Cofilin(s) and Mitochondria: Function Beyond Actin Dynamics
Abstract
1. Introduction
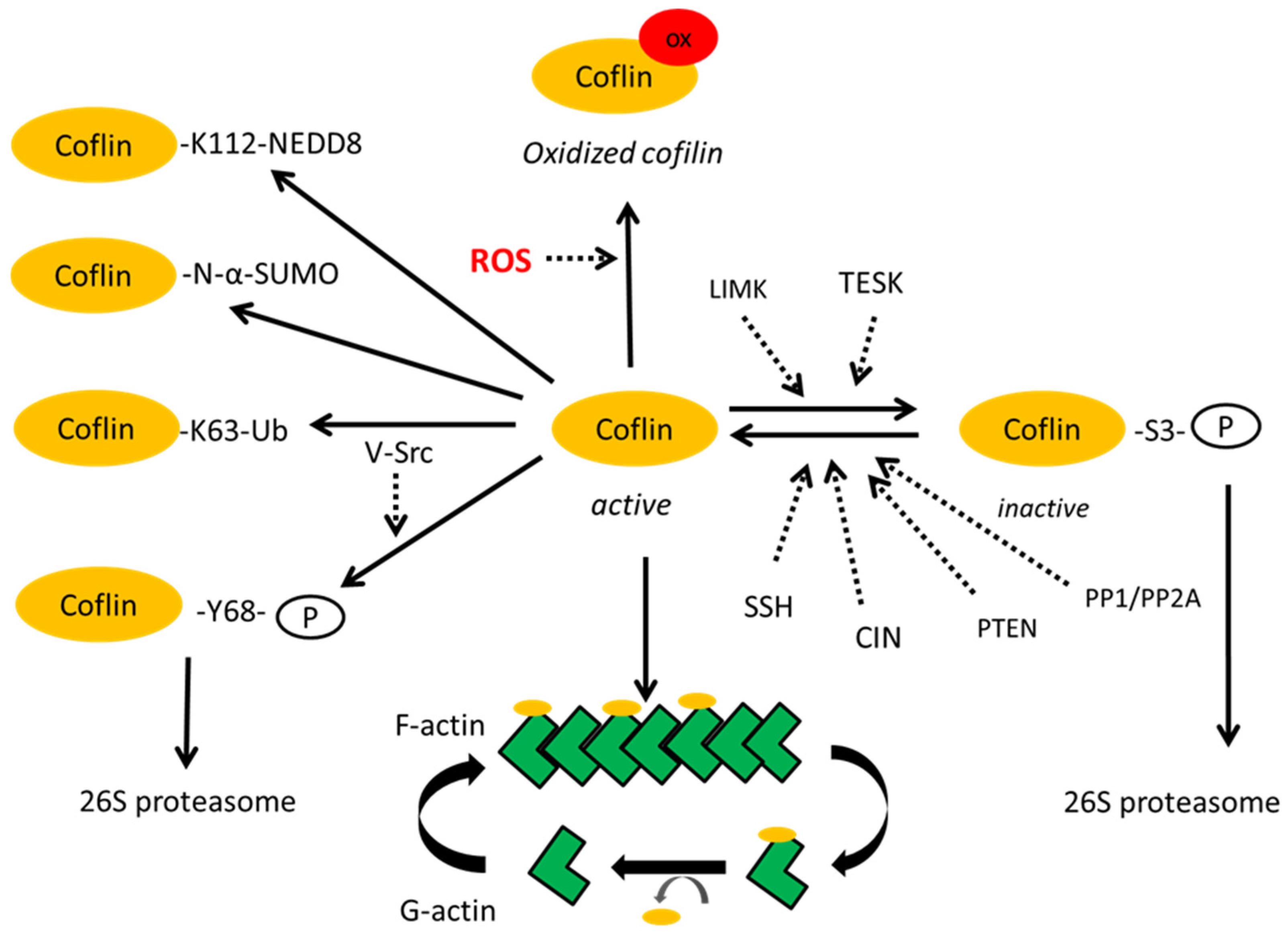
2. Post-Translational Modifications of Cofilin
3. The Mitochondrial Localization of Cofilin
4. Cofilin Mediated Mitochondrial Dysfunction During Neurodegeneration
5. Cofilin Mediated Mitochondrial Dysfunction During Tumorigenesis
6. Cofilin and Lipid Metabolism

7. Conclusions
| Function | Nerve Cells | Cancer Cells | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Actin dynamics and cytoskeleton remodeling | Regulates dendritic spine morphology via actin filament reorganization, synaptic plasticity, and cognitive functions | Drives cell migration and invasion via formation of lamellipodia/invadopodia | [22,123,124,125,126] |
| Controls axon guidance and long-term potentiation (LTP) | Promotes metastasis by regulating cytoskeleton remodeling and EMT | ||
| Mitochondrial dynamics | Oxidized cofilin translocates to mitochondria, initiating the release of cytochrome c, caspase activation, and apoptosis | Regulates cancer cell apoptosis depending on its activation state (phosphorylated/dephosphorylated) | [22,49,72,91] |
| Mitochondrial fission mediated by both cofilin and Drp1 | Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fission is a target for drug development | ||
| Redox regulation | Serves as a cellular redox sensor. Oxidized cofilin forms rods with actin during ATP depletion (ischemia, Alzheimer’s disease) | Cancer cells modulate ROS to maintain cofilin in active/inactive states for invasion | [11,29] |
| Cofilin-actin rods disrupt axonal transport and mitochondrial functions, impair synaptic function | Redox homeostasis affects cofilin-driven migration and survival | ||
| Lipid signaling | PIP2 binding at the plasma membrane | Membrane PIP2 hydrolysis releases and activates cofilin | [8,127] |
| PIP2 hydrolysis by PLC regulates cofilin activity and indirectly modulates synaptic vesicle trafficking | Supports proliferation and survival | ||
| Lipid droplet dynamics | Potentially mediates LD-ER/mitochondria tethering via actin cytoskeleton | Potentially modulates actin-LD interaction | [106,112,118,128] |
| LDs contribute to the pathogenesis of neurodegeneration | LDs promote cancer cell adaptation to oxidative stress and starvation | ||
| Regulatory pathways | Phosphorylation/dephosphorylation (LIMK1/SSH etc.) | Phosphorylation/dephosphorylation (PTEN/PI3K and Src/Akt/mTOR signaling etc.) | [8,36,38,56] |
| Ubiquitination | Ubiquitination | ||
| Pathology | Neurodegeneration | Cancer | [22,42,44,76] |
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| ADF | Actin depolymerizing factor |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| ATGL | Adipose triglyceride lipase |
| CIN | Chronophin |
| C | Cysteine |
| DIF-1 | Differentiation-inducing factor 1 |
| Drp1 | Dynamin-related protein 1 |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| EMT | Epithelial-mesenchymal transition |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| F-actin | Filamentous actin |
| G-actin | Globular actin |
| K | Lysine |
| LD | Lipid droplet |
| LIMK | LIM kinase |
| LTP | Long-term potentiation |
| MFN2 | Mitofusin 2 |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| PG | Prostaglandin |
| PI(4,5)P2 | Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate |
| PLC | Phospholipase C |
| PLIN | Perilipin |
| PP1 | Serine/threonine phosphatase type 1 |
| PP2A | Serine/threonine phosphatase type 2A |
| PTEN | Phosphatase and tensin homolog |
| PTM | Post-translational modification |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| S | Serine |
| SSH | Slingshot phosphatase |
| T | Threonine |
| TESK | TES kinase |
| VDAC | Voltage-dependent anion channel |
| Y | Tyrosine |
References
- Moura, J.P.; Oliveira, P.J.; Urbano, A.M. Mitochondria: An Overview of Their Origin, Genome, Architecture, and Dynamics. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Basis Dis. 2025, 1871, 167803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Ji, Q.; Tang, Y.; Chen, T.; Pan, G.; Hu, S.; Bao, Y.; Peng, W.; Yin, P. Mitochondrial Translocation of Cofilin-1 Promotes Apoptosis of Gastric Cancer BGC-823 Cells Induced by Ursolic Acid. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 2451–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, L.; Rust, M.B.; Culmsee, C. Actin(g) on Mitochondria—A Role for Cofilin1 in Neuronal Cell Death Pathways. Biol. Chem. 2019, 400, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.-B.; Zhang, H.-W.; Fu, R.-Q.; Hu, X.-Y.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.-N.; Liu, Y.-X.; Liu, X.; Hu, J.