A Multi-Modal Graph Neural Network Framework for Parkinson’s Disease Therapeutic Discovery
Abstract
1. Introduction
Literature Review
2. Results and Discussions
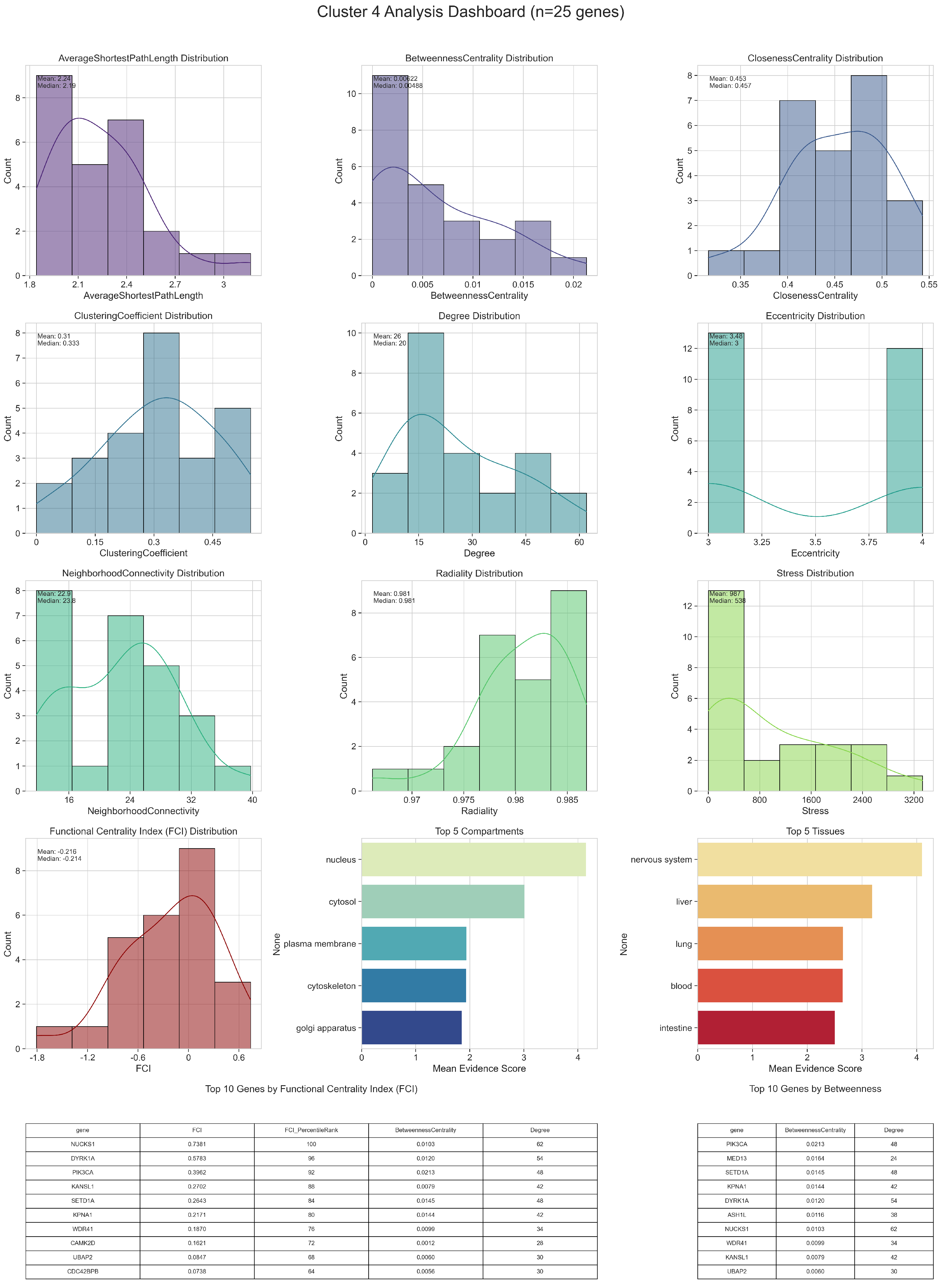
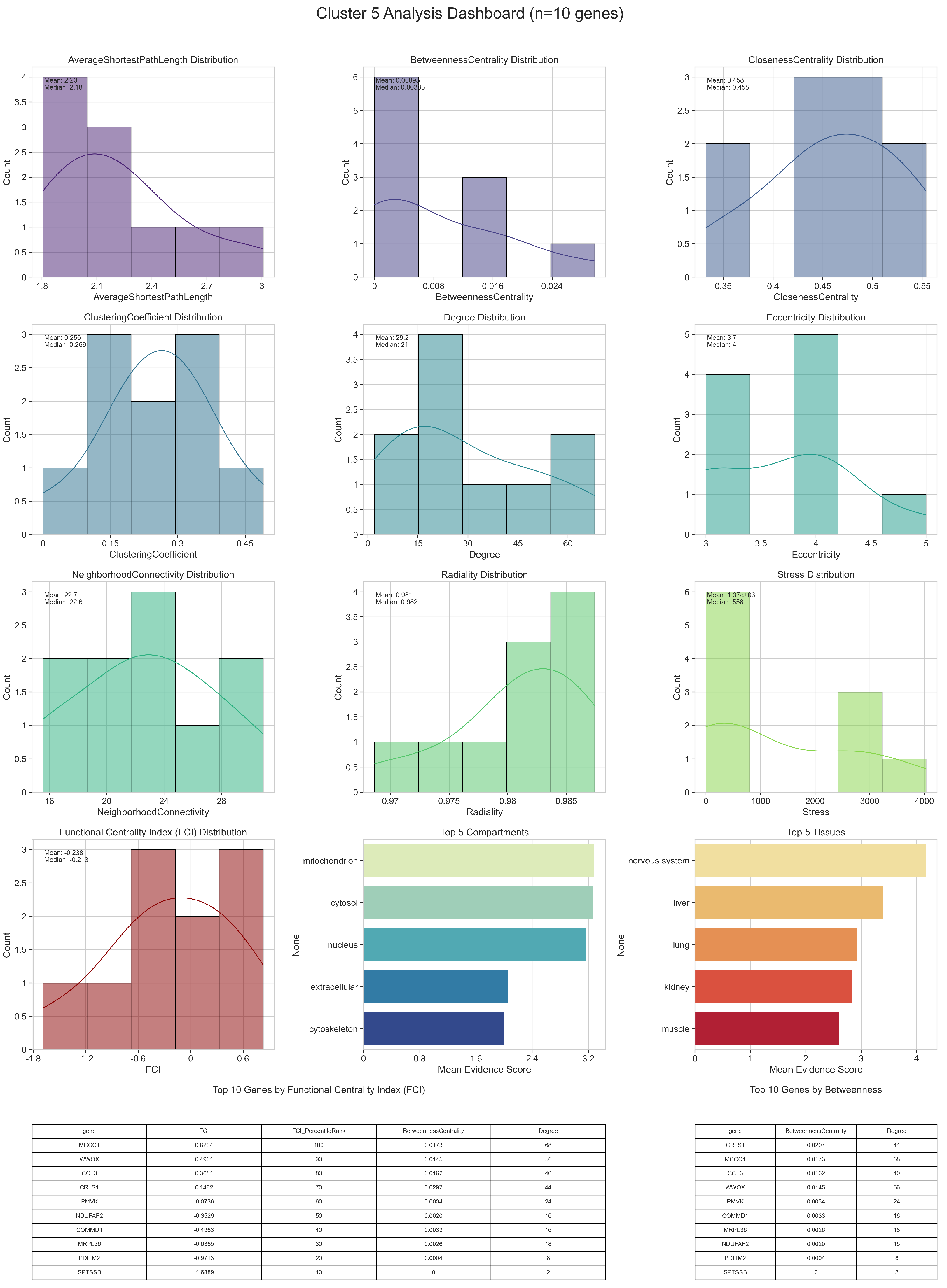
2.1. Parkinson’s Disease Network
2.2. Gene Enrichment Results
2.3. Multi-Modal GNN Results
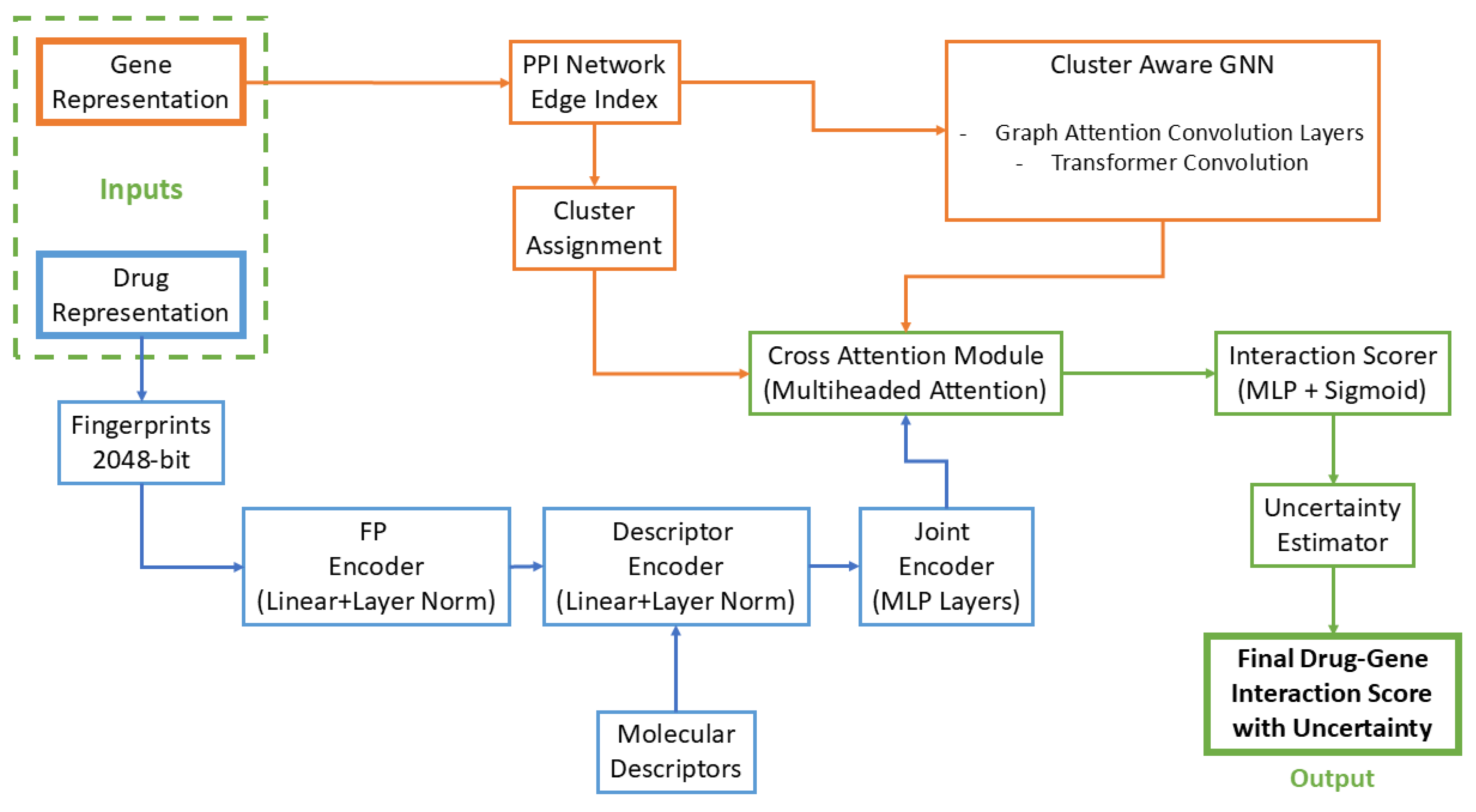
3. Methodology
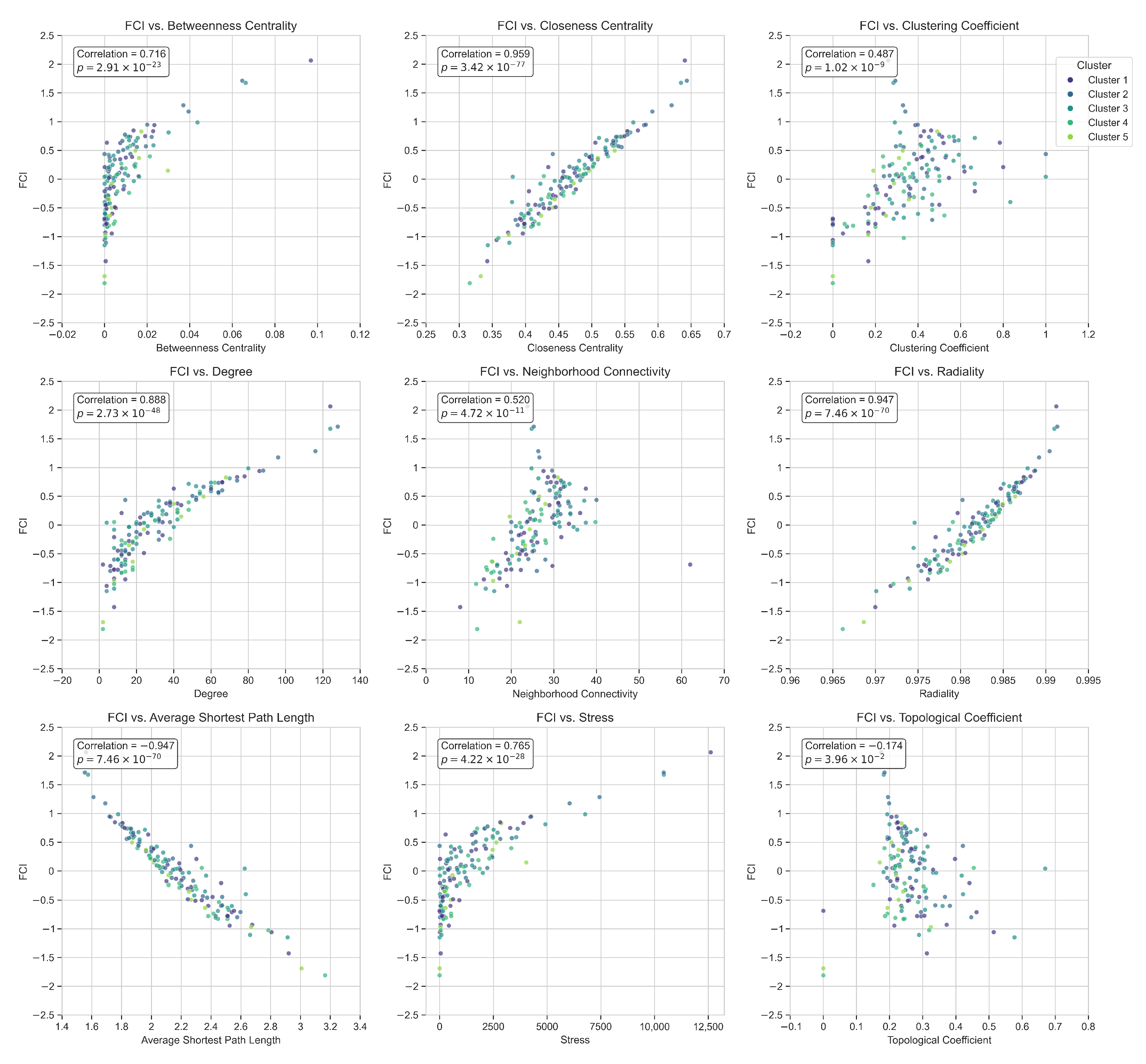
3.1. Network Analysis
3.1.1. Centralities and Functional Centrality Index
3.1.2. Node Clustering
3.2. Multi-Modal Graph Neural Network Architecture
3.2.1. Molecular Representation Learning
3.2.2. Cluster-Aware Gene Network Embedding
3.2.3. Uncertainty-Aware Drug-Gene Interaction Modeling
3.2.4. Multi-Objective Optimization
- Drug-Target Interaction Prediction:
- PD Gene Classification:
- Molecular Autoencoding:where BCE denotes Binary Cross-Entropy.
3.2.5. Uncertainty-Quantified Drug Prioritization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Drug Name | DrugBank ID | Raw Scpre | z-Score | Uncertainty | Percentile | Elite Percentile | Probability | Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glycochenodeoxycholic Acid | DB02123 | 0.8317 | 3.676 | 0.2944 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | DGKQ |
| Vilazodone | DB06684 | 0.7994 | 3.2732 | 0.3351 | 99.9919 | 99.8374 | 94.5108 | DGKQ |
| Ferrous chloride | DB13569 | 0.7989 | 3.268 | 0.343 | 99.9837 | 99.6748 | 94.4401 | DGKQ |
| S-Butyryl-Cystein | DB02160 | 0.7959 | 3.2302 | 0.3005 | 99.9756 | 99.5122 | 93.926 | DGKQ |
| 2-{4-[4-(4-Chloro-Phenoxy)-Benzenesulfonyl] -Tetrahydro-Pyran-4-Yl}-N-Hydroxy-Acetamide | DB02049 | 0.7891 | 3.1451 | 0.3196 | 99.9675 | 99.3496 | 92.7659 | DGKQ |
| Flutemetamol | DB15058 | 0.7808 | 3.0415 | 0.2691 | 99.9593 | 99.187 | 91.3541 | DGKQ |
| Netarsudil | DB13931 | 0.7769 | 2.9937 | 0.2364 | 99.9512 | 99.0244 | 90.7025 | DGKQ |
| D-Borneol | DB17066 | 0.7753 | 2.9737 | 0.2433 | 99.9431 | 98.8618 | 90.4295 | DGKQ |
| Ticagrelor | DB08816 | 0.7723 | 2.9359 | 0.2601 | 99.9349 | 98.6992 | 89.9147 | DGKQ |
| 6-Chloro-2-(2-Hydroxy-Biphenyl-3-Yl) -1h-Indole-5-Carboxamidine | DB03865 | 0.7714 | 2.9256 | 0.2983 | 99.9268 | 98.5366 | 89.774 | DGKQ |
| Indobufen | DB12545 | 0.8207 | 3.5023 | 0.3538 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | GAK |
| Netarsudil | DB13931 | 0.8005 | 3.2541 | 0.3399 | 99.9919 | 99.8374 | 96.4035 | GAK |
| alpha-D-Xylopyranose | DB03389 | 0.7999 | 3.2471 | 0.3363 | 99.9837 | 99.6748 | 96.3025 | GAK |
| Mibefradil | DB01388 | 0.7891 | 3.1136 | 0.249 | 99.9756 | 99.5122 | 94.3682 | GAK |
| Fluprednisolone | DB09378 | 0.7826 | 3.0336 | 0.3111 | 99.9675 | 99.3496 | 93.2086 | GAK |
| Ciclesonide | DB01410 | 0.7801 | 3.0036 | 0.3088 | 99.9593 | 99.187 | 92.7734 | GAK |
| Imiglitazar | DB12511 | 0.7801 | 3.0027 | 0.3701 | 99.9512 | 99.0244 | 92.7611 | GAK |
| L-Baclofen | DB12098 | 0.7747 | 2.9364 | 0.3532 | 99.9431 | 98.8618 | 91.8 | GAK |
| 3-(4-nitrophenyl)-1H-pyrazole | DB08695 | 0.7736 | 2.9233 | 0.2412 | 99.9349 | 98.6992 | 91.6099 | GAK |
| Flortaucipir | DB15033 | 0.7723 | 2.908 | 0.3114 | 99.9268 | 98.5366 | 91.3885 | GAK |
| Cortisone acetate | DB01380 | 0.8146 | 3.2992 | 0.3751 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | GBA |
| Perillyl alcohol | DB15289 | 0.8067 | 3.202 | 0.386 | 99.9919 | 99.8374 | 98.6197 | GBA |
| 2-(2-{2-[(BIPHENYL-4-YLMETHYL)-AMINO] -3-MERCAPTO-PENTANOYLAMINO}-ACETYLAMINO) -3-METHYL-BUTYRIC ACID METHYL ESTER | DB08643 | 0.8015 | 3.1366 | 0.3976 | 99.9837 | 99.6748 | 97.6906 | GBA |
| alpha-N-Acetyl-D-galactosamine | DB03567 | 0.7976 | 3.0891 | 0.3389 | 99.9756 | 99.5122 | 97.0158 | GBA |
| Landiolol | DB12212 | 0.7936 | 3.0387 | 0.3038 | 99.9675 | 99.3496 | 96.2997 | GBA |
| (1S)-2-[(2S,5R)-2-(AMINOMETHYL) -5-ETHYNYLPYRROLIDIN-1-YL]-1 -CYCLOPENTYL-2-OXOETHANAMINE | DB07356 | 0.7927 | 3.0278 | 0.3095 | 99.9593 | 99.187 | 96.1442 | GBA |
| N-(2-(((5-CHLORO-2-PYRIDINYL)AMINO)SULFONYL) PHENYL)-4-(2-OXO-1(2H)-PYRIDINYL)BENZAMIDE | DB07800 | 0.7918 | 3.0163 | 0.3405 | 99.9512 | 99.0244 | 95.9808 | GBA |
| LY-294002 | DB02656 | 0.7884 | 2.9744 | 0.3492 | 99.9431 | 98.8618 | 95.3856 | GBA |
| N-{2-[4-(AMINOSULFONYL)PHENYL]ETHYL}ACETAMIDE | DB08155 | 0.7848 | 2.9302 | 0.2484 | 99.9349 | 98.6992 | 94.7587 | GBA |
| Quinolinic Acid | DB01796 | 0.7848 | 2.9302 | 0.3113 | 99.9268 | 98.5366 | 94.7577 | GBA |
| (1R,2R,3S,4R,6S)-3,4,6-Trihydroxy-5 -{[(S)-hydroxy(3-hydroxy-2-oxopropoxy)phosphoryl]oxy} -1,2-cyclohexanediyl bis[dihydrogen (phosphate)] | DB02028 | 0.8299 | 3.7466 | 0.2958 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | TMEM175 |
| CTS-1027 | DB08490 | 0.8296 | 3.7434 | 0.2995 | 99.9919 | 99.8374 | 99.9583 | TMEM175 |
| Vibegron | DB14895 | 0.8257 | 3.6942 | 0.3392 | 99.9837 | 99.6748 | 99.3229 | TMEM175 |
| Ranolazine | DB00243 | 0.8225 | 3.6551 | 0.3184 | 99.9756 | 99.5122 | 98.8164 | TMEM175 |
| 3-nitro-L-tyrosine | DB03867 | 0.8093 | 3.4922 | 0.3465 | 99.9675 | 99.3496 | 96.7083 | TMEM175 |
| 3-hydroxyglutaric acid | DB04594 | 0.8037 | 3.4226 | 0.2793 | 99.9593 | 99.187 | 95.8081 | TMEM175 |
| LG-100268 | DB01941 | 0.7891 | 3.2414 | 0.2456 | 99.9512 | 99.0244 | 93.4636 | TMEM175 |
| Atecegatran metoxil | DB12507 | 0.782 | 3.1547 | 0.3315 | 99.9431 | 98.8618 | 92.3408 | TMEM175 |
| (1S)-1-AMINO-2-(1H-INDOL-3-YL)ETHANOL | DB08649 | 0.7792 | 3.1189 | 0.3247 | 99.9349 | 98.6992 | 91.8777 | TMEM175 |
| Topiramate | DB00273 | 0.777 | 3.0928 | 0.2848 | 99.9268 | 98.5366 | 91.5404 | TMEM175 |
| Ramelteon | DB00980 | 0.8421 | 3.7712 | 0.3392 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | BCKDK |
| Indomethacin | DB00328 | 0.7894 | 3.119 | 0.3447 | 99.9919 | 99.8374 | 91.6803 | BCKDK |
| (1S,2S,5S)2-(4-GLUTARIDYLBENZYL) -5-PHENYL-1-CYCLOHEXANOL | DB07909 | 0.7893 | 3.1178 | 0.3616 | 99.9837 | 99.6748 | 91.6656 | BCKDK |
| Zinc Substituted Heme C | DB04249 | 0.7863 | 3.081 | 0.3536 | 99.9756 | 99.5122 | 91.1965 | BCKDK |
| 3-{[(3-FLUORO-3’-METHOXYBIPHENYL-4-YL)AMINO] CARBONYL}THIOPHENE-2-CARBOXYLIC ACID | DB07976 | 0.7831 | 3.0412 | 0.3324 | 99.9675 | 99.3496 | 90.6886 | BCKDK |
| Pipequaline | DB13991 | 0.7806 | 3.0107 | 0.2865 | 99.9593 | 99.187 | 90.2999 | BCKDK |
