C.; Haas, M.J.W.; Borruto, A.M.; Giannone, F.; Hade, A.C.; Yu, Y.; Gao, L.; Sutherland, G.T.; Hitzemann, R.; et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis on the transcriptomic signatures in alcohol use disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2025, 30, 310–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berridge, M.J.; Bootman, M.D.; Roderick, H.L. Calcium signalling: Dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.R.; Lee, H.J.; Jung, Y.H.; Kim, J.S.; Chae, C.W.; Kim, S.Y.; Han, H.J. Ethanol-activated CaMKII signaling induces neuronal apoptosis through Drp1-mediated excessive mitochondrial fission and JNK1-dependent NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaidullov, I.; Ermakova, E.; Gaifullina, A.; Mosshammer, A.; Yakovlev, A.; Weiger, T.M.; Hermann, A.; Sitdikova, G. Alcohol metabolite acetic acid activates BK channels in a pH-dependent manner and decreases calcium oscillations and exocytosis of secretory granules in rat pituitary GH3 cells. Pflugers Arch. 2021, 473, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Kusumanchi, P.; Han, S.; Yang, Z.; Liangpunsakul, S. Alcohol Metabolizing Enzymes, Microsomal Ethanol Oxidizing System, Cytochrome P450 2E1, Catalase, and Aldehyde Dehydrogenase in Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, J. Epigenetic modification in alcohol use disorder and alcoholic cardiomyopathy: From pathophysiology to therapeutic opportunities. Metabolism 2021, 125, 154909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangra, A.; Sriram, C.S.; Pandey, S.; Choubey, P.; Rajput, P.; Saroha, B.; Bezbaruah, B.K.; Lahkar, M. Epigenetic Modifications, Alcoholic Brain and Potential Drug Targets. Ann. Neurosci. 2016, 23, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanfarillo, F.; Ferraguti, G.; Lucarelli, M.; Fuso, A.; Ceccanti, M.; Terracina, S.; Micangeli, G.; Tarani, L.; Fiore, M. The Impact of Alcohol-Induced Epigenetic Modifications in the Treatment of Alcohol use Disorders. Curr. Med. Chem. 2024, 31, 5837–5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Liu, B.; Chen, H.; Xu, P.; Guo, X.; Yao, D.; Li, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y.; Yao, H.; et al. The role of DNA methylation in alcohol-mediated neurodevelopmental toxicity. Toxicology 2026, 519, 154315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Gelernter, J. Human genetics and epigenetics of alcohol use disorder. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e172885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, A.; Friske, M.; Edelmann, S.; Bender, A.; Fischer, L.; Zill, P.; Koller, G.; Bakalkin, G.; Sommer, W.H.; Hansson, A.C.; et al. Validation of GDAP1 and HECW2 as Epigenetic Markers of Alcohol Use Disorder in Blood and Brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbanna, S.; Nagre, N.N.; Shivakumar, M.; Umapathy, N.S.; Psychoyos, D.; Basavarajappa, B.S. Ethanol induced acetylation of histone at G9a exon1 and G9a-mediated histone H3 dimethylation leads to neurodegeneration in neonatal mice. Neuroscience 2014, 258, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawecka, E.; Plättner, H.; Ederer, L.; Niemann, K.; Pasche, S.; Zimmermann, M.; Edelmann, S.; Nieratschker, V. GDAP1 Is Dysregulated at DNA Methylation and H3K4me3 Levels in Alcohol Use Disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ockner, R.K. Apoptosis and liver diseases: Recent concepts of mechanism and significance. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2001, 16, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.C. A Critical Role of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Alcohol Consumption. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 79, 427–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peregud, D.I.; Baronets, V.Y.; Terebilina, N.N.; Gulyaeva, N.V. Role of BDNF in Neuroplasticity Associated with Alcohol Dependence. Biochemistry 2023, 88, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-González, C.; Romero-Acevedo, L.; Fernández-Rodríguez, C.M.; Medina-Vega, L.; García-Rodríguez, A.; Ortega-Toledo, P.; González-Navarrete, L.; Vera-Delgado, V.E.; González-Reimers, E. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor among patients with alcoholism. CNS Spectr. 2021, 26, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiee, A.; Jafarabady, K.; Rafiei, M.A.; Beiky, M.; Seighali, N.; Golpayegani, G.; Jalali, M.; Soltani Abhari, F.; Arabzadeh Bahri, R.; Safari, O.; et al. Effect of alcohol on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) blood levels: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malewska-Kasprzak, M.; Skibińska, M.; Dmitrzak-Węglarz, M. Alterations in Neurotrophins in Alcohol-Addicted Patients during Alcohol Withdrawal. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, J.; Gu, C. Function and Mechanism of Myelin Regulation in Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. BioEssays 2019, 41, e1800255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Li, M.; Qiao, Z.; Zhou, H.; Cai, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, J. Effects of adolescent alcohol exposure on oligodendrocyte lineage cells and myelination in mice: Age and subregion differences. IBRO Neurosci. Rep. 2024, 17, 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Monte, S.M.; Tong, M. Molecular and biochemical pathologies in human alcohol-related cerebellar white matter degeneration. Adv. Drug Alcohol Res. 2025, 5, 15342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharavath, R.N.; Pina-Leblanc, C.; Tang, V.M.; Sloan, M.E.; Nikolova, Y.S.; Pangarov, P.; Ruocco, A.C.; Shield, K.; Voineskos, D.; Blumberger, D.M.; et al. GABAergic signaling in alcohol use disorder and withdrawal: Pathological involvement and therapeutic potential. Front. Neural Circuits 2023, 17, 1218737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogawski, M.A. Update on the neurobiology of alcohol withdrawal seizures. Epilepsy Curr. 2005, 5, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Ren, J. Chronic alcohol consumption alters mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), reduces ribosomal p70s6 kinase and p4E-BP1 levels in mouse cerebral cortex. Exp. Neurol. 2007, 204, 840–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
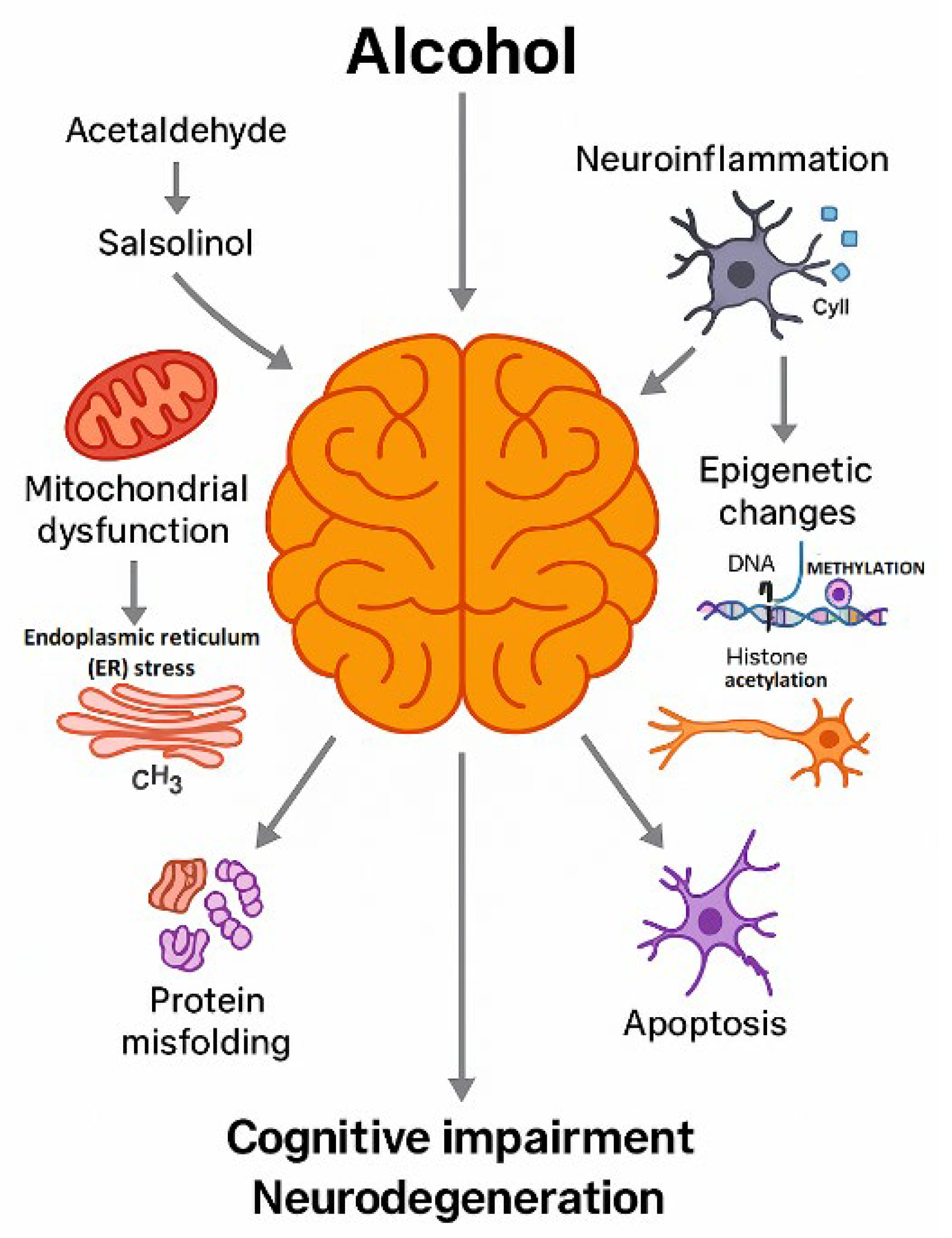
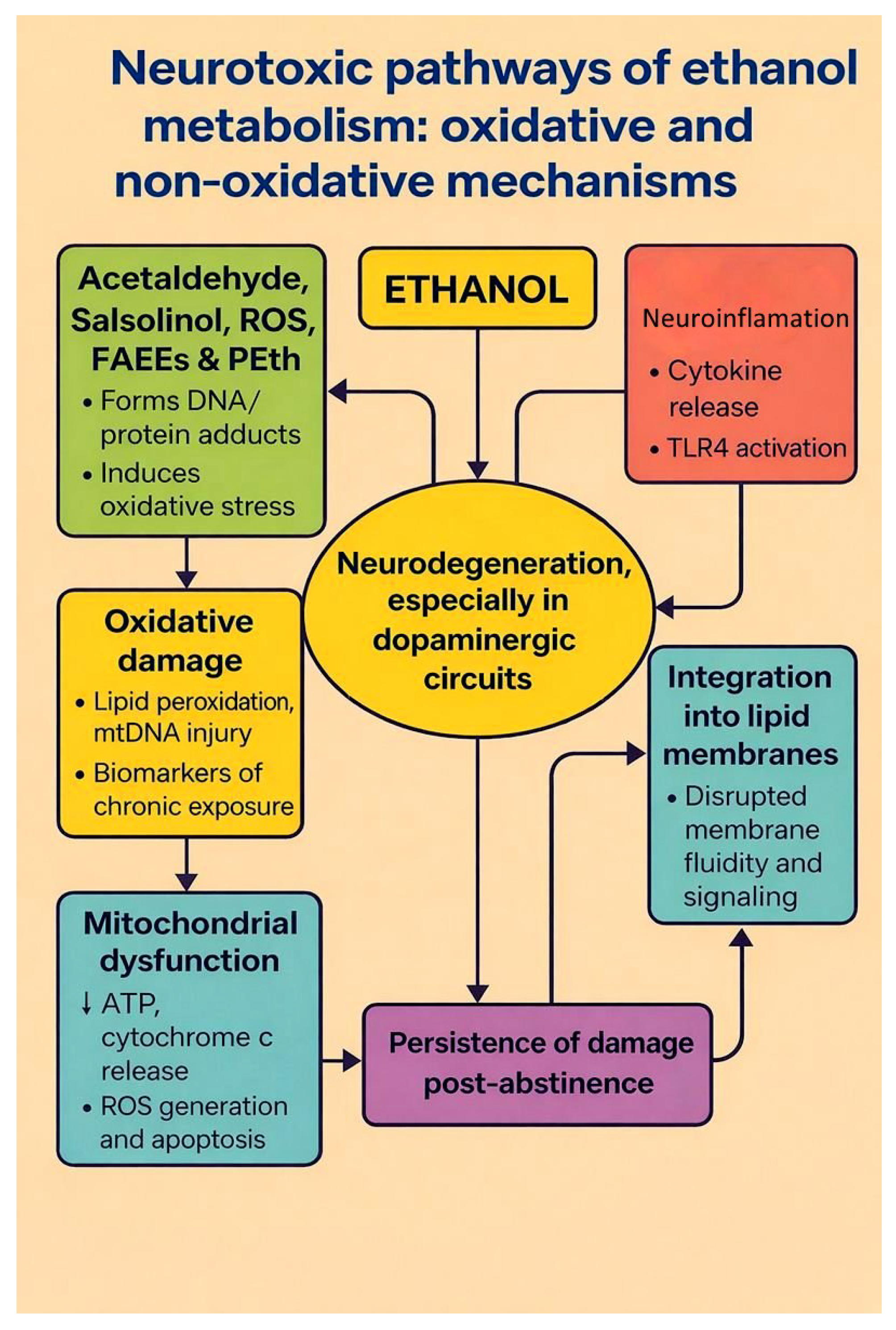
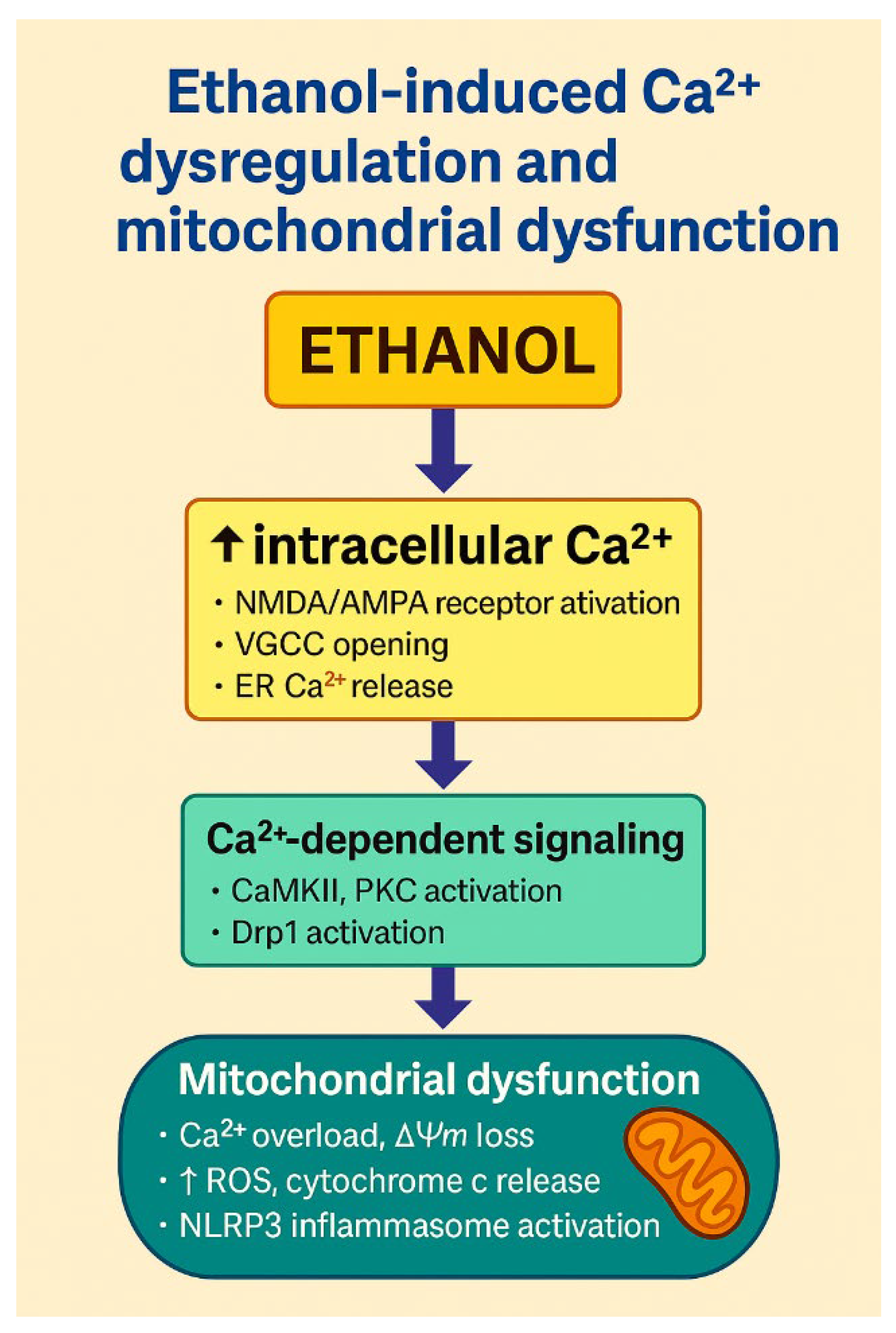
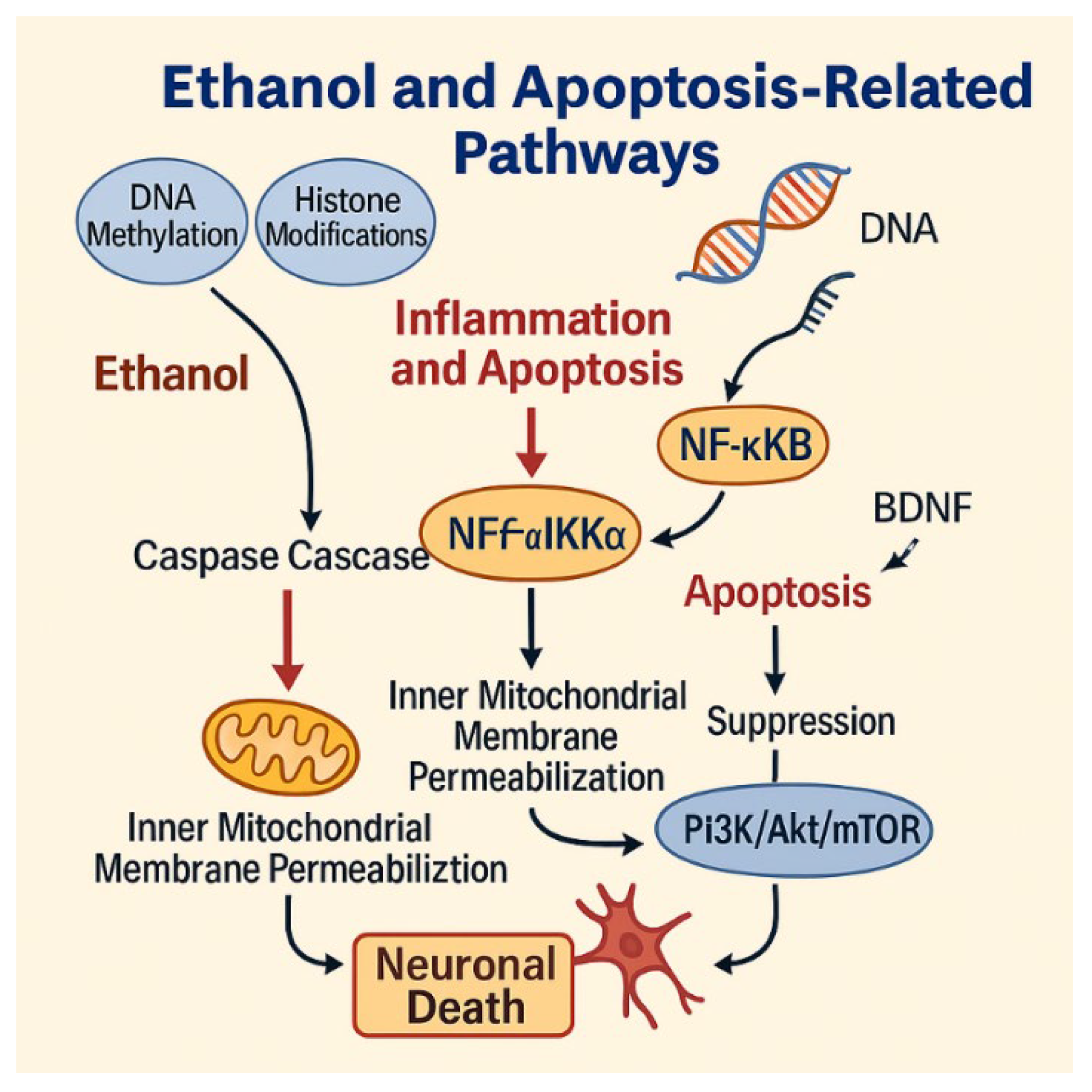
| Mechanism | Molecular Pathways | Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Oxidative stress | Excess ROS/RNS production, NOX activation, lipid peroxidation, impaired antioxidant defence | DNA and mitochondrial DNA damage, loss of membrane integrity, synaptic loss, impaired neurotransmission |
