Integrated Analysis of Disulfidptosis-Related Genes Identifies CD2AP as a Potential Therapeutic Target for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
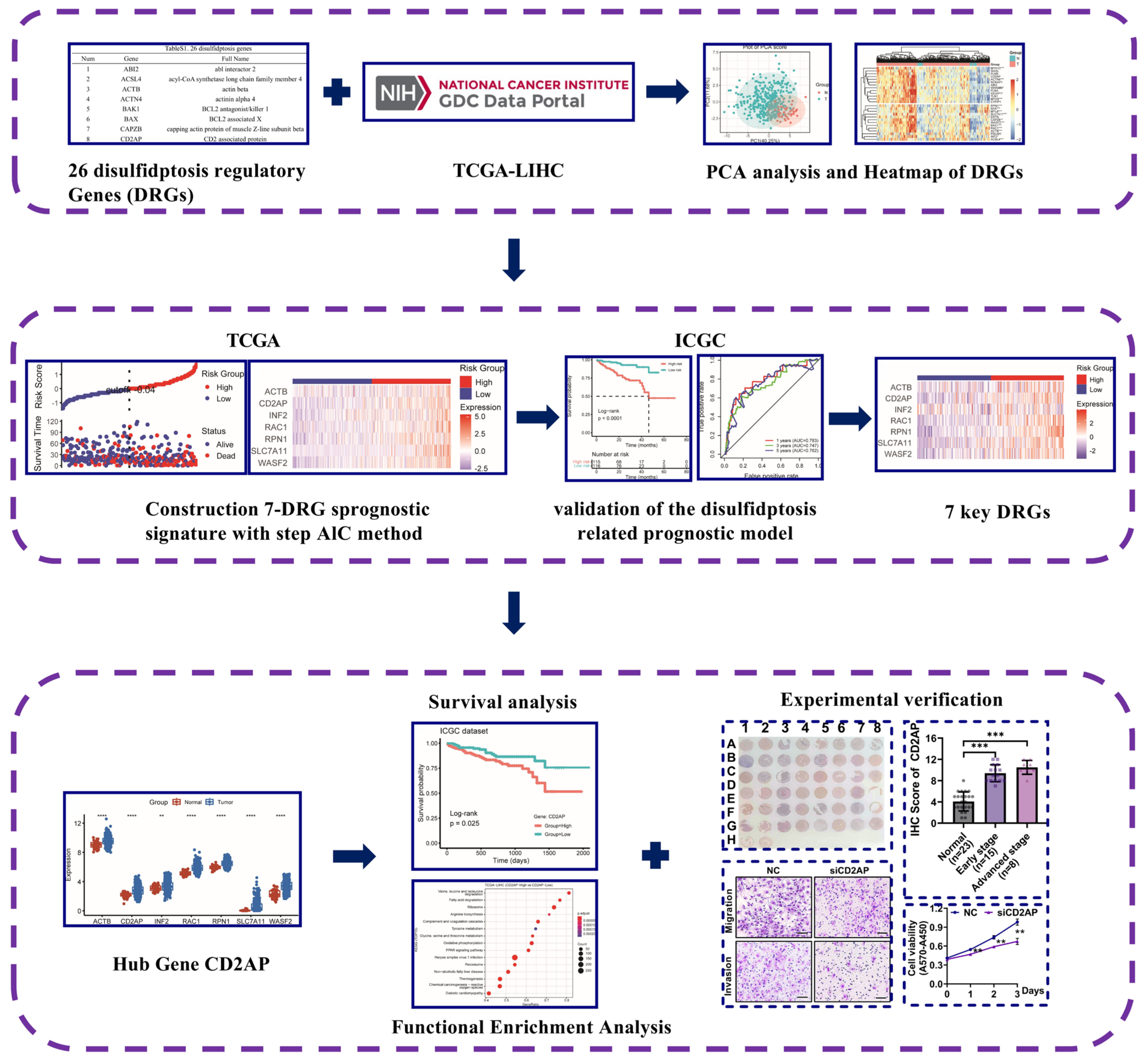
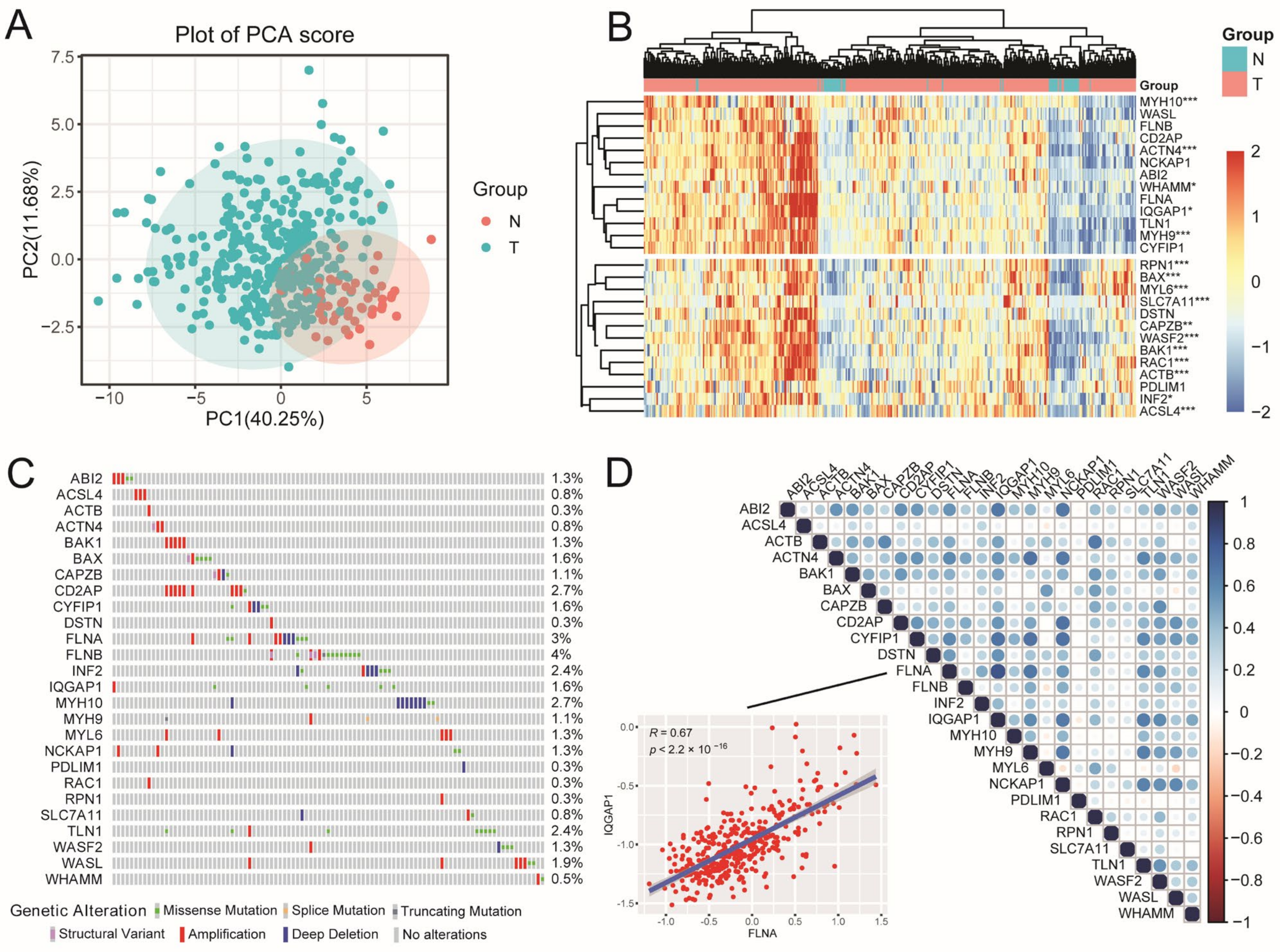
2.1. The Landscape of DRGs in HCC
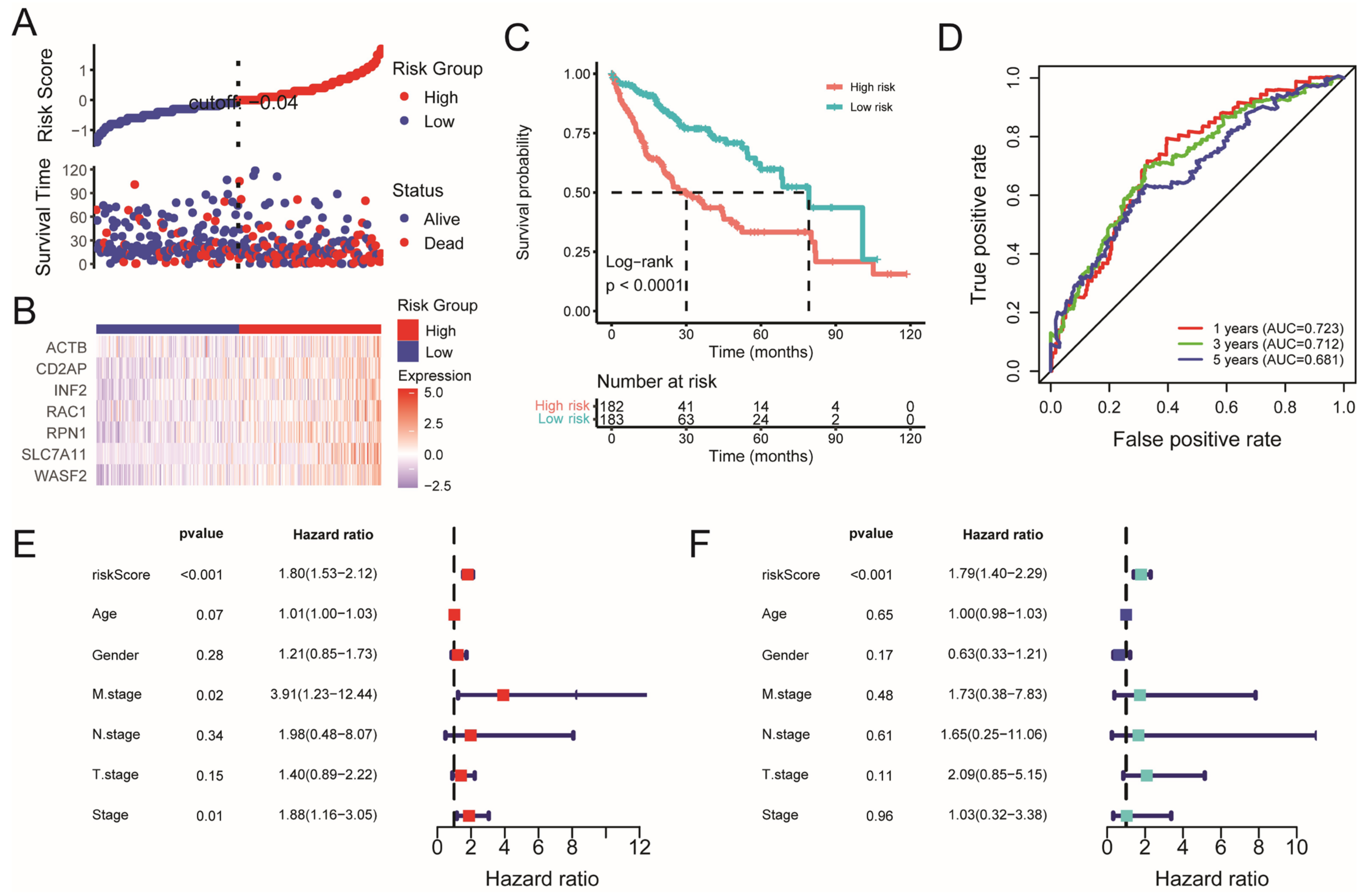
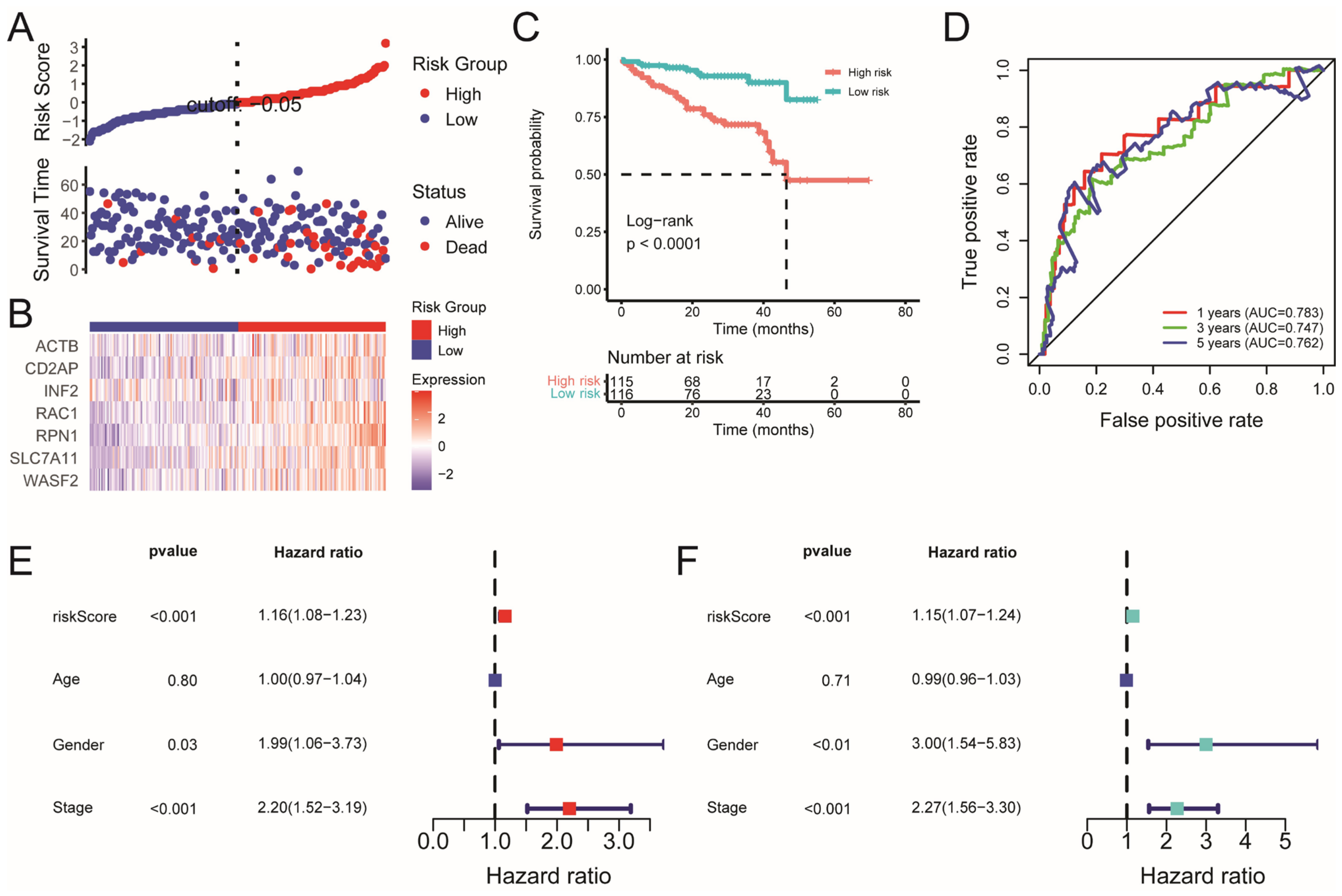
2.2. Construction and Validation of the Disulfidptosis-Related Prognostic Model
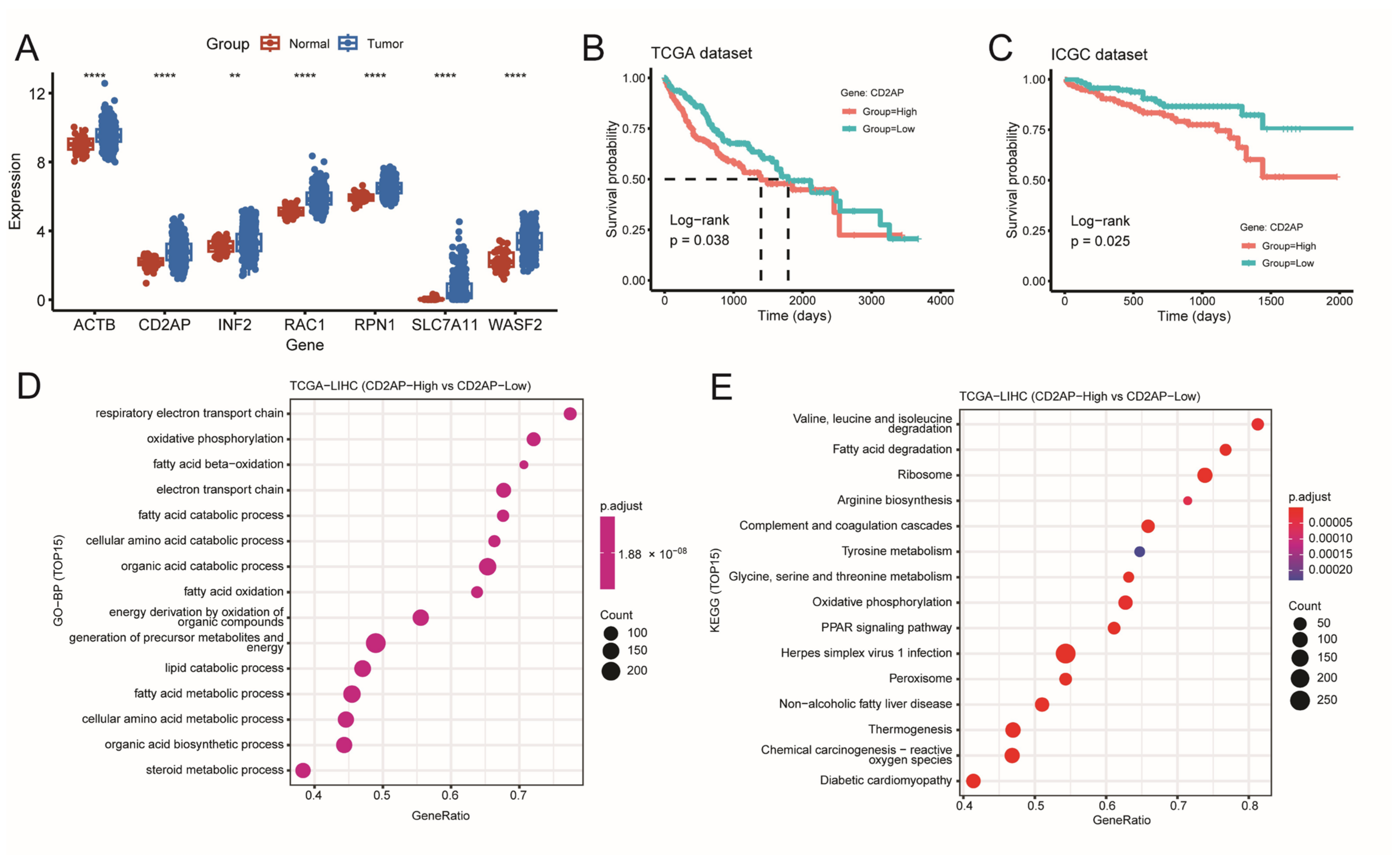
2.3. Identifying CD2AP as a New Hub DRG for HCC
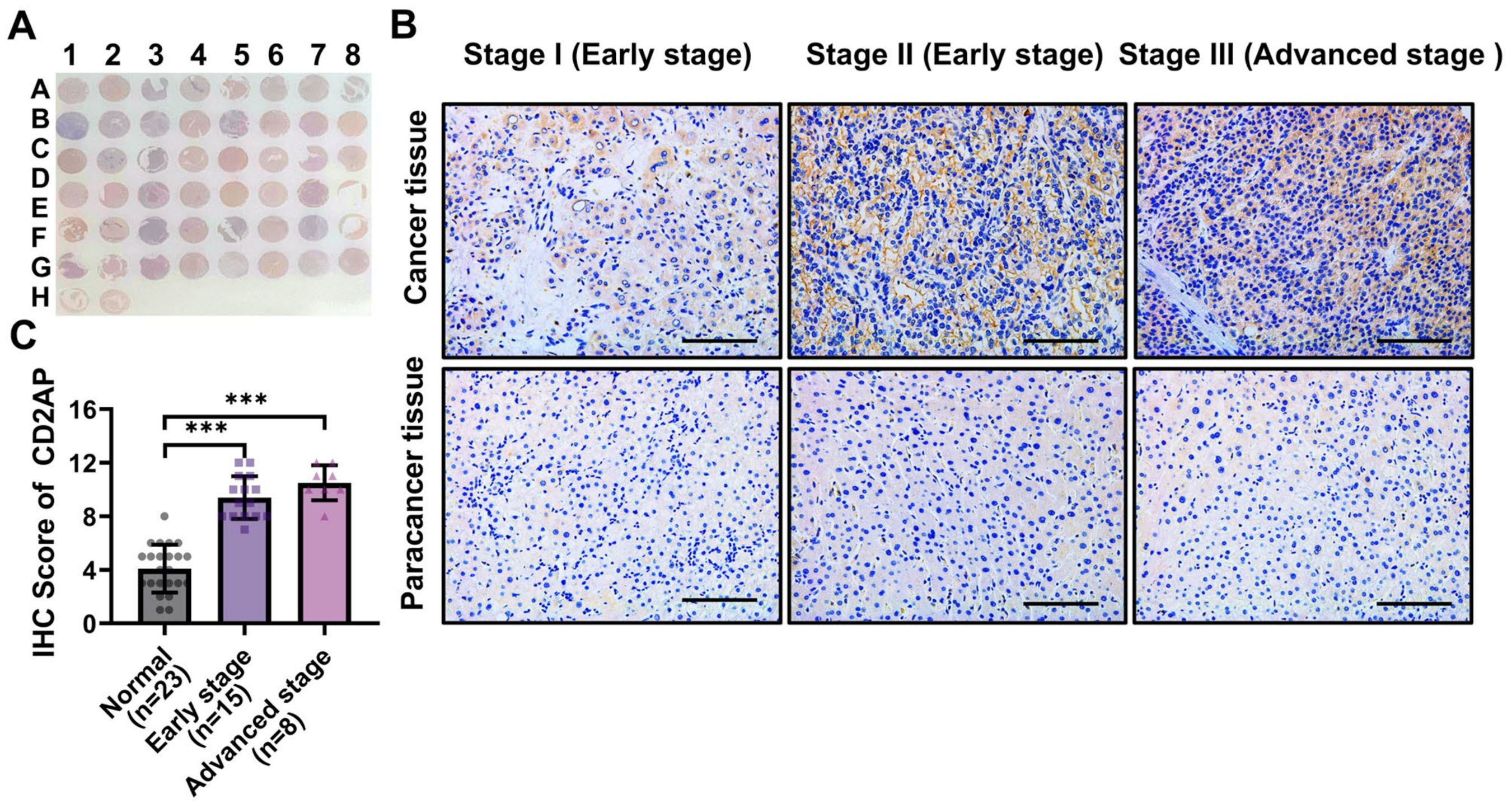
2.4. CD2AP Is Highly Expressed in HCC Cells and Tissues
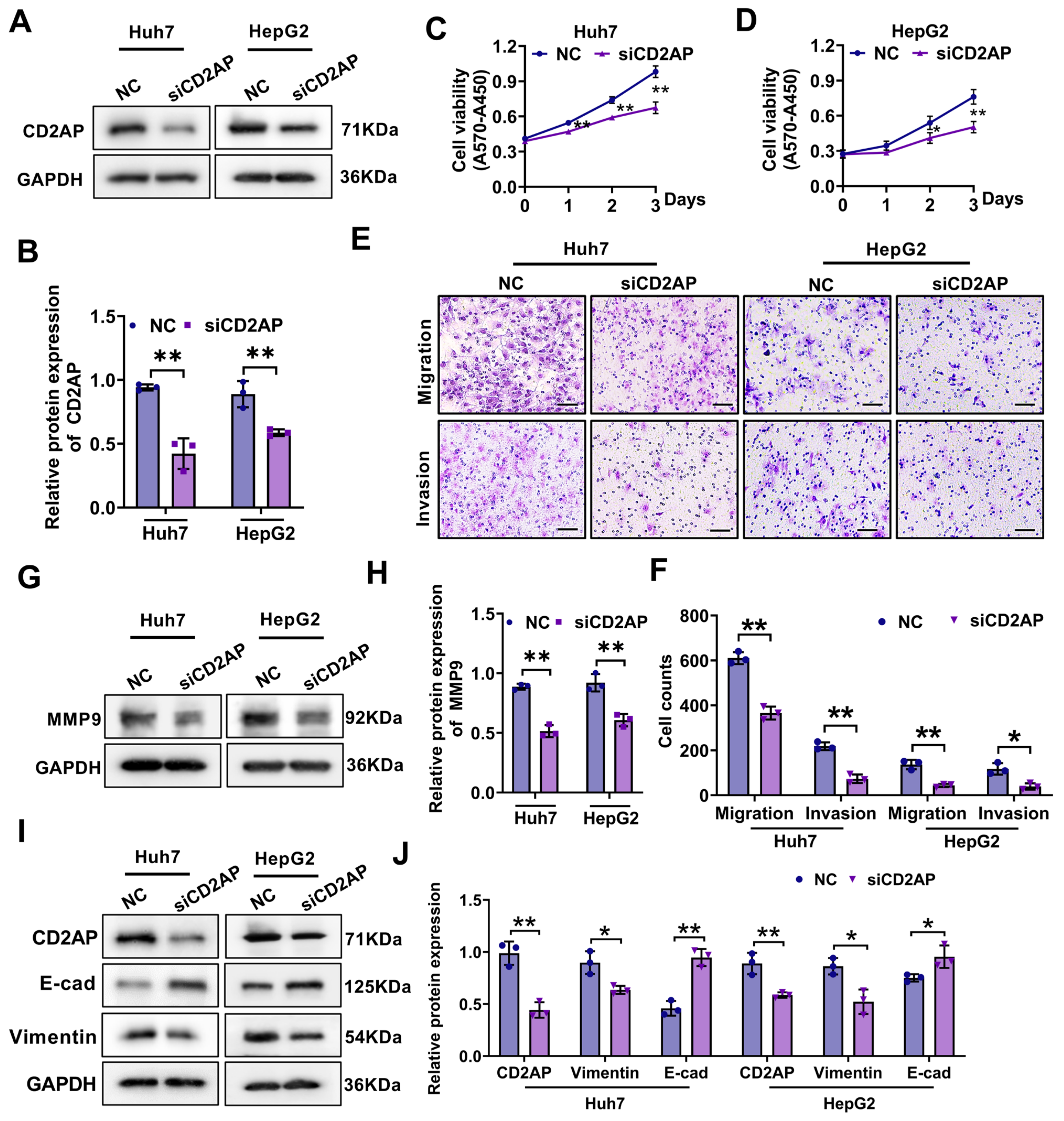
2.5. CD2AP Knockdown Restrains the Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion Abilities of HCC Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Acquisition
4.2. Construction of Risk Prognostic Signature
4.3. Survival Analysis
4.4. Functional Enrichment Analysis
4.5. Human Liver Specimens
4.6. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Staining
4.7. Cell Culture
4.8. Cell Viability
4.9. Migration and Invasion Assay
4.10. Western Blot Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jemal, A.; Ward, E.M.; Johnson, C.J.; Cronin, K.A.; Ma, J.; Ryerson, A.B.; Mariotto, A.; Lake, A.J.; Wilson, R.; Sherman, R.L.; et al. Annual Report to the Nation on the Status of Cancer, 1975–2014, Featuring Survival. JNCI-J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109, djx030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.J.; Liu, S.S.; Zeng, S.; Shen, H. From bench to bed: The tumor immune microenvironment and current immunotherapeutic strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allemani, C.; Weir, H.K.; Carreira, H.; Harewood, R.; Spika, D.; Wang, X.S.; Bannon, F.; Ahn, J.V.; Johnson, C.J.; Bonaventure, A.; et al. Global surveillance of cancer survival 1995–2009: Analysis of individual data for 25,676,887 patients from 279 population-based registries in 67 countries (CONCORD-2). Lancet 2015, 385, 977–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyoda, H.; Kumada, T.; Tada, T.; Sone, Y.; Kaneoka, Y.; Maeda, A. Tumor Markers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Simple and Significant Predictors of Outcome in Patients with HCC. Liver Cancer 2015, 4, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Qu, K.Z.; Ner, R.M.; Sferruzza, A.D.; Bender, R.A. Preliminary study of three tumor markers for hepatocellular carcinoma: AFP, AFP-L3, and Glypican-3. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 15014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Liao, M.; Qin, R.; Zhu, S.; Peng, C.; Fu, L.; Chen, Y.; Han, B. Regulated cell death (RCD) in cancer: Key pathways and targeted therapies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seehawer, M.; Heinzmann, F.; D’Artista, L.; Harbig, J.; Roux, P.F.; Hoenicke, L.; Dang, H.; Klotz, S.; Robinson, L.; Doré, G.; et al. Necroptosis microenvironment directs lineage commitment in liver cancer. Nature 2018, 562, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.C.; Jiang, Q.; Yang, K.P.; Wang, L.; Sethi, G.; Ma, Z. Extracellular vesicle-mediated ferroptosis, pyroptosis, and necroptosis: Potential clinical applications in cancer therapy. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Tian, S.W.; Pan, Y.T.; Li, W.; Wang, Q.M.; Tang, Y.; Yu, T.; Wu, X.; Shi, Y.K.; Ma, P.; et al. Pyroptosis: A new frontier in cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 121, 109595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.H.; Li, S.; Qi, J.; Chen, Z.L.; Wu, Y.H.; Guo, J.; Wang, K.; Sun, X.J.; Zheng, J.B. Cleavage of GSDME by caspase-3 determines lobaplatin-induced pyroptosis in colon cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.C.; Chen, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.; Yao, Y.B.; Xiao, S.; Fu, K. Identification of Ferroptosis-related molecular model and immune subtypes of hepatocellular carcinoma for individual therapy. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 2134–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.J.; Yao, S.M.; Huang, H.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, H.M.; Wei, Q.S.; Bian, T.T.; Sun, H.; Li, X.L.; Zhang, J.G.; et al. Molecular subtypes based on ferroptosis-related genes and tumor microenvironment infiltration characterization in lung adenocarcinoma. OncoImmunology 2021, 10, 1959977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.G.; Zhuang, L.; Gan, B.Y. Disulfidptosis: Disulfide stress-induced cell death. Trends Cell Biol. 2024, 34, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.J.; Zhou, C.T.; Ding, Y.M.; Duan, S.W. Disulfidptosis: A new target for metabolic cancer therapy. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, D.; Xie, R.; Wang, L.; Hong, J. Glycolysis in Chronic Liver Diseases: Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Opportunities. Cells 2023, 12, 1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuvalov, O.; Daks, A.; Fedorova, O.; Petukhov, A.; Barlev, N. Linking Metabolic Reprogramming, Plasticity and Tumor Progression. Cancers 2021, 13, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Yu, M.C.; Ma, X.L.; Sun, J.L.; Liu, C.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Wu, S.Y.; Fu, P.Y.; Yang, Z.; He, Y.G.; et al. IFNa Potentiates Anti-PD-1 Efficacy by Remodeling Glucose Metabolism in the Hepatocellular Carcinoma Microenvironment. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 1718–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppula, P.; Zhuang, L.; Gan, B.Y. Cystine transporter SLC7A11/xCT in cancer: Ferroptosis, nutrient dependency, and cancer therapy. Protein Cell 2021, 12, 599–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.X.; Qian, H.Y.; Sun, Z.A.; Yi, Q.; Liu, Y.; Lan, G.Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, G.R. Investigating the role of disulfidptosis related genes in radiotherapy resistance of lung adenocarcinoma. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1473080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Y.Y.; Cai, G.Y.; Ding, C.C.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.P.; Luo, S.W.; Liu, J.H. Disulfidptosis-related signature elucidates the prognostic, immunologic, and therapeutic characteristics in ovarian cancer. Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1378907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.Y.; Wang, L.Y.; Ding, W.; Ye, B.C.; Cheng, C.; Shao, J.F.; Liu, J.H.; Zhou, H.Y. Crosstalk of disulfidptosis-related subtypes, establishment of a prognostic signature and immune infiltration characteristics in bladder cancer based on a machine learning survival framework. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1180404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.X.; Yuan, D.L.; Liu, X.; Zhuo, S.C.; Liu, X.Y.; Sheng, H.H.; Sha, M.; Ye, J.; Yu, H. A demonstration based on multi-omics transcriptome sequencing data revealed disulfidptosis heterogeneity within the tumor microenvironment of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Discov. Oncol. 2023, 14, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Ma, J.M.; Sun, J.J.; Wu, X.L.; Ding, J. The role of molecular subtypes and immune infiltration characteristics based on disulfidptosis-associated genes in lung adenocarcinoma. Aging 2023, 15, 5075–5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Hori, M.; Iha, H. Disulfidptosis: A Novel Prognostic Criterion and Potential Treatment Strategy for Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, N.N.; Zhu, J.J.; Thompson, C.B. The hallmarks of cancer metabolism: Still emerging. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 355–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.G.; Nie, L.T.; Zhang, Y.L.; Yan, Y.L.; Wang, C.; Colic, M.; Olszewski, K.; Horbath, A.; Chen, X.; Lei, G.; et al. Actin cytoskeleton vulnerability to disulfide stress mediates disulfidptosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2023, 25, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zheng, Y.; Bai, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, L.; Ji, D.; Leng, K.; Meng, N.; Wang, H.; Huang, Z.; et al. RPNs Levels Are Prognostic and Diagnostic Markers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 7270541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.R.; Baek, G.O.; Yoon, M.G.; Son, J.A.; Yoon, J.H.; Cheong, J.Y.; Cho, H.J.; Kang, H.C.; Eun, J.W.; Kim, S.S. Hypomethylation-mediated upregulation of the WASF2 promoter region correlates with poor clinical outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauzeau, V.; Beignet, J.; Bailly, C.; Vergoten, G. Overexpressed or hyperactivated Rac1 as a target to treat hepatocellular carcinoma. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 179, 106220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.Z.; Yi, J.W.; Wu, H.J.; Wang, K.; Zhou, B.H. SLC7A11 in hepatocellular carcinoma: Potential mechanisms, regulation, and clinical significance. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2024, 14, 2326–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero-Fabián, S.; Arreola, R.; Becerril-Villanueva, E.; Torres-Romero, J.C.; Arana-Argáez, V.; Lara-Riegos, J.; Ramírez-Camacho, M.A.; Alvarez-Sánchez, M.E. Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Angiogenesis and Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheau, C.; Badarau, I.A.; Costache, R.; Caruntu, C.; Mihai, G.L.; Didilescu, A.C.; Constantin, C.; Neagu, M. The Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2019, 2019, 9423907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurilla, A.; László, L.; Takács, T.; Tilajka, A.; Lukács, L.; Novák, J.; Pancsa, R.; Buday, L.; Vas, V. Studying the Association of TKS4 and CD2AP Scaffold Proteins and Their Implications in the Partial Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) Process. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Zhang, X.; Gracia-Sancho, J.; Xie, W.F. Liver regeneration: Cellular origin and molecular mechanisms. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 1486–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Jin, W.; Tong, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L.; Lin, N. Therapeutic strategies of targeting non-apoptotic regulated cell death (RCD) with small-molecule compounds in cancer. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2024, 14, 2815–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, J.M.; Zhou, J.Y.; Wu, G.S. Autophagy and cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2024, 605, 217285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Kroemer, G.; Kang, R. Targeting cuproplasia and cuproptosis in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 21, 370–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Song, J.; She, J.; He, W.; Guo, S.; Dong, B. Constructing a disulfidptosis-related prognostic signature of hepatocellular carcinoma based on single-cell sequencing and weighted co-expression network analysis. Apoptosis 2024, 29, 1632–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wu, Y.; Ji, P.; Qi, J.; Yang, X.; Pocha, C.; Tustumi, F.; Biachi de Castria, T. Identification of a prognostic disulfidptosis-related gene signature in hepatocellular cancer. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2024, 15, 1647–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.Y.; Wang, D.S.; Lin, H.C.; Chen, X.X.; Yang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.H. A Novel Ferroptosis-related Gene Signature for Overall Survival Prediction in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 2430–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushue, N.; Wan, Y.-J.Y. Retinoid pathway and cancer therapeutics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J.X.; Chen, L.Y.; Wei, Y.A.; Zhang, W.M.; Shao, P.F.; Xu, H.G. CD2AP is a potential prognostic biomarker of renal clear cell carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2024, 13, e7055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.W.; Ren, H.; Dai, C.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Xu, K.; Li, J.; Ju, Y.; Pan, X.; et al. RNF5 exacerbates steatotic HCC by enhancing fatty acid oxidation via the improvement of CPT1A stability. Cancer Lett. 2024, 611, 217415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leahy, C.; Osborne, N.; Shirota, L.; Rote, P.; Lee, Y.K.; Song, B.J.; Yin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Garcia, V.; Hardwick, J.P. The fatty acid omega hydroxylase genes (CYP4 family) in the progression of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD): An RNA sequence database analysis and review. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 228, 116241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.K.; Chen, C.; Han, Z.; Huang, J.J.; Liu, X.; Chen, H.J.; Zhang, T.M.; Chen, S.; Chen, C.B.; Lu, M.D.; et al. CD2AP inhibits metastasis in gastric cancer by promoting cellular adhesion and cytoskeleton assembly. Mol. Carcinog. 