Identification and Functional Exploration of the ALKBH Gene Family in Oriental Melon Fruit Ripening
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Direct MA Injection on Oriental Melon Fruit Ripening
2.2. Identification of ALKBH Genes in the Melon Genome
2.3. Phylogenetic Tree of ALKBH Proteins
2.4. Motifs and Gene Structures of ALKBH from Cucumis melo
2.5. Synteny Analysis of Melon ALKBH Genes
2.6. Cis-Acting Elements in the Promoter Regions of Melon ALKBH Genes
2.7. Impact of 1-MCP Treatment on Melon ALKBH Gene Expression
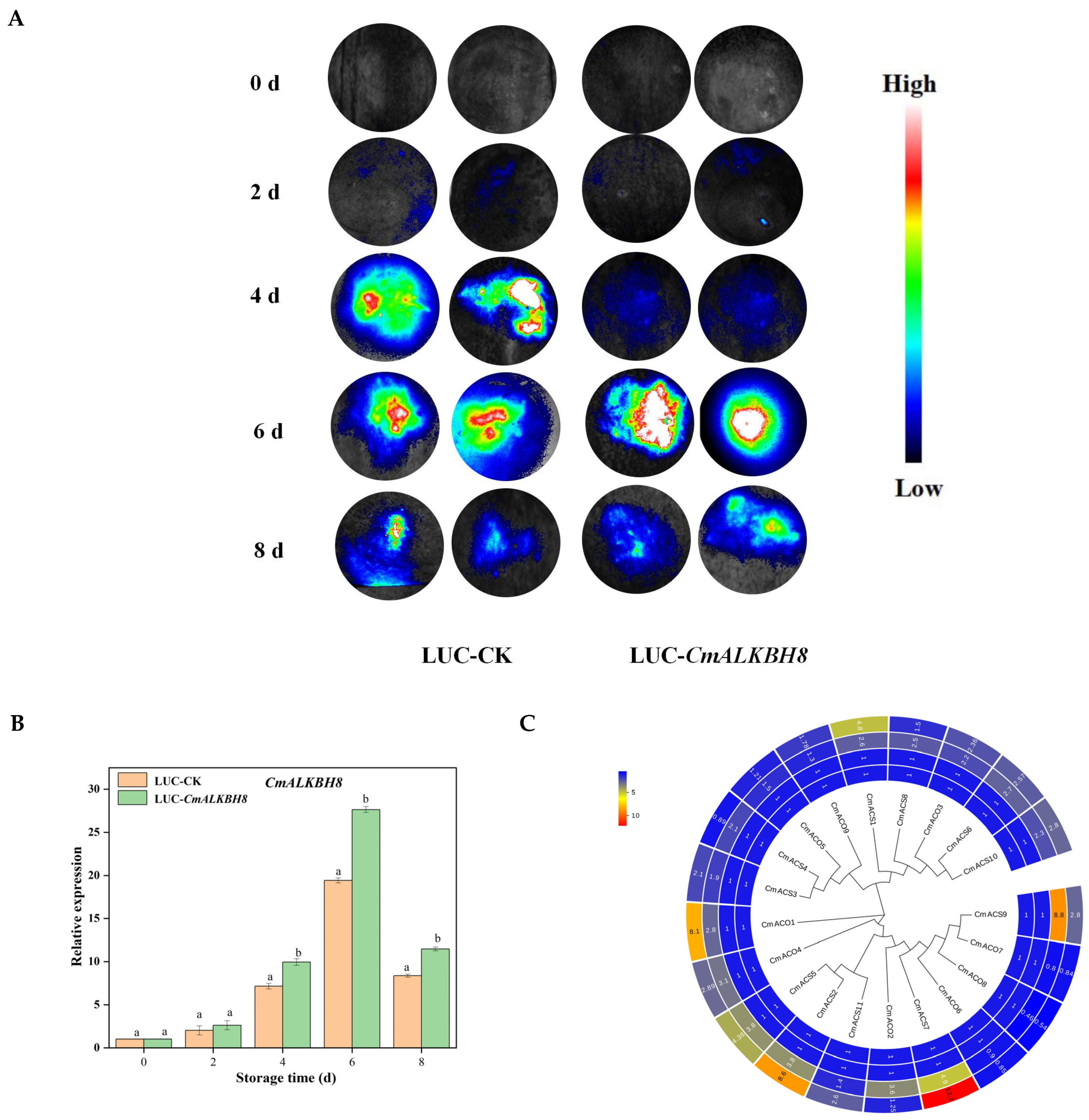
2.8. Functional Exploration of CmALKBH8 in Melon Fruit Ripening
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Treatment
4.2. Identification of ALKBH Genes Within the Melon Genome
4.3. Phylogenetic Analysis, Gene Structure, Protein Motifs, and Syntenic Analysis
4.4. Cis-Acting Elements Analysis of Promoter Regions and Gene Expression
4.5. Transient Expression of Oriental Melon Fruit
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chmielowska-Bąk, J.; Arasimowicz-Jelonek, M.; Deckert, J. In search of the mRNA modification landscape in plants. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishnan, M.; Rajan, K.S.; Mullasseri, S.; Ahmad, Z.; Zhou, M.; Sharma, A.; Ramasamy, S.; Wei, Q. Exploring N 6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification in tree species: Opportunities and challenges. Hortic. Res. 2024, 11, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Wang, R.Y.; Xiong, F.; Krakowiak, J.; Liao, Z.; Nguyen, P.T.; Moroz-Omori, E.V.; Shao, J.F.; Zhu, J.F.; Zhu, X.Y.; et al. Enhancer RNA m6A methylation facilitates transcriptional condensate formation and gene activation. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 3368–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; MacQueen, A.; Zheng, G.; Duan, H.; Dore, L.C.; Lu, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, K.; Jia, G.; Bergelson, J.; et al. Unique features of the m6 A methylome in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, C.; Hu, S.; Yu, J.; Song, S. Transcriptome-wide N6 -methyladenosine profiling of rice callus and leaf reveals the presence of tissue-specific competitors involved in selective mRNA modification. RNA Biol. 2014, 11, 1180–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Zhang, T.; Qi, Y.; Song, J.; Han, Z.; Ma, C. Evolution of the RNA N6-Methyladenosine Methylome Mediated by Genomic Duplication. Plant Physiol. 