New Therapeutic Targets TIGIT, LAG-3 and TIM-3 in the Treatment of Advanced, Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Introduction to Immunotherapy NSCLC
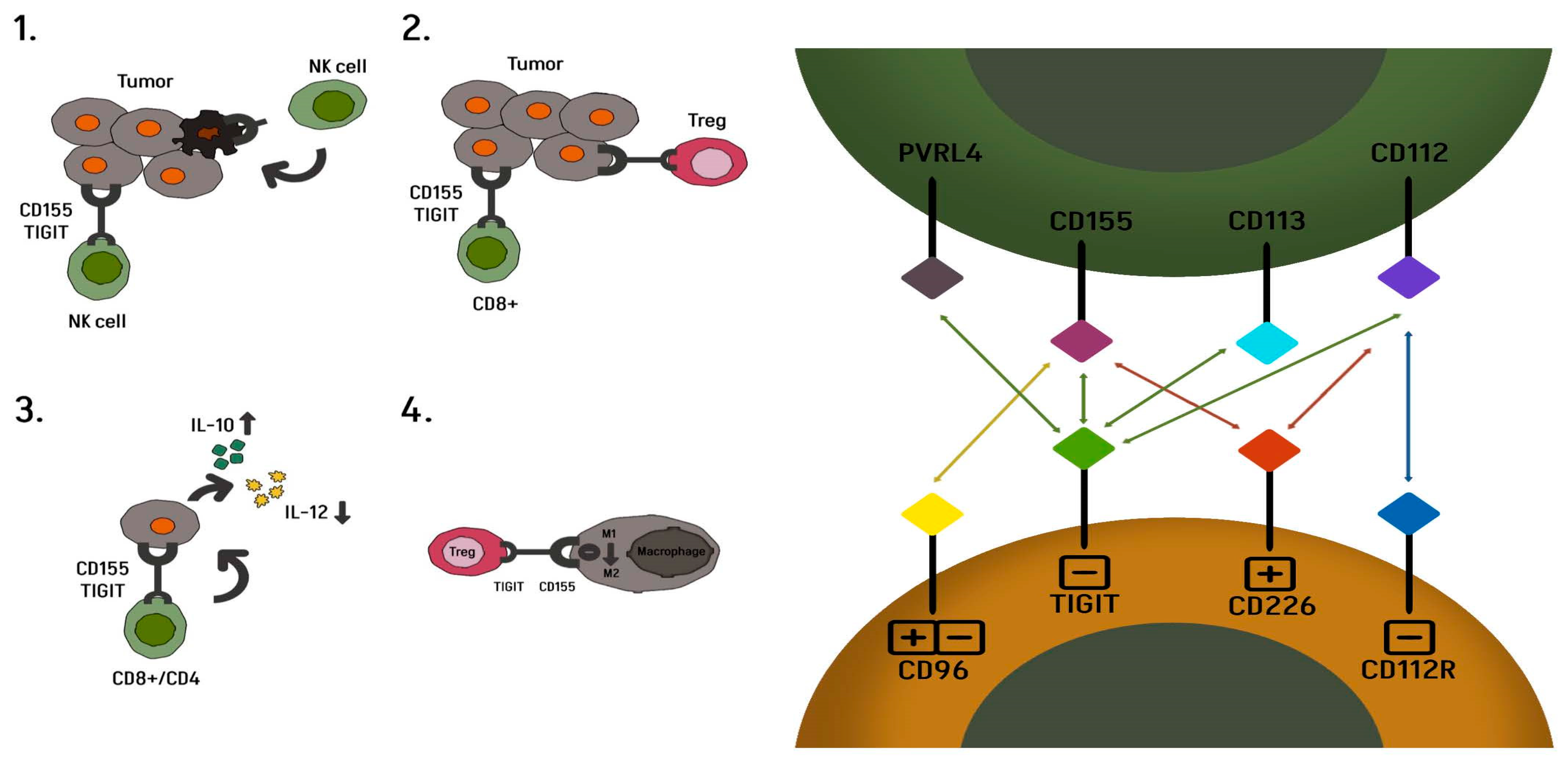
3. T Cell Immunoreceptor with Ig and Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-Based Inhibitory Motif (ITIM) Domains
3.1. Vibostolimab
3.2. Tiragolumab
3.3. Domvanalimab
3.4. Belrestotug
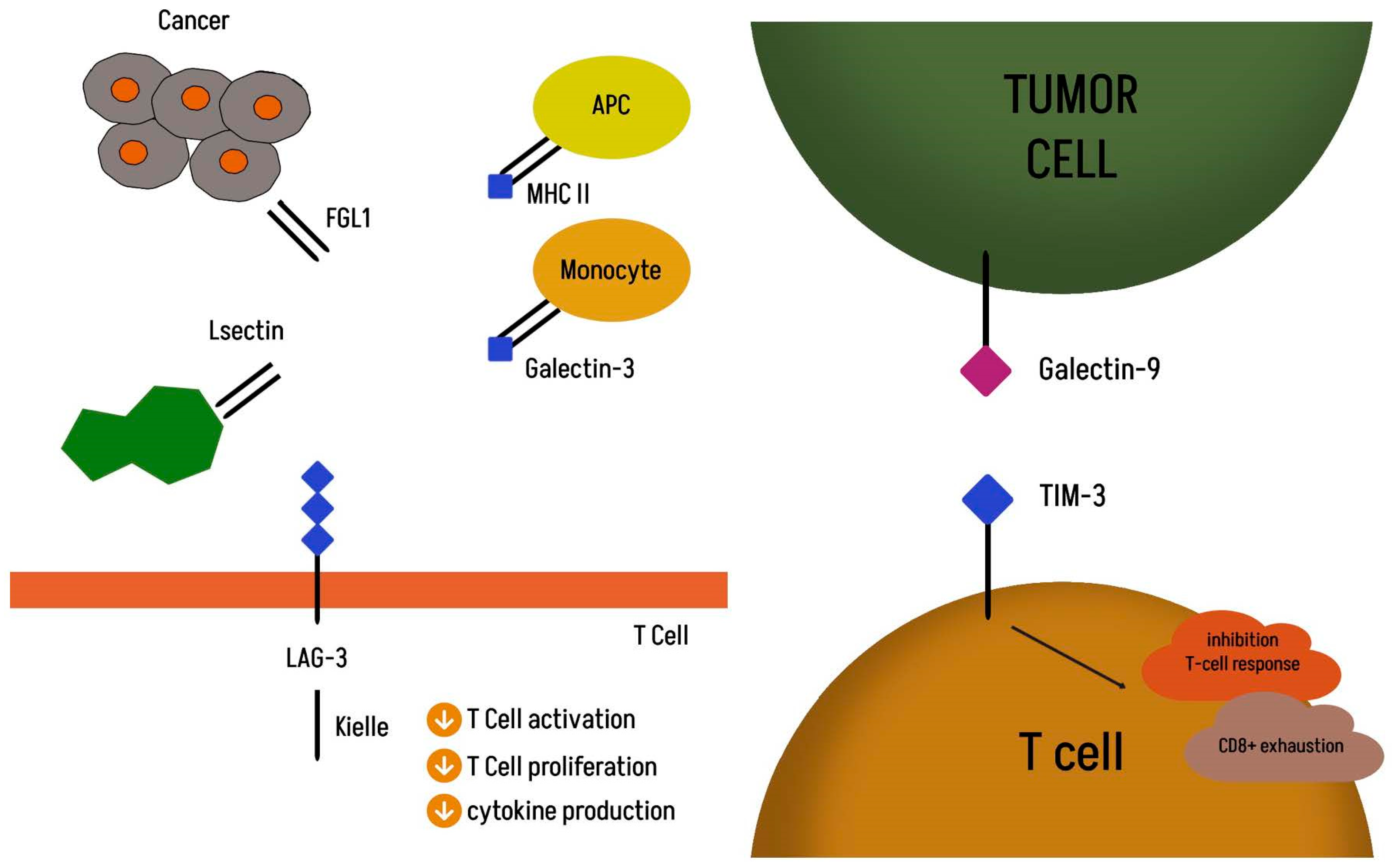
3.5. Lymphocyte Activation Gene 3 (LAG-3)
3.6. TIM-3
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, J.; Xu, Y.; Liu, J.; Feng, L.; Yu, J.; Chen, D. Global burden of lung cancer in 2022 and projections to 2050: Incidence and mortality estimates from GLOBOCAN. Cancer Epidemiol. 2024, 93, 102693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen-Heijnen, M.L.G.; van Erning, F.N.; De Ruysscher, D.K.; Coebergh, J.W.W.; Groen, H.J.M. Variation in causes of death in patients with non-small cell lung cancer according to stage and time since diagnosis. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 902–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, J.; Velcheti, V.; Gao, F.; Govindan, R. Presentation and Stage-Specific Outcomes of Lifelong Never-smokers with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2007, 2, 827–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, J.H.; Harrington, D.; Belani, C.P.; Langer, C.; Sandler, A.; Krook, J.; Zhu, J.; Johnson, D.H. Comparison of Four Chemotherapy Regimens for Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobosz, P.; Dzieciątkowski, T. The Intriguing History of Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, A.A.; Patel, V.G. The role of PD-L1 expression as a predictive biomarker: An analysis of all US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approvals of immune checkpoint inhibitors. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, J. Efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 blockade monotherapy in clinical trials. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2020, 12, 1758835920937612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sordo-Bahamonde, C.; Lorenzo-Herrero, S.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, A.P.; Martínez-Pérez, A.; Rodrigo, J.P.; García-Pedrero, J.M.; Gonzalez, S. Chemo-Immunotherapy: A New Trend in Cancer Treatment. Cancers 2023, 15, 2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Li, Y.; Tan, J.; Xu, L.; Li, Y. Targeting LAG-3, TIM-3, and TIGIT for cancer immunotherapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 16, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xin, D.; Guan, L.; Luo, X.; Wu, H.; Chu, J.; Xing, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, F. Dual immunotherapy in advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: A network meta-analysis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e27576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, R.D.; Old, L.J.; Smyth, M.J. Cancer Immunoediting: Integrating Immunity’s Roles in Cancer Suppression and Promotion. Science 2011, 331, 1565–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardoll, D.M. