The Possibility of Plasma Membrane Transporters as Drug Targets in Oral Cancers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. ABC Transporters
2.1. Drug Excretion from Cancer Cells by ABC Transporters
| Family Name | Approved Symbol | Alias Symbol | HGNC # ID | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABCA (ABC I family) | ABCA3 | ABC-C | 33 | [39] |
| ABCB (MDR/TAP family) | ABCB1 | P-gy (MDR1) | 40 | [3,14,18,19,20,21,22,23,40,41] |
| ABCB4 | MDR2 | 45 | [39] | |
| ABCB5 | EST422562 | 46 | [3,42] | |
| ABCB10 * | EST20237 | 41 | [43] | |
| ABCC (CFTE/MRP family) | ABCC1 | MRP1 | 51 | [19,20,21,25,26,27,40,41] |
| ABCC2 | MRP2 | 53 | [44] | |
| ABCC3 * | MRP3 | 54 | [26] | |
| ABCC5 * | MRP5 | 56 | [36] | |
| ABCC10 * | MRP7 | 52 | [26] | |
| ABCE (OABP family) | ABCE1 | OABP | 69 | [45] |
| ABCG (WHITE family) | ABCG1 * | ABC8 | 73 | [38] |
| ABCG2 | BCRP | 74 | [19,20,21,27,29,30,31,32,33,34,40,41,44] |
2.2. Cancer Stem Cells and ABC Transporters
2.3. OSCC and ABC Transporters
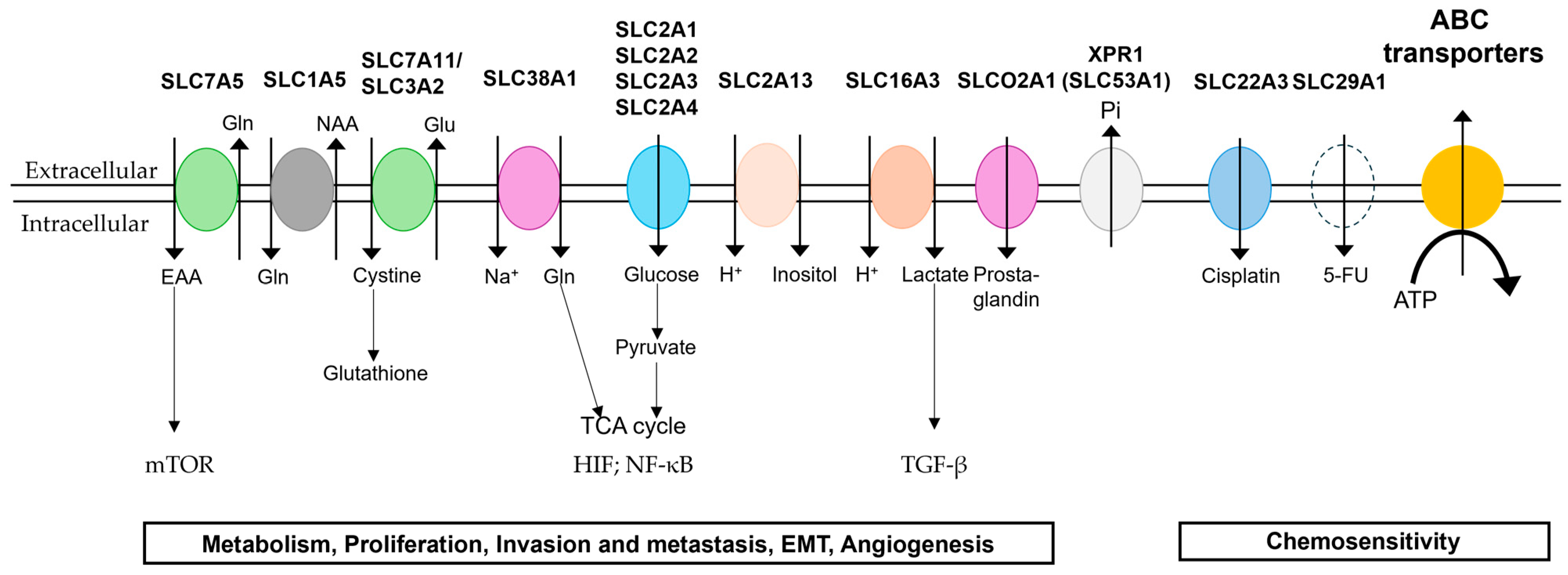
3. SLC Transporters
3.1. Glucose Transporters
3.2. Amino Acid Transporters
3.3. Other SLC Transporters
4. Plasma Membrane Transporters as Potential Drug Targets
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABC | ATP-binding cassette |
| SLC | solute carrier |
| OSCC | oral squamous cell carcinoma |
| HNSCC | head and neck squamous cell carcinoma |
| HPV | human papilloma virus |
| NBDs | nucleotide-binding domains |
| 5-FU | 5-fluorouracil |
| TMDs | transmembrane domains |
| MDR 1 | multidrug resistance 1 |
| BCRP | breast cancer resistance protein |
| CSCs | cancer stem cells |
| FACS | fluorescence-activated cell sorting |
| SP | side population |
| IL | interleukin |
| STAT3 | signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| EMT | epithelial-mesenchymal transition |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa B |
| OCT | organic cation transporter |
| MCT | monocarboxylic amino acid transporter |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
| HPA | Human Protein Atlas |
| MTF | mitochondrial folate transporter |
References
- Schinkel, A.H.; Jonker, J.W. Mammalian drug efflux transporters of the ATP binding cassette (ABC) family: An overview. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.H. ABC transporters as multidrug resistance mechanisms and the development of chemosensitizers for their reversal. Cancer Cell Int. 2005, 5, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Muriithi, W.; Macharia, L.W.; Heming, C.P.; Echevarria, J.L.; Nyachieo, A.; Filho, P.N.; Neto, V.M. ABC transporters and the hallmarks of cancer: Roles in cancer aggressiveness beyond multidrug resistance. Cancer Biol. Med. 2020, 17, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Gebali, S.; Bentz, S.; Hediger, M.; Anderle, P. Solute carriers (SLCs) in cancer. Mol. Asp. Med. 2013, 34, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, L.Q.M. Head and Neck Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, E.; Panwar, A.; Mosher, C.H.; Lydiatt, D. Cancers of the Major Salivary Gland. J. Oncol. Pract. 2018, 14, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagan, J.; Sarrión, G.; Jiménez, Y. Oral cancer: Clinical features. Oral Oncol. 2010, 46, 414–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Li, S.; Gao, L.; Zhi, K.; Ren, W. The Molecular Basis and Therapeutic Aspects of Cisplatin Resistance in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 761379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaeedi, S.M.; Aggarwal, S. The Holistic Review on Occurrence, Biology, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cureus 2022, 14, e30226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiliou, V.; Vasiliou, K.; Nebert, D.W. Human ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter family. Hum. Genom. 2009, 3, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, M.; Uchiumi, T.; Kuwano, M. Novel insights on the structure and function of ABC transporters. Seikagaku 2001, 73, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ford, R.C.; Beis, K. Learning the ABCs one at a time: Structure and mechanism of ABC transporters. