Comparative Brain and Serum Exosome Expression of Biomarkers in an Experimental Model of Alzheimer-Type Neurodegeneration: Potential Relevance to Liquid Biopsy Diagnostics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Definition |
| 4-HNE | 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal |
| AD | Alzheimer’s Disease |
| Aβ | Amyloid β Peptide, 1-42) |
| AβPP | Amyloid β-Precursor Protein |
| BCA | Bicinchoninic Assay |
| CNPase (11-5B) | 2′,3′-cyclic nucleotide 3′ phosphodiesterase |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal Fluid |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| EV | Extracellular Vesicles or Exosomes |
| FLEV | Frontal Lobe Extracellular Vesicles |
| FLTX | Frontal Lobe Tissue |
| GALC | Group-specific component Vitamin D Binding protein; Gc-globulin |
| GFAP | Glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| HRP | Horseradish Peroxidase |
| HSP70 | Heat Shock Protein 70 |
| MAG | Myelin-Associated Glycoprotein |
| MBP | Myelin basic protein |
| MOG | Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein |
| MWM | Morris water maze |
| NTA | Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis |
| PDGFRA | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor, alpha polypeptide |
| PLP | Proteolipid Protein 1 |
| pTau (PHF; S396) | Phosphorylated Tau |
| RPLPO | Large acidic ribonuclear protein |
| SEV | Serum Extracellular Vesicles |
| STZ | Streptozotocin |
| Tau | Tubulin-associated unit |
| WM | White Matter |
References
- Bloom, G.S. Amyloid-beta and tau: The trigger and bullet in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Monte, S.M. Malignant Brain Aging: The Formidable Link Between Dysregulated Signaling Through Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin Pathways and Alzheimer’s Disease (Type 3 Diabetes). J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2023, 95, 1301–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahami Monfared, A.A.; Byrnes, M.J.; White, L.A.; Zhang, Q. The Humanistic and Economic Burden of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurol. Ther. 2022, 11, 525–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Andrews, J.S.; Beach, T.G.; Buracchio, T.; Dunn, B.; Graf, A.; Hansson, O.; Ho, C.; Jagust, W.; McDade, E.; et al. Revised criteria for diagnosis and staging of Alzheimer’s disease: Alzheimer’s Association Workgroup. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 20, 5143–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloch, K.; Gil-Ad, I.; Vanichkin, A.; Hornfeld, S.H.; Koroukhov, N.; Taler, M.; Vardi, P.; Weizman, A. Intracerebroventricular Streptozotocin Induces Obesity and Dementia in Lewis Rats. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 60, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, M.; Caobi, A.; Miles, J.S.; Vashist, A.; Ruiz, M.A.; Raymond, A.D. Diagnostic potential of exosomal extracellular vesicles in oncology. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal, L.; Fothi, A.; Orosz, G.; Nagy, S.; Than, N.G.; Orban, T.I. Exosomal small RNA profiling in first-trimester maternal blood explores early molecular pathways of preterm preeclampsia. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1321191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.J.; Cheng, Z.Y.; Gao, Y.; Xin, L.; Yu, C.T.; Wang, T.L.; Li, Z.S.; Wang, L.W. Liquid biopsy of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Implications in diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment monitoring. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 59, 698–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Agbisit, C.; Noel, M.; Mukherji, R. Evolving applications of liquid biopsies in gastrointestinal cancers. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 22, 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Zhen, S.; Ping, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. Metabolomic biomarkers in liquid biopsy: Accurate cancer diagnosis and prognosis monitoring. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1331215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Qin, F.; Chen, J. Exosomes: A promising avenue for cancer diagnosis beyond treatment. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1344705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, S.; Bhattacharya, B.; Dutta, S.; Mandal, D.; Mukherjee, S.; Anand, K.; Eswaramoorthy, R.; Thorat, N.; Jha, S.K.; Gorai, S. Clinical Theranostics Trademark of Exosome in Glioblastoma Metastasis. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 9, 5205–5221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, P.; Biswas, A.; Biswas, S.C. Brain-enriched miR-128: Reduced in exosomes from Parkinson’s patient plasma, improves synaptic integrity, and prevents 6-OHDA mediated neuronal apoptosis. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1037903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, J.C. Extracellular vesicles, from the pathogenesis to the therapy of neurodegenerative diseases. Transl. Neurodegener. 2022, 11, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natale, F.; Fusco, S.; Grassi, C. Dual role of brain-derived extracellular vesicles in dementia-related neurodegenerative disorders: Cargo of disease spreading signals and diagnostic-therapeutic molecules. Transl. Neurodegener. 2022, 11, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banack, S.A.; Dunlop, R.A.; Stommel, E.W.; Mehta, P.; Cox, P.A. miRNA extracted from extracellular vesicles is a robust biomarker of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 442, 120396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doroszkiewicz, J.; Groblewska, M.; Mroczko, B. Molecular Biomarkers and Their Implications for the Early Diagnosis of Selected Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanardini, R.; Saraceno, C.; Benussi, L.; Squitti, R.; Ghidoni, R. Exploring Neurofilament Light Chain and Exosomes in the Genetic Forms of Frontotemporal Dementia. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 758182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Zhang, L.; Su, Y.; Liang, X.; Yang, J.; Luo, Q.; Luo, H. Sensitive detection of multiple blood biomarkers via immunomagnetic exosomal PCR for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eabm3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xia, X.; Zheng, J.C. Neural stem/progenitor cell-derived extracellular vesicles: A novel therapy for neurological diseases and beyond. MedComm 2023, 4, e214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminski, V.L.; Michita, R.T.; Ellwanger, J.H.; Veit, T.D.; Schuch, J.B.; Riesgo, R.D.S.; Roman, T.; Chies, J.A.B. Exploring potential impacts of pregnancy-related maternal immune activation and extracellular vesicles on immune alterations observed in autism spectrum disorder. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppesen, D.K.; Zhang, Q.; Franklin, J.L.; Coffey, R.J. Extracellular vesicles and nanoparticles: Emerging complexities. Trends Cell Biol. 2023, 33, 667–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegtel, D.M.; Gould, S.J. Exosomes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2019, 88, 487–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebjedi, B.; Tasnim, N.; Hoorfar, M.; Mastromonaco, G.F.; De Almeida Monteiro Melo Ferraz, M. Exploiting Microfluidics for Extracellular Vesicle Isolation and Characterization: Potential Use for Standardized Embryo Quality Assessment. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 620809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galazka, G.; Mycko, M.P.; Selmaj, I.; Raine, C.S.; Selmaj, K.W. Multiple sclerosis: Serum-derived exosomes express myelin proteins. Mult. Scler. 2018, 24, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picciolini, S.; Gualerzi, A.; Vanna, R.; Sguassero, A.; Gramatica, F.; Bedoni, M.; Masserini, M.; Morasso, C. Detection and Characterization of Different Brain-Derived Subpopulations of Plasma Exosomes by Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 8873–8880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurwitz, S.N.; Olcese, J.M.; Meckes, D.G., Jr. Extraction of Extracellular Vesicles from Whole Tissue. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 7, 10–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhit, K.K.; Wanjari, A.; Menon, S.; Siddhaarth, K. Liquid Biopsy: An Evolving Paradigm for Non-invasive Disease Diagnosis and Monitoring in Medicine. Cureus 2023, 15, e50176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. Role of extracellular vesicle in human papillomavirus-associated cervical cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 16203–16212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Duijf, P.H.G.; Sriram, S.; Perera, G.; Vasani, S.; Kenny, L.; Leo, P.; Punyadeera, C. Circulating tumour DNA alterations: Emerging biomarker in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 30, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levkova, M.; Chervenkov, T.; Angelova, L.; Dzenkov, D. Oxford Nanopore Technology and its Application in Liquid Biopsies. Curr. Genom. 2023, 24, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, S.; Miras, M.C.M.; Pappolla, A.; Montalban, X.; Comabella, M. Liquid Biopsy in Neurological Diseases. Cells 2023, 12, 1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santini, D.; Botticelli, A.; Galvano, A.; Iuliani, M.; Incorvaia, L.; Gristina, V.; Taffon, C.; Foderaro, S.; Paccagnella, E.; Simonetti, S.; et al. Network approach in liquidomics landscape. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Deng, D.; Li, S.; Ren, J.; Huang, W.; Liu, D.; Wang, W. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid assessment facilitates precision medicine for lung cancer. Cancer Biol. Med. 2023, 21, 230–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Gupta, S.; Das, B.C. Saliva as a potential non-invasive liquid biopsy for early and easy diagnosis/prognosis of head and neck cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2024, 40, 101827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, H.; Kang, C.; Wang, C. Cancer diagnosis using label-free SERS-based exosome analysis. Theranostics 2024, 14, 1966–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Singh, A.V.; Kushwaha, S.; Chauhan, D.S. Emerging role of exosomes as a liquid biopsy tool for diagnosis, prognosis & monitoring treatment response of communicable & non-communicable diseases. Indian J. Med. Res. 2024, 159, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wijerathne, H.; Godwin, A.K.; Soper, S.A. Isolation and analysis methods of extracellular vesicles (EVs). Extracell. Vesicles Circ. Nucleic Acids 2021, 2, 80–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakubovich, E.I.; Polischouk, A.G.; Evtushenko, V.I. Principles and Problems of Exosome Isolation from Biological Fluids. Biochem. Suppl. Ser. A Membr. Cell Biol. 2022, 16, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malm, T.; Loppi, S.; Kanninen, K.M. Exosomes in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem. Int. 2016, 97, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornung, S.; Dutta, S.; Bitan, G. CNS-Derived Blood Exosomes as a Promising Source of Biomarkers: Opportunities and Challenges. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brun, A.; Englund, E. A white matter disorder in dementia of the Alzheimer type: A pathoanatomical study. Ann. Neurol. 1986, 19, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Monte, S.M. Disproportionate atrophy of cerebral white matter in chronic alcoholics. Arch. Neurol. 1988, 45, 990–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sams, E.C. Oligodendrocytes in the aging brain. Neuronal Signal. 2021, 5, NS20210008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, M.; Nave, K.A. Oligodendrocytes: Myelination and Axonal Support. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 8, a020479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.C.; Morrison, E.H. Histology, Astrocytes; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann, K.; Rodriguez-Rodriguez, R.; Gaebler, A.; Casals, N.; Scheller, A.; Kuerschner, L. Astrocytes and oligodendrocytes in grey and white matter regions of the brain metabolize fatty acids. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutma, E.; van Gent, D.; Amor, S.; Peferoen, L.A.N. Astrocyte and Oligodendrocyte Cross-Talk in the Central Nervous System. Cells 2020, 9, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, B.; Villain, N.; Frisoni, G.B.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Sabbagh, M.; Cappa, S.; Bejanin, A.; Bombois, S.; Epelbaum, S.; Teichmann, M.; et al. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations of the International Working Group. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, B.; Lautner, R.; Andreasson, U.; Ohrfelt, A.; Portelius, E.; Bjerke, M.; Holtta, M.; Rosen, C.; Olsson, C.; Strobel, G.; et al. CSF and blood biomarkers for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.C.; Han, S.H.; Mook-Jung, I. Peripheral inflammatory biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease: A brief review. BMB Rep. 2020, 53, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Bautista, C.; Tirle, T.; Lopez-Nogueroles, M.; Vento, M.; Baquero, M.; Chafer-Pericas, C. Oxidative Damage of DNA as Early Marker of Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaffer, C.; Sarad, N.; DeCrumpe, A.; Goswami, D.; Herrmann, S.; Morales, J.; Patel, P.; Osborne, J. Biomarkers in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Lab. Autom. 