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinleye, A.; Rasool, Z. Immune checkpoint inhibitors of PD-L1 as cancer therapeutics. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Mezzadra, R.; Schumacher, T.N. Regulation and Function of the PD-L1 Checkpoint. Immunity 2018, 48, 434–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fares, C.M.; Van Allen, E.M.; Drake, C.G.; Allison, J.P.; Hu-Lieskovan, S. Mechanisms of Resistance to Immune Checkpoint Blockade: Why Does Checkpoint Inhibitor Immunotherapy Not Work for All Patients? Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2019, 39, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Q.; Wang, D.; Sun, K.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. Resistance Mechanisms of Anti-PD1/PDL1 Therapy in Solid Tumors. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cowley, L.A.; Liu, X.-S. Sex Differences in Cancer Immunotherapy Efficacy, Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Strategy. Molecules 2019, 24, 3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvin, J.-M.; Zarour, H.M. TIGIT in cancer immunotherapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, A.; Parisi, C.; Barlesi, F. Anti-TIGIT therapies for solid tumors: A systematic review. ESMO Open 2023, 8, 101184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Harden, K.; Gonzalez, L.C.; Francesco, M.; Chiang, E.; Irving, B.; Tom, I.; Ivelja, S.; Refino, C.J.; Clark, H.; et al. The surface protein TIGIT suppresses T cell activation by promoting the generation of mature immunoregulatory dendritic cells. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 10, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harjunpää, H.; Guillerey, C. TIGIT as an emerging immune checkpoint. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2020, 200, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Mao, L.; Liu, J.-F.; Chen, L.; Yu, G.-T.; Yang, L.-L.; Wu, H.; Bu, L.-L.; Kulkarni, A.B.; Zhang, W.-F.; et al. Blockade of TIGIT/CD155 Signaling Reverses T-cell Exhaustion and Enhances Antitumor Capability in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 1700–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shan, S. TIGIT enhances CD4+ regulatory T-cell response and mediates immune suppression in a murine ovarian cancer model. