Intraplantar β-Caryophyllene Alleviates Pain and Inflammation in STZ-Induced Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy via CB2 Receptor Activation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
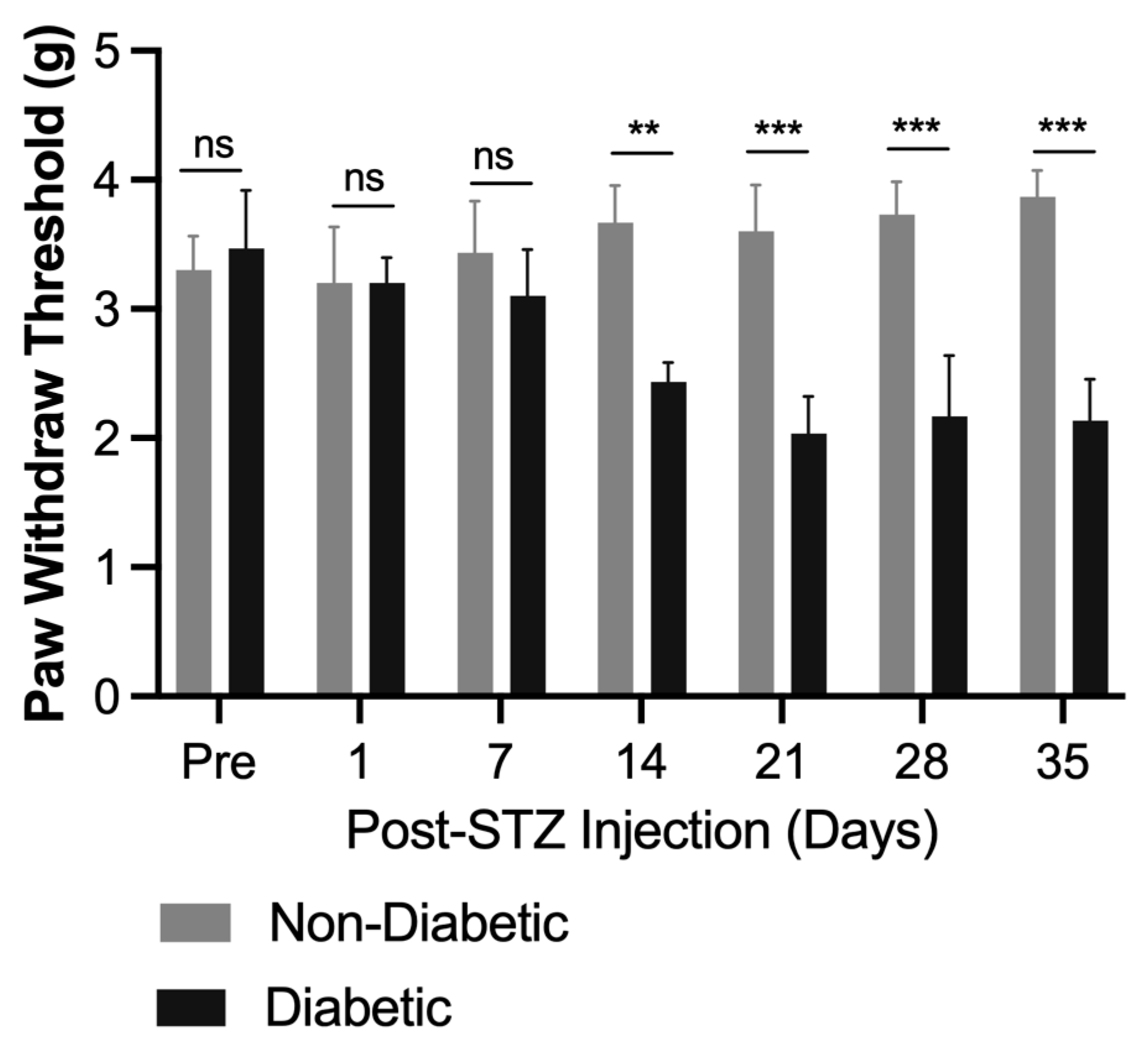
2.1. Impact of BCP on Body Weight and Blood Glucose Levels in an STZ-Induced DPN Mouse Model
2.2. Acute Local BCP Injections Alleviate Mechanical Allodynia in STZ-Induced DPN Mouse Model via Peripheral CB2 Receptor Mediation
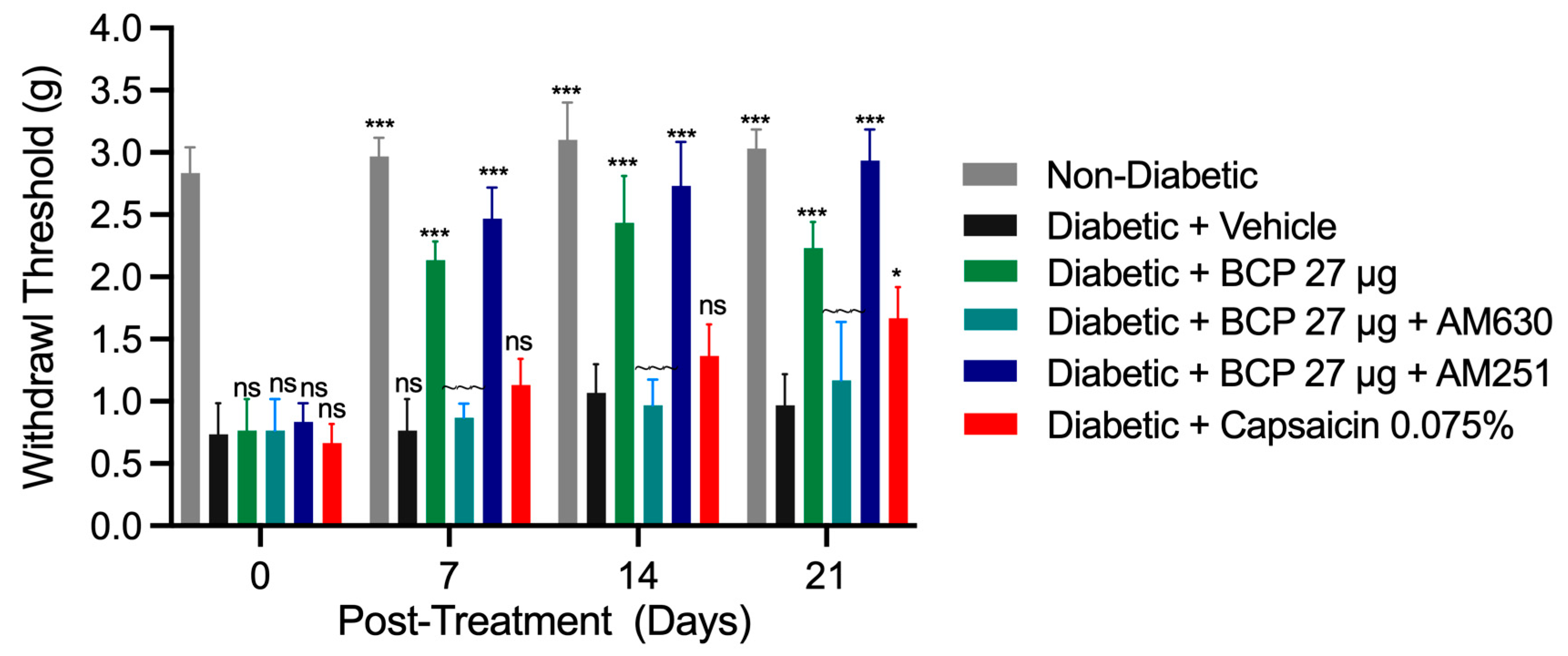
2.3. Sustained Anti-Allodynic Effects of Chronic Topical BCP Injections in STZ-Induced DPN Mouse Model
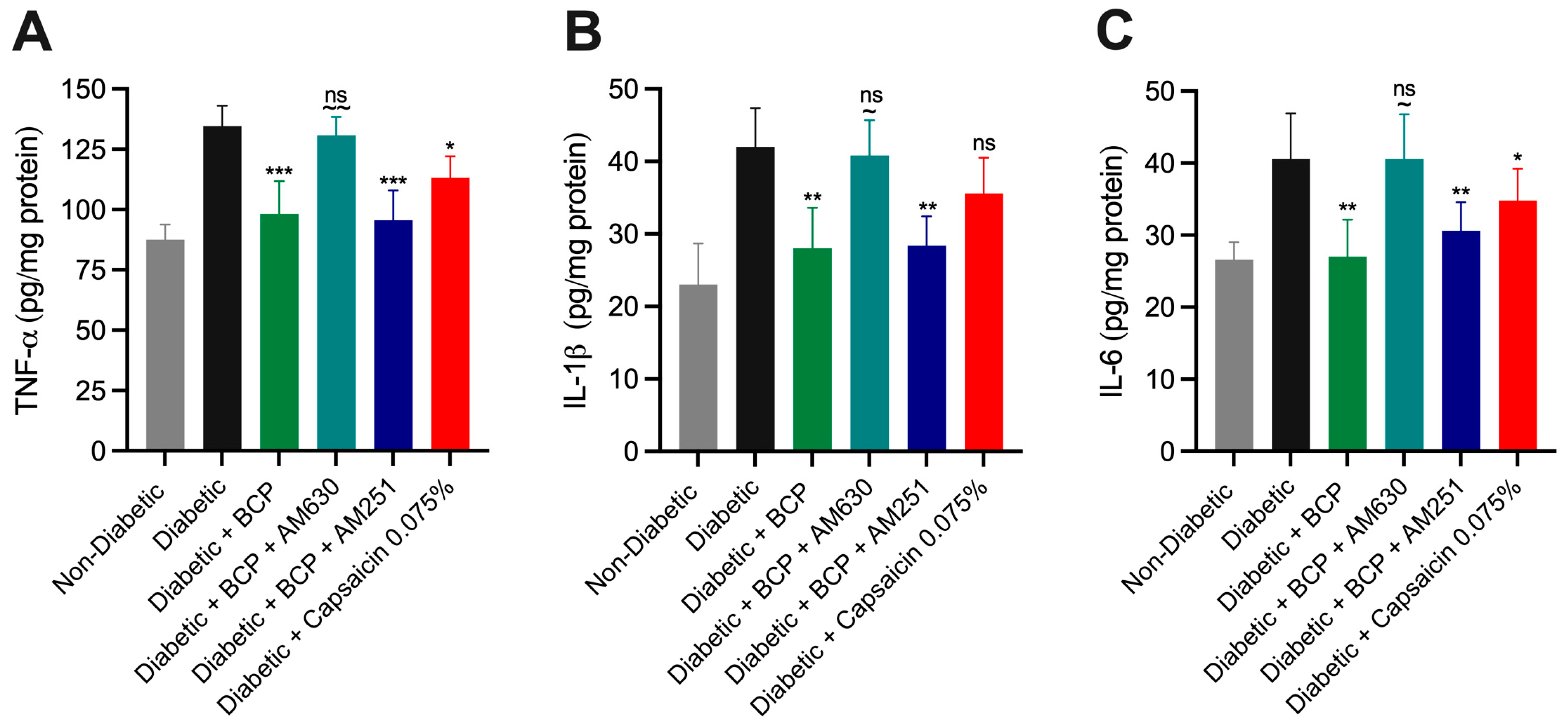
2.4. Chronic Topical BCP Administration Modulates Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Levels in STZ-Induced DPN Mouse Model
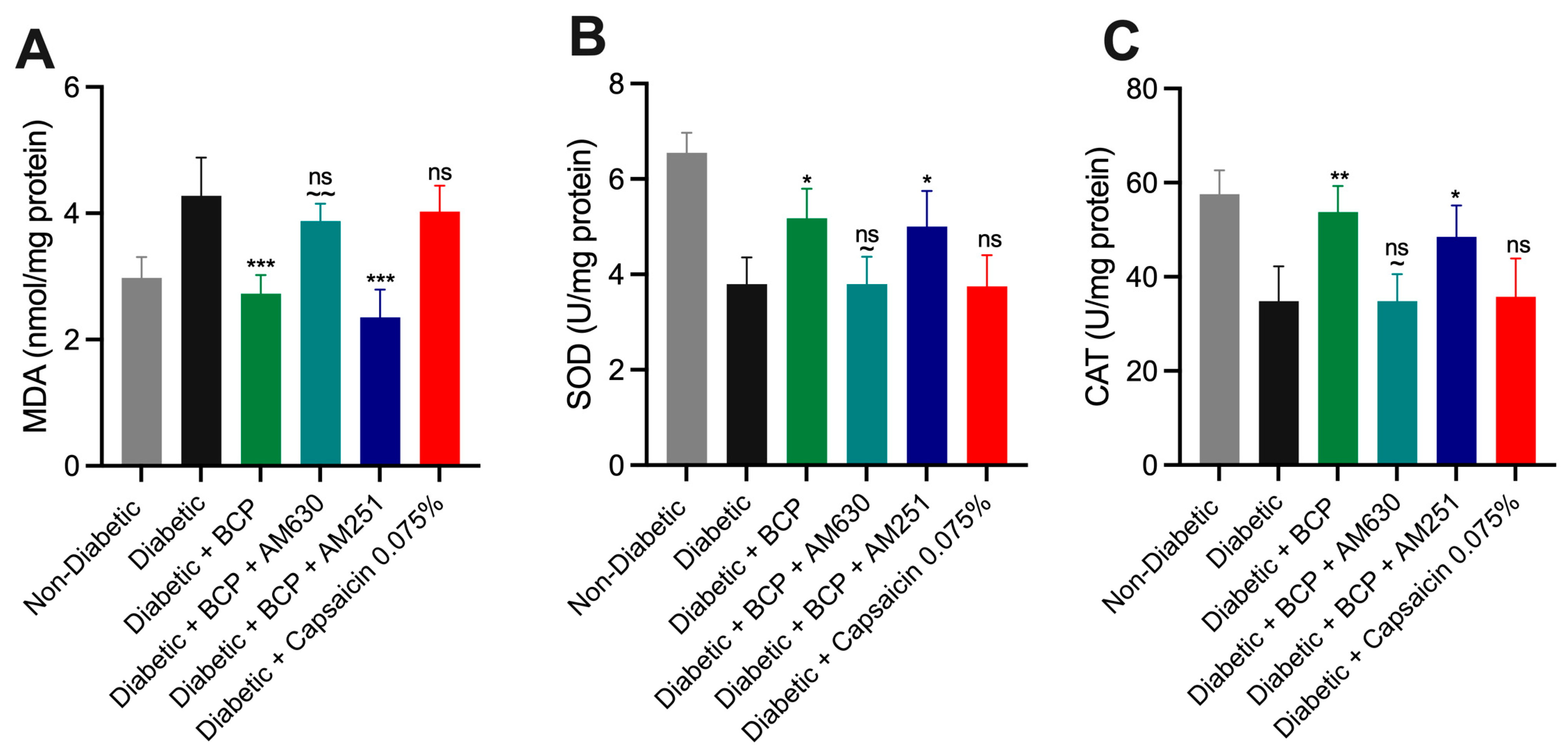
2.5. Effect of BCP on Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Hind Paw Skin Tissues of STZ-Induced DPN Mice
3. Discussion
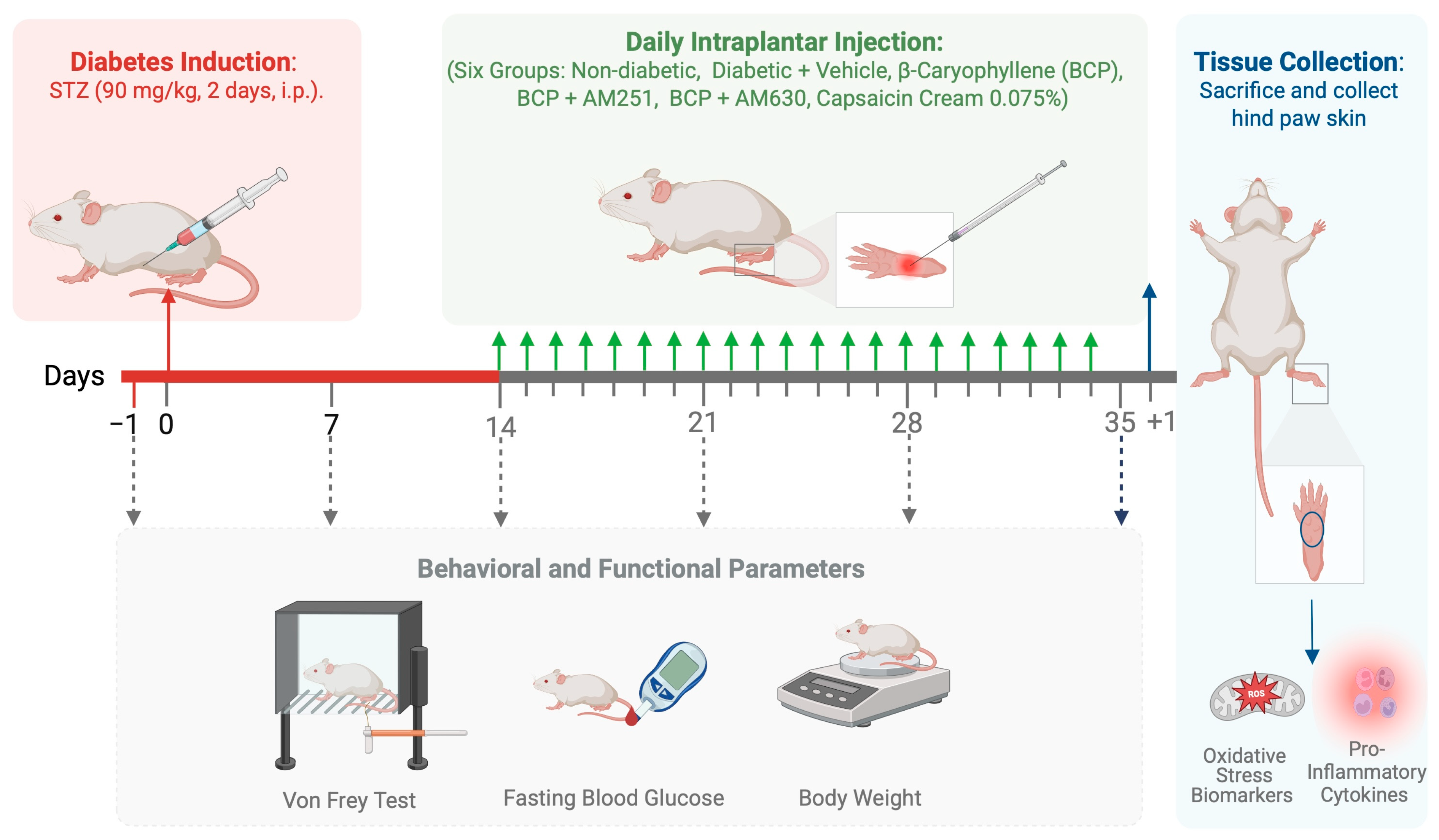
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Drugs and Reagents
4.2. Ethics Statement
4.3. Experimental Diabetes Induction
4.4. Assessment of Mechanical Allodynia
4.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.6. Assessment of Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Hind Paw Skin Tissues
4.7. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pop-Busui, R.; Boulton, A.J.M.; Feldman, E.L.; Bril, V.; Freeman, R.; Malik, R.A.; Sosenko, J.M.; Ziegler, D. Diabetic Neuropathy: A Position Statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop-Busui, R.; Ang, L.; Boulton, A.; Feldman, E.; Marcus, R.; Mizokami-Stout, K.; Singleton, J.R.; Ziegler, D. Diagnosis and Treatment of Painful Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. Compendia 2022, 2022, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Hu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Luo, W.; Du, X.; Luo, Z.; Hu, J.; Peng, S. Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: Pathogenetic Mechanisms and Treatment. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 14, 1265372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owolabi, L.F.; Alghamdi, M.; Adamu, B.; Taura, M.G.; Jibo, A.; Almansour, M.; Alaklabi, S.N.; Alghamdi, M.A.; Alotaibi, Y.A.; Imam, I.A.; et al. Magnitude of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Saudi Arabia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2022, 22, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaghan, B.C.; Cheng, H.T.; Stables, C.L.; Smith, A.L.; Feldman, E.L. Diabetic Neuropathy: Clinical Manifestations and Current Treatments. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfaye, S.; Boulton, A.J.M.; Dyck, P.J.; Freeman, R.; Horowitz, M.; Kempler, P.; Lauria, G.; Malik, R.A.; Spallone, V.; Vinik, A.; et al. Diabetic Neuropathies: Update on Definitions, Diagnostic Criteria, Estimation of Severity, and Treatments. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2285–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, E.L.; Callaghan, B.C.; Pop-Busui, R.; Zochodne, D.W.; Wright, D.E.; Bennett, D.L.; Bril, V.; Russell, J.W.; Viswanathan, V. Diabetic Neuropathy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, D. Pathogenetic Treatments for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 206, 110764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khdour, M.R. Treatment of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Review. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2020, 72, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, A.K. Diabetic Neuropathic Pain: Physiopathology and Treatment. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Fang, P.; Xiang, D.; Yang, Y. Topical Treatments for Diabetic Neuropathic Pain (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, preview. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gertsch, J.; Leonti, M.; Raduner, S.; Racz, I.; Chen, J.-Z.; Xie, X.-Q.; Altmann, K.