2015, 20, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wurtman, R. Biomarkers in the diagnosis and management of Alzheimer’s disease. Metabolism 2015, 64, S47–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Monte, S.M.; Tong, M.; Schiano, I.; Didsbury, J. Improved Brain Insulin/IGF Signaling and Reduced Neuroinflammation with T3D-959 in an Experimental Model of Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 55, 849–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Monte, S.M.; Tong, M.; Vimbela, G. Oligodendroglial and neuroglial molecular abnormalities in the intracerebral streptozotocin model of sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Park. Dement. 2016, 1, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Lester-Coll, N.; Rivera, E.J.; Soscia, S.J.; Doiron, K.; Wands, J.R.; de la Monte, S.M. Intracerebral streptozotocin model of type 3 diabetes: Relevance to sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2006, 9, 13–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Monte, S.M.; Tong, M.; Lester-Coll, N.; Plater, M., Jr.; Wands, J.R. Therapeutic rescue of neurodegeneration in experimental type 3 diabetes: Relevance to Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2006, 10, 89–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Monte, S.M.; Tong, M. Mechanisms of nitrosamine-mediated neurodegeneration: Potential relevance to sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2009, 17, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, M.; Naeem-ul-Hassan Naqvi, S. Effects of STZ-Induced Diabetes on the Relative Weights of Kidney, Liver and Pancreas in Albino Rats: A Comparative Study. Int. J. Morphol. 2010, 28, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Monte, S.M. Quantitation of cerebral atrophy in preclinical and end-stage Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 1989, 25, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, A.; Englund, E. Brain changes in dementia of Alzheimer’s type relevant to new imaging diagnostic methods. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 1986, 10, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quarles, R.H. Myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG): Past, present and beyond. J. Neurochem. 2007, 100, 1431–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Qiu, J.; Nikulina, E.; Filbin, M.T. Soluble myelin-associated glycoprotein released from damaged white matter inhibits axonal regeneration. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2001, 18, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiese, C.; Rolletschek, A.; Kania, G.; Blyszczuk, P.; Tarasov, K.V.; Tarasova, Y.; Wersto, R.P.; Boheler, K.R.; Wobus, A.M. Nestin expression—A property of multi-lineage progenitor cells? Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 2510–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyer, S. Glucose metabolism and insulin receptor signal transduction in Alzheimer disease. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 490, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyer, S.; Muller, D.; Plaschke, K. Desensitization of brain insulin receptor. Effect on glucose/energy and related metabolism. J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 1994, 44, 259–268. [Google Scholar]