| (1S,7S,8S,8AR)-1,2,3,7,8,8A-HEXAHYDRO-7-METHYL -8-[2-[(2R,4R)-TETRAHYDRO-4-HY DROXY-6-OXO-2H-PYRAN -2-YL]ETHYL]-1-NAPHTHALENOL | DB08224 | 0.7727 | 2.913 | 0.365 | 99.9512 | 99.0244 | 89.0531 | BCKDK |
| Fluocortolone | DB08971 | 0.7698 | 2.8768 | 0.3908 | 99.9431 | 98.8618 | 88.5921 | BCKDK |
| Ganaplacide | DB16173 | 0.7693 | 2.8711 | 0.3198 | 99.9349 | 98.6992 | 88.5191 | BCKDK |
| Anisotropine methylbromide | DB00517 | 0.7655 | 2.8238 | 0.3696 | 99.9268 | 98.5366 | 87.9157 | BCKDK |
| Drug Name | DrugBank ID | Raw Score | z-Score | Uncertainty | Percentile | Elite Percentile | Probability | Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clorotepine | DB15971 | 0.8113 | 3.4489 | 0.3352 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | MAPT |
| Oxtriphylline | DB01303 | 0.7911 | 3.2018 | 0.2308 | 99.9919 | 99.8374 | 96.3726 | MAPT |
| Verdoheme | DB04803 | 0.786 | 3.1402 | 0.3065 | 99.9837 | 99.6748 | 95.468 | MAPT |
| Dodecyltrimethylammonium | DB02779 | 0.7725 | 2.9742 | 0.2759 | 99.9756 | 99.5122 | 93.0316 | MAPT |
| R-95845 | DB07327 | 0.7703 | 2.9473 | 0.3677 | 99.9675 | 99.3496 | 92.6366 | MAPT |
| TP-1287 | DB18104 | 0.7685 | 2.9257 | 0.271 | 99.9593 | 99.187 | 92.3184 | MAPT |
| TG100-115 | DB05552 | 0.7669 | 2.9061 | 0.3139 | 99.9512 | 99.0244 | 92.0308 | MAPT |
| Bamethan | DB13206 | 0.7627 | 2.8551 | 0.3252 | 99.9431 | 98.8618 | 91.2826 | MAPT |
| 4-{5-[(1Z)-1-(2-IMINO-4-OXO-1,3 -THIAZOLIDIN-5-YLIDENE)ETHYL] -2-FURYL}BENZENESULFONAMIDE | DB07540 | 0.7618 | 2.8442 | 0.319 | 99.9349 | 98.6992 | 91.1232 | MAPT |
| Phenaglycodol | DB19373 | 0.7605 | 2.8277 | 0.3134 | 99.9268 | 98.5366 | 90.8806 | MAPT |
| Desmopressin | DB00035 | 0.7938 | 3.3745 | 0.3725 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | SNCA |
| Simenepag isopropyl | DB12977 | 0.7846 | 3.2621 | 0.2972 | 99.9919 | 99.8374 | 98.3222 | SNCA |
| Bolasterone | DB01471 | 0.7774 | 3.1734 | 0.3701 | 99.9837 | 99.6748 | 96.9989 | SNCA |
| Sodium tetradecyl sulfate | DB00464 | 0.7735 | 3.1264 | 0.24 | 99.9756 | 99.5122 | 96.2981 | SNCA |
| Florbenazine F-18 | DB14945 | 0.7687 | 3.0674 | 0.2229 | 99.9675 | 99.3496 | 95.417 | SNCA |
| MALP-2 | DB18482 | 0.768 | 3.059 | 0.2854 | 99.9593 | 99.187 | 95.292 | SNCA |
| Metoprine | DB04655 | 0.7666 | 3.042 | 0.3034 | 99.9512 | 99.0244 | 95.0387 | SNCA |
| Medifoxamine | DB13219 | 0.7645 | 3.0162 | 0.3691 | 99.9431 | 98.8618 | 94.6535 | SNCA |
| Nimesulide | DB04743 | 0.7631 | 2.9993 | 0.3322 | 99.9349 | 98.6992 | 94.4003 | SNCA |
| Chlorotoxin I-131 | DB05462 | 0.7629 | 2.997 | 0.3783 | 99.9268 | 98.5366 | 94.3666 | SNCA |
| (R)-methylmalonyl-CoA | DB04045 | 0.789 | 2.9323 | 0.3501 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | RIT2 |
| Gestrinone | DB11619 | 0.7884 | 2.9254 | 0.3161 | 99.9919 | 99.8374 | 99.8871 | RIT2 |
| 2-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENOXY) -5-(PYRIDIN-2-YLMETHYL)PHENOL | DB07287 | 0.7807 | 2.8289 | 0.3101 | 99.9837 | 99.6748 | 98.3112 | RIT2 |
| Tetrazepam | DB13324 | 0.7784 | 2.7995 | 0.2862 | 99.9756 | 99.5122 | 97.8325 | RIT2 |
| Tetragalacturonic acid hydroxymethylester | DB13621 | 0.7765 | 2.7756 | 0.2442 | 99.9675 | 99.3496 | 97.4415 | RIT2 |
| Nojirimycine Tetrazole | DB02471 | 0.7761 | 2.771 | 0.3202 | 99.9593 | 99.187 | 97.3674 | RIT2 |
| Deudextromethorphan | DB19054 | 0.7737 | 2.7408 | 0.3655 | 99.9512 | 99.0244 | 96.8746 | RIT2 |
| Deoxyamidinoproclavaminic acid | DB02475 | 0.7719 | 2.7174 | 0.2686 | 99.9431 | 98.8618 | 96.492 | RIT2 |
| Levobetaxolol | DB09351 | 0.7715 | 2.7127 | 0.3006 | 99.9349 | 98.6992 | 96.4154 | RIT2 |
| Prasterone enantate | DB16625 | 0.7712 | 2.7092 | 0.3265 | 99.9268 | 98.5366 | 96.3585 | RIT2 |
| 2c-Methyl-D-Erythritol 2,4 -Cyclodiphosphate | DB03961 | 0.8126 | 3.3758 | 0.3139 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | PRKN |
| Sanfetrinem cilexetil | DB19135 | 0.8105 | 3.3497 | 0.3219 | 99.9919 | 99.8374 | 99.6261 | PRKN |
| Acetarsol | DB13268 | 0.808 | 3.3186 | 0.2309 | 99.9837 | 99.6748 | 99.1797 | PRKN |
| N-(4-{[(3S)-3-(dimethylamino)pyrrolidin-1-yl] carbonyl}phenyl)-5-fluoro-4-[2-methyl-1 -(1-methylethyl)-1H-imidazol-5-yl]pyrimidin -2-amine | DB07936 | 0.7921 | 3.1223 | 0.3362 | 99.9756 | 99.5122 | 96.3617 | PRKN |
| (1R,4S,7AS)-1-(1-FORMYLPROP-1-EN-1-YL) -4-METHOXY-2,4,5,6,7,7A-HEXAHYDRO -1H-ISOINDOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID | DB08110 | 0.7845 | 3.0285 | 0.2737 | 99.9675 | 99.3496 | 95.0164 | PRKN |
| Halothane | DB01159 | 0.7844 | 3.0265 | 0.2784 | 99.9593 | 99.187 | 94.987 | PRKN |
| Phendimetrazine | DB01579 | 0.7841 | 3.0227 | 0.301 | 99.9512 | 99.0244 | 94.9334 | PRKN |
| Uridine diphosphate glucose | DB01861 | 0.7838 | 3.0192 | 0.3706 | 99.9431 | 98.8618 | 94.8823 | PRKN |
| Icaritin | DB12672 | 0.7794 | 2.9643 | 0.3944 | 99.9349 | 98.6992 | 94.0949 | PRKN |
| Indralin | DB18220 | 0.7774 | 2.9395 | 0.354 | 99.9268 | 98.5366 | 93.7393 | PRKN |
| Genz-10850 | DB04289 | 0.802 | 3.194 | 0.3738 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | STX1B |
| Brasofensine | DB04857 | 0.7981 | 3.1468 | 0.3115 | 99.9919 | 99.8374 | 99.2901 | STX1B |
| 5-(3-{3-[3-HYDROXY-2-(METHOXYCARBONYL) PHENOXY]PROPENYL}PHENYL) -4-(HYDROXYMETHYL)ISOXAZOLE -3-CARBOXYLIC ACID | DB08001 | 0.7884 | 3.0266 | 0.3049 | 99.9837 | 99.6748 | 97.4823 | STX1B |
| Tavapadon | DB14899 | 0.7817 | 2.9442 | 0.2889 | 99.9756 | 99.5122 | 96.2434 | STX1B |
| 3-[(9H-fluoren-9-ylideneamino)oxy]propanoic acid | DB07240 | 0.78 | 2.9226 | 0.2985 | 99.9675 | 99.3496 | 95.9172 | STX1B |
| Pirepemat | DB19165 | 0.7799 | 2.9212 | 0.3235 | 99.9593 | 99.187 | 95.8969 | STX1B |
| Epibatidine | DB07720 | 0.7785 | 2.9049 | 0.37 | 99.9512 | 99.0244 | 95.651 | STX1B |
| Clonazepam | DB01068 | 0.7766 | 2.8814 | 0.2408 | 99.9431 | 98.8618 | 95.2977 | STX1B |
| Osalmid | DB16273 | 0.773 | 2.8367 | 0.3213 | 99.9349 | 98.6992 | 94.626 | STX1B |
| 4,5-Dimethyl-1,2-phenylenediamine | DB03180 | 0.7725 | 2.8304 | 0.3054 | 99.9268 | 98.5366 | 94.5305 | STX1B |
| Drug Name | DrugBank ID | Raw Score | z-Score | Uncertainty | Percentile | Elite Percentile | Probability | Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Henatinib | DB13019 | 0.8187 | 3.1505 | 0.3136 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | LRRK2 |