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 3584–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, E.Y.; Mellman, I. TIGIT-CD226-PVR axis: Advancing immune checkpoint blockade for cancer immunotherapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e004711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Wang, W.; Fang, C.; Bai, C. TIGIT presents earlier expression dynamic than PD-1 in activated CD8+ T cells and is upregulated in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 396, 112260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepletier, A.; Madore, J.; O’Donnell, J.S.; Johnston, R.L.; Li, X.-Y.; McDonald, E.; Ahern, E.; Kuchel, A.; Eastgate, M.; Pearson, S.-A.; et al. Tumor CD155 Expression Is Associated with Resistance to Anti-PD1 Immunotherapy in Metastatic Melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 3671–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Zheng, Q.; Xin, N.; Wang, W.; Zhao, C. CD155, an onco-immunologic molecule in human tumors. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 1934–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, K.E.; Eustace, B.K.; Stewart, J.K.; Zehetmeier, C.; Torella, C.; Simeone, M.; Roy, J.E.; Unger, C.; Louis, D.N.; Ilag, L.L.; et al. CD155/PVR plays a key role in cell motility during tumor cell invasion and migration. BMC Cancer 2004, 4, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Gu, Y.; Yan, X.; Huo, C.; Wang, G.; Zhao, Y.; Teng, M.; Li, Y. Role of CD155/TIGIT in Digestive Cancers: Promising Cancer Target for Immunotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 844260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Bi, J.; Zheng, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, W.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Peng, H.; Wei, H.; et al. Blockade of the checkpoint receptor TIGIT prevents NK cell exhaustion and elicits potent anti-tumor immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffo, E.; Wu, R.C.; Bruno, T.C.; Workman, C.J.; Vignali, D.A. Lymphocyte-activation gene 3 (LAG3): The next immune checkpoint receptor. Semin. Immunol. 2019, 42, 101305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graydon, C.G.; Mohideen, S.; Fowke, K.R. LAG3’s Enigmatic Mechanism of Action. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 615317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemon, P.; Jean-Louis, F.; Ramgolam, K.; Brignone, C.; Viguier, M.; Bachelez, H.; Triebel, F.; Charron, D.; Aoudjit, F.; Al-Daccak, R.; et al. MHC Class II Engagement by Its Ligand LAG-3 (CD223) Contributes to Melanoma Resistance to Apoptosis. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 5173–5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, L.P.; Marciscano, A.E.; Drake, C.G.; Vignali, D.A.A. LAG3 (CD223) as a cancer immunotherapy target. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 276, 80–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Sanmamed, M.F.; Datar, I.; Su, T.T.; Ji, L.; Sun, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, G.; Yin, W.; et al. Fibrinogen-like Protein 1 Is a Major Immune Inhibitory Ligand of LAG-3. Cell 2019, 176, 334–347.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, N.; Szlasa, W.; Jonderko, L.; Oślizło, M.; Kunachowicz, D.; Kulbacka, J.; Karłowicz-Bodalska, K. LAG-3 as a Potent Target for Novel Anticancer Therapies of a Wide Range of Tumors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhu, C.; Anderson, A.C.; Kuchroo, V.K. TIM-3 and its regulatory role in immune responses. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2011, 350, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Liu, J.; Liu, D.; Liu, B.; Wang, M.; Hu, Z.; Du, X.; Tang, L.; He, F. LSECtin Expressed on Melanoma Cells Promotes Tumor Progression by Inhibiting Antitumor T-cell Responses. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 3418–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monney, L.; Sabatos, C.A.; Gaglia, J.L.; Ryu, A.; Waldner, H.; Chernova, T.; Manning, S.; Greenfield, E.A.; Coyle, A.J.; Sobel, R.A.; et al. Th1-specific cell surface protein Tim-3 regulates macrophage activation and severity of an autoimmune disease. Nature 2002, 415, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuishi, K.; Apetoh, L.; Sullivan, J.M.; Blazar, B.R.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Anderson, A.C. Targeting Tim-3 and PD-1 pathways to reverse T cell exhaustion and restore anti-tumor immunity. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 2187–2194, Erratum in J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Zhang, X.; Xia, X.; Zhang, C.; Liang, X.; Gao, L.; Zhang, X.; Ma, C. Ectopic Expression of TIM-3 in Lung Cancers. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 137, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, K.; Hui, L.; Wang, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Yao, B. TIM-3 as a Prognostic Marker and a Potential Immunotherapy Target in Human Malignant Tumors: A Meta-Analysis and Bioinformatics Validation. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 579351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, J.; Maurice-Dror, C.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, D.W.; Nagrial, A.; Voskoboynik, M.; Chung, H.C.; Mileham, K.; Vaishampayan, U.; Rasco, D.; et al. First-in-human phase 1 study of the anti-TIGIT antibody vibostolimab as monotherapy or with pembrolizumab for advanced solid tumors, including non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapira-Frommer, R.; Niu, J.; Perets, R.; Peters, S.; Shouse, G.; Lugowska, I.; Garassino, M.C.; Sands, J.; Keenan, T.; Zhao, B.; et al. The KEYVIBE program: Vibostolimab and pembrolizumab for the treatment of advanced malignancies. Futur. Oncol. 