AI/ML-Assisted Detection of HMGA2 RNA Isoforms in Prostate Cancer Patient Tissue
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
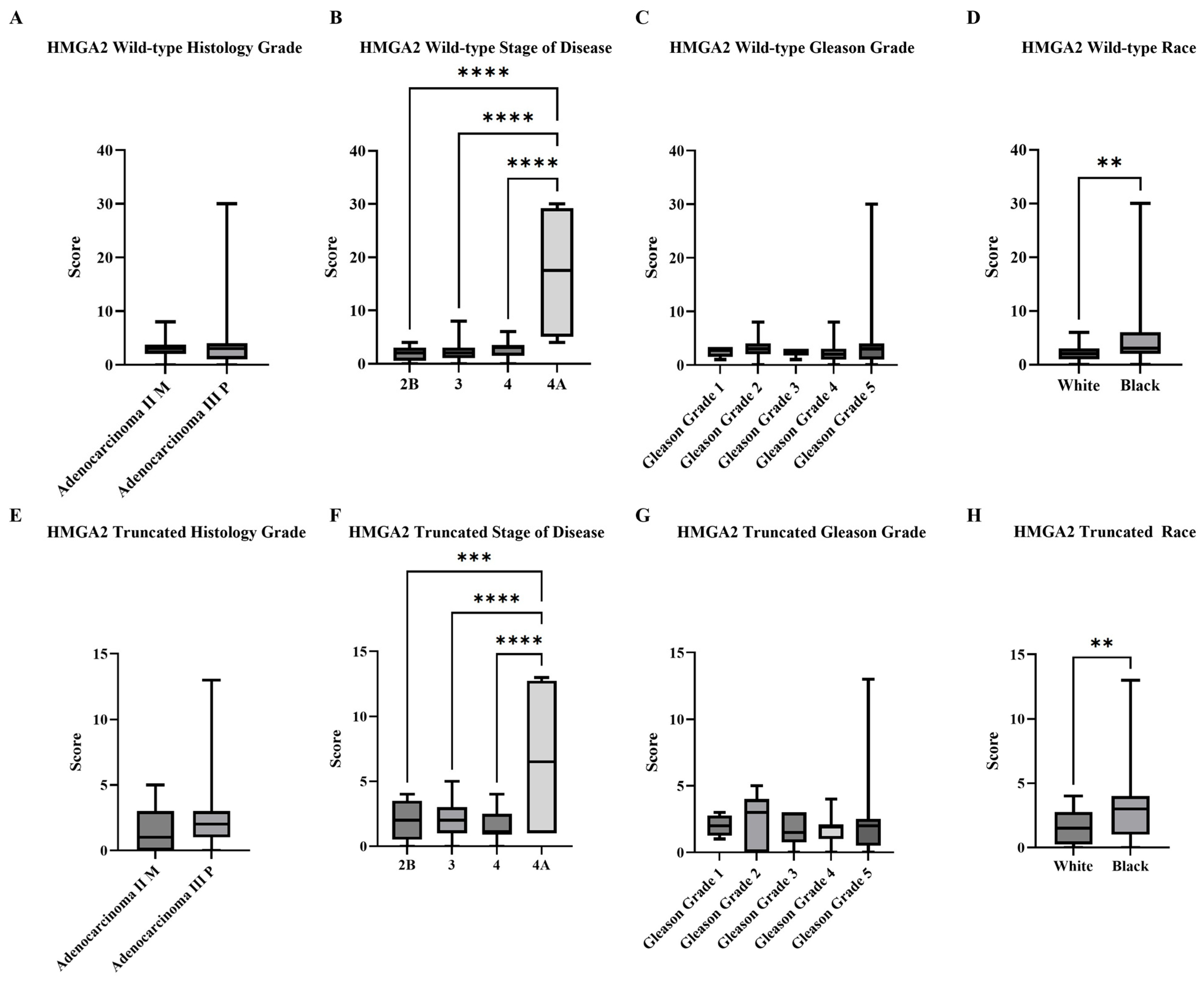
2.1. RISH Staining of a Cohort of PCa Patient Tissue and Subjective Analysis of HMGA2 Isoform