| Betameprodine | DB01552 | 0.8183 | 3.146 | 0.3601 | 99.9919 | 99.8374 | 99.9323 | LRRK2 |
| Vatalanib | DB04879 | 0.8087 | 3.0278 | 0.3496 | 99.9837 | 99.6748 | 98.158 | LRRK2 |
| Histapyrrodine | DB13479 | 0.8045 | 2.9753 | 0.2981 | 99.9756 | 99.5122 | 97.3698 | LRRK2 |
| P-Anisic Acid | DB02795 | 0.7954 | 2.8626 | 0.3591 | 99.9675 | 99.3496 | 95.6782 | LRRK2 |
| Limonene, (+/-)- | DB19146 | 0.7935 | 2.8393 | 0.2723 | 99.9593 | 99.187 | 95.3283 | LRRK2 |
| Cemdomespib | DB18953 | 0.793 | 2.8332 | 0.2955 | 99.9512 | 99.0244 | 95.2376 | LRRK2 |
| (3S)-1-CYCLOHEXYL-5-OXO -N-PHENYLPYRROLIDINE -3-CARBOXAMIDE | DB07155 | 0.7915 | 2.815 | 0.2881 | 99.9431 | 98.8618 | 94.9635 | LRRK2 |
| Carbapenem | DB18912 | 0.7895 | 2.7894 | 0.3668 | 99.9349 | 98.6992 | 94.5795 | LRRK2 |
| Monoisopropylphosphorylserine | DB01805 | 0.7883 | 2.7748 | 0.2895 | 99.9268 | 98.5366 | 94.3604 | LRRK2 |
| TNP-2092 | DB16312 | 0.8257 | 3.5258 | 0.3485 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | APOE |
| Tropatepine | DB13252 | 0.8048 | 3.267 | 0.3413 | 99.9919 | 99.8374 | 96.4046 | APOE |
| Penfluridol | DB13791 | 0.7925 | 3.1144 | 0.3497 | 99.9837 | 99.6748 | 94.2841 | APOE |
| 2-PHENYLAMINO-4-METHYL -5-ACETYL THIAZOLE | DB08359 | 0.7856 | 3.0288 | 0.2741 | 99.9756 | 99.5122 | 93.0947 | APOE |
| GW-590735 | DB07215 | 0.7847 | 3.0171 | 0.3103 | 99.9675 | 99.3496 | 92.9328 | APOE |
| Spiradoline | DB12704 | 0.7784 | 2.9386 | 0.3268 | 99.9593 | 99.187 | 91.8418 | APOE |
| Ginsenoside Rg3 | DB19257 | 0.7745 | 2.891 | 0.339 | 99.9512 | 99.0244 | 91.1806 | APOE |
| 2-[(2’,3’,4’-TRIFLUOROBIPHENYL -2-YL)OXY]ETHANOL | DB08611 | 0.7739 | 2.8836 | 0.3161 | 99.9431 | 98.8618 | 91.0774 | APOE |
| 6-(4-chloro-2-fluoro-3-phenoxybenzyl) pyridazin-3(2H)-one | DB08379 | 0.7732 | 2.8746 | 0.2895 | 99.9349 | 98.6992 | 90.9535 | APOE |
| Palovarotene | DB05467 | 0.7674 | 2.8021 | 0.3271 | 99.9268 | 98.5366 | 89.9458 | APOE |
| Chloroxylenol | DB11121 | 0.7924 | 3.3041 | 0.3651 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | FYN |
| (6-METHYL-3,4-DIHYDRO-2H -CHROMEN-2-YL)METHYLPHOSPHINATE | DB07487 | 0.7839 | 3.2009 | 0.35 | 99.9919 | 99.8374 | 98.5094 | FYN |
| Soblidotin | DB12677 | 0.7825 | 3.1837 | 0.3229 | 99.9837 | 99.6748 | 98.2605 | FYN |
| IOWH-032 | DB12959 | 0.7802 | 3.1558 | 0.3662 | 99.9756 | 99.5122 | 97.8585 | FYN |
| Felodipine | DB01023 | 0.7783 | 3.1326 | 0.2964 | 99.9675 | 99.3496 | 97.5222 | FYN |
| Transcrocetinate | DB05974 | 0.775 | 3.0924 | 0.3199 | 99.9593 | 99.187 | 96.9417 | FYN |
| Zolazepam | DB11555 | 0.7705 | 3.0375 | 0.3856 | 99.9512 | 99.0244 | 96.1488 | FYN |
| (2S,3S)-3-AMINO-4-[(3S)-3-FLUOROPYRROLIDIN -1-YL]-N,N-DIMETHYL-4-OXO -2-(TRANS-4-[1,2,4]TRIAZOLO[1,5-A] PYRIDIN-5-YLCYCLOHEXYL)BUTANAMIDE | DB07135 | 0.769 | 3.0194 | 0.366 | 99.9431 | 98.8618 | 95.8886 | FYN |
| Zuretinol acetate | DB12112 | 0.7688 | 3.0168 | 0.3115 | 99.9349 | 98.6992 | 95.851 | FYN |
| 5-(4-CHLORO-5-PHENYL-3-THIENYL) -1,2,5-THIADIAZOLIDIN-3-ONE 1,1-DIOXIDE | DB07134 | 0.7655 | 2.976 | 0.3377 | 99.9268 | 98.5366 | 95.2617 | FYN |
| Sodium stibogluconate | DB05630 | 0.7811 | 3.1995 | 0.3156 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | GPNMB |
| 2-[5-Methanesulfonylamino-2-(4-Aminophenyl) -6-Oxo-1,6-Dihydro-1-Pyrimidinyl] -N-(3,3,3-Trifluoro-1-Isopropyl -2-Oxopropyl)Acetamide | DB03202 | 0.7783 | 3.1639 | 0.2998 | 99.9919 | 99.8374 | 99.4792 | GPNMB |
| Ilginatinib | DB12784 | 0.7731 | 3.0989 | 0.3404 | 99.9837 | 99.6748 | 98.5272 | GPNMB |
| 2-{[4-(TRIFLUOROMETHOXY)BENZOYL] AMINO}ETHYL DIHYDROGEN PHOSPHATE | DB07745 | 0.7716 | 3.0801 | 0.1946 | 99.9756 | 99.5122 | 98.252 | GPNMB |
| Brotizolam | DB09017 | 0.7662 | 3.0133 | 0.3337 | 99.9675 | 99.3496 | 97.2749 | GPNMB |
| Gunagratinib | DB18191 | 0.7659 | 3.0097 | 0.3445 | 99.9593 | 99.187 | 97.2221 | GPNMB |
| D-tartaric acid | DB01694 | 0.7659 | 3.0092 | 0.2981 | 99.9512 | 99.0244 | 97.215 | GPNMB |
| Citraconic acid | DB04734 | 0.7653 | 3.0017 | 0.3137 | 99.9431 | 98.8618 | 97.1049 | GPNMB |
| VB-309 | DB18539 | 0.765 | 2.9978 | 0.3683 | 99.9349 | 98.6992 | 97.0487 | GPNMB |
| VP-14637 | DB12195 | 0.7563 | 2.8891 | 0.3066 | 99.9268 | 98.5366 | 95.4582 | GPNMB |
| Hydrolyzed Cephalothin | DB02247 | 0.8197 | 3.3124 | 0.3474 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | BST1 |
| Oxytetracycline | DB00595 | 0.8004 | 3.0762 | 0.379 | 99.9919 | 99.8374 | 96.7303 | BST1 |
| Dyclonine | DB00645 | 0.7999 | 3.0701 | 0.3148 | 99.9837 | 99.6748 | 96.6471 | BST1 |
| N-(5-chloro-1,3-benzodioxol-4-yl) -6-methoxy-7-(3-piperidin-1-ylpropoxy) quinazolin-4-amine | DB07249 | 0.7991 | 3.0604 | 0.3241 | 99.9756 | 99.5122 | 96.5123 | BST1 |
| (METHYLPYRIDAZINE PIPERIDINE PROPYLOXYPHENYL)ETHYLACETATE | DB08013 | 0.7983 | 3.0505 | 0.3066 | 99.9675 | 99.3496 | 96.3748 | BST1 |
| Ghavamiol | DB02492 | 0.7973 | 3.0384 | 0.2712 | 99.9593 | 99.187 | 96.2078 | BST1 |
| Cryptoxanthin | DB15914 | 0.7925 | 2.979 | 0.2972 | 99.9512 | 99.0244 | 95.3855 | BST1 |
| Emetonium iodide | DB13769 | 0.7916 | 2.9692 | 0.2971 | 99.9431 | 98.8618 | 95.2496 | BST1 |
| Isocyanomethane | DB04337 | 0.7875 | 2.9187 | 0.3061 | 99.9349 | 98.6992 | 94.5519 | BST1 |
| 5-(PARA-NITROPHENYL PHOSPHONATE) -PENTANOIC ACID | DB08296 | 0.7864 | 2.9055 | 0.3235 | 99.9268 | 98.5366 | 94.3682 | BST1 |
| Drug Name | DrugBank ID | Raw Score | Z-Score | Uncertainty | Percentile | Elite Percentile | Probability | Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Latamoxef | DB04570 | 0.8272 | 3.6216 | 0.3132 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | NUCKS1 |
| N-[4-(2-CHLOROPHENYL)-1,3-DIOXO -1,2,3,6-TETRAHYDROPYRROLO [3,4-C]CARBAZOL-9-YL]FORMAMIDE | DB07226 | 0.8099 | 3.4112 | 0.2473 | 99.9919 | 99.8374 | 97.0681 | NUCKS1 |
| Acetic Acid Salicyloyl-Amino-Ester | DB03667 | 0.7999 | 3.2887 | 0.3413 | 99.9837 | 99.6748 | 95.3599 | NUCKS1 |
| DCFBC F-18 | DB14772 | 0.7974 | 3.2579 | 0.3708 | 99.9756 | 99.5122 | 94.9308 | NUCKS1 |
| Etoposide toniribate | DB17255 | 0.7858 | 3.1171 | 0.2376 | 99.9675 | 99.3496 | 92.9677 | NUCKS1 |
| Batefenterol | DB12526 | 0.7837 | 3.0912 | 0.4028 | 99.9593 | 99.187 | 92.6068 | NUCKS1 |
