Isorhapontigenin Inhibits Cell Growth, Angiogenesis, Migration, and Invasion of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells Through NEDD9 Signaling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
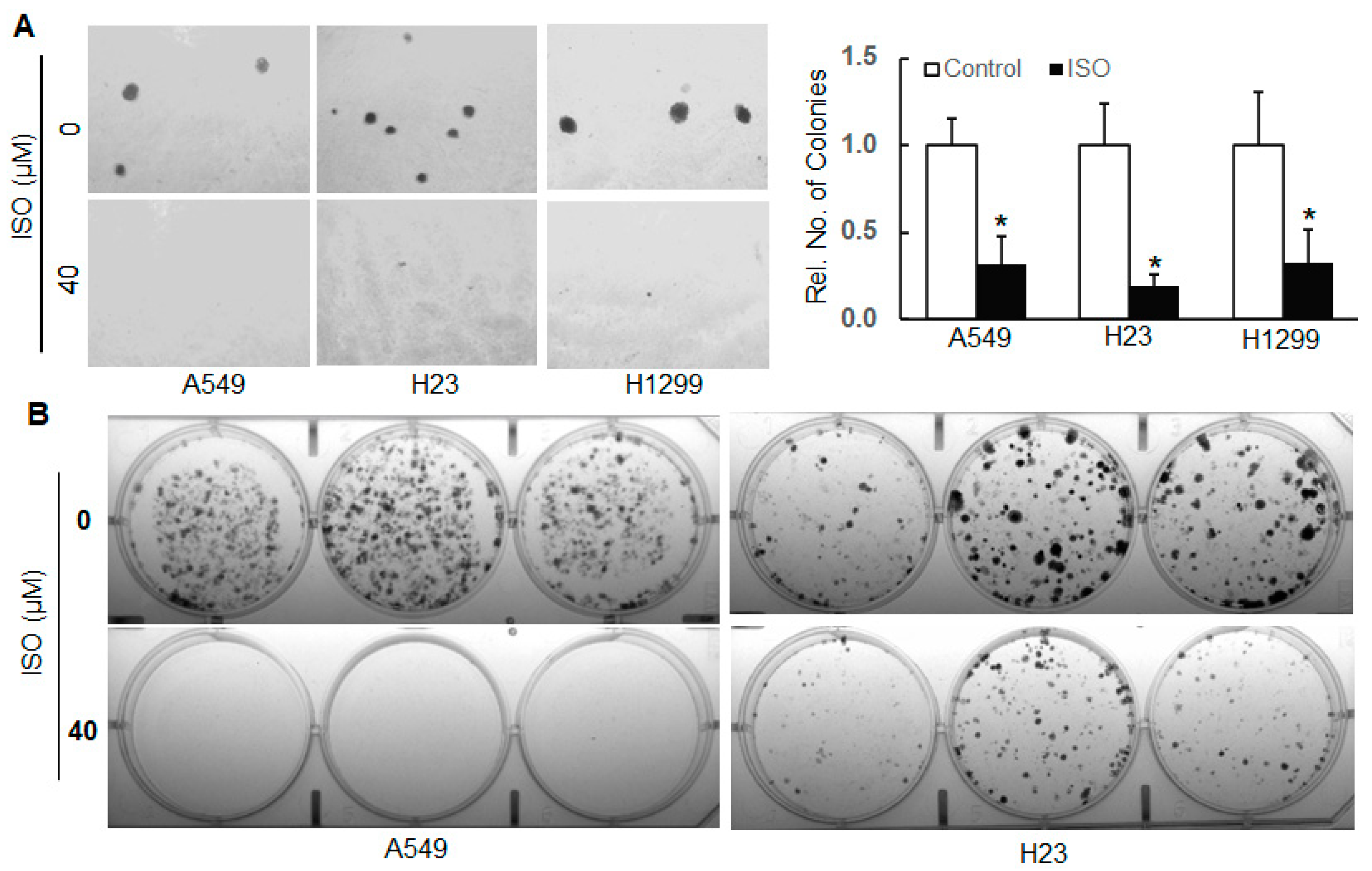