2.2. Numerical Results of AI/ML Training/Validation Model
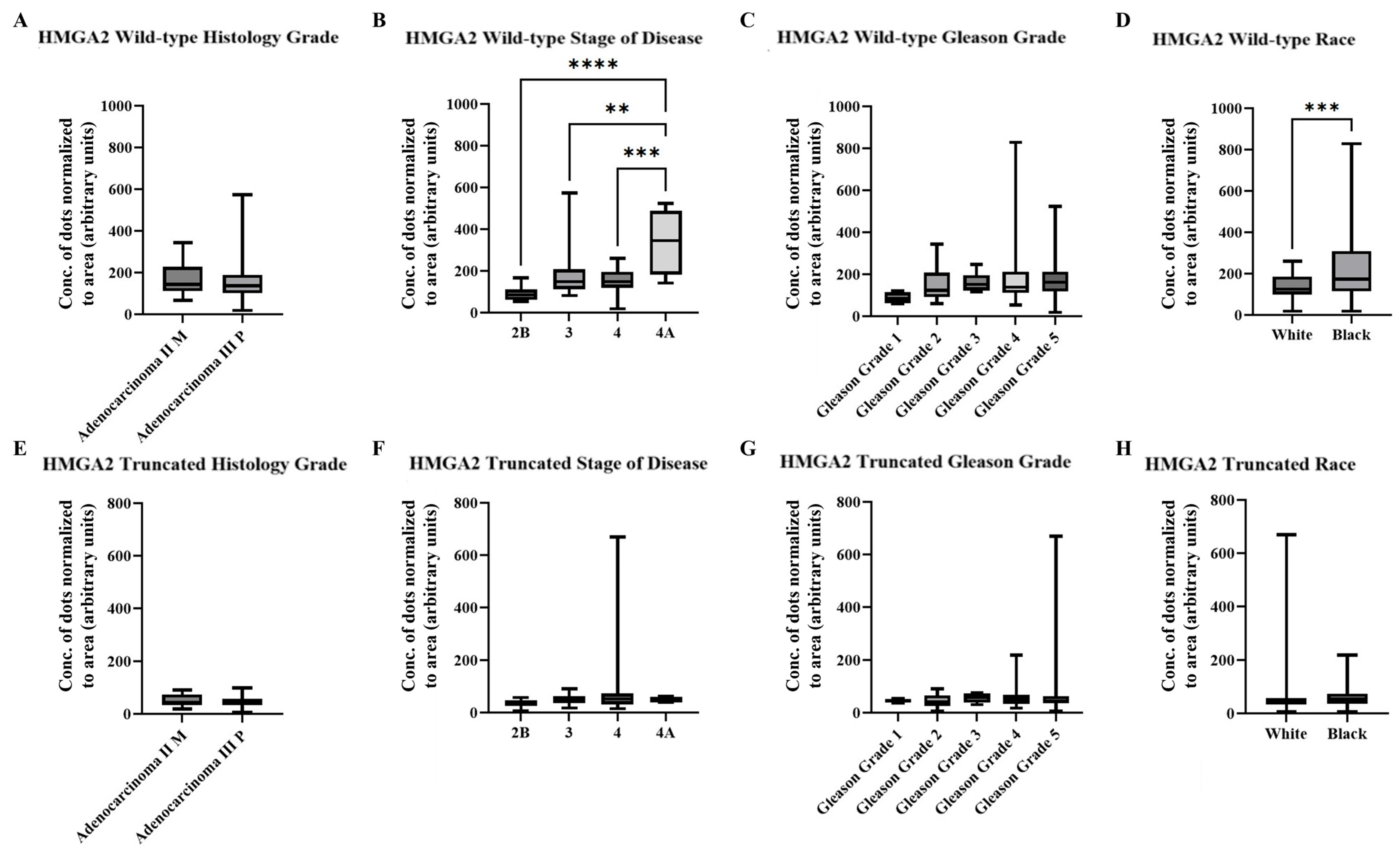
2.3. AI/ML Objective Analysis of HMGA2 Isoforms in a Cohort of PCa Patient Tissue
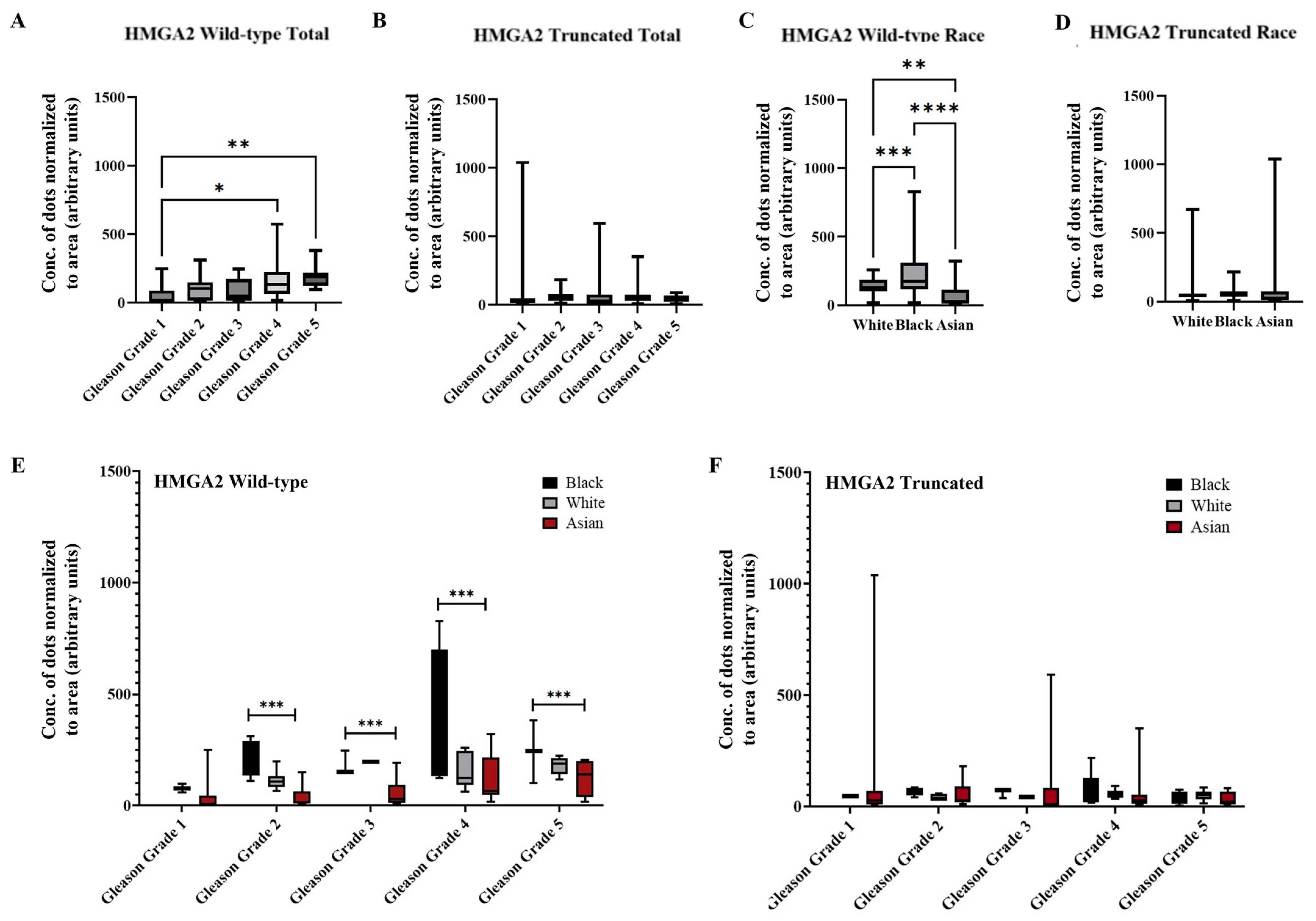
2.4. AI/ML Objective Analysis of HMGA2 Isoforms in a Larger Cohort of PCa Patient Tissue