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2019, 47, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasello, M.; Giudice, A.M.; Scotlandi, K. The ABC subfamily A transporters: Multifaceted players with incipient potentialities in cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 60, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, M. Role of ABC Transporters in Cancer Development and Malignant Alteration. Yakugaku Zasshi 2022, 142, 1201–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, K.; Cornwell, M.M.; Gottesman, M.M.; Pastan, I.; Roninson, I.B.; Ling, V.; Riordan, J.R. The mdrl gene, responsible for multidrug-resistance, codes for P-glycoprotein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1986, 141, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-j.; Chin, J.E.; Ueda, K.; Clark, D.P.; Pastan, I.; Gottesman, M.M.; Roninson, I.B. Internal duplication and homology with bacterial transport proteins in the mdr1 (P-glycoprotein) gene from multidrug-resistant human cells. Cell 1986, 47, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralhan, R.; Narayan, M.; Salotra, P.; Shukla, N.K.; Chauhan, S. Evaluation of P-glycoprotein expression in human oral oncogenesis: Correlation with clinicopathological features. Int. J. Cancer J. Int. Cancer 1997, 72, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottesman, M.M.; Ling, V. The molecular basis of multidrug resistance in cancer: The early years of P-glycoprotein research. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begicevic, R.R.; Falasca, M. ABC Transporters in Cancer Stem Cells: Beyond Chemoresistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, L.; Tian, L.; Sun, Q. Clinically-Relevant ABC Transporter for Anti-Cancer Drug Resistance. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 648407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.S.; Kim, M.J. Expression of multidrug resistance-related genes in oral squamous cell carcinomas. Oral Oncol. 2001, 37, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, P.P.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Panda, P.K.; Sinha, N.; Das, C.K.; Mishra, R.; Patil, S.; Bhutia, S.K. Autophagy regulates cisplatin-induced stemness and chemoresistance via the upregulation of CD44, ABCB1 and ADAM17 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Prolif. 2018, 51, e12411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lv, C.; Aghayants, S.; Wang, Y. MiR-15a-5p Knockdown up-Regulated ABCB1 Expression and Abated HNSCC Progression via the NF-κB Signaling Pathway. J. Investig. Surg. 2024, 37, 2434096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, Z.; He, Z.; Meng, Q.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y. A study of natural IgG antibodies against ATP-binding cassette subfamily C member 3 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2019, 15, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, R.E.; Punke, C.; Reymann, A. Expression of multi-drug resistance genes (mdr1, mrp1, bcrp) in primary oral squamous cell carcinoma. In Vivo 2004, 18, 133–147. [Google Scholar]
- Mesci, S.; Marakli, S.; Yazgan, B.; Yıldırım, X. The effect of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters in human cancers. Int. J. Sci. Lett. 2019, 1, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Ecker, G.F. A Structure-Based View on ABC-Transporter Linked to Multidrug Resistance. Molecules 2023, 28, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuthapisith, S.; Eremin, J.; El-Sheemey, M.; Eremin, O. Breast cancer chemoresistance: Emerging importance of cancer stem cells. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 19, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westover, D.; Li, F. New trends for overcoming ABCG2/BCRP-mediated resistance to cancer therapies. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 34, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, K.; Katayama, K.; Sugimoto, Y. Human ABC transporter ABCG2/BCRP expression in chemoresistance: Basic and clinical perspectives for molecular cancer therapeutics. Pharmgenom. Pers. Med. 2014, 7, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel, J.; Chmielewski, J.; Hrycyna, C.A. The roles of the human ATP-binding cassette transporters P-glycoprotein and ABCG2 in multidrug resistance in cancer and at endogenous sites: Future opportunities for structure-based drug design of inhibitors. Cancer Drug Resist. 2021, 4, 784–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalley, A.J.; Pitty, L.P.; Major, A.G.; Abdulmajeed, A.A.; Farah, C.S. Expression of ABCG2 and Bmi-1 in oral potentially malignant lesions and oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2014, 3, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, H.G.; Yu, H.L.; Ma, X.N.; Xu, X. Multidrug resistance and tumor-initiating capacity of oral cancer stem cells. J. BUON 2016, 21, 461–465. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Wei, Y.C.; Li, W.C.; Chen, H.Y.; Lin, H.Y.; Chiang, C.P.; Chen, H.M. Natural Compounds Modulate Drug Transporter Mediated Oral Cancer Treatment. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viaud, M.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Gall, J.; Ivanov, S.; Guinamard, R.; Sore, S.; Merlin, J.; Ayrault, M.; Guilbaud, E.; Jacquel, A.; et al. ABCA1 Exerts Tumor-Suppressor Function in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 3397–3410 e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wu, M.; Cai, H. Role of ABCC5 in cancer drug resistance and its potential as a therapeutic target. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1446418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y.; Song, W.; Lin, J.; Li, J.; Guan, X. p62/mTOR/LXRalpha pathway inhibits cholesterol efflux mediated by ABCA1 and ABCG1 during autophagy blockage. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 514, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namba, Y.; Sogawa, C.; Okusha, Y.; Kawai, H.; Itagaki, M.; Ono, K.; Murakami, J.; Aoyama, E.; Ohyama, K.; Asaumi, J.I.; et al. Depletion of Lipid Efflux Pump ABCG1 Triggers the Intracellular Accumulation of Extracellular Vesicles and Reduces Aggregation and Tumorigenesis of Metastatic Cancer Cells. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Si, Q.; Lu, W.; Song, Y.; Jin, W.; Yang, X.; Li, Z.; Hu, X.; Ding, L.; et al. Complex IIa formation and ABC transporters determine sensitivity of OSCC to Smac mimetics. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.D.; Ghuwalewala, S.; Das, P.; Mandloi, S.; Alam, S.K.; Chakraborty, J.; Sarkar, S.; Chakrabarti, S.; Panda, C.K.; Roychoudhury, S. MicroRNA profiling of cisplatin-resistant oral squamous cell carcinoma cell lines enriched with cancer-stem-cell-like and epithelial-mesenchymal transition-type features. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.S.; Kim, Y.K.; Yun, P.Y. Upregulation of MDR- and EMT-Related Molecules in Cisplatin-Resistant Human Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, M.; Krimmel, M.; Polligkeit, J.; Alexander, D.; Munz, A.; Kluba, S.; Keutel, C.; Hoffmann, J.; Reinert, S.; Hoefert, S. ABCB5 expression and cancer stem cell hypothesis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 3186–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Li, X.H.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.J. Circ-ABCB10 accelerates the malignant progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma by absorbing miRNA-145-5p. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 681–690. [Google Scholar]
- Tonigold, M.; Rossmann, A.; Meinold, M.; Bette, M.; Märken, M.; Henkenius, K.; Bretz, A.C.; Giel, G.; Cai, C.; Rodepeter, F.R.; et al. A cisplatin-resistant head and neck cancer cell line with cytoplasmic p53mut exhibits ATP-binding cassette transporter upregulation and high glutathione levels. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 140, 1689–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Liu, D.X. Knock-down of ABCE1 gene induces G1/S arrest in human oral cancer cells. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 5495–5504. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, H.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Huang, W. Recent advances in drug delivery systems for targeting cancer stem cells. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Schuetz, J.D.; Bunting, K.D.; Colapietro, A.M.; Sampath, J.; Morris, J.J.; Lagutina, I.; Grosveld, G.C.; Osawa, M.; Nakauchi, H.; et al. The ABC transporter Bcrp1/ABCG2 is expressed in a wide variety of stem cells and is a molecular determinant of the side-population phenotype. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 1028–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susanto, J.; Lin, Y.H.; Chen, Y.N.; Shen, C.R.; Yan, Y.T.; Tsai, S.T.; Chen, C.H.; Shen, C.N. Porphyrin homeostasis maintained by ABCG2 regulates self-renewal of embryonic stem cells. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wang, Z.; Huang, H.; Wang, H. Hedgehog signaling promotes multidrug resistance by regulation of ABC transporters in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2020, 49, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, A.; Rubab, I.; Malik, S.; Khan, A.; Khan, M.J.; Fatmi, M.Q. Meta-Analysis of miRNAs and Their Involvement as Biomarkers in Oral Cancers. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8439820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.; Doherty, E.; Ortega-Prieto, P.; Arizanova, J.; Fets, L. Membrane transporters in cell physiology, cancer metabolism and drug response. Dis. Model. Mech. 2023, 16, dmm050404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Piscitelli, C.L.; Yamashita, A.; Gouaux, E. A competitive inhibitor traps LeuT in an open-to-out conformation. Science 2008, 322, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anzai, N. Transporters: Toward the renal control of the body. Jpn. J. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2012, 26, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Colas, C.; Ung, P.M.-U.; Schlessinger, A. SLC transporters: Structure, function, and drug discovery. MedChemComm 2016, 7, 1069–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garibsingh, R.A.; Schlessinger, A. Advances and Challenges in Rational Drug Design for SLCs. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 40, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.D.; Li, S.J.; Liao, J.X. Inhibition of glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) chemosensitized head and neck cancer cells to cisplatin. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 12, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botha, H.; Farah, C.S.; Koo, K.; Cirillo, N.; McCullough, M.; Paolini, R.; Celentano, A. The Role of Glucose Transporters in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.X.; Sun, J.L.; Gong, Z.C.; Lin, Z.Q.; Liu, H. Prognostic value of GLUT-1 expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma: A prisma-compliant meta-analysis. Medicine 2016, 95, e5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyquist, M.D.; Prasad, B.; Mostaghel, E.A. Harnessing Solute Carrier Transporters for Precision Oncology. Molecules 2017, 22, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, L.; Yao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Chu, M.; Bhutia, Y.D.; Chen, R.; Ganapathy, V. Transporter-Targeted Nano-Sized Vehicles for Enhanced and Site-Specific Drug Delivery. Cancers 2020, 12, 2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwosu, Z.C.; Song, M.G.; di Magliano, M.P.; Lyssiotis, C.A.; Kim, S.E. Nutrient transporters: Connecting cancer metabolism to therapeutic opportunities. Oncogene 2023, 42, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharadwaj, R.; Jaiswal, S.; De La Cruz, E.V.; Thakare, R. Targeting Solute Carrier Transporters (SLCs) as a Therapeutic Target in Different Cancers. Diseases 2024, 12, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisetto, S.; Whitaker-Menezes, D.; Wilski, N.A.; Tuluc, M.; Curry, J.; Zhan, T.; Snyder, C.M.; Martinez-Outschoorn, U.E.; Philp, N.J. Monocarboxylate Transporter 4 (MCT4) Knockout Mice Have Attenuated 4NQO Induced Carcinogenesis; A Role for MCT4 in Driving Oral Squamous Cell Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, J.J.G.; Macias, R.I.R.; Cives-Losada, C.; Peleteiro-Vigil, A.; Herraez, E.; Lozano, E. Plasma Membrane Transporters as Biomarkers and Molecular Targets in Cholangiocarcinoma. Cells 2020, 9, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoda, M.; Kaira, K.; Ohshima, Y.; Ishioka, N.S.; Shino, M.; Sakakura, K.; Takayasu, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Tominaga, H.; Oriuchi, N.; et al. Prognostic significance of amino-acid transporter expression (LAT1, ASCT2, and xCT) in surgically resected tongue cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 2506–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Liu, T.; Li, L.; Liu, Q.; Huang, C.; Liang, Y.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lu, X. SLC1A5, unrelated to prognosis, was associated with CD8(+) T-cell exclusion in the tumor microenvironment of squamous cell carcinoma. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hushmandi, K.; Einollahi, B.; Saadat, S.H.; Lee, E.H.C.; Farani, M.R.; Okina, E.; Huh, Y.S.; Nabavi, N.; Salimimoghadam, S.; Kumar, A.P. Amino acid transporters within the solute carrier superfamily: Underappreciated proteins and novel opportunities for cancer therapy. Mol. Metab. 2024, 84, 101952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutia, Y.D.; Babu, E.; Ramachandran, S.; Ganapathy, V. Amino Acid transporters in cancer and their relevance to “glutamine addiction”: Novel targets for the design of a new class of anticancer drugs. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 1782–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, J.H.; Mazambani, S.