The Role of the Glucocorticoid Receptor and Its Phosphorylation in Neurological Disorders
Abstract
1. Introduction
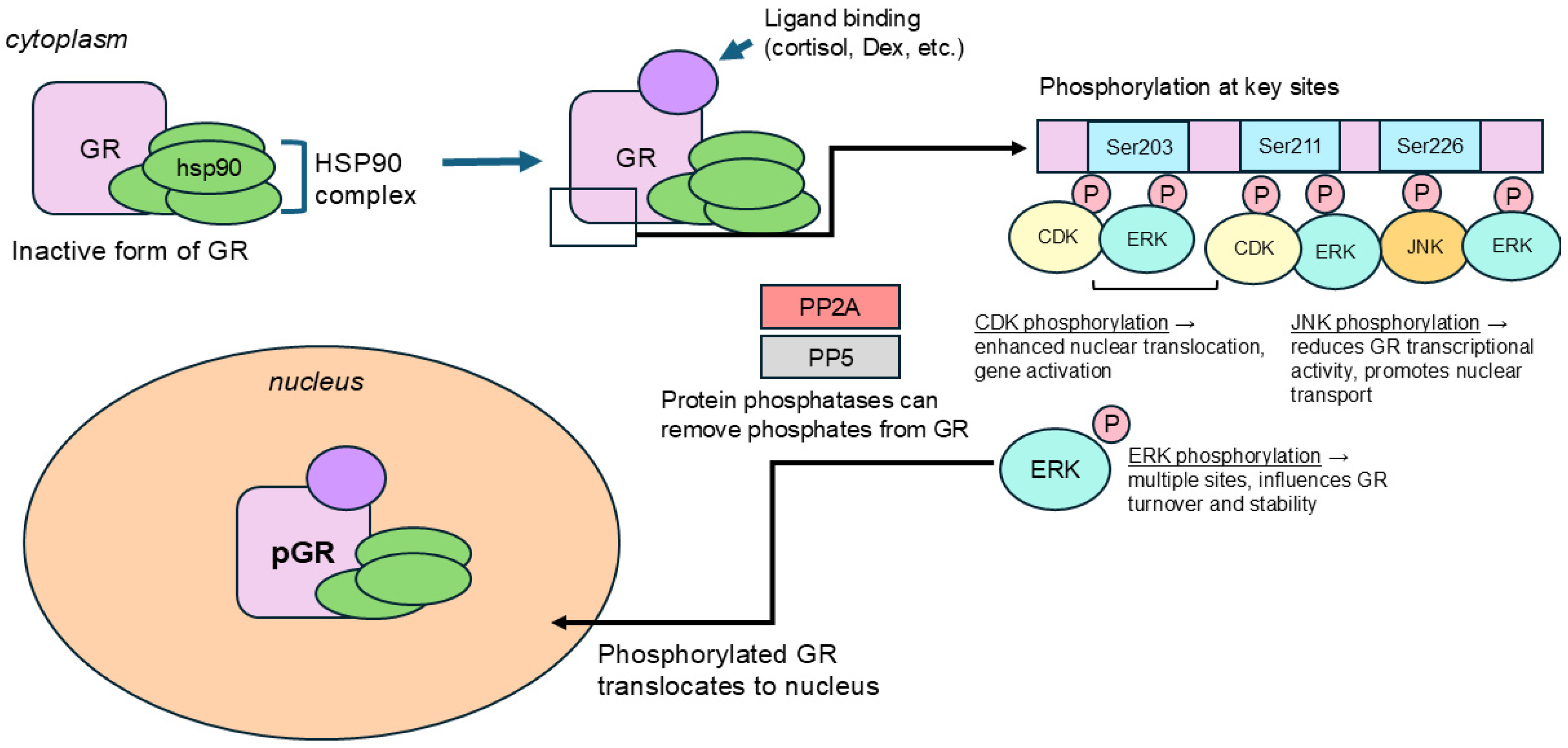
2. Regulatory Mechanism of GR Phosphorylation in Brain
2.1. Ser203
2.2. Ser211
2.3. Ser226
3. Impact of GR Phosphorylation at the Cellular and Molecular Level Affecting the Neurovascular Interface
4. GR Phosphorylation in Brain Disorder
4.1. Epilepsy
4.2. Stroke
4.3. Brain Tumor
4.4. Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
4.5. Neurodegenerative Disorders
4.5.1. Alzheimer’s Disease
4.5.2. Huntington’s Disease
4.5.3. Multiple Sclerosis
4.6. Psychiatric Disorders
4.6.1. Metabolic Syndrome (MetS)
4.6.2. Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)
4.6.3. Bipolar Disorder (BD)
| Brain Disorder | Changes in GR Phosphorylation | Effects on Pathology | Potential Therapeutic Targets | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epilepsy | ↓ pGR-Ser203, ↓ pGR-Ser211 | Impaired anti-inflammatory response, GR desensitization | Enhancing pGR, ANXA1-GR axis | [29] |
| Ischemic Stroke | Dysregulated pGR, GR degradation in hypoxia | Increased inflammation, BBB disruption, impaired recovery | Proteasome inhibitors may restore GR function | [23] |
| Brain Tumors (Glioblastoma) | Circadian linked pGR influences tumor progression | High GR expression worsens prognosis, dexamethasone reduces peritumoral edema | Glucocorticoid therapy timed in sync with circadian activity | [36,37] |
| Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) | ↓ pGR at neurotrophic sites Ser134, Ser267 | ↑ Tau phosphorylation, synaptic loss, cognitive decline | BDNF signaling to enhance neuroprotective GR phosphorylation | [41] |
| Huntington’s Disease (HD) | ↑ Cortisol, altered pGR | ↑ Mutant huntingtin toxicity, brain atrophy | GR antagonists (CORT113176) to reduce neurotoxicity | [44] |
| Multiple Sclerosis (MS) | Dysregulated pGR and sensitivity | Impaired glucocorticoid response, neuroinflammation | Enhancing GR response via GRα and FKBP5 modulation | [46,47,48] |
| Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) | ↑ pGR-Ser226, ↓ pGR-Ser211/pGR-Ser226 ratio | Reduced GR-induced transcriptional activity, HPA axis dysfunction | Enhancing pGR at Ser211, FKBP5 modulation via antidepressants | [12] |
| Bipolar Disorder (BD) | ↓ Overall, pGR, ↑ pGR-Ser211 in depressive states | Altered stress response, glucocorticoid resistance | GR modulation for phase-dependent treatment | [11] |
5. Factors Influencing GR Phosphorylation
5.1. Exogenous Factors
5.1.1. Protein Phosphatase Inhibitors
5.1.2. External Signaling Molecules
5.1.3. MAPK Pathway Activation by External Stimuli
5.1.4. UV Irradiation
5.2. Endogenous Factors
5.2.1. Heat Shock Protein 90 Complex
5.2.2. Kinases (CDKs, JNKs)
5.2.3. Protein Phosphatases
5.3. Sex/Gender
6. Modulatory Approaches and Drug Therapies Proposed to Tackle GR Phosphorylation
6.1. pGR Agonist
6.2. pGR Antagonist and Modulators
| Drug | Mechanism | Effects on GR Phosphorylation | Therapeutic Applications | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dexamethasone (Dex) | Full GR agonist binds to GR and activates anti-inflammatory and metabolic pathways | ↑ pGR-Ser211 (↑ nuclear retention and transcription), ↓ pGR-Ser226 (↓ nuclear transport) | Brain edema, multiple sclerosis, brain tumors, increases BBB integrity (↑ ZO-1, ↑ occludin, ↑ claudin-5) | [19,22] |