- de La Monte, S.M.; Yang, Y.; Tong, M. Brain and Serum Membrane Vesicle (Exosome) Profiles in Experimental Alcohol-Related Brain Degeneration: Forging the Path to Non-Invasive Liquid Biopsy Diagnostics. J. Mol. Pathol. 2024, 5, 360–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DaDalt, A.A.; Bonham, C.A.; Lotze, G.P.; Luiso, A.A.; Vacratsis, P.O. Src-mediated phosphorylation of the ribosome biogenesis factor hYVH1 affects its localization, promoting partitioning to the 60S ribosomal subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.T.; Zou, Y.X.; Zhu, W.J.; Sen, L.; Zhang, G.H.; Ma, R.R.; Guo, X.Y.; Gao, P. lncRNA THAP7-AS1, transcriptionally activated by SP1 and post-transcriptionally stabilized by METTL3-mediated m6A modification, exerts oncogenic properties by improving CUL4B entry into the nucleus. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevigny, M.; Bourdeau Julien, I.; Venkatasubramani, J.P.; Hui, J.B.; Dutchak, P.A.; Sephton, C.F. FUS contributes to mTOR-dependent inhibition of translation. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 18459–18473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.J.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Jiang, Y.; Li, C.Q.; Lim, M.C.; An, O.; Mayakonda, A.; Ding, L.W.; Long, L.; Sun, C.; et al. Super-Enhancer-Driven Long Non-Coding RNA LINC01503, Regulated by TP63, Is Over-Expressed and Oncogenic in Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 2137–2151.e2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebenau, J.L.; Timmers, T.; Wesselman, L.M.P.; Verberk, I.M.W.; Verfaillie, S.C.J.; Slot, R.E.R.; van Harten, A.C.; Teunissen, C.E.; Barkhof, F.; van den Bosch, K.A.; et al. ATN classification and clinical progression in subjective cognitive decline: The SCIENCe project. Neurology 2020, 95, e46–e58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
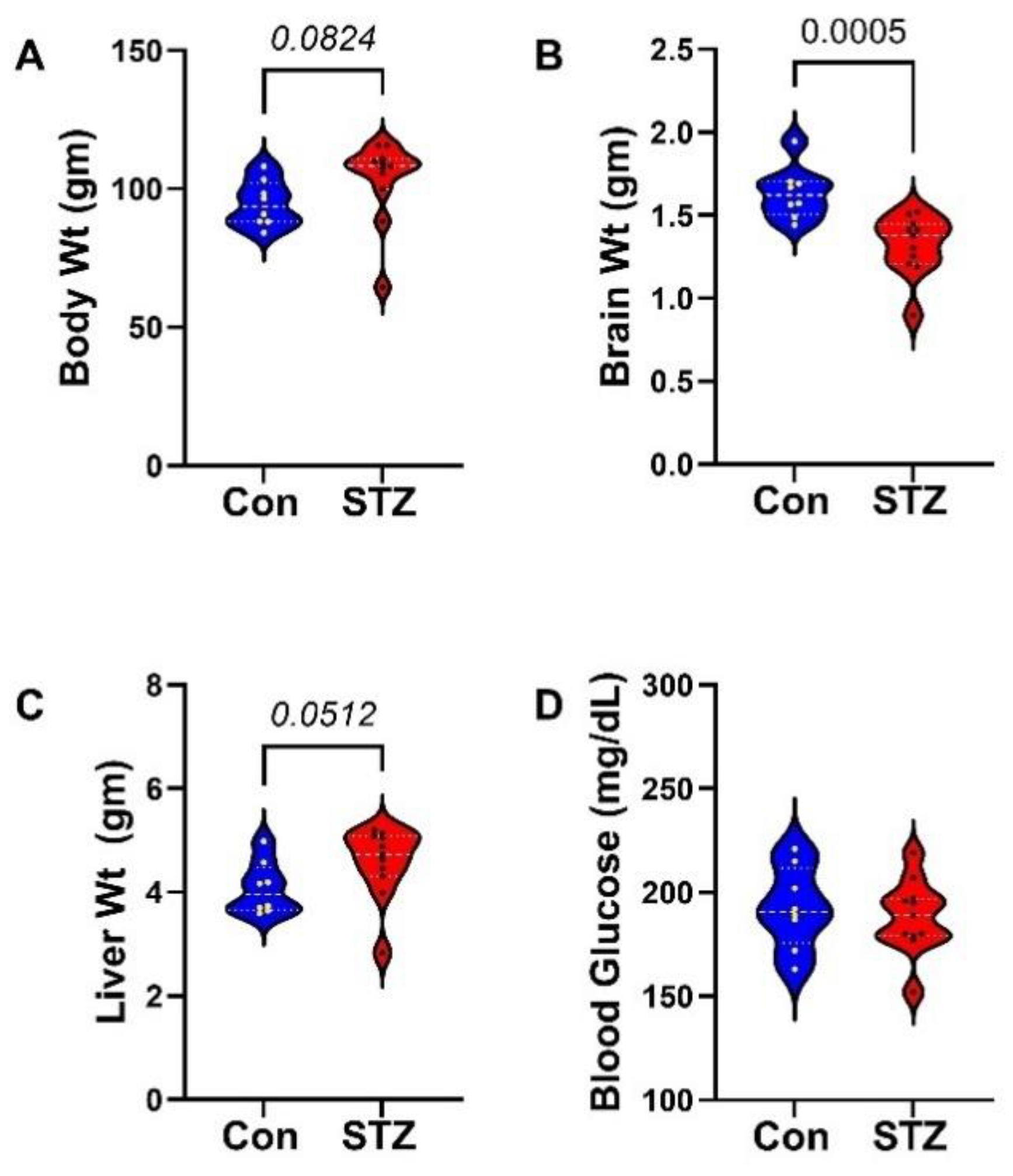
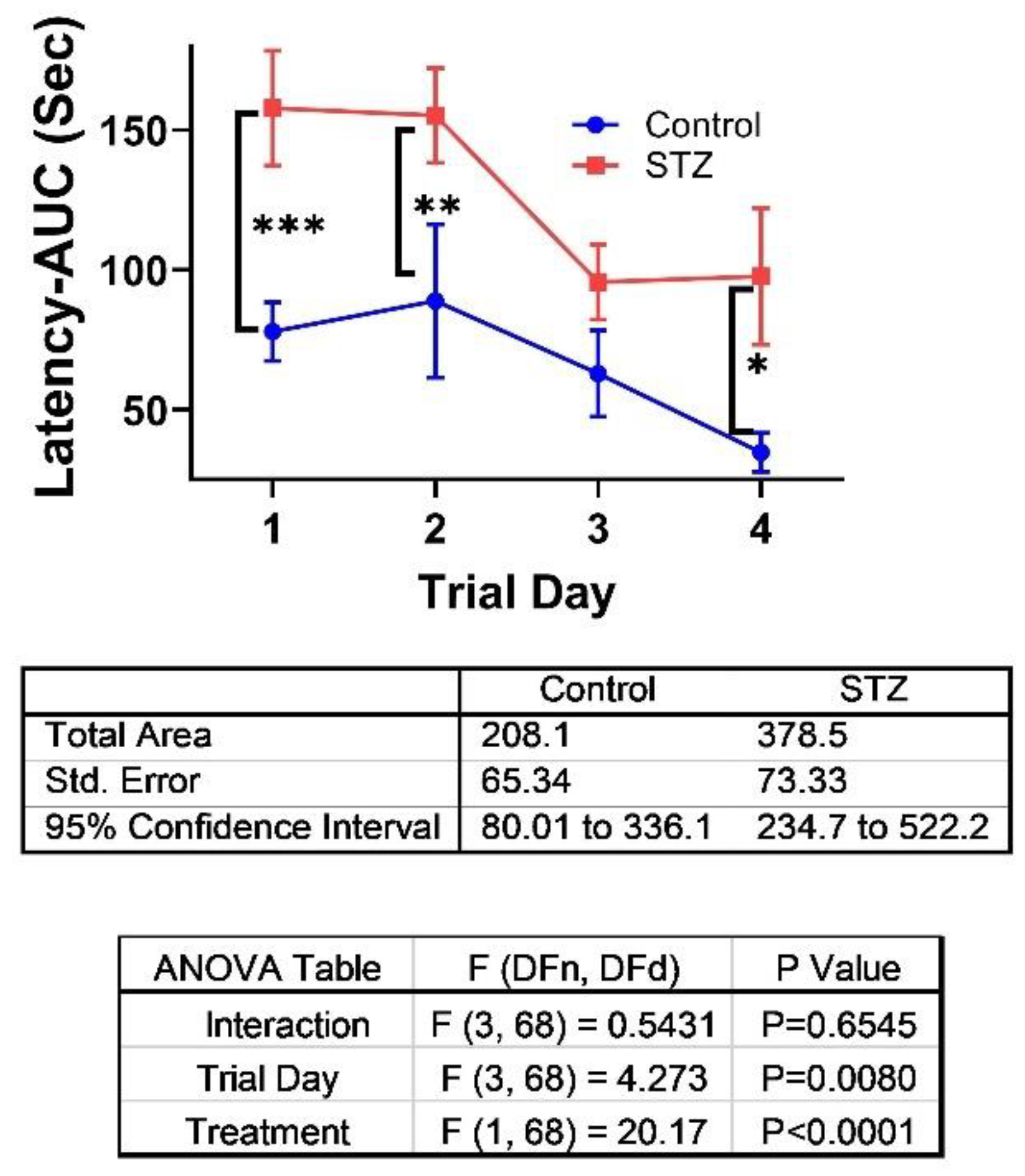
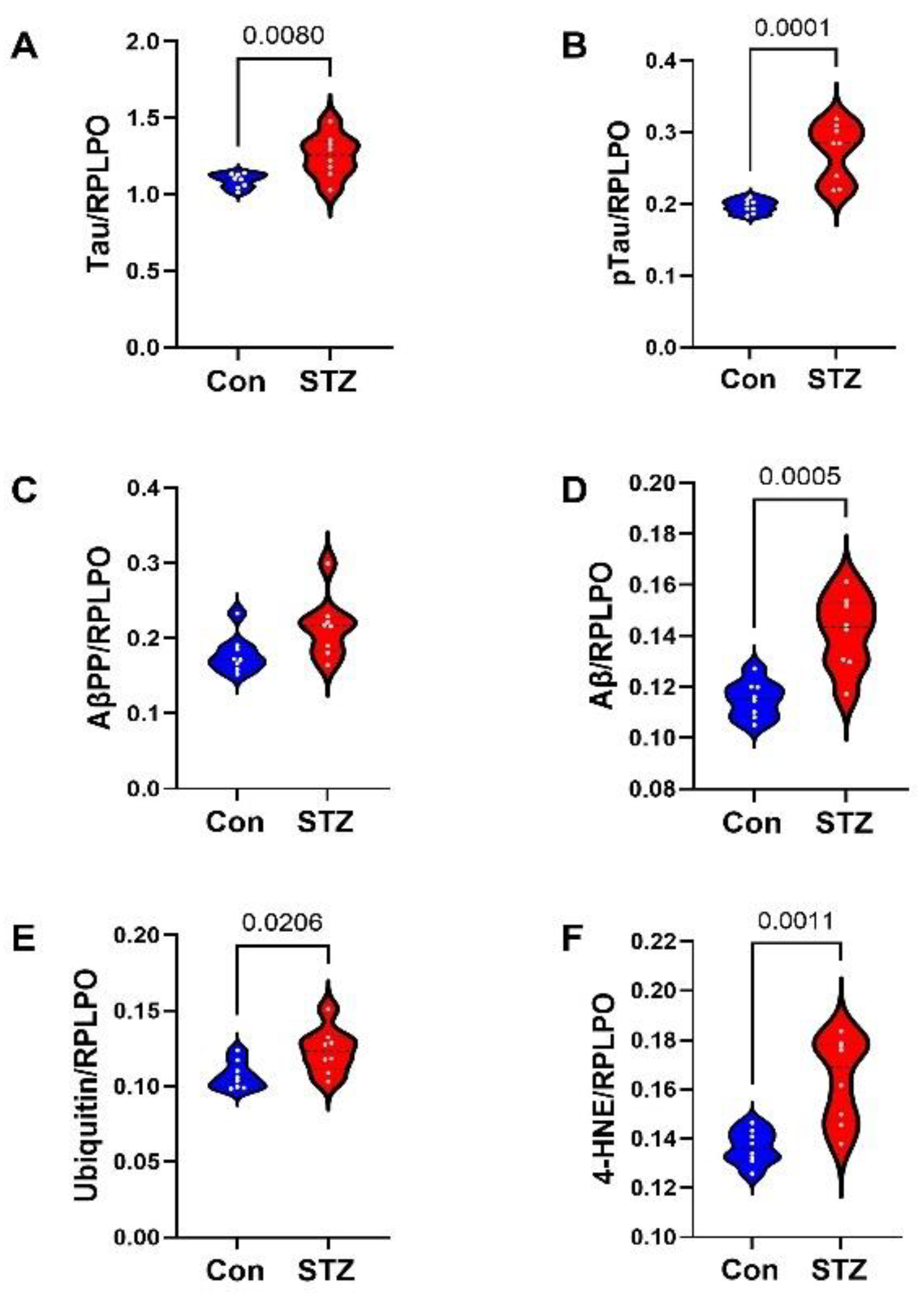
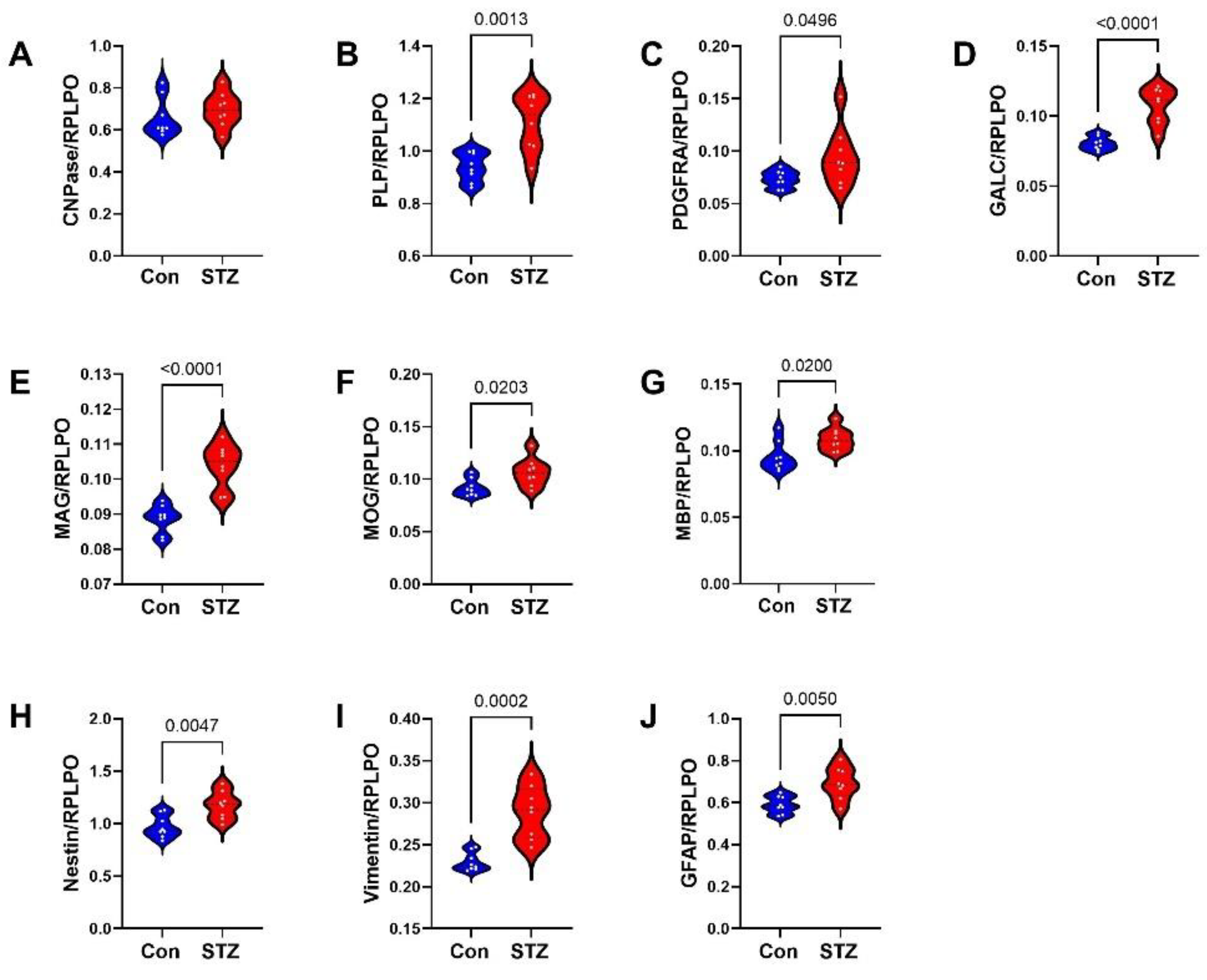
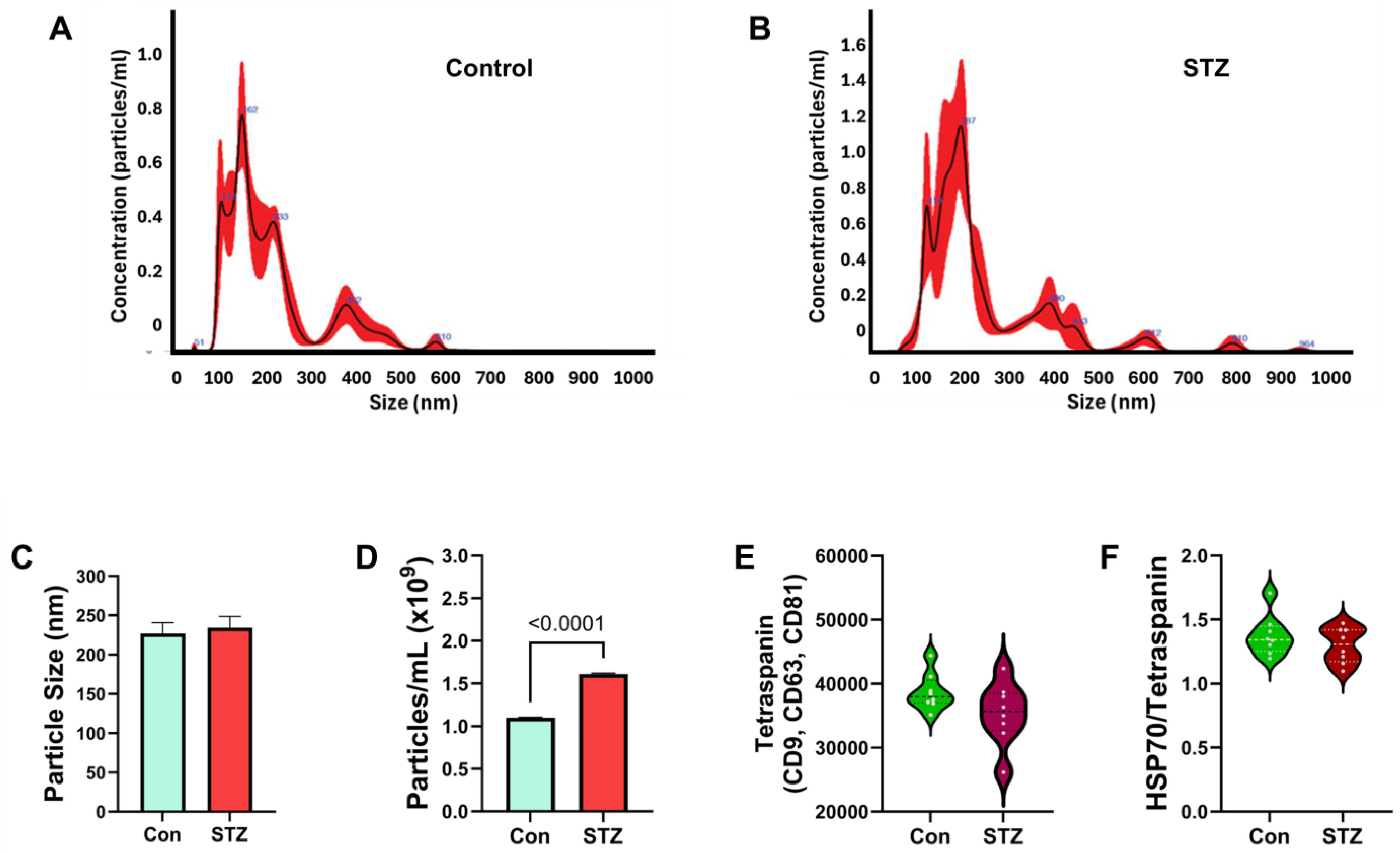
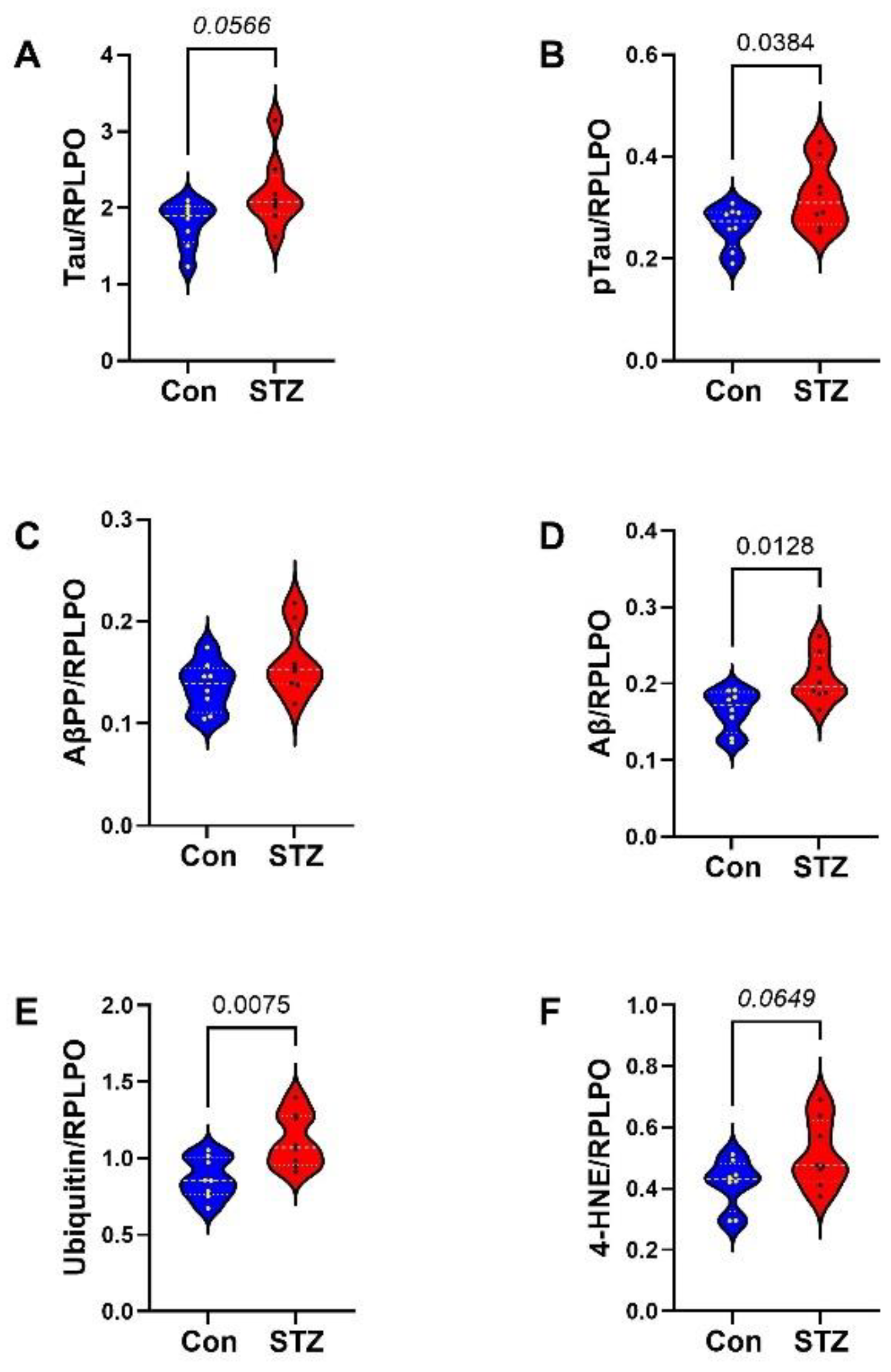
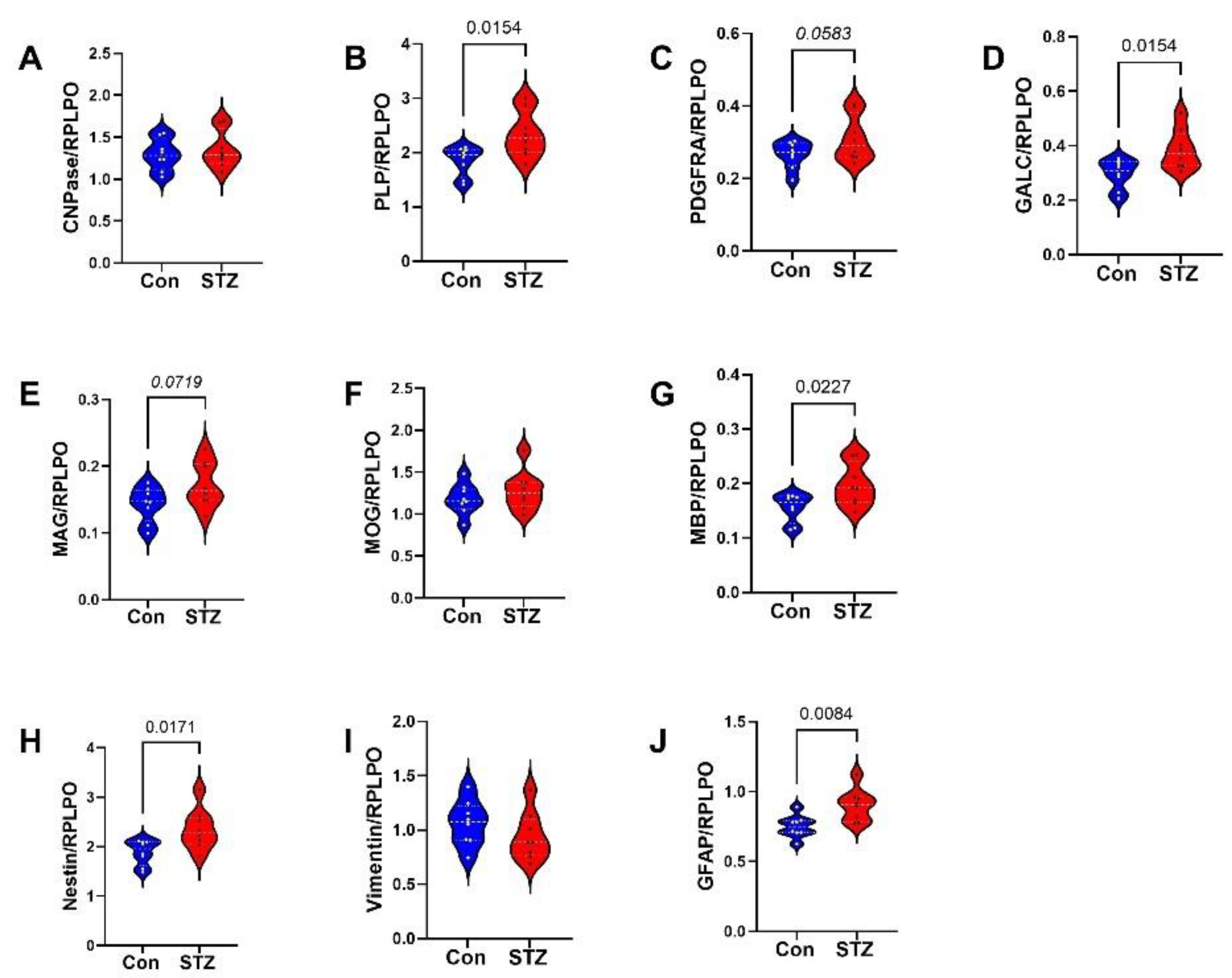
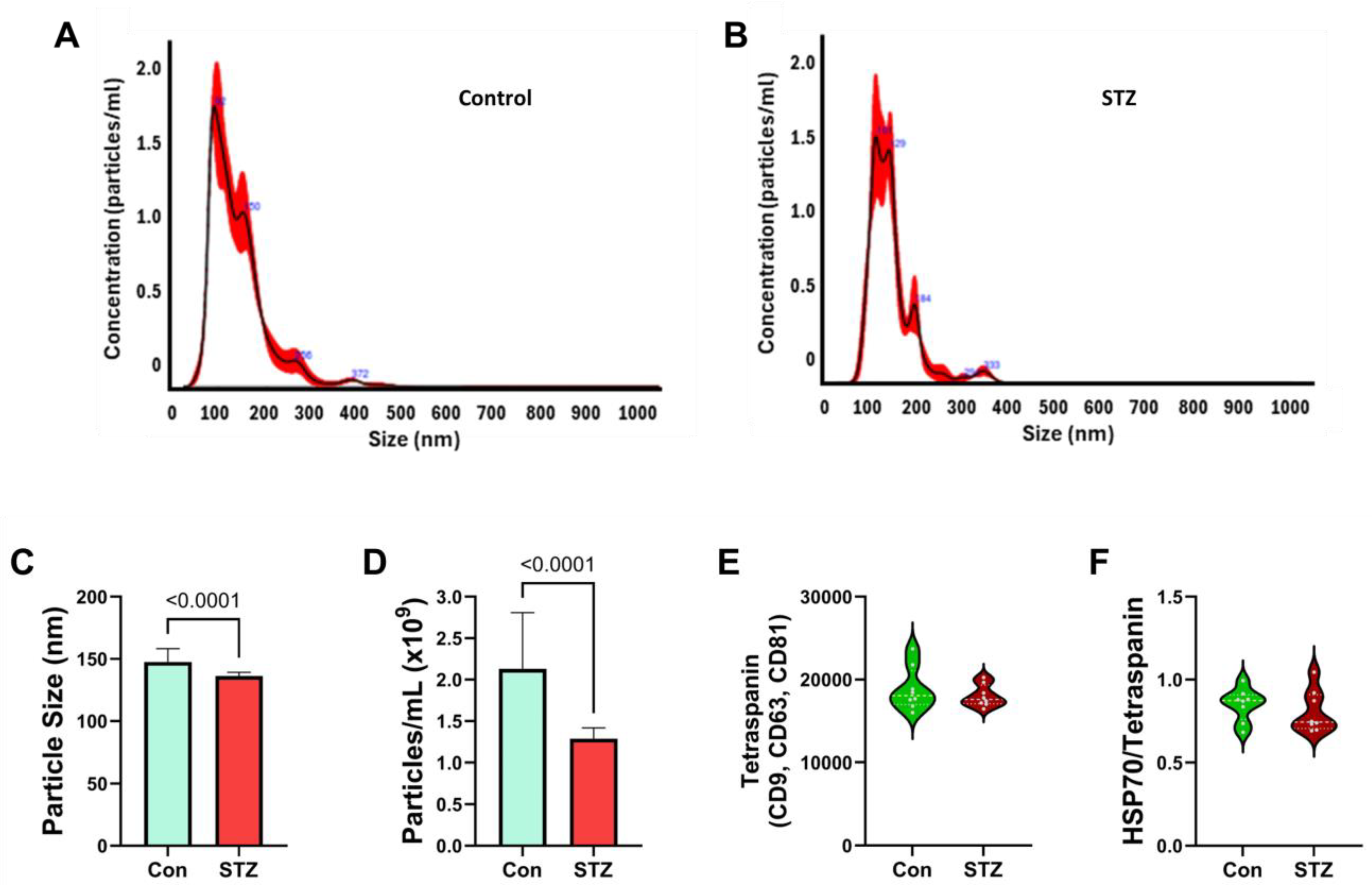
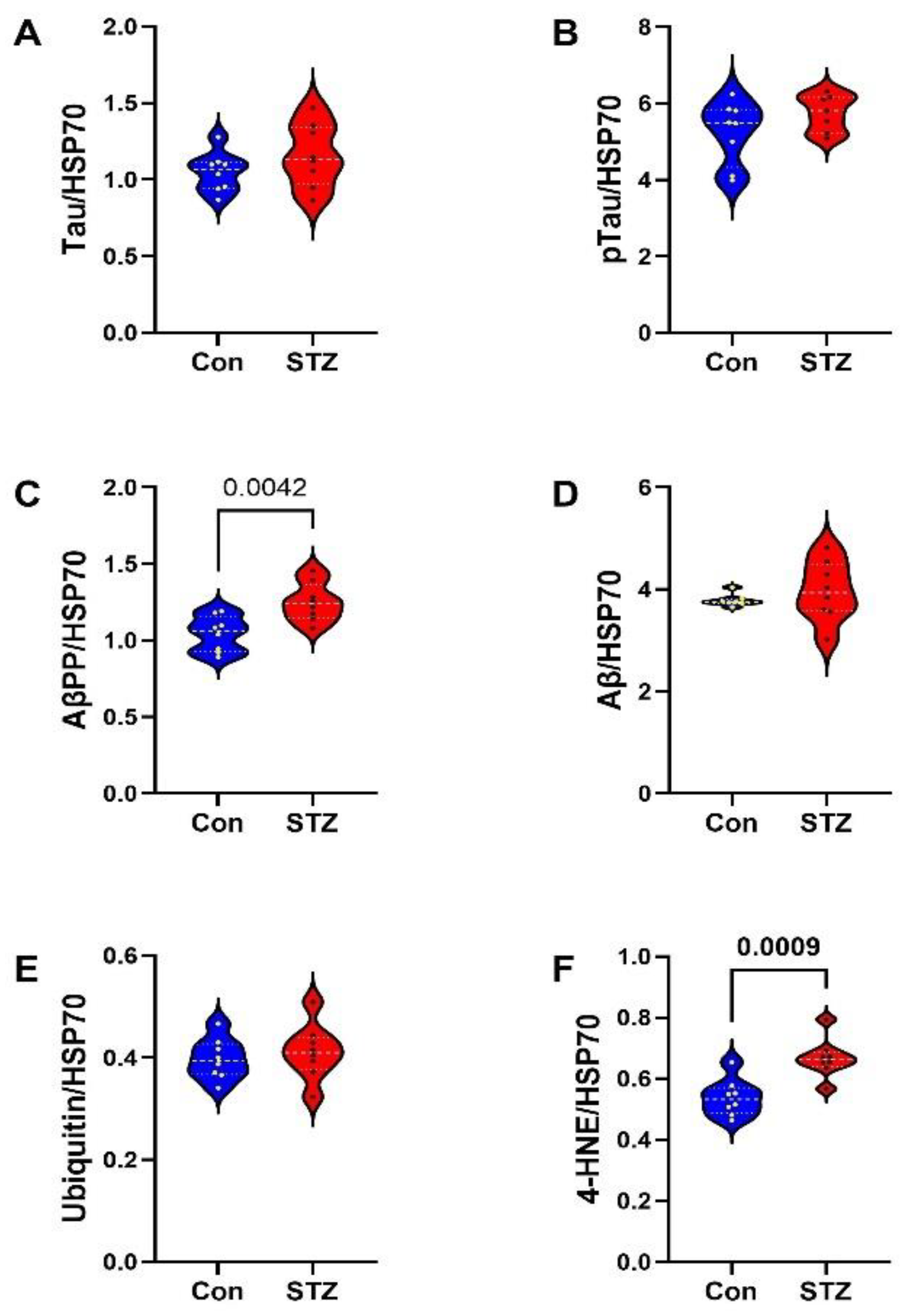
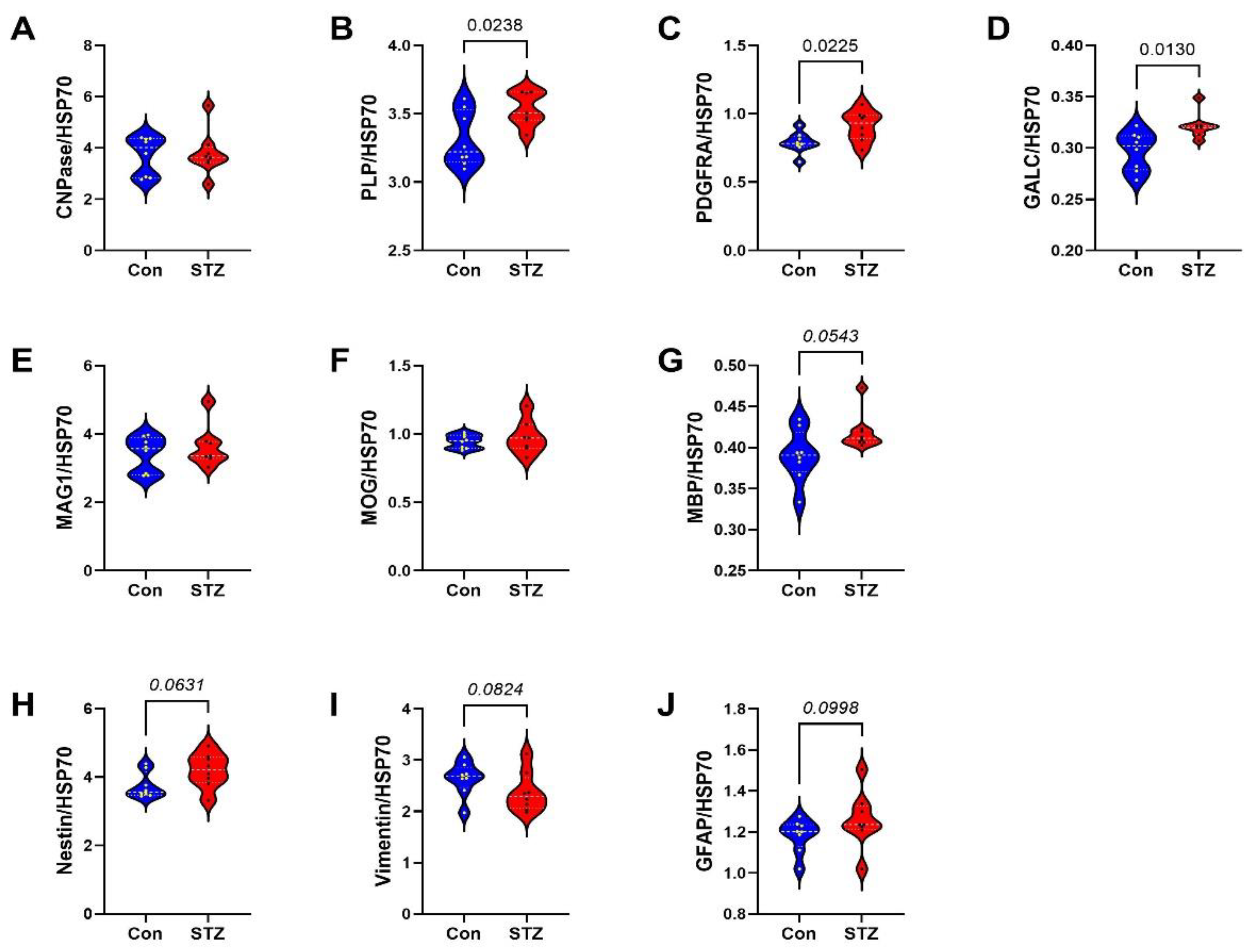
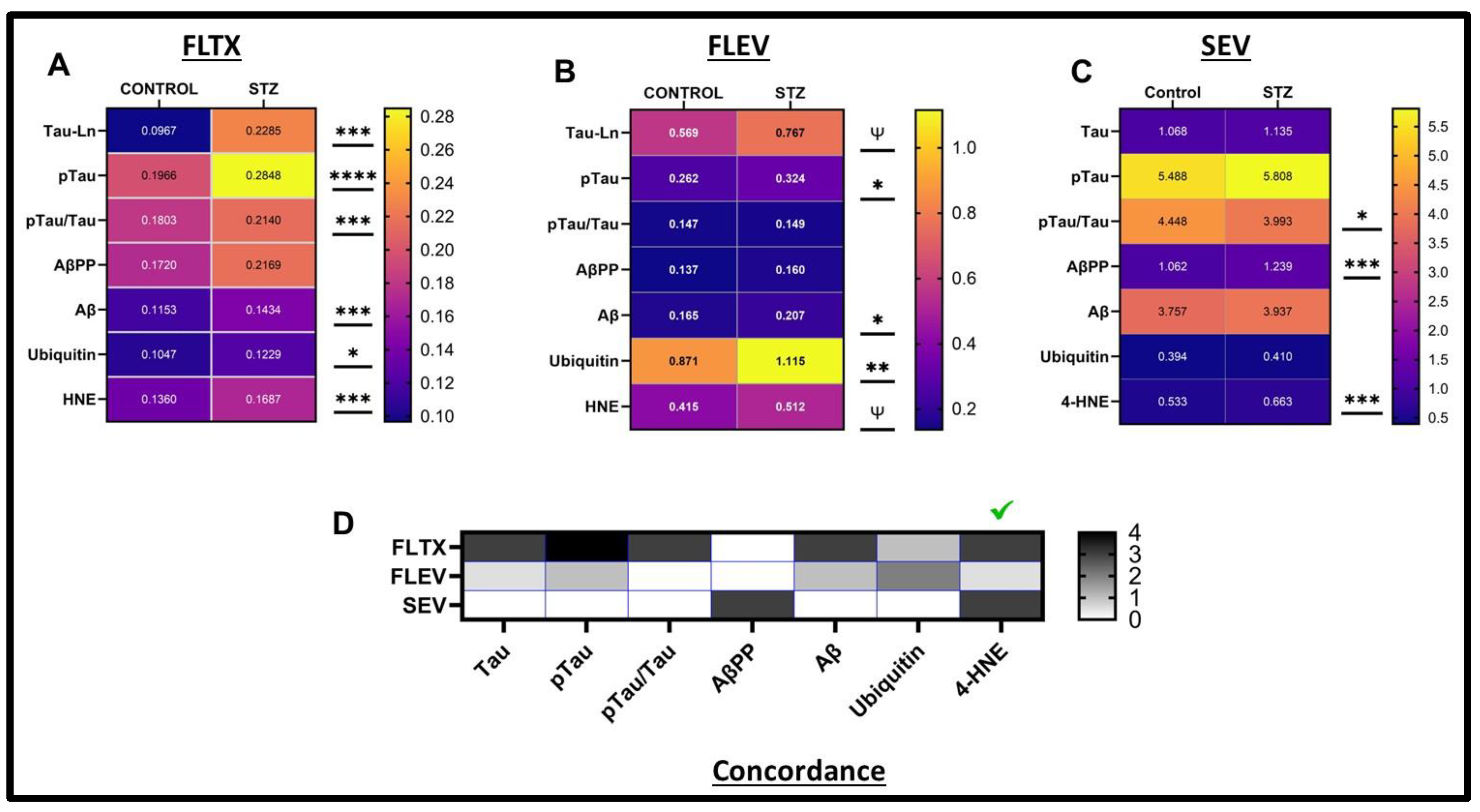

| Variable | Treatment Effect- | Molecule Effect | Treatment × Molecule Effect | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FLTX | F-Ratio | DFn, DFd | p-Value | F-Ratio | DFn, DFd | p-Value | F-Ratio | DFn, DFd | p-Value |
| AD Biomarkers | 16.89 | 1, 14 | 0.001 | 29.61 | 6, 84 | <0.0001 | 6.795 | 6, 84 | <0.0001 |
| Glial Proteins | 50.64 | 1, 140 | <0.0001 | 754.0 | 9, 140 | <0.0001 | 5.55 | 9, 140 | <0.0001 |
| FLEV | F-Ratio | DFn, DFd | p-Value | F-Ratio | DFn, DFd | p-Value | F-Ratio | DFn, DFd | p-Value |
| AD Biomarkers | 24.17 | 1, 98 | <0.0001 | 153.4 | 6, 98 | <0.0001 | 3.176 | 6, 98 | 0.0069 |
| Glial Proteins | 26.35 | 1, 168 | <0.0001 | 195.4 | 11, 168 | <0.0001 | 3.291 | 11, 168 | 0.0004 |
| SEV | F-Ratio | DFn, DFd | p-Value | F-Ratio | DFn, DFd | p-Value | F-Ratio | DFn, DFd | p-Value |
| AD Biomarkers | 1.476 | 1, 96 | N.S. | 490.6 | 6, 96 | <0.0001 | 2.978 | 6, 96 | 0.01 |
| Glial Proteins | 244.5 | 1, 136 | <0.0001 | 2.931 | 9, 136 | 0.089 | 1.176 | 9, 136 | N.S. |