| Enalaprilat | DB09477 | 0.7827 | 3.0786 | 0.3313 | 99.9512 | 99.0244 | 92.4319 | NUCKS1 |
| Acetylcysteine zinc | DB14479 | 0.779 | 3.034 | 0.2801 | 99.9431 | 98.8618 | 91.8091 | NUCKS1 |
| 7-thionicotinamide-adenine -dinucleotide phosphate | DB01763 | 0.776 | 2.9968 | 0.3188 | 99.9349 | 98.6992 | 91.2906 | NUCKS1 |
| 4-(2,4-Dimethyl-1,3-thiazol-5-yl) -N-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl] -2-pyrimidinamine | DB02915 | 0.774 | 2.9726 | 0.2886 | 99.9268 | 98.5366 | 90.954 | NUCKS1 |
| Ruzinurad | DB19209 | 0.8245 | 3.5258 | 0.28 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | DYRK1A |
| LY-2300559 | DB13016 | 0.821 | 3.4832 | 0.3023 | 99.9919 | 99.8374 | 99.3795 | DYRK1A |
| Nerandomilast | DB18237 | 0.8104 | 3.3521 | 0.2565 | 99.9837 | 99.6748 | 97.4689 | DYRK1A |
| Dodecyltrimethylammonium | DB02779 | 0.8083 | 3.3269 | 0.2834 | 99.9756 | 99.5122 | 97.102 | DYRK1A |
| 3-(6-HYDROXY-NAPHTHALEN -2-YL)-BENZO[D]ISOOXAZOL-6-OL | DB07236 | 0.7954 | 3.1681 | 0.3167 | 99.9675 | 99.3496 | 94.7897 | DYRK1A |
| 2’-Deoxyuridine | DB02256 | 0.7953 | 3.1675 | 0.3452 | 99.9593 | 99.187 | 94.7809 | DYRK1A |
| Alpha-D-Galactose-1-Phosphate | DB02317 | 0.7947 | 3.1601 | 0.2815 | 99.9512 | 99.0244 | 94.6729 | DYRK1A |
| Zk-806450 | DB02112 | 0.7854 | 3.0455 | 0.3473 | 99.9431 | 98.8618 | 93.0045 | DYRK1A |
| Mibolerone | DB11429 | 0.7833 | 3.0204 | 0.3261 | 99.9349 | 98.6992 | 92.6387 | DYRK1A |
| (5R)-N,N-DIETHYL-5-METHYL -2-[(THIOPHEN-2-YLCARBONYL)AMINO] -4,5,6,7-TETRAHYDRO-1-BENZOTHIOPHENE -3-CARBOXAMIDE | DB08033 | 0.779 | 2.9674 | 0.2347 | 99.9268 | 98.5366 | 91.8665 | DYRK1A |
| AZD-9977 | DB15418 | 0.8003 | 3.3393 | 0.3033 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | PIK3CA |
| Rupintrivir | DB05102 | 0.7916 | 3.2311 | 0.3329 | 99.9919 | 99.8374 | 98.4824 | PIK3CA |
| Algestone | DB18000 | 0.7852 | 3.1511 | 0.2734 | 99.9837 | 99.6748 | 97.3593 | PIK3CA |
| (5S)-2-(Cyclooctylamino)-5-methyl -5-propyl-1,3-thiazol-4(5H)-one | DB07866 | 0.7799 | 3.0857 | 0.2671 | 99.9756 | 99.5122 | 96.4422 | PIK3CA |
| N-({(3R,4R)-4-[(benzyloxy)methyl]pyrrolidin -3-yl}methyl)-N-(2-methylpropyl) benzenesulfonamide | DB07505 | 0.7797 | 3.0838 | 0.2617 | 99.9675 | 99.3496 | 96.4161 | PIK3CA |
| 4-[4-(4-Methyl-2-Methylamino-Thiazol -5-Yl)-Pyrimidin-2-Ylamino]-Phenol | DB04407 | 0.7788 | 3.0719 | 0.3167 | 99.9593 | 99.187 | 96.2493 | PIK3CA |
| N-acetylsulfanilyl chloride | DB12337 | 0.7786 | 3.0698 | 0.2934 | 99.9512 | 99.0244 | 96.2189 | PIK3CA |
| Florantyrone | DB08975 | 0.7718 | 2.9847 | 0.3435 | 99.9431 | 98.8618 | 95.0261 | PIK3CA |
| Nateglinide | DB00731 | 0.7689 | 2.9488 | 0.3018 | 99.9349 | 98.6992 | 94.523 | PIK3CA |
| Thioctic acid tromethamine | DB06253 | 0.7683 | 2.9424 | 0.3525 | 99.9268 | 98.5366 | 94.4332 | PIK3CA |
| Ferrous ascorbate | DB14490 | 0.814 | 3.3529 | 0.2848 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | KANSL1 |
| Ilepatril | DB06604 | 0.809 | 3.2914 | 0.2804 | 99.9919 | 99.8374 | 99.0953 | KANSL1 |
| N-Pyridoxyl-2-Methylalanine-5-Phosphate | DB04241 | 0.7919 | 3.0815 | 0.3613 | 99.9837 | 99.6748 | 96.0113 | KANSL1 |
| Didesmethylrocaglamide | DB15496 | 0.791 | 3.0701 | 0.3166 | 99.9756 | 99.5122 | 95.8439 | KANSL1 |
| 4-Nitrophenyl Phosphate | DB04214 | 0.7902 | 3.0599 | 0.2966 | 99.9675 | 99.3496 | 95.6938 | KANSL1 |
| Apstatin | DB04092 | 0.782 | 2.96 | 0.3656 | 99.9593 | 99.187 | 94.2249 | KANSL1 |
| Odevixibat | DB16261 | 0.7805 | 2.9408 | 0.3857 | 99.9512 | 99.0244 | 93.9427 | KANSL1 |
| CRS-3123 | DB12262 | 0.7804 | 2.9395 | 0.2526 | 99.9431 | 98.8618 | 93.9245 | KANSL1 |
| 2-KETO-6-PHOSPHATE-D -GLUCONIC ACID, ALPHA -FURANOSE FORM | DB04663 | 0.7793 | 2.9267 | 0.2983 | 99.9349 | 98.6992 | 93.7364 | KANSL1 |
| Coproporphyrin I containing CO(III) | DB04423 | 0.778 | 2.9106 | 0.2759 | 99.9268 | 98.5366 | 93.4998 | KANSL1 |
| 1-Hydroxyamine-2-Isobutylmalonic Acid | DB02326 | 0.8038 | 3.3643 | 0.2747 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | SETD1A |
| Vinflunine | DB11641 | 0.7996 | 3.3134 | 0.2182 | 99.9919 | 99.8374 | 99.2457 | SETD1A |
| Sobetirome | DB07425 | 0.7993 | 3.3099 | 0.3475 | 99.9837 | 99.6748 | 99.1936 | SETD1A |
| Ellagic acid | DB08846 | 0.7843 | 3.1277 | 0.2739 | 99.9756 | 99.5122 | 96.4966 | SETD1A |
| Paeonol | DB16830 | 0.7745 | 3.0087 | 0.2397 | 99.9675 | 99.3496 | 94.7347 | SETD1A |
| Cladribine | DB00242 | 0.7733 | 2.994 | 0.3192 | 99.9593 | 99.187 | 94.5164 | SETD1A |
| [(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(4-acetonyl-3-carbamoyl -pyridin-1-ium-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroxy -tetrahydrofuran-2-yl]methyl [[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl) -3,4-dihydroxy-tetrahydrofuran-2-yl] methoxy-hydroxy-phosphoryl] phosphate | DB02732 | 0.7688 | 2.9399 | 0.3621 | 99.9512 | 99.0244 | 93.7162 | SETD1A |
| Canrenoic acid | DB09015 | 0.766 | 2.9063 | 0.3699 | 99.9431 | 98.8618 | 93.219 | SETD1A |
| ACV tripeptide | DB02025 | 0.7629 | 2.869 | 0.3143 | 99.9349 | 98.6992 | 92.6663 | SETD1A |
| alpha-Amyl cinnamaldehyde | DB14175 | 0.7624 | 2.8624 | 0.3083 | 99.9268 | 98.5366 | 92.569 | SETD1A |
| Drug Name | DrugBank ID | Raw Score | z-Sscore | Uncertainty | Percentile | Elite Percentile | Probability | Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMI-175 | DB02378 | 0.8096 | 3.4908 | 0.2966 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | MCCC1 |
| Gedatolisib | DB11896 | 0.7983 | 3.352 | 0.3406 | 99.9919 | 99.8374 | 98.0308 | MCCC1 |
| (1S)-2-[(2S,5R)-2-(AMINOMETHYL)-5 -ETHYNYLPYRROLIDIN-1-YL]-1 -CYCLOPENTYL-2-OXOETHANAMINE | DB07356 | 0.789 | 3.2374 | 0.3992 | 99.9837 | 99.6748 | 96.4038 | MCCC1 |
| N-(3-chlorophenyl)-N-methyl-2-oxo-3 -[(3,4,5-trimethyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methyl] -2H-indole-5-sulfonamide | DB07369 | 0.7753 | 3.0683 | 0.4258 | 99.9756 | 99.5122 | 94.0031 | MCCC1 |
| Testosterone decanoate | DB16001 | 0.7739 | 3.0506 | 0.289 | 99.9675 | 99.3496 | 93.7512 | MCCC1 |
| N-Alpha-(2-Naphthylsulfonyl)-N(3-Amidino -L-Phenylalaninyl)-4-Acetyl-Piperazine | DB04125 | 0.7727 | 3.036 | 0.3411 | 99.9593 | 99.187 | 93.5443 | MCCC1 |