| Mitochondrial dysfunction | ETC impairment, reduced ATP synthesis, mPTP opening, altered Ca2+ buffering, Drp1-mediated fission, defective mitophagy | Bioenergetic failure, cytochrome c release, activation of intrinsic apoptosis, axonal transport and synaptic transmission deficits |
| ER stress and protein misfolding | PERK–eIF2α–ATF4 pathway activation, CHOP induction, unfolded protein response (UPR) dysregulation, impaired UPS/autophagy | Accumulation of misfolded/aggregated proteins, ER-stress-induced apoptosis, loss of proteostasis in neurons and glia |
| Calcium dysregulation | NMDA/AMPA overactivation, opening of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels (VGCCs), ER Ca2+ release, mitochondrial Ca2+ overload | Excitotoxic neuronal injury, cytoskeletal disintegration, mPTP opening, amplification of ROS production |
| Neuroinflammation | TLR4–MyD88/TRIF–NF-κB activation, microglial cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6), MCP-1/CCR2 chemokine signalling, recruitment of peripheral immune cells | Synaptic pruning and loss, gliosis, disruption of neuron–glial communication, chronic neuronal loss |
| Epigenetic remodeling | DNMT/HDAC imbalance, altered DNA methylation, histone acetylation/methylation changes, dysregulated miRNA profiles | Stable reprogramming of gene expression, impaired neurotrophic and survival signalling, increased susceptibility to stress and neurodegeneration |
| White matter injury and oligodendrocyte vulnerability | Ethanol-induced oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and lipid peroxidation in oligodendrocytes; impaired myelin protein expression; disrupted OPC proliferation and differentiation; microglial cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6); astrocytic connexin dysfunction; activation of Wnt/β-catenin and Notch signalling | Myelin thinning and loss, reduced remyelination capacity, axonal conduction deficits, disconnection of cortico–subcortical circuits, cognitive slowing and processing-speed deficits |
| Apoptotic signalling | Bax translocation, mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP), caspase-9/3 activation, TRAIL/death-receptor pathway activation, suppression of PI3K/Akt/mTOR survival signalling | Programmed neuronal cell death, synaptic and circuit degeneration |