| Antibody Targets | Source | Monoclonal/ Polyclonal | Stock (mg/mL) | µg/mL or Dilution | Commercial Source | RRID or Reference * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD9 (Tetraspanin-29) | Rabbit | Polyclonal | 8.66 | 0.5 | ABclonal, Woburn, MA, USA | A1703 |
| CD63 (Tetraspanin-30) | Rabbit | Polyclonal | 1.03 | 0.5 | ABclonal, Woburn, MA, USA | A5271 |
| CD81 (Tetraspanin-28) | Rabbit | Polyclonal | 1.76 | 0.5 | ABclonal, Woburn, MA, USA | A5270 |
| HSP70 (Heat Shock Protein 70) | Rabbit | Polyclonal | 1.84 | 0.5 | ABclonal, Woburn, MA, USA | A0284 |
| AβPP (Amyloid β-Precursor Protein) | Rabbit | Polyclonal | 0.197 | 0.0985 | Cell Signaling, Danvers MA, USA | Cat. #2452 |
| Aβ (Amyloid β Peptide, 1-42) | Mouse | Monoclonal | 0.2 | 0.8 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Cat. #sc-28365 |
| Tau (Tubulin-associated unit) | Rabbit | Polyclonal | 6.2 | 3.1 | Agilent/Dako, Santa Clara, CA, USA | REF A0024 |
| pTau (PHF; S396) (Phosphorylated Tau | Mouse | Monoclonal | 1.21 | 0.40 | Cell Signaling, Danvers MA, USA | #9632 |
| HNE (4-hydroxy-2-nonenal) | Goat | Polyclonal | 0.8 | 1.6 | Abcam, Boston, MA, USA | ab46544 |
| Ubiquitin | Rabbit | Polyclonal | 0.25 | 0.5 | Abcam, Boston, MA, USA | ab7780-500 |
| CNPase (11-5B) (2′,3′-cyclic nucleotide 3′ phosphodiesterase) | Mouse | Monoclonal | 1.0 | 2.0 | Abcam, Boston, MA, USA | ab6319 |
| GALC (Group-specific component Vitamin D Binding protein; Gc-globulin) | Rabbit | Polyclonal | 1.0 | 2.0 | Abcam, Boston, MA, USA | ab83752 |
| MAG (Myelin-Associated Glycoprotein 1) | Mouse | Monoclonal | 0.5 | 0.25 | Abcam, Boston, MA, USA | ab89780 |
| MOG (Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein) | Rabbit | Polyclonal | 1.0 | 2.0 | Abcam, Boston, MA, USA | ab32760 |
| MBP (Myelin basic protein) | Rabbit | Polyclonal | 1.0 | 2.0 | MilliporeSigma, Burlington, MA, USA | M3821 |
| PLP (Proteolipid Protein 1) | Rabbit | Polyclonal | Serum | 1:2000 | Abcam, Boston, MA, USA | ab28486 |
| PDGFRA (Platelet-derived growth factor receptor, alpha polypeptide) | Rabbit | Polyclonal | 1.0 | 1.0 | Abcam, Boston, MA, USA | ab61219 |
| Nestin | Rabbit | Polyclonal | Serum | 1:2000 | Abcam, Boston, MA, USA | ab27952 |
| Vimentin | Mouse | Monoclonal | 1.0 | 2.5 | Abcam, Boston, MA, USA | ab8978 |
| GFAP (Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein) | Goat | Polyclonal | 0.5 | 0.5 | Abcam, Boston, MA, USA | ab53554 |
| RPLPO (Large acidic ribosomal protein) | Mouse | Monoclonal | 0.1 | 0.1 | Proteintech, Chicago, IL, USA | AG1829 |
| Abbreviation | Full Name | Gene Names | Product Functions |
|---|---|---|---|
| CD9 | Tetraspanin-29 | CD9, TSPAN29 | Many cellular processes including adhesion, differentiation, signal transduction, suppression of cancer cell motility, and metastatic spread. |
| CD63 | Tetraspanin-30 | CD63, TSPAN30 | Cell surface glycoprotein that complexes with integrins. CD63 is associated with tumor progression. |
| CD81 | Tetraspanin-28 | CD81; TSPAN28 | Cell surface glycoprotein that complexes with integrins, promotes muscle cell fusion, supports myotube maintenance, has roles in signal transduction and possibly tumor suppression in malignancies. |
| HSP70 | Heat Shock Protein 70 | HSPA | A critical 70 kDa molecular component of cellular machinery utilized for protein folding and protecting cells from stress. |
