Emerging Role of Long, Non-Coding RNA Nuclear-Enriched Abundant Transcript 1 in Stress- and Immune-Related Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of Long, Non-Coding RNAs (lncRNAs)
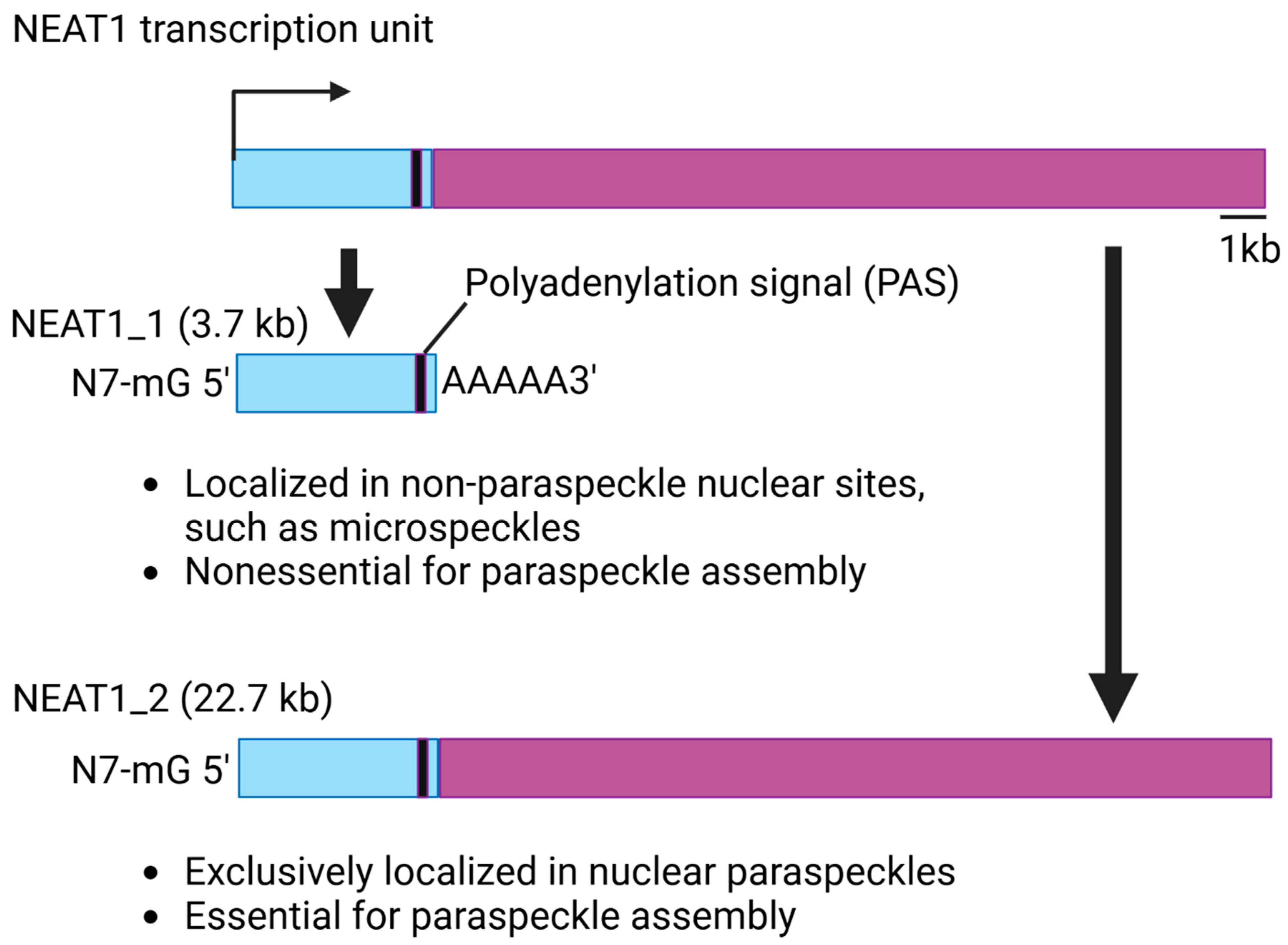
3. Structure and Function of NEAT1
4. NEAT1 in Stress Regulation
4.1. NEAT1 Regulates Genotoxic Stress
4.2. NEAT1 Regulates Oxidative Stress
4.3. NEAT1 Regulates Hypoxia
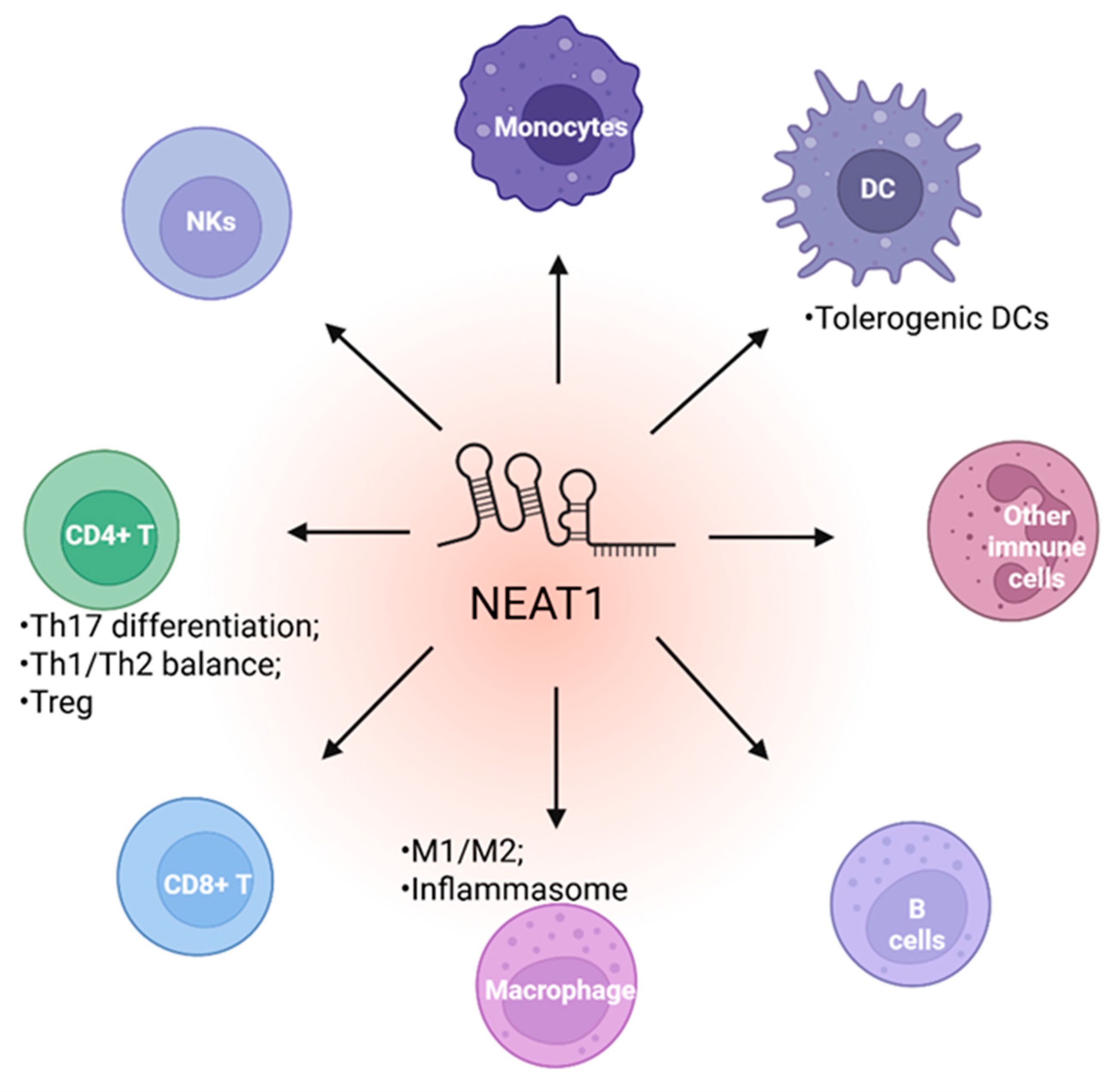
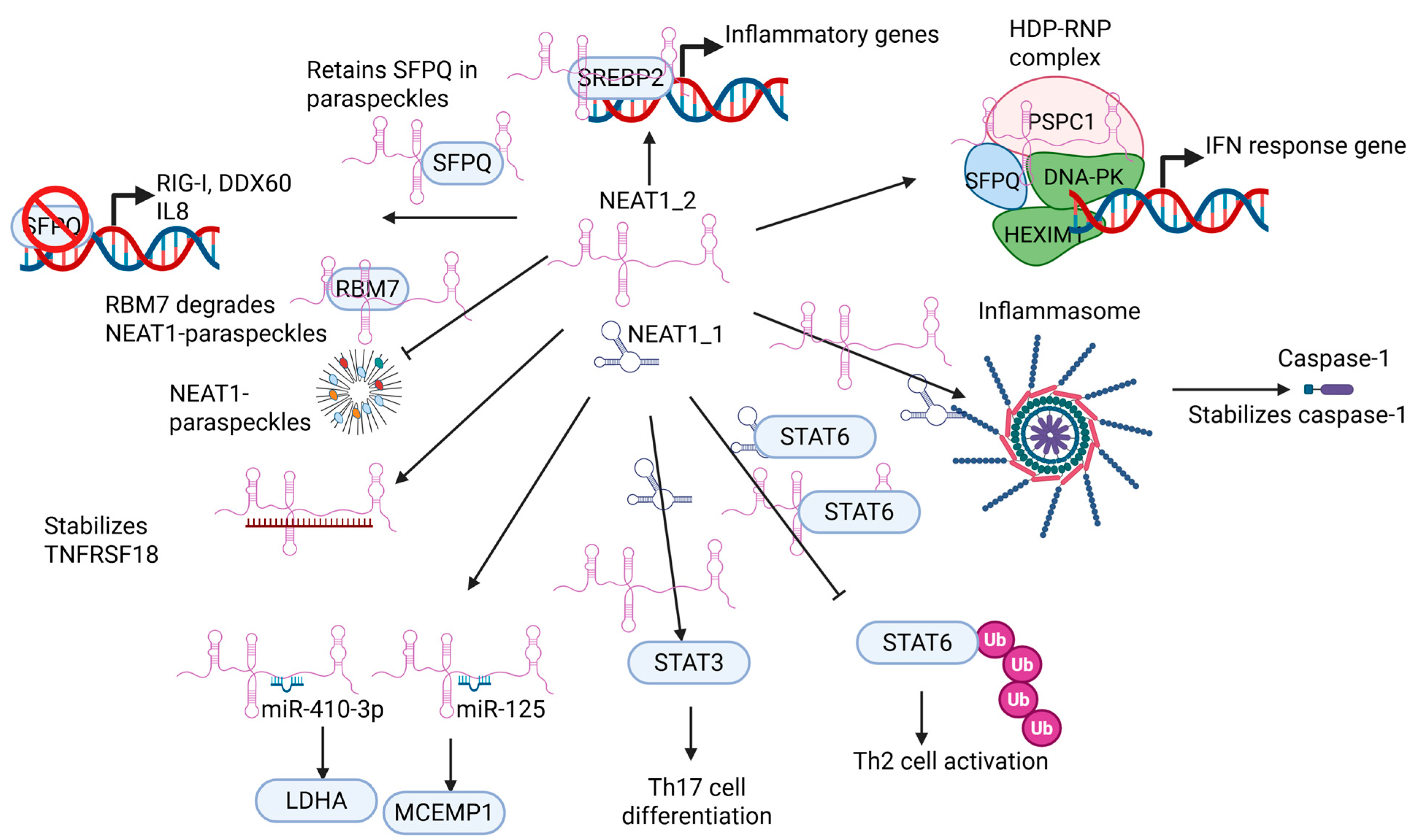
5. NEAT1 in Immune Cell Function
5.1. NEAT1 Regulates Innate Immune Cell
5.2. NEAT1 Regulates Adaptive Immune Cell Function
6. NEAT1 as a Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Stress- and Immune-Related Diseases
6.1. NEAT1 as a Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Stress-Related Diseases
6.2. NEAT1 as a Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Immune-Related Diseases
6.3. Current Limitations of the Application of NEAT1 as a Therapeutic Target
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yi, Q.; Feng, J.; Lan, W.; Shi, H.; Sun, W.; Sun, W. CircRNA and lncRNA-encoded peptide in diseases, an update review. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y. LncRNA-encoded peptides in cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 17, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Tang, L.; Yang, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Min, Q.; Yin, M.; You, H.; Xiao, Z.; Shen, J. Current understanding of functional peptides encoded by lncRNA in cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2024, 24, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponting, C.P.; Oliver, P.L.; Reik, W. Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell 2009, 136, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, A.M.; Chang, H.Y. Long Noncoding RNAs in Cancer Pathways. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Tu, C.; Liu, Y. Role of lncRNAs in aging and age-related diseases. Aging Med. 2018, 1, 158–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Sachdeva, M.; Xu, E.; Robinson, T.J.; Luo, L.; Ma, Y.; Williams, N.T.; Lopez, O.; Cervia, L.D.; Yuan, F.; et al. The Long Noncoding RNA NEAT1 Promotes Sarcoma Metastasis by Regulating RNA Splicing Pathways. Mol. Cancer Res. 2020, 18, 1534–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, J.J.; Chang, H.Y. Unique features of long non-coding RNA biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Feng, C.; Qin, Y.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, L. LncBook 2.0: Integrating human long non-coding RNAs with multi-omics annotations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D186–D191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, P.; Kwon, E.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Weng, Z.; Zhou, C. Flnc: Machine learning improves the identification of novel long noncoding RNAs from stand-alone RNA-seq data. Noncoding RNA 2022, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarropoulos, I.; Marin, R.; Cardoso-Moreira, M.; Kaessmann, H. Developmental dynamics of lncRNAs across mammalian organs and species. Nature 2019, 571, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bignold, L.P. Sublethal injuries and deaths of cells and tissues. In Principles of Tumors; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 603–624. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.-W.; Papadopoli, D.; Szkop, K.J.; Guan, B.-J.; Alzahrani, M.; Wu, J.; Jobava, R.; Asraf, M.M.; Krokowski, D.; Vourekas, A.; et al. Plasticity of the mammalian integrated stress response. Nature 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhapola, R.; Beura, S.K.; Sharma, P.; Singh, S.K.; HariKrishnaReddy, D. Oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease: Current knowledge of signaling pathways and therapeutics. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickerson, J.A.; Momen-Heravi, F. Long non-coding RNAs: Roles in cellular stress responses and epigenetic mechanisms regulating chromatin. Nucleus 2024, 15, 2350180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Castillo, M.; MElsayed, A.; López-Berestein, G.; Amero, P.; Rodríguez-Aguayo, C. An overview of the immune modulatory properties of long non-coding RNAs and their potential use as therapeutic targets in cancer. Noncoding RNA 2023, 9, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statello, L.; Guo, C.-J.; Chen, L.-L.; Huarte, M. Gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 96–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atianand, M.K.; Caffrey, D.R.; Fitzgerald, K.A. Immunobiology of long noncoding RNAs. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 35, 177–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-L.; Carmichael, G.G. Altered nuclear retention of mRNAs containing inverted repeats in human embryonic stem cells: Functional role of a nuclear noncoding RNA. Mol. Cell 2009, 35, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemson, C.M.; Hutchinson, J.N.; Sara, S.A.; Ensminger, A.W.; Fox, A.H.; Chess, A.; Lawrence, J.B. An architectural role for a nuclear noncoding RNA: NEAT1 RNA is essential for the structure of paraspeckles. Mol. Cell 2009, 33, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, Y.T.F.; Ideue, T.; Sano, M.; Mituyama, T.; Hirose, T. MENepsilon/beta noncoding RNAs are essential for structural integrity of nuclear paraspeckles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2525–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naganuma, T.; Nakagawa, S.; Tanigawa, A.; Sasaki, Y.F.; Goshima, N.; Hirose, T. Alternative 3′-end processing of long noncoding RNA initiates construction of nuclear paraspeckles. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 4020–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Harvey, A.R.; Hodgetts, S.I.; Fox, A.H. Functional dissection of NEAT1 using genome editing reveals substantial localization of the NEAT1_1 isoform outside paraspeckles. RNA 2017, 23, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, T.; Souquere, S.; Chujo, T.; Kobelke, S.; Chong, Y.S.; Fox, A.H.; Bond, C.S.; Nakagawa, S.; Pierron, G.; Hirose, T. Functional Domains of NEAT1 Architectural lncRNA Induce Paraspeckle Assembly through Phase Separation. Mol. Cell 2018, 70, 1038–1053.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, K.; Imamachi, N.; Akizuki, G.; Kumakura, M.; Kawaguchi, A.; Nagata, K.; Kato, A.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Sato, H.; Yoneda, M.; et al. Long noncoding RNA NEAT1-dependent SFPQ relocation from promoter region to paraspeckle mediates IL8 expression upon immune stimuli. Mol. Cell 2014, 53, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, A.; Cooper, J.A.; Li, R.; Hubbard, A.; Chen, J.; Liu, T.; Wilton, S.D.; Fletcher, S.; Fox, A.H. NEAT1 polyA-modulating antisense oligonucleotides reveal opposing functions for both long non-coding RNA isoforms in neuroblastoma. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 2213–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isobe, M.; Toya, H.; Mito, M.; Chiba, T.; Asahara, H.; Hirose, T.; Nakagawa, S. Forced isoform switching of Neat1_1 to Neat1_2 leads to the loss of Neat1_1 and the hyperformation of paraspeckles but does not affect the development and growth of mice. RNA 2020, 26, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasca, D.; Hähnel, P.S.; Szybinski, J.; Khawaja, K.; Kriege, O.; Pante, S.V.; Bullinger, L.; Strand, S.; Strand, D.; Theobald, M.; et al. SIRT1 prevents genotoxic stress-induced p53 activation in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2014, 124, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriaens, C.; Standaert, L.; Barra, J.; Latil, M.; Verfaillie, A.; Kalev, P.; Boeckx, B.; Wijnhoven, P.W.G.; Radaelli, E.; Vermi, W.; et al. Publisher Correction: p53 induces formation of NEAT1 lncRNA-containing paraspeckles that modulate replication stress response and chemosensitivity. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, S.S.; Sinow, C.; Raj, N.; Mazur, P.K.; Bieging-Rolett, K.; Broz, D.K.; Imam, J.F.C.; Vogel, H.; Wood, L.D.; Sage, J.; et al. Neat1 is a p53-inducible lincRNA essential for transformation suppression. Genes Dev. 2017, 31, 1095–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamontova, V.; Trifault, B.; Gribling-Burrer, A.-S.; Bohn, P.; Boten, L.; Preckwinkel, P.; Gallant, P.; Solvie, D.; Ade, C.P.; Papadopoulos, D.; et al. NEAT1 promotes genome stability via m6A methylation-dependent regulation of CHD4. Genes. Dev. 2024, 38, 915–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilgas, S.; Syed, A.; Toolan-Kerr, P.; Swift, M.L.; Roychoudhury, S.; Sarkar, A.; Wilkins, S.; Quigley, M.; Poetsch, A.R.; Botuyan, M.V.; et al. NEAT1 modulates the TIRR/53BP1 complex to maintain genome integrity. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsukawa, K.; Kukharsky, M.S.; Park, S.-K.; Park, S.; Watanabe, N.; Iwatsubo, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Liebman, S.W.; Shelkovnikova, T.A. Long non-coding RNA NEAT1_1 ameliorates TDP-43 toxicity in in vivo models of TDP-43 proteinopathy. RNA Biol. 2021, 18, 1546–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanda, K.; Das, S.; Chakraborty, J.; Bucha, S.; Maitra, A.; Chatterjee, R.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Bhattacharyya, N.P. Altered levels of long NcRNAs Meg3 and Neat1 in cell and animal models of Huntington’s disease. RNA Biol. 2018, 15, 1348–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Williams, N.G.; Shelkovnikova, T.A. NEAT1 and paraspeckles in neurodegenerative diseases: A missing lnc found? Noncoding RNA Res. 2018, 3, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boros, F.A.; Vécsei, L.; Klivényi, P. NEAT1 on the field of Parkinson’s disease: Offense, defense, or a player on the bench? J. Parkinsons. Dis. 2021, 11, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Royo, T.; Moreno-Martínez, L.; Zaragoza, P.; García-Redondo, A.; Manzano, R.; Osta, R. Differentially expressed lncRNAs in SOD1G93A mice skeletal muscle: H19, Myhas and Neat1 as potential biomarkers in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Open Biol. 2024, 14, 240015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Wang, Z. lncRNA NEAT1: Key player in neurodegenerative diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 86, 101878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, G.; Kowluru, R.A. Nuclear genome-encoded long noncoding RNAs and mitochondrial damage in diabetic retinopathy. Cells 2021, 10, 3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, Y. Oxidative Stress; Springer: Singapore, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.-A.; Bauer, S.; Ho, Y.-C.; Sotzny, F.; Chang, J.