A Novel Small Molecule Enhances Stable Dopamine Delivery to the Brain in Models of Parkinson’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Tolerated Dose and Tissue Toxicity
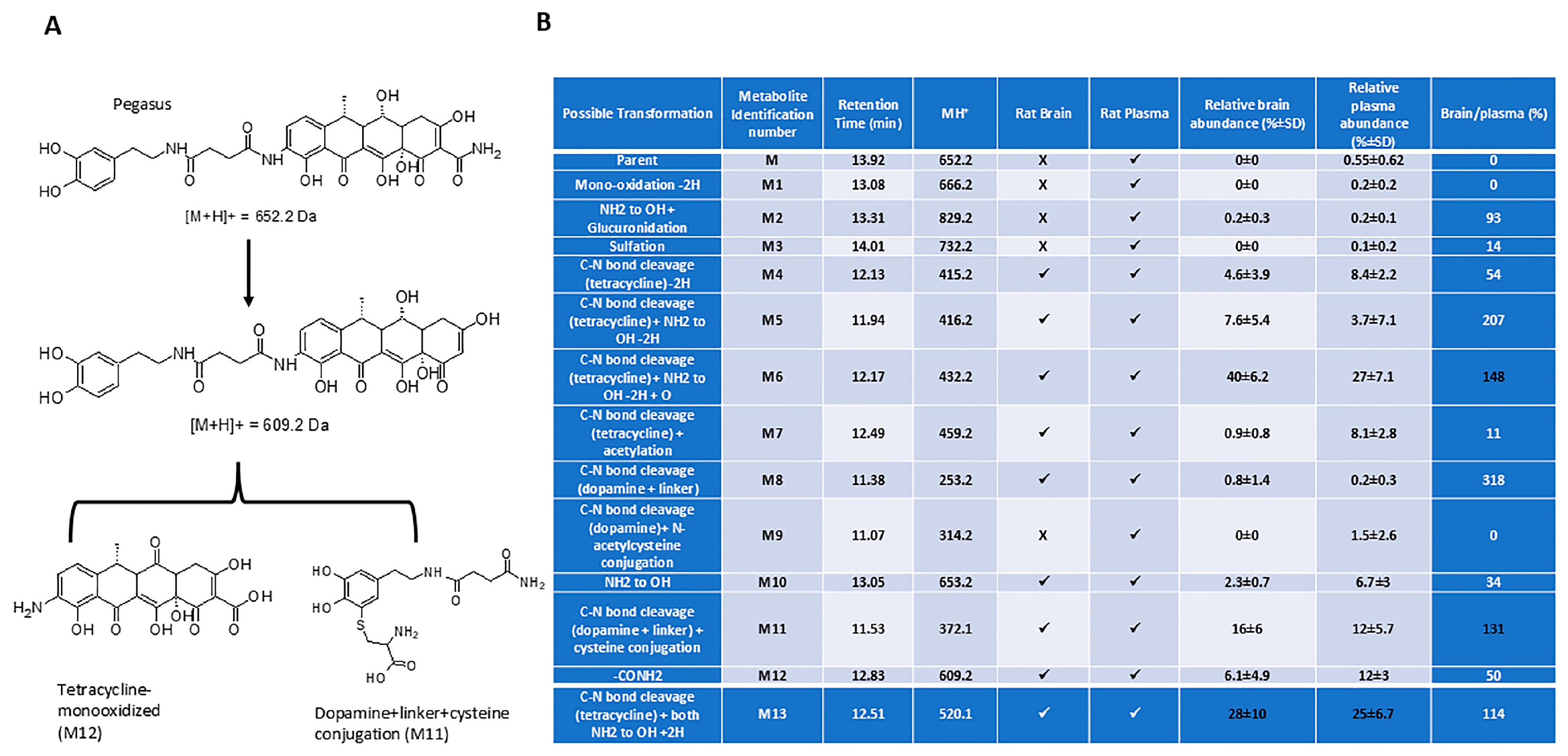
2.2. Pharmacokinetics
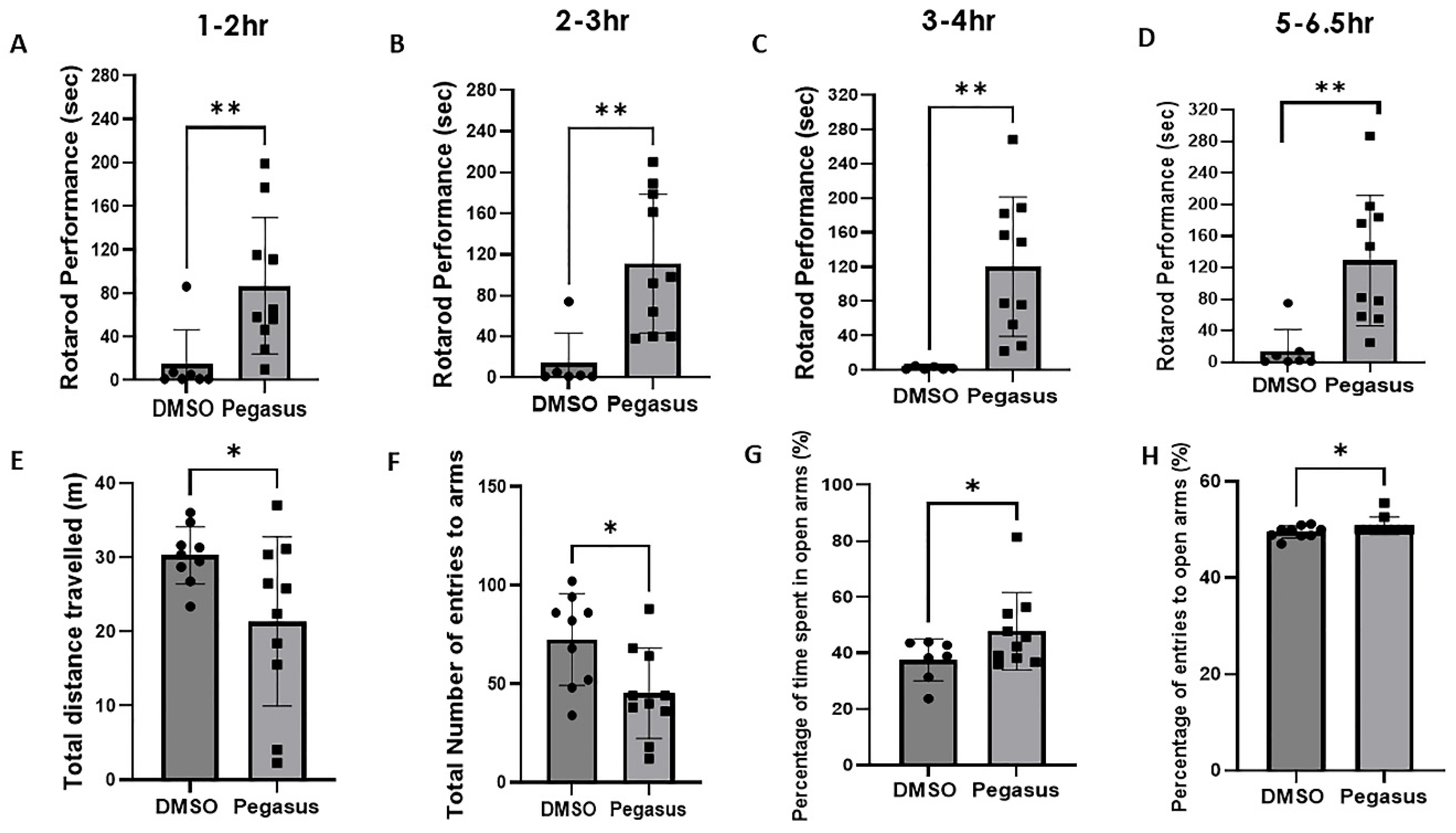
2.3. Pegasus Profoundly Alleviates Anxiety and Improves Motor Performance in TgA53T Mice
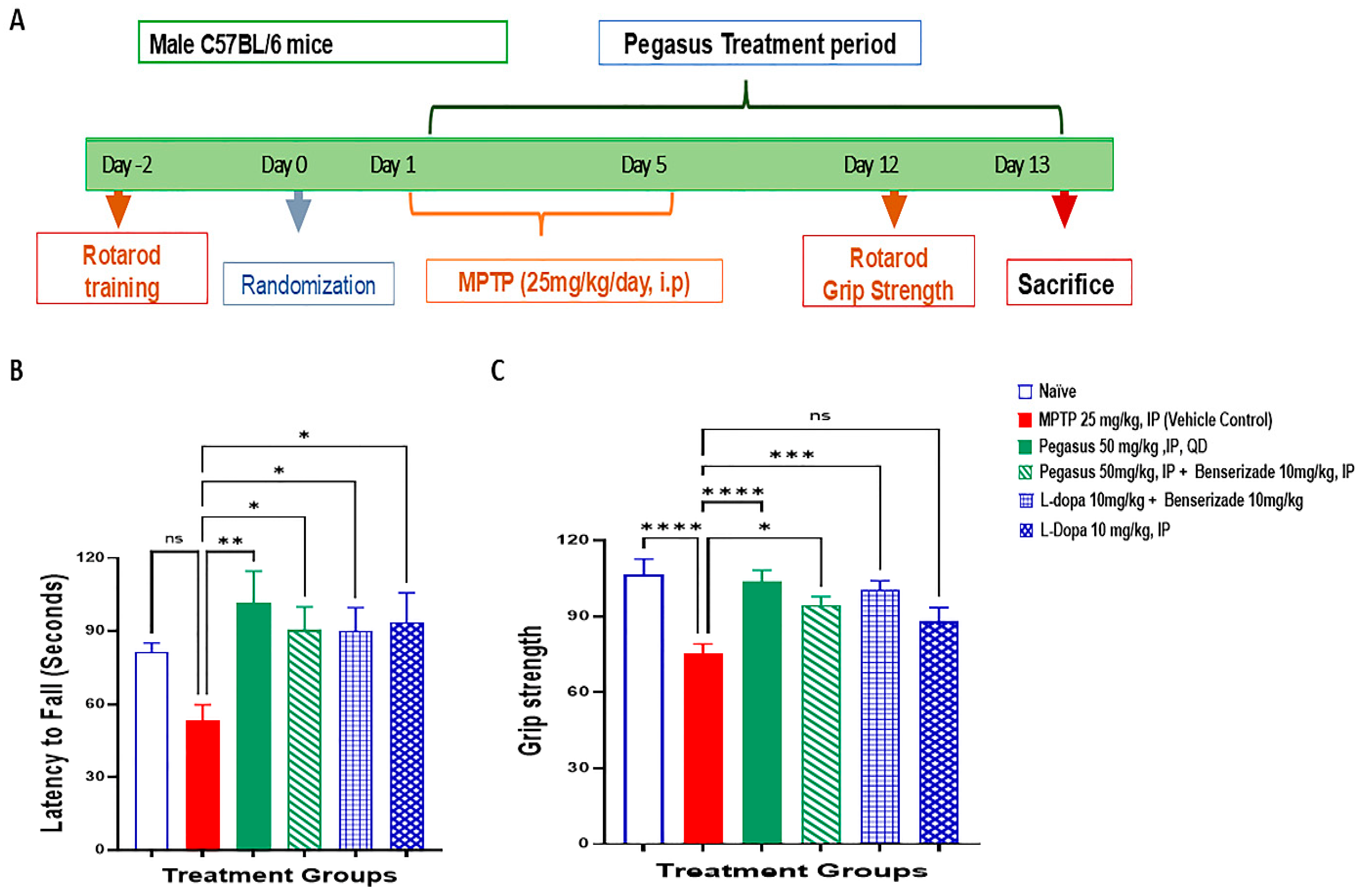
2.4. Pegasus Improves Behavioral Deficits of MPTP-Treated Mice
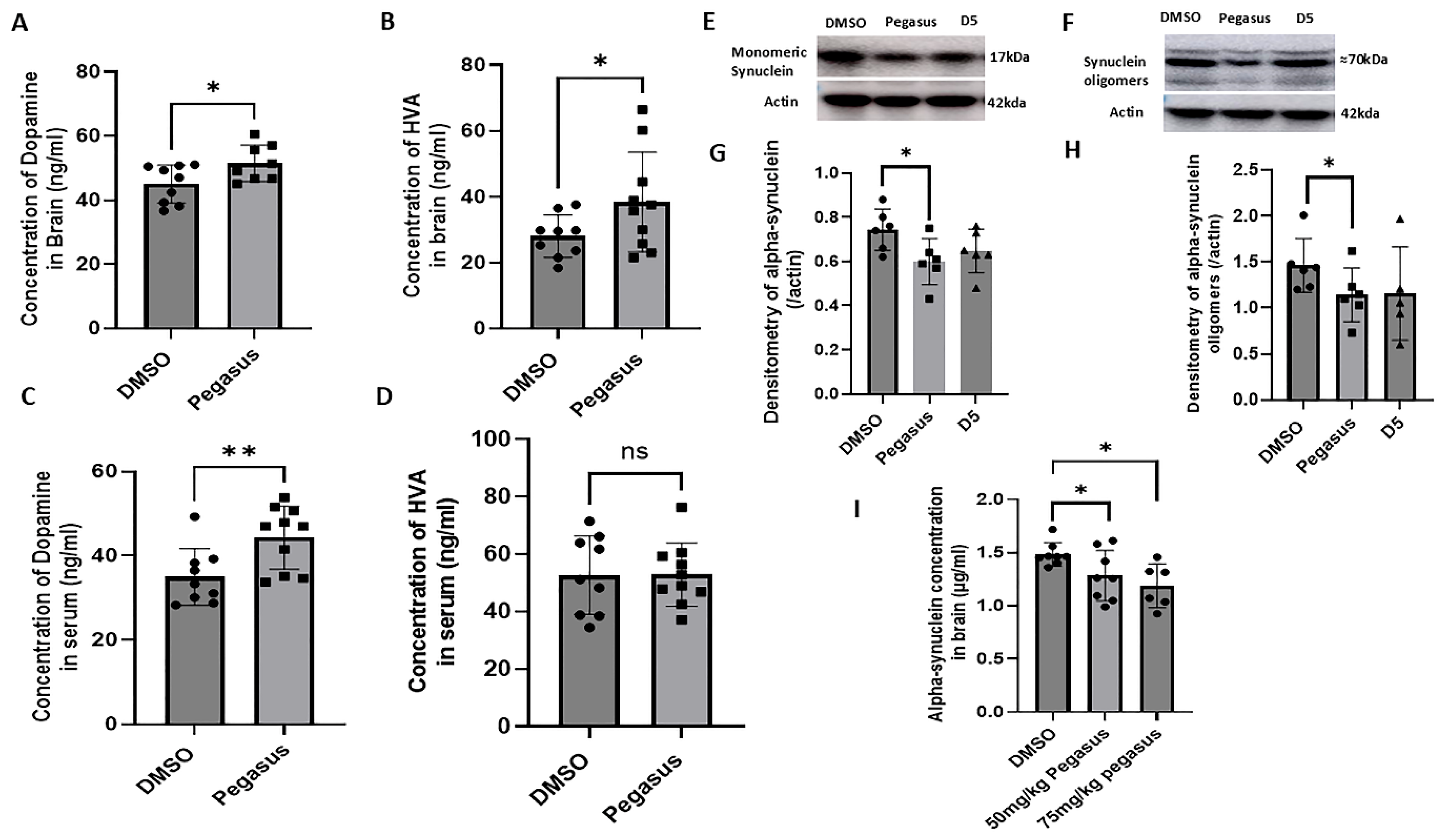
2.5. Pegasus Reduces Alpha-Synuclein Levels and Increases DA and Its Metabolite HVA Levels in the Brain of TgA53T Mice
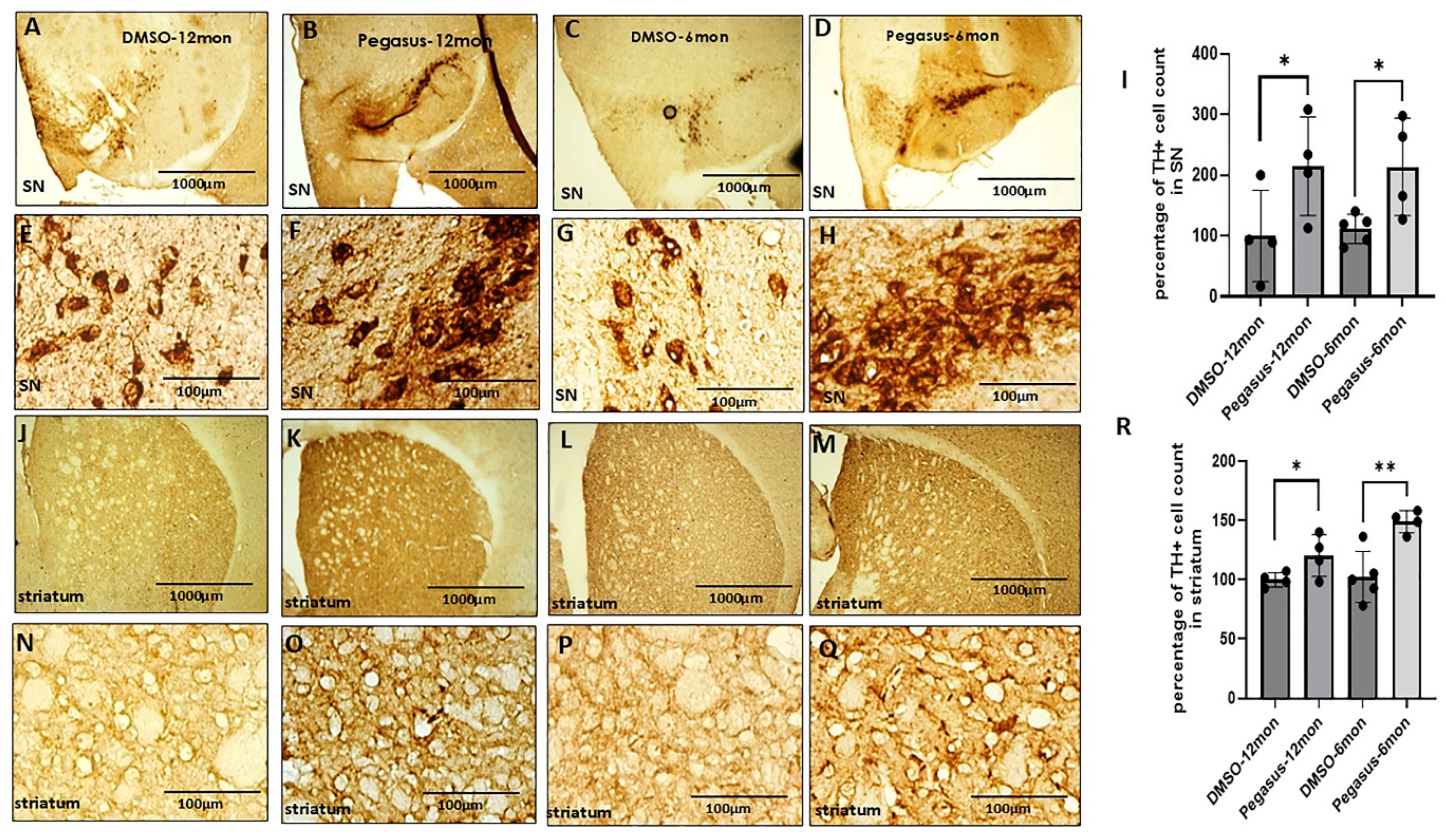
2.6. Pegasus Significantly Increases the Number of DA-Producing Neurons in the SN and Striatum
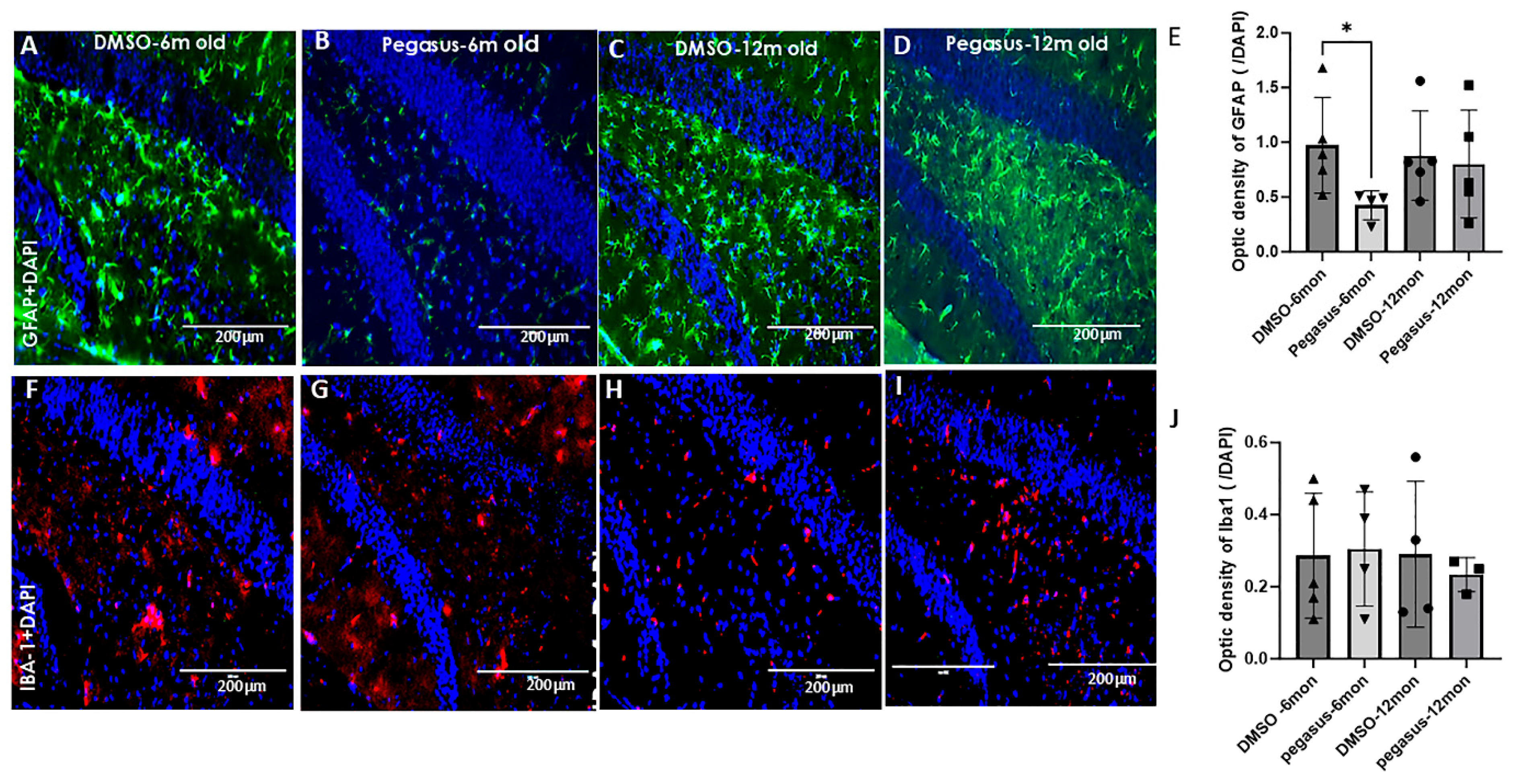
2.7. Pegasus Reduces Astrocytic Staining in TgA53T Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Pharmacokinetics
4.2. TgA53T Mouse Experiment
4.3. Dose Escalation Study and Tissue Toxicity via Caspase-3 Activity
4.4. In Vivo Metabolism
4.5. MPTP Experiment
4.6. Administration of MPTP
4.7. Rotarod Test
4.8. Elevated Plus Maze Test
4.9. Grip Strength Test
4.10. Immunohistochemistry
4.11. Western Blot
4.12. ELISA
4.13. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| i.p. | Intraperitoneal |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| PK | Pharmacokinetics |