-H.; Karsak, M.; Zimmer, A. Beta-Caryophyllene Is a Dietary Cannabinoid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9099–9104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashiesh, H.M.; Meeran, M.F.N.; Sharma, C.; Sadek, B.; Kaabi, J.A.; Ojha, S.K. Therapeutic Potential of β-Caryophyllene: A Dietary Cannabinoid in Diabetes and Associated Complications. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klauke, A.-L.; Racz, I.; Pradier, B.; Markert, A.; Zimmer, A.M.; Gertsch, J.; Zimmer, A. The Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor-Selective Phytocannabinoid Beta-Caryophyllene Exerts Analgesic Effects in Mouse Models of Inflammatory and Neuropathic Pain. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 24, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segat, G.C.; Manjavachi, M.N.; Matias, D.O.; Passos, G.F.; Freitas, C.S.; Costa, R.; Calixto, J.B. Antiallodynic Effect of β-Caryophyllene on Paclitaxel-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Mice. Neuropharmacology 2017, 125, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Nikfarjam, B.; Dolati-Somarin, A.; Baradaran Rahimi, V.; Askari, V.R. Cannabinoids in Neuroinflammatory Disorders: Focusing on Multiple Sclerosis, Parkinsons, and Alzheimers Diseases. BioFactors 2023, 49, 560–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askari, V.R.; Baradaran Rahimi, V.; Shafiee-Nick, R. Low Doses of β-Caryophyllene Reduced Clinical and Paraclinical Parameters of an Autoimmune Animal Model of Multiple Sclerosis: Investigating the Role of CB2 Receptors in Inflammation by Lymphocytes and Microglial. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnes, J.P.; Dos Santos, B.; Das Neves, R.N.; Luciano, V.M.M.; Benvenutti, L.; Goldoni, F.C.; Schran, R.G.; Santin, J.R.; Quintão, N.L.M.; Zanotto-Filho, A. β-Caryophyllene Inhibits Oxaliplatin-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Mice: Role of Cannabinoid Type 2 Receptors, Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Kaur, S.; Rishi, A.K.; Boire, B.; Aare, M.; Singh, M. Cannabidiol and Beta-Caryophyllene Combination Attenuates Diabetic Neuropathy by Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome/NFκB through the AMPK/sirT3/Nrf2 Axis. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagher, A.M. The Endocannabinoid System as a Therapeutic Target in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain: A Review. J. Microsc. Ultrastruct. 2022, 10, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, J.; Hohmann, A.G. Cannabinoid CB 2 Receptors: A Therapeutic Target for the Treatment of Inflammatory and Neuropathic Pain: Cannabinoid CB 2 Mechanisms of Pain Suppression. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, U.; Otto, W.R.; Sanchez-Herrera, D.; Facer, P.; Yiangou, Y.; Korchev, Y.; Birch, R.; Benham, C.; Bountra, C.; Chessell, I.P.; et al. Cannabinoid Receptor CB2 Localisation and Agonist-Mediated Inhibition of Capsaicin Responses in Human Sensory Neurons. Pain 2008, 138, 667–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baradaran Rahimi, V.; Askari, V.R. A Mechanistic Review on Immunomodulatory Effects of Selective Type Two Cannabinoid Receptor Β-caryophyllene. BioFactors 2022, 48, 857–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwahata, H.; Katsuyama, S.; Komatsu, T.; Nakamura, H.; Corasaniti, M.T.; Bagetta, G.; Sakurada, S.; Sakurada, T.; Takahama, K. Local Peripheral Effects of β-Caryophyllene through CB2 Receptors in Neuropathic Pain in Mice. Pharmacol. Pharm. 2012, 3, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Ávila, D.S.; Flores-Soto, M.E.; Tapia-Vázquez, C.; Pastor-Zarandona, O.A.; López-Roa, R.I.; Viveros-Paredes, J.M. β -Caryophyllene, a Natural Sesquiterpene, Attenuates Neuropathic Pain and Depressive-Like Behavior in Experimental Diabetic Mice. J. Med. Food 2019, 22, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcotte, C.; Blanchet, M.-R.; Laviolette, M.; Flamand, N. The CB2 Receptor and Its Role as a Regulator of Inflammation. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 4449–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, S.B.; Lewin, G.; Bloom, S.R. The Consequences of Long-Term Topical Capsaicin Application in the Rat. Pain 1991, 44, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolivalt, C.G.; Frizzi, K.E.; Guernsey, L.; Marquez, A.; Ochoa, J.; Rodriguez, M.; Calcutt, N.A. Peripheral Neuropathy in Mouse Models of Diabetes. Curr. Protoc. Mouse Biol. 2016, 6, 223–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nackley, A.G.; Suplita, R.L.; Hohmann, A.G. A Peripheral Cannabinoid Mechanism Suppresses Spinal Fos Protein Expression and Pain Behavior in a Rat Model of Inflammation. Neuroscience 2003, 117, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.M.; Porreca, F.; Lai, J.; Albrecht, P.J.; Rice, F.L.; Khodorova, A.; Davar, G.; Makriyannis, A.; Vanderah, T.W.; Mata, H.P.; et al. CB2 Cannabinoid Receptor Activation Produces Antinociception by Stimulating Peripheral Release of Endogenous Opioids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 3093–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, G.C.; Pai, M.; Chandran, P.; Hooker, B.A.; Zhu, C.Z.; Salyers, A.K.; Wensink, E.J.; Zhan, C.; Carroll, W.A.; Dart, M.J.; et al. Central and Peripheral Sites of Action for CB2 Receptor Mediated Analgesic Activity in Chronic Inflammatory and Neuropathic Pain Models in Rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 162, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrhart, J.; Obregon, D.; Mori, T.; Hou, H.; Sun, N.; Bai, Y.; Klein, T.; Fernandez, F.; Tan, J.; Shytle, R.D. Stimulation of Cannabinoid Receptor 2 (CB2) Suppresses Microglial Activation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2005, 2, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Wu, Y.; Tian, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wu, C.; Wang, Z. Microglial Cannabinoid CB2 Receptors in Pain Modulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barutta, F.; Piscitelli, F.; Pinach, S.; Bruno, G.; Gambino, R.; Rastaldi, M.P.; Salvidio, G.; Di