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, J.-W. Oxidative Stress and the Intersection of Oncogenic Signaling and Metabolism in Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Cells 2021, 10, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuzumi, M.; Hamakawa, H.; Onishi, A.; Sumida, T.; Tanioka, H. Gene expression of GLUT isoforms and VHL in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2000, 161, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkel, M.; Reichert, T.E.; Benz, P.; Lehr, H.A.; Jeong, J.H.; Wieand, S.; Bartenstein, P.; Wagner, W.; Whiteside, T.L. Overexpression of Glut-1 and increased glucose metabolism in tumors are associated with a poor prognosis in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer 2003, 97, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.R.; Jiang, T.; Wu, T.T.; Zhou, S.H.; Yao, H.T.; Wang, Q.Y.; Lu, Z.J. Expression of hypoxia-related markers in inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors of the head and neck. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 11, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, C.Y. Targeting cancer stem cells in squamous cell carcinoma. Precis. Clin. Med. 2019, 2, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attur, S.K.; Patel, A.; Attur, K.M. Study of expression of GLUT-1 in oral potentially malignant disorders and oral squamous cell carcinoma: An immuno-histochemical analysis. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2024, 28, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshan, S.; Mahdavi, N.; Kardouni Khoozestani, N.; Nasr Esfahani, B.; Heidarian, F.; Rahrotaban, S.; Abdolrahmani, A. Assessment of the association of OCT3/4 with GLUT1 and CD105 in oral squamous cell carcinoma using dual immunohistochemistry. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhong, J.T.; Zhou, S.H.; Han, H.M. Roles of GLUT-1 and HK-II expression in the biological behavior of head and neck cancer. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 3066–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.J.; Yuan, J.; Sun, W.J.; Chen, Q.Y.; Lin, Y.; Tang, L.; Liang, L.Z. Inhibition of microRNA-218 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma growth by targeting GLUT1 to affect glucose metabolism. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 7726–7734. [Google Scholar]
- Gholami, S.; Chamorro-Petronacci, C.; Perez-Sayans, M.; Suarez Penaranda, J.; Longatto-Filho, A.; Baltazar, F.; Afonso, J. Immunoexpression profile of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) targets in potentially malignant and malignant oral lesions: A pilot study. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2023, 31, e20220461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feitosa, S.G.; Viana, K.F.; Luna, E.C.M.; Costa, F.W.G.; Cavalcante, R.B.; Chaves, F.N.; Chaves, H.V.; Pereira, K.M.A. Immunohistochemical Evaluation of GLUT-3 and GLUT-4 in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 19, 1779–1783. [Google Scholar]
- Ayala, F.R.; Rocha, R.M.; Carvalho, K.C.; Carvalho, A.L.; da Cunha, I.W.; Lourenco, S.V.; Soares, F.A. GLUT1 and GLUT3 as potential prognostic markers for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Molecules 2010, 15, 2374–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, F.; Zhang, J.; Fu, T.; Jiang, P.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Yan, S.; Yan, X.; Yu, L.; Xu, Z.; et al. Identification of SLC2A3 as a prognostic indicator correlated with the NF-κB/EMT axis and immune response in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Channels 2023, 17, 2208928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.Y.; Kang, N.S. The Solute Carrier (SLC) Transporter Superfamily as Therapeutic Targets for the Treatment of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2024, 16, 3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Xu, S.; Li, P. SLC2A3 promotes tumor progression through lactic acid-promoted TGF-beta signaling pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0301724. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Fang, J.; Lai, W.; Hu, Y.; Li, L.; Zhong, Y.; Yang, S.; He, D.; Liu, R.; Tang, Q. IL-6/STAT3 Axis Activates Glut5 to Regulate Fructose Metabolism and Tumorigenesis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 3668–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.G.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, B.K.