Discovery of Triazone Derivatives Containing Acylhydrazone and Phenoxypyridine Motifs as Novel Insecticidal and Antiphytopathogenic Fungus Agents
Abstract
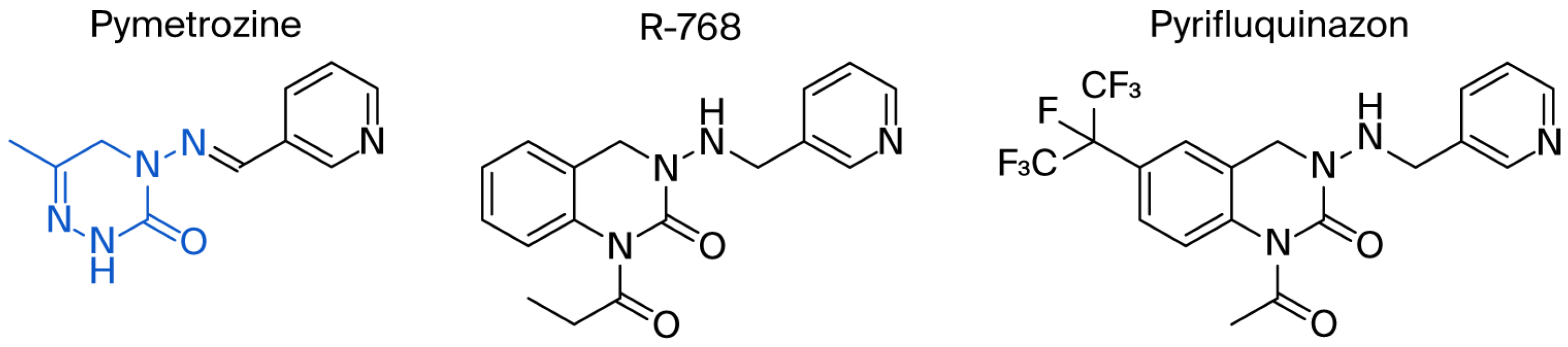
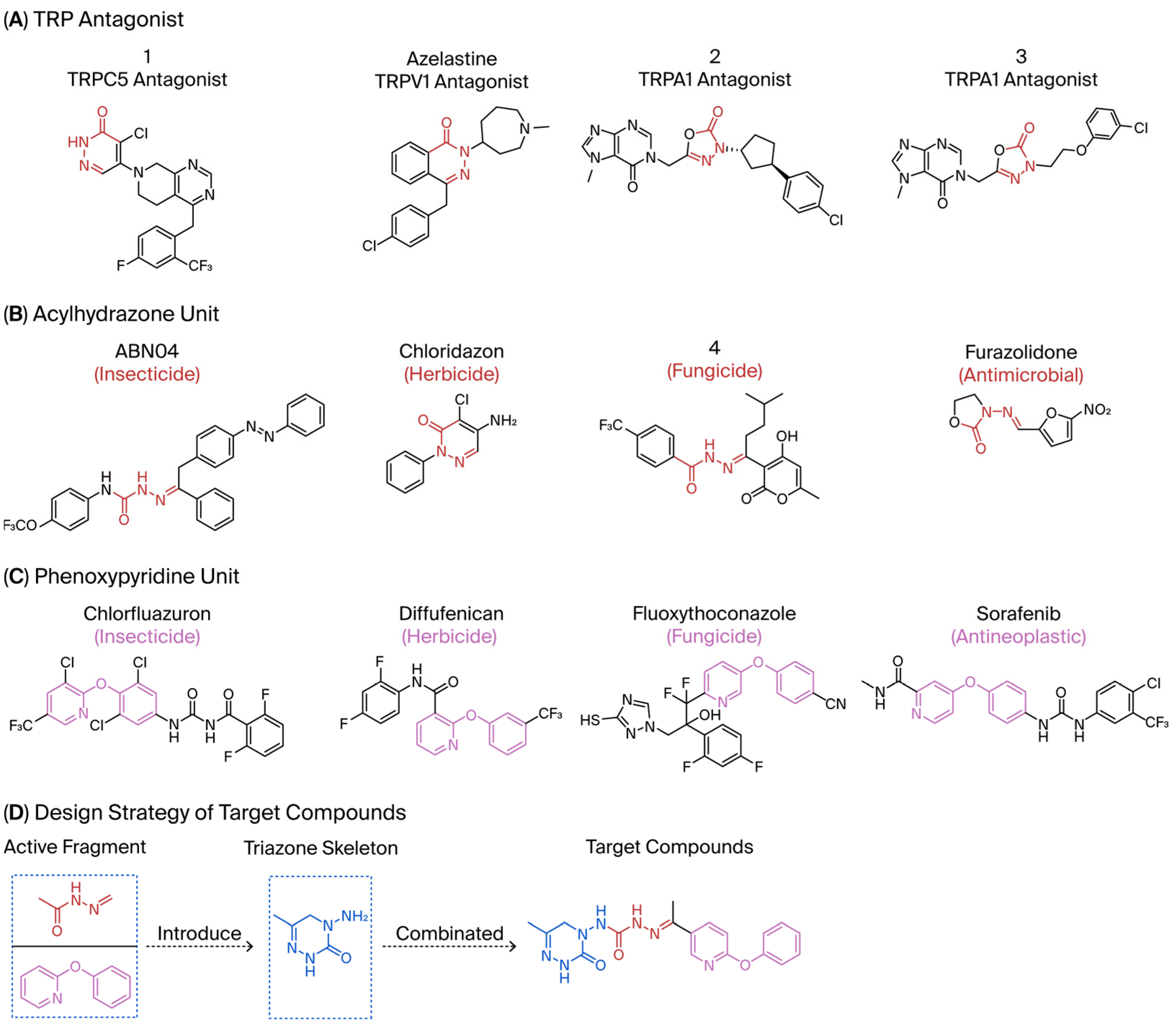
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
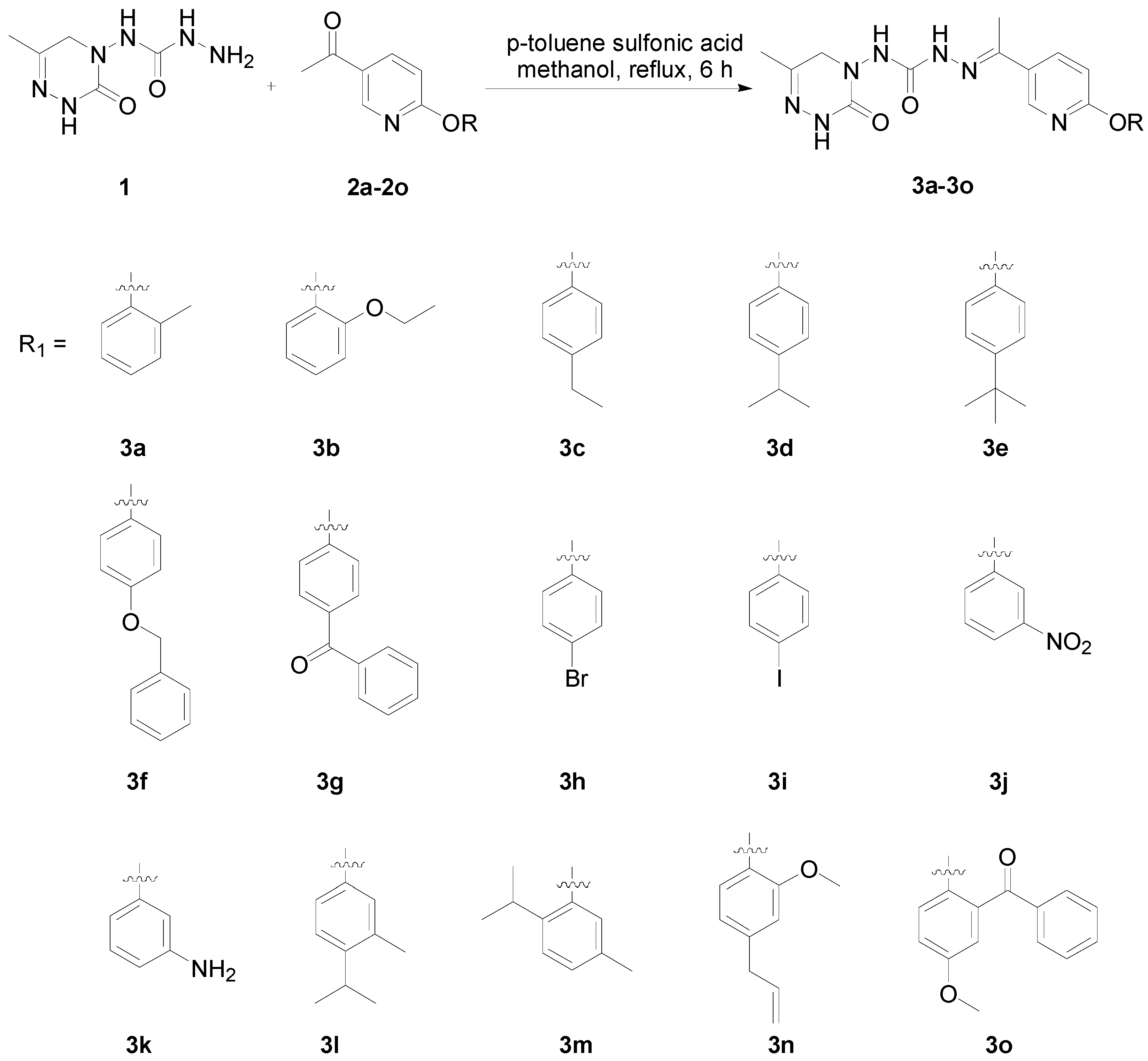
2.1. General Synthesis
2.2. Biological Evaluation
2.2.1. Foliar Contact Activity Against Bean Aphid (A. craccivora)
2.2.2. Larvicidal Activities
2.2.3. Fungicidal Activities
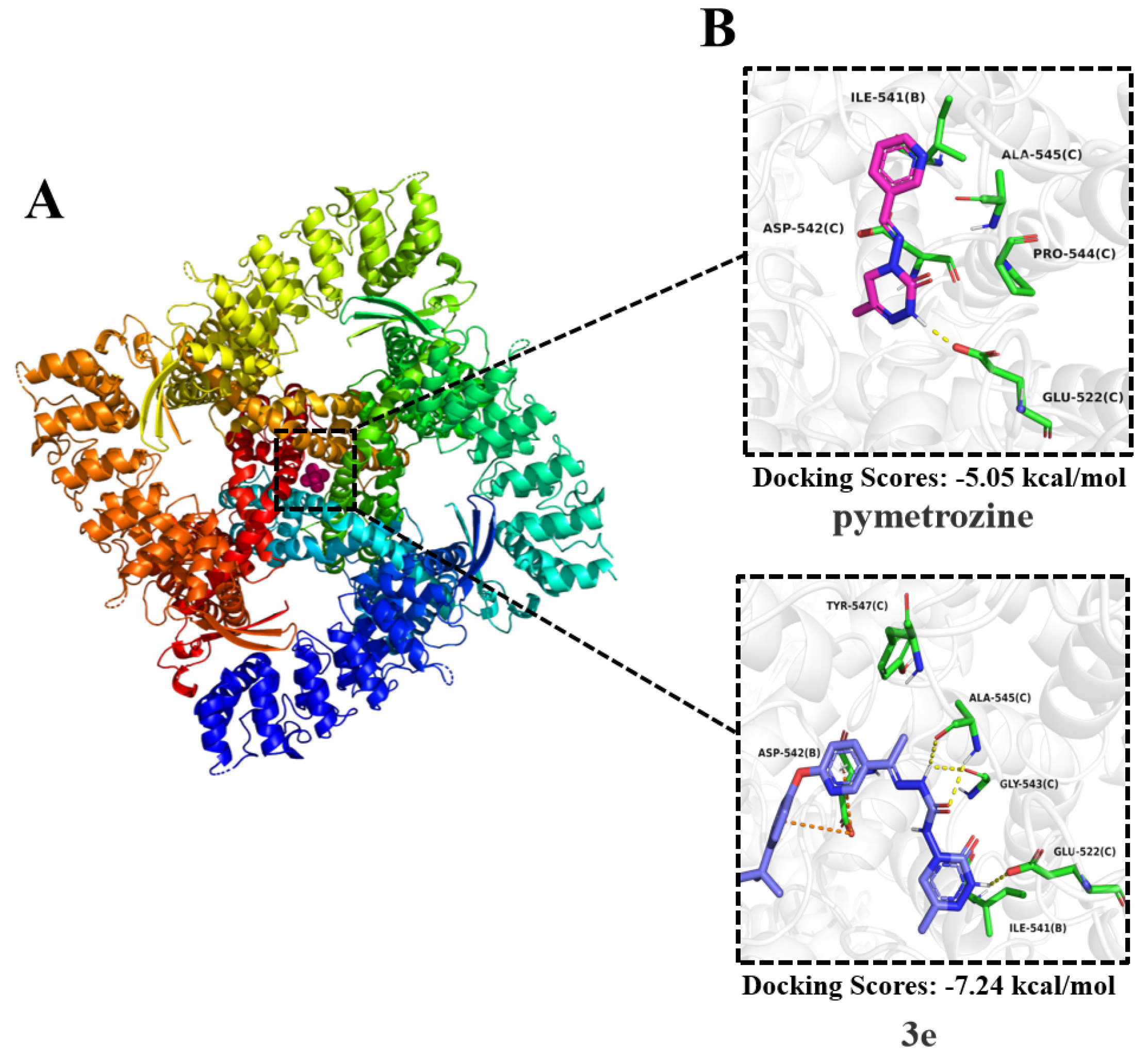
2.2.4. Toxicity
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malinga, L.N.; Laing, M.D. Efficacy of three biopesticides against cotton pests under field conditions in South Africa. Crop Prot. 2021, 145, 105578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrewijn, P. Pymetrozine, a fast-acting and selective inhibitor of aphid feeding. In-situ studies with electronic monitoring of feeding behaviour. Pestic. Sci. 1997, 49, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaal, Y.A.I.; Lampert, E.P.; Wolff, M.A.; Roe, R.M. Novel substrates for the kinetic assay of esterases associated with insecticide resistance. Experientia 1993, 49, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.B.; Silva-Torres, C.S.A.; Oliveira, J.V.D. Toxicity of pymetrozine and thiamethoxam to Aphelinus gossypii and Delphastus pusillus. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 2003, 38, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristinsson, H. Pesticides. US4931439A, 5 June 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Mulvihill, M.J.; Shaber, S.H.; Kelly, M.J. Enhanced Propertied Pesticides. WO2001056358A2, 9 August 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Sebastian, R.; Jurgen, S.; Shuji, H. Insecticidal Triazinone Derivatives. WO2013079350A1, 6 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.S.; Willke, J.S.; Winzenberg, K.N. Synthesis of some hydrazone derivatives structurally related to the insecticide pymetrozine. Aust. J. Chem. 1996, 49, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uehara, M.; Shimizu, T.; Fujioka, S. Substituted Aminoquinzaolinone (Thione) Derivatives or Salts Thereof, Intermediates Thereof, and Pest Controllers and a Method for Using the Same. EP0735035A1, 2 October 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Osamus, S.; Masahiro, U.; Nobuyuki, N. Process for Producing Substituted Aminoquinazolinone Derivative, Intermediate Therefor, and Pest Control Agent. WO2004099184A1, 18 November 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.Z.; Ke, S.Y.; Kishore, B.; Xu, X.Y.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Li, Z. A facile synthesis of pyrimidone derivatives and single-crystal characterization of pymetrozine. Synth. Commun. 2012, 42, 2327–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Song, H.J.; Li, Y.Q.; Wang, Q.M. Design, synthesis, insecticidal activity, and structure-activity relationship (SAR): Studies of novel triazone derivatives containing a urea bridge group based on transient receptor potential (TRP) channels. Mol. Divers. 2016, 20, 919–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Song, H.J.; Li, Y.Q.; Wang, Q.M. Additive effects on the improvement of insecticidal activity: Design, synthesis, and insecticidal activity of novel pymetrozine derivatives. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Song, H.J.; Li, Y.Q.; Wang, Q.M. Design, synthesis, and insecticidal activity of novel triazone derivatives containing sulfonamide or sulfonimide moieties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 10790–10796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cui, P.P. Synthesis and insecticidal/fungicidal activities of triazone derivatives containing acylhydrazone moieties. Molecules 2025, 30, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uehara, M.; Shimizu, T.; Fujioka, S.; Kimura, M.; Seo, A. Synthesis and insecticidal activity of 3-aminoquinazolinone derivatives. Pestic. Sci. 1999, 55, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesterov, A.; Spalthoff, C.; Kandasamy, R.; Katana, R.; Rankl, N.B.; Andrés, M.; Jähde, P.; Dorsch, J.A.; Stam, L.F.; Braun, F.J.; et al. TRP channels in insect stretch receptors as insecticide targets. Neuron 2015, 86, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clapham, D.E. TRP