2020, 182, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Dong, H.; Wang, M.; Liu, Q. Evolutionary divergence of function and expression of laccase genes in plants. J. Genet. 2020, 99, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Hou, N.; Liu, Z.; He, J. Profiling of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification landscape in response to drought stress in apple (Malus prunifolia (Willd.) Borkh). Plants 2021, 11, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, Y.; Jiang, L.; Ji, D. Epigenetic regulation in tomato fruit ripening. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1269090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.; Shu, P.; Hu, N.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Deng, H.; Du, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, R.; Li, H.; et al. Dynamic m6A mRNA methylation reveals the involvement of AcALKBH10 in ripening-related quality regulation in kiwifruit. New Phytol. 2024, 243, 2265–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Tang, R.; Li, X.; Tian, S.; Li, B.; Qin, G. N6-methyladenosine RNA modification regulates strawberry fruit ripening in an ABA-dependent manner. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Yi, C. Switching Demethylation Activities between AlkB Family RNA/DNA Demethylases through Exchange of Active-Site Residues. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 3659–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Luo, B.B.; Wang, Y.S.; Li, J.; Hu, Z.L.; Xie, Q.L.; Wu, T.; Chen, G.P. Genome-wide identification, classification and expression analysis of m6A gene family in Solanum lycopersicum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dong, X.M.; Ma, J.Y.; Sui, C.X.; Jian, H.J.; Lv, D.Q. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the ALKB Homolog Gene Family in Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, A.; Wang, Y.; Gu, P.; Yang, Z.; Han, J.; Yi, L. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of the AlkB Gene Family in Sweet Orange (Citrus sinensis). Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 45, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merret, R.; Nagarajan, V.K.; Carpentier, M.C.; Park, S.; Favory, J.J.; Descombin, J.; Picart, C.; Charng, Y.Y.; Green, P.J.; Deragon, J.M.; et al. Heat-induced ribosome pausing triggers mRNA co-translational decay in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 4121–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huong, T.T.; Ngoc, L.N.T.; Kang, H. Functional Characterization of a Putative RNA Demethylase ALKBH6 in Arabidopsis Growth and Abiotic Stress Responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.D.; Xu, H.C.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.Z.; Ali, M.; Xu, X.Y.; Lu, G. RNA N6-Methyladenosine Responds to LowTemperature Stress in Tomato Anthers. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 687826. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Yang, J.B.; Duan, H.C.; Jia, G.F. ALKBH10B, an mRNA m(6)A Demethylase, Modulates ABA Response During Seed Germination in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 712713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, Y.; Hu, J.Z.; Manduzio, S.; Kang, H. Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase homolog 10B, an N6-methyladenosine mRNA demethylase, plays a role in salt stress and abscisic acid responses in Arabidopsis thaliana. Physiol. Plant. 2021, 173, 1078–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Liu, J.L.; Li, J.; Dai, C.H.; Li, L.P. Transcriptome and metabolome analyses revealed the response mechanism of sugar beet to salt stress of different durations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.L.; Tian, S.P.; Qin, G.Z. RNA methylomes reveal the m6A-mediated regulation of DNA demethylase gene SlDML2 in tomato fruit ripening. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, T.T.; Li, Y.Y.; Tang, B.Y.; Chen, Y.T.; Chen, X.R.; Xie, Q.L.; Hu, Z.L.; Chen, G.P. Knockout of SlALKBH2 weakens the DNA damage repair ability of tomato. Plant Sci. 2022, 319, 111266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.L.; Gao, G.T.; Tang, R.K.; Liu, J.