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Cohort and Sample Collection
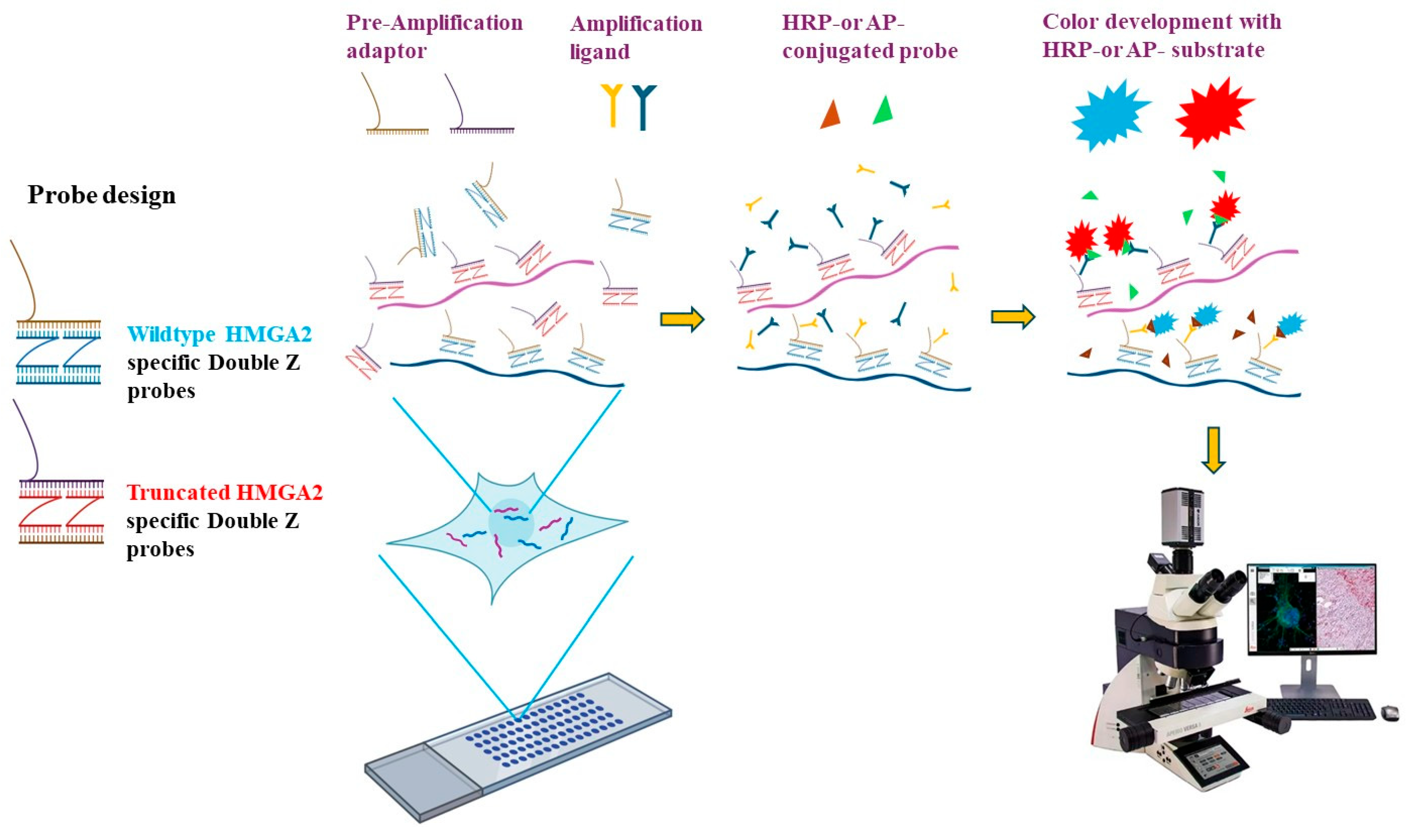
4.2. RNA In Situ Hybridization (RISH) Probe Design
4.3. RISH Assay
4.4. RISH Analysis Using Subjective Scoring Methods
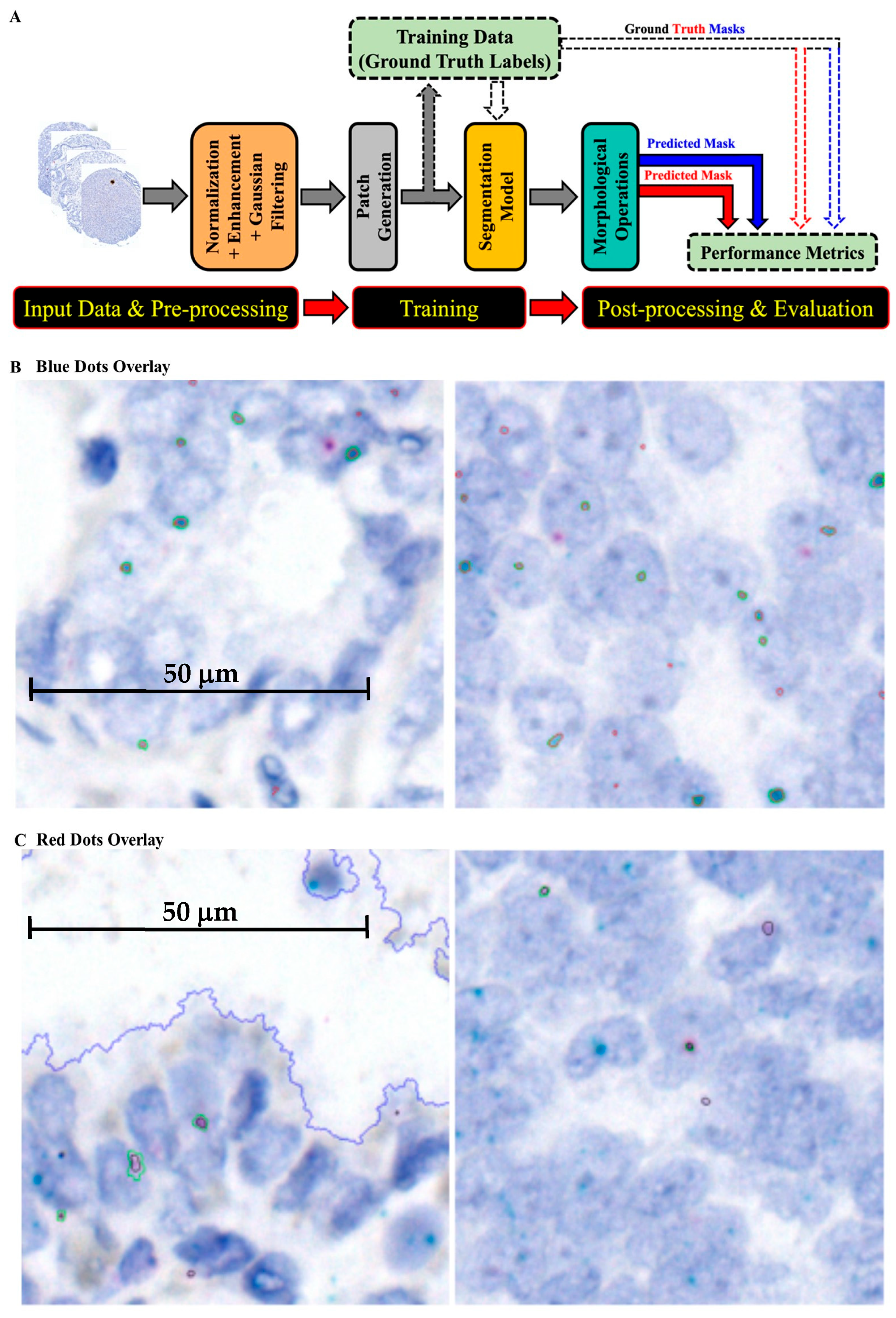
4.5. AI/ML Pipeline for RISH Analysis
4.6. Preprocessing Stage
4.7. Model Training and Experimental Settings
4.8. Post-Processing and Evaluation
- ▪
- Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC): Measures the overlap between the model’s predictions and the ground truth labels.