2024, 20, 1983–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garralda, E.; Oh, D.Y.; Italiano, A.; Bedard, P.L.; Delord, J.; Calvo, E.; LoRusso, P.; Wainberg, Z.; Cervantes, A.; Rodriguez-Vida, A.; et al. Pharmacokinetics (PK) of Tiragolumab in First-in-Human Study in Patients with Mixed Solid Tumors (GO30103). J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2024, 64, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.C.; Abreu, D.R.; Hussein, M.; Cobo, M.; Patel, A.J.; Secen, N.; Lee, K.H.; Massuti, B.; Hiret, S.; Yang, J.C.H.; et al. Tiragolumab plus atezolizumab versus placebo plus atezolizumab as a first-line treatment for PD-L1-selected non-small-cell lung cancer (CITYSCAPE): Primary and follow-up analyses of a randomised, double-blind, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, C.M.; Liu, S.V.; Soo, R.A.; Lu, S.; Hong, M.H.; Lee, J.-S.; Bryl, M.; Dumoulin, D.W.; Rittmeyer, A.; Chiu, C.-H.; et al. SKYSCRAPER-02: Tiragolumab in Combination with Atezolizumab Plus Chemotherapy in Untreated Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche Reports Update on Phase III SKYSCRAPER-01 Study Results. Available online: https://www.roche.com/media/releases/med-cor-2024-11-26 (accessed on 26 November 2024).
- Genentech Provides Update of Phase 2/3 Skyscraper-06 Study in Metastatic Nonsquamous Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. News Release. Genentech. 3 July 2024. Available online: https://www.gene.com/media/press-releases/15029/2024-07-03/genentech-provides-update-on-phase-iiiii (accessed on 11 July 2024).
- Johnson, M.L. Updates on abstract 397600: ARC-7: Randomized phase 2 study of domvanalimab + zimberelimab ± etrumadenant versus zimberelimab in first-line, metastatic, PD-L1-high non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In Proceedings of the 2023 ASCO Annual Meeting, Chicago, IL, USA, 2–6 June 2023. Abstract 397600. [Google Scholar]
- ASCO 2023: Arcus Update on Anti-TIGIT Program & ARC-7 Results. Available online: https://investors.arcusbio.com/investors-and-media/events-and-presentations/corporate-presentation/presentation-details/2023/ASCO-2023-Arcus-Update-on-Anti-TIGIT-Program--ARC-7-Results-2023-h018XgDEp8/default.aspx (accessed on 3 June 2023).
- Arcus Biosciences. Arcus Biosciences. Arcus Biosciences announces that domvanalimab plus zimberelimab improved overall survival in ARC-10, a randomized study in patients with PD-L1-high non-small cell lung cancer. In News Release; Arcus Biosciences, Inc.: Hayward, CA, USA, 2024; Available online: https://tinyurl.com/yck58s43 (accessed on 6 November 2024).