| Nemonoxacin | DB06600 | 0.766 | 2.953 | 0.3403 | 99.9512 | 99.0244 | 92.3665 | MCCC1 |
| Fludeoxyglucose | DB15107 | 0.7655 | 2.9465 | 0.2928 | 99.9431 | 98.8618 | 92.274 | MCCC1 |
| GSK-2881078 | DB16888 | 0.7615 | 2.8972 | 0.2934 | 99.9349 | 98.6992 | 91.5738 | MCCC1 |
| Valspodar | DB11869 | 0.7581 | 2.8552 | 0.3053 | 99.9268 | 98.5366 | 90.9779 | MCCC1 |
| Zinc cation | DB14532 | 0.7966 | 3.285 | 0.274 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | WWOX |
| Cyproterone acetate | DB04839 | 0.7818 | 3.1064 | 0.3301 | 99.9919 | 99.8374 | 97.3973 | WWOX |
| Norethandrolone | DB12787 | 0.7746 | 3.0186 | 0.2726 | 99.9837 | 99.6748 | 96.1187 | WWOX |
| Lutein | DB00137 | 0.7739 | 3.0108 | 0.3759 | 99.9756 | 99.5122 | 96.0039 | WWOX |
| Hydrocortisone acetate | DB14539 | 0.7716 | 2.9825 | 0.2526 | 99.9675 | 99.3496 | 95.5923 | WWOX |
| Cytidine-5’-Monophosphate | DB03403 | 0.7698 | 2.9607 | 0.2689 | 99.9593 | 99.187 | 95.2748 | WWOX |
| Brivudine | DB03312 | 0.7687 | 2.9482 | 0.2961 | 99.9512 | 99.0244 | 95.092 | WWOX |
| THIOPHENE-2,5-DISULFONIC ACID 2 -AMIDE-5-(4-METHYL-BENZYLAMIDE) | DB07363 | 0.7674 | 2.9324 | 0.2946 | 99.9431 | 98.8618 | 94.8617 | WWOX |
| 2-Methyl-3-(2-Aminothiazolo)Propanal | DB03024 | 0.7664 | 2.9202 | 0.2721 | 99.9349 | 98.6992 | 94.6842 | WWOX |
| Talinolol | DB11770 | 0.7652 | 2.9057 | 0.325 | 99.9268 | 98.5366 | 94.4735 | WWOX |
| Acteoside | DB12996 | 0.7781 | 3.2404 | 0.3076 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | CCT3 |
| Hypophosphite | DB04053 | 0.7778 | 3.2365 | 0.3599 | 99.9919 | 99.8374 | 99.9413 | CCT3 |
| (2S)-2-[(2,1,3-BENZOTHIADIAZOL-4 -YLSULFONYL)AMINO]-2-PHENYL-N -PYRIDIN-4-YLACETAMIDE | DB07568 | 0.776 | 3.2149 | 0.2205 | 99.9837 | 99.6748 | 99.6192 | CCT3 |
| Osalmid | DB16273 | 0.7715 | 3.1599 | 0.3294 | 99.9756 | 99.5122 | 98.7977 | CCT3 |
| Open Form of 2’-Deoxy-Ribofuranose -5’-Phosphate | DB04087 | 0.77 | 3.1406 | 0.3502 | 99.9675 | 99.3496 | 98.5106 | CCT3 |
| UK-390957 | DB11719 | 0.7684 | 3.1212 | 0.3623 | 99.9593 | 99.187 | 98.2208 | CCT3 |
| SRA-737 | DB16876 | 0.7674 | 3.1096 | 0.3314 | 99.9512 | 99.0244 | 98.047 | CCT3 |
| Iodo-Willardiine | DB02818 | 0.7649 | 3.079 | 0.3202 | 99.9431 | 98.8618 | 97.5903 | CCT3 |
| Protokylol | DB06814 | 0.7633 | 3.0585 | 0.3364 | 99.9349 | 98.6992 | 97.284 | CCT3 |
| XL-888 | DB12981 | 0.7605 | 3.0253 | 0.3113 | 99.9268 | 98.5366 | 96.7882 | CCT3 |
| Candoxatrilat | DB11623 | 0.8117 | 3.4084 | 0.3816 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | CRLS1 |
| Tivantinib | DB12200 | 0.8109 | 3.3979 | 0.3615 | 99.9919 | 99.8374 | 99.8439 | CRLS1 |
| (R)-tacrine(10)-hupyridone | DB04614 | 0.8096 | 3.3829 | 0.2907 | 99.9837 | 99.6748 | 99.6194 | CRLS1 |
| 9(S)-HODE | DB07302 | 0.7971 | 3.228 | 0.2996 | 99.9756 | 99.5122 | 97.3065 | CRLS1 |
| GSK-2982772 | DB16875 | 0.7934 | 3.1826 | 0.3392 | 99.9675 | 99.3496 | 96.6298 | CRLS1 |
| RU82197 | DB03268 | 0.7882 | 3.118 | 0.2283 | 99.9593 | 99.187 | 95.6651 | CRLS1 |
| Sulthiame | DB08329 | 0.7774 | 2.9851 | 0.3236 | 99.9512 | 99.0244 | 93.6806 | CRLS1 |
| Naluzotan | DB05562 | 0.7746 | 2.951 | 0.3131 | 99.9431 | 98.8618 | 93.1709 | CRLS1 |
| EP-217609 | DB18393 | 0.7741 | 2.944 | 0.2171 | 99.9349 | 98.6992 | 93.0661 | CRLS1 |
| Brefeldin A | DB07348 | 0.7731 | 2.9318 | 0.3294 | 99.9268 | 98.5366 | 92.885 | CRLS1 |
| 25-desacetylrifapentine | DB15213 | 0.7947 | 3.31 | 0.3141 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | PMVK |
| Diethylcarbamazine | DB00711 | 0.7928 | 3.2864 | 0.3038 | 99.9919 | 99.8374 | 99.6637 | PMVK |
| Dexepicatechin | DB19253 | 0.7925 | 3.2826 | 0.2872 | 99.9837 | 99.6748 | 99.6098 | PMVK |
| 5-ALPHA-PREGNANE-3-BETA -OL-HEMISUCCINATE | DB08510 | 0.7908 | 3.262 | 0.3144 | 99.9756 | 99.5122 | 99.3156 | PMVK |
| L-Histidine Beta Naphthylamide | DB01938 | 0.7906 | 3.2594 | 0.3844 | 99.9675 | 99.3496 | 99.2781 | PMVK |
| (5E)-14-CHLORO-15,17-DIHYDROXY -4,7,8,9,10,11-HEXAHYDRO-2 -BENZOXACYCLOPENTADECINE -1,12(3H,13H)-DIONE | DB08153 | 0.7792 | 3.12 | 0.318 | 99.9593 | 99.187 | 97.2896 | PMVK |
| Indeglitazar | DB07724 | 0.7773 | 3.0965 | 0.271 | 99.9512 | 99.0244 | 96.9553 | PMVK |
| Deoxycytidylyl-3’,5’-guanosine | DB03326 | 0.7708 | 3.0171 | 0.3722 | 99.9431 | 98.8618 | 95.8224 | PMVK |
| Formaldehyde | DB03843 | 0.7693 | 2.9986 | 0.1982 | 99.9349 | 98.6992 | 95.5585 | PMVK |
| Drostanolone | DB00858 | 0.7673 | 2.974 | 0.3675 | 99.9268 | 98.5366 | 95.208 | PMVK |
References
- Keane, H.; Ryan, B.J.; Jackson, B.; Whitmore, A.; Wade-Martins, R. Protein-protein interaction networks identify targets which rescue the MPP+ cellular model of Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17004. [Google Scholar]
- Akki, A.J.; Patil, S.A.; Hungund, S.; Sahana, R.; Patil, M.M.; Kulkarni, R.V.; Reddy, K.R.; Zameer, F.; Raghu, A.V. Advances in Parkinson’s disease research—A computational network pharmacological approach. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 139, 112758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, H.N.; Esteves, A.R.; Empadinhas, N.; Cardoso, S.M. Parkinson’s disease: A multisystem disorder. Neurosci. Bull. 2023, 39, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomkins, J.E.; Manzoni, C. Advances in protein-protein interaction network analysis for Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 155, 105395. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, A.; Ash, P.E.; Wolozin, B.; Emili, A. Protein interaction network biology in neuroscience. Proteomics 2021, 21, 1900311. [Google Scholar]