- ▪
- Intersection over Union (IoU): Assesses the agreement between predicted and actual RNA dots.
- ▪
- Precision and Recall: Evaluate how many RNA dots were correctly identified versus those missed (false negatives) or incorrectly marked (false positives).
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | artificial intelligence |
| AI/ML | artificial intelligence and machine learning |
| ANOVA | analysis of variance |
| AP | alkaline phosphatase |
| AR | androgen receptor |
| CEAMLS | Center for Equitable AI and Machine Learning Systems |
| CLAHE | contrast-limited adaptive histogram equal ization |
| CNNs | convolutional neural networks |
| DSC | dice similarity coefficient |
| DL | deep learning |
| EMT | epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| FFPE | formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded |
| HMGA2 | High Mobility Group AT-Hook 2 |
| HMGA2-WT | High Mobility Group AT-Hook 2-wild-type |
| HMGA2-TR | High Mobility Group AT-Hook 2-truncated |
| HRP | horseradish peroxidase |
| IOU | Intersection over Union |
| L-3′UTR | long 3′ untranslated region |
| ML | machine learning |
| PCa | prostate cancer |
| ReLU | rectified linear unit |
| RISH | RNA in situ hybridization |
| RT-PCR | reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction |
| S-3′UTR | short 3′untranslated region |
| TMAs | tissue microarrays |
| UTR | 3′ untranslated region |
References
- American Cancer Society. Key Statistics for Prostate Cancer. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/prostate-cancer/about/key-statistics.html (accessed on 11 December 2025).
- Lowder, D.; Rizwan, K.; McColl, C.; Paparella, A.; Ittmann, M.; Mitsiades, N.; Kaochar, S. Racial disparities in prostate cancer: A complex interplay between socioeconomic inequities and genomics. Cancer Lett. 2022, 531, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.-P.; Zhang, H.; Jiao, J.-Y.; Tang, D.-X.; Wu, Y.-l.; Pan, C.-B. Overexpression of HMGA2 promotes tongue cancer metastasis through EMT pathway. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.; Chang, T.-M.; Yeh, S.; Ma, W.-L.; Wang, Y.Z.; Chang, C. Differential androgen receptor signals in different cells explain why androgen-deprivation therapy of prostate cancer fails. Oncogene 2010, 29, 3593–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawsawi, O.; Henderson, V.; Burton, L.J.; Dougan, J.; Nagappan, P.; Odero-Marah, V. High mobility group A2 (HMGA2) promotes EMT via MAPK pathway in prostate cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 504, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Shen, G.; Liu, S.; Meng, Q. Downregulation of HMGA2 inhibits cellular proliferation and invasion, improves cellular apoptosis in prostate cancer. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dike, P.E.; Hwang, B.-J.; Campbell, T.; Awolowo, M.; Elliott, B.; Odero-Marah, V. HMGA2 regulates GPX4 expression and ferroptosis in prostate cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2024, 736, 150859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liadi, Y.M.; Campbell, T.; Hwang, B.-J.; Elliott, B.; Odero-Marah, V. High Mobility Group AT-hook 2: A Biomarker Associated with Resistance to Enzalutamide in Prostate Cancer Cells. Cancers 2024, 16, 2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriksen, J.; Stabell, M.; Meza-Zepeda, L.A.; Lauvrak, S.A.; Kassem, M.; Myklebost, O. Identification of target genes for wild type and truncated HMGA2 in mesenchymal stem-like cells. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, T.; Hawsawi, O.; Henderson, V.; Dike, P.; Hwang, B.-J.; Liadi, Y.; White, E.Z.; Zou, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Novel roles for HMGA2 isoforms in regulating oxidative stress and sensitizing to RSL3-Induced ferroptosis in prostate cancer cells. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, A.; Jones, J. Developments in in situ hybridisation. Methods 2014, 70, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Flanagan, J.; Su, N.; Wang, L.-C.; Bui, S.; Nielson, A.; Wu, X.; Vo, H.-T.; Ma, X.-J.; Luo, Y. RNAscope: A novel in situ RNA analysis platform for formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues. J. Mol. Diagn. 2012, 14, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooper, L.M.; Gandhi, M.; Bishop, J.A.; Westra, W.H. RNA in-situ hybridization is a practical and effective method for determining HPV status of oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma including discordant cases that are p16 positive by immunohistochemistry but HPV negative by DNA in-situ hybridization. Oral Oncol. 2016, 55, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R, A.B.; Pulari, S.R.; Murugesh, T.S.; Vasudevan, S.K. Machine Learning: A Comprehensive Beginner’s Guide; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; p. 258. [Google Scholar]