| DA | Dopamine |
| MPTP | 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine |
| SN | Substantia nigra |
| BBB | Blood–brain barrier |
| A53T | Alanine to threonine mutations |
| Tg | Transgenic |
| TH | Tyrosine hydroxylase |
| DMSO | Dimethylsulfide |
| HVA | Homovanillic acid |
References
- Spillantini, M.G.; Schmidt, M.L.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M. Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 1997, 388, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Crowther, R.A.; Jakes, R.; Hasegawa, M.; Goedert, M. α-Synuclein in filamentous inclusions of Lewy bodies from Parkinson’s disease and dementia with lewy bodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6469–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goedert, M. Alpha-synuclein and neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabreira, V.; Massano, J. Parkinson’s Disease: Clinical Review and Update. Acta Medica Port. 2019, 32, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Okun, M.S. Diagnosis and Treatment of Parkinson Disease: A Review. JAMA 2020, 323, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olanow, C.W.; Obeso, J.A.; Stocchi, F. Drug insight: Continuous dopaminergic stimulation in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Clin. Pract. Neurol. 2006, 2, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploper, D.; Pernicone, A.O.; Tomas-Grau, R.H.; Manzano, V.E.; Socías, S.B.; Teran, M.D.M.; Budeguer Isa, V.; Sosa-Padilla, B.; González-Lizárraga, F.; Avila, C.L.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of a Novel Conjugate Molecule with Dopaminergic and Neuroprotective Activities for Parkinson’s Disease. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2024, 15, 2795–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardridge, W.M. The blood-brain barrier: Bottleneck in brain drug development. NeuroRx 2005, 2, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansey, M.G.; Wallings, R.L.; Houser, M.C.; Herrick, M.K.; Keating, C.E.; Joers, V. Inflammation and immune dysfunction in Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 657–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troncoso-Escudero, P.; Parra, A.; Nassif, M.; Vidal, R.L. Outside in: Unraveling the Role of Neuroinflammation in the Progression of Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J. Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease and its potential as therapeutic target. Transl. Neurodegener. 2015, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo-Rangel, C.; Marin, G.; Hernández-Contreras, K.A.; Vichi-Ramírez, M.M.; Zarate-Calderon, C.; Torres-Pineda, O.; Diaz-Chiguer, D.L.; González, D.D.l.M.; Apo, E.G.; Teco-Cortes, J.A.; et al. Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s Disease: From Gene to Clinic: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutt, J.G. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of levodopa. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23 (Suppl. 3), S580–S584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershanik, O.S. Improving L-dopa therapy: The development of enzyme inhibitors. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, J.F.; Santos, A.; Falcão, A.; Lopes, N.; Nunes, T.; Pinto, R.; Soares-da-Silva, P. Effect of moderate liver impairment on the pharmacokinetics of opicapone. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 70, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houghton, R.; Boess, F.; Verselis, L.; Ding, Y.; Freitas, R.; Constantinovici, N.; Ong, R. Treatment Patterns in Patients with Incident Parkinson’s Disease in the United States. J. Park. Dis. 2019, 9, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, D. Optimizing levodopa therapy for Parkinson’s disease with levodopa/carbidopa/entacapone: Implications from a clinical and patient perspective. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2008, 4, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pringsheim, T.; Day, G.S.; Smith, D.B.; Rae-Grant, A.; Licking, N.; Armstrong, M.J.; de Bie, R.M.A.; Roze, E.; Miyasaki, J.M.; Hauser, R.A.; et al. Dopaminergic Therapy for Motor Symptoms in Early Parkinson Disease Practice Guideline Summary: A Report of the AAN Guideline Subcommittee. Neurology 2021, 97, 942–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, C.I.; Limone, B.; Sobieraj, D.M.; Lee, S.; Roberts, M.S.; Kaur, R.; Alam, T. Dosing frequency and medication adherence in chronic disease. J. Manag. Care Pharm. 2012, 18, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocchi, F.; Bonamartini, A.; Vacca, L.; Ruggieri, S. Motor fluctuations in levodopa treatment: Clinical pharmacology. Eur. Neurol. 1996, 36, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Lizárraga, F.; Ploper, D.; Ávila, C.L.; Socías, S.B.; Dos-Santos-Pereira, M.; Machín, B.; Del-Bel, E.; Michel, P.P.; Pietrasanta, L.I.; Raisman-Vozari, R.; et al. CMT-3 targets different alpha-synuclein aggregates mitigating their toxic and inflammogenic effects. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Vitola, P.; Artioli, L.; Cerovic, M.; Poletto, C.; Dacomo, L.; Leva, S.; Balducci, C.; Forloni, G. Repositioning doxycycline for treating synucleinopathies: Evidence from a pre-clinical mouse model. Park. Relat. Disord. 