| Neurotransmitter System | Ethanol-Related Changes (Dose/Pattern) | Functional and Behavioural Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| GABAergic | Acute low–moderate doses: positive allosteric modulation of GABA_A receptors, enhanced inhibitory tone. Chronic and heavy use: downregulation and altered subunit composition of GABA_A receptors, reduced inhibitory transmission, impaired GABA release. | Sedation and anxiolysis in acute use; during chronic exposure and withdrawal neuronal hyperexcitability, anxiety, seizures, heightened vulnerability to excitotoxic injury. |
| Glutamatergic | Acute exposure: transient inhibition of NMDA receptor function. Chronic and binge drinking: upregulation and hyperactivation of NMDA receptors, elevated extracellular glutamate, impaired glutamate uptake by astrocytes. | Excitotoxicity, Ca2+ overload, mitochondrial dysfunction, dendritic spine loss, cognitive impairment and increased risk of neurodegeneration |
| Dopaminergic (mesolimbic) | Acute exposure: increased phasic dopamine release in ventral tegmental area (VTA) → nucleus accumbens (NAc). Chronic use: blunted dopaminergic responses, altered firing patterns, accumulation of ethanol-derived metabolites (e.g., salsolinol). | Reward dysregulation, reinforcement of alcohol-seeking, anhedonia and motivational deficits during withdrawal, dependence-related synaptic plasticity |
| Serotonergic | Dose and pattern-dependent alterations in 5-HT release and turnover; changes in 5-HT_1A/5-HT_2A receptor expression and signalling in prefrontal and limbic regions, particularly with chronic exposure. | Dysregulation of mood, anxiety, impulsivity and sleep–wake cycles; contribution to comorbid depression and anxiety in AUD. |
| Noradrenergic | Disruption of locus coeruleus noradrenergic output, especially during chronic use and withdrawal; increased noradrenergic tone and receptor sensitivity in stress-related circuits | Autonomic hyperarousal, irritability, insomnia and stress-related relapse; amplification of withdrawal symptoms and negative affect. |
| Cholinergic interneurons (striatum/NAc) | Modulation of ethanol-sensitive GABA_A receptors on striatal and nucleus accumbens cholinergic interneurons; altered acetylcholine release and integration of cortical and dopaminergic inputs | Abnormal gating of striatal circuits, disturbed action selection and habit formation, reinforcement of alcohol-seeking and long-term synaptic instability |
