A Novel Supramolecular Salt of Hypoxanthine with Maleic Acid as a Potential Weight-Loss Drug
Abstract
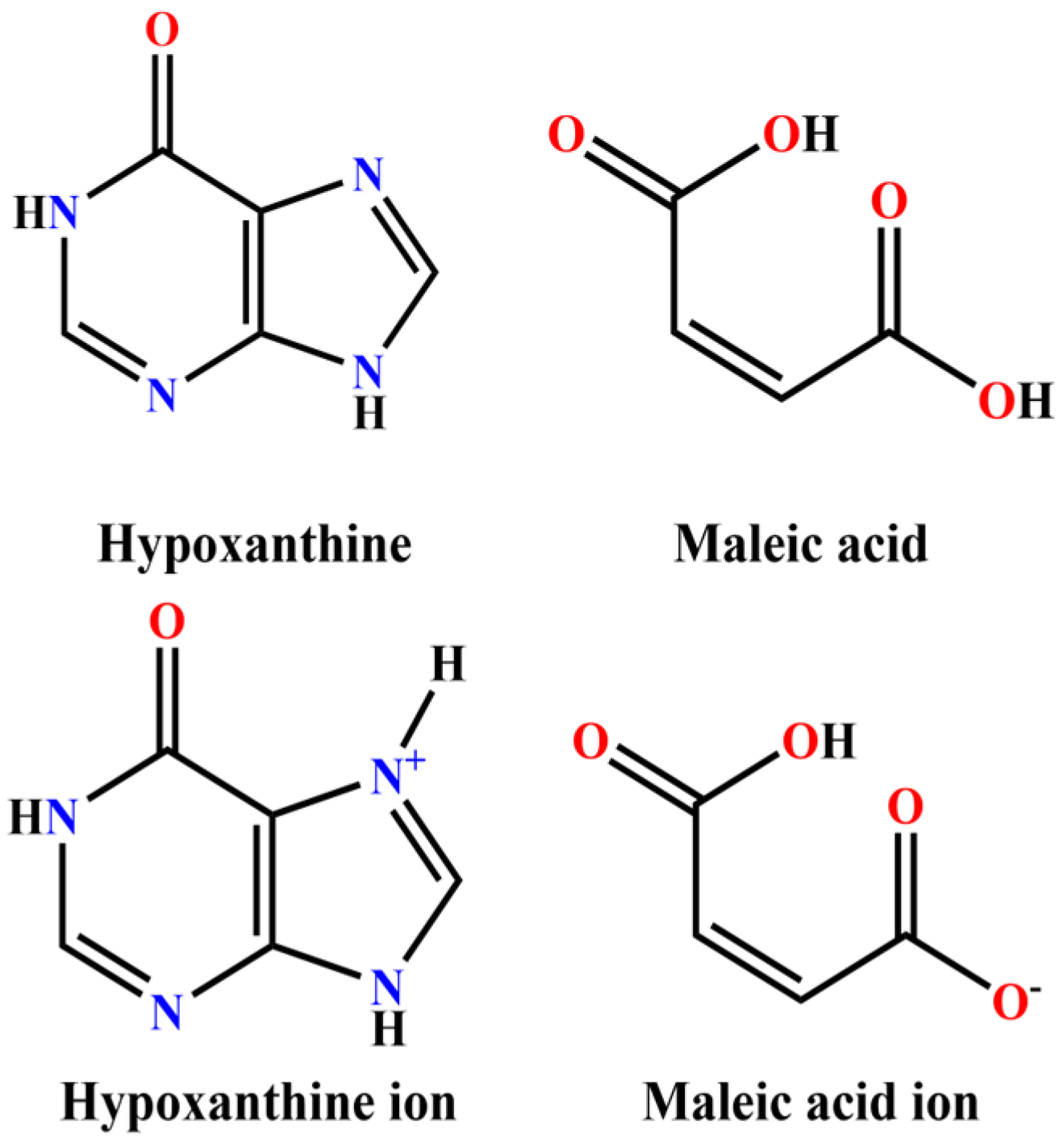
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
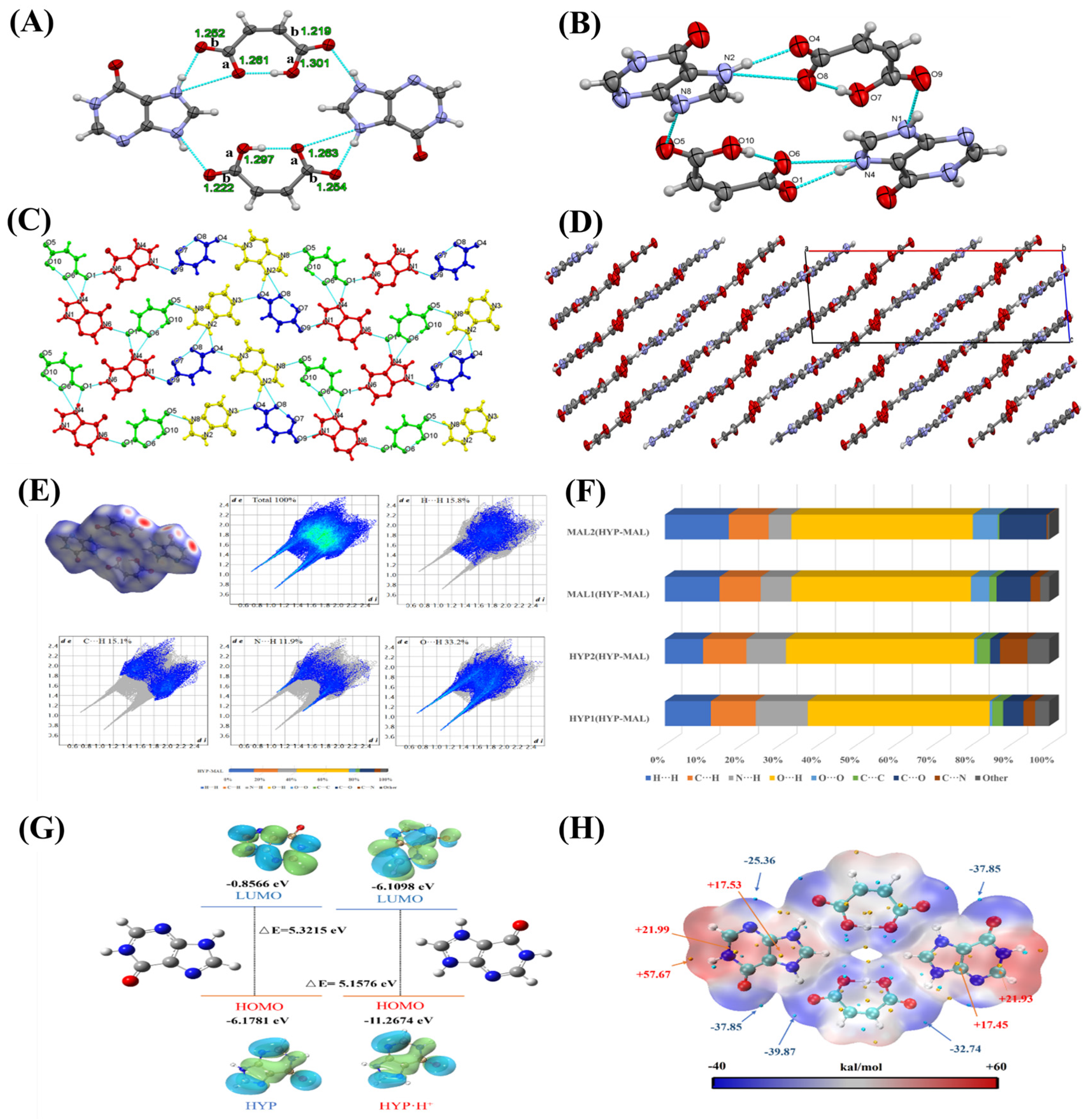
2.1. Single-Crystal X-Ray Diffraction (SXRD) Analysis
2.2. Theoretical Calculation
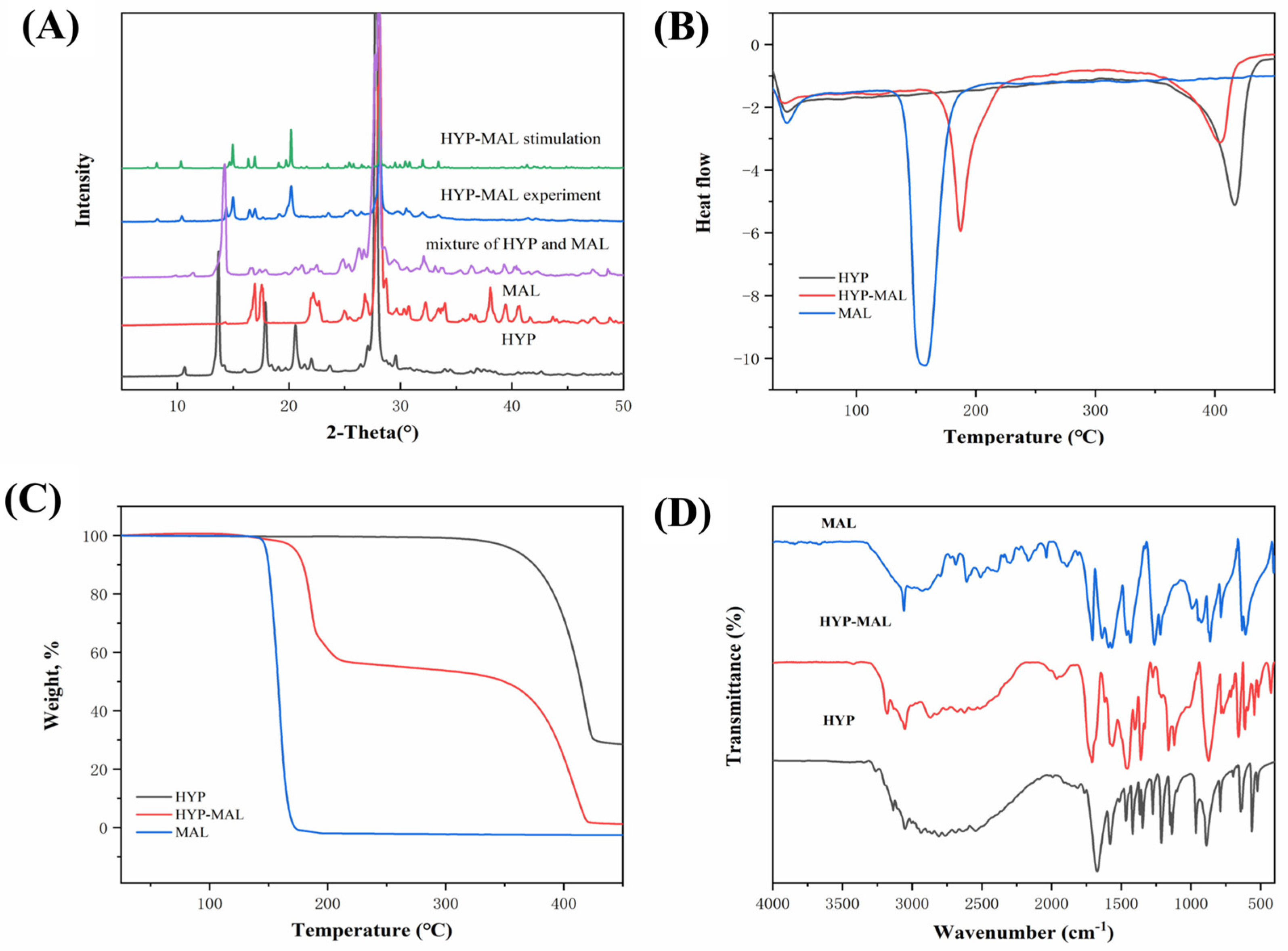
2.3. Powder X-Ray Diffraction (PXRD) Analysis
2.4. Thermal Analysis
2.5. FT-IR and 1H NMR Spectroscopy
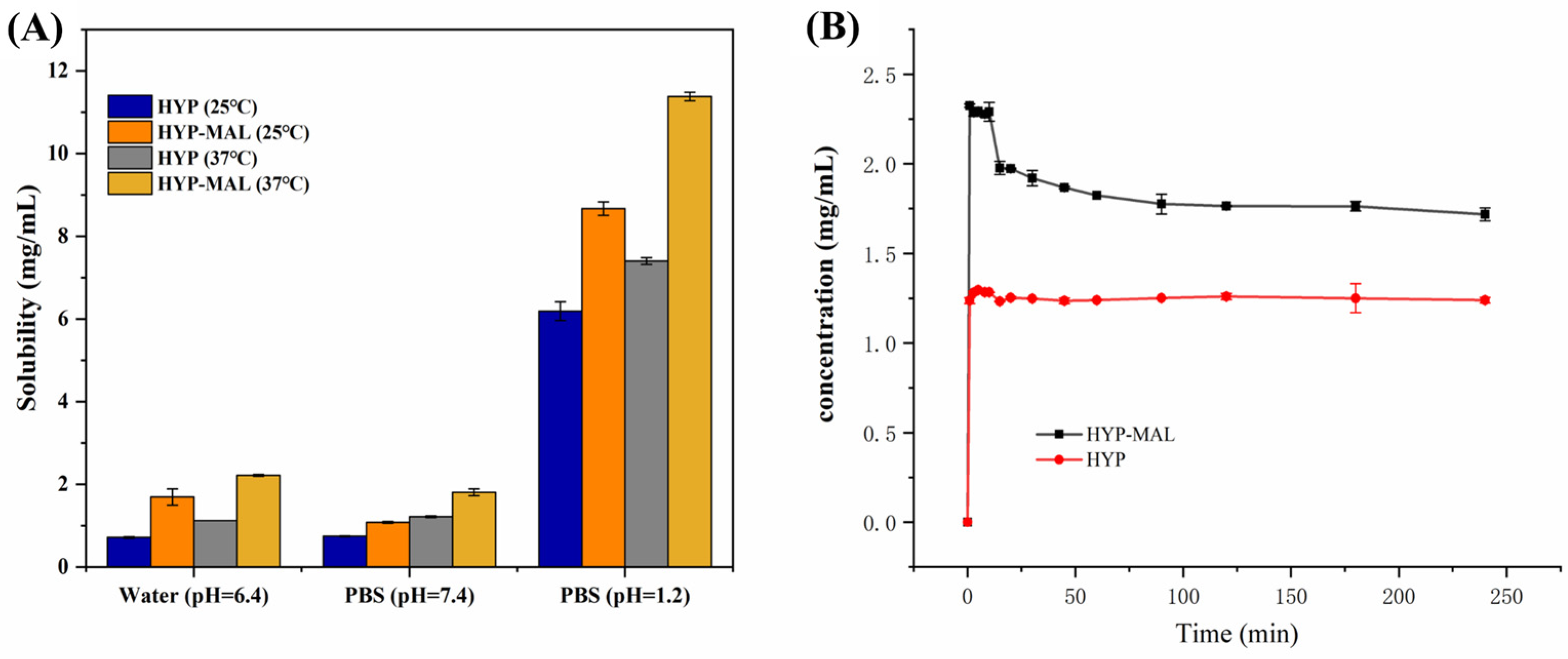
2.6. Equilibrium Solubility
2.7. Powder Dissolution Experiments
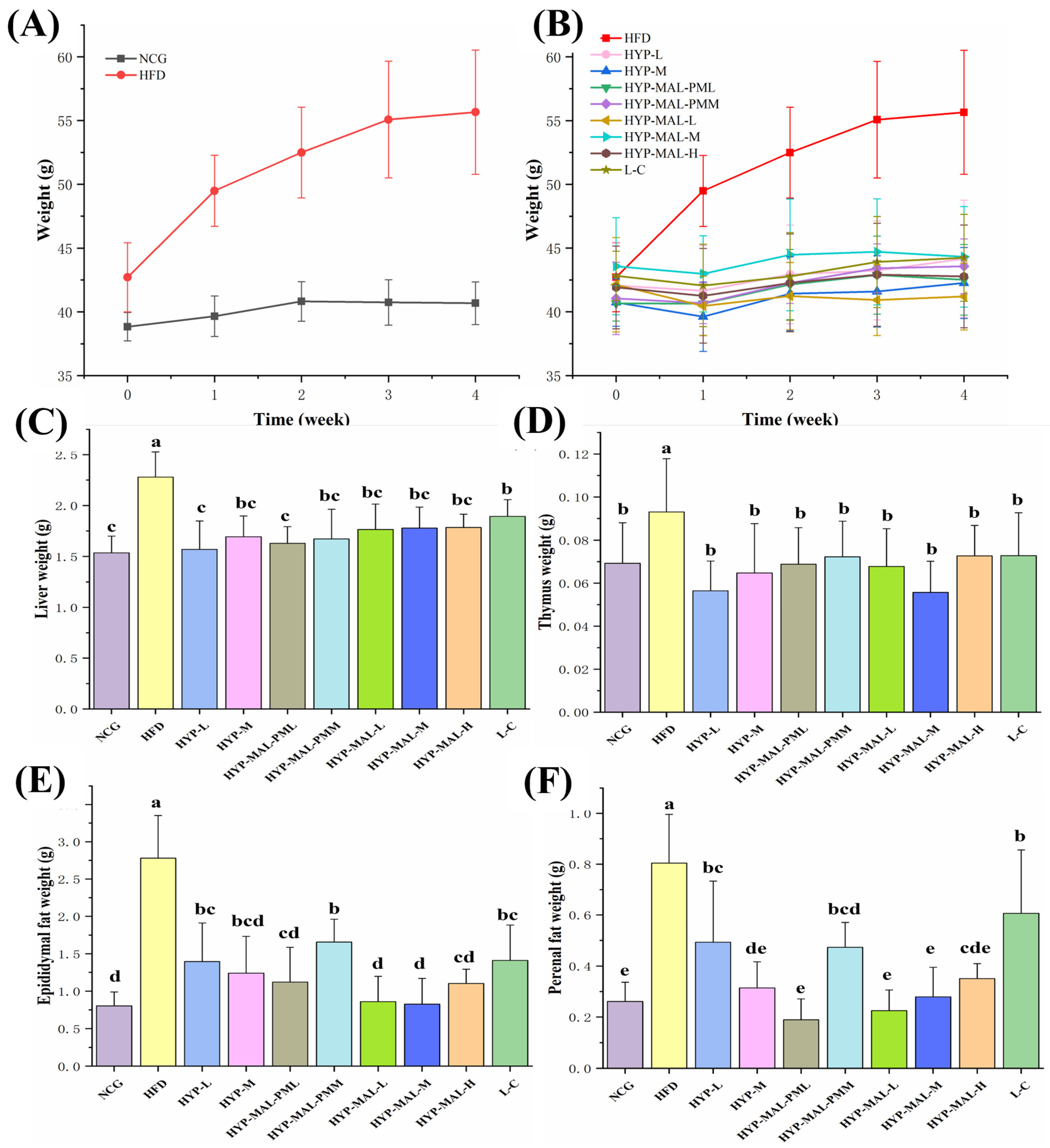
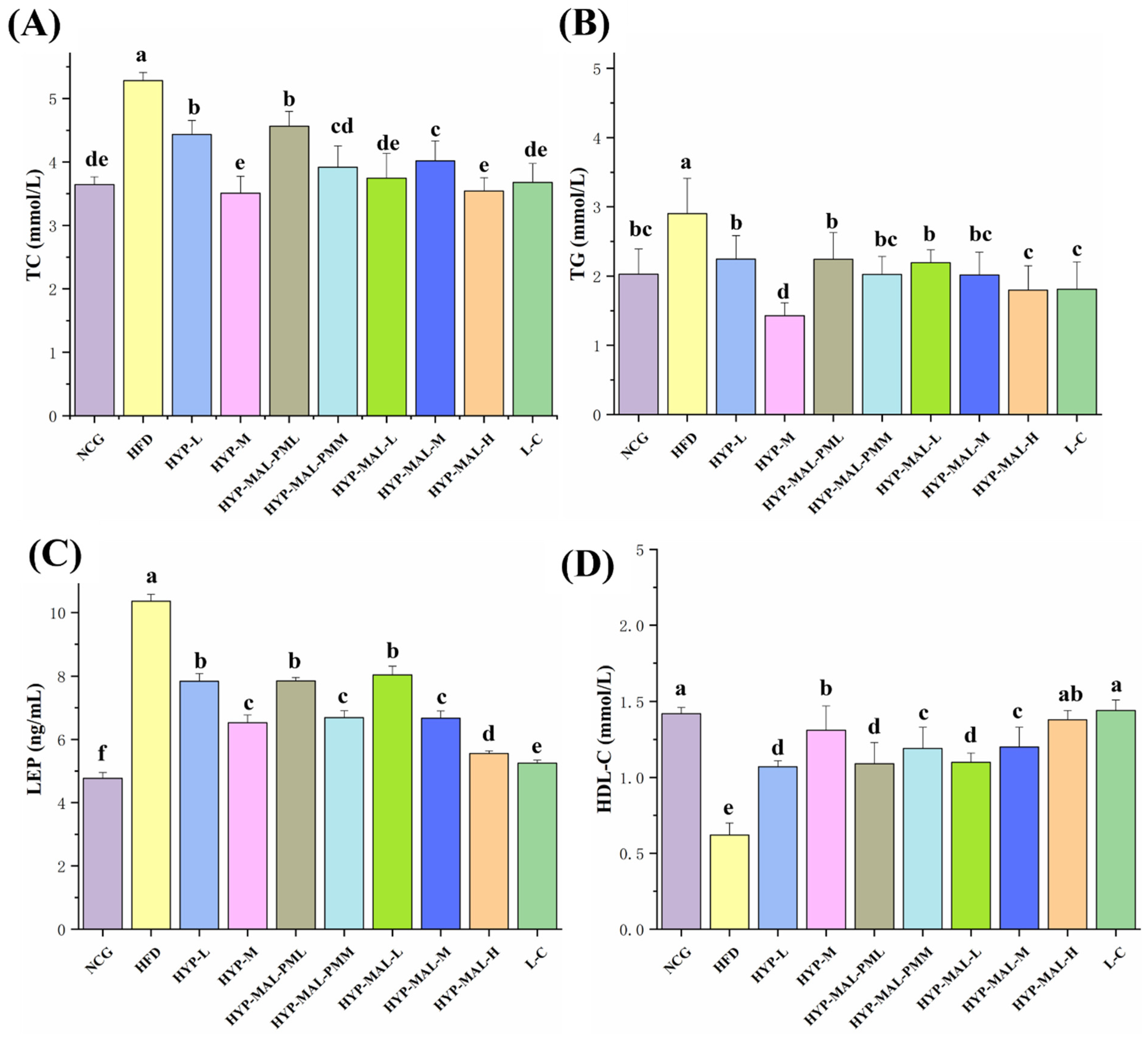
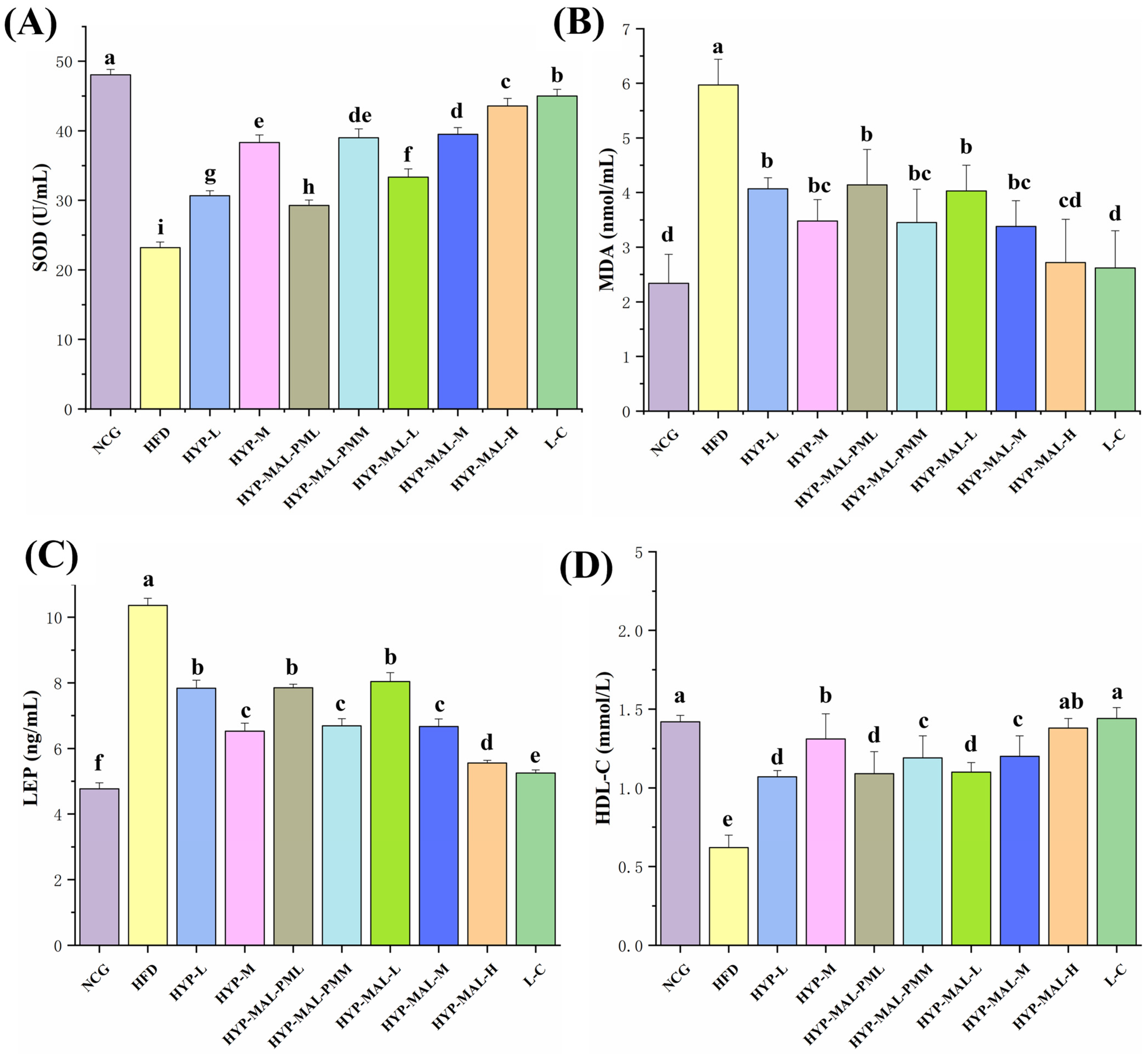
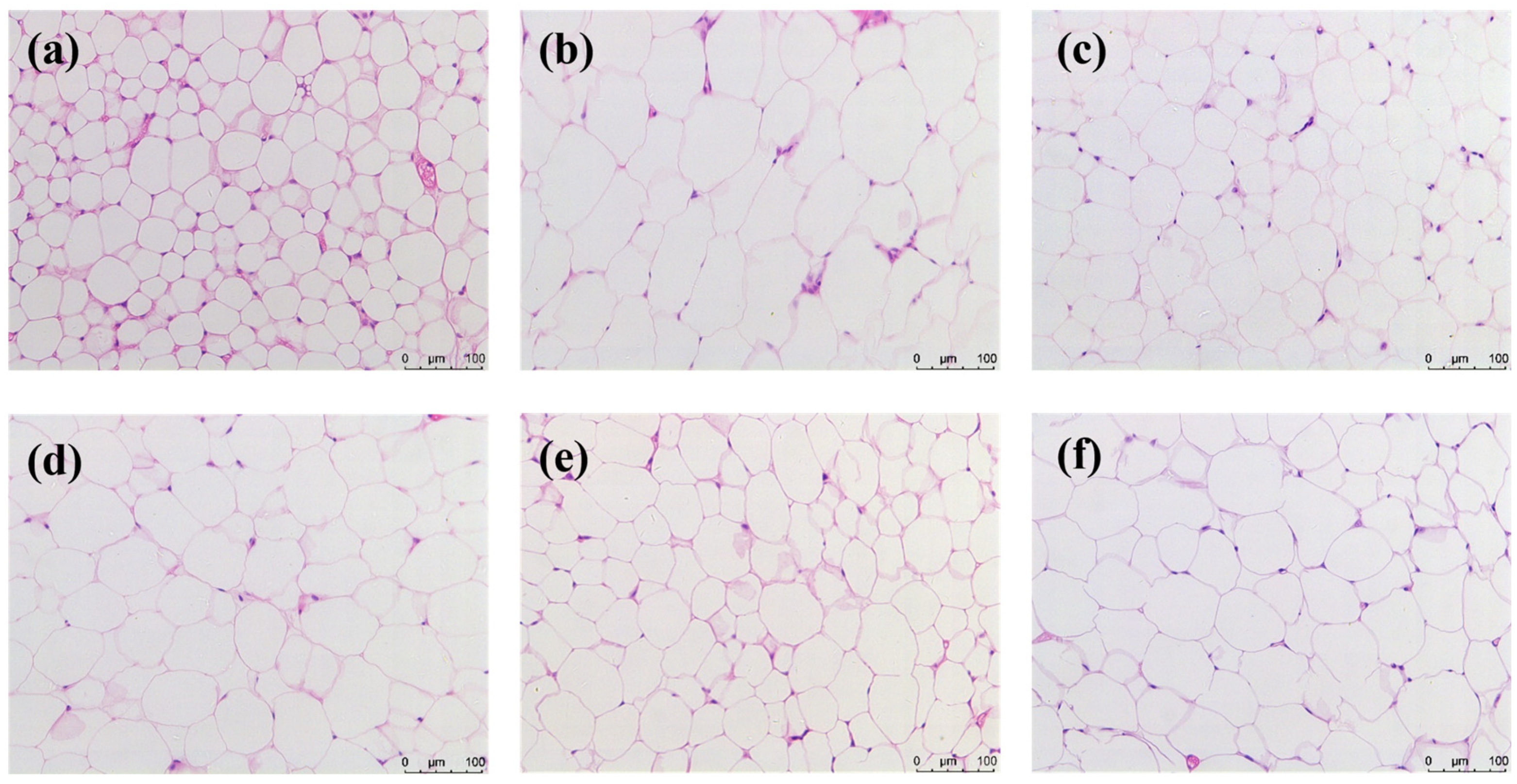
2.8. Anti-Obesity Effect of HYP-MAL in Nutritionally Obese Mice
3. Experimental Procedures
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation Methods
3.3. General Characterization
3.4. HPLC Analysis
3.5. Equilibrium Solubility and Dissolution Experiments
3.6. Density Functional Theory (DFT) Study
3.7. Animal Model and Subject Details
3.7.1. Ethics Statement
3.7.2. Animals
3.7.3. Culture of Normal and High-Fat Mice
3.7.4. Groups and Dosage
3.7.5. Sample Collection
3.7.6. Blood Lipid Testing
3.7.7. Measurement of Serum Leptin (LEP) and Liver Adiponectin (ADP) Levels
3.7.8. Determination of Liver Malondialdehyde (MDA) Content and Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Activity
3.7.9. Histological Staining of Adipose Tissue
3.7.10. RNA Extraction and Gene Expression Analysis