- Santos-Lobato, B.L.; Vidal, A.F.; Ribeiro-dos Santos, Â. Regulatory miRNA–mRNA networks in Parkinson’s disease. Cells 2021, 10, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvam, S.; Ayyavoo, V. Biomarkers in neurodegenerative diseases: A broad overview. Explor. Neuroprotective Ther. 2024, 4, 119–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiscon, G.; Conte, F.; Farina, L.; Paci, P. Network-based approaches to explore complex biological systems towards network medicine. Genes 2018, 9, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Park, J.H.; Cho, Y.R. Network-based approaches for disease-gene association prediction using protein-protein interaction networks. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.H.; Yi, H.C.; You, Z.H. Construction and comprehensive analysis of a molecular association network via lncRNA–miRNA–disease–drug–protein graph. Cells 2019, 8, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z.; Arora, I.; Zhang, E.Y.; Laufer, V.; Bridges, S.L.; Chen, J.Y. Repositioning drugs by targeting network modules: A Parkinson’s disease case study. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salemi, M.; Marchese, G.; Lanza, G.; Cosentino, F.I.; Salluzzo, M.G.; Schillaci, F.A.; Ventola, G.M.; Cordella, A.; Ravo, M.; Ferri, R. Role and Dysregulation of miRNA in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellucci, A.; Bubacco, L.; Longhena, F.; Parrella, E.; Faustini, G.; Porrini, V.; Bono, F.; Missale, C.; Pizzi, M. Nuclear factor-κB dysregulation and α-synuclein pathology: Critical interplay in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 68. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Ding, Q.; Wang, X. “Network target” theory and network pharmacology. In Network Pharmacology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, J.; Yin, N.; Ma, X.; Lai, L. Systems biology brings new dimensions for structure-based drug design. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 11556–11565. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, R.J.; Avramopoulos, D.; Jantzie, L.L.; McCallion, A.S. Neuroinflammation represents a common theme amongst genetic and environmental risk factors for Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 223. [Google Scholar]
- Toader, C.; Tataru, C.P.; Munteanu, O.; Serban, M.; Covache-Busuioc, R.A.; Ciurea, A.V.; Enyedi, M. Decoding Neurodegeneration: A Review of Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Advances in Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and ALS. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtiani, M.; Salehzadeh-Yazdi, A.; Razaghi-Moghadam, Z.; Hennig, H.; Wolkenhauer, O.; Mirzaie, M.; Jafari, M. A systematic survey of centrality measures for protein-protein interaction networks. BMC Syst. Biol. 2018, 12, 80. [Google Scholar]
- Rout, T.; Mohapatra, A.; Kar, M. A systematic review of graph-based explorations of PPI networks: Methods, resources, and best practices. Netw. Model. Anal. Health Inform. Bioinform. 2024, 13, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Nayar, G.; Altman, R.B. Heterogeneous network approaches to protein pathway prediction. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2024, 23, 2727–2739. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, K.; Lee, H.; Jeon, J.; Lee, J.; Yoon, J. The protein-protein interaction network of hereditary parkinsonism genes is a hierarchical scale-free network. Yonsei Med J. 2022, 63, 724. [Google Scholar]
- Parikshak, N.N.; Gandal, M.J.; Geschwind, D.H. Systems biology and gene networks in neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 16, 441–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoletti, V.; Palermo, G.; Del Prete, E.; Mancuso, M.; Ceravolo, R. Understanding the multiple role of mitochondria in Parkinson’s disease and related disorders: Lesson from genetics and protein–interaction network. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 636506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bele, T. Network-based investigation to identify the common gene-disease linkage between Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and epilepsy’. Netw. Biol. 2024, 14, 254. [Google Scholar]
- Rakshit, H.; Rathi, N.; Roy, D. Construction and analysis of the protein-protein interaction networks based on gene expression profiles of Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, K.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Z.; Savitz, S.; Jiang, X.; Tang, J.; Kim, Y. Drug repurposing for COVID-19 using graph neural network and harmonizing multiple evidence. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.G.; Saha, A.; Hasan, M.Z.; Noori, S.R.H.; Moustafa, A. A systematic review of graph neural network in healthcare-based applications: Recent advances, trends, and future directions. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 15145–15170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Dai, H.; Knight, E.; Wu, F.; Li, Y.; Li, T.; Gerstein, M. A survey of generative AI for de novo drug design: New frontiers in molecule and protein generation. Briefings Bioinform. 2024, 25, bbae338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Yao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z. Customized subgraph selection and encoding for drug-drug interaction prediction. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 109582–109608. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Pan, S.; Chen, F.; Long, G.; Zhang, C.; Yu, P.S. A comprehensive survey on graph neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 32, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Cui, G.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, C.; Sun, M. Graph neural networks: A review of methods and applications. AI Open 2020, 1, 57–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Hou, Y.; Shen, J.; Huang, Y.; Martin, W.; Cheng, F. Network-based drug repurposing for novel coronavirus 2019-nCoV/SARS-CoV-2. Cell Discov. 2020, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paranjpe, M.D.; Taubes, A.; Sirota, M. Insights into computational drug repurposing for neurodegenerative disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 40, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vicidomini, C.; Fontanella, F.; D’Alessandro, T.; Roviello, G.N. A Survey on Computational Methods in Drug Discovery for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldewachi, H.; Al-Zidan, R.N.; Conner, M.T.; Salman, M.M. High-throughput screening platforms in the discovery of novel drugs for neurodegenerative diseases. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Song, X.; Ma, T.; Pan, X.; Zhou, Y.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, K.; Karypis, G.; Cheng, F. Repurpose open data to discover therapeutics for COVID-19 using deep learning. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 4624–4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ma, W.; Yang, M.; Tang, X. Drug repurposing based on the DTD-GNN graph neural network: Revealing the relationships among drugs, targets and diseases. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yella, J.K.; Ghandikota, S.K.; Jegga, A.G. GraMDTA: Multimodal graph neural networks for predicting drug-target associations. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 6–8 December 2022; pp. 1957–1965. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Li, Z.; Ni, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, D.; Liu, Q.; Wu, S.; Yu, J.; Wang, L. Beyond efficiency: Molecular data pruning for enhanced generalization. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 18036–18061. [Google Scholar]