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, K.S.; Chang, K.; Park, S.H.; Bae, Y.S.; Kwon, B.S. H+-myo-inositol transporter SLC2A13 as a potential marker for cancer stem cells in an oral squamous cell carcinoma. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2011, 11, 966–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.E.; Li, Y.; Hou, J. Downregulation of SLC3A2 mediates immune evasion and accelerates metastasis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e18010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaresima, B.; Scicchitano, S.; Faniello, M.C.; Mesuraca, M. Role of solute carrier transporters in ovarian cancer (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2025, 55, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrodter, S.; Braun, M.; Syring, I.; Klumper, N.; Deng, M.; Schmidt, D.; Perner, S.; Muller, S.C.; Ellinger, J. Identification of the dopamine transporter SLC6A3 as a biomarker for patients with renal cell carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2016, 15, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, J.; Lindgren, D.; Nilsson, H.; Johansson, E.; Johansson, M.; Gustavsson, L.; Axelson, H. Overexpression of Functional SLC6A3 in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2105–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogawa, C.; Eguchi, T.; Tran, M.T.; Ishige, M.; Trin, K.; Okusha, Y.; Taha, E.A.; Lu, Y.; Kawai, H.; Sogawa, N.; et al. Antiparkinson Drug Benztropine Suppresses Tumor Growth, Circulating Tumor Cells, and Metastasis by Acting on SLC6A3/DAT and Reducing STAT3. Cancers 2020, 12, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurth, I.; Yamaguchi, N.; Andreu-Agullo, C.; Tian, H.S.; Sridhar, S.; Takeda, S.; Gonsalves, F.C.; Loo, J.M.; Barlas, A.; Manova-Todorova, K.; et al. Therapeutic targeting of SLC6A8 creatine transporter inhibits KRAS mutant and wildtype colon cancer and modulates human creatine levels. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabi7511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xu, J.; Liang, C.; Meng, Q.; Hua, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Yu, X.; Shi, S. Emerging roles of the solute carrier family in pancreatic cancer. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puris, E.; Fricker, G.; Gynther, M. The Role of Solute Carrier Transporters in Efficient Anticancer Drug Delivery and Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppula, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhuang, L.; Gan, B. Amino acid transporter SLC7A11/xCT at the crossroads of regulating redox homeostasis and nutrient dependency of cancer. Cancer Commun. 2018, 38, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Gu, J.; Yang, Y.; Liang, J.; Wang, Y.; Ji, N.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, S.; et al. PPARγ Antagonists Exhibit Antitumor Effects by Regulating Ferroptosis and Disulfidptosis. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Shu, Y. Role of solute carriers in response to anticancer drugs. Mol. Cell. Ther. 2014, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolk, O.; Schnepf, R.; Muschler, M.; Fromm, M.F.; Wendler, O.; Traxdorf, M.; Iro, H.; Zenk, J. Transporter Gene Expression in Human Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Associated Epigenetic Regulatory Mechanisms. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.M.; Lin, P.M.; Chang, J.G.; Lin, H.C.; Li, S.H.; Lin, S.F.; Yang, M.Y. Upregulated SLC22A3 has a potential for improving survival of patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma receiving cisplatin treatment. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 74348–74358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehvy, A.I.; Horev, G.; Golan, Y.; Glaser, F.; Shammai, Y.; Assaraf, Y.G. Alterations in ZnT1 expression and function lead to impaired intracellular zinc homeostasis in cancer. Cell Death Discov. 2019, 5, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, L.C.; Costello, L.C.; Zou, J.; Franklin, R.B. A Potential Zinc Treatment for Patients with Terminal Advanced Laryngeal or Tongue Carcinoma: Clioquinol Zinc Ionophore. Dent. Oral Biol. Craniofac. Res. 2020, 3, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, D.; Wang, D.; Schreurs, O.; Vallenari, E.M.; Pandey Dhakal, S.; Küntziger, T.; Toközlü, B.S.; Utheim, T.P.; Chaudhry, F.A. Investigation of Roles of SLC38A1 in Proliferation and Differentiation of Mouse Tongue Epithelium and Expression in Human Oral Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2024, 16, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harshani, J.M.; Yeluri, S.; Guttikonda, V.R. Glut-1 as a prognostic biomarker in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2014, 18, 372–378. [Google Scholar]