-J.; Deng, Q.; et al. Mitochondrial Fission and Mitophagy Depend on Cofilin-Mediated Actin Depolymerization Activity at the Mitochondrial Fission Site. Oncogene 2018, 37, 1485–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, S.; Woo, J.A.; Lakshmana, M.K.; Uhlar, C.; Ankala, V.; Boggess, T.; Liu, T.; Hong, Y.; Mook-Jung, I.; Kim, S.J.; et al. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Calcium Deregulation by the RanBP9-cofilin Pathway. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 4776–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, E.; Maekawa, S.; Sakai, H. Cofilin, a Protein in Porcine Brain That Binds to Actin Filaments and Inhibits Their Interactions with Myosin and Tropomyosin. Biochemistry 1984, 23, 5307–5313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsegiani, A.S.; Shah, Z. The Role of Cofilin in Age-Related Neuroinflammation. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 1451–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamburg, J.R.; Minamide, L.S.; Wiggan, O.; Tahtamouni, L.H.; Kuhn, T.B. Cofilin and Actin Dynamics: Multiple Modes of Regulation and Their Impacts in Neuronal Development and Degeneration. Cells 2021, 10, 2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremneva, E.; Makkonen, M.H.; Skwarek-Maruszewska, A.; Gateva, G.; Michelot, A.; Dominguez, R.; Lappalainen, P. Cofilin-2 Controls Actin Filament Length in Muscle Sarcomeres. Dev. Cell 2014, 31, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, S. Cofilin-Induced Structural Changes in Actin Filaments Stay Local. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 3349–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanellos, G.; Frame, M.C. Cellular Functions of the ADF/Cofilin Family at a Glance. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 3211–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuchero, J.B.; Fu, M.; Sloan, S.A.; Ibrahim, A.; Olson, A.; Zaremba, A.; Dugas, J.C.; Wienbar, S.; Caprariello, A.V.; Kantor, C.; et al. CNS Myelin Wrapping Is Driven by Actin Disassembly. Dev. Cell 2015, 34, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, S.; Minami, N.; Abe, H.; Obinata, T. Characterization of a Novel Cofilin Isoform That Is Predominantly Expressed in Mammalian Skeletal Muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 15280–15286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamburg, J.R. Proteins of the ADF/Cofilin Family: Essential Regulators of Actin Dynamics. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1999, 15, 185–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollis, E.; Mosaku, A.; Abid, A.; Buniello, A.; Cerezo, M.; Gil, L.; Groza, T.; Güneş, O.; Hall, P.; Hayhurst, J.; et al. The NHGRI-EBI GWAS Catalog: Knowledgebase and Deposition Resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D977–D985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellenchi, G.C.; Gurniak, C.B.; Perlas, E.; Middei, S.; Ammassari-Teule, M.; Witke, W. N-Cofilin Is Associated with Neuronal Migration Disorders and Cell Cycle Control in the Cerebral Cortex. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 2347–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, A.L.; Janmey, P.A.; Louie, K.A.; Drubin, D.G. Cofilin Is an Essential Component of the Yeast Cortical Cytoskeleton. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 120, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The UniProt Consortium; Bateman, A.; Martin, M.-J.; Orchard, S.; Magrane, M.; Adesina, A.; Ahmad, S.; Bowler-Barnett, E.H.; Bye-A-Jee, H.; Carpentier, D.; et al. UniProt: The Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2025. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D609–D617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Söding, J.; et al. Fast, Scalable Generation of High-quality Protein Multiple Sequence Alignments Using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, F.; Higgins, D.G. Clustal Omega for Making Accurate Alignments of Many Protein Sequences. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappalainen, P. Essential Functions and Actin-Binding Surfaces of Yeast Cofilin Revealed by Systematic Mutagenesis. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 5520–5530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wu, L.; Qi, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, G.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Wu, H. Cofilin: A Promising Protein Implicated in Cancer Metastasis and Apoptosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 599065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schratt, G.M.; Tuebing, F.; Nigh, E.A.; Kane, C.G.; Sabatini, M.E.; Kiebler, M.; Greenberg, M.E. A Brain-Specific microRNA Regulates Dendritic Spine Development. Nature 2006, 439, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Zeng, M.; Zhao, Y.; Fang, X. Upregulation of Limk1 Caused by microRNA-138 Loss Aggravates the Metastasis of Ovarian Cancer by Activation of Limk1/Cofilin Signaling. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 2070–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.-X.; Wang, X.-L.; Zhang, L.-N.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, W. MicroRNA-384 Inhibits the Progression of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma through Blockade of the LIMK1/Cofilin Signaling Pathway by Binding to LIMK1. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ockeloen, C.W.; Gilhuis, H.J.; Pfundt, R.; Kamsteeg, E.J.; Agrawal, P.B.; Beggs, A.H.; Dara Hama-Amin, A.; Diekstra, A.; Knoers, N.V.A.M.; Lammens, M.; et al. Congenital Myopathy Caused by a Novel Missense Mutation in the CFL2 Gene. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2012, 22, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabur, S.; Oztuzcu, S.; Oguz, E.; Demiryürek, S.; Dagli, H.; Alasehirli, B.; Ozkaya, M.; Demiryürek, A.T. Evidence for Elevated (LIMK2 and CFL1) and Suppressed (ICAM1, EZR, MAP2K2, and NOS3) Gene Expressions in Metabolic Syndrome. Endocrine 2016, 53, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.-H.; Han, J.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, Y.-S.; Park, H.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, H.; Kaang, B.-K. Cofilin Expression Induces Cofilin-Actin Rod Formation and Disrupts Synaptic Structure and Function in Aplysia Synapses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 16072–16077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamburg, J.R.; Bernstein, B.W. Actin Dynamics and Cofilin-actin Rods in Alzheimer Disease. Cytoskeleton 2016, 73, 477–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Fu, N.; Luo, X.; Li, X.-Y.; Li, X.-P. Overexpression of Cofilin 1 in Prostate Cancer and the Corresponding Clinical Implications. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 9, 2757–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wu, D.; He, F.; Fu, H.; Xu, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, W. Study on the Significance of Cofilin 1 Overexpression in Human Bladder Cancer. Tumori J. 2017, 103, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wu, D.; Fu, H.; He, F.; Xu, C.; Zhou, J.; Li, D.; Li, G.; Xu, J.; Wu, Q.; et al. Cofilin 1 Promotes Bladder Cancer and Is Regulated by TCF7L2. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 92043–92054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa-Squiavinato, A.C.M.; Vasconcelos, R.I.; Gehren, A.S.; Fernandes, P.V.; De Oliveira, I.M.; Boroni, M.; Morgado-Díaz, J.A. Cofilin-1, LIMK1 and SSH1 Are Differentially Expressed in Locally Advanced Colorectal Cancer and According to Consensus Molecular Subtypes. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, T.; Li, M.; Mao, Y.; Yang, Z. Epigenetic Regulation Mechanisms of the Cofilin-1 Gene in the Development and Differentiation of Bovine Primary Myoblasts. Genes 2022, 13, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liao, R.; Li, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Chen, H. Expression of Cofilin-1 and Transgelin in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2015, 21, 2659–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, R.; Yang, H.; Chen, S.; Wang, L.; Li, M.; Yang, S.; Feng, Z.; Bi, J. NCAM Regulates the Proliferation, Apoptosis, Autophagy, EMT, and Migration of Human Melanoma Cells via the Src/Akt/mTOR/Cofilin Signaling Pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 121, 1192–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X.; Ma, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yi, X.; Chen, R.; Han, F.; Zhang, N.; et al. Downregulation of Glycine Decarboxylase Enhanced Cofilin-Mediated Migration in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 120, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainullin, M.R.; Zhukov, I.Y.; Zhou, X.; Mo, Y.; Astakhova, L.; Ernberg, I.; Matskova, L. Degradation of Cofilin Is Regulated by Cbl, AIP4 and Syk Resulting in Increased Migration of LMP2A Positive Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samstag, Y.; John, I.; Wabnitz, G.H. Cofilin: A Redox Sensitive Mediator of Actin Dynamics during T-cell Activation and Migration. Immunol. Rev. 2013, 256, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Liu, X.; Cao, J.; Chen, B. SEPT7 Overexpression Inhibits Glioma Cell Migration by Targeting the Actin Cytoskeleton Pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 2003–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toshima, J.; Toshima, J.Y.; Amano, T.; Yang, N.; Narumiya, S.; Mizuno, K. Cofilin Phosphorylation by Protein Kinase Testicular Protein Kinase 1 and Its Role in Integrin-Mediated Actin