Marzo, V.; Cavallo Perin, P.; Gruden, G. Protective Role of Cannabinoid Receptor Type 2 in a Mouse Model of Diabetic Nephropathy. Diabetes 2011, 60, 2386–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincenzi, F.; Targa, M.; Corciulo, C.; Tabrizi, M.A.; Merighi, S.; Gessi, S.; Saponaro, G.; Baraldi, P.G.; Borea, P.A.; Varani, K. Antinociceptive Effects of the Selective CB2 Agonist MT178 in Inflammatory and Chronic Rodent Pain Models. Pain 2013, 154, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidyt, K.; Fiedorowicz, A.; Strządała, L.; Szumny, A. β -Caryophyllene and β -Caryophyllene Oxide-Natural Compounds of Anticancer and Analgesic Properties. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 3007–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niri, P.; Saha, A.; Polopalli, S.; Kumar, M.; Das, S.; Saha, B.; Goyary, D.; Bhutia, Y.D.; Karmakar, S.; Kishor, S.; et al. β-Caryophyllene Attenuates Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response in LPS Induced Acute Lung Injury by Targeting ACE2/MasR and Nrf2/HO-1/NF-κB Axis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2025, 746, 151286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seekins, C.A.; Welborn, A.M.; Schwarz, A.M.; Streicher, J.M. Select Terpenes from Cannabis Sativa Are Antinociceptive in Mouse Models of Post-Operative Pain and Fibromyalgia via Adenosine A2a Receptors. Pharmacol. Rep. 2025, 77, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, M.P.; Boi, M.; Carta, A.; Murru, E.; Carta, G.; Banni, S.; Quartu, M. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Beta-Caryophyllene Mediated by the Involvement of TRPV1, BDNF and trkB in the Rat Cerebral Cortex after Hypoperfusion/Reperfusion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, J.; Brock, C.; Olesen, A.E.; Andresen, T.; Nilsson, M.; Dickenson, A.H. Unravelling the Mystery of Capsaicin: A Tool to Understand and Treat Pain. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 939–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.C.; Lee, M.-S.; Huang, W.-C.; Chang, W.-Y.; Krueger, J.G.; Tsai, T.-F. Capsaicin Attenuates Imiquimod-Induced Epidermal Hyperplasia and Cutaneous Inflammation in a Murine Model of Psoriasis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattori, V.; Hohmann, M.; Rossaneis, A.; Pinho-Ribeiro, F.; Verri, W. Capsaicin: Current Understanding of Its Mechanisms and Therapy of Pain and Other Pre-Clinical and Clinical Uses. Molecules 2016, 21, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalraj, A.; Jacob, J.; Varma, K.; Gopi, S. Preparation and Characterization of Liposomal β-Caryophyllene (Rephyll) by Nanofiber Weaving Technology and Its Effects on Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness (DOMS) in Humans: A Randomized, Double-Blinded, Crossover-Designed, and Placebo-Controlled Study. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 24045–24056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.S.; Oliveira, T.C.; Júnior, L.M.R.; Figueiras, A.; Nunes, L.C.C. β-Caryophyllene Delivery Systems: Enhancing the Oral Pharmacokinetic and Stability. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 3440–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, T.B.; Coelho, D.S.; Maraschin, M. β-Caryophyllene Nanoparticles Design and Development: Controlled Drug Delivery of Cannabinoid CB2 Agonist as a Strategic Tool towards Neurodegeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 121, 111824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghazwani, M.; Hani, U.; Alqarni, M.H.; Alam, A. Beta Caryophyllene-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Topical Management of Skin Disorders: Statistical Optimization, In Vitro and Dermatokinetic Evaluation. Gels 2023, 9, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals: Eighth Edition; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; p. 12910. ISBN 978-0-309-15400-0.