- Ganvir, S.M.; Bamane, S.A.; Katkade, S.P.; Khobragade, P.G.; Hazarey, V.P.; Gosavi, S.R. Depth of invasion and GLUT-1 as risk predictors in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Transl. Res. Oral Oncol. 2017, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Mohiddin, G.; Raghuvanshi, M.; Sahoo, S.K.; Bhuyan, L. Can Increased Metabolic Status be a Grading Tool for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma? A Glucose Transporter 1 Immunoexpression Study. Niger. J. Surg. 2019, 25, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patlolla, P.; Shyam, N.D.V.N.; Kumar, G.K.; Narayen, V.; Konda, P.; Mudududla, P. Evaluation of glucose transporter-1 expression in oral epithelial dysplasia and oral squamous cell carcinoma: An immunohistochemical study. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2020, 24, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.; Yu, A.M. MicroRNAs in the Regulation of Solute Carrier Proteins Behind Xenobiotic and Nutrient Transport in Cells. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 893846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-Pouso, A.I.; Perez-Sayans, M.; Rodriguez-Zorrilla, S.; Chamorro-Petronacci, C.; Garcia-Garcia, A. Dissecting the Proton Transport Pathway in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: State of the Art and Theranostics Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaruskova, M.; Curik, N.; Hercog, R.; Polivkova, V.; Motlova, E.; Benes, V.; Klamova, H.; Pecherkova, P.; Belohlavkova, P.; Vrbacky, F.; et al. Genotypes of SLC22A4 and SLC22A5 regulatory loci are predictive of the response of chronic myeloid leukemia patients to imatinib treatment. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kędzia, K.; Szmajda-Krygier, D.; Krygier, A.; Jabłoński, S.; Balcerczak, E.; Wcisło, S. Altered carnitine transporter genes (SLC22A5, SLC22A16, SLC6A14) expression pattern among lung cancer patients. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2024, 13, 2903–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Yu, P.; Chan, W.N.; Xie, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, L.; Leung, K.T.; Lo, K.W.; Yu, J.; Tse, G.M.K.; et al. Cellular zinc metabolism and zinc signaling: From biological functions to diseases and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCracken, A.N.; Edinger, A.L. Targeting cancer metabolism at the plasma membrane by limiting amino acid access through SLC6A14. Biochem. J. 2015, 470, e17–e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamska, A.; Falasca, M. ATP-binding cassette transporters in progression and clinical outcome of pancreatic cancer: What is the way forward? World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 3222–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krchniakova, M.; Skoda, J.; Neradil, J.; Chlapek, P.; Veselska, R. Repurposing Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors to Overcome Multidrug Resistance in Cancer: A Focus on Transporters and Lysosomal Sequestration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyimesi, G.; Hediger, M.A. Transporter-Mediated Drug Delivery. Molecules 2023, 28, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Abdulla, R.; Perez-Silva, L.; Abete, L.; Romero, M.R.; Briz, O.; Marin, J.J.G. Unraveling ‘The Cancer Genome Atlas’ information on the role of SLC transporters in anticancer drug uptake. Expert. Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 12, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.; Watkins, N.H.; Brown-Harding, H.; Bierbach, U. A membrane transporter determines the spectrum of activity of a potent platinum-acridine hybrid anticancer agent. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Tang, C.; Shi, G.; Wang, G.; Du, Y.; Tian, J.; Zhang, H. Novel fluorescent GLUT1 inhibitor for precision detection and fluorescence image-guided surgery in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2022, 151, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolini, R.; Moore, C.; Matthyssen, T.; Cirillo, N.; McCullough, M.; Farah, C.S.; Botha, H.; Yap, T.; Celentano, A. Transcriptional regulation of glucose transporters in human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2022, 51, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Yee, S.W.; Kim, R.B.; Giacomini, K.M. SLC transporters as therapeutic targets: Emerging opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 543–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xie, J.; Wu, D.; Chen, L.; Gong, Z.; Wu, R.