- Lysenko, A.; Sharma, A.; Boroevich, K.A.; Tsunoda, T. An integrative machine learning approach for prediction of toxicity-related drug safety. Life Sci. Alliance 2018, 1, e201800098. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Qin, S.; Van Lehn, R.C.; Balaprakash, P.; Zavala, V.M. Uncertainty quantification for molecular property predictions with graph neural architecture search. Digit. Discov. 2024, 3, 1534–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utriainen, M.; Morris, J.H. clusterMaker2: A major update to clusterMaker, a multi-algorithm clustering app for Cytoscape. BMC Bioinform. 2023, 24, 134. [Google Scholar]
- Maere, S.; Heymans, K.; Kuiper, M. BiNGO: A Cytoscape plugin to assess overrepresentation of gene ontology categories in biological networks. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3448–3449. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Knox, C.; Wilson, M.; Klinger, C.M.; Franklin, M.; Oler, E.; Wilson, A.; Pon, A.; Cox, J.; Chin, N.E.; Strawbridge, S.A.; et al. DrugBank 6.0: The DrugBank knowledgebase for 2024. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D1265–D1275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Group, P.S. Effects of tocopherol and deprenyl on the progression of disability in early Parkinson’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 328, 176–183. [Google Scholar]
- Group, P.S. Impact of deprenyl and tocopherol treatment on Parkinson’s disease in DATATOP patients requiring levodopa. Ann. Neurol. 1996, 39, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Seth, P.K. Functional association between NUCKS1 gene and Parkinson disease: A potential susceptibility biomarker. Bioinformation 2019, 15, 548. [Google Scholar]
- Wainberg, M.; Andrews, S.J.; Tripathy, S.J. Shared genetic risk loci between Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias, Parkinson’s disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2023, 15, 113. [Google Scholar]
- Popescu, M.C.; Balas, V.E.; Perescu-Popescu, L.; Mastorakis, N. Multilayer perceptron and neural networks. WSEAS Trans. Circuits Syst. 2009, 8, 579–588. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Li, Z.; Du, B.; Zhang, M.; Liu, J. Reluplex made more practical: Leaky ReLU. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications (ISCC), Rennes, France, 7–10 July 2020; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
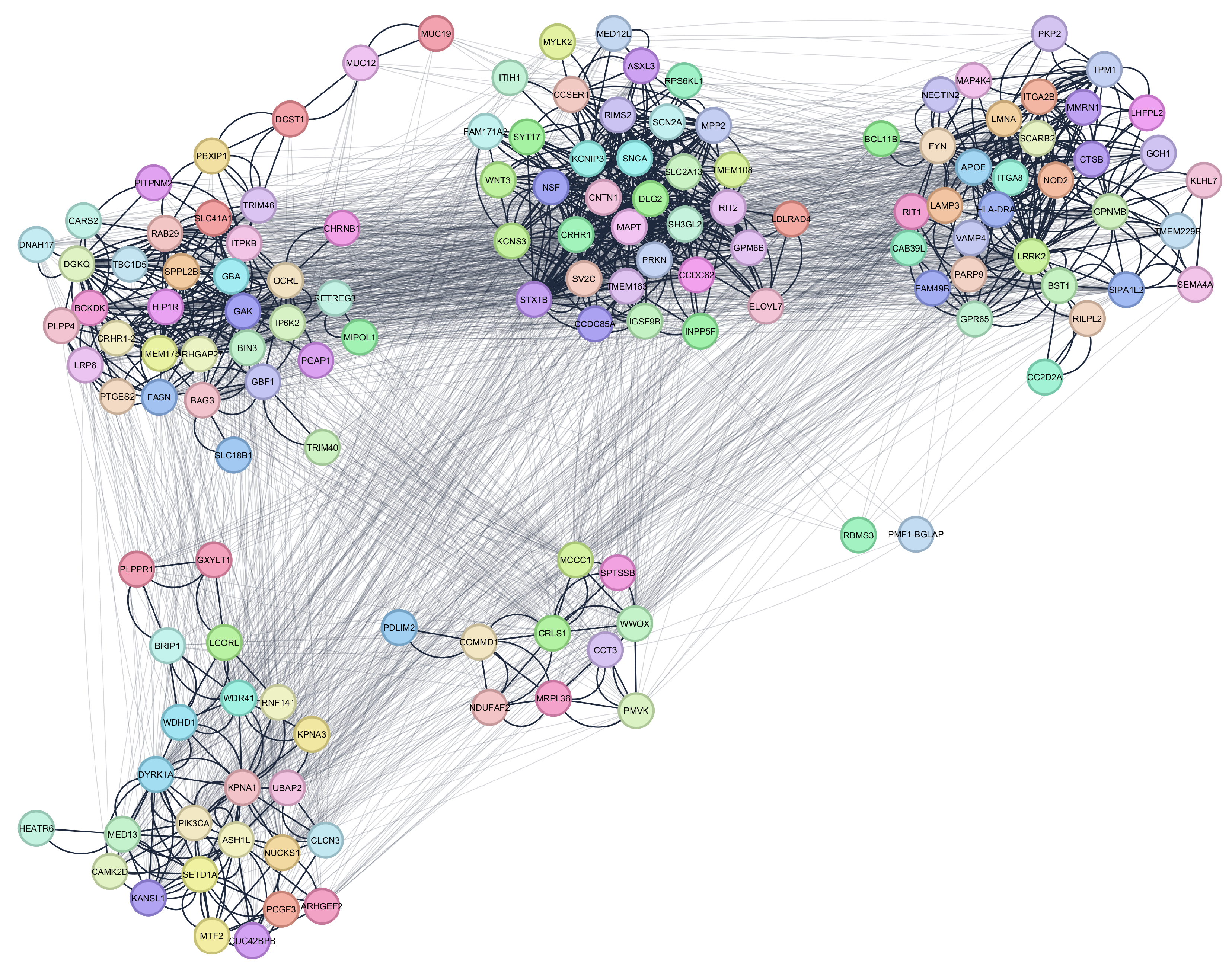
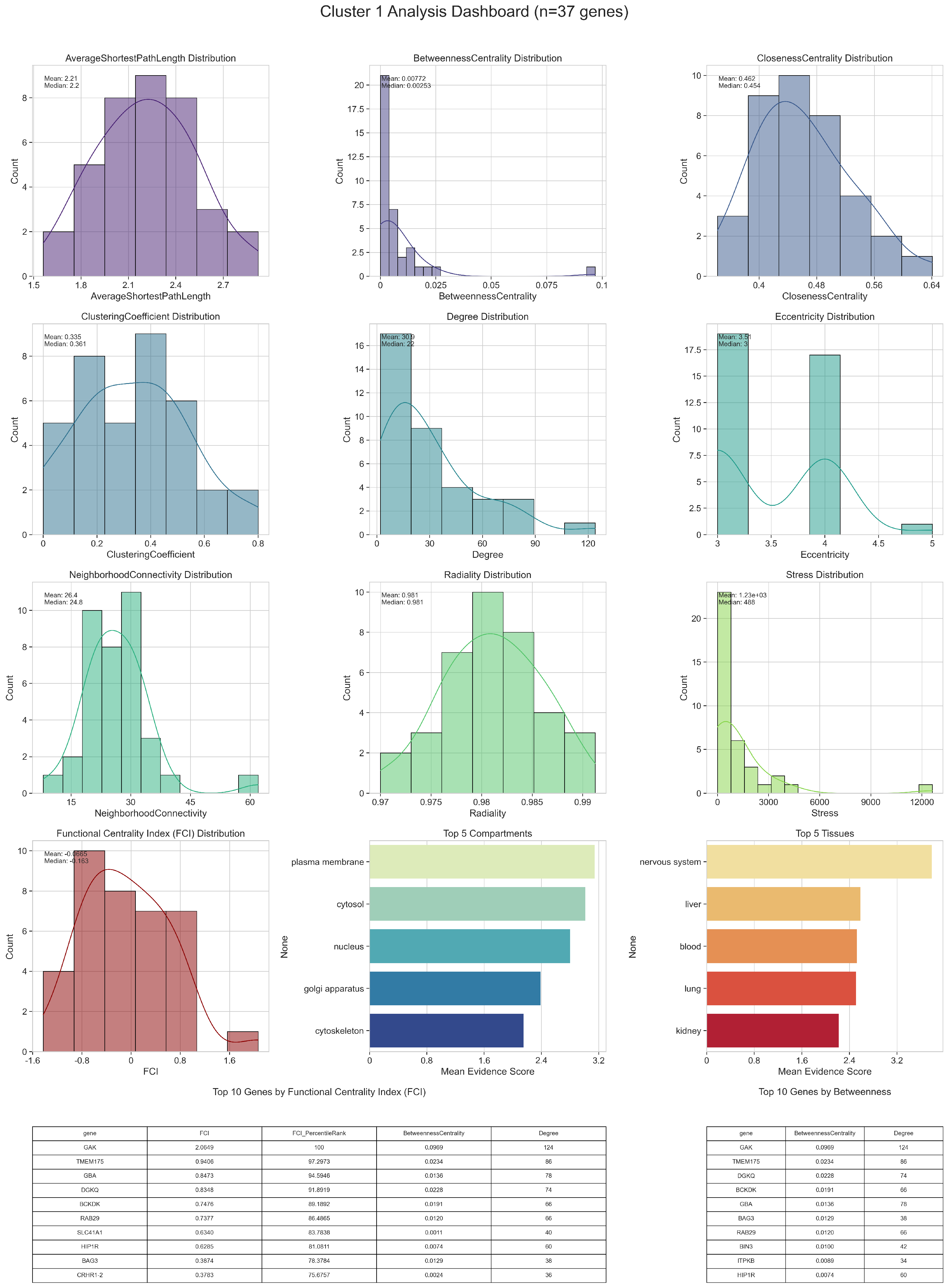
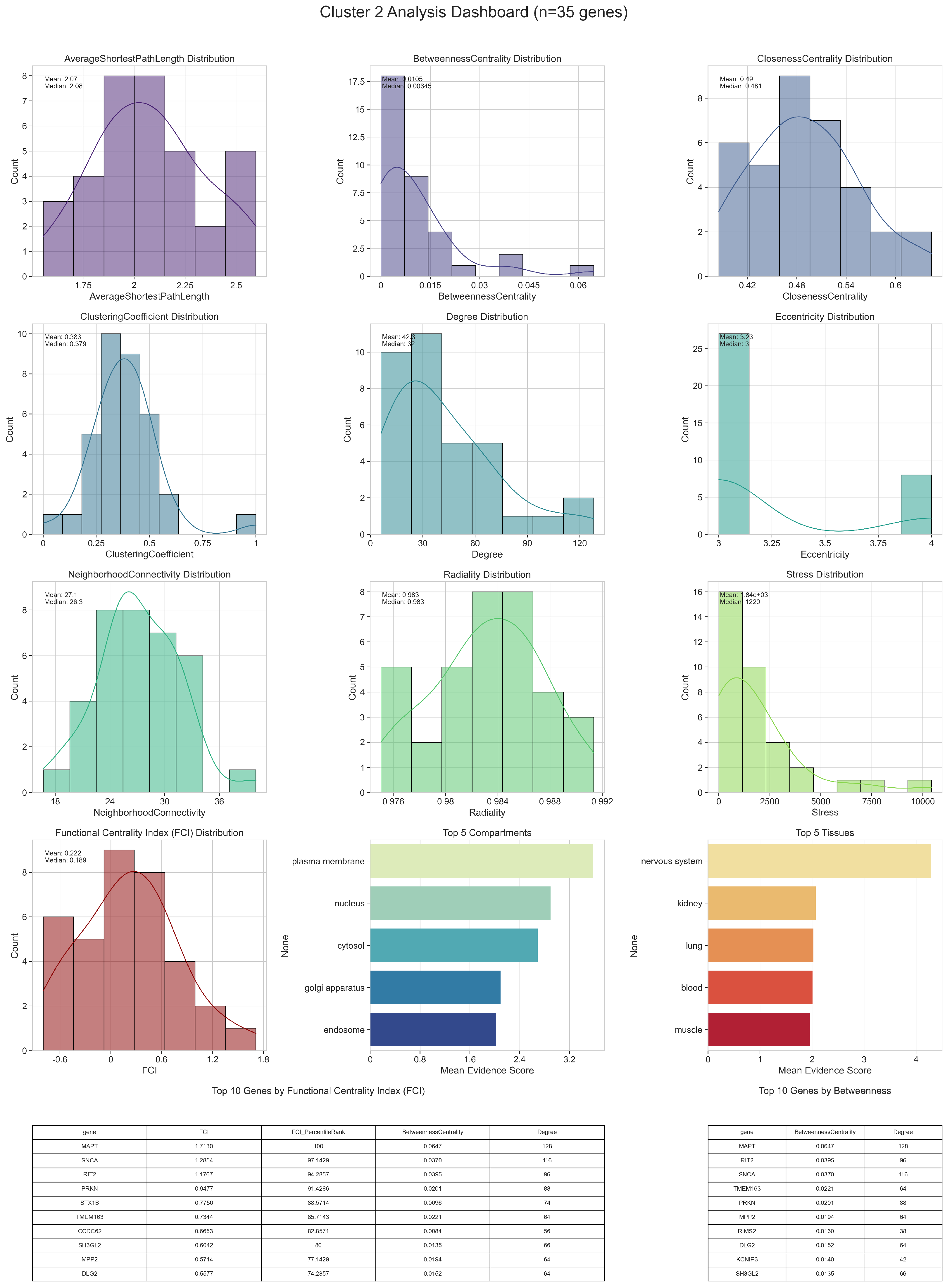
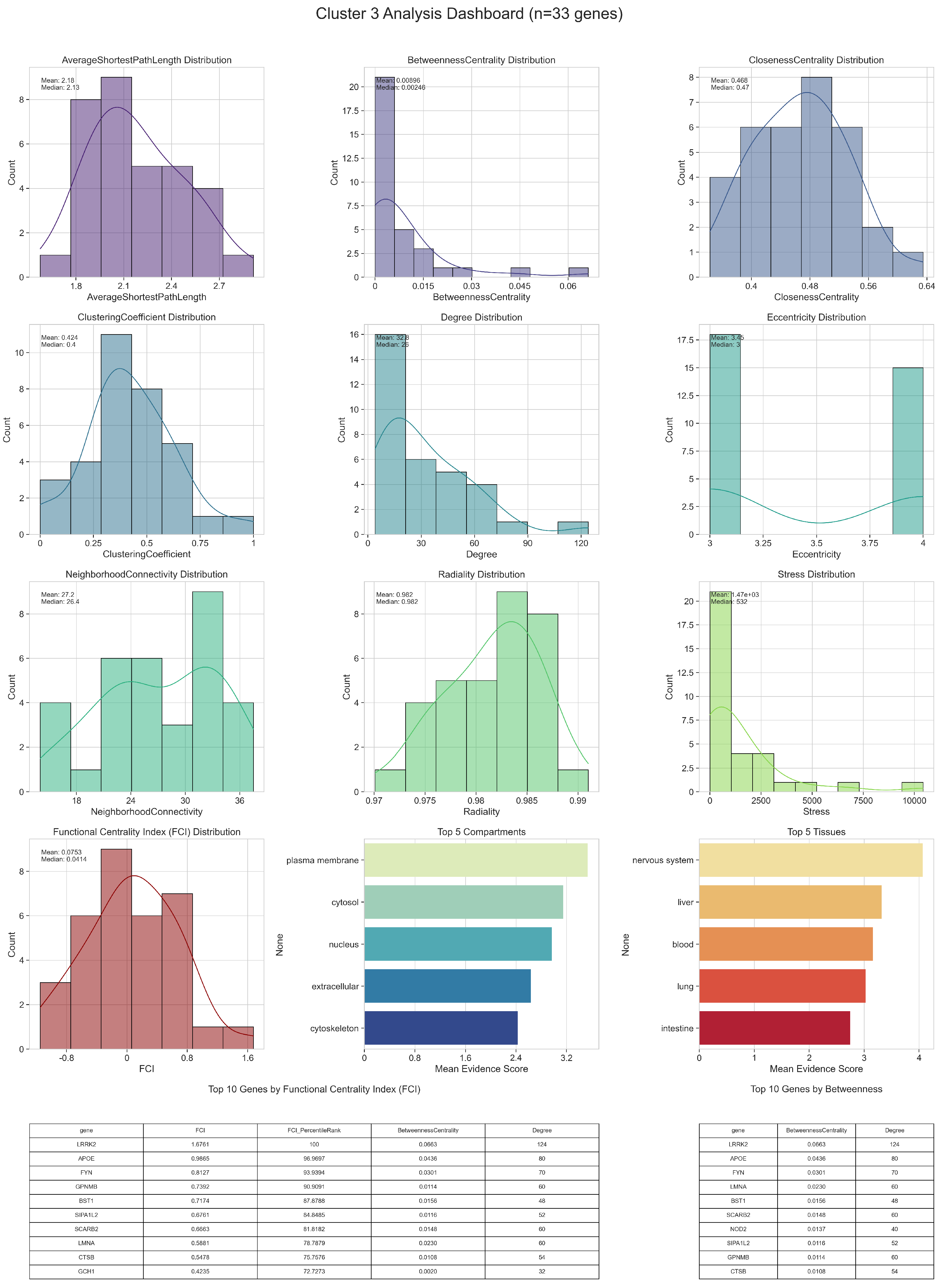
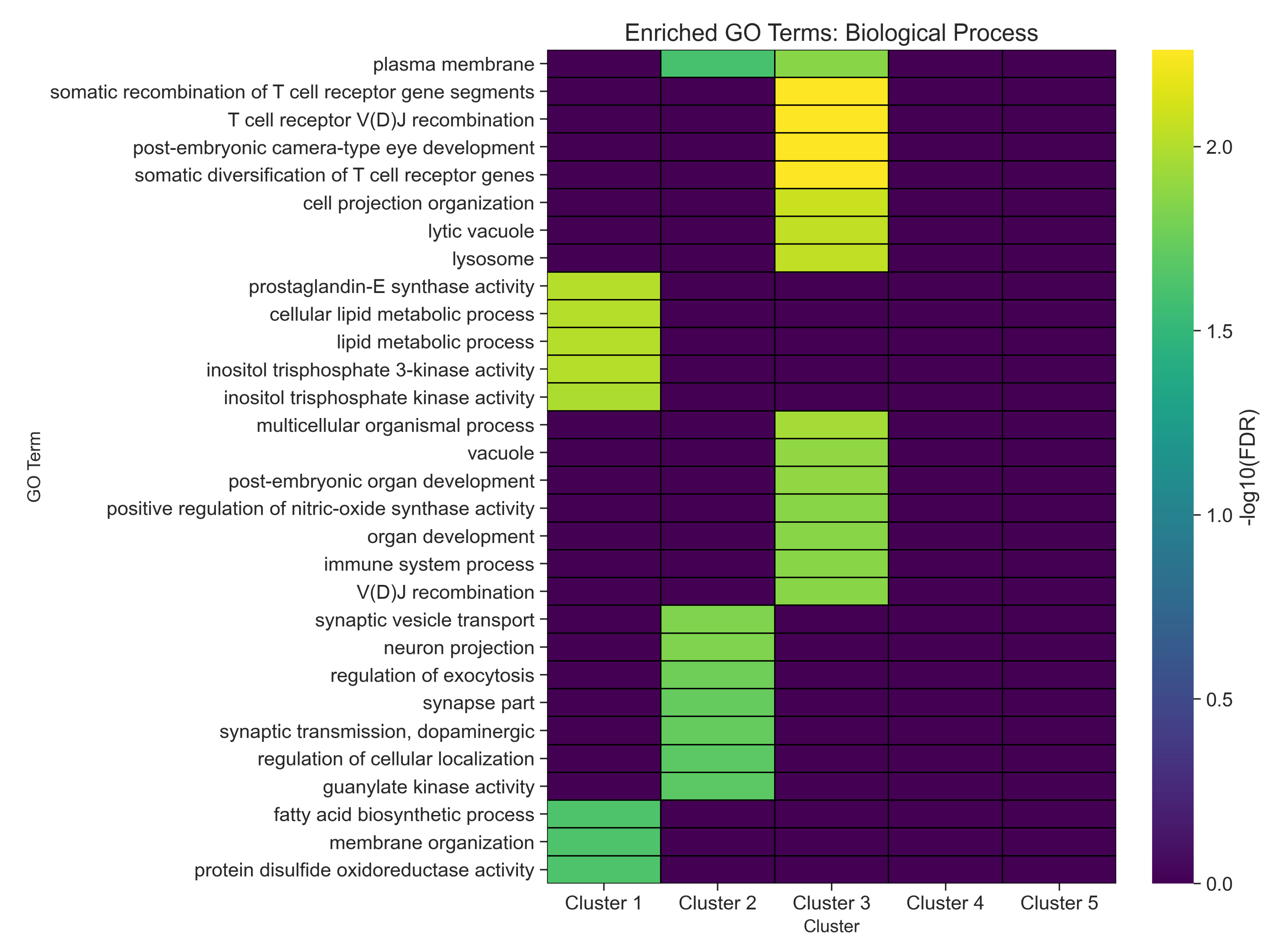

| GO ID | GO Term | p-Value | FDR | Cluster Frequency (%) | Background Frequency (%) | Enrichment Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50220 | prostaglandin-E synthase activity | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 8440 | inositol trisphosphate 3-kinase activity | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 44255 | cellular lipid metabolic process | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 6629 | lipid metabolic process | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 51766 | inositol trisphosphate kinase activity | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 30384 | phosphoinositide metabolic process | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 6633 | fatty acid biosynthetic process | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 46457 | prostanoid biosynthetic process | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 16044 | cellular membrane organization | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 61024 | membrane organization | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 1516 | prostaglandin biosynthetic process | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 15035 | protein disulfide oxidoreductase activity | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 15036 | disulfide oxidoreductase activity | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 46578 | regulation of Ras protein signal transduction | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 6692 | prostanoid metabolic process | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 6693 | prostaglandin metabolic process | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 917 | barrier septum formation | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 47323 | [3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate dehydrogenase (acetyl-transferring)] kinase activity | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 4316 | 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase activity | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 19171 | 3-hydroxyacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] dehydratase activity | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 |