- Laubscher, E.; Wang, X.; Razin, N.; Dougherty, T.; Xu, R.J.; Ombelets, L.; Pao, E.; Graf, W.; Moffitt, J.R.; Yue, Y.; et al. Accurate single-molecule spot detection for image-based spatial transcriptomics with weakly supervised deep learning. Cell Syst. 2024, 15, 475–482.e476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouilhol, E.; Savulescu, A.F.; Lefevre, E.; Dartigues, B.; Brackin, R.; Nikolski, M. DeepSpot: A deep neural network for RNA spot enhancement in single-molecule fluorescence in-situ hybridization microscopy images. Biol. Imaging 2022, 2, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.J.; Cahill, R.; Abbasi-Asl, R. Machine Learning for Uncovering Biological Insights in Spatial Transcriptomics Data. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.16725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojewski, A.; Schweiger, M.; Kruithoff, R.; Shepherd, D.P.; Pressé, S. Advancing RNA FISH image analysis with 3D deep learning. Biophys. J. 2024, 123, 552a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Wan, X.; Xiao, J.; Yang, C. UCS: A unified approach to cell segmentation for subcellular spatial transcriptomics. Small Methods 2025, 9, 2400975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilesanmi, A.E.; Ilesanmi, T.O.; Ajayi, B.O. Reviewing 3D convolutional neural network approaches for medical image segmentation. Heliyon 2024, 10, e27398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauke, S.; Leopold, S.; Schlueter, C.; Flohr, A.M.; Murua Escobar, H.; Rogalla, P.; Bullerdiek, J. Extensive expression studies revealed a complex alternative splicing pattern of the HMGA2 gene. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1729, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Ha, S.; Jung, C.K.; Lee, H.H. High-mobility-group A2 overexpression provokes a poor prognosis of gastric cancer through the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 2431–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Qin, J.; Song, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Guo, H.; Shao, C.; et al. Splicing factor USP39 promotes ovarian cancer malignancy through maintaining efficient splicing of oncogenic HMGA2. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebratie, D.Y.; Dagnaw, G.G. Review of immunohistochemistry techniques: Applications, current status, and future perspectives. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2024, 41, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonner, M.A.; Morales-Hernandez, A.; Zhou, S.; Ma, Z.; Condori, J.; Wang, Y.D.; Fatima, S.; Palmer, L.E.; Janke, L.J.; Fowler, S.; et al. 3′ UTR-truncated HMGA2 overexpression induces non-malignant in vivo expansion of hematopoietic stem cells in non-human primates. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2021, 21, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, U.; Weigert, M.; Broaddus, C.; Myers, G. Cell Detection with Star-Convex Polygons; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 265–273. [Google Scholar]
- He, D.; Xie, L. A cross-level information transmission network for hierarchical omics data integration and phenotype prediction from a new genotype. Bioinformatics 2021, 38, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Garcia-Seisdedos, D.; Prakash, A.; Kundu, D.J.; Collins, A.; George, N.; Fexova, S.; Moreno, P.; Papatheodorou, I.; Jones, A.R.; et al. Integrated view and comparative analysis of baseline protein expression in mouse and rat tissues. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2022, 18, e1010174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, D.; Hou, W.; Zhou, T.; Ji, Z. GeneSegNet: A deep learning framework for cell segmentation by integrating gene expression and imaging. Genome Biol. 2023, 24, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debesh, J.; Michael, R.; Dag, J.; Pål, H.; Håvard, D.J. DoubleU-Net: A Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.04868. [Google Scholar]

| TMA Spot | Case ID * | Specimen ID | Race | Disease Stage | Metastatic | Year | Histology Grade | Gleason Pattern | Subjective Scoring HMGA2 WT (1–40) | Subjective Scoring HMGA2 TR (1–40) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pos Ctrl | 21-4309 | 17 | 26 | |||||||
| Pos Ctrl | 21-4310 | 4 | 4 | |||||||
| Pos Ctrl | 21-4312 | 30 | 30 | |||||||
| Pos Ctrl | 21-4316 | 40 | 40 | |||||||
| B2 | 40 | 1012050 | White | 2B | Non-Meta | 2011 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 034 | 4 | 4 |
| B5 | 41 | 1012216 | White | 2B | Non-Meta | 2011 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 033 | 3 | 3 |