Reorganization and Focal Adhesion Formation. Mol. Biol. Cell 2001, 12, 1131–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa-Squiavinato, A.C.M.; Rocha, M.R.; Barcellos-de-Souza, P.; De Souza, W.F.; Morgado-Diaz, J.A. Cofilin-1 Signaling Mediates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition by Promoting Actin Cytoskeleton Reorganization and Cell-Cell Adhesion Regulation in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Cell Res. 2019, 1866, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrianantoandro, E.; Pollard, T.D. Mechanism of Actin Filament Turnover by Severing and Nucleation at Different Concentrations of ADF/Cofilin. Mol. Cell 2006, 24, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namme, J.N.; Bepari, A.K.; Takebayashi, H. Cofilin Signaling in the CNS Physiology and Neurodegeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleinik, N.V.; Krupenko, N.I.; Krupenko, S.A. ALDH1L1 Inhibits Cell Motility via Dephosphorylation of Cofilin by PP1 and PP2A. Oncogene 2010, 29, 6233–6244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, C.T.; Simpson, T.I.; Pratt, T.; Price, D.J.; Maciver, S.K. The Motility of Glioblastoma Tumour Cells Is Modulated by Intracellular Cofilin Expression in a Concentration-Dependent Manner. Cell Motil. Cytoskelet. 2005, 60, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-H.; Chiu, S.-J.; Liu, C.-C.; Sheu, T.-J.; Hsieh, C.-H.; Keng, P.C.; Lee, Y.-J. Regulated Expression of Cofilin and the Consequent Regulation of P27kip1 Are Essential for G1 Phase Progression. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 2365–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, L.; Waclawczyk, M.S.; Tang, S.; Hanschmann, E.-M.; Gellert, M.; Rust, M.B.; Culmsee, C. Cofilin1 Oxidation Links Oxidative Distress to Mitochondrial Demise and Neuronal Cell Death. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klamt, F.; Zdanov, S.; Levine, R.L.; Pariser, A.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yu, L.-R.; Veenstra, T.D.; Shacter, E. Oxidant-Induced Apoptosis Is Mediated by Oxidation of the Actin-Regulatory Protein Cofilin. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 1241–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova-Sepúlveda, G.; Boggon, T.J. Regulation and Signaling of the LIM Domain Kinases. Bioessays 2025, 47, e2400184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Guan, X.; Jia, X.; Li, H.; Chen, R.; Lu, Y. In-Depth Profiling and Quantification of the Lysine Acetylome in Hepatocellular Carcinoma with a Trapped Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometer. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2022, 21, 100255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Lechuga, T.J.; Tith, T.; Wang, W.; Wing, D.A.; Chen, D. S-Nitrosylation of Cofilin-1 Mediates Estradiol-17β-Stimulated Endothelial Cytoskeleton Remodeling. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 29, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallée, B.; Doudeau, M.; Godin, F.; Bénédetti, H. Characterization at the Molecular Level Using Robust Biochemical Approaches of a New Kinase Protein. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2019, 148, 59820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmiere, P.D.; Bamburg, J.R. Regulation of the Neuronal Actin Cytoskeleton by ADF/Cofilin. J. Neurobiol. 2004, 58, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.Y.; DerMardirossian, C.; Bokoch, G.M. Cofilin Phosphatases and Regulation of Actin Dynamics. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2006, 18, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, K. Signaling Mechanisms and Functional Roles of Cofilin Phosphorylation and Dephosphorylation. Cell. Signal. 2013, 25, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitolo, M.I.; Boggs, A.E.; Whipple, R.A.; Yoon, J.R.; Thompson, K.; Matrone, M.A.; Cho, E.H.; Balzer, E.M.; Martin, S.S. Loss of PTEN Induces Microtentacles through PI3K-Independent Activation of Cofilin. Oncogene 2013, 32, 2200–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prudent, R.; Demoncheaux, N.; Diemer, H.; Collin-Faure, V.; Kapur, R.; Paublant, F.; Lafanechère, L.; Cianférani, S.; Rabilloud, T. A Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Cofilin Phosphorylation in Myeloid Cells and Its Modulation Using the LIM Kinase Inhibitor Pyr1. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, Y.; Ho, H.J.; Wang, C.; Guan, J.-L. Tyrosine Phosphorylation of Cofilin at Y68 by V-Src Leads to Its Degradation through Ubiquitin–Proteasome Pathway. Oncogene 2010, 29, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogl, A.M.; Phu, L.; Becerra, R.; Giusti, S.A.; Verschueren, E.; Hinkle, T.B.; Bordenave, M.D.; Adrian, M.; Heidersbach, A.; Yankilevich, P.; et al. Global Site-Specific Neddylation Profiling Reveals That NEDDylated Cofilin Regulates Actin Dynamics. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2020, 27, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrao, P.; Albanèse, V.; Kenner, L.R.; Swaney, D.L.; Burlingame, A.; Villén, J.; Lim, W.A.; Fraser, J.S.; Frydman, J.; Krogan, N.J. Systematic Functional Prioritization of Protein Posttranslational Modifications. Cell 2012, 150, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, T. The Age of Crosstalk: Phosphorylation, Ubiquitination, and Beyond. Mol. Cell 2007, 28, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimov, V.; Rigbolt, K.T.G.; Nielsen, M.M.; Blagoev, B. Characterization of Ubiquitination Dependent Dynamics in Growth Factor Receptor Signaling by Quantitative Proteomics. Mol. Biosyst. 2011, 7, 3223–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfannstiel, J.; Cyrklaff, M.; Habermann, A.; Stoeva, S.; Griffiths, G.; Shoeman, R.; Faulstich, H. Human Cofilin Forms Oligomers Exhibiting Actin Bundling Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 49476–49484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, W.; Gu, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, Q.; Zhou, J.; Cheng, J.; Zhu, M.X.; Feng, J.; Huang, O.; et al. N-Terminal α-Amino SUMOylation of Cofilin-1 Is Critical for Its Regulation of Actin Depolymerization. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, R. Towards Computational Models of Identifying Protein Ubiquitination Sites. Curr. Drug Targets 2019, 20, 565–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buneeva, O.; Medvedev, A. Atypical Ubiquitination and Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Liu, X.; Zheng, B.; Xing, C.; Liu, J. Role of K63-Linked Ubiquitination in Cancer. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madiraju, C.; Novack, J.P.; Reed, J.C.; Matsuzawa, S. K63 Ubiquitination in Immune Signaling. Trends Immunol. 2022, 43, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Weng, W.; Guo, R.; Zhou, J.; Xue, J.; Zhong, S.; Cheng, J.; Zhu, M.X.; Pan, S.-J.; Li, Y. Olig2 SUMOylation Protects against Genotoxic Damage Response by Antagonizing P53 Gene Targeting. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 3146–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unwin, R.D.; Craven, R.A.; Harnden, P.; Hanrahan, S.; Totty, N.; Knowles, M.; Eardley, I.; Selby, P.J.; Banks, R.E. Proteomic Changes in Renal Cancer and Co-ordinate Demonstration of Both the Glycolytic and Mitochondrial Aspects of the Warburg Effect. Proteomics 2003, 3, 1620–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, B.T.; Volbracht, C.; Tan, K.O.; Li, R.; Yu, V.C.; Li, P. Mitochondrial Translocation of Cofilin Is an Early Step in Apoptosis Induction. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 5, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, S.; Sharma, R.; Gupta, R.; Ast, T.; Chan, C.; Durham, T.J.; Goodman, R.P.; Grabarek, Z.; Haas, M.E.; Hung, W.H.W.; et al. MitoCarta3.0: An Updated Mitochondrial Proteome Now with Sub-Organelle Localization and Pathway Annotations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1541–D1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehklau, K.; Gurniak, C.B.; Conrad, M.; Friauf, E.; Ott, M.; Rust, M.B. ADF/Cofilin Proteins Translocate to Mitochondria during Apoptosis but Are Not Generally Required for Cell Death Signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovaleva, T.F.; Maksimova, N.S.; Pchelin, P.V.; Pershin, V.I.; Tkachenko, N.M.; Gainullin, M.R.; Mukhina, I.V. A New Cofilin-Dependent Mechanism for the Regulation of Brain Mitochondria Biogenesis and Degradation. Sovrem. Tehnol. Med. 2020, 12, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapeña-Luzón, T.; Rodríguez, L.R.; Beltran-Beltran, V.; Benetó, N.; Pallardó, F.V.; Gonzalez-Cabo, P. Cofilin and Neurodegeneration: New Functions for an Old but Gold Protein. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhou, J.; Budhraja, A.; Hu, X.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhou, T.; Li, P.; Liu, E.; et al. Mitochondrial Translocation and Interaction of Cofilin and Drp1 Are Required for Erucin-Induced Mitochondrial Fission and Apoptosis. Oncotarget 2014, 6, 1834–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Shen, L.; Shi, J.; Gao, N. ROCK1 Activation-Mediated Mitochondrial Translocation of Drp1 and Cofilin Are Required for Arnidiol-Induced Mitochondrial Fission and Apoptosis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Miura, K.; Han, R.; Seto-Tetsuo, F.; Arioka, M.; Igawa, K.; Tomooka, K.; Sasaguri, T. Differentiation-Inducing Factor 1 Activates Cofilin through Pyridoxal Phosphatase and AMP-Activated Protein Kinase, Resulting in Mitochondrial Fission. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 152, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, W.; Kahle, P.J. Regulation of PINK1-Parkin-Mediated Mitophagy. Autophagy 2011, 7, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotiadis, V.N.; Leadsham, J.E.; Bastow, E.L.; Gheeraert, A.; Whybrew, J.M.; Bard, M.; Lappalainen, P.; Gourlay, C.W. Identification of New Surfaces of Cofilin That Link Mitochondrial Function to the Control of Multi-Drug Resistance. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 2288–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichon, J.; Sun, C.; Chen, B.; Jiang, M.; Chen, X.A.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, G. Cofilin Aggregation Blocks Intracellular Trafficking and Induces Synaptic Loss in Hippocampal Neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 3919–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovaleva, T.F.; Maksimova, N.S.; Zhukov, I.Y.; Pershin, V.I.; Mukhina, I.V.; Gainullin, M.R. Cofilin: Molecular and Cellular Functions and Its Role in the Functioning of the Nervous System. Neurochem. J. 2019, 13, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Meng, L.; Dai, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Zheng, Y.; Zha, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, Z. Cofilin 1 Promotes the Aggregation and Cell-to-Cell Transmission of α-Synuclein in Parkinson’s Disease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 529, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordonez, D.G.; Lee, M.K.; Feany, M.B. α-Synuclein Induces Mitochondrial Dysfunction through Spectrin and the Actin Cytoskeleton. Neuron 2018, 97, 108–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.E.; Woo, J.A. Cofilin, a Master Node Regulating Cytoskeletal Pathogenesis in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2019, 72, S131–S144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximova, N.S.; Pershin, V.I.; Tkachenko, N.M.; Gainullin, M.; Mukhina, I.V.; Kovaleva, T.F. Study of the Effect of a Proteasome Inhibitor on Actin Cytoskeleton Remodeling in the Nerve Cells by Fluorescence Imaging. In Proceedings of the Saratov Fall Meeting 2019: Optical and Nano-Technologies for Biology and Medicine, Saratov, Russia, 23–27 September 2019; Tuchin, V.V., Genina, E.A., Eds.; SPIE: Saratov, Russia, 2020; pp. 86–94. [Google Scholar]
- Minamide, L.S.; Maiti, S.; Boyle, J.A.; Davis, R.C.; Coppinger, J.A.; Bao, Y.; Huang, T.Y.; Yates, J.; Bokoch, G.M.; Bamburg, J.R. Isolation and Characterization of Cytoplasmic Cofilin-Actin Rods. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 5450–5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munsie, L.N.; Desmond, C.R.; Truant, R. Cofilin Nuclear-Cytoplasmic Shuttling Affects Cofilin-Actin Rod Formation During Stress. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 3977–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, B.W.; Chen, H.; Boyle, J.A.; Bamburg, J.R. Formation of Actin-ADF/Cofilin Rods Transiently Retards Decline of Mitochondrial Potential and ATP in Stressed Neurons. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2006, 291, C828–C839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehklau, K.; Hoffmann, L.; Gurniak, C.B.; Ott, M.; Witke, W.; Scorrano, L.; Culmsee, C.; Rust, M.B. Cofilin1-Dependent Actin Dynamics Control DRP1-Mediated Mitochondrial Fission. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraschiakos, T.; Li, J.; Scholz, J.; Han, S.-J.; Deckers, M.; Pogenberg, V.; Faix, J.; Windhorst, S. A High Affinity Sybody Blocks Cofilin-1 Binding to F-Actin in Vitro and in Cancer Cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2025, 236, 116866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izdebska, M.; Zielińska, W.; Hałas-Wiśniewska, M.; Grzanka, A. Involvement of Actin and Actin-Binding Proteins in Carcinogenesis. Cells 2020, 9, 2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Chen, Z.; Mi, H.; Yu, X. Cofilin Acts as a Booster for Progression of Malignant Tumors Represented by Glioma. Cancer Manag. Res. 2022, 14, 3245–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Cui, S.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X. The Role of Cofilin-l in Vulvar Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Marker of Carcinogenesis, Progression and Targeted Therapy. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 2743–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Satoh, M.; Takano, S.; Sogawa, K.; Noda, K.; Yoshitomi, H.; Ishibashi, M.; Mogushi, K.; Takizawa, H.; Otsuka, M.; Shimizu, H.; et al. Immune-complex Level of Cofilin-1 in Sera Is Associated with Cancer Progression and Poor Prognosis in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdanov, S.; Klamt, F.; Shacter, E. Importance of Cofilin Oxidation for Oxidant-Induced Apoptosis. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 1675–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa-Squiavinato, A.C.M.; Morgado-Díaz, J.A. A Glimpse into Cofilin-1 Role in Cancer Therapy: A Potential Target to Improve Clinical Outcomes? Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Rev. Cancer 2024, 1879, 189087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Cheng, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhou, T.; Shan, C.; Hu, X.; Zhou, J.; Liu, E.; Li, P.; Gao, N. Mitochondrial Translocation of Cofilin Is Required for Allyl Isothiocyanate-Mediated Cell Death via ROCK1/PTEN/PI3K Signaling Pathway. Cell Commun. Signal. 2013, 11, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Tian, R.; Han, H.; Slone, J.; Wang, C.; Ke, X.; Zhang, T.; Li, X.; He, Y.; Liao, P.; et al. PINK1-Mediated Drp1S616 Phosphorylation Modulates Synaptic Development and Plasticity via Promoting Mitochondrial Fission. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Luan, S.; Fan, X.; Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Gao, X.; Han, D. The Emerging Multifaceted Role of PINK1 in Cancer Biology. Cancer Sci. 2022, 113, 4037–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Tan, Y. Lipid Droplet–Mitochondria Contacts in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.; Meyer, T.; Smolnig, M.; Smethurst, D.G.J.; Neuhaus, L.; Heyden, J.; Broeskamp, F.; Edrich, E.S.M.; Knittelfelder, O.; Kolb, D.; et al. A Dynamic Actin Cytoskeleton Is Required to Prevent Constitutive VDAC-Dependent MAPK Signalling and Aberrant Lipid Homeostasis. iScience 2023, 26, 107539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Liu, P. Two Types of Contact Between Lipid Droplets and Mitochondria. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 618322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miner, G.E.; So, C.M.; Edwards, W.; Ragusa, J.V.; Wine, J.T.; Wong Gutierrez, D.; Airola, M.V.; Herring, L.E.; Coleman, R.A.; Klett, E.L.; et al. PLIN5 Interacts with FATP4 at Membrane Contact Sites to Promote Lipid Droplet-to-Mitochondria Fatty Acid Transport. Dev. Cell 2023, 58, 1250–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giedt, M.S.; Thomalla, J.M.; White, R.P.; Johnson, M.R.; Lai, Z.W.; Tootle, T.L.; Welte, M.A. Adipose Triglyceride Lipase Promotes Prostaglandin-Dependent Actin Remodeling by Regulating Substrate Release from Lipid Droplets. Development 2023, 150, dev201516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serezani, C.H.; Kane, S.; Medeiros, A.I.; Cornett, A.M.; Kim, S.-H.; Marques, M.M.; Lee, S.-P.; Lewis, C.; Bourdonnay, E.; Ballinger, M.N.; et al. PTEN Directly Activates the Actin Depolymerization Factor Cofilin-1 During PGE 2 -Mediated Inhibition of Phagocytosis of Fungi. Sci. Signal. 2012, 5, ra12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Thein, S.; Wang, X.; Bi, X.; Ericksen, R.E.; Xu, F.; Han, W. BSCL2/Seipin Regulates Adipogenesis through Actin Cytoskeleton Remodelling. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fang, N.; Xiong, J.; Du, Y.; Cao, Y.; Ji, W.-K. An ESCRT-Dependent Step in Fatty Acid Transfer from Lipid Droplets to Mitochondria through VPS13D−TSG101 Interactions. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfisterer, S.G.; Gateva, G.; Horvath, P.; Pirhonen, J.; Salo, V.T.; Karhinen, L.; Varjosalo, M.; Ryhänen, S.J.; Lappalainen, P.; Ikonen, E. Role for Formin-like 1-Dependent Acto-Myosin Assembly in Lipid Droplet Dynamics and Lipid Storage. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Man, S.; Tao, J.; Liu, Y.; Ma, L.; Guo, L.; Huang, L.; Liu, C.; Gao, W. The Lipid Droplet in Cancer: From Being a Tumor-supporting Hallmark to Clinical Therapy. Acta Physiol. 2024, 240, e14087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safi, R.; Menéndez, P.; Pol, A. Lipid Droplets Provide Metabolic Flexibility for Cancer Progression. FEBS Lett. 2024, 598, 1301–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petan, T. Lipid Droplets in Cancer. In Organelles in Disease; Reviews of Physiology, Biochemistry and Pharmacology; Pedersen, S.H.F., Barber, D.L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 185, pp. 53–86. ISBN 978-3-031-22594-9. [Google Scholar]