| GO ID | GO Term | p-Value | FDR | Cluster Frequency (%) | Background Frequency (%) | Enrichment Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 48489 | synaptic vesicle transport | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 43005 | neuron projection | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 17157 | regulation of exocytosis | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 44456 | synapse part | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 1963 | synaptic transmission, dopaminergic | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 60341 | regulation of cellular localization | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 4385 | guanylate kinase activity | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 5886 | plasma membrane | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 80010 | regulation of oxygen and reactive oxygen species metabolic process | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 6836 | neurotransmitter transport | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 8021 | synaptic vesicle | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 44463 | cell projection part | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 19226 | transmission of nerve impulse | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 45202 | synapse | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 30424 | axon | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 23046 | signaling process | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 42417 | dopamine metabolic process | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 23060 | signal transmission | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 46928 | regulation of neurotransmitter secretion | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 6810 | transport | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 |
| GO ID | GO Term | p-Value | FDR | Cluster Frequency (%) | Background Frequency (%) | Enrichment Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31077 | post-embryonic camera-type eye development | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 33153 | T cell receptor V(D)J recombination | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 2568 | somatic diversification of T cell receptor genes | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 2681 | somatic recombination of T cell receptor gene segments | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 30030 | cell projection organization | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 323 | lytic vacuole | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 5764 | lysosome | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 32501 | multicellular organismal process | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 48569 | post-embryonic organ development | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 5773 | vacuole | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 51000 | positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 48513 | organ development | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 2376 | immune system process | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 33151 | V(D)J recombination | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 5886 | plasma membrane | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 31982 | vesicle | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 7275 | multicellular organismal development | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 51496 | positive regulation of stress fiber assembly | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 32770 | positive regulation of monooxygenase activity | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 | ||
| 45471 | response to ethanol | 0.17% | 10.0% | 0.02 |
| GO ID | GO Term | p-Value | FDR | Cluster Frequency (%) | Background Frequency (%) | Enrichment Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8139 | nuclear localization sequence binding | 0.12% | 10.0% | 0.01 | ||
| 6607 | NLS-bearing substrate import into nucleus | 0.12% | 10.0% | 0.01 | ||
| 17048 | Rho GTPase binding | 0.12% | 10.0% | 0.01 | ||
| 18024 | histone-lysine N-methyltransferase activity | 0.12% | 10.0% | 0.01 | ||
| 16279 | protein-lysine N-methyltransferase activity | 0.12% | 10.0% | 0.01 | ||
| 5048 | signal sequence binding | 0.12% | 10.0% | 0.01 | ||
| 5654 | nucleoplasm | 0.12% | 10.0% | 0.01 | ||
| 16278 | lysine N-methyltransferase activity | 0.12% | 10.0% | 0.01 | ||
| 31252 | cell leading edge | 0.12% | 10.0% | 0.01 | ||
| 42054 | histone methyltransferase activity | 0.12% | 10.0% | 0.01 |
| GO ID | GO Term | p-Value | FDR | Cluster Frequency (%) | Background Frequency (%) | Enrichment Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4631 | phosphomevalonate kinase activity | 0.05% | 10.0% | 0.01 | ||
| 5739 | mitochondrion | 0.05% | 10.0% | 0.01 | ||
| 6768 | biotin metabolic process | 0.05% | 10.0% | 0.01 | ||
| 5737 | cytoplasm | 0.05% | 10.0% | 0.01 | ||
| 4485 | methylcrotonoyl-CoA carboxylase activity | 0.05% | 10.0% | 0.01 |
| Drug | DrugBank ID | Targets | z-Score | Percentile (%) | Probability (%) | Uncertainty |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dithiazanine | DB11516 | GAK, KANSL1 | 3.01 | 99.9 | 94.7 | 0.1425 |
| Ceftolozane | DB09050 | TMEM175, RIT2 | 2.96 | 99.9 | 89.1 | 0.2589 |
| DL-alpha-Tocopherol | DB14476 | BCKDK, MAPT | 3.15 | 100.0 | 93.6 | 0.2629 |
| Bromisoval | DB13370 | LRRK2, APOE | 3.37 | 100.0 | 98.6 | 0.2198 |
| Imidurea | DB14075 | APOE, CRLS1 | 2.97 | 99.9 | 94.8 | 0.2147 |
| Medronic acid | DB14078 | GPNMB, BST1 | 2.97 | 99.9 | 85.8 | 0.2464 |
| Modufolin | DB12676 | NUCKS1, WWOX | 2.83 | 99.8 | 89.6 | 0.3004 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akgüller, Ö.; Balcı, M.A.; Cioca, G. A Multi-Modal Graph Neural Network Framework for Parkinson’s Disease Therapeutic Discovery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094453
Akgüller Ö, Balcı MA, Cioca G. A Multi-Modal Graph Neural Network Framework for Parkinson’s Disease Therapeutic Discovery. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094453
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkgüller, Ömer, Mehmet Ali Balcı, and Gabriela Cioca. 2025. "A Multi-Modal Graph Neural Network Framework for Parkinson’s Disease Therapeutic Discovery" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094453
APA StyleAkgüller, Ö., Balcı, M. A., & Cioca, G. (2025). A Multi-Modal Graph Neural Network Framework for Parkinson’s Disease Therapeutic Discovery. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094453