| RU486 (Mifepristone) | GR antagonist prevents GR phosphorylation | RU486 has been shown to induce phosphorylation at Ser226 (transcriptional repression), but not Ser211 (transcriptional activation). With GR antagonist and CDK5 inhibitor, reduction in BDNF and cognitive dysfunction in aged mice were both rescued. | Inhibition of GR activation has potential for controlling postoperative cognitive dysfunction in aged individuals | [3,61] |
| CORT113176 | Selective GR modulator targets GR without full activation | ↓ pGR-Ser226 (restores GR function in stress-related disorders) | Reduces HPA axis hyperactivity, investigated for Huntington’s Disease, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, Alzheimer’s Disease | [44] |
7. Concluding Remarks and Future Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GR | Glucocorticoid Receptor |
| HPA | Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Adrenal |
| NTD | N-terminal domain |
| DNB | DNA binding domain |
| LBD | Ligand-binding domain |
| AF | Transactivation function |
| pGR | Phosphorylated GR |
| BBB | Blood–brain barrier |
| TLE | Temporal lobe epilepsy |
| LTP | Long term potentiation |
| HSP | Heat Shock Protein |
| Ang-1 | Angiopoietin-1 |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| ZO | Zonula Occludens |
| MS | Multiple Sclerosis |
| AD | Alzheimer’s Disease |
| GBM | Glioblastoma |
| HD | Huntington’s Disease |
| BD | Bipolar Disorder |
| Hap1 | Huntingtin-associated protein 1 |
| MDD | Major Depressive Disorder |
| ANXA1 | Annexin A1 |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-related kinase |
| CDK | Cyclin-dependent kinases |
| PP5 | protein-phosphatase five |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| eNOS | endothelial nitric oxide synthase |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| FKBP5 | FK506 binding protein 51 also called FKBP5 |
References
- Guidotti, G.; Calabrese, F.; Anacker, C.; Racagni, G.; Pariante, C.M.; Riva, M.A. Glucocorticoid receptor and FKBP5 expression is altered following exposure to chronic stress: Modulation by antidepressant treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolaides, N.C.; Galata, Z.; Kino, T.; Chrousos, G.P.; Charmandari, E. The human glucocorticoid receptor: Molecular basis of biologic function. Steroids 2010, 75, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Dang, T.; Blind, R.D.; Wang, Z.; Cavasotto, C.N.; Hittelman, A.B.; Rogatsky, I.; Logan, S.K.; Garabedian, M.J. Glucocorticoid receptor phosphorylation differentially affects target gene expression. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 22, 1754–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Williams, S.; Ferguson, L.; Bingaman, W.; Ghosh, A.; Najm, I.M.; Ghosh, C. Heat Shock Proteins Accelerate the Maturation of Brain Endothelial Cell Glucocorticoid Receptor in Focal Human Drug-Resistant Epilepsy. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 4511–4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.; Ghosh, C. Neurovascular glucocorticoid receptors and glucocorticoids: Implications in health, neurological disorders and drug therapy. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Thompson, E.B. Role of Phosphorylation in the Modulation of the Glucocorticoid Receptor’s Intrinsically Disordered Domain. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borin, C.; Pieters, T.; Serafin, V.; Ntziachristos, P. Emerging Epigenetic and Posttranslational Mechanisms Controlling Resistance to Glucocorticoids in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Hemasphere 2023, 7, e916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce-Lina, R.; Serafin, N.; Carranza, M.; Aramburo, C.; Prado-Alcala, R.A.; Luna, M.; Quirarte, G.L. Differential Phosphorylation of the Glucocorticoid Receptor in Hippocampal Subregions Induced by Contextual Fear Conditioning Training. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouazza, B.; Krytska, K.; Debba-Pavard, M.; Amrani, Y.; Honkanen, R.E.; Tran, J.; Tliba, O. Cytokines alter glucocorticoid receptor phosphorylation in airway cells: Role of phosphatases. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 47, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galliher-Beckley, A.J.; Cidlowski, J.A. Emerging roles of glucocorticoid receptor phosphorylation in modulating glucocorticoid hormone action in health and disease. IUBMB Life 2009, 61, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bei, E.; Salpeas, V.; Pappa, D.; Anagnostara, C.; Alevizos, V.; Moutsatsou, P. Phosphorylation status of glucocorticoid receptor, heat shock protein 70, cytochrome c and Bax in lymphocytes of euthymic, depressed and manic bipolar patients. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2009, 34, 1162–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simic, I.; Maric, N.P.; Mitic, M.; Soldatovic, I.; Pavlovic, Z.; Mihaljevic, M.; Andric, S.; Radojcic, M.B.; Adzic, M. Phosphorylation of leukocyte glucocorticoid receptor in patients with current episode of major depressive disorder. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 40, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, W.; Kono, E.; Dang, T.; Garabedian, M.J. Modulation of glucocorticoid receptor phosphorylation and transcriptional activity by a C-terminal-associated protein phosphatase. Mol. Endocrinol. 2007, 21, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, R.H.; Cidlowski, J.A. The biology of the glucocorticoid receptor: New signaling mechanisms in health and disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Frederick, J.; Garabedian, M.J. Deciphering the phosphorylation “code” of the glucocorticoid receptor in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 26573–26580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.W.; Gillette, M.U. Development of circadian neurovascular function and its implications. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1196606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, N.J.; Patabendige, A.A.; Dolman, D.E.; Yusof, S.R.; Begley, D.J. Structure and function of the blood-brain barrier. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 37, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, N.J.; Ronnback, L.; Hansson, E. Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hue, C.D.; Cho, F.S.; Cao, S.; Dale Bass, C.R.; Meaney, D.F.; Morrison, B., 3rd. Dexamethasone potentiates in vitro blood-brain barrier recovery after primary blast injury by glucocorticoid receptor-mediated upregulation of ZO-1 tight junction protein. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2015, 35, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limbourg, F.P.; Huang, Z.; Plumier, J.C.; Simoncini, T.; Fujioka, M.; Tuckermann, J.; Schutz, G.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Liao, J.K. Rapid nontranscriptional activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase mediates increased cerebral blood flow and stroke protection by corticosteroids. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 1729–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.; Hossain, M.; Ferguson, L.; Busch, R.M.; Marchi, N.; Gonzalez-Martinez, J.; Perucca, E.; Najm, I.M.; Ghosh, C. Neurovascular Drug Biotransformation Machinery in Focal Human Epilepsies: Brain CYP3A4 Correlates with Seizure Frequency and Antiepileptic Drug Therapy. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 8392–8407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Lee, J.M.; Park, J.S.; Jo, S.A.; Kim, Y.O.; Kim, C.W.; Jo, I. Dexamethasone coordinately regulates angiopoietin-1 and VEGF: A mechanism of glucocorticoid-induced stabilization of blood-brain barrier. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 372, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinschnitz, C.; Blecharz, K.; Kahles, T.; Schwarz, T.; Kraft, P.; Gobel, K.; Meuth, S.G.; Burek, M.; Thum, T.; Stoll, G.; et al. Glucocorticoid insensitivity at the hypoxic blood-brain barrier can be reversed by inhibition of the proteasome. Stroke 2011, 42, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, C.; Silwedel, C.; Golenhofen, N.; Burek, M.; Kietz, S.; Mankertz, J.; Drenckhahn, D. Occludin as direct target for glucocorticoid-induced improvement of blood-brain barrier properties in a murine in vitro system. J. Physiol. 2005, 565 Pt 2, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unemura, K.; Kume, T.; Kondo, M.; Maeda, Y.; Izumi, Y.; Akaike, A. Glucocorticoids decrease astrocyte numbers by reducing glucocorticoid receptor expression in vitro and in vivo. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 119, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, S.; El-Gindi, J.; Thanabalasundaram, G.; Panpumthong, P.; Schrot, S.; Hartmann, C.; Galla, H.J. Control of the blood-brain barrier by glucocorticoids and the cells of the neurovascular unit. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1165, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, S.Y.; Cho, M.R.; Kim, S.Y.; Koo, B.N. The immune-inflammatory responses on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and the neurovascular unit in perioperative neurocognitive disorder. Exp. Neurol. 2025, 386, 115146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandner, S.; Schroeter, S.; Caliskan, G.; Salar, S.; Kobow, K.; Coras, R.; Blumcke, I.; Hamer, H.; Schwarz, M.; Buchfelder, M.; et al. Glucocorticoid modulation of synaptic plasticity in the human temporal cortex of epilepsy patients: Does chronic stress contribute to memory impairment? Epilepsia 2022, 63, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zub, E.; Canet, G.; Garbelli, R.; Blaquiere, M.; Rossini, L.; Pastori, C.; Sheikh, M.; Reutelingsperger, C.; Klement, W.; de Bock, F.; et al. The GR-ANXA1 pathway is a pathological player and a candidate target in epilepsy. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 13998–14009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilkens, N.A.; Casolla, B.; Leung, T.W.; de Leeuw, F.E. Stroke. Lancet 2024, 403, 2820–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Huang, T.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, X. Glucocorticoid receptor signaling in the brain and its involvement in cognitive function. Neural Regen. Res. 2025, 20, 2520–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, R.; Willing, L.B.; Jefferson, L.S.; Simpson, I.A.; Kimball, S.R. REDD1 (regulated in development and DNA damage response 1) expression in skeletal muscle as a surrogate biomarker of the efficiency of glucocorticoid receptor blockade. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 412, 644–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucchi, F.C.; Matthies, N.F.; Badr, N.; Metz, G.A. Stress-induced glucocorticoid receptor activation determines functional recovery following ischemic stroke. Exp. Transl. Stroke Med. 2010, 2, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopatkiewicz, A.M.; Gradek-Kwinta, E.; Czyzycki, M.; Pera, J.; Slowik, A.; Dziedzic, T. Glucocorticoid Resistance is Associated with Poor Functional Outcome After Stroke. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 40, 1321–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulyaeva, N.V.; Onufriev, M.V.; Moiseeva, Y.V. Ischemic Stroke, Glucocorticoids, and Remote Hippocampal Damage: A Translational Outlook and Implications for Modeling. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 781964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, J.; Rao, K.; Pastorino, S.; Kesari, S. Corticosteroids in brain cancer patients: Benefits and pitfalls. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 4, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Aponte, M.F.; Damato, A.R.; Simon, T.; Aripova, N.; Darby, F.; Jeon, M.S.; Luo, J.; Rubin, J.B.; Herzog, E.D. Daily glucocorticoids promote glioblastoma growth and circadian synchrony to the host. Cancer Cell 2025, 43, 144–160.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.A.; Kokiko-Cochran, O.N. Context is key: Glucocorticoid receptor and corticosteroid therapeutics in outcomes after traumatic brain injury. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1351685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fucich, E.A.; Mayeux, J.P.; McGinn, M.A.; Gilpin, N.W.; Edwards, S.; Molina, P.E. A Novel Role for the Endocannabinoid System in Ameliorating Motivation for Alcohol Drinking and Negative Behavioral Affect after Traumatic Brain Injury in Rats. J. Neurotrauma 2019, 36, 1847–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dromard, Y.; Arango-Lievano, M.; Borie, A.; Dedin, M.; Fontanaud, P.; Torrent, J.; Garabedian, M.J.; Ginsberg, S.D.; Jeanneteau, F. Loss of glucocorticoid receptor phosphorylation contributes to cognitive and neurocentric damages of the amyloid-beta pathway. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2022, 10, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arango-Lievano, M.; Peguet, C.; Catteau, M.; Parmentier, M.L.; Wu, S.; Chao, M.V.; Ginsberg, S.D.; Jeanneteau, F. Deletion of Neurotrophin Signaling through the Glucocorticoid Receptor Pathway Causes Tau Neuropathology. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arango-Lievano, M.; Lambert, W.M.; Bath, K.G.; Garabedian, M.J.; Chao, M.V.; Jeanneteau, F. Neurotrophic-priming of glucocorticoid receptor signaling is essential for neuronal plasticity to stress and antidepressant treatment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 15737–15742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufour, B.D.; McBride, J.L. Normalizing glucocorticoid levels attenuates metabolic and neuropathological symptoms in the R6/2 mouse model of huntington’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 121, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentenaar, M.; Meulmeester, F.L.; van der Burg, X.R.; Hoekstra, A.T.; Hunt, H.; Kroon, J.; van Roon-Mom, W.M.C.; Meijer, O.C. Glucocorticoid receptor antagonist CORT113176 attenuates motor and neuropathological symptoms of Huntington’s disease in R6/2 mice. Exp. Neurol. 2024, 374, 114675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xin, N.; Pan, Y.; Zhu, L.; Yin, P.; Liu, Q.; Yang, W.; Xu, X.; Li, S.; Li, X.J. Huntingtin-Associated Protein 1 in Mouse Hypothalamus Stabilizes Glucocorticoid Receptor in Stress Response. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Winsen, L.L.; Hooper-van Veen, T.; van Rossum, E.F.; Polman, C.H.; van den Berg, T.K.; Koper, J.W.; Uitdehaag, B.M. The impact of glucocorticoid receptor gene polymorphisms on glucocorticoid sensitivity is outweighted in patients with multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2005, 167, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Winsen, L.M.; Muris, D.F.; Polman, C.H.; Dijkstra, C.D.; van den Berg, T.K.; Uitdehaag, B.M. Sensitivity to glucocorticoids is decreased in relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Chang, H.; Du, L.; Yin, L.; Shi, F.; Zhang, X. Glucocorticoid receptor mutations and clinical sensitivity to glucocorticoid in Chinese multiple sclerosis patients. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 41, 2767–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechmann, L.; Busse, K.; Stoppe, M.; Cotte, S.; Ettrich, B.; Then Bergh, F. Corticosteroid receptor expression and in vivo glucocorticoid sensitivity in multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2014, 276, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, H.J.; Finck, T.L.K.; Pellkofer, H.L.; Reichardt, H.M.; Luhder, F. Glucocorticoid Therapy of Multiple Sclerosis Patients Induces Anti-inflammatory Polarization and Increased Chemotaxis of Monocytes. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Yang, F.; Cai, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Cai, M.; Li, X.; Xiang, J.; Cai, D. Role of glucocorticoid receptor phosphorylation-mediated synaptic plasticity in anxiogenic and depressive behaviors induced by monosodium glutamate. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2021, 394, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.Y.; Zhu, Z.M.; Cui, S.; Wang, J.H. Glucocorticoid Induces Incoordination between Glutamatergic and GABAergic Neurons in the Amygdala. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Leung, D.Y.; Nordeen, S.K.; Goleva, E. Estrogen inhibits glucocorticoid action via protein phosphatase 5 (PP5)-mediated glucocorticoid receptor dephosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 24542–24552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogatsky, I.; Logan, S.K.; Garabedian, M.J. Antagonism of glucocorticoid receptor transcriptional activation by the c-Jun N-terminal kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 2050–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J.T.; Rajendran, R.; Xenaki, G.; Berrou, I.; Demonacos, C.; Krstic-Demonacos, M. The role of glucocorticoid receptor phosphorylation in Mcl-1 and NOXA gene expression. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patt, M.; Gysi, J.; Faresse, N.; Cidlowski, J.A.; Odermatt, A. Protein phosphatase 1 alpha enhances glucocorticoid receptor activity by a mechanism involving phosphorylation of serine-211. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2020, 518, 110873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzic, M.; Lukic, I.; Mitic, M.; Djordjevic, J.; Elakovic, I.; Djordjevic, A.; Krstic-Demonacos, M.; Matic, G.; Radojcic, M. Brain region- and sex-specific modulation of mitochondrial glucocorticoid receptor phosphorylation in fluoxetine treated stressed rats: Effects on energy metabolism. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2013, 38, 2914–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adzic, M.; Djordjevic, A.; Demonacos, C.; Krstic-Demonacos, M.; Radojcic, M.B. The role of phosphorylated glucocorticoid receptor in mitochondrial functions and apoptotic signalling in brain tissue of stressed Wistar rats. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 2181–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Cheng, P.Y.; Hsiao, M.; Liu, Y.P. Effects of RU486 in Treatment of Traumatic Stress-Induced Glucocorticoid Dysregulation and Fear-Related Abnormalities: Early versus Late Intervention. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canet, G.; Pineau, F.; Zussy, C.; Hernandez, C.; Hunt, H.; Chevallier, N.; Perrier, V.; Torrent, J.; Belanoff, J.K.; Meijer, O.C.; et al. Glucocorticoid receptors signaling impairment potentiates amyloid-beta oligomers-induced pathology in an acute model of Alzheimer’s disease. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 1150–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.S.; Tong, Y.W.; Li, Z.Q.; Li, L.X.; Zhang, T.; Ren, T.Y.; Zhou, T.; Wang, H.C.; Zhan, R.; Sun, Y.; et al. Surgical stress induces brain-derived neurotrophic factor reduction and postoperative cognitive dysfunction via glucocorticoid receptor phosphorylation in aged mice. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2015, 21, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| GR Phosphorylation Sites | Function | References |
|---|---|---|
| Ser203 | Inverse phosphorylation relationship with Ser226, cytoplasmic localization, may be prerequisite for Ser211 phosphorylation, may be required for full transcriptional activation | [3,10,15] |
| Ser211 | Strongly linked to GR transcriptional activation, mainly nuclear localization, interdependent with Ser203 phosphorylation, may enhance interactions with transcriptional co-factors, phosphorylation required for full transcriptional activation | [3,10,15] |
| Ser226 | Inverse phosphorylation relationship with Ser203, blocked phosphorylation may enhance GR’s transcriptional response, phosphorylation may inhibit GR function | [3,10,15] |
| Process | Possible Effect on BBB | References |
|---|---|---|
| GR Activation (Not Directly Through Phosphorylation) | Enhances BBB integrity via upregulation of tight junction proteins (occludin, claudin-5, ZO-1) | [24] |
| GR Phosphorylation | Alters GR interaction with co-regulators and transcriptional activity, still needs further investigation | [14] |
| GR Phosphorylation in Neuroinflammation | Enhances or weakens neurovascular function, depending on GR phosphorylation state | [2,3,27] |
| GR Phosphorylation in Hypoxia | Promotes BBB protection or disruption, depending on dynamics of GR phosphorylation | [12,23] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gadwala, S.; Ghosh, C. The Role of the Glucocorticoid Receptor and Its Phosphorylation in Neurological Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4213. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094213
Gadwala S, Ghosh C. The Role of the Glucocorticoid Receptor and Its Phosphorylation in Neurological Disorders. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4213. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094213
Chicago/Turabian StyleGadwala, Saranya, and Chaitali Ghosh. 2025. "The Role of the Glucocorticoid Receptor and Its Phosphorylation in Neurological Disorders" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4213. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094213
APA StyleGadwala, S., & Ghosh, C. (2025). The Role of the Glucocorticoid Receptor and Its Phosphorylation in Neurological Disorders. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4213. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094213