channels as cellular sensors. Nature 2003, 426, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montell, C.; Birnbaumer, L.; Flockerzi, V. The TRP channels, a remarkably functional family. Cell 2002, 108, 595–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Hopkins, C.R. Review of transient receptor potential canonical (TRPC5) channel modulators and diseases. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 7589–7602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabnis, R.W. Novel pyridazinones as TRPC5 inhibitors for treating kidney diseases. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 526–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.; Bernstein, J.A.; Haar, L.; Luther, K.; Jones, W.K. Azelastine desensitization of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1: A potential mechanism explaining its therapeutic effect in nonallergic rhinitis. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2014, 28, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Ledeboer, M.W.; Daniels, M.; Malojcic, G.; Tibbitts, T.T.; Gal, M.C.L.; Pan-Zhou, X.R.; Westerling-Bui, A.; Beconi, M.; Reilly, J.F.; et al. Tetrahydrofuran-based transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 (TRPA1) antagonists: Ligand-based discovery, activity in a rodent asthma model, and mechanism-of-action via cryogenic Electron Microscopy. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 3843–3869. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, Z.; Fu, W.; Zhang, Y.C.; Chen, R.J.; Xu, Z.P.; Li, Z.; Shao, X.S. Azobenzene-semicarbazone enables optical control of insect sodium channels and behavior. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 15554–15561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.F.; Zuo, Y.; Yang, W.Y.; Liu, H.; Wu, Q.Y.; Yang, G.F. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of pyridazinone containing derivatives as novel protoporphyrinogen IX oxidase inhibitor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 10772–10780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.Z.; Wang, D.L.; Han, Y.; Wang, K.; Lei, P.; Ma, Z.Q.; Feng, J.T.; Liu, X.L.; Gao, Y.Q.; Wang, Y. Synthesis, antifungal activity, and potential mechanism of natural product pogostone derivatives containing an acylhydrazone scaffold. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 15491–15499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.; Peng, D.P.; Wu, J.E.; Wang, Y.L.; Yuan, Z.H. Development of an indirect competitive ELISA for the detection of furazolidone marker residue in animal edible tissues. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 1525–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.Y.; Zen, J.J.; Dai, W.; Zhang, C.N. Three chemosensory proteins contribute to chlorffuazuron tolerance in bradysia odoriphaga. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 16754–16765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, E.; Morali, G.; Galli, M.; Imbroglini, G.; Leake, C.R. Long-term degradation and potential plant uptake of diflufenicanunder field conditions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 4766–4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Du, X.W.; Zhang, A.; Bi, Q.J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.X. Synthesis and fungicidal activity of novel fungicide fluoxytioconazole. Agrochemicals 2024, 63, 717–722. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, W.S. A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 1987, 3, 302–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.J.; Liu, Y.X.; Xiong, L.X.; Li, Y.Q.; Yang, N.; Wang, Q.M. Design, synthesis, and insecticidal activity of novel pyrazole derivatives containing α-hydroxymethyl-N-benzyl carboxamide, α-chloromethyl-N-benzyl carboxamide, and 4,5-dihydrooxazole moieties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1470–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.Q.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhang, P.X.; Li, Y.Q.; Xiong, L.X.; Wang, Q.M. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of various α-substituted benzylpyrroles based on the structures of insecticidal chlorfenapyr and natural pyrrolomycins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 6072–6081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.; Chen, Y.L.; Shi, T.Z.; Wu, X.W.; Li, Q.X.; Hua, R.M. Synthesis and fungicidal activities of sanguinarine derivatives. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 147, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compound | 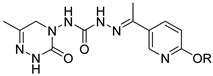 R | Mortality (%) at Concentration (mg/kg) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 600 | 100 | 10 | 5 | ||
| 3a | 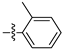 | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 | 40 ± 0 | - |
| 3b | 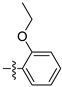 | 100 ± 0 | 90 ± 0 | 75 ± 2 | 10 ± 0 |
| 3c | 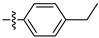 | 100 ± 0 | 95 ± 1 | 70± 0 | 10 ± 0 |
| 3d | 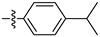 | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 | 80 ± 0 | 15 ± 1 |
| 3e |  | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 | 90 ± 0 | 35 ± 2 |
| 3f | 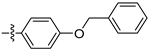 | 100 ± 0 | 90 ± 0 | 45 ± 2 | - |
| 3g | 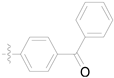 | 100 ± 0 | 85 ± 1 | 25 ± 2 | - |
| 3h | 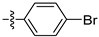 | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 | 70 ± 0 | 10 ± 0 |
| 3i | 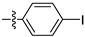 | 100 ± 0 | 95 ± 2 | 80 ± 0 | 20 ± 0 |
| 3j | 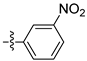 | 100 ± 0 | 80 ± 0 | 30 ± 0 | - |
| 3k | 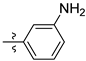 | 100 ± 0 | 90 ± 0 | 20 ± 0 | - |
| 3l | 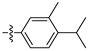 | 100 ± 0 | 95 ± 2 | 75 ± 1 | 10 ± 0 |
| 3m | 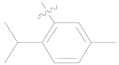 | 100 ± 0 | 85 ± 2 | 30 ± 0 | - |
| 3n | 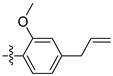 | 100 ± 0 | 80 ± 0 | 20 ± 0 | - |
| 3o | 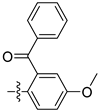 | 100 ± 0 | 90 ± 0 | 35 ± 2 | - |
| pymetrozine |  | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 | 90 ± 0 | 30 ± 0 |
| Compound | Correcting Mortality (%) at Concentration (mg/kg) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 0.5 | |
| 3a | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 | 40 ± 0 |
| 3b | 100 ± 0 | 40 ± 0 | - | - | - |
| 3c | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 | 60 ± 0 |
| 3d | 100 ± 0 | 20 ± 0 | - | - | - |