-G.; Scheibenbogen, C. The expression signature of very long non-coding RNA in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Yang, M.; Zhang, G.; Kang, L.; Yang, L.; Guan, H. Long non-coding RNA nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 protects human lens epithelial cells against H2O2 stimuli through the nuclear factor kappa b/p65 and p38/mitogen-activated protein kinase axis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Zheng, Z.; Zha, Z.; Xiong, T.; Pan, Y. Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 enhances hydrogen peroxide-induced human vascular smooth muscle cell injury by regulating miR-30d-5p/A disintegrin and metalloprotease 10. Circ. J. 2022, 86, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Chen, Y.; Feng, X.; Sun, D.; Sun, J.; Mou, S.; Zhao, K.; An, R. Oxidative stress-induced endothelial cells-derived exosomes accelerate skin flap survival through Lnc NEAT1-mediated promotion of endothelial progenitor cell function. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Xu, H.; Guo, X.; Guo, Q.; Zhao, C.; Yao, H.; Jia, Y.; Zhu, H. Melatonin attenuates H2O2-induced oxidative injury by upregulating LncRNA NEAT1 in HT22 hippocampal cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.; Jiang, P.; Zeb, F.; Wu, X.; Xu, C.; Chen, L.; Feng, Q. EGCG regulates CTR1 expression through its pro-oxidative property in non-small-cell lung cancer cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 7970–7981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Lv, K.; Lou, P.; Zhou, P.; Zhu, J.; Li, L.; Cheng, J.; Lu, Y.; et al. The mitochondria–paraspeckle axis regulates the survival of transplanted stem cells under oxidative stress conditions. Theranostics 2024, 14, 1517–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Zhou, H.; Chen, L.; Liu, Z. NEAT1 promotes valproic acid-induced autism spectrum disorder by recruiting YY1 to regulate UBE3A transcription. Mol. Neurobiol. 2025, 62, 846–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, X.; Si, H.; Wu, T.; Nasir, A.; Ma, H.; Xing, J.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, X.; et al. Correction: Mitochondria-targeting nanozyme alleviating temporomandibular joint pain by inhibiting the TNFα/NF-κB/NEAT1 pathway. J. Mater. Chem. B Mater. Biol. Med. 2023, 12, 275–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Yang, L. Long non-coding RNA nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 downregulation protects lens epithelial cells from oxidative stress-induced apoptosis by regulating the microRNA-124-3p/death-associated protein kinase 1 axis in age-related cataract. Int. Ophthalmol. 2023, 43, 3413–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Hu, Q.; Li, G.; Qi, Q.; Song, Z.; Shu, J.; Liang, H.; Liu, H.; Hao, Z. NEAT1 regulates calcium oxalate crystal-induced renal tubular oxidative injury via miR-130/IRF1. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2023, 38, 731–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Yao, J.; Qiu, Z. Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 inhibits oxidative stress-induced vascular endothelial cell injury by activating the miR-181d-5p/CDKN3 axis. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 3129–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xufei, F.; Xiujuan, Z.; Jianyi, L.; Liyan, Y.; Ting, Y.; Min, H. Up-regulation of LncRNA NEAT1 induces apoptosis of human placental trophoblasts. Free Radic. Res. 2020, 54, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, G.; Zhong, W.; Wu, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, L. Inhibition of lncRNA Neat1 by catalpol via suppressing transcriptional activity of NF-κB attenuates cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Cell Cycle 2019, 18, 3432–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’aiuto, N.; Hochmann, J.; Millán, M.; Di Paolo, A.; Bologna-Molina, R.; Silveira, J.S.; Arocena, M. Hypoxia, acidification and oxidative stress in cells cultured at large distances from an oxygen source. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhry, H.; Albukhari, A.; Morotti, M.; Haider, S.; Moralli, D.; Smythies, J.; Schödel, J.; Green, C.M.; Camps, C.; Buffa, F.; et al. Tumor hypoxia induces nuclear paraspeckle formation through HIF-2α dependent transcriptional activation of NEAT1 leading to cancer cell survival. Oncogene 2015, 34, 4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenger, R.H.; Lelli, A.; Nolan, K.; Santambrogio, S.; Marti, H.H.; Hoogewijs, D.; Frew, I.J.; Goncalves, A.F.; Schönenberger, M.J.; Guinot, A. Induction of long noncoding RNA MALAT1 in hypoxic mice. Hypoxia 2015, 3, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.-W.; Zheng, L.-J.; Ren, X.; Li, A.-P.; Zhou, W.-S. LncRNA NEAT1 facilitates survival and angiogenesis in oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD)-induced brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMECs) via targeting miR-377 and upregulating SIRT1, VEGFA, and BCL-XL. Brain Res. 2019, 1707, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck-Swain, K.-L.; Koeppen, M. The intriguing role of hypoxia-inducible factor in myocardial ischemia and reperfusion: A comprehensive review. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2023, 10, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.-J.; Wei, J.; Tian, D.; Yan, C.; Hu, P.; Wu, X.; Yang, W.; Hu, X. NEAT1 promotes myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via activating the MAPK signaling pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 18773–18780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Li, D.; Shen, W.; Shen, X.; Liu, Y. LncRNA NEAT1 promotes hypoxia-induced renal tubular epithelial apoptosis through downregulating miR-27a-3p. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 16273–16282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Liu, Z.; Huang, J.; Yu, J.; Dong, Y.; Wang, J. LncRNA nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1 regulates hypoxia-evoked apoptosis and autophagy via mediation of microRNA-181b. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 464, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Duan, X.-J.; Li, L.-R.; Chen, Y.-P. lncRNA NEAT1 promotes hypoxia-induced inflammation and fibrosis of alveolar epithelial cells via targeting miR-29a/NFATc3 axis. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2022, 38, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Guo, X.; Tian, Y.; Wang, J. Knockdown of lncRNA-NEAT1 expression inhibits hypoxia-induced scar fibroblast proliferation through regulation of the miR-488-3p/COL3A1 axis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2022, 24, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.-J.; Tang, G.; Shao, P.; Zou, H.; Shen, W.; Huang, M.; Pan, H.; Zhai, C.; Qian, G. Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 modulates hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cardiomyocyte injury via targeting microRNA-520a. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 2199–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Zhou, H.-Y.; Shi, X.-D.; Cao, H.-Y.; Qin, L. Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 promotes myocardiocyte apoptosis and suppresses proliferation through regulation of miR-129-5p. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2019, 74, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, F.; Ma, W.; Zhang, P. Suppression of long noncoding RNA NEAT1 attenuates hypoxia-induced cardiomyocytes injury by targeting miR-378a-3p. Gene 2020, 731, 144324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; He, L.; Yin, L. LncRNA NEAT1 binds to MiR-339-5p to increase HOXA1 and alleviate ischemic brain damage in neonatal mice. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 20, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-S.; Ouyang, B.; Ji, X.-Y.; Liu, M.-F. Gastrodin alleviates cerebral ischaemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting pyroptosis by regulating the lncRNA NEAT1/miR-22-3p axis. Neurochem. Res. 2021, 46, 1747–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Song, Y.; Li, S.; Gu, J.; Yan, X. Inhibition of lncRNA NEAT1 protects endothelial cells against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation by targeting the miR-204/BRCC3 axis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2022, 25, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidlöf, O.; Bader, K.; Celik, S.; Grossi, M.; Nakagawa, S.; Hirose, T.; Metzler, B.; Olde, B.; Erlinge, D. Inhibition of the long non-coding RNA NEAT1 protects cardiomyocytes from hypoxia in vitro via decreased pri-miRNA processing. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godet, A.-C.; Roussel, E.; David, F.; Hantelys, F.; Morfoisse, F.; Alves, J.; Pujol, F.; Ader, I.; Bertrand, E.; Burlet-Schiltz, O.; et al. Long non-coding RNA Neat1 and paraspeckle components are translational regulators in hypoxia. eLife 2022, 11, e69162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Ou, B.; Huang, Q.; Deng, D.; Xiang, Y.; Hu, F. LncRNA NEAT1 aggravates human microvascular endothelial cell injury by inhibiting the Apelin/Nrf2/HO-1 signalling pathway in type 2 diabetes mellitus with obstructive sleep apnoea. Epigenetics 2024, 19, 2293409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Ma, Y.; Ye, W.; Si, Y.; Zheng, X.; Liu, H.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; et al. LncRNA NEAT1 potentiates SREBP2 activity to promote inflammatory macrophage activation and limit Hantaan virus propagation. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 849020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Han, P.; Ye, W.; Chen, H.; Zheng, X.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, L.; Yu, L.; Wu, X.; Xu, Z.; et al. The Long Noncoding RNA NEAT1 Exerts Antihantaviral Effects by Acting as Positive Feedback for RIG-I Signaling. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e02250-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnodi, E.; Mancuso, C.; Elli, L.; Ballarini, E.; Meneveri, R.; Beaulieu, J.F.; Barisani, D. Gliadin, through the activation of innate immunity, triggers lncRNA NEAT1 expression in celiac disease duodenal mucosa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morchikh, M.; Cribier, A.; Raffel, R.; Amraoui, S.; Cau, J.; Severac, D.; Dubois, E.; Schwartz, O.; Bennasser, Y.; Benkirane, M. HEXIM1 and NEAT1 Long Non-coding RNA Form a Multi-subunit Complex that Regulates DNA-Mediated Innate Immune Response. Mol. Cell 2017, 67, 387–399.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Cao, L.; Zhou, R.; Yang, X.; Wu, M. The lncRNA Neat1 promotes activation of inflammasomes in macrophages. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Dong, L.; Liu, Y.-M.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, C.; Liu, K.; Liu, L.; Song, Y.-H.; Sun, M.; Xiang, X.-C.; et al. Nickle-cobalt alloy nanocrystals inhibit activation of inflammasomes. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2023, 10, nwad179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, K.; Satoh, T.; Sugihara, F.; Sato, Y.; Okamoto, T.; Mitsui, Y.; Yoshio, S.; Li, S.; Nojima, S.; Motooka, D.; et al. Dysregulated Expression of the Nuclear Exosome Targeting Complex Component Rbm7 in Nonhematopoietic Cells Licenses the Development of Fibrosis. Immunity 2020, 52, 542–556.