LPAR6 Inhibits the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) by Suppressing the Nuclear Translocation of YAP/TAZ
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
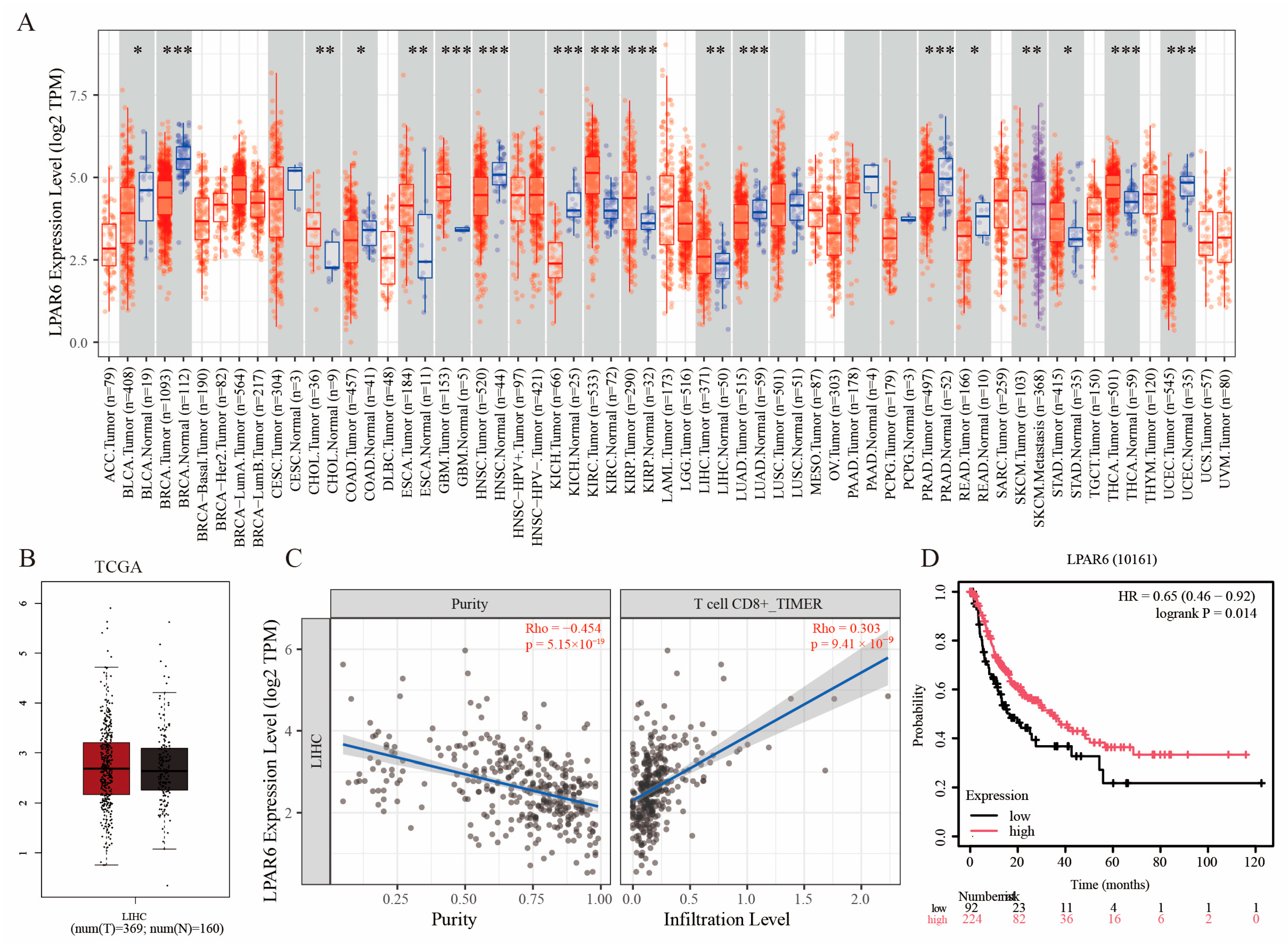
2.1. Expression Pattern and Immune Correlation of LPAR6 Based on Multi-Database Analysis
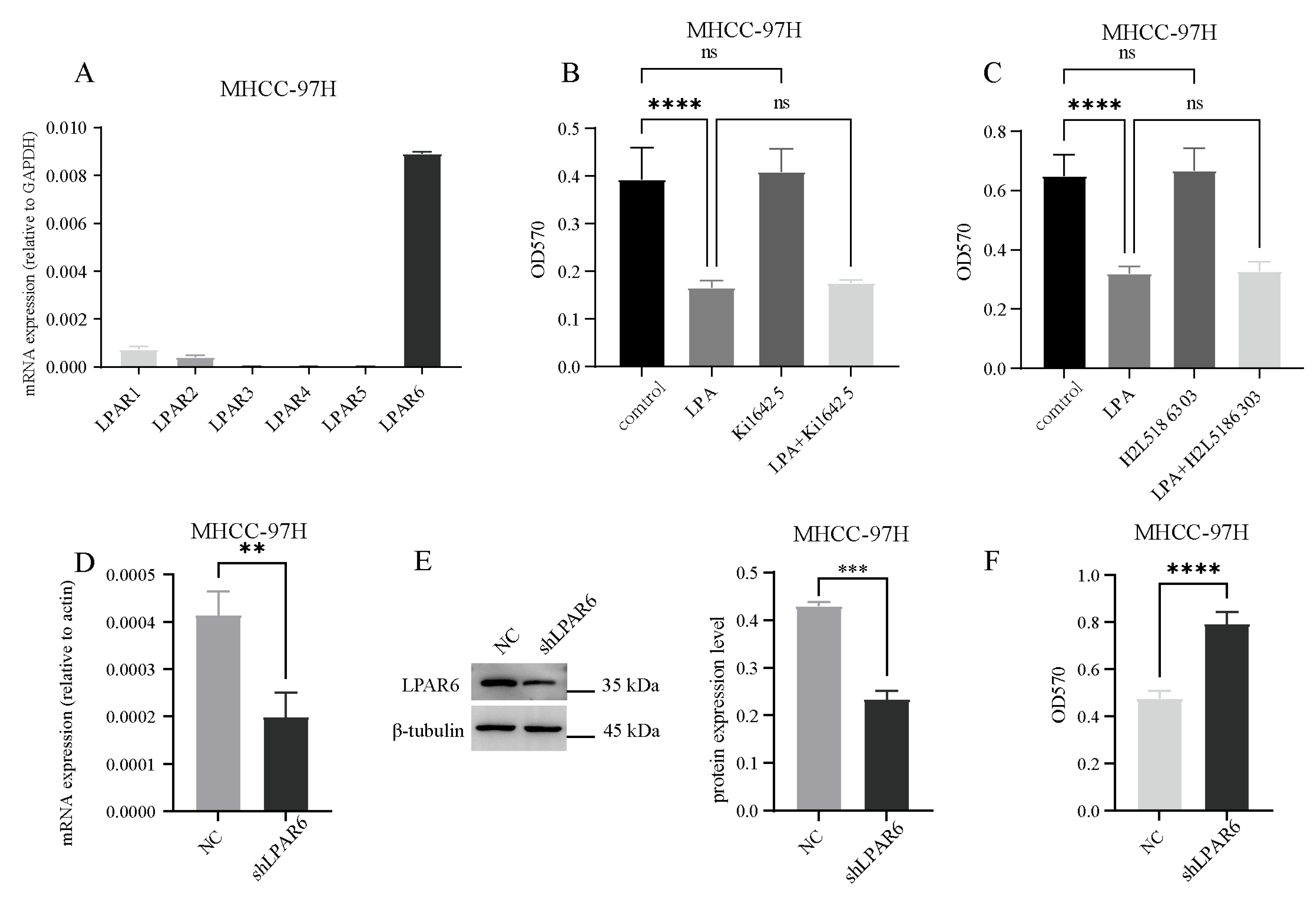
2.2. LPA Inhibits the Activity of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) Cells Through the LPAR6 Receptor
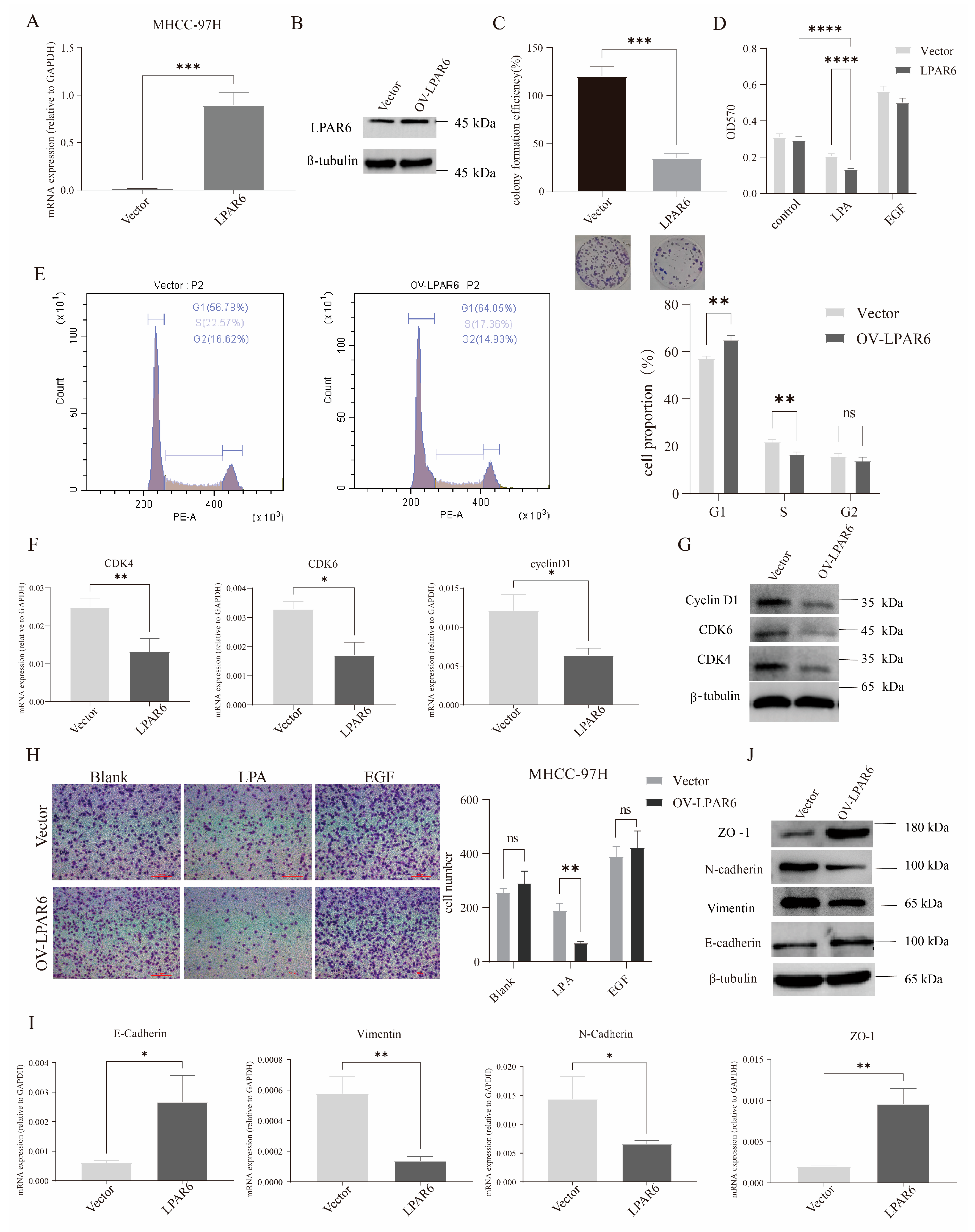
2.3. LPA Inhibits HCC Cell Proliferation, Migration, and EMT via LPAR6
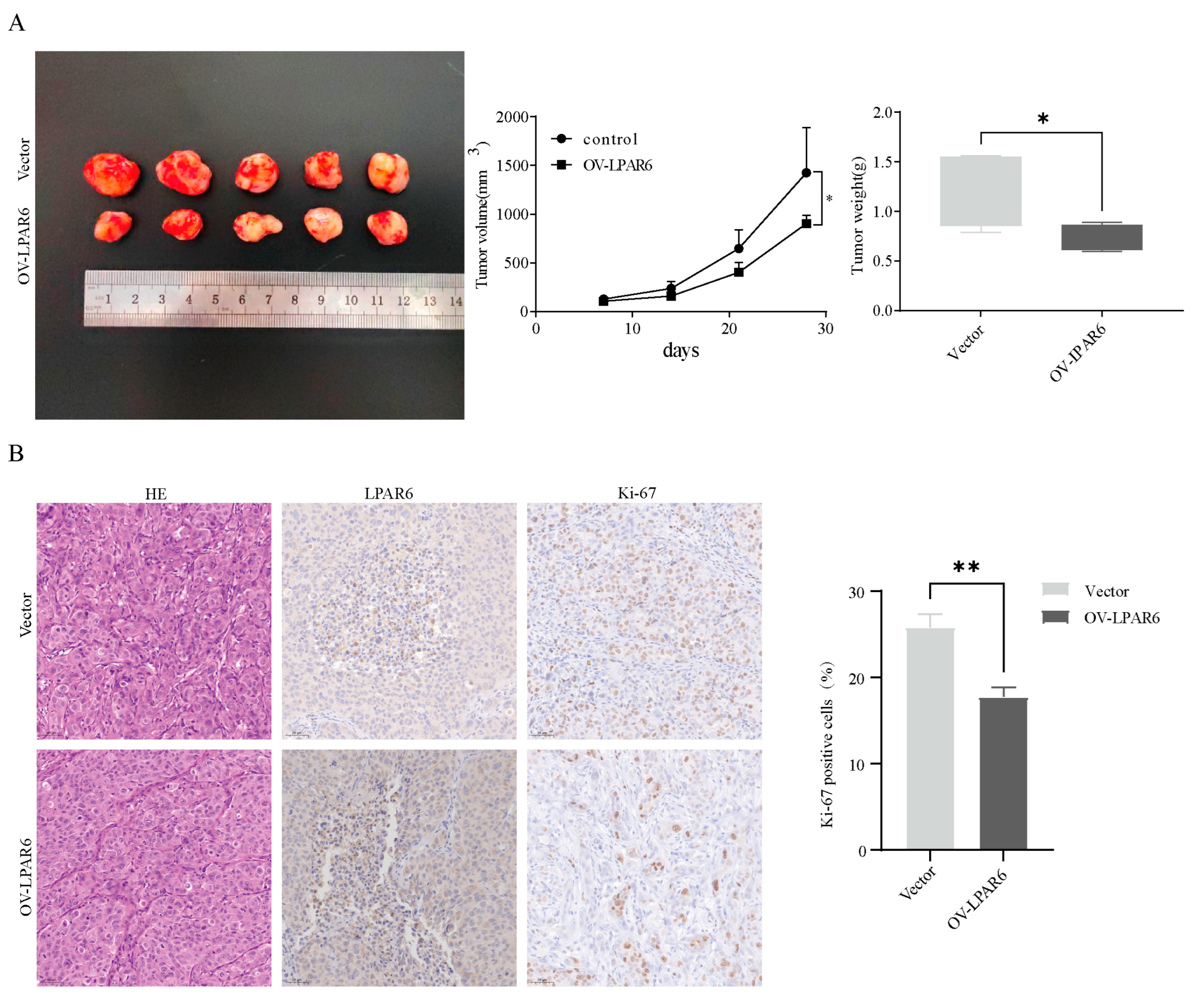
2.4. The LPA/LPAR6 Axis Can Suppress the Occurrence of Tumors In Vivo
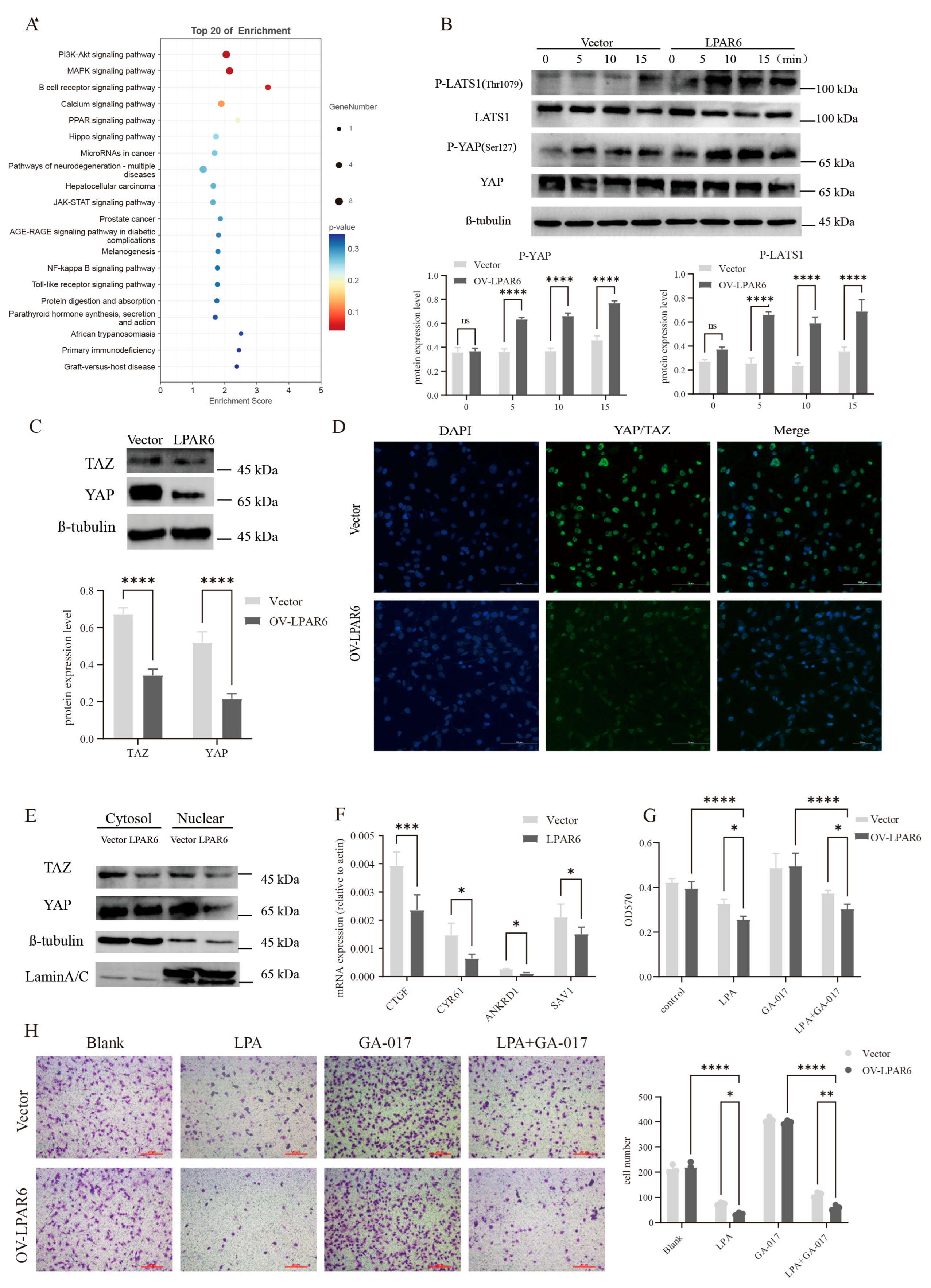
2.5. The Hippo Signaling Pathway Is Involved in LPAR6-Mediated Inhibition of HCC Cell Proliferation and Migration
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Cell Proliferation and Colony Formation
4.3. Cell Cycle Analysis and Cell Migration
4.4. Cell Transfection
4.5. RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR
4.6. Western Blot Analysis
4.7. Xenograft Models
4.8. RNA Sequencing
4.9. H&E Stain, Immunohistochemistry (IHC), and Cell Immunofluorescence
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.Q.; Singal, A.G.; Kono, Y.; Tan, D.J.; El-Serag, H.B.; Loomba, R. Changing global epidemiology of liver cancer from 2010 to 2019: NASH is the fastest growing cause of liver cancer. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 969–977.