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Liang, Z.C.; Tian, S.P.; Qin, G.Z. Redox modification of m6A demethylase SlALKBH2 in tomato regulates fruit ripening. Nat. Plants 2025, 11, 218–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.K.; Duan, X.Y.; Zhou, L.L.; Gao, G.T.; Liu, J.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Shao, X.F.; Qin, G.Z. The FvABF3-FvALKBH10B-FvSEP3 cascade regulates fruit ripening in strawberry. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 10912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyama, K.; Guis, M.; Rose, J.K.; Kubo, Y.; Bennett, K.A.; Wangjin, L.; Kato, K.; Ushijima, K.; Nakano, R.; Inaba, A.; et al. Ethylene regulation of fruit softening and cell wall disassembly in Charentais melon. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 1281–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pech, J.C.; Bouzayen, M.; Latché, A.J. Climacteric fruit ripening: Ethylene-dependent and independent regulation of ripening pathways in melon fruit. Plant Sci. 2008, 175, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vegas, J.; Garcia-Mas, J.; Monforte, A.J. Interaction between QTLs induces an advance in ethylene biosynthesis during melon fruit ripening. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2013, 126, 1531–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qi, H.Y.; Liu, Y.F.; Guan, X.C.; Liu, Y.F. Effects of ethephon and 1-methylcyclopropene on fruit ripening and the biosynthesis of volatiles in oriental sweet melon (Cucumis melo var. makuwa Makino). J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2011, 86, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.M.; Fang, M.H.; Zhai, B.Q.; Ma, L.L.; Fu, A.Z.; Gao, L.P.; Kou, X.H.; Meng, D.M.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, S.F.; et al. Regulations of m6A methylation on tomato fruit chilling injury. Hortic. Plant J. 2021, 7, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.Z.; Cai, J.; Umme, A.; Chen, Y.; Xu, T.; Kang, H.S. Unique features of mRNA m6A methylomes during expansion of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) fruits. Plant Physiol. 