2020, 59, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; He, J.W.; Zhao, W.T.; Zhou, Y.H.; Li, J.; Li, S.B.; Zhao, W.P.; Zhang, L.L.; Tang, Z.Q.; Tan, G.W.; et al. CD2AP promotes the progression of glioblastoma multiforme via TRIM5-mediated NF-kB signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirfakhar, F.S.; Castanheira, J.; Domingues, R.; Ramalho, J.S.; Guimas Almeida, C. The Alzheimer’s Disease Risk Gene CD2AP Functions in Dendritic Spines by Remodeling F-Actin. J. Neurosci. 2024, 44, e1734232024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibue, T.; Weinberg, R.A. EMT, CSCs, and drug resistance: The mechanistic link and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shang, N.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, G.; Guan, X. Integrated Analysis of Disulfidptosis-Related Genes Identifies CD2AP as a Potential Therapeutic Target for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4454. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094454
Shang N, Wang J, Liu Z, Wang Y, Zhang D, Liu H, Zhang Y, Dai G, Guan X. Integrated Analysis of Disulfidptosis-Related Genes Identifies CD2AP as a Potential Therapeutic Target for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4454. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094454
Chicago/Turabian StyleShang, Ning, Jianwei Wang, Zihan Liu, Yake Wang, Di Zhang, Huanfei Liu, Yaqing Zhang, Guifu Dai, and Xiaowen Guan. 2025. "Integrated Analysis of Disulfidptosis-Related Genes Identifies CD2AP as a Potential Therapeutic Target for Hepatocellular Carcinoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4454. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094454
APA StyleShang, N., Wang, J., Liu, Z., Wang, Y., Zhang, D., Liu, H., Zhang, Y., Dai, G., & Guan, X. (2025). Integrated Analysis of Disulfidptosis-Related Genes Identifies CD2AP as a Potential Therapeutic Target for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4454. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094454