2023, 106, 105229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.d.S.; Nascimento, G.C.D.; Bortolanza, M.; Michel, P.P.; Raisman-Vozari, R.; Del Bel, E. Doxycycline attenuates l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia through an anti-inflammatory effect in a hemiparkinsonian mouse model. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1045465. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Mai, D.; Qu, S. Molecular Mechanisms of Glutamate Toxicity in Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 585584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sechi, G.P.; Sechi, M.M. Small Molecules, alpha-Synuclein Pathology, and the Search for Effective Treatments in Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos-Santos-Pereira, M.; Acuna, L.; Hamadat, S.; Rocca, J.; Gonzalez-Lizarraga, F.; Chehin, R.; Sepulveda-Diaz, J.; Del-Bel, E.; Raisman-Vozari, R.; Michel, P.P. Microglial glutamate release evoked by alpha-synuclein aggregates is prevented by dopamine. Glia 2018, 66, 2353–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orsucci, D.; Calsolaro, V.; Mancuso, M.; Siciliano, G. Neuroprotective effects of tetracyclines: Molecular targets, animal models and human disease. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2009, 8, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soory, M. A role for non-antimicrobial actions of tetracyclines in combating oxidative stress in periodontal and metabolic diseases: A literature review. Open Dent. J. 2008, 2, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Ma, Z.; Lin, S.; Dodel, R.C.; Gao, F.; Bales, K.R.; Triarhou, L.C.; Chernet, E.; Perry, K.W.; Nelson, D.L.; et al. Minocycline prevents nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurodegeneration in the MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 14669–14674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhofer, G.; Kopin, I.J.; Goldstein, D.S. Catecholamine metabolism: A contemporary view with implications for physiology and medicine. Pharmacol. Rev. 2004, 56, 331–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.K.; Stirling, W.; Xu, Y.; Xu, X.; Qui, D.; Mandir, A.S.; Dawson, T.M.; Copeland, N.G.; Jenkins, N.A.; Price, D.L. Human α-synuclein-harboring familial Parkinson’s disease-linked Ala-53 → Thr mutation causes neurodegenerative disease with α-synuclein aggregation in transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 8968–8973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khandelwal, P.J.; Herman, A.M.; Hoe, H.-S.; Rebeck, G.W.; Moussa, C.E.-H. Parkin mediates beclin-dependent autophagic clearance of defective mitochondria and ubiquitinated Aβ in AD models. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 2091–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonskaya, I.; Hebron, M.L.; Desforges, N.M.; Franjie, A.; Moussa, C.E. Tyrosine kinase inhibition increases functional parkin-Beclin-1 interaction and enhances amyloid clearance and cognitive performance. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 1247–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Hebron, M.L.; Stevenson, M.; Moussa, C. A Novel Small Molecule Enhances Stable Dopamine Delivery to the Brain in Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4251. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094251
Liu X, Hebron ML, Stevenson M, Moussa C. A Novel Small Molecule Enhances Stable Dopamine Delivery to the Brain in Models of Parkinson’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4251. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094251
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiaoguang, Michaeline L. Hebron, Max Stevenson, and Charbel Moussa. 2025. "A Novel Small Molecule Enhances Stable Dopamine Delivery to the Brain in Models of Parkinson’s Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4251. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094251
APA StyleLiu, X., Hebron, M. L., Stevenson, M., & Moussa, C. (2025). A Novel Small Molecule Enhances Stable Dopamine Delivery to the Brain in Models of Parkinson’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4251. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094251