2022, 188, 2215–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, T.; Qin, G.; Tian, S. Current insights into posttranscriptional regulation of fleshy fruit ripening. Plant Physiol. 2023, 192, 1785–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, G.F.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Dai, Q.; Zheng, G.K.; Yang, Y.; Yi, C.Q.; Lindahl, T.; Pan, T.; Yang, Y.G.; et al. N6-methyladenosine in nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 885–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yan, J.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Gong, S.; Zhou, H.; Gan, J.; Jiang, H.; Jia, G.F.; Luo, C.; et al. Meclofenamic acid selectively inhibits FTO demethylation of m6 A over ALKBH5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, C.J.; Ma, Z.F.; Wan, H.; Gao, J.B.; Zhou, B.L. GhALKBH10 negatively regulates salt tolerance in cotton. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 192, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Guo, Q.; Cao, S.; Tian, Y.T.; Han, K.J.; Sun, Y.H.; Li, J.; Yang, Q.S.; Ji, Q.J.; Sederoff, R.; et al. Genome-wide identification of the AlkB homologs gene family, PagALKBH9B and PagALKBH10B regulated salt stress response in Populus. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 994154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Nie, X.J.; Yan, Z.G.; Weining, S. N6-methyladenosine regulatory machinery in plants: Composition, function and evolution. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 1194–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, S.T.; Zhou, C.Z.; Xie, S.Y.; Chen, G.W.; Tian, C.Y.; Xu, K.; Lin, Y.L.; Lai, Z.X.; Guo, Y.Q. Genome-Wide Investigation of N6-Methyladenosine Regulatory Genes and Their Roles in Tea (Camellia sinensis) Leaves During Withering Process. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 702303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.W.; Xue, J.L.; Ren, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Du, L.Q.; Ding, F.; Zhou, K.B.; Ma, W.Q. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of m6A writers, erasers, and readers in litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.). Genes 2022, 13, 2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.C.; Wei, L.H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Lu, Z.; Chen, P.R.; He, C.; Jia, G. ALKBH10B is an RNA N6-methyladenosine demethylase affecting Arabidopsis floral transition. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 2995–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkowski, M.; Pilzys, T.; Garbicz, D.; Steciuk, J.; Zugaj, D.; Mielecki, D.; Sarnowski, T.J.; Grzesiuk, E. Human and Arabidopsis alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase homolog proteins-New players in important regulatory processes. IUBMB Life 2020, 72, 1126–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Pérez, M.; Aparicio, F.; López-Gresa, M.P.; Bellés, J.M.; Sánchez-Navarro, J.A.; Pallás, V. Arabidopsis m(6)A demethylase activity modulates viral infection of a plant virus and the m(6)A abundance in its genomic RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10755–10760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.H.; Sun, Q.G.; Wu, J.X.; Zhao, P.C.; Sun, Y.M.; Guo, Z.F. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of Short-Chain Dehydrogenase/Reductase (SDR) Gene Family in Medicago truncatula. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambhir, P.; Singh, V.; Parida, A.; Raghuvanshi, U.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, A.K. Ethylene response factor ERF. D7 activates auxin response factor 2 paralogs to regulate tomato fruit ripening. Plant Physiol. 2022, 190, 2775–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Wei, S.; Zheng, X.D.; Tu, P.C.; Tao, F. APETALA2/ethylene-responsive factors in higher plant and their roles in regulation of plant stress response. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2024, 44, 1533–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, J.; Chuguransky, S.; Williams, L.; Qureshi, M.; Salaza, G.A.; Sonnhammer, E.L.; Tosatto, S.C.; Paladin, L.; Raj, S.; Richardson, L.J.; et al. Pfam: The protein families database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvaud, S.; Gabella, C.; Lisacek, F.; Stockinger, H.; Ioannidis, V.; Durinx, C. Expasy, the Swiss Bioinformatics Resource Portal, as designed by its users. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, K.C.; Shen, H.B. Cell-PLoc: A package of Web servers for predicting subcellular localization of proteins in various organisms. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. ClustalW and ClustalX version 2. 0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7. 0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Jin, J.; Guo, A.Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. GSDS 2.0: An upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1296–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Song, X.; Shang, Q.; Feng, S.; Ge, W. CFVisual: An interactive desktop platform for drawing gene structure and protein architecture. BMC Bioinform. 2022, 23, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Tang, H.B.; DeBarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.P.; Wang, X.Y.; Lee, T.; Jin, H.Z.; Marler, B.; Guo, H.; et al. MCScanX: A toolkit for the detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzywinski, M.; Schein, J.; Birol, I.; Connors, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Horsman, D.; Jones, S.J.; Marra, M.A. Circos: An information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van, D.P.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Jin, Y.Z.; Liu, J.Y.; Tang, Y.F.; Cao, S.X.; Qi, H.Y. The phylogeny and expression profiles of the lipoxygenase (LOX) family genes in the melon (Cucumis melo L.) genome. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 170, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Yang, F.; Wang, C.; Duan, X.Y.; Li, M.; Ma, Y.; Wang, F.; Qi, H.Y. The transcription factor CmERFI-2 represses CmMYB44 expression to increase sucrose levels in oriental melon fruit. Plant Physiol. 2023, 192, 1378–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
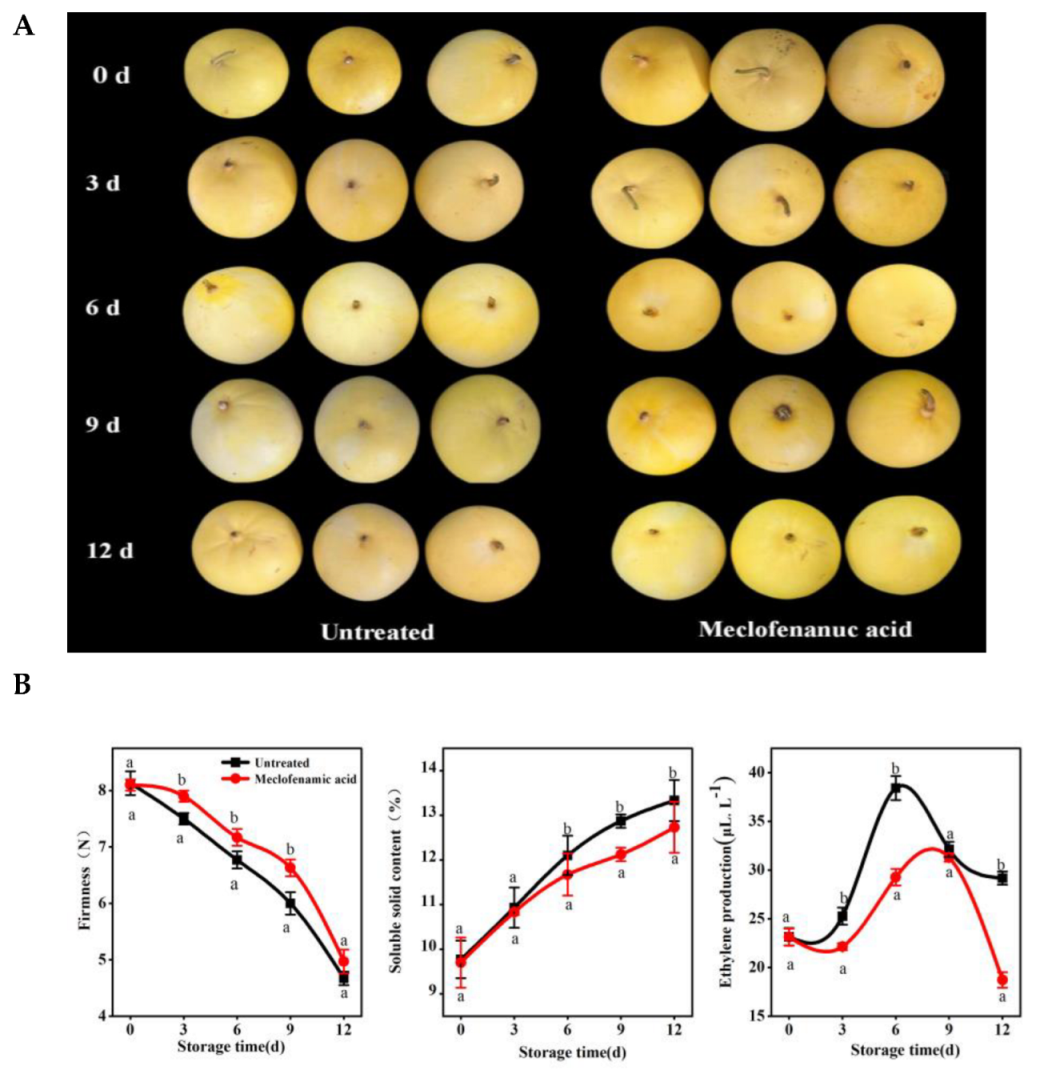
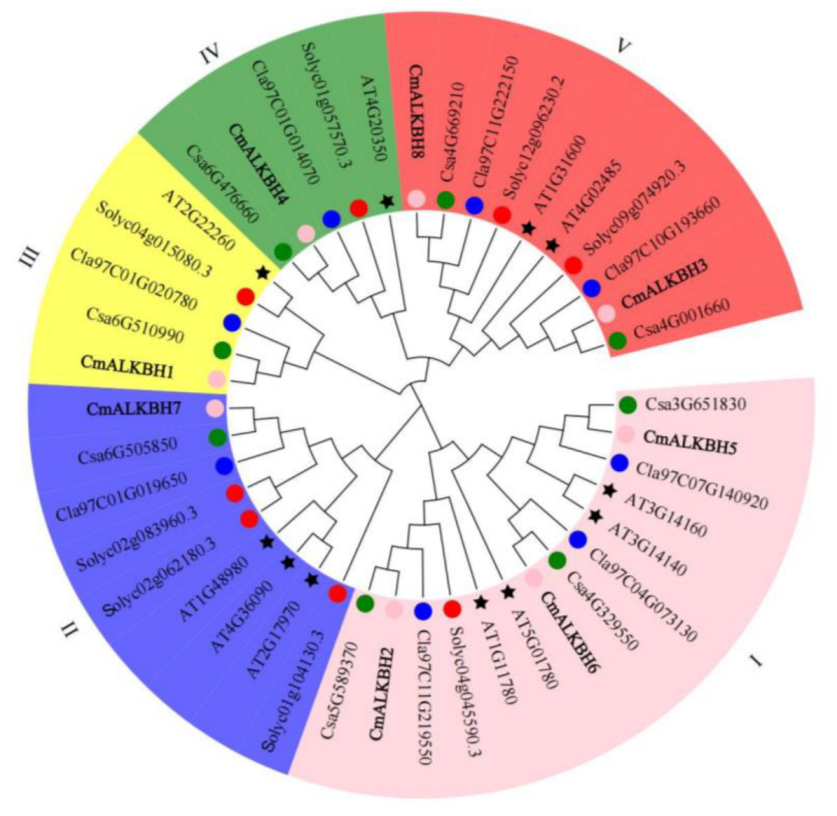

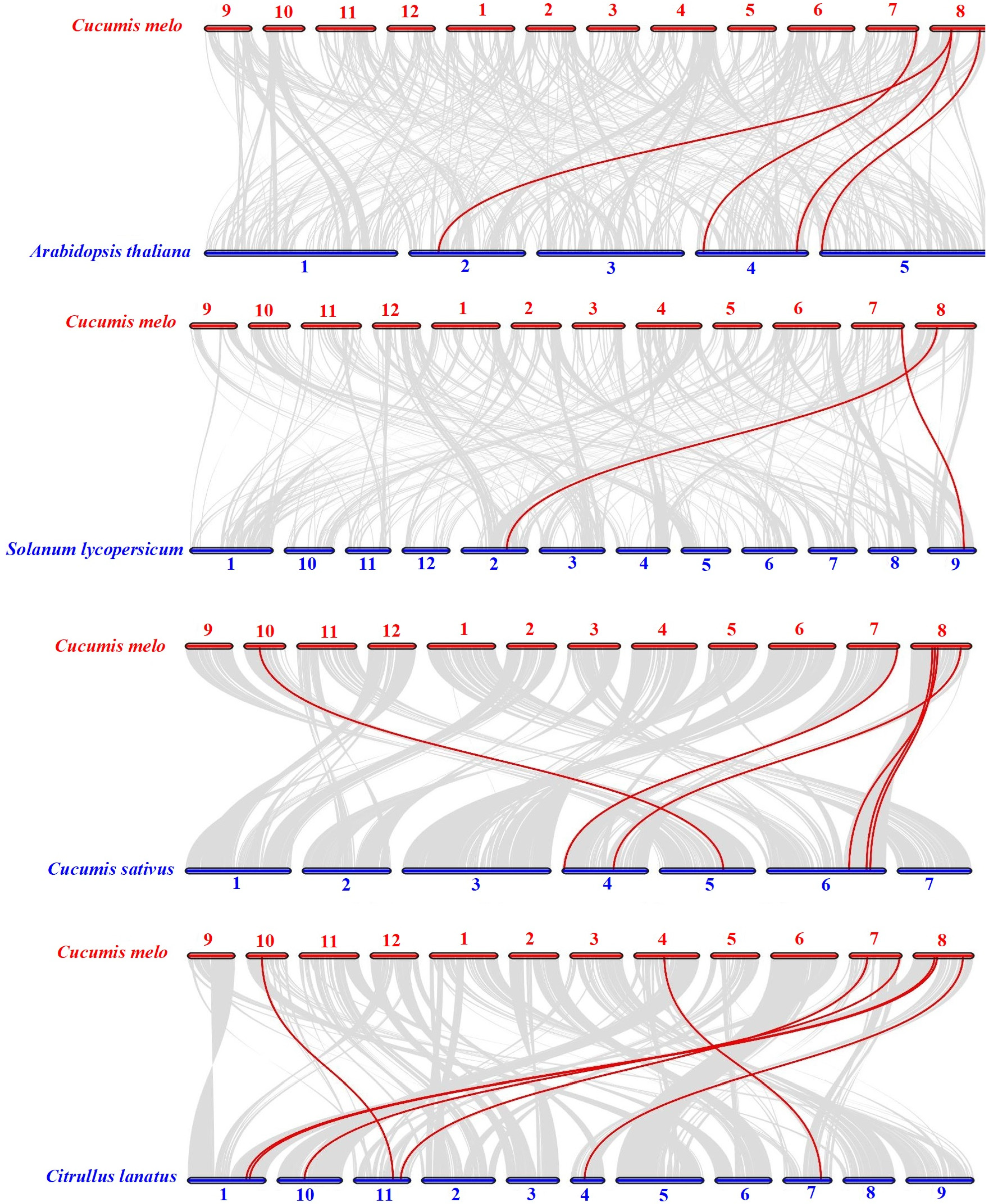