| 3e | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 | 60 ± 0 |
| 3f | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 | 60 ± 0 |
| 3g | 40 ± 0 | - | - | - | - |
| 3h | 20 ± 0 | - | - | - | - |
| 3i | 100 ± 0 | 30 ± 0 | - | - | - |
| 3j | 100 ± 0 | 30 ± 0 | - | - | - |
| 3k | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 | 60 ± 0 | - | - |
| 3l | 30 ± 0 | - | - | - | - |
| 3m | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 | 60 ± 0 | - | - |
| 3n | 100 ± 0 | 40 ± 0 | - | - | - |
| 3o | 70 ± 0 | - | - | - | - |
| pymetrozine | 100 ± 0 | 40 ± 0 | - | - | - |
| Compound | Correcting Mortality (%) at Concentration 600 mg/kg | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| H. armigera | O. ubilalis | M. eparata | |
| 3a | 45 ± 2 | 40 ± 0 | 65 ± 1 |
| 3b | 35 ± 1 | 30 ± 0 | 45 ± 2 |
| 3c | 0 | 0 | 5 ± 0 |
| 3d | 20 ± 0 | 10 ± 0 | 20 ± 0 |
| 3e | 15 ± 1 | 10 ± 0 | 20 ± 0 |
| 3f | 0 | 0 | 5 ± 0 |
| 3g | 10 ± 0 | 5 ± 1 | 20 ± 0 |
| 3h | 15 ± 1 | 10 ± 0 | 20 ± 0 |
| 3i | 40 ± 0 | 35 ± 2 | 65 ± 2 |
| 3j | 10 ± 0 | 5 ± 0 | 10 ± 0 |
| 3k | 40 ± 0 | 35 ± 2 | 50 ± 0 |
| 3l | 20 ± 0 | 15 ± 1 | 20 ± 0 |
| 3m | 30 ± 0 | 25 ± 2 | 45 ± 2 |
| 3n | 20 ± 0 | 15 ± 1 | 25 ± 0 |
| 3o | 40 ± 0 | 35 ± 2 | 65 ± 2 |
| pymetrozine | 20 ± 0 | 40 ± 0 | 50 ± 0 |
| Compound | Fungicidal Activity (%) a at 50 mg/kg | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AS b | FG | PI | PC | SS | BC | RS | FC | CH | PP | RC | BM | WA | FM | |
| 3a | 18.8 ± 0.6 | 38.5 ± 1.4 | 4.8 ± 2.2 | 24.1 ± 1.9 | 12.1 ± 0.7 | 18.4 ± 0.5 | 10.5 ± 1.8 | 60.0 ± 2.3 | 60.0 ± 0.7 | 80.3 ± 0.9 | 74.1 ± 2.0 | 50.0 ± 1.1 | 39.3 ± 0.9 | 46.7 ± 0.6 |
| 3b | 18.8 ± 1.3 | 57.7 ± 0.5 | 23.8 ± 1.4 | 31.0 ± 0.7 | 20.7 ± 1.3 | 10.5 ± 0.9 | 68.4 ± 1.5 | 52.5 ± 1.8 | 56.0 ± 0.9 | 82.0 ± 1.3 | 80.2 ± 2.6 | 60.0 ± 3.4 | 50.0 ± 1.6 | 63.3 ± 1.7 |
| 3c | 12.5 ± 2.5 | 38.5 ± 1.8 | 9.5 ± 1.9 | 31.0 ± 1.5 | 24.1 ± 1.7 | 13.2 ± 0.5 | 14.0 ± 0.7 | 37.5 ± 1.4 | 52.0 ± 2.1 | 72.1 ± 1.6 | 72.8 ± 2.4 | 47.5 ± 0.6 | 50.0 ± 0.9 | 60.0 ± 2.2 |
| 3d | 12.5 ± 0.8 | 46.2 ± 1.8 | 4.8 ± 1.2 | 27.6 ± 0.9 | 20.7 ± 0.7 | 10.5 ± 0.4 | 22.8 ± 0.5 | 67.5 ± 0.7 | 56.0 ± 0.9 | 73.8 ± 1.6 | 79.0 ± 2.1 | 57.5 ± 2.3 | 53.6 ± 0.9 | 50.0 ± 0.7 |