- Recognition and Alleviation of Pain in Laboratory Animals; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; p. 12526. ISBN 978-0-309-12834-6.
- Authier, N.; Fialip, J.; Eschalier, A.; Coudoré, F. Assessment of Allodynia and Hyperalgesia after Cisplatin Administration to Rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 291, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, K.; Dubner, R.; Brown, F.; Flores, C.; Joris, J. A New and Sensitive Method for Measuring Thermal Nociception in Cutaneous Hyperalgesia. Pain 1988, 32, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagher, A.M.; Binmahfouz, L.S.; Shaik, R.A.; Eid, B.G. Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Positive Allosteric Modulator (GAT229) Attenuates Cisplatin-Induced Neuropathic Pain in Mice. Saudi Pharm. J. 2023, 31, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bagher, A.M. Intraplantar β-Caryophyllene Alleviates Pain and Inflammation in STZ-Induced Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy via CB2 Receptor Activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4430. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094430
Bagher AM. Intraplantar β-Caryophyllene Alleviates Pain and Inflammation in STZ-Induced Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy via CB2 Receptor Activation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4430. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094430
Chicago/Turabian StyleBagher, Amina M. 2025. "Intraplantar β-Caryophyllene Alleviates Pain and Inflammation in STZ-Induced Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy via CB2 Receptor Activation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4430. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094430
APA StyleBagher, A. M. (2025). Intraplantar β-Caryophyllene Alleviates Pain and Inflammation in STZ-Induced Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy via CB2 Receptor Activation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4430. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094430