2.1. ISO Inhibited Cell Growth/Survival, Angiogenesis, Migration, and Invasion
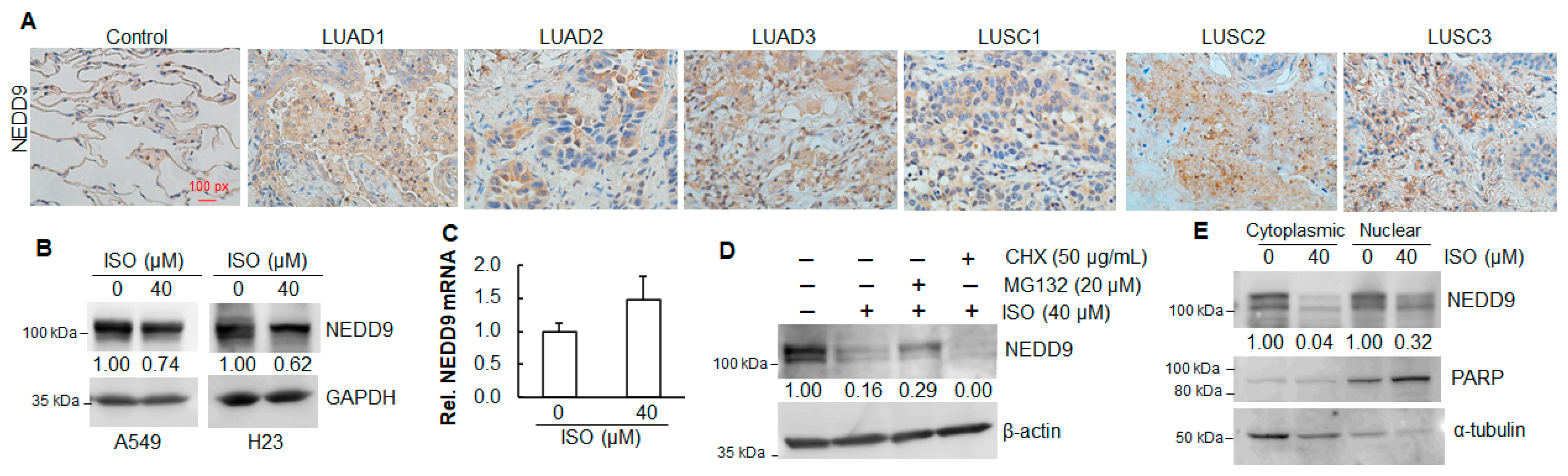
2.2. Elevated Expression of NEDD9 in Human Lung Tumor Tissues
2.3. ISO Decreased NEDD9 Protein Levels in Human Lung Cancer Cell Lines