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Liu, R.; Wu, X.; Ma, K.; Luo, W.; Nie, K.; Zhang, C.; Meng, X.; Tong, T.; Chen, X.; et al. LncRNA NEAT1 mediates intestinal inflammation by regulating TNFRSF1B. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Tang, A.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Zhao, L.; Xiao, Z.; Shen, S. Inhibition of lncRNA NEAT1 suppresses the inflammatory response in IBD by modulating the intestinal epithelial barrier and by exosome-mediated polarization of macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 2903–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, J.; Shen, Y. Inhibition of LncRNA-NEAT1 alleviates intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) dysfunction in ulcerative colitis by maintaining the homeostasis of the glucose metabolism through the miR-410-3p-LDHA axis. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 8961–8971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gast, M.; Rauch, B.H.; Haghikia, A.; Nakagawa, S.; Haas, J.; Stroux, A.; Schmidt, D.; Schumann, P.; Weiss, S.; Jensen, L.; et al. Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 modulates immune cell functions and is suppressed in early onset myocardial infarction patients. Cardiovasc. Res. 2019, 115, 1886–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Wu, W.; Fu, Y.; Chen, S.; Chen, T.; Yang, B.; Ou, Q. Toll-like receptors, long non-coding RNA NEAT1, and RIG-I expression are associated with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients in the active phase. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2019, 33, e22886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azam, S.; Armijo, K.S.; Weindel, C.G.; Chapman, M.J.; Devigne, A.; Nakagawa, S.; Hirose, T.; Carpenter, S.; Watson, R.O.; Patrick, K.L. The early macrophage response to pathogens requires dynamic regulation of the nuclear paraspeckle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2312587121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, L.; Jin, X.; Hou, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Li, J.; et al. Knockdown of NEAT1 induces tolerogenic phenotype in dendritic cells by inhibiting activation of NLRP3 inflammasome. Theranostics 2019, 9, 3425–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Peng, X.; Xie, T.; Lu, X.; Liu, F.; Wu, H.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Cheng, L.; Wu, N. Detection of the long noncoding RNAs nuclear-enriched autosomal transcript 1 (NEAT1) and metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 in the peripheral blood of HIV-1-infected patients. HIV Med. 2016, 17, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imam, H.; Bano, A.S.; Patel, P.; Holla, P.; Jameel, S. The lncRNA NRON modulates HIV-1 replication in a NFAT-dependent manner and is differentially regulated by early and late viral proteins. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, C.-Y.; Yedavalli, V.S.R.K.; Jeang, K.-T. NEAT1 long noncoding RNA and paraspeckle bodies modulate HIV-1 posttranscriptional expression. MBio 2013, 4, e00596-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hu, P.-W.; Couturier, J.; Lewis, D.E.; Rice, A.P. HIV-1 replication in CD4+ T cells exploits the down-regulation of antiviral NEAT1 long non-coding RNAs following T cell activation. Virology 2018, 522, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, X.; Chen, S.; Lin, J.; Kong, J.; Zhou, C.; Wu, J. Knockdown of lncRNA NEAT1 inhibits Th17/CD4+ T cell differentiation through reducing the STAT3 protein level. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 22477–22484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Lin, X.; Chen, M. LncRNA NEAT1 correlates with Th17 cells and proinflammatory cytokines, also reflects stenosis degree and cholesterol level in coronary heart disease patients. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e23975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Smet, M.D.; Taylor, S.R.; Bodaghi, B.; Miserocchi, E.; Murray, P.I.; Pleyer, U.; Zierhut, M.; Barisani-Asenbauer, T.; LeHoang, P.; Lightman, S. Understanding uveitis: The impact of research on visual outcomes. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2011, 30, 452–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, K.; Ma, B.; Li, X.; Wei, R.; Nian, H. LncRNA Neat1 targets NonO and miR-128-3p to promote antigen-specific Th17 cell responses and autoimmune inflammation. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhao, S.; Huang, W.; Huang, L.; Huang, M.; Luo, X.; Chang, S. Aberrant expressions of circulating lncRNA NEAT1 and microRNA-125a are linked with Th2 cells and symptom severity in pediatric allergic rhinitis. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Liu, H.; Li, T. Lncrna NEAT1 regulates Th1/Th2 in pediatric asthma by targeting MicroRNA-217/GATA3. Iran. J. Public Health 2023, 52, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Han, J.; Cui, R.; Peng, M.; Song, H.; Li, R.; Chen, G. The promotion of humoral immune responses in humans via SOCS1-mediated Th2-bias following SARS-CoV-2 vaccination. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Dong, D.