3.7.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yin, C.; Ma, Z.; Li, F.; Duan, C.; Yuan, Y.; Zhu, C.; Wang, L.; Zhu, X.; Wang, S.; Gao, P.; et al. Hypoxanthine induces muscular ATP depletion and fatigue via UCP2. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 647743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagao, H.; Nishizawa, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Fukata, T.; Mizushima, T.; Furuno, M.; Bamba, T.; Tsushima, Y.; Fujishima, Y.; Kita, S.; et al. Hypoxanthine secretion from human adipose tissue and its increase in hypoxia. Obesity 2018, 26, 1168–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Wang, R.X.; Alexeev, E.E.; Lanis, J.M.; Battista, K.D.; Glover, L.E.; Colgan, S.P. Hypoxanthine is a checkpoint stress metabolite in colonic epithelial energy modulation and barrier function. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 6039–6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, V.H.; Kaiser, K.K.; Brooke, M.H. Forearm exercise increases plasma hypoxanthine. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1982, 45, 552–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuhashi, M.; Koyama, M.; Higashiura, Y.; Murase, T.; Nakamura, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Sakai, A.; Ohnishi, H.; Tanaka, M.; Saitoh, S.; et al. Differential regulation of hypoxanthine and xanthine by obesity in a general population. J. Diabetes Investig. 