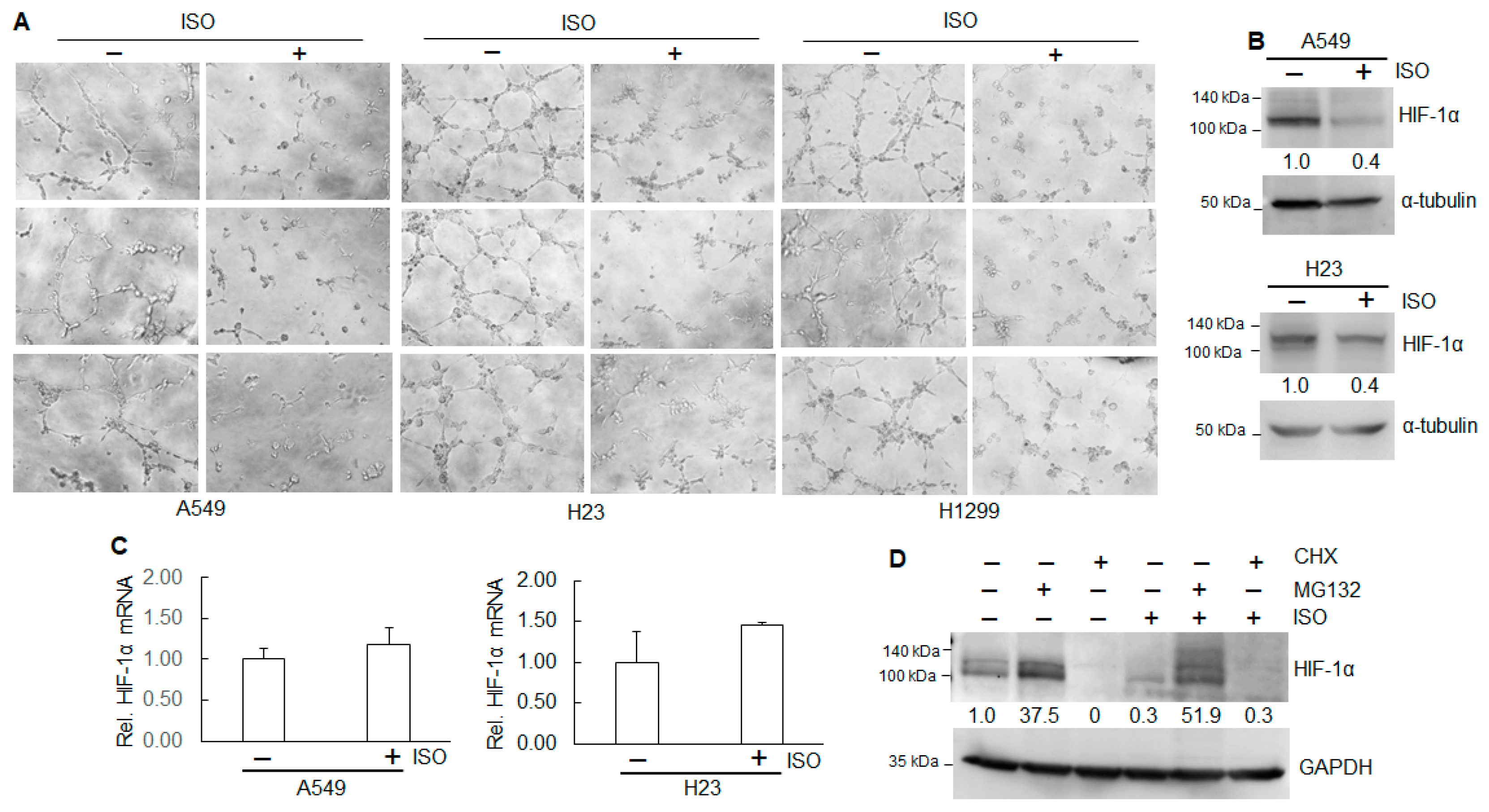
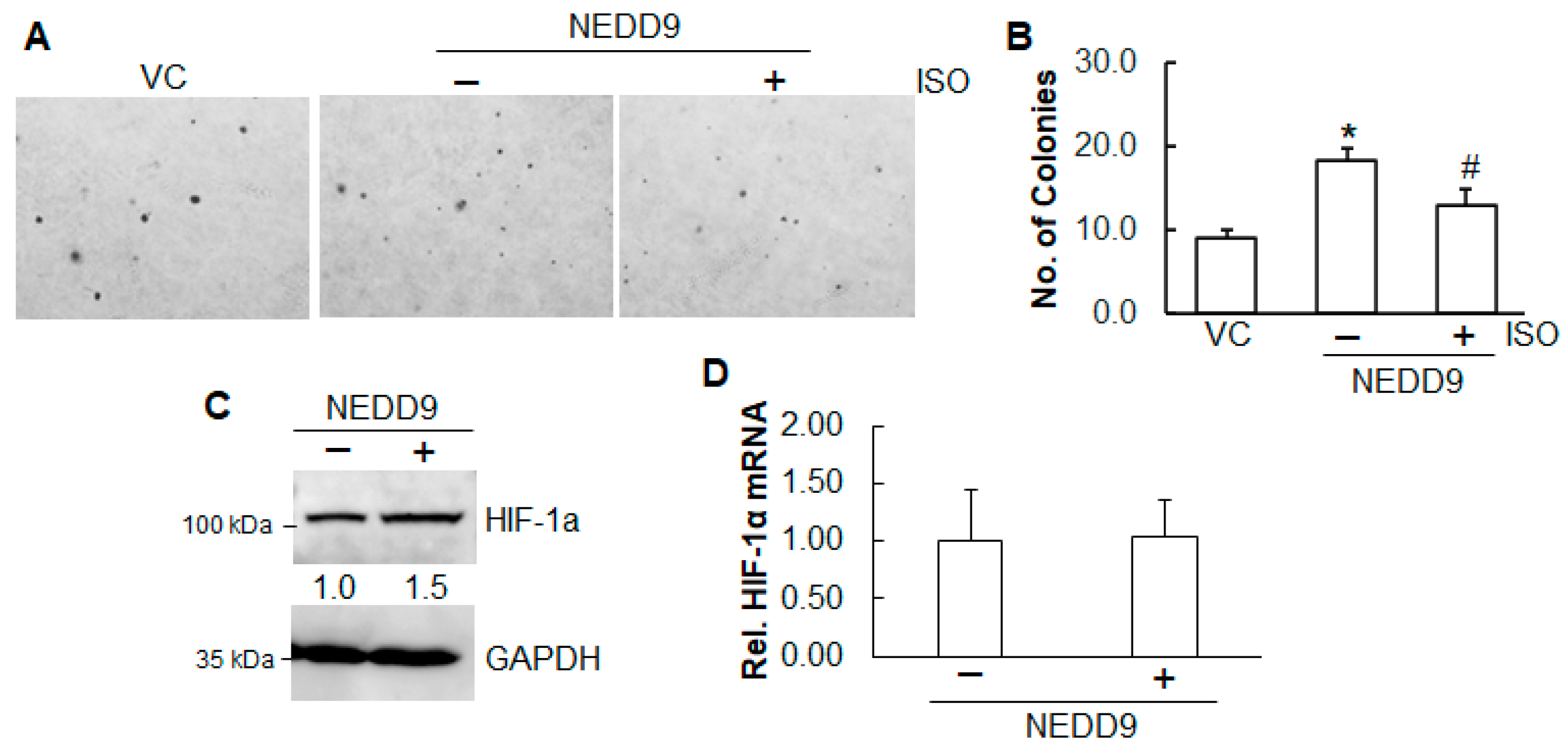
2.4. Inhibition of ISO on Cell Growth and Angiogenesis Is Through NEDD9
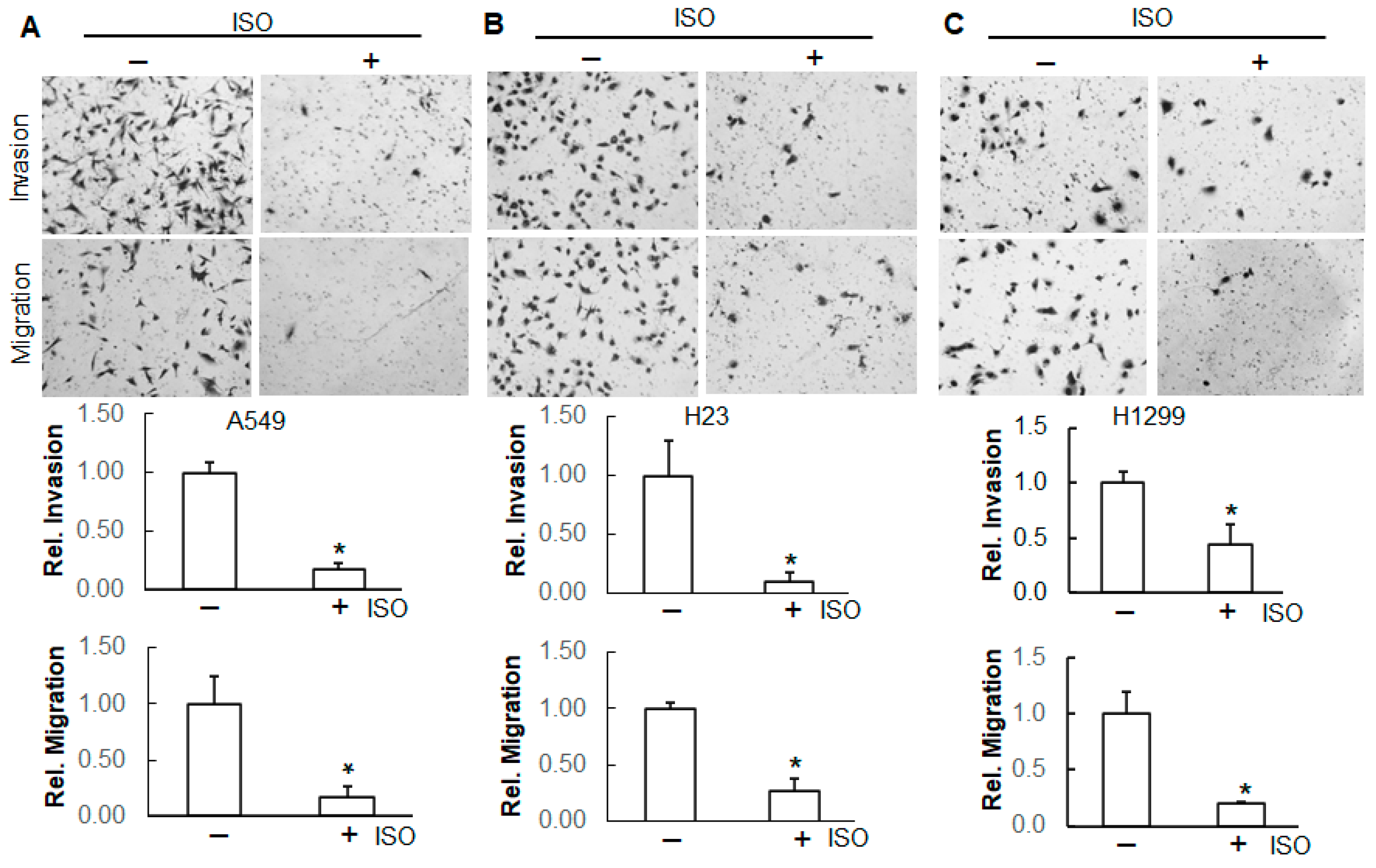
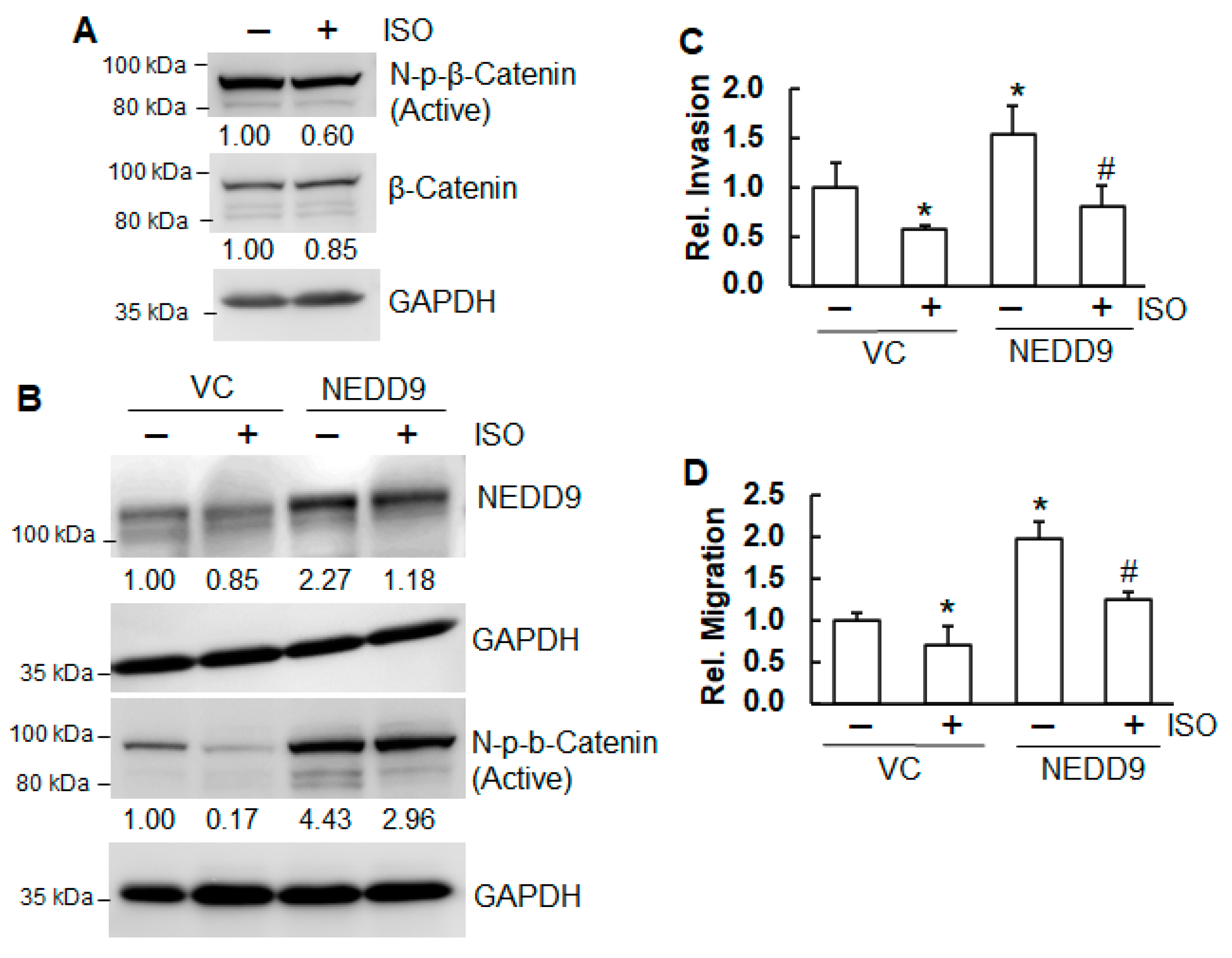
2.5. ISO Suppressed Migration and Invasion Through NEDD9/β-Catenin Signaling
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Plasmids
4.3. Cell Culture and Stably Expressing Cells
4.4. Immunoblotting Analysis
4.5. Real-Time qPCR
4.6. Soft Agar Assay
4.7. Clonogenicity Assay
4.8. Tube Formation Assay
4.9. Invasion and Migration Assays
4.10. Nuclear Extraction
4.11. Human Lung Tissues and Immunohistochemistry Staining
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/lung-cancer/about/key-statistics.html (accessed on 28 January 2025).