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Geng, J.; Zhao, Y. Long non-coding RNA nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 promotes activation of T helper 2 cells via inhibiting STAT6 ubiquitination. Hum. Cell 2021, 34, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-X.; Xu, X.; Zhang, S. Silence of long noncoding RNA NEAT1 exerts suppressive effects on immunity during sepsis by promoting microRNA-125-dependent MCEMP1 downregulation. IUBMB Life 2019, 71, 956–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Wang, X.-S.; Yao, Y.; Si, Y.-M.; Wang, X.-Z.; Jia, M.-N.; Zhou, D.-B.; Yu, J.; Cao, X.-X.; Li, J. Single-cell transcriptome analysis reveals stem cell-like subsets in the progression of Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, P.; Mehta, P.; Soni, J.; Tardalkar, K.; Joshi, M.; Pandey, R. Cell-specific housekeeping role of lncRNAs in COVID-19-infected and recovered patients. NAR Genom. Bioinform. 2024, 6, lqae023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wu, K.; Mo, X.; Yang, Z. LncRNA NEAT1, an important biomarker involved in the pathological and physiological processes of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2025, 20, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senousy, M.A.; Shaker, O.G.; Elmaasrawy, A.H.; Ashour, A.M.; Alsufyani, S.E.; Arab, H.H.; Ayeldeen, G. Serum lncRNAs TUG1, H19, and NEAT1 and their target miR-29b/SLC3A1 axis as possible biomarkers of preeclampsia: Potential clinical insights. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024, 9, 995–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, X.; Ma, Y.; Qin, Y.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, S.; Tian, R.; Pan, M. NEAT1 silencing alleviates pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation under hypoxia through regulation of miR-34a-5p/KLF4 in vitro. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 24, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhang, N.; Lu, J.; Gan, X.; Chen, L.; Liang, R.; Jian, J. Silencing of lncRNA NEAT1 alleviates acute myocardial infarction by suppressing miR-450-5p/ACSL4-mediated ferroptosis. Exp. Cell Res. 2024, 442, 114217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ding, J.; Zhang, Q.; Lv, S.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, R.; Lu, D. Chlorogenic acid protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice by inhibiting Lnc Neat1/NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simchovitz, A.; Hanan, M.; Niederhoffer, N.; Madrer, N.; Yayon, N.; Bennett, E.R.; Greenberg, D.S.; Kadener, S.; Soreq, H. NEAT1 is overexpressed in Parkinson’s disease substantia nigra and confers drug-inducible neuroprotection from oxidative stress. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 11223–11234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Su, Q.; Xia, W.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, K.; Su, Z.; Li, G. Knockdown lncRNA NEAT1 regulates the activation of microglia and reduces AKT signaling and neuronal apoptosis after cerebral ischemic reperfusion. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Wang, C.; Vagts, C.; Raguveer, V.; Finn, P.W.; Perkins, D.L. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) NEAT1 and MALAT1 are differentially expressed in severe COVID-19 patients: An integrated single-cell analysis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0261242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.C.; Adamoski, D.; Genelhould, G.; Zhen, F.; Yamaguto, G.E.; Araujo-Souza, P.S.; Nogueira, M.B.; Raboni, S.M.; Bonatto, A.C.; Gradia, D.F.; et al. NEAT1 and MALAT1 are highly expressed in saliva and nasopharyngeal swab samples of COVID-19 patients. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2021, 36, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahni, Z.; Hosseini, S.M.; Shahrokh, S.; Niasar, M.S.; Shoraka, S.; Mirjalali, H.; Nazemalhosseini-Mojarad, E.; Rostami-Nejad, M.; Malekpour, H.; Zali, M.R.; et al. Long non-coding RNAs ANRIL, THRIL, and NEAT1 as potential circulating biomarkers of SARS-CoV-2 infection and disease severity. Virus Res. 2023, 336, 199214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.A.; Shaker, O.G.; Ezzat, E.M.; Ali, E.S.; Aboelor, M.I.; Ahmed, M.I.; Hassan, E.A.; Ali, D.Y.; Ahmed, H.M.; Khalefa, A.A.; et al. Peripheral lncRNA NEAT-1, miR374b-5p, and IL6 panel to guide in COVID-19 patients’ diagnosis and prognosis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0313042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Duan, S.; Fu, A. Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 correlates with higher disease risk, worse disease condition, decreased miR-124 and miR-125a and predicts poor recurrence-free survival of acute ischemic stroke. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, F.; Ou, W.; Wei, B.; Fan, H.; Wei, C.; Fang, D.; Li, G.; Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Jin, L.; et al. Transcriptome-wide analysis to identify the inflammatory role of lncRNA Neat1 in experimental ischemic stroke. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 2667–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lu, X.; Wang, T.; Xu, S.; Kong, T.; Bo, C.; Li, L.; Ning, S.; et al. Construction of lncRNA-mediated ceRNA network for investigating immune pathogenesis of ischemic stroke. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 4758–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathi Dizaji, B. Strategies to target long non-coding RNAs in cancer treatment: Progress and challenges. Egypt. J. Med. Hum. Genet. 2020, 21, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguchi, S.; Ohka, F.; Shiba, Y.; Yamaguchi, J.; Sato, A.; Shinjo, K.; Arakawa, Y.; Narita, Y.; Kondo, Y.; Saito, R. Investigator-initiated phase I trial of an oligonucleotide therapeutic targeting long noncoding RNA TUG 1 for recurrent glioblastoma. BMC Cancer 2025, 25, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Pan, L.; Chen, W.; Wu, Y. Long non-coding RNAs MALAT1, NEAT1 and DSCR4 can be serum biomarkers in predicting urosepsis occurrence and reflect disease severity. Exp. Ther. Med. 2024, 28, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Huang, C.; Luo, Y.; He, F.; Zhang, R. Circulating lncRNA NEAT1 correlates with increased risk, elevated severity and unfavorable prognosis in sepsis patients. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 36, 1659–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, M.; Cai, G.; Ye, J.; Liu, X.; Ding, H.; Zeng, H. Single-cell transcriptomics reveals the alteration of peripheral blood mononuclear cells driven by sepsis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.R.; Abdelaleem, O.O.; Ahmed, F.A.; Abdelaziz, A.A.; Hussein, H.A.; Eid, H.M.; Kamal, M.; Ezzat, M.A.; Ali, M.A. Expression of lncRNAs NEAT1 and lnc-DC in Serum From Patients With Behçet’s Disease Can Be Used as Predictors of Disease. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 797689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Shaker, O.G.; Khalil, M.A.; Elsabagh, Y.A.; Gomaa, M.; Ahmed, A.M.; Erfan, R. Association of long non-coding RNAs NEAT1, and MALAT1 expression and pathogenesis of Behçet’s disease among Egyptian patients. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 103344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdy, S.M.; Ali, M.S.; Abd El-Hmid, R.G.; Abdelghaffar, N.K.; Abdelaleem, O.O. Role of long non coding RNAs, NEAT1 and Lnc-DC expression in pediatric immune thrombocytopenic Purpura. Rep. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2023, 11, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghpour, S.; Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Mazdeh, M.; Nicknafs, F.; Nazer, N.; Sayad, A.; Taheri, M. Over-expression of immune-related lncRNAs in inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathies. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 71, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, I.-R.; Huang, C.-C.; Tu, S.-J.; Wang, G.-J.; Lai, P.-C.; Lee, Y.-T.; Yen, J.-C.; Chang, Y.-S.; Chang, J.-G. Dysregulation of immune cell subpopulations in atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shobeiri, P.; Alilou, S.; Jaberinezhad, M.; Zare, F.; Karimi, N.; Maleki, S.; Teixeira, A.L.; Perry, G.; Rezaei, N. Circulating long non-coding RNAs as novel diagnostic biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease (AD): A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0281784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballonová, L.; Souček, P.; Slanina, P.; Réblová, K.; Zapletal, O.; Vlková, M.; Hakl, R.; Bíly, V.; Grombiříková, H.; Svobodová, E.; et al. Myeloid lineage cells evince distinct steady-state level of certain gene groups in dependence on hereditary angioedema severity. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1123914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, O.J.; Lei, W.; Zhu, G.; Ren, Z.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, C.; Zhang, H.; Cai, J.; Luo, Z.; Gao, L.; et al. Multidimensional single-cell analysis of human peripheral blood reveals characteristic features of the immune system landscape in aging and frailty. Nat. Aging 2022, 2, 348–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, W.; Chen, F.; Mo, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Z. Landscape of tumoral ecosystem for enhanced anti-PD-1 immunotherapy by gut Akkermansia muciniphila. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, K.; Yang, X.; Zou, H.; Zhou, J.; Miao, X.; Chen, W.; Xiong, L.; Wen, Y. Neat1-miRNA204-5p-PI3K-AKT axis as a potential mechanism for photodynamic therapy treated colitis in mice. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2018, 24, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Jiang, C.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, L.; Yun, H.; Xu, W.; Fan, W.; Liu, Q.; Dong, H. Serum-derived exosomes containing NEAT1 promote the occurrence of rheumatoid arthritis through regulation of miR-144-3p/ROCK2 axis. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2021, 12, 2040622321991705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Shi, H.; Yu, C.; Fu, J.; Chen, C.; Wu, S.; Zhan, T.; Wang, B.; Zheng, L. LncRNA Neat1 positively regulates MAPK signaling and is involved in the pathogenesis of Sjögren’s syndrome. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 88, 106992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero, J.J.; Trozzo, R.; Sugden, M.; Öllinger, R.; Belka, A.; Zhigalova, E.; Waetzig, P.; Engleitner, T.; Schmidt-Supprian, M.; Saur, D.; et al. Genome-scale pan-cancer interrogation of lncRNA dependencies using CasRx. Nat. Methods 2024, 21, 584–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessels, H.-H.; Méndez-Mancilla, A.; Guo, X.; Legut, M.; Daniloski, Z.; Sanjana, N.E. Massively parallel Cas13 screens reveal principles for guide RNA design. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 722–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| DISEASE TYPE | NEAT1 Expression | Mechanisms | References (Ref.) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stress-related | Neurodegenerative diseases (Huntington’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease, Huntington’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis) | Upregulated | Induced by genotoxic stress, regulating genome integrity through TIRR/53BP1 complex | [32,33,34,35,36,37,38] |