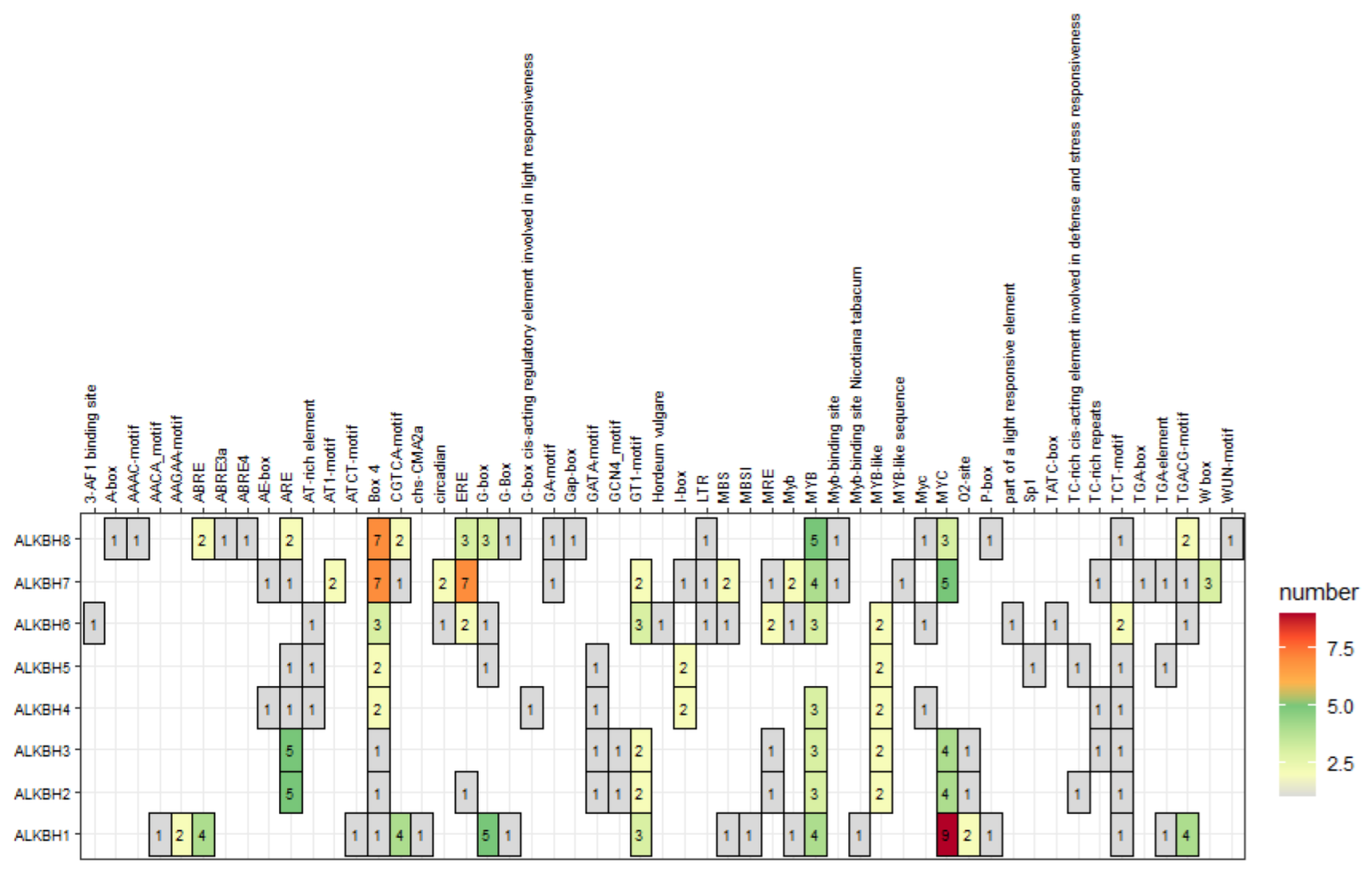

| Name | ID | Protein Length (bp) | CD Length (aa) | Molecular Weight (kDa) | Theoretical pI | Chromosome Location | Predicted Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CmALKBH1 | MELO3C007897.2 | 500 | 1503 | 55.85 | 6.16 | chr08:6086321 … 6092751 (+) | Nucleus |
| CmALKBH2 | MELO3C008006.2 | 244 | 735 | 28.06 | 9.3 | chr08:6722153 … 672334 (−) | Nucleus |
| CmALKBH3 | MELO3C010538.2 | 342 | 1029 | 38.52 | 6.83 | chr07:7974500 … 7982220 (−) | Chloroplast |
| CmALKBH4 | MELO3C011863.2 | 363 | 1092 | 41.21 | 6.18 | chr10:4296265 … 4298586 (−) | Cytoplasm |
| CmALKBH5 | MELO3C017969.2 | 260 | 783 | 29.54 | 4.68 | chr07:28389212 … 28391906 (+) | Nucleus |
| CmALKBH6 | MELO3C024592.2 | 250 | 753 | 28.45 | 7.27 | chr08:9071712 … 9074429 (+) | Exracellular |
| CmALKBH7 | MELO3C025799.2 | 502 | 1509 | 54.91 | 9.01 | chr04:18571821 … 18576784 (−) | Nucleus |
| CmALKBH8 | MELO3C026046.2 | 472 | 1419 | 53.44 | 9.32 | chr08:28592781 … 28595439 (+) | Chloroplast |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Pang, H.; Chen, Q. Identification and Functional Exploration of the ALKBH Gene Family in Oriental Melon Fruit Ripening. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4254. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094254
Zhang C, Guo X, Zhang Y, Pang H, Chen Q. Identification and Functional Exploration of the ALKBH Gene Family in Oriental Melon Fruit Ripening. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4254. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094254
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chong, Xinqi Guo, Ying Zhang, Hongbo Pang, and Qiang Chen. 2025. "Identification and Functional Exploration of the ALKBH Gene Family in Oriental Melon Fruit Ripening" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4254. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094254
APA StyleZhang, C., Guo, X., Zhang, Y., Pang, H., & Chen, Q. (2025). Identification and Functional Exploration of the ALKBH Gene Family in Oriental Melon Fruit Ripening. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4254. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094254