| B6 | 42 | 1012220 | White | 2B | Non-Meta | 2011 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 034 | 2 | 4 |
| B9 | 43 | 1012335 | White | 2B | Non-Meta | 2011 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 034 | 3 | 3 |
| B10 | 44 | 1012402 | White | 2B | Non-Meta | 2011 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 034 | 2 | 4 |
| C6 | 47 | 1013484 | White | 4 | 2012 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 045 | 5 | 4 | |
| C9 | 48 | 1014164 | Black | 3 | Non-Meta | 2013 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 044 | 4 | 4 |
| D2 | 50 | 1015479 | Black | 3 | 2014 | Adenocarcinoma II M | 034 | 6 | 3 | |
| D5 | 51 | 1015775 | Black | 3 | 2014 | Adenocarcinoma | 034 | 3 | 3 | |
| D6 | 52 | 1015805 | Black | 3 | Non-Meta | 2014 | Adenocarcinoma II M | 034 | 8 | 5 |
| D8 | 53 | 1015945 | Black | 3 | 2014 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 044 | 3 | 3 | |
| D10 | 54 | 1017035 | White | 4 | 2015 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 044 | 4 | 1 | |
| E5 | 56 | 1017270 | White | 4 | 2015 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 044 | 5 | 3 | |
| E6 | 57 | 1017534 | White | 4 | 2015 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 044 | 3 | 3 | |
| E9 | 58 | 1017541 | Black | 3 | Non-Meta | 2015 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 043 | 3 | 3 |
| F5 | 61 | 1017903 | White | 4 | 2016 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 034 | 3 | 3 | |
| G3 | 65 | 1019042 | White | 4 | 2017 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 054 | 4 | 2 | |
| G4 | 66 | 1019132 | White | 4 | C0 | 2017 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 045 | 3 | 3 |
| H2 | 70 | 1019428 | White | 4 | 2017 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 054 | 6 | 2 | |
| H6 | 72 | 1019693 | White | 3 | c0 | 2017 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 045 | 4 | 2 |
| I3 | 75 | 1020025 | White | 4 | c1B | 2017 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 045 | 4 | 1 |
| I6 | 77 | 1020766 | Black | 4A | p1 | 2018 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 045 | 30 | 13 |
| I9 | 78 | 1022418 | Black | 4A | p1 | 2020 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 053 | 7 | 1 |
| TMA Spot | Case ID * | Specimen ID | Race | Stage | Metastatic | Year | Histology Grade | Gleason Pattern | Wild-Type HMGA2 | Truncated HMGA2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B3 | 40 | 1012050 | White | 2B | Non-Meta | 2011 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 034 | 166.64 | 40.25 |
| B4 | 41 | 1012216 | White | 2B | Non-Meta | 2011 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 033 | 57.64 | 46.17 |
| B7 | 42 | 1012220 | White | 2B | Non-Meta | 2011 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 034 | 125.79 | 18.90 |
| B9 | 43 | 1012335 | White | 2B | Non-Meta | 2011 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 034 | 84.87 | 41.67 |
| B10 | 44 | 1012402 | White | 2B | Non-Meta | 2011 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 034 | 101.82 | 57.47 |
| C2 | 45 | 1012441 | White | 2B | Non-Meta | 2011 | Adenocarcinoma II M | 033 | 97.59 | 44.32 |
| C5 | 46 | 1012914 | White | 2B | Non-Meta | 2011 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 044 | 61.33 | 40.12 |
| C8 | 48 | 1014164 | Black | 3 | Non-Meta | 2013 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 044 | 125.15 | 17.73 |
| C10 | 49 | 1014392 | Black | 3 | 2013 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 045 | 100.00 | 36.82 | |
| D3 | 50 | 1015479 | Black | 3 | 2014 | Adenocarcinoma II M | 034 | 236.45 | 65.45 | |
| D6 | 52 | 1015805 | Black | 3 | Non-Meta | 2014 | Adenocarcinoma II M | 034 | 310.18 | 85.89 |
| D8 | 53 | 1015945 | Black | 3 | 2014 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 044 | 572.71 | 29.49 | |
| E8 | 58 | 1017541 | Black | 3 | Non-Meta | 2015 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 043 | 148.25 | 73.65 |
| F2 | 60 | 1017845 | Black | 3 | Non-Meta | 2016 | Adenocarcinoma II M | 043 | 151.03 | 38.03 |
| F6 | 62 | 1018076 | Black | 3 | Non-Meta | 2016 | Adenocarcinoma II M | 034 | 111.02 | 76.47 |
| F10 | 64 | 1018715 | White | 3 | C0 | 2016 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 055 | 161.40 | 56.31 |
| G9 | 68 | 1019179 | White | 3 | c0 | 2017 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 044 | 116.58 | 57.76 |
| G10 | 69 | 1019424 | White | 3 | c0 | 2017 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 044 | 150.33 | 33.24 |
| H4 | 71 | 1019525 | White | 3 | c0 | 2017 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 045 | 123.62 | 36.36 |
| H6 | 72 | 1019693 | White | 3 | c0 | 2017 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 045 | 215.96 | 51.40 |