| CNPase | 2′,3′-cyclic nucleotide 3′ phosphodiesterase | CNP, EC, CNP1 | Myelin-associated marker of oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells that may play an important role in the development of myelin membranes and sustain axonal integrity. |
| PLP1 | Proteolipid Protein 1 | PLP; SPG2 | Transmembrane proteolipid protein, dominant in CNS myelin. It may be involved in compaction, stabilization, and maintenance of myelin sheaths, oligodendrocyte development, and axonal survival. |
| PDGFRA | Platelet Derived Growth Factor Receptor, alpha polypeptide | PDGFRA; CD140a | Cell surface tyrosine protein kinase receptor required for skeleton development and cephalic closure during embryonic development. Survival factor for oligodendrocyte progenitor cells. |
| GALC | Galactosylceramidase | GALC; Galactosylceramidase | Encodes a lysosomal protein that catabolizes/ hydrolyzes galactose ester bonds of galactosylceramide, lactosylceramide and galactosylsphingosine; major lipid in myelin. |
| MAG | Myelin Associated Glycoprotein | MAG; GMA | Glycoprotein that facilitates sialic acid-dependent cell-cell interactions between neuronal and myelinating cells. Found on oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells. |
| MOG | Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein | MOGIG2 | Expressed on oligodendrocyte cell surfaces and the outer surface of myelin sheaths. It may be involved in the completion or maintenance of myelin sheaths. |
| MBP | Myelin Basic Protein | MBP; Myelin A1 Protein | Major component of myelin sheaths in both oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells. Aids in the formation and stabilization of myelin membranes. |
| NES | Nestin | NES | Intermediate protein promoting disassembly of phosphorylated vimentin during mitosis. Required for survival, renewal, and mitogen-stimulated proliferation of neural progenitor cells. |
| VIM | Vimentin | VIM; CTRCT30 | Class-III intermediate filament that maintains cell shape and cytoplasm integrity, stabilizing cytoskeletal interactions. May be involved in peripheral nerve myelination. |
| GFAP | Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein | GFAP; Intermediate Filament Protein | Astrocyte intermediate filament cytoskeletal protein. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de la Monte, S.M.; Yang, Y.; Prabhu, A.; Tong, M. Comparative Brain and Serum Exosome Expression of Biomarkers in an Experimental Model of Alzheimer-Type Neurodegeneration: Potential Relevance to Liquid Biopsy Diagnostics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094190
de la Monte SM, Yang Y, Prabhu A, Tong M. Comparative Brain and Serum Exosome Expression of Biomarkers in an Experimental Model of Alzheimer-Type Neurodegeneration: Potential Relevance to Liquid Biopsy Diagnostics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094190
Chicago/Turabian Stylede la Monte, Suzanne M., Yiwen Yang, Anjali Prabhu, and Ming Tong. 2025. "Comparative Brain and Serum Exosome Expression of Biomarkers in an Experimental Model of Alzheimer-Type Neurodegeneration: Potential Relevance to Liquid Biopsy Diagnostics" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094190
APA Stylede la Monte, S. M., Yang, Y., Prabhu, A., & Tong, M. (2025). Comparative Brain and Serum Exosome Expression of Biomarkers in an Experimental Model of Alzheimer-Type Neurodegeneration: Potential Relevance to Liquid Biopsy Diagnostics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094190