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singal, A.G.; Kanwal, F.; Llovet, J.M. Global trends in hepatocellular carcinoma epidemiology: Implications for screening, prevention and therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 864–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naugler, W.E.; Sakurai, T.; Kim, S.; Maeda, S.; Kim, K.; Elsharkawy, A.M.; Karin, M. Gender Disparity in Liver Cancer Due to Sex Differences in MyD88-Dependent IL-6 Production. Science 2007, 317, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, A.B.; Zhu, A.X. Metabolic syndrome and hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 2009, 115, 5651–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.Y.; Danpanichkul, P.; Agopian, V.; Mehta, N.; Parikh, N.D.; Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Singal, A.G.; Yang, J.D. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Updates on epidemiology, surveillance, diagnosis and treatment. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2024, 31, S228–S254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, F.; Dong, J.; Jin, C.; Niu, Z.; Yang, W.; He, Y.; Yu, D.; Sun, M.; Wang, T.; Yin, X.; et al. Iparomlimab (QL1604) in patients with microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) or mismatch repair-deficient (dMMR) unresectable or metastatic solid tumors: A pivotal, single-arm, multicenter, phase II trial. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 17, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Hong, Y.; Huang, J.; Qu, X.; Sooranna, S.R.; Lu, S.; Li, T.; Niu, B. Targeting PD-1/PD-L1 in tumor immunotherapy: Mechanisms and interactions with host growth regulatory pathways. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2024, 79, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhao, W.; Chen, H.; Zhu, X.; You, J.; Jin, C. Evaluation of the effectiveness and safety of combining PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors with anti-angiogenic agents in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1468440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panupinthu, N.; Lee, H.Y.; Mills, G.B. Lysophosphatidic acid production and action: Critical new players in breast cancer initiation and progression. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraldo, L.H.M.; de Sampaio Spohr, T.C.L.; do Amaral, R.F.; da Fonseca, A.C.C.; Garcia, C.; de Almeida Mendes, F.; Freitas, C.; Fabio dosSantos, M.; Lima, F.R.S. Role of lysophosphatidic acid and its receptors in health and disease: Novel therapeutic strategies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoddard, N.C.; Chun, J. Promising Pharmacological Directions in the World of Lysophosphatidic Acid Signaling. Biomol. Ther. 2015, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatraman, G.; Benesch, M.G.K.; Tang, X.; Dewald, J.; McMullen, T.P.W.; Brindley, D.N. Lysophosphatidate signaling stabilizes Nrf2 and increases the expression of genes involved in drug resistance and oxidative stress responses: Implications for cancer treatment. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 772–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, R.; Inoue, A.; Sayama, M.; Uwamizu, A.; Yamashita, K.; Hirata, K.; Yoshida, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Kato, H.E.; Nakada-Nakura, Y.; et al. Structural insights into ligand recognition by the lysophosphatidic acid receptor LPA6. Nature 2017, 548, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Zhou, Q.; Labroska, V.; Qin, S.; Darbalaei, S.; Wu, Y.; Yuliantie, E.; Xie, L.; Tao, H.; Cheng, J.; et al. G protein-coupled receptors: Structure- and function-based drug discovery. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatakrishnan, A.J.; Deupi, X.; Lebon, G.; Tate, C.G.; Schertler, G.F.; Babu, M.M. Molecular signatures of G-protein-coupled receptors. Nature 2013, 494, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.-F.; Wu, S.; Li, Y.; Bao, G.; Pei, J.-Y.; Wang, Y.-W.; Ma, Q.; Sun, H.-J.; Damirin, A. LPA receptor1 antagonists as anticancer agents suppress human lung tumours. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 868, 172886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qi, Z.; Li, Z.; Bai, S.; Damirin, A. LPAR2-mediated action promotes human renal cell carcinoma via MAPK/NF-κB signaling to regulate cytokine network. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 149, 2041–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, D.; Lin, Z.; Wu, J. Near-Infrared Fluorogenic Probes with Polarity-Sensitive Emission for in Vivo Imaging of an Ovarian Cancer Biomarker. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 5847–5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Yun, Q.; Li, A.; Li, R.; Yan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, H.; Damirin, A. LPA3 is a precise therapeutic target and potential biomarker for ovarian cancer. Med. Oncol. 2022, 39, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, T.; Sicinski, P. Cell cycle proteins as promising targets in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibue, T.; Weinberg, R.A. EMT, CSCs, and drug resistance: The mechanistic link and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, V. Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition in Tumor Metastasis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2018, 13, 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, C.G.; Moroishi, T.; Guan, K.-L. YAP and TAZ: A nexus for Hippo signaling and beyond. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aihara, A.; Iwawaki, T.; Abe-Fukasawa, N.; Otsuka, K.; Saruhashi, K.; Mikashima, T.; Nishino, T. Small molecule LATS kinase inhibitors block the Hippo signaling pathway and promote cell growth under 3D culture conditions. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, J.; Inoue, A.; Okudaira, S. Two pathways for lysophosphatidic acid production. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1781, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, N.; Ishii, S.; Tsujiuchi, T.; Kagawa, N.; Katoh, K. Comparative analyses of lysophosphatidic acid receptor-mediated signaling. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 2377–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Hopkins, A.M.; Hou, J. The development of modulators for lysophosphatidic acid receptors: A comprehensive review. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 117, 105386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagida, K.; Ishii, S. Non-Edg family LPA receptors: The cutting edge of LPA research. J. Biochem. 2011, 150, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Xu, Z.; Hao, B.; Zhang, A.; Guo, C.; He, Y. Molecular mechanism of ligand recognition and activation of lysophosphatidic acid receptor LPAR6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2025, 122, e2415426122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagida, K.; Masago, K.; Nakanishi, H.; Kihara, Y.; Hamano, F.; Tajima, Y.; Taguchi, R.; Shimizu, T.; Ishii, S. Identification and Characterization of a Novel Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor, p2y5/LPA6. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 17731–17741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasternack, S.M.; Von Kügelgen, I.; Al Aboud, K.; Lee, Y.-A.; Rüschendorf, F.; Voss, K.; Hillmer, A.M.; Molderings, G.J.; Franz, T.; Ramirez, A.; et al. G protein–coupled receptor P2Y5 and its ligand LPA are involved in maintenance of human hair growth. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Choi, S.; Halldén, G.; Yo, S.J.; Schichnes, D.; Aponte, G.W. P2Y5 is a Gαi, Gα12/13G protein-coupled receptor activated by lysophosphatidic acid that reduces intestinal cell adhesion. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2009, 297, G641–G654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzocca, A.; Dituri, F.; De Santis, F.; Filannino, A.; Lopane, C.; Betz, R.C.; Li, Y.-Y.; Mukaida, N.; Winter, P.; Tortorella, C.; et al. Lysophosphatidic acid receptor LPAR6 supports the tumorigenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, J.; Guo, S.; Li, K.; Tian, J.; Zong, B.; Ai, T.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S. Lysophosphatidic acid receptor 6 regulated by miR-27a-3p attenuates tumor proliferation in breast cancer. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 24, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.; Guo, S.; Chen, R.; Yang, C.; Jian, L.; Yu, H.; Liu, S. Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 6 (LPAR6) Expression and Prospective Signaling Pathway Analysis in Breast Cancer. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2019, 23, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Bao, G.; Pei, J.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, Y.; Damirin, A. NF-κB and EGFR participate in S1PR3-mediated human renal cell carcinomas progression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2022, 1868, 166401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bao, G.; Zhai, M.; Yan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Damirin, A. LPAR6 Inhibits the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) by Suppressing the Nuclear Translocation of YAP/TAZ. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094205
Bao G, Zhai M, Yan Y, Wang Y, Damirin A. LPAR6 Inhibits the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) by Suppressing the Nuclear Translocation of YAP/TAZ. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094205
Chicago/Turabian StyleBao, Gegentuya, Manjue Zhai, Yali Yan, Yuewu Wang, and Alatangaole Damirin. 2025. "LPAR6 Inhibits the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) by Suppressing the Nuclear Translocation of YAP/TAZ" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094205
APA StyleBao, G., Zhai, M., Yan, Y., Wang, Y., & Damirin, A. (2025). LPAR6 Inhibits the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) by Suppressing the Nuclear Translocation of YAP/TAZ. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094205