- Hendriks, L.E.L.; Remon, J.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Garassino, M.C.; Heymach, J.V.; Kerr, K.M.; Tan, D.S.W.; Veronesi, G.; Reck, M. Non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2024, 10, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.lung.org/research/trends-in-lung-disease/lung-cancer-trends-brief/lung-cancer-prevalence-and-incidence-(1) (accessed on 28 January 2025).
- Available online: https://www.lung.org/research/trends-in-lung-disease/lung-cancer-trends-brief (accessed on 28 January 2025).
- Ko, J.H.; Sethi, G.; Um, J.Y.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Arfuso, F.; Kumar, A.P.; Bishayee, A.; Kwang Ahn, S. The Role of Resveratrol in Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Jin, H.; Liu, F.; Liu, H.; Ho, P.C.; Lin, H.S. Exploration of Nutraceutical Potentials of Isorhapontigenin, Oxyresveratrol, and Pterostilbene: A Metabolomic Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Yeo, S.C.; Barnes, P.I.; Donnelly, B.L.E.; Loo, L.C.; Lin, H.S. Pre-clinical pharmacokinetic and metabolomic analyses of isorhapontigenin, a dietary resveratrol derivative. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, S.C.M.; Fenwick, P.S.; Barnes, P.J.; Lin, H.S.; Donnelly, L.E. Isorhapontigenin, a bioavailable dietary polyphenol, suppresses airway epithelial cell inflammation through a corticosteroid independent mechanism. Br. J. Pharm. 2017, 174, 2043–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, D.; Fang, Y.; Huang, H.; Chen, X.; Huang, C. Isorhapontigenin (ISO) inhibited cell transformation by inducing G0/G1 phase arrest via increasing MKP-1 mRNA Stability. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 2664–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Zhu, Q.; Wu, Z.; Yin, Y.; Kang, D.; Lu, S.; Liu, P. Isorhapontigenin induced cell growth inhibition and apoptosis by targeting EGFR-related pathways in prostate cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 1104–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Hua, X.; Tu, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Max, C. Isorhapontigenin (ISO) inhibits EMT through FOXO3A/METTL14/VIMENTIN pathway in bladder cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2021, 520, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Ramsey, M.R.; Hayes, D.N.; Fan, C.; McNamara, K.; Kozlowski, P.; Torrice, C.; Wu, M.C.; Shimamura, T.; Perera, S.A.; et al. LKB1 modulates lung cancer differentiation and metastasis. Nature 2007, 448, 807–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikonova, A.S.; Plotnikova, O.V.; Serzhanova, V.; Efimov, A.; Bogush, I.; Cai, K.Q.; Hensley, H.H.; Egleston, B.L.; Klein-Szanto, A.; Seeger-Nukpezah, T.; et al. Nedd9 restrains renal cystogenesis in Pkd1 −/− mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 12859–12864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shagisultanova, E.; Gaponova, A.V.; Gabbasov, R.; Nicolas, E.; Golemis, E.A. Preclinical and clinical studies of the NEDD9 scaffold protein in cancer and other diseases. Gene 2015, 567, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xiao, Q.; Xiao, J.; Niu, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Shu, G.; Yin, G. Wnt/β-catenin signaling: Function, biological mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities. Signal Transduction. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, S.; Hua, F.; Hu, Z.W. The regulation of β-Catenin activity and function in cancer: Therapeutic opportunities. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 33972–33989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurice, M.M.; Angers, S. Mechanistic insights into Wnt–β-catenin pathway activation and signal transduction. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2025, 26, 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenta, T.; Hausmann, G.; Basler, K. The many faces and functions of β-catenin. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 2714–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bavara, J.H.; Wang, Z.; Guo, J.; Qian, C.; Thibodeau, S.N.; Golemis, E.A.; Liu, W. HEF1, a novel target of Wnt signaling, promotes colonic cell migration and cancer progress. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2633–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes-Coelho, F.; Martins, F.; Pereira, S.A.; Serpa, J. Anti-Angiogenic Therapy: Current Challenges and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmgren, L.; O’Reilly, M.S.; Folkman, J. Dormancy of micrometastases: Balance proliferation and apoptosis in the presence of angiogenesis suppression. Nat. Med. 1995, 1, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movafagh, S.; Crook, S.; Vo, K. Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1a by reactive oxygen species: New developments in an old debate. J. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 116, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoud, G.N.; Li, W. HIF-1α pathway: Role, regulation and intervention for cancer therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin B 2015, 5, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infantino, V.; Santarsiero, A.; Convertini, P.; Todisco, S.; Iacobazzi, V. Cancer Cell Metabolism in Hypoxia: Role of HIF-1 as Key Regulator and Therapeutic Target. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Xia, D.; Kim, S.W.; Holla, V.; Menter, D.G.; Duboia, R.N. Human enhancer of filamentation 1 is a mediator of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha-mediated migration in colorectal carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 4054–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Tu, H.; Max, C. Isorhapontigenin (ISO) inhibits malignant cell transformation, migration, and invasion through MEG3/NEDD9 signaling in Cr(VI)-transformed cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2023, 476, 11661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Han, F.; Du, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhou, W. Hypoxic microenvironment in cancer: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparini, G.; Longo, R.; Toi, M.; Ferrara, N. Angiogenic inhibitors: A new therapeutic strategy in oncology. Nat. Rev. Pract. Oncol. 2005, 2, 562–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.L.; Chen, H.H.; Sun, L.P.; Shi, L. Angiogenic signaling pathways and anti-angiogenic therapy for cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saman, H.; Raza, S.S.; Uddin, S.; Rasul, K. Inducing Angiogenesis, a Key Step in Cancer Vascularization, and Treatment Approaches. Cancers 2020, 12, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, S.Y.; Wu, V.W.C.; Law, H.K.W. Hypoxia-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Cancers: HIF-1α and Beyond. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, G.M.; Seo, S.; Serebriiskii, I.G.; Lessin, S.R.; Golemis, E.A. A new central scaffold for metastasis: Parsing HEF1/Cas-L/NEDD9. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 8975–8979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabbasov, R.; Xiao, F.; Howe, C.G.; Bickel, L.E.; O’Brien, S.W.; Benrubi, D.; Do, T.V.; Zhou, Y.; Nicolas, E.; Cai, K.Q.; et al. NEDD9 promotes oncogenic signaling, a stem/mesenchymal gene signature, and aggressive ovarian cancer growth in mice. Oncogene 2018, 37, 4854–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sima, N.; Cheng, X.; Ye, F.; Ma, D.; Xie, X.; Lü, W. The Overexpression of Scaffolding Protein NEDD9 Promotes Migration and Invasion in Cervical Cancer via Tyrosine Phosphorylated FAK and SRC. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Ji, S.; Li, Y.; Fu, L.; Jiang, T.; Meng, F. β-Catenin promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion but induces apoptosis in renal cell carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2017, 10, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Yan, B.; Tu, H.; Huang, C.; Costa, M. Loss of MEG3 and upregulation of miR-145 play an important role in the invasion and migration of Cr(VI)-transformed cells. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennoll, S.; Yochum, G. Regulation of MYC gene expression by aberrant Wnt/β-catenin signaling in colorectal cancer. World J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 6, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtutman, M.; Zhurinsky, J.; Simcha, I.; Albanese, C.; D’Amico, M.; Pestell, R.; Ben-Ze’ev, A. The cyclin D1 gene is a target of the β-catenin/LEF-1 pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 5522–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Collaborative Group. Chemotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2000, 2000, CD002139. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, Y.; Lee, H.L.; Song, J.; Lee, Y.; Kim, B.G.; Mok, H.; Ahn, J.H. Biosynthesis of resveratrol derivatives and evaluation of their anti-inflammatory activity. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2021, 64, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangaru, S.; Madhu, G.; Srinivasan, M.; Manivannan, P. Exploring flexibility, intermolecular interactions and ADMET profiles of anti-influenza agent isorhapontigenin: A quantum chemical and molecular docking study. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, M.; Hu, Y.; Chen, J.; Cao, Y.; Liu, C.; Wu, Z.; Shen, J.; Lu, J.; Liu, P. Isorhapontigenin protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity via increasing YAP1 expression. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 680–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sie, Y.Y.; Chen, L.C.; Li, C.J.; Yuan, Y.H.; Hsiao, S.H.; Lee, M.H.; Wang, C.C.; Hou, W.C. Inhibition of Acetylcholinesterase and Amyloid-β Aggregation by Piceatannol and Analogs: Assessing In Vitro and In Vivo Impact on a Murine Model of Scopolamine-Induced Memory Impairment. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Zheng, X.; Wang, H. Isorhapontigenin ameliorates high glucose-induced podocyte and vascular endothelial cell injuries via mitigating oxidative stress and autophagy through the AMPK/Nrf2 pathway. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2023, 55, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Hou, Q.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, D.; Li, J.; Wu, X.R.; Huang, C. The Chinese herb isolate isorhapontigenin induces apoptosis in human cancer cells by down-regulating overexpression of antiapoptotic protein XIAP. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 35234–35243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambow, F.; Bechadergue, A.; Luciani, F.; Gros, G.; Domingues, M.; Bonaventure, J.; Meurice, G.; Marine, J.C.; Lionel Larue, L. Regulation of Melanoma Progression through the TCF4/miR-125b/NEDD9 Cascade. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minn, A.J.; Gupta, G.P.; Siegel, P.M.; Bos, P.D.; Shu, W.; Giri, D.D.; Viale, A.; Olsehen, A.B.; Geralk, W.L.; Massague, J. Genes that mediate breast cancer metastasis to lung. Nature 2005, 436, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.X.; Gao, F.; Zhao, G.Q.; Zhang, G.J. Role of NEDD9 in invasion and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2012, 4, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Do, T.V.; Xiao, F.; Bickel, L.E.; Klein-Szanto, A.J.; Pathak, H.B.; Hua, X.; Howe, C.; O’Brien, S.W.; Maglaty, M.; Ecsedy, J.A.; et al. Aurora kinase A mediates epithelial ovarian cancer cell migration and adhesion. Oncogene 2014, 33, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deneka, A.Y.; Nikonova, A.S.; Lee, H.O.; Kruger, W.D.; Golemis, E.A. NEDD9 sustains hexokinase expression to promote glycolysis. Oncogenesis 2022, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivan, M.; Kondo, K.; Yang, H.; Kim, W.; Valiando, J.; Ohh, M.; Salic, A.; Asara, J.M.; Lane, W.S.; Kaelin, W.G. HIFalpha targeted for VHL-mediated destruction by proline hydroxylation: Implication for O2 sensing. Science 2001, 292, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugter, J.M.; Fenderico, N.; Maurice, M.M. Mutations and mechanisms of WNT pathway tumour suppressors in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Yan, R.; Ke, X.; Qu, Y. Modulating β-catenin homeostasis for cancer therapy. Trends Cancer 2024, 10, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, L.C. Nedd9/Hef1/Cas-L mediates the effects of environmental pollutants on cell migration and plasticity. Oncogene 2009, 28, 3642–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tikhmyanova, N.; Golemis, E.A. NEDD9 and BCAR1 negatively regulate E-cadherin membrane localization and promote E-cadherin degradation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Shi, S.; Costa, M. Loss of MEG3 contributes to the enhanced migration and invasion in arsenic-induced carcinogenesis through NQO1/FSCN1 pathway. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2023, 13, 2307–2322. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Willis, D.; Shi, S.; Tu, H.; Costa, M. Isorhapontigenin Inhibits Cell Growth, Angiogenesis, Migration, and Invasion of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells Through NEDD9 Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4207. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094207
Zhang Z, Li J, Willis D, Shi S, Tu H, Costa M. Isorhapontigenin Inhibits Cell Growth, Angiogenesis, Migration, and Invasion of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells Through NEDD9 Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4207. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094207
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhuo, Jingxia Li, Daneah Willis, Sophia Shi, Huailu Tu, and Max Costa. 2025. "Isorhapontigenin Inhibits Cell Growth, Angiogenesis, Migration, and Invasion of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells Through NEDD9 Signaling" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4207. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094207
APA StyleZhang, Z., Li, J., Willis, D., Shi, S., Tu, H., & Costa, M. (2025). Isorhapontigenin Inhibits Cell Growth, Angiogenesis, Migration, and Invasion of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells Through NEDD9 Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4207. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094207