| Sex/Comparison | Biological Determinants | Neurotoxic Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Female | Higher blood alcohol concentration (BAC) for a given dose due to lower gastric ADH activity and higher body fat; estrogen-enhanced TLR4–NFκB-driven inflammation; greater oxidative stress and microglial activation; enhanced mitochondrial dysfunction and Ca2+ dysregulation under equivalent exposure; stronger microglial and astrocytic inflammatory responses. | Greater white matter and hippocampal damage; earlier onset of cognitive decline; increased anxiety- and depression-like symptoms at lower cumulative exposure; increased oligodendrocyte and myelin damage, reduced remyelination capacity, and greater vulnerability to disconnection/processing-speed deficits. |
| Male | Greater absolute alcohol intake and more frequent binge patterns; higher gastric ADH activity and total body water; testosterone-related support of PI3K/Akt signalling and antioxidant capacity; lower basal cytokine reactivity | Higher total lifetime dose before overt deficits; relatively slower structural decline, but pronounced executive and decision making impairments with prolonged heavy use |
| Female > Male | Enhanced mitochondrial dysfunction and Ca2+ dysregulation in several brain regions under equivalent exposure; stronger microglial and astrocytic inflammatory responses | Increased oligodendrocyte and myelin damage; reduced remyelination capacity; greater vulnerability to disconnection and processing-speed deficits |
| Male ≈ Female | Shared epigenetic remodeling (DNMT/HDAC imbalance, altered DNA methylation and histone marks, dysregulated miRNA profiles); overlapping excitotoxic, oxidative and apoptotic cascades | Convergent long-term transcriptional reprogramming; persistent neuroinflammation and synaptic loss in both sexes |
| Therapeutic Strategy | Molecular Target | Rationale/Intended Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Antioxidants (N-acetylcysteine, glutathione donors) | ROS, lipid peroxidation | Reduce oxidative damage and lipid peroxidation, protect mitochondria |
| Mitochondrial stabilizers (coenzyme Q10, SS-peptides, MitoQ) | ETC complexes, mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) | Restore mitochondrial efficiency, maintain ΔΨm, prevent cytochrome c release and apoptosis |
| HDAC inhibitors/DNMT modulators | Epigenetic markers (histones, DNA methylation) | Normalize gene expression, reverse maladaptive epigenetic remodeling |
| TLR4 antagonists/microglial inhibitors | Microglial NFκB pathway | Reduce neuroinflammation and cytokine release, limit microglial activation |
| Calcium channel blockers | NMDA and VGCC-mediated Ca2+ influx | Prevent excitotoxicity and Ca2+-dependent mitochondrial injury |
| Memantine/other NMDA antagonists | NMDA receptor signaling | Attenuate glutamate-driven excitotoxic injury |
| BDNF enhancers/TrkB agonists, PI3K/Akt/mTOR activators | Neurotrophic and survival signaling | Support neuronal survival and plasticity, promote structural and functional recovery |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Gołaszewski, P.; Wawrzyniak, A.; Kłosowicz, M.; Burbelka, A.; Balawender, K. Neurotoxicity of Chronic Alcohol Exposure: Mechanistic Insights, Cellular Disruption, and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2026, 27, 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010299
Gołaszewski P, Wawrzyniak A, Kłosowicz M, Burbelka A, Balawender K. Neurotoxicity of Chronic Alcohol Exposure: Mechanistic Insights, Cellular Disruption, and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2026; 27(1):299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010299
Chicago/Turabian StyleGołaszewski, Philip, Agata Wawrzyniak, Maksymilian Kłosowicz, Aleksandra Burbelka, and Krzysztof Balawender. 2026. "Neurotoxicity of Chronic Alcohol Exposure: Mechanistic Insights, Cellular Disruption, and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 27, no. 1: 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010299
APA StyleGołaszewski, P., Wawrzyniak, A., Kłosowicz, M., Burbelka, A., & Balawender, K. (2026). Neurotoxicity of Chronic Alcohol Exposure: Mechanistic Insights, Cellular Disruption, and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 27(1), 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010299