- Rodriguez-Abreu, D.; Gray, J.E.; Ahn, M.-J.; Johnson, M.L.; Yu, X.; Chen, X.; Phuong, P.H.; Kim, J.; Reck, M. STAR-121: A phase 3, randomized study of domvanalimab (DOM) and zimberelimab (ZIM) in combination with chemotherapy vs pembrolizumab (pembro) and chemotherapy in patients with untreated metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (mNSCLC) with no actionable gene alterations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, TPS9141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgüroğlu, M.; Levy, B.P.; Horinouchi, H.; Yu, J.; Grainger, E.; Phuong, P.H.; Peterson, D.; Newton, M.D.; Spira, A.I. Phase 3 trial of durvalumab combined with domvanalimab following concurrent chemoradiotherapy (cCRT) in patients with unresectable stage III NSCLC (PACIFIC-8). J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, TPS8609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, A.A.; Shamai, S.; Lin, S.-H.; Han, J.-Y.; Baijal, S.; Yazici, O.; Barrios, C.H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, K.; Kim, Y.; et al. VELOCITY-Lung substudy-03: A phase 2 study of neoadjuvant domvanalimab (dom)+zimberelimab (zim)+chemotherapy (chemo) or zim+chemo followed by adjuvant dom+zim or zim in patients with resectable stage II-III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, TPS8121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spigel, D.R.; Korbenfeld, E.P.; Hayashi, H.; Corre, R.; Cho, B.C.; Psyrri, A.; Cobo Dols, M.; Parkhomenko, E.; Baxter, D.; Patel, N.; et al. LBA52 Interim analysis of GALAXIES Lung-201: Phase II, randomized, open-label platform study of belrestotug plus dostarlimab in patients (pts) with previously untreated locally advanced/metastatic (LA/M) PD-L1 high (TPS >/=50%) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Ann. Oncol. 2024, 35, S1242–S1243. [Google Scholar]
- A Study of Belrestotug Plus Dostarlimab Compared with Placebo Plus Pembrolizumab in Previously Untreated Participants with Programmed Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1) High Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC), ClinicalTrials.gov ID NCT06472076. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06472076 (accessed on 19 April 2025).
- Lipson, E.; Gopal, A.; Neelapu, S.S.; Armand, P.; Spurgeon, S.; Leonard, J.; Hodi, F.; Sanborn, R.; Melero, I.; Gajewski, T. Initial experience administering BMS-986016, a monoclonal antibody that targets lymphocyte activation gene (LAG)-3, alone and in combination with nivolumab to patients with hematologic and solid malignancies. J. Immunother. Cancer 2016, 4 (Suppl. 1), 232. [Google Scholar]
- Tawbi, H.A.; Hodi, F.S.; Lipson, E.J.; Schadendorf, D.; Ascierto, P.A.; Matamala, L.; Gutiérrez, E.C.; Rutkowski, P.; Gogas, H.; Lao, C.D.; et al. Three-Year Overall Survival with Nivolumab Plus Relatlimab in Advanced Melanoma From RELATIVITY-047. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, JCO2401124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, N.E.; Melkadze, T.; Nair, S.; Gabrail, N.; Kunta, G.; Ibrahim, E.; Dreisbach, L.; Brungs, D.; Chikhladze, N.; Gogishvili, M.; et al. A phase 2/3 study of fianlimab plus cemiplimab versus cemiplimab in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer with tumors expressing PD-L1 ≥ 50%. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, TPS8663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, J.J.; Moreno, V.; Bang, Y.J.; Hong, M.H.; Patnaik, A.; Trigo, J.; Szpurka, A.M.; Yamamoto, N.; Doi, T.; Fu, S.; et al. Blocking TIM-3 in treatment-refractory advanced solid tumors: A phase Ia/b study of LY3321367 with or without an anti-PD-L1 antibody. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 2168–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garon, E.B.; Hellmann, M.D.; Rizvi, N.A.; Carcereny, E.; Leighl, N.B.; Ahn, M.-J.; Eder, J.P.; Balmanoukian, A.S.; Aggarwal, C.; Horn, L.; et al. Five-Year Overall Survival for Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Pembrolizumab: Results From the Phase I KEYNOTE-001 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2518–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Rodríguez–Abreu, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Hui, R.; Csőszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peled, N.; Tafreshi, A.; Cuffe, S.; et al. Updated Analysis of KEYNOTE-024: Pembrolizumab Versus Platinum-Based Chemotherapy for Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer with PD-L1 Tumor Proportion Score of 50% or Greater. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmann, M.D.; Paz-Ares, L.; Bernabe Caro, R.; Zurawski, B.; Kim, S.-W.; Carcereny Costa, E.; Park, K.; Alexandru, A.; Lupinacci, L.; de la Mora Jimenez, E.; et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab in Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2020–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Ciuleanu, T.-E.; Cobo, M.; Schenker, M.; Zurawski, B.; Menezes, J.; Richardet, E.; Bennouna, J.; Felip, E.; Juan-Vidal, O.; et al. First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab combined with two cycles of chemotherapy in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 9LA): An international, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guégan, J.P.; Peyraud, F.; Dadone-Montaudie, B.; Teyssonneau, D.; Palmieri, L.J.; Clot, E.; Cousin, S.; Roubaud, G.; Cabart, M.; Leroy, L.; et al. Analysis of PD1, LAG3, TIGIT, and TIM3 expression in human lung adenocarcinoma reveals a 25-gene signature predicting immunotherapy response. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCCN. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer; Version 3.2025; NCCN: Plymouth Meeting, PA, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, H.; Elkord, E. Turning Cancer Immunotherapy to the Emerging Immune Checkpoint TIGIT: Will This Break Through the Limitations of the Legacy Approach? Vaccines 2024, 12, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attili, I.; Passaro, A.; de Marinis, F. Anti-TIGIT to overcome resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors in lung cancer: Limits and potentials. Ann Oncol. 2022, 33, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, N.; Janicka, N.; Szlasa, W.; Skinderowicz, B.; Kołodzińska, K.; Dwernicka, W.; Oślizło, M.; Kulbacka, J.; Novickij, V.; Karłowicz-Bodalska, K. TIM-3 as a promising target for cancer immunotherapy in a wide range of tumors. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2023, 72, 3405–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Guo, H.; Kong, S.; Li, W.; He, Q.; Ding, L.; Yang, B. The role of Tim-3 blockade in the tumor immune microenvironment beyond T cells. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 209, 107458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.H.; Liang, Y.P.; Yang, L.; Zhu, F.; Jia, L.J.; Li, H.G. Cycloastragenolinduces apoptosis and protective autophagy through AMPK/ULK1/mTOR axis in human non-small celllung cancer cell lines. J. Integr. Med. 2024, 22, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Wang, Z.; Ding, C.; Liu, P.; Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Yan, Y.; Yin, X.; Chen, B.; Gu, B. Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Microbiota is Associated with the Diagnosis and Prognosis Evaluation of Lung Cancer. Phenomics 2024, 4, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kabut, J.; Gorzelak-Magiera, A.; Gisterek-Grocholska, I. New Therapeutic Targets TIGIT, LAG-3 and TIM-3 in the Treatment of Advanced, Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4096. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094096
Kabut J, Gorzelak-Magiera A, Gisterek-Grocholska I. New Therapeutic Targets TIGIT, LAG-3 and TIM-3 in the Treatment of Advanced, Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4096. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094096
Chicago/Turabian StyleKabut, Jacek, Anita Gorzelak-Magiera, and Iwona Gisterek-Grocholska. 2025. "New Therapeutic Targets TIGIT, LAG-3 and TIM-3 in the Treatment of Advanced, Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4096. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094096
APA StyleKabut, J., Gorzelak-Magiera, A., & Gisterek-Grocholska, I. (2025). New Therapeutic Targets TIGIT, LAG-3 and TIM-3 in the Treatment of Advanced, Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4096. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094096