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xu, Y. A pan-cancer analysis revealed the role of the SLC16 family in cancer. Channels 2021, 15, 528–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavoro, A.; Falzone, L.; Tomasello, B.; Conti, G.N.; Libra, M.; Candido, S. In silico analysis of the solute carrier (SLC) family in cancer indicates a link among DNA methylation, metabolic adaptation, drug response, and immune reactivity. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1191262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Family Name | Approved Symbol | Alias Symbol | HGNC # ID | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLC1 (High-affinity glutamate and neutral amino acid transporter family) | ||||
| SLC1A5 | AAAT; ASCT2 | 10943 | [65,66,67,68,69] | |
| SLC2 (Facilitative glucose transporter family (previous name GLUT)) | ||||
| SLC2A1 | GLUT-1; DYT18; DYT19 | 11005 | [57,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78] | |
| SLC2A2 | GLUT-2 | 11006 | [70,79] | |
| SLC2A3 | 11007 | [4,80,81,82,83] | ||
| SLC2A4 | 11009 | [4,70,79] | ||
| SLC2A5 * | 11010 | [61,84] | ||
| SLC2A13 | HMIT | 15956 | [4,85] | |
| SLC3 (Heavy subunits of the heteromeric amino acid transporters) | ||||
| SLC3A2 | 4T2HC; 4F2 | 11026 | [62,86,87] | |
| SLC5 (Sodium-glucose cotransporter family) | ||||
| SLC5A1 | SGLT-1 | 11036 | [4,57] | |
| SLC6 (Na+- and Cl−-dependent neurotransmitter transporter family) | ||||
| SLC6A3 * | DAT | 11049 | [88,89,90] | |
| SLC6A8 * | CRTR; CT1 | 11055 | [91] | |
| SLC6A14 * | CRTR; CT1 | 11047 | [92] | |
| SLC7 (Cationic amino acid transporter/glycoprotein-associated family) | ||||
| SLC7A5 | LAT1 | 11063 | [4,62,65,68,69,82,87,93] | |
| SLC7A11 | xCT | 11059 | [68,94,95] | |
| SLC16 (Monocarboxylate transporter family) | ||||
| SLC16A3 | MCT3; MCT4 | 10924 | [4,59,63,82] | |
| SLCO (Organic anion transporting family (previous family name SLC21)) | ||||
| SLCO1A2 | OATP; OATP1A2 | 10956 | [62] | |
| SLCO1B3 | OATP8; OATP1B3 | 10961 | [62] | |
| SLCO2A1 | PGT; OATP2A1 | 10955 | [96] | |
| SLCO2B1 | OATP-8; OATP2B1 | 10962 | [97] | |
| SLC22 (Organic cation/anion/zwitterion transporter family) | ||||
| SLC22A3 | OCT3; EMT | 10967 | [96,98] | |
| SLC22A4 | OCTN1 | 10968 | [93,96] | |
| SLC22A5 | OCTN2 | 10969 | [93,96] | |
| SLC22A16 | CT2; OAT6 | 20302 | [96] | |
| SLC25 (Mitochondrial carrier family) | ||||
| SLC25A32 | MFTC | 29683 | [87] | |
| SLC29 (Facilitative nucleoside transporter family) | ||||
| SLC29A1 * | ENT1 | 11003 | [62] | |
| SLC30 (Zinc efflux family) | ||||
| SLC30A1 * | ZRC1 (ZNT1) | 11012 | [4,99,100] | |
| SLC31 (Copper transporter family) | ||||
| SLC31A1 * | CTR1 | 11016 | [87] | |
| SLC34 (Type II Na+ Phosphate cotransporter family) | ||||
| SLC34A2 * | NAPI-3B; NaPi-2b | 11020 | [87] | |
| SLC38 (System A & N, Na+-coupled neutral amino acid transporter family) | ||||
| SLC38A1 | SNAT1; ATA1 | 13447 | [59,101] | |
| SLC39 (Metal ion transporter family) | ||||
| SLC39A1 * | ZIP1 | 12876 | [99,100] | |
| SLC39A4 * | ZIP4 | 17129 | [87] | |
| SLC39A13 * | ZIP13 | 20859 | [87] | |
| SLC53 (Phosphate carriers (phosphate exporter) | ||||
| XPR1 | SLC53A1; SYG1 | 12827 | [82,87] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sogawa, C.; Shimada, K.; Nakano, K. The Possibility of Plasma Membrane Transporters as Drug Targets in Oral Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4310. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094310
Sogawa C, Shimada K, Nakano K. The Possibility of Plasma Membrane Transporters as Drug Targets in Oral Cancers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4310. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094310
Chicago/Turabian StyleSogawa, Chiharu, Katsumitsu Shimada, and Keisuke Nakano. 2025. "The Possibility of Plasma Membrane Transporters as Drug Targets in Oral Cancers" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4310. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094310
APA StyleSogawa, C., Shimada, K., & Nakano, K. (2025). The Possibility of Plasma Membrane Transporters as Drug Targets in Oral Cancers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4310. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094310