| 3e | 25.0 ± 1.2 | 11.5 ± 0.9 | 9.5 ± 0.7 | 17.2 ± 0.8 | 24.1 ± 1.3 | 26.3 ± 1.3 | 33.3 ± 1.8 | 47.5 ± 2.2 | 52.0 ± 2.1 | 82.0 ± 0.6 | 80.2 ± 1.2 | 57.5 ± 2.1 | 42.9 ± 1.5 | 60.0 ± 2.4 |
| 3f | 6.3 ± 0.9 | 19.2 ± 0.7 | 4.8 ± 2.1 | 24.1 ± 0.7 | 12.1 ± 0.8 | 10.5 ± 0.5 | 40.4 ± 0.8 | 40.0 ± 2.2 | 44.0 ± 2.6 | 73.8 ± 1.7 | 79.0 ± 1.5 | 60.0 ± 2.7 | 35.7 ± 1.1 | 33.3 ± 0.3 |
| 3g | 6.3 ± 1.1 | 11.5 ± 0.5 | 14.3 ± 0.7 | 10.3 ± 0.9 | 12.1 ± 0.3 | 7.9 ± 0.6 | 10.5 ± 2.6 | 57.5 ± 1.9 | 56.0 ± 0.6 | 83.6 ± 0.9 | 82.7 ± 1.3 | 50.0 ± 1.7 | 57.1 ± 2.1 | 66.7 ± 2.5 |
| 3h | 12.5 ± 1.4 | 30.8 ± 0.5 | 9.5 ± 0.5 | 31.0 ± 1.7 | 20.7 ± 0.7 | 18.4 ± 2.4 | 10.5 ± 1.6 | 35.0 ± 1.2 | 60.0 ± 1.5 | 80.3 ± 2.7 | 82.7 ± 1.9 | 55.0 ± 2.5 | 46.4 ± 1.5 | 50.0 ± 0.8 |
| 3i | 12.5 ± 0.8 | 46.2 ± 2.3 | 9.5 ± 0.9 | 34.5 ± 0.7 | 20.7 ± 1.3 | 10.5 ± 0.5 | 31.6 ± 0.8 | 45.0 ± 1.9 | 56.0 ± 2.5 | 85.2 ± 1.7 | 80.2 ± 2.1 | 62.5 ± 1.2 | 50.0 ± 0.7 | 46.7 ± 0.9 |
| 3j | 12.5 ± 0.8 | 23.1 ± 0.7 | 4.8 ± 0.5 | 6.9 ± 0.9 | 20.7 ± 1.4 | 10.5 ± 1.8 | 14.0 ± 0.5 | 37.5 ± 1.8 | 40.0 ± 0.9 | 55.7 ± 1.4 | 59.3 ± 1.3 | 40.0 ± 1.5 | 35.7 ± 2.2 | 53.3 ± 1.1 |
| 3k | 6.3 ± 0.5 | 19.2 ± 1.4 | 9.5 ± 0.8 | 17.2 ± 0.9 | 15.5 ± 0.7 | 10.5 ± 1.2 | 19.3 ± 0.7 | 35.0 ± 1.5 | 52.0 ± 1.8 | 78.7 ± 2.1 | 77.8 ± 2.6 | 50.0 ± 0.6 | 50.0 ± 1.7 | 56.7 ± 1.3 |
| 3l | 6.3 ± 0.8 | 50.0 ± 3.0 | 4.8 ± 0.5 | 17.2 ± 0.9 | 20.7 ± 0.3 | 18.4 ± 0.5 | 14.0 ± 0.9 | 72.5 ± 3.2 | 36.0 ± 1.2 | 78.7 ± 2.7 | 80.2 ± 1.9 | 47.5 ± 1.5 | 50.0 ± 0.3 | 30.0 ± 0.9 |
| 3m | 12.5 ± 0.5 | 30.8 ± 0.4 | 4.8 ± 0.3 | 20.7 ± 0.7 | 24.1 ± 0.9 | 10.5 ± 1.2 | 36.8 ± 1.0 | 47.5 ± 1.8 | 64.0 ± 3.3 | 77.0 ± 2.4 | 76.5 ± 2.0 | 55.0 ± 1.4 | 53.6 ± 1.6 | 63.3 ± 1.5 |
| 3n | 12.5 ± 0.8 | 46.2 ± 0.7 | 14.3 ± 0.6 | 37.9 ± 0.8 | 20.7 ± 1.6 | 28.9 ± 1.7 | 14.0 ± 0.9 | 47.5 ± 1.2 | 60.0 ± 2.1 | 82.0 ± 0.6 | 80.2 ± 1.8 | 52.5 ± 2.2 | 57.1 ± 0.9 | 70.0 ± 1.3 |
| 3o | 12.5 ± 0.7 | 50.0 ± 1.5 | 23.8 ± 1.0 | 27.6 ± 0.6 | 29.3 ± 0.9 | 10.5 ± 0.6 | 19.3 ± 1.3 | 42.5 ± 1.0 | 52.0 ± 2.3 | 63.9 ± 2.1 | 55.6 ± 2.5 | 35.0 ± 1.3 | 42.9 ± 2.2 | 46.7 ± 1.2 |