2020, 11, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichimura, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Yoshida, Y.; Hattori, A. Hypoxanthine enhances the cured meat taste. Anim. Sci. J. 2016, 88, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo-Ibelles, P.; Gutierrez-Vidal, R.; Calixto-Tlacomulco, S.; Delgado-Coello, B.; Mas-Oliva, J. Hepatic accumulation of hypoxanthine: A link between hyperuricemia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Arch. Med. Res. 2021, 52, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mink, R.; Johnston, J. The effect of infusing hypoxanthine or xanthine on hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in rabbits. Brain Res. 2007, 1147, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.C. Cocrystallization for successful drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, L.; Yao, J.; Ma, Y.-Y.; Chen, J.-M.; Lu, T.-B. Improving the solubility and bioavailability of apixaban via apixaban–oxalic acid cocrystal. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 2923–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Mei, X. Cocrystals of baicalein with higher solubility and enhanced bioavailability. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 1893–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadha, R.; Bhandari, S.; Khullar, S.; Mandal, S.K.; Jain, D.V.S. Characterization and evaluation of multi-component crystals of hydrochlorothiazide. Pharm. Res. 2014, 31, 2479–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Cao, J.; Jiao, L.; Yang, S.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Y.; Du, G. Solubility and stability advantages of a new cocrystal of berberine chloride with fumaric acid. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 8283–8292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, F.A.; Pop, M.M.; Borodi, G.; Filip, X.; Kacso, I. Ketoconazole salt and co-crystals with enhanced aqueous solubility. Cryst. Growth Des. 2013, 13, 4295–4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ober, C.A.; Montgomery, S.E.; Gupta, R.B. Formation of itraconazole/l-malic acid cocrystals by gas antisolvent cocrystallization. Powder Technol. 2013, 236, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surov, A.O.; Voronin, A.P.; Vener, M.V.; Churakov, A.V.; Perlovich, G.L. Specific features of supramolecular organisation and hydrogen bonding in proline cocrystals: A case study of fenamates and diclofenac. CrystEngComm 2018, 20, 6970–6981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Zhan, J.; Liao, Y.; Wu, C.; Yu, W.; Zhang, J. A matrine-based supramolecular ionic salt that enhances the water solubility, transdermal delivery, and bioactivity of salicylic acid. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 468, 143480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, F.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yudintceva, N.; Shevtsov, M.; Gao, H. Supramolecular nanomedicines based on host-guest interactions of cyclodextrins. Exploration 2023, 3, 20210111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.F.; Tong, W. Impact of solid state properties on developability assessment of drug candidates. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitra, R.; Choudhury, R.R.; Capet, F.; Roussel, P.; Bhatt, P. Crystal structure of 4-aminopyridinium 3-(4-aminopyridinium) succinate tetra hydrate: A new salt from 4-aminopyridine and maleic acid crystallization. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1234, 130142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, X. Pharmaceutical salt hydrates of vortioxetine with maleic acid and fumaric acid: Crystal structures, characterisation and solubility performance. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1250, 131847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; An, Q.; Shi, J.; Liu, L. Salt cocrystal and salt of marbofloxacin with butenedioic acid, Impact of cis–trans isomerism of coformer on the conformation and properties of marbofloxacin. Cryst. Growth Des. 2024, 24, 1339–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.D.; Blüher, M.; Tschöp, M.H.; DiMarchi, R.D. Anti-obesity drug discovery, advances and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 201–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.W.; Kim, S. Comprehensive review of current and upcoming anti-obesity drugs. Diabetes Metab. J. 2020, 44, 802–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsutsumi, S.; Iida, M.; Tada, N.; Kojima, T.; Ikeda, Y.; Moriwaki, T.; Higashi, K.; Moribe, K.; Yamamoto, K. Characterization and evaluation of miconazole salts and cocrystals for improved physicochemical properties. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 421, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Cabeza, A.J. Acid–base crystalline complexes and the pKa rule. CrystEngComm 2012, 14, 6362–6365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, S.; Friščić, T.; Jones, W.; Motherwell, W.D.S. Screening for pharmaceutical cocrystal hydrates via neat and liquid-assisted grinding. Mol. Pharm. 2007, 4, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetouh, H.A.; Aleem, E.E.A.; Mohammed, N.H.; Aldesouky, J.M.A.-A.; Ismail, A.M. Formulation of new drug delivery systems for insulin from natural bioactive biocompatible polymers. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, E.; Palleschi, S.; Aspichueta, P.; Buqué, X.; Rossi, B.; Cano, A.; Napolitano, M.; Ochoa, B.; Botham, K.M. High fat diet-induced non alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats is associated with hyperhomocysteinemia caused by down regulation of the transsulphuration pathway. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, A.; Jeon, S.; Kim, M.; Yeo, J.; Seo, K.-I.; Choi, M.-S.; Lee, M.-K. Chlorogenic acid exhibits anti-obesity property and improves lipid metabolism in high-fat diet-induced-obese mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 937–943. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.; Li, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q. Effects of hypoxanthine on lipid metabolism of mice. J. Jilin Agric. Univ. 2017, 39, 337–342. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, F.; Scholz, G.; Benemann, S.; Rademann, K.; Emmerling, F. Evaluation of the formation pathways of cocrystal polymorphs in liquid-assisted syntheses. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 8272–8278. [Google Scholar]
- Thanigaimani, K.; Khalib, N.C.; Temel, E.; Arshad, S.; Razak, I.A. New supramolecular cocrystal of 2-amino-5-chloropyridine with 3-methylbenzoic acids: Syntheses, structural characterization, hirshfeld surfaces and quantum chemical investigations. J. Mol. Struct. 2015, 1099, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spackman, P.R.; Turner, M.J.; McKinnon, J.J.; Wolff, S.K.; Grimwood, D.J.; Jayatilaka, D.; Spackman, M.A. Crystalexplorer: A program for hirshfeld surface analysis, visualization and quantitative analysis of molecular crystals. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2021, 54, 1006–1011. [Google Scholar]
- Aakeröy, C.B.; Wijethunga, T.K.; Desper, J. Molecular electrostatic potential dependent selectivity of hydrogen bonding. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Chen, F. Multiwfn: A multifunctional wavefunction analyzer. J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 33, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.; Chen, F. Quantitative analysis of molecular surface based on improved marching tetrahedra algorithm. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2012, 38, 314–323. [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. Vmd: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | HYP-MAL |