| H11 | 74 | 1019931 | White | 3 | c0 | 2017 | Adenocarcinoma II M | 034 | 135.55 | 31.80 |
| C6 | 47 | 1013484 | White | 4 | 2012 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 045 | 190.05 | 54.83 | |
| D11 | 54 | 1017035 | White | 4 | 2015 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 044 | 148.89 | 48.22 | |
| E2 | 55 | 1017126 | White | 4 | 2015 | Adenocarcinoma II M | 034 | 111.47 | 44.46 | |
| E4 | 56 | 1017270 | White | 4 | 2015 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 044 | 245.57 | 71.05 | |
| E6 | 57 | 1017534 | White | 4 | 2015 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 044 | 259.68 | 91.99 | |
| E11 | 59 | 1017573 | White | 4 | 2015 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 044 | 120.11 | 26.39 | |
| F4 | 61 | 1017903 | White | 4 | 2016 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 034 | 197.77 | 58.38 | |
| F8 | 63 | 1018329 | White | 4 | p1A | 2016 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 045 | 118.17 | 78.32 |
| G2 | 65 | 1019042 | White | 4 | 2017 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 054 | 193.60 | 40.00 | |
| G4 | 66 | 1019132 | White | 4 | C0 | 2017 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 045 | 212.07 | 87.14 |
| G6 | 67 | 1019161 | White | 4 | 2017 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 044 | 122.64 | 70.32 | |
| H3 | 70 | 1019428 | White | 4 | 2017 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 054 | 257.86 | 63.63 | |
| H8 | 73 | 1019800 | White | 4 | 2017 | Adenocarcinoma II M | 043 | 195.24 | 42.96 | |
| I2 | 75 | 1020025 | White | 4 | c1B | 2017 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 045 | 188.67 | 14.54 |
| I4 | 76 | 1020541 | Black | 4 | p1 | 2018 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 053 | 179.88 | 20.00 |
| I6 | 77 | 1020766 | Black | 4A | p1 | 2018 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 045 | 523.59 | 62.86 |
| I9 | 78 | 1022418 | Black | 4A | p1 | 2020 | Adenocarcinoma III P | 053 | 307.92 | 52.06 |
| No. | Age | PSA | Year of Diagnosis | Gleason Score | MRI | Bone Scan | Blue Spots HMGA2 WT | Red Spots HMGA2 TR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 64 | 41 | 2022 | 5 + 4 | Negative | Negative | 19.15 | 5.245 |
| 3 | 63 | 80 | 2022 | 4 + 3 | Positive | Not done | 246.1603448 | 74.11603448 |
| 20 | 73 | 193 | 2021 | 4 + 4 | Not done | Not done | 829.0873913 | 218.5 |
| Method | Method | Accuracy/Performance | Computational Complexity | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| StarDist [26] | CNN object detection | Very high for well-separated RNA dots, Average precision 86.41% | Fast inference; lightweight | Fails on tiny granular ISH dots; shape-biased |
| DeepSpot [27] | CNN enhancement → thresholding | Improves spot SNR by ~30%. Pearson 76.40% | Lightweight | Not a full segmentation model |
| SpotLearn [28] | CNN dot detection | High accuracy in dense tissues | Medium | Needs large annotated data |
| Proposed | U-Net segmentation of RNA dots | High accuracy is detecting RNA dots. DC 99.2% and 99.0% for blue and red dots simultaneously. | Medium | manual annotation for ground truth and external validation is required |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Hwang, B.-J.; Akinniyi, O.; Harrison, S.; Gibbs, D.; Waihenya, C.; Gachii, A.; Dike, P.E.; Elliott, B.; Khalifa, F.; Ragin, C.; et al. AI/ML-Assisted Detection of HMGA2 RNA Isoforms in Prostate Cancer Patient Tissue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2026, 27, 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010196
Hwang B-J, Akinniyi O, Harrison S, Gibbs D, Waihenya C, Gachii A, Dike PE, Elliott B, Khalifa F, Ragin C, et al. AI/ML-Assisted Detection of HMGA2 RNA Isoforms in Prostate Cancer Patient Tissue. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2026; 27(1):196. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010196
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Bor-Jang, Oluwatunmise Akinniyi, Sharon Harrison, Denise Gibbs, Charles Waihenya, Andrew Gachii, Precious E. Dike, Bethtrice Elliott, Fahmi Khalifa, Camille Ragin, and et al. 2026. "AI/ML-Assisted Detection of HMGA2 RNA Isoforms in Prostate Cancer Patient Tissue" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 27, no. 1: 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010196
APA StyleHwang, B.-J., Akinniyi, O., Harrison, S., Gibbs, D., Waihenya, C., Gachii, A., Dike, P. E., Elliott, B., Khalifa, F., Ragin, C., & Odero-Marah, V. (2026). AI/ML-Assisted Detection of HMGA2 RNA Isoforms in Prostate Cancer Patient Tissue. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 27(1), 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010196