| Carbendazim c | <50 | 100 ± 0.0 | 100 ± 0.0 | <50 | 100 ± 0.0 | <50 | 100 ± 0.0 | <50 | <50 | <50 | 100 ± 0.0 | 100 ± 0.0 | 100 ± 0.0 | <50 |
| chlorothalonil c | 73 ± 1 | <50 | 86 ± 1 | 100 ± 0.0 | <50 | 100 ± 0.0 | 100 ± 0.0 | 100 ± 0.0 | 73 ± 1 | 100 ± 0.0 | 100 ± 0.0 | 91 ± 1 | 91 ± 1 | 100 ± 0.0 |
| Compounds | Acut Tox. Pred. (mg/kg) a | Mutigenic Tox. Pred. | Carcinogenic Tox. Pred. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3a | 75 | negative | negative |
| 3b | 1000 | negative | negative |
| 3c | 75 | negative | positive |
| 3d | 75 | negative | positive |
| 3e | 75 | negative | negative |
| 3f | 75 | negative | positive |
| 3g | 1000 | negative | positive |
| 3h | 75 | negative | negative |
| 3i | 75 | negative | negative |
| 3j | 1000 | positive | positive |
| 3k | 1000 | positive | positive |
| 3l | 200 | negative | negative |
| 3m | 75 | negative | negative |
| 3n | 200 | negative | positive |
| 3o | 75 | negative | negative |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Cui, P.; Yang, Y. Discovery of Triazone Derivatives Containing Acylhydrazone and Phenoxypyridine Motifs as Novel Insecticidal and Antiphytopathogenic Fungus Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2026, 27, 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010260
Cui P, Yang Y. Discovery of Triazone Derivatives Containing Acylhydrazone and Phenoxypyridine Motifs as Novel Insecticidal and Antiphytopathogenic Fungus Agents. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2026; 27(1):260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010260
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Peipei, and Yan Yang. 2026. "Discovery of Triazone Derivatives Containing Acylhydrazone and Phenoxypyridine Motifs as Novel Insecticidal and Antiphytopathogenic Fungus Agents" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 27, no. 1: 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010260
APA StyleCui, P., & Yang, Y. (2026). Discovery of Triazone Derivatives Containing Acylhydrazone and Phenoxypyridine Motifs as Novel Insecticidal and Antiphytopathogenic Fungus Agents. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 27(1), 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010260