- Jarc, E.; Petan, T. A Twist of FATe: Lipid Droplets and Inflammatory Lipid Mediators. Biochimie 2020, 169, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira-Dutra, F.S.; Bozza, P.T. Lipid Droplets Diversity and Functions in Inflammation and Immune Response. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2021, 18, 809–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zadoorian, A.; Du, X.; Yang, H. Lipid Droplet Biogenesis and Functions in Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 443–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welte, M.A. Expanding Roles for Lipid Droplets. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, R470–R481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, B.C.; Walsh, A.E.; Kluemper, J.C.; Johnson, L.A. Lipid Droplets in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F. Lipid Metabolism and Alzheimer’s Disease: Clinical Evidence, Mechanistic Link and Therapeutic Promise. FEBS J. 2023, 290, 1420–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, L.; Luo, W.; Li, F.; Qin, S.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Wu, Y.; et al. Dysregulation of Cofilin-1 Activity—The Missing Link between Herpes Simplex Virus Type-1 Infection and Alzheimer’s Disease. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 46, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.K.; Babcock, I.W.; Minamide, L.S.; Shaw, A.E.; Bamburg, J.R.; Kuhn, T.B. Direct Interaction of HIV Gp120 with Neuronal CXCR4 and CCR5 Receptors Induces Cofilin-Actin Rod Pathology via a Cellular Prion Protein- and NOX-Dependent Mechanism. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ding, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Huo, C.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhang, P.; Na, H.; Zhang, H.; et al. The Proteomics of Lipid Droplets: Structure, Dynamics, and Functions of the Organelle Conserved from Bacteria to Humans. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rust, M.B. ADF/Cofilin: A Crucial Regulator of Synapse Physiology and Behavior. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 3521–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidani, M.; Wessels, D.; Mouneimne, G.; Ghosh, M.; Goswami, S.; Sarmiento, C.; Wang, W.; Kuhl, S.; El-Sibai, M.; Backer, J.M.; et al. Cofilin Determines the Migration Behavior and Turning Frequency of Metastatic Cancer Cells. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 179, 777–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, K.C.; Hellal, F.; Neukirchen, D.; Jacob, S.; Tahirovic, S.; Dupraz, S.; Stern, S.; Garvalov, B.K.; Gurniak, C.; Shaw, A.E.; et al. ADF/Cofilin-Mediated Actin Retrograde Flow Directs Neurite Formation in the Developing Brain. Neuron 2012, 76, 1091–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Zablah, Y.; Merovitch, N.; Jia, Z. The Role of ADF/Cofilin in Synaptic Physiology and Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 594998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rheenen, J.; Song, X.; Van Roosmalen, W.; Cammer, M.; Chen, X.; DesMarais, V.; Yip, S.-C.; Backer, J.M.; Eddy, R.J.; Condeelis, J.S. EGF-Induced PIP2 Hydrolysis Releases and Activates Cofilin Locally in Carcinoma Cells. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 179, 1247–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.-C.; Yang, E.J.; Borgman, T.; Boldogh, I.R.; Sing, C.N.; Swayne, T.C.; Pon, L.A. Touch and Go: Membrane Contact Sites Between Lipid Droplets and Other Organelles. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 852021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-Y.; Leu, J.-D.; Lee, Y.-J. The Actin Depolymerizing Factor (ADF)/Cofilin Signaling Pathway and DNA Damage Responses in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 4095–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Elzakra, N.; Xu, S.; Xiao, G.G.; Yang, Y.; Hu, S. Investigation of Three Potential Autoantibodies in Sjogren’s Syndrome and Associated MALT Lymphoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 30039–30049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kovaleva, T.; Gainullin, M.; Mukhina, I.; Pershin, V.; Matskova, L. Cofilin(s) and Mitochondria: Function Beyond Actin Dynamics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4094. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094094
Kovaleva T, Gainullin M, Mukhina I, Pershin V, Matskova L. Cofilin(s) and Mitochondria: Function Beyond Actin Dynamics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4094. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094094
Chicago/Turabian StyleKovaleva, Tatiana, Murat Gainullin, Irina Mukhina, Vladimir Pershin, and Liudmila Matskova. 2025. "Cofilin(s) and Mitochondria: Function Beyond Actin Dynamics" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4094. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094094
APA StyleKovaleva, T., Gainullin, M., Mukhina, I., Pershin, V., & Matskova, L. (2025). Cofilin(s) and Mitochondria: Function Beyond Actin Dynamics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4094. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094094