| Stress-related | Diabetic retinopathy | Upregulated | Induced in mitochondria by high glucose | [39] |
| Stress-related | Autism spectrum disorder | Upregulated | NEAT1 promotes apoptosis and oxidative stress through UBE3A | [48] |
| Stress-related | Temporomandibular joint disorders | Upregulated | NEAT1 promotes ROS in mitochondria | [49] |
| Stress-related | Intervertebral disc degeneration | Upregulated | NEAT1 induces oxidative stress-induced apoptosis through sponging miR-124-3p | [50] |
| Stress-related | Myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury | Upregulated | NEAT1 induces apoptosis through MAPK pathway, sponging miRNAs, promoting pri-miRNA processing, and promoting translation initiation | [54,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,106,109] |
| Stress-related | Type 2 diabetes | Upregulated | NEAT1 regulates hypoxia-induced damage | [73] |
| Immune-related | Influenza | Upregulated | NEAT1 induces transcription of IL8 | [25] |
| Immune-related | Hantaan virus | Upregulated | NEAT1 activates inflammatory macrophages through Srebp2 | [74,75] |
| Immune-related | Celiac disease | Downregulated | IL15 induces transcription of NEAT1 | [76] |
| Immune-related | Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus | N/A | NEAT1 activates innate immune response through HDP-RNP complex | [77] |
| Immune-related | Peritonitis and pneumonia | N/A | NEAT1 activates NLRP3, NLRC4, and AIM2 inflammasomes | [78] |
| Immune-related | Fibrosis | N/A | NEAT1 represses fibrosis through interacting with Rbm7 | [80] |
| Immune-related | Inflammatory bowel disease | N/A | Knockdown of NEAT1 promotes macrophage M2 | [81,82,83,107] |
| Immune-related | Atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction | Downregulated | NEAT1 regulate generation of tolerogenic DCs and CD4+ T cell balance | [84] |
| Immune-related | Hepatitis B virus | Downregulated | N/A | [85] |
| Immune-related | Human immunodeficiency virus 1 | Upregulated | N/A | [88,89,90] |
| Immune-related | Rheumatoid arthritis | Upregulated | NEAT1 promotes CD4+ T cells differentiating into Th17 cells | [92] |
| Immune-related | Coronary heart disease | Upregulated | NEAT1 promotes CD4+ T cells differentiating into Th17 cells | [95] |
| Immune-related | Autoimmune uveitis | Upregulated | NEAT1 promotes CD4+ T cells differentiating into Th17 cells | [94,95] |
| Immune-related | Allergic rhinitis | Upregulated | NEAT1 regulates Th1/Th2 balance | [96] |
| Immune-related | Asthma | Upregulated | NEAT1 promotes Th2 cell activation | [97,100] |
| Immune-related | SARS-CoV-2 | Upregulated | N/A | [98,102,110,111,112,113] |
| Immune-related | Systemic lupus erythematosus | Upregulated | NEAT1 promotes Th2 cell activation through STAT6 | [99] |
| Immune-related | Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia | Upregulated | N/A | [101] |
| Immune-related | Parkinson’s disease | Upregulated | N/A | [102,108] |
| Immune-related | Preeclampsia | Upregulated | N/A | [104] |
| Immune-related | Pulmonary arterial hypotension | Upregulated | N/A | [105] |
| Immune-related | Acute ischemic stroke | Upregulated | N/A | [114,115,116,117,118] |
| Immune-related | Sepsis | Upregulated | NEAT1 induces MCEMP1 by sponging miR-125 | [119,120,121] |
| Immune-related | Behçet’s disease | Upregulated | N/A | [122,123] |
| Immune-related | Immune thrombocytopenic purpura | Upregulated | N/A | [124] |
| Immune-related | Acute/chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathies | Upregulated | N/A | [125] |
| Immune-related | Atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome | Upregulated | N/A | [126] |
| Immune-related | Alzheimer’s disease | Upregulated | N/A | [127] |
| Immune-related | Hereditary angioedema | Upregulated | N/A | [128] |
| Immune-related | Sjögren’s syndrome | Upregulated | N/A | [129] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Haugh, W.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, J. Emerging Role of Long, Non-Coding RNA Nuclear-Enriched Abundant Transcript 1 in Stress- and Immune-Related Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4413. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094413
Liu X, Haugh W, Zhang Z, Huang J. Emerging Role of Long, Non-Coding RNA Nuclear-Enriched Abundant Transcript 1 in Stress- and Immune-Related Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4413. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094413
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xingliang, William Haugh, Ziqiang Zhang, and Jianguo Huang. 2025. "Emerging Role of Long, Non-Coding RNA Nuclear-Enriched Abundant Transcript 1 in Stress- and Immune-Related Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4413. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094413
APA StyleLiu, X., Haugh, W., Zhang, Z., & Huang, J. (2025). Emerging Role of Long, Non-Coding RNA Nuclear-Enriched Abundant Transcript 1 in Stress- and Immune-Related Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4413. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094413