|---|---|
| Moiety formula | C5H4N4O, C4H3O4 |
| Sum formula | C9H7N4O5 |
| MW | 251.19 |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic |
| Space group | P21/c |
| Hall group | 2ybc |
| a (Å) | 24.3661 (5) |
| b (Å) | 12.2508 (3) |
| c (Å) | 7.0398 (2) |
| α (deg) | 90 |
| β (deg) | 95.862 (2) |
| γ (deg) | 90 |
| Volume | 2090.42 (9) |
| Z | 8 |
| Data completeness | 0.989 |
| R (reflections) | 0.0395 (2974) |
| wR2 (reflections) | 0.1192 (3702) |
| S | 1.049 |
| Npar | 327 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, F.; Yuan, X.; Li, X.; Fang, S.; Cheng, Y. A Novel Supramolecular Salt of Hypoxanthine with Maleic Acid as a Potential Weight-Loss Drug. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094266
Xue F, Yuan X, Li X, Fang S, Cheng Y. A Novel Supramolecular Salt of Hypoxanthine with Maleic Acid as a Potential Weight-Loss Drug. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094266
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Fumin, Xinyue Yuan, Xingyi Li, Shimin Fang, and Yan Cheng. 2025. "A Novel Supramolecular Salt of Hypoxanthine with Maleic Acid as a Potential Weight-Loss Drug" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094266
APA StyleXue, F., Yuan, X., Li, X., Fang, S., & Cheng, Y. (2025). A Novel Supramolecular Salt of Hypoxanthine with Maleic Acid as a Potential Weight